Hair Histology and Glycosaminoglycans Distribution Probed by Infrared Spectral Imaging: Focus on Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and Glypican-1 during Hair Growth Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
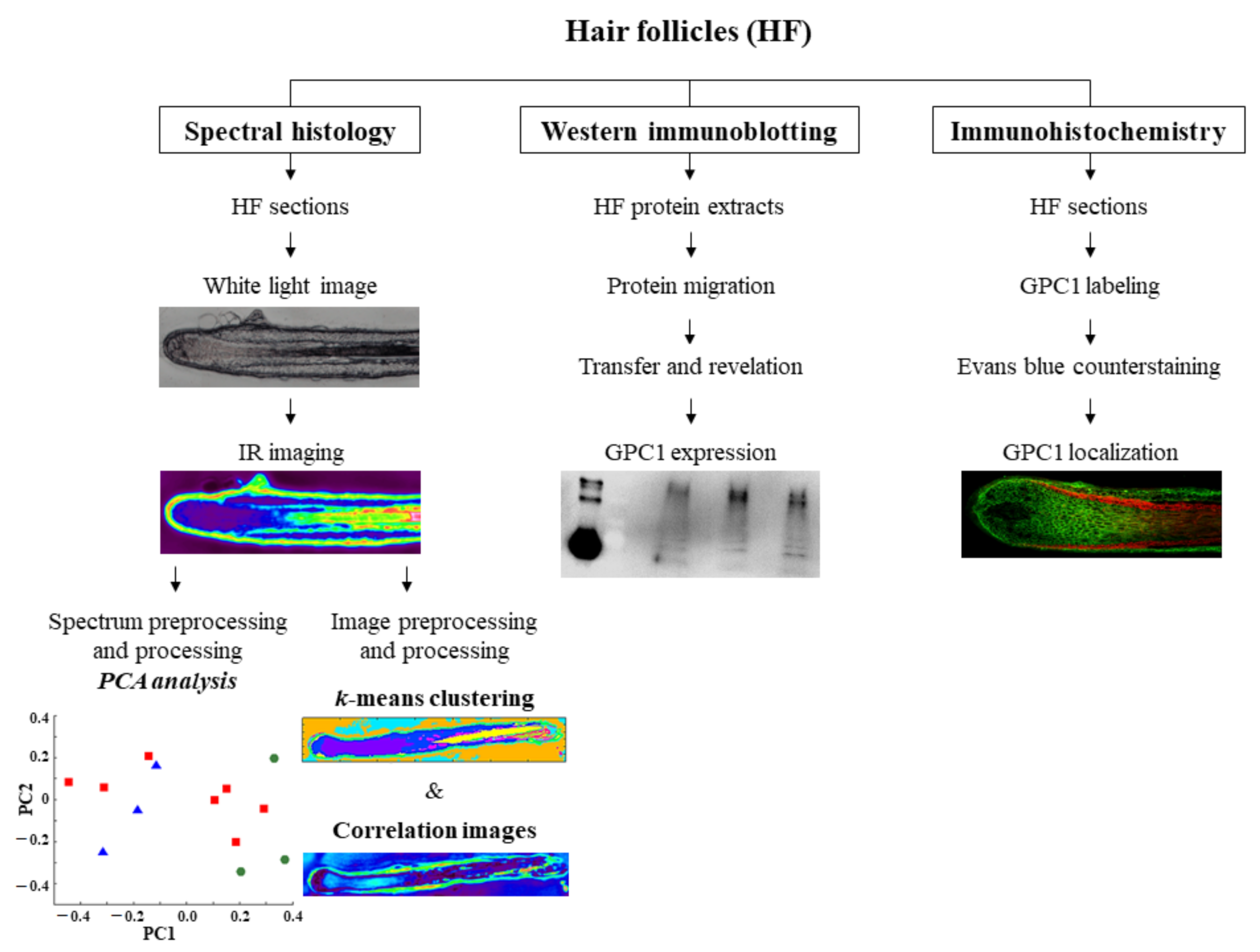
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Hair Follicle Sample Isolation and Preparation
2.2.1. Hair Follicle Isolation
2.2.2. Hair Follicle Preparation for Infrared Analysis
2.2.3. Hair Follicle Preparation for Immunohistochemistry
2.3. IR Spectral Imaging of Hair Follicle Sections
2.4. IR Spectral Preprocessing
2.5. IR Spectral Processing by Principal Component Analysis
2.6. IR Image Preprocessing
2.7. IR Image Processing by k-Means Algorithm
2.8. IR Correlation Images Using Spectra of Standard Compounds
2.9. Hair Follicle Protein Extract Preparation for Western Immunoblotting
2.10. Western Immunoblotting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Discrimination of HF Structures, Distribution of HSPG and GPC1 Using IR Spectral Imaging Analysis
3.1.1. Different Structures of the Hair Follicle are Discriminated by IR Spectral Imaging Analysis Based on the Variation of GAGs and Their Sulfation
3.1.2. Focus on GPC1 Distribution in Hair Follicles by Spectral Imaging Analysis and Immunohistochemistry
3.2. Different Phases of Hair Growth Cycle and Spatial Distribution of HS and GPC1 Determined by IR Spectral Imaging Analysis
3.2.1. k-Means Clustering Identifies the Hair Follicle Structures in the Different Phases Based on the Protein and HSPG Spectral Information
3.2.2. IR Correlation Maps Highlight Spatial Distribution of HS and GPC1 in the Different Phases
3.3. Discrimination of Hair Growth Cycle Phases, Distribution of Sulfated GAG and GPC1 Using IR Spectral Imaging Analysis
3.3.1. Different Phases of the Hair Growth Cycle are Discriminated by PCA of IR Spectra Based on the Variation of GAGs and Their Sulfation
3.3.2. GPC1 Expression Corroborated with IR Spectral Maps of Sulfated GAG Distribution, Discriminates Different Phases during the Hair Growth Cycle
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernard, B.A. La vie révélée du follicule de cheveu humain. Med. Sci. (Paris) 2006, 22, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Picardo, M.; Ju, Q.; Kurokawa, I.; Törőcsik, D.; Bíró, T.; Schneider, M.R. Beyond Acne: Current Aspects of Sebaceous Gland Biology and Function. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sada, A.; Tumbar, T. New Insights into Mechanisms of Stem Cell Daughter Fate Determination in Regenerative Tissues. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 300, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stenn, K. Exogen Is an Active, Separately Controlled Phase of the Hair Growth Cycle. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 374–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, Y.; Sudnik, J.; Filippi, M.; Kizoulis, M.; Kashgarian, M.; Stenn, K. Exogen, Shedding Phase of the Hair Growth Cycle: Characterization of a Mouse Model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, B.A.; Commo, S.; Gerst, C.; Mahé, F.Y.; Pruche, F. Données récentes sur la biologie du cheveu. Bull. Esthet. Dermatol. Cosmetol. 1996, 4, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, H.B.; Rauch, R.; Smith, V.W. Critical Stages of Hair Development and Pigmentation in the Mouse. Physiol. Zool. 1951, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Röver, S.; Handjiski, B.; van der Veen, C.; Eichmüller, S.; Foitzik, K.; McKay, I.A.; Stenn, K.S.; Paus, R. A Comprehensive Guide for the Accurate Classification of Murine Hair Follicles in Distinct Hair Cycle Stages. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botchkarev, V.A.; Paus, R. Molecular Biology of Hair Morphogenesis: Development and Cycling. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2003, 298, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filmus, J.; Capurro, M.; Rast, J. Glypicans. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Chan, T.M. Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans: Overlooked Entities? Perit. Dial. Int. 2007, 27, S104–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, L.; Iozzo, R.V. Biological Functions of the Small Leucine-Rich Proteoglycans: From Genetics to Signal Transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21305–21309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tkachenko, E.; Rhodes, J.M.; Simons, M. Syndecans: New Kids on the Signaling Block. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayers, K.L.; Gallet, A.; Staccini-Lavenant, L.; Thérond, P.P. The Long-Range Activity of Hedgehog Is Regulated in the Apical Extracellular Space by the Glypican Dally and the Hydrolase Notum. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capurro, M.; Izumikawa, T.; Suarez, P.; Shi, W.; Cydzik, M.; Kaneiwa, T.; Gariepy, J.; Bonafe, L.; Filmus, J. Glypican-6 Promotes the Growth of Developing Long Bones by Stimulating Hedgehog Signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2911–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreuger, J.; Perez, L.; Giraldez, A.J.; Cohen, S.M. Opposing Activities of Dally-like Glypican at High and Low Levels of Wingless Morphogen Activity. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, S.; Nakase, H.; Matsuura, M.; Honzawa, Y.; Matsumura, K.; Uza, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Mizoguchi, E.; Chiba, T. Heparan Sulfate on Intestinal Epithelial Cells Plays a Critical Role in Intestinal Crypt Homeostasis via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G241–G249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, P.P.; Grose, R.H.; Filmus, J.; Hii, C.S.T.; Xian, C.J.; Anderson, P.J.; Powell, B.C. Regulation of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signalling and Cranial Osteogenesis by Gpc1 and Gpc3. Bone 2013, 55, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Li, L.; Fuchs, E. Transit-Amplifying Cells Orchestrate Stem Cell Activity and Tissue Regeneration. Cell 2014, 157, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sennett, R.; Rendl, M. Mesenchymal-Epithelial Interactions during Hair Follicle Morphogenesis and Cycling. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malgouries, S.; Thibaut, S.; Bernard, B.A. Proteoglycan Expression Patterns in Human Hair Follicle. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer-Garner, I.B.; Sanderson, R.D.; Smoller, B.R. Syndecan-1 Is Strongly Expressed in the Anagen Hair Follicle Outer Root Sheath and in the Dermal Papilla but Expression Diminishes with Involution of the Hair Follicle. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2002, 24, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulson-Thomas, V.J.; Gesteira, T.F.; Esko, J.; Kao, W. Heparan Sulfate Regulates Hair Follicle and Sebaceous Gland Morphogenesis and Homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25211–25226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mainreck, N.; Brézillon, S.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Maquart, F.-X.; Manfait, M.; Wegrowski, Y. Characterization of Glycosaminoglycans by Tandem Vibrational Microspectroscopy and Multivariate Data Analysis. In Proteoglycans: Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology; Rédini, F., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 117–130. ISBN 978-1-61779-498-8. [Google Scholar]
- Draux, F.; Jeannesson, P.; Gobinet, C.; Sule-Suso, J.; Pijanka, J.; Sandt, C.; Dumas, P.; Manfait, M.; Sockalingum, G.D. IR Spectroscopy Reveals Effect of Non-Cytotoxic Doses of Anti-Tumour Drug on Cancer Cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, D.; Miljković, M.; Bird, B.; Lenau, K.; Old, O.; Almond, M.; Kendall, C.; Lloyd, G.; Shepherd, N.; Barr, H.; et al. Infrared Micro-Spectroscopy for Cyto-Pathological Classification of Esophageal Cells. Analyst 2015, 140, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Bhargava, R. A Comparison of Mid-Infrared Spectral Regions on Accuracy of Tissue Classification. Analyst 2019, 144, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach-Thieltges, A.; Großerüschkamp, F.; Mosig, A.; Diem, M.; Tannapfel, A.; Gerwert, K. Immunohistochemistry, Histopathology and Infrared Spectral Histopathology of Colon Cancer Tissue Sections. J Biophotonics 2013, 6, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainreck, N.; Brézillon, S.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Maquart, F.-X.; Manfait, M.; Wegrowski, Y. Rapid Characterization of Glycosaminoglycans Using a Combined Approach by Infrared and Raman Microspectroscopies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brézillon, S.; Untereiner, V.; Lovergne, L.; Tadeo, I.; Noguera, R.; Maquart, F.-X.; Wegrowski, Y.; Sockalingum, G.D. Glycosaminoglycan Profiling in Different Cell Types Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5795–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.T.; Untereiner, V.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Brézillon, S. Implementation of Infrared and Raman Modalities for Glycosaminoglycan Characterization in Complex Systems. Glycoconj. J. 2017, 34, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philpott, M.P.; Sanders, D.A.; Kealey, T. Whole Hair Follicle Culture. Dermatol. Clin. 1996, 14, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macqueen, J. Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Beckeley, CA, USA; 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, G.; Colin-Pierre, C.; Ramont, L.; Proult, I.; Garbar, C.; Bardey, V.; Jeanmaire, C.; Mine, S.; Danoux, L.; Berthélémy, N.; et al. Decreased Expression of GPC1 in Human Skin Keratinocytes and Epidermis during Ageing. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 126, 110693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Aoi, N.; Sato, T.; Yamauchi, Y.; Suga, H.; Eto, H.; Kato, H.; Araki, J.; Yoshimura, K. Differential Expression of Stem-Cell-Associated Markers in Human Hair Follicle Epithelial Cells. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panteleyev, A.A. Functional Anatomy of the Hair Follicle: The Secondary Hair Germ. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purba, T.S.; Haslam, I.S.; Poblet, E.; Jiménez, F.; Gandarillas, A.; Izeta, A.; Paus, R. Human Epithelial Hair Follicle Stem Cells and Their Progeny: Current State of Knowledge, the Widening Gap in Translational Research and Future Challenges. Bioessays 2014, 36, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloepper, J.E.; Tiede, S.; Brinckmann, J.; Reinhardt, D.P.; Meyer, W.; Faessler, R.; Paus, R. Immunophenotyping of the Human Bulge Region: The Quest to Define Useful in Situ Markers for Human Epithelial Hair Follicle Stem Cells and Their Niche. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 592–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couchman, J.R.; King, J.L.; McCarthy, K.J. Distribution of Two Basement Membrane Proteoglycans through Hair Follicle Development and the Hair Growth Cycle in the Rat. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 94, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colin-Pierre, C.; Untereiner, V.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Berthélémy, N.; Danoux, L.; Bardey, V.; Mine, S.; Jeanmaire, C.; Ramont, L.; Brézillon, S. Hair Histology and Glycosaminoglycans Distribution Probed by Infrared Spectral Imaging: Focus on Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and Glypican-1 during Hair Growth Cycle. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020192
Colin-Pierre C, Untereiner V, Sockalingum GD, Berthélémy N, Danoux L, Bardey V, Mine S, Jeanmaire C, Ramont L, Brézillon S. Hair Histology and Glycosaminoglycans Distribution Probed by Infrared Spectral Imaging: Focus on Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and Glypican-1 during Hair Growth Cycle. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(2):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020192
Chicago/Turabian StyleColin-Pierre, Charlie, Valérie Untereiner, Ganesh D. Sockalingum, Nicolas Berthélémy, Louis Danoux, Vincent Bardey, Solène Mine, Christine Jeanmaire, Laurent Ramont, and Stéphane Brézillon. 2021. "Hair Histology and Glycosaminoglycans Distribution Probed by Infrared Spectral Imaging: Focus on Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and Glypican-1 during Hair Growth Cycle" Biomolecules 11, no. 2: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020192
APA StyleColin-Pierre, C., Untereiner, V., Sockalingum, G. D., Berthélémy, N., Danoux, L., Bardey, V., Mine, S., Jeanmaire, C., Ramont, L., & Brézillon, S. (2021). Hair Histology and Glycosaminoglycans Distribution Probed by Infrared Spectral Imaging: Focus on Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and Glypican-1 during Hair Growth Cycle. Biomolecules, 11(2), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020192






