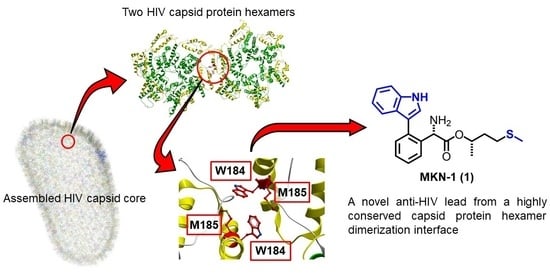
Small-Molecule Anti-HIV-1 Agents Based on HIV-1 Capsid Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
2.2. In Silico Screening of Antiviral Candidates
2.3. Evaluation of Anti-HIV-1 Activity and Cytotoxicity
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Screening to Find Drug Leads Targeting CA Proteins
3.1.1. Structural Analysis of CA Proteins
3.1.2. Results of the In Silico Screening
3.2. Synthesis of Novel CA-Targeting Anti-HIV Agents
3.2.1. Synthesis of MKN-1 (1)
3.2.2. Stereoselective Synthesis of MKN-1 (1)
3.2.3. Synthesis of MKN-1 Derivatives
Synthesis of MKN-1 Derivatives with Aryl Ring Substitution 22, 24, 27, and 28
Synthesis of MKN-1 Derivatives with Sulfide Substitution 30, 34–36, and 38
3.3. Evaluation of Anti-HIV Activity and Cytotoxicity of the Synthesized Compounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohashi, N.; Tamamura, H. Peptide-derived mid-sized anti-HIV agents. In Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins; Ryadnov, M., Hudecz, F., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2017; Volume 41, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tamamura, H.; Kobayakawa, T.; Ohashi, N. Mid-size drugs based on peptides and peptidomimetics: A new drug category. In Springer Briefs in Pharmaceutical Science & Drug Development; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Das, D.; Kobayakawa, T.; Tamamura, H.; Takeuch, H. Discovery and Development of Anti-HIV Therapeutic Agents: Progress Towards Improved HIV Medication. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1621–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuya, H.; Weinhold, K.J.; Furman, P.A.; Clair, M.H.S.; Lehrman, S.N.; Gallo, R.C.; Bolognesi, D.; Barry, D.W.; Broder, S. 3’-Azido-3’-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): An antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7096–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Dawson, Z.L.; Mitsuya, H. Darunavir, a conceptually new HIV-1 protease inhibitor for the treatment of drug-resistant HIV. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 7576–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cahn, P.; Sued, O. Raltegravir: A new antiretroviral class for salvage therapy. Lancet 2007, 369, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsztejn, B.; Nguyen, B.-Y.; Katlama, C.; Gatell, J.M.; Lazzarin, A.; Vittecoq, D.; Gonzalez, C.J.; Chen, J.; Harvey, C.M.; Isaacs, R.D. Safety and efficacy of the HIV-1 integrase inhibitor raltegravir (MK-0518) in treatment-experienced patients with multidrug-resistant virus: A phase II randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 369, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Nakajima, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Fujii, N.; Tamamura, H.; Yoshida, N.; Waki, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Yoshie, O.; et al. A Small Molecule CXCR4 Inhibitor that Blocks T Cell Line–tropic HIV-1 Infection. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamamura, H.; Xu, Y.; Hattori, T.; Zhang, X.; Arakaki, R.; Kanbara, K.; Omagari, A.; Otaka, A.; Ibuka, T.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. A Low-Molecular-Weight Inhibitor against the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4: A Strong Anti-HIV Peptide T140. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 253, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Oishi, S.; Hiramatsu, K.; Araki, T.; Ueda, S.; Tamamura, H.; Otaka, A.; Kusano, S.; Terakubo, S.; Nakashima, H.; et al. Molecular-Size Reduction of a Potent CXCR4-Chemokine Antagonist Using Orthogonal Combination of Conformation- and Sequence-Based Libraries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3251–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamamura, H.; Hiramatsu, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Ueda, S.; Kusano, S.; Terakubo, S.; Akamatsu, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Trent, J.O.; Wang, Z.; et al. Enhancement of the T140-based pharmacophores leads to the development of more potent and bio-stable CXCR4 antagonists. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 3663–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nomura, W.; Narumi, T.; Masuda, A.; Tamamura, H. Bivalent Ligands of CXCR4 with Rigid Linkers for Elucidation of Dimerization State in Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15899–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narumi, T.; Ozaki, T.; Sohma, A.; Ohashi, N.; Hashimoto, C.; Itotani, K.; Nomura, W.; Murakami, T.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Azamacrocyclic-metal Complexes as CXCR4 Antagonists. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakyiamah, M.M.; Kobayakawa, T.; Fujino, M.; Konno, M.; Narumi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nomura, W.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; Tamamura, H. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Low Molecular Weight CXCR4 Ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Ochiai, C.; Yoshimura, K.; Tanaka, T.; Ohashi, N.; Narumi, T.; Nomura, W.; Harada, S.; Matsushita, S.; Tamamura, H. CD4 Mimics Targeting the Mechanism of HIV. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, K.; Harada, S.; Shibata, J.; Hatada, M.; Yamada, Y.; Ochiai, C.; Tamamura, H.; Matsushita, S. Enhanced Exposure of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Primary Isolate Neutralization Epitopes through Binding of CD4 Mimetic Compounds. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7558–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, T.; Harada, S.; Miura, T.; Ohashi, N.; Narumi, T.; Mori, H.; Irahara, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Nomura, W.; Matsushita, S.; et al. A Minimally Cytotoxic CD4 Mimic as an HIV Entry Inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, N.; Harada, S.; Mizuguchi, T.; Irahara, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Kotani, M.; Nomura, W.; Matsushita, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Tamamura, H. Small Molecular CD4 Mimics Containing Mono-cyclohexyl Moieties as HIV Entry Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayakawa, T.; Konno, K.; Ohashi, N.; Takahashi, K.; Masuda, A.; Yoshimura, K.; Harada, S.; Tamamura, H. Soluble-type Small-molecule CD4 Mimics as HIV Entry Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaka, A.; Nakamura, M.; Nameki, D.; Kodama, E.; Uchiyama, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nakano, H.; Tamamura, H.; Kobayashi, Y.L.; Matsuoka, M.; et al. Remodeling of gp41-C34 Peptide Leads to Highly Effective Inhibitors of the Fusion of HIV-1 with Target Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2937–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, W.; Hashimoto, C.; Ohya, A.; Miyauchi, K.; Urano, E.; Tanaka, T.; Narumi, T.; Nakahara, T.; Komano, J.A.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. A Synthetic C34 Trimer of HIV-1 gp41 Shows Significant Increase of Inhibition Potency. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 205–208, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, W.; Hashimoto, C.; Suzuki, T.; Ohashi, N.; Fujino, M.; Murakami, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tamamura, H. Multimerized CHR-derived Peptides as HIV-1 Fusion Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4452–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayakawa, T.; Ebihara, K.; Honda, Y.; Fujino, M.; Nomura, W.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; Tamamura, H. Dimeric C34 Derivatives Linked through Disulfide Bridges as New HIV-1 Fusion Inhibitors. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Urano, E.; Hashimoto, C.; Tsutsumi, H.; Nakahara, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Maddali, K.; Han, Y.; Hamatake, M.; et al. Peptide HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors from HIV-1 Gene Products. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5356–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Maddali, K.; Hashimoto, C.; Urano, E.; Ohashi, N.; Tanaka, T.; Ozaki, T.; Arai, H.; Tsutsumi, H.; Narumi, T.; et al. Peptidic HIV Integrase Inhibitors Derived from HIV Gene Products: Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6771–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomura, W.; Aikawa, H.; Ohashi, N.; Urano, E.; Metifiot, M.; Fujino, M.; Maddali, K.; Ozaki, T.; Nozue, A.; Narumi, T.; et al. Cell-Permeable Stapled Peptides Based on HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors Derived from HIV-1 Gene Products. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumi, T.; Komoriya, M.; Hashimoto, C.; Wu, H.; Nomura, W.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, T.; Chiba, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; et al. Conjugation of Cell-penetrating Peptides Leads to Identification of Anti-HIV Peptides from Matrix Proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, T.; Ohashi, N.; Nomura, W.; Komoriya, M.; Hashimoto, C.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; Tamamura, H. Anti-HIV Screening for Cell-Penetrating Peptides Using Chloroquine and Identification of Anti-HIV Peptides Derived from Matrix Proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 4423–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, T.; Ohashi, N.; Matsumoto, D.; Hashimoto, C.; Nomura, W.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; Tamamura, H. Development of Anti-HIV Peptides Based on a Viral Capsid Protein. Biopolym. Pept. Sci. 2017, 108, e22920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Owusu, K.B.; Kobayakawa, T.; Wang, R.; Fujino, M.; Kaneko, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, T.; Tamamura, H. Exploratory Studies on CA-15L, an Anti-HIV Active HIV-1 Capsid Fragment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnqadharan, M.G.; Bruch, L.; Popovic, M.; Gallo, R.C. Immunological properties of the Gag protein p24 of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus (human T-cell leukemia virus type III). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 3481–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mervis, R.J.; Ahmad, N.; Lillehoj, E.P.; Raum, M.G.; Salazar, F.H.; Chan, H.W.; Venkatesan, S. The gag gene products of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: Alignment within the gag open reading frame, identification of posttranslational modifications, and evidence for alternative gag precursors. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 3993–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pornillos, O.; Ganser-Pornillos, B.K.; Kelly, B.N.; Hua, Y.; Whitby, F.G.; Stout, C.D.; Sundquist, W.I.; Hill, C.P.; Yeager, M. X-Ray Structures of the Hexameric Building Block of the HIV Capsid. Cell 2009, 137, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganser, B.K.; Li, S.; Klishko, V.Y.; Finch, J.T.; Sundquist, W.I. Assembly and Analysis of Conical Models for the HIV-1 Core. Science 1999, 283, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornillos, O.; Ganser-Pornillos, B.K.; Yeager, M. Atomic-level modelling of the HIV capsid. Nature 2011, 469, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, E.O. HIV-1 Gag Proteins: Diverse Functions in the Virus Life Cycle. Virology 1998, 251, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bukrinskaya, A. HIV-1 matrix protein: A mysterious regulator of the viral life cycle. Virus Res. 2007, 124, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentner, I.; Sierra, L.-J.; Maciunas, L.; Vinnik, A.; Fedichev, P.; Mankowski, M.K.; Ptak, R.G.; Martin-Garcia, J.; Cocklin, S. Discovery of a small-molecule antiviral targeting the HIV-1 matrix protein. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niedrig, M.; Gelderblom, H.R.; Pauli, G.; März, J.; Bickhard, H.; Wolf, H.; Modrow, S. Inhibition of infectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particle formation by Gag protein-derived peptides. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, P.M.; Matthews, S.; Clark, N.; Byles, E.D.; Lourin, O.; Hockley, D.J.; Kingsman, S.M.; Kingsman, A.J. Structure-function studies of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 matrix protein, p17. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morikawa, Y.; Kishi, T.; Zhang, W.H.; Nermut, M.V.; Hockley, D.J.; Jones, I.M. A molecular determinant of human immunodeficiency virus particle assembly located in matrix antigen p17. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4519–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Futaki, S.; Niwa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ueda, K.; Sugiura, Y. Possible Existence of Common Internalization Mechanisms among Arginine-rich Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Loeliger, E.; Kinde, I.; Kyere, S.; Mayo, K.; Barklis, E.; Sun, Y.; Huang, M.; Summers, M.F. Antiviral Inhibition of the HIV-1 Capsid Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.N.; Kyere, S.; Kinde, I.; Tang, C.; Howard, B.R.; Robinsin, H.; Sundquist, W.I.; Summers, M.F.; Hill, C.P. Structure of the Antiviral Assembly Inhibitor CAP-1 Complex with the HIV-1 CA Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blair, W.S.; Pickford, C.; Irving, S.L.; Brown, D.G.; Anderson, M.; Bazin, R.; Cao, J.; Ciaramella, G.; Issacson, J.; Jackon, L.; et al. HIV Capsid is a Tractable Target for Small Molecule Therapeutic Intervention. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, J.; Shah, V.B.; Aiken, C.; Whitby, K. Small-Molecule Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection by Virus Capsid Destabilization. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamorte, L.; Titolo, S.; Lemke, C.T.; Goudreau, N.; Mercier, J.-F.; Wardop, E.; Snah, V.B.; Schwedler, U.K.; Langelier, C.; Banik, S.S.R.; et al. Discovery of Novel Small-Molecule HIV-1 Replication Inhibitors That Stabilize Capsid Complexes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4622–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thenin-Houssier, S.; Valente, S.T. HIV-1 Capsid Inhibitors as Antiretroviral Agents. Curr. HIV Res. 2016, 14, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thenin-Houssier, S.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Pedro-Rosa, L.; Brady, A.; Richard, A.; Konnic, B.; Opp, S.; Buffone, C.; Fuhrmann, J.; Kota, S.; et al. Ebselen, a Small-Molecule Capsid Inhibitor of HIV-1 Replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.P.; Branson, J.D.; Lawrence, R.; Cocklin, S. Identification of a small molecule HIV-1 inhibitor that targets the capsid hexamer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rankovic, S.; Ramalho, R.; Aiken, C.; Rousso, I. PF74 Reinforces the HIV-1 Capsid To Impair Reverse Transcription-Induced Uncoating. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Zalloum, W.A.; Meuser, M.E.; Jing, L.; Kang, D.; Chen, C.-H.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, F.; Cocklin, S.; Lee, K.-H.; et al. Discovery of phenylalanine derivatives as potent HIV-1 capsid inhibitors from click chemistry-based compound library. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnes, S.K.; Sheehan, J.H.; Aiken, C. Inhibitors of the HIV-1 Capsid, A Target of Opportunity. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2018, 13, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Wu, G.C.; Zalloum, W.A.; Meuser, M.E.; Dick, A.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.-H.; Kang, D.; Jing, L.; Jia, R.; et al. Discovery of novel 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole phenylalanine derivatives as HIV-1 capsid inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28961–28986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.; Gallazzi, F.; Hill, K.J.; Burke, D.H.; Lange, M.J.; Quinn, T.P.; Neogi, U.; Sönnerborg, A. GS-CA Compounds: First-In-Class HIV-1 Capsid Inhibitors Covering Multiple Grounds. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yant, S.R.; Mulato, A.; Hansen, D.; Tse, W.C.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; Zhang, J.R.; Stephen, G.J.; Jin, D.; Wong, M.H.; Perreira, J.M.; et al. A highly potent long-acting small-molecule HIV-1 capsid inhibitor with efficacy in a humanized mouse model. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, J.O.; Rhee, M.S.; Tse, W.C.; Zheng, J.; Somoza, J.R.; Rowe, W.; Begley, R.; Chiu, A.; Mulato, A.; Hansen, D.; et al. Clinical targeting of HIV capsid protein with a long-acting small molecule. Nature 2020, 584, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Dick, A.; Meuser, M.E.; Huang, T.; Zalloum, W.A.; Chen, C.-H.; Cherukupalli, S.; Xu, S.; Ding, X.; Gao, P.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Mechanism Study of Benzenesulfonamide-Containing Phenylalanine Derivatives as Novel HIV-1 Capsid Inhibitors with Improved Antiviral Activities. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4790–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernekar, S.K.V.; Sahani, R.L.; Casey, M.C. Toward Structurally Novel and Metabolically Stable HIV-1 Capsid-Targeting Small Molecules. Viruses 2020, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Darden, T.A.; Cheatham, T.E.; Simmerling, C.L.; Wang, J.; Duke, R.E.; Luo, R.; Crowley, M.; Walker, R.C.; Zhang, W.; et al. AMBER 10; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, P.R.; Müller, K. MAB, a generally applicable molecular force field for structure modelling in medicinal chemistry. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 1995, 9, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, S.; Koyanagi, Y.; Yamamoto, N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science 1985, 229, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Perilla, J.R.; Yufenyuy, E.L.; Meng, X.; Chen, B.; Ning, J.; Ahn, J.; Gronenborn, A.M.; Schulten, K.; Aiken, C.; et al. Mature HIV-1 capsid structure by cryo-electron microscopy and all-atom molecular dynamics. Nature 2013, 497, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Schwedler, U.K.; Stray, K.M.; Garrus, J.E.; Sundquist, W.I. Functional Surfaces of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5439–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- HIV Sequence Database. Triad National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration. Available online: http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/sequence/HIV/mainpage.html/ (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Wildman, S.A.; Crippen, G.M. Prediction of Physicochemical Parameters by Atomic Contributions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, H.; Li, J.; Fu, C.; Zaburannyi, N.; Kunze, B.; Harmrolfs, K.; Schmitt, V.; Herrmann, J.; Reichenbach, H.; Höfle, G.; et al. Isolation, Structure Elucidation, and (Bio)Synthesis of Haprolid, a Cell-Type-Specific Myxobacterial Cytotoxin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10113–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.G.; Aggarwal, V.K. Asymmetric Synthesis of 1-Heteroaryl-1-arylalkyl Tertiary Alcohols and 1-Pyridyl-1-arylethanes by Lithiation–Borylation Methodology. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Fuertes, Y.; Taylor, J.E.; Tickell, D.A.; Mahon, M.F.; Bull, S.D.; James, J.D. Asymmetric Strecker Synthesis of α-Arylglycines. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 6038–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosse, K.; Marineau, J.; Nason, D.M.; Fliri, A.J.; Segelstein, B.E.; Desai, K.; Volkmann, R.A. Expanding the medicinal chemistry toolbox: Stereospecific generation of methyl group-containing propylene linkers. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 7285–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahata, T.; Takeda, E.; Tobiume, M.; Tokunaga, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Huang, Y.-L.; Hasegawa, A.; Shioda, T.; Sato, H.; Kannagi, M.; et al. Critical contribution of Tyr15 in the HIV-1 integrase (IN) in facilitating IN assembly and nonenzymatic function through the IN precursor form with reverse transcriptase. J. Virol. 2016, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Compound | MTT Assay | p24 ELISA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 (μM) a | CC50 (μM) b | EC50 (μM) c | |
| MKN-1A (1A) | 8.0 (2) e | 38 (2) | 14 (1) |
| MKN-1B (1B) | 24 (2) | 37 (2) | 22 (1) |
| MKN-1 (1) | 4.5 ± 2.3 (10) | 26 ± 8.8 (10) | 8.5 (1) |
| 22 | 31 ± 8.5% at 25 μM d (3) | 33 ± 1.5 (3) | not tested |
| 24 | 40 ± 4.6% at 25 μM d (3) | 30 ± 2.0 (3) | not tested |
| 27 | 11% at 25 μM d (2) | 34 (2) | not tested |
| 28 | 31% at 25 μM d (2) | 45 (2) | not tested |
| 30 | 26 ± 2.9 (3) | > 50 (3) | not tested |
| 34 | 12 (2) | 17 (2) | not tested |
| 35 | 10 (2) | 18 (2) | not tested |
| 36 | 11 (2) | 17 (2) | not tested |
| 38 | 34% at 25 μM d (2) | > 50 (2) | not tested |
| AZT | 0.024 ± 0.015 (10) | 79 ± 42 (7) | 0.047 (2) |
| AMD3100 | 0.027 ± 0.0077 (10) | > 50 (10) | 0.029 (2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayakawa, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Tsuji, K.; Fujino, M.; Kurakami, M.; Boku, S.; Nakayama, M.; Kaneko, M.; Ohashi, N.; Kotani, O.; et al. Small-Molecule Anti-HIV-1 Agents Based on HIV-1 Capsid Proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020208
Kobayakawa T, Yokoyama M, Tsuji K, Fujino M, Kurakami M, Boku S, Nakayama M, Kaneko M, Ohashi N, Kotani O, et al. Small-Molecule Anti-HIV-1 Agents Based on HIV-1 Capsid Proteins. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020208
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayakawa, Takuya, Masaru Yokoyama, Kohei Tsuji, Masayuki Fujino, Masaki Kurakami, Sayaka Boku, Miyuki Nakayama, Moemi Kaneko, Nami Ohashi, Osamu Kotani, and et al. 2021. "Small-Molecule Anti-HIV-1 Agents Based on HIV-1 Capsid Proteins" Biomolecules 11, no. 2: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020208
APA StyleKobayakawa, T., Yokoyama, M., Tsuji, K., Fujino, M., Kurakami, M., Boku, S., Nakayama, M., Kaneko, M., Ohashi, N., Kotani, O., Murakami, T., Sato, H., & Tamamura, H. (2021). Small-Molecule Anti-HIV-1 Agents Based on HIV-1 Capsid Proteins. Biomolecules, 11(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020208