Imbalance in Coagulation/Fibrinolysis Inhibitors Resulting in Extravascular Thrombin Generation in Gliomas of Varying Levels of Malignancy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
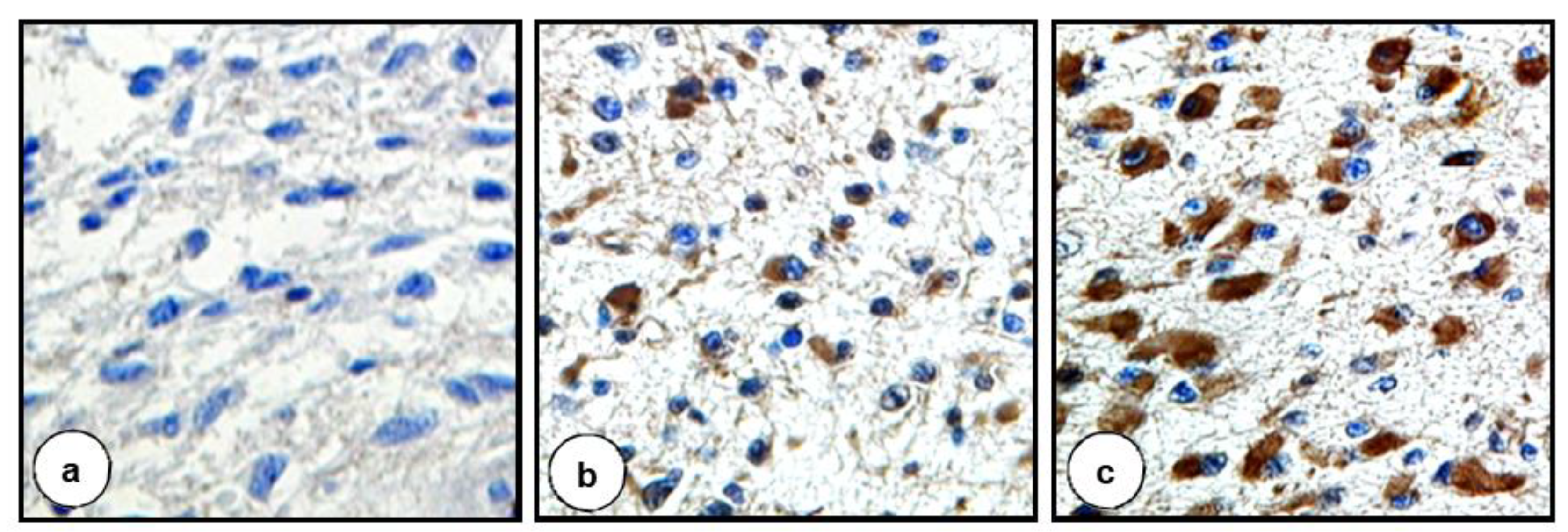
3. Results
3.1. TFPI
3.2. TFPI-2
3.3. PC
3.4. PS
3.5. TM
3.6. PAI-1
3.7. F1+2
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandel, J.J.; Yust-Katz, S.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Webre, C.C.; Pawar, H.L.T.; Gilbert, M.R.; Armstrong, T.S. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) and glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. 15), 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, N.C.; Elson, P.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Khorana, A.A. Venous thromboembolism in patients with glioblastoma, risk factors and prognostic importance. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 15), e13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, S.; Tsuboi, K.; Tomono, Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Nose, T. Tissue factor, osteopontin, αυβ3 integrin expression in microvasculature of gliomas associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fadul, C.E.; Zacharski, L.R. Coagulation biology in glioma pathogenesis, a missing link? J. Throm. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1915–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Sierko, E.; Rak, J. Contribution of the hemostatic system to angiogenesis in cancer. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2004, 30, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruf, W.; Muller, B.M. Tissue factor in cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1996, 3, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornstein, D.L.; Zacharski, L. The coagulation system as a target for the treatment of human gliomas. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardos, H.; Molnar, P.; Csecsei, G.; Adany, R. Fibrin deposition in primary and metastatic human brain tumors. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis. 1996, 7, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broze, G.J., Jr. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 74, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, R.; Scheuer, T.; Bohm, M.; Beck, J.; Woszczyk, A.; Raabe, A.; Scharrer, I.; Seifert, V. Increased levels of plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with glioblastoma and intracerebral metastases. Neurol. Res. 2003, 25, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radziwon, P.; Schenk, J.F.; Mazgajska, K.; Boczkowska-Radziwon, B.; Galar, M.; Kloczko, J.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z. Tissue factor (TF) and inhibitor (TFPI) concentrations in patients with urinary tract tumors and haematological malignancies. [in Polish]. Pol. Merkur. Lekarski. 2002, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar]
- Sierko, E.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Zimnoch, L.; Kisiel, W. Expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) in human breast and colon cancer tissue. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 103, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Nordfang, O.; Petersen, J.G.; Foster, D.C.; Kisiel, W. Inhibitory properties of full-length and truncated recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8704–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L.H.; Okholm, M.; Thorlacius-Ussing, O.O. Pre- and postoperative state of coagulation and fibrinolysis in plasma of patients with benign and malignant colorectal disease—A preliminary study. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 76, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erman, M.; Abali, H.; Oran, B.; Haznedaroglu, I.C.; Canpinar, H.; Kirazli, S.; Celik, I. Tamoxifen-induced tissue factor pathway inhibitor reduction, a clue for an acquired thrombophilic state? Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, K.; Miyagi, Y.; Hirahara, F.; Miyagi, E.; Nagashima, Y.; Minaguchi, H.; Misugi, K.; Yasumitsu, H.; Miyazaki, K. Specific expression of PP5/TFPI-2 mRNA by syncytiotrophoblasts in human placenta as revealed by in situ hybridization. Placenta 1998, 19, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Takahashi, C.; Oh, J.; Noda, M. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 suppresses the production of active matrix metalloproteinase-2 and is down-regulated in cells harboring activated ras oncogene. FEBS Lett. 2000, 481, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, E.; Okamoto, A.; Saito, M.; Shinozaki, H.; Takakura, S.; Yanaihara, N.; Ochiai, K.; Tanaka, T. Genes associated with the genesis of leiomyoma of the uterus in a commonly deleted chromosomal region at 7q22. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Gondi, C.S.; Dinh, D.H.; Gujrati, M.; Rao, J.S. Restoration of tissue factor patway inhibitor-2 in a human glioblastoma cell line triggers caspase-mediated pathway and apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3507–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanamandra, N.; Kondraganti, S.; Gondi, C.S.; Gujrati, M.; Olivero, W.C.; Dinh, D.H.; Rao, J.S. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) expressing TFPI-2 inhibits invasion, angiogenesis and tumor growth in a human glioblastoma cell line. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 115, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanciu, L.; Gerard, R.D.; Tang, H.; Lupu, F.; Lupu, C. Adenovirus-mediated expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 inhibits endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmon, C.T. The endothelial cell protein C receptor. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmon, C.T. Role of coagulation inhibitors in inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, J.; Kaneda, A.; Umebayashi, Y.; Otsuka, F.; Sugimura, T.; Ushijama, T. Silencing of the thrombomodulin gene in human malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2005, 15, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Weiler-Guettler, H.; Chen, J.; Wilhelm, O.; Deng, Y.; Qiu, F.; Nakagawa, K.; Klevesath, M.; Wilhelm, S.; Böhrer, H.; et al. Thrombomodulin modulates growth of tumor cells independent of its anticoagulant activity. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benzakour, O.; Kanthou, C. The anticoagulant factor, protein S, is produced by cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells and its expression is up-regulated by thrombin. Blood 2000, 95, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthou, C.; Benzakour, O. Cellular effects and signalling pathways activated by the anti-coagulant factor, protein S, in vascular cells protein S cellular effects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000, 476, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl, A.K.; Sandset, P.M.; Abildgaard, U.; Adersson, T.R.; Harbitz, T.B. High plasma levels of extrinsic pathway inhibitor and low levels of other coagulation inhibitors in advanced cancer. Acta Chir. Scand. 1989, 155, 389–393. [Google Scholar]
- Pavon, M.A.; Arroyo-Solera, I.; Téllez-Gabriel, M.; Leon, X.; Viros, D.; Lopez, M.; Gallardo, A.; Cespedes, M.V.; Casanova, I.; López-Pousa, A.; et al. Enhanced cell migration and apoptosis resistance may underlie the association between high SERPINE1 expression and poor outcome in head and neck carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29016–29033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakakibara, T.; Hibi, K.; Koike, M.; Fujiwara, M.; Kodera, Y.; Ito, K.; Nakao, A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 as a potential marker for the malignancy of colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, M.; Szarvas, T.; Wittschier, M.; vom Dorp, F.; Tötsch, M.; Schmid, K.W.; Rübben, H.; Ergün, S. Prognostic impact of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 expression in bladder cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 4502–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, X.; Liu, N.; Wang, Q.; Chu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Y. ACT001, a novel PAI-1 inhibitor; exerts synergistic effects in combination with cisplatin by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blasi, F. Proteolysis, cell adhesion, chemotaxis and invasiveness are regulated by the u-PA-u-PAR-PAI-1 system. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, X.; He, J.; Tian, X.; Yuan, S.; Sun, L. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cancer research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placencio, V.R.; DeClerck, Y.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cancer: Rationale and insight for future therapeutic testing. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavon, M.A.; Arroyo-Solera, I.; Cespedes, M.V.; Casanova, I.; Leon, X.; Mangues, R. uPA/uPAR and SERPINE1 in head and neck cancer: Role in tumor resistance, metastasis, prognosis and therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57351–57366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, H.; Jin, J.; Huang, D.; Yang, F.; Guan, X. PAI-1 induces Src inhibitor resistance via CCL5 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kit, O.I.; Frantsiyants, E.M.; Kozlova, L.S.; Rostorguev, E.E.; Balyazin-Parfenov, V.; Pogorelova, Y.A. A plasminogen regulation system in brain tumors. Zhurnal Vopr. Neirokhirurgii Imeni N. N. Burdenko 2017, 81, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Candida, E. Mechanisms of platelet activation by thrombin, a short history. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, C.; Vormittag, R.; Dunkler, D.; Simanek, R.; Chiriac, A.L.; Drach, J.; Quehenberger, P.; Wagner, O.; Zielinski, C.; Pabinger, I. D-dimer and prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 predict venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer, results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4124–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Rucinska, M.; Zimnoch, L.; Jaromin, J.; Piotrowski, Z.; Rozanska-Kudelska, M.; Kisiel, W.; Kudryk, B.J. Expression of prothrombin fragment 1+2 in cancer tissue as an indicator of local activation of blood coagulation. Thromb. Res. 2000, 97, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, S.; Wada, H.; Abe, Y.; Yamada, E.; Sakaguchi, A.; Nishioka, J.; Hatada, T.; Ishikura, K.; Yamada, N.; Sudo, A.; et al. Elevated levels of prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 indicate high risk of thrombosis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2008, 14, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.; Raine, L.; Fanger, H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques, a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1981, 29, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sierko, E.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Zawadzki, R.; Zimnoch, L.; Kisiel, W. Expression of protein C (PC), protein S (PS), and thrombomodulin (TM) in loco in human colorectal cancer. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, e71–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Sierko, E.; Zimnoch, L.; Kozłowski, L.; Sulkowski, S.; Kisiel, W. Immunohistochemical localization of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in human tumor tissue. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Di Maria, M.V.; Veve, R.; Bremmes, R.M.; Barón, A.E.; Zeng, C.; Franklin, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas, correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 15, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, R.; Pereira, J.R.; von Pawel, J.; Krzakowski, M.; Ramlau, R.; Park, K.; de Marinis, F.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Paz-Ares, L.; Störkel, S.; et al. EGFR expression as a predictor of survival for first-line chemotherapy plus cetuximab in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer, analysis of data from the phase 3 FLEX study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Koizume, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoshihara, M.; Takahashi, T.; Sato, S.; Myoba, S.; Ohtake, N.; Kato, H.; Yokose, T.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is specifically expressed in ovarian clear cell carcinoma tissues in the nucleus, cytoplasm and extracellular matrix. Ocol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Hirata, H.; Ueno, K.; Samoto, M.; Mori, J.; Fujii, N.; Kawai, Y.; Inoue, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. ARHGAP29 expression may be a novel prognostic factor of cell proliferation and invasion in prostate cancer. Ocol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Hempel, D.; Sierko, E.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Thrombin—unique coagulation system protein with multifaceted impacts on cancer and metastasis. Cancer Met. Rev. 2016, 35, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, N.; Bassawon, R.; Rak, J. Oncogenes and clotting factors, the emerging role of tumor cell genome and epigenome in cancer-associated thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawil, N.; Spinelli, C.; Bassawon, R.; Rak, J. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of cancer coagulome—Lessons from heterogeneity of cancer cell populations. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191 (Suppl. 1), S99–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Sierko, E.; Kisiel, W. The role of hemostatic system inhibitors in malignancy. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2007, 33, 621–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sierko, E.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Zimnoch, L.; Thorpe, P.E.; Brekken, R.A.; Kisiel, W. Co-localization of prothrombin fragment F1+2 and VEGF-R2-bound VEGF in human colon cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 843–847. [Google Scholar]
- Falanga, A.; Schieppati, F.; Russo, D. Cancer tissue procoagulant mechanisms and the hypercoagulable state of patients with cancer. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 756–764. [Google Scholar]
- Pindon, A.; Hantai, D.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Festoff, B.W. Novel expression and localization of active thrombomodulin on the surface of mouse brain astrocytes. Glia 1997, 19, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneyoshi, N.; Fukudome, K.; Horiguchi, S.; Ye, X.; Matsuzaki, M.; Toi, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kimoto, M. Expression and anticoagulant function of the endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) in cancer cell lines. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 85, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shua, F.; Kobayashia, H.; Fukudomeb, K.; Tsuneyoshib, N.; Kimotob, M. Activated protein C suppresses tissue factor expression on U937 cells in the endothelial protein C receptor-dependent manner. FEBS Lett. 2000, 477, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, K.; Hayashi, T. Protein C and its inhibitor in malignancy. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2007, 33, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, D.J.; Greengard, J.S.; Fernandez, J.A.; Ribeiro, M.; Evatt, B.L.; Griffin, J.H.; Hooper, W.C. Protein S, an antithrombotic factor, is synthesized and released by neural tumor cells. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmel, A.; Rohner, I.; Ramaswamy, A.; Heidtmann, H.H.; Seitz, R.; Kraus, M.; Schuermann, M. Synthesis and secretion of the anticoagulant protein S and coexpression of the Tyro3 receptor in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer 1999, 86, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Zacharski, L.R.; Memoli, V.A.; Kisiel, W.; Kudryk, B.J.; Rousseau, S.M.D.; Stump, C. Malignant melanoma. Interaction with coagulation and fibrinolysis pathways in situ. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1990, 93, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Zacharski, L.R.; Memoli, V.A.; Kisiel, W.; Kudryk, B.J.; Rousseau, S.M.; Moritz, T.E.; Stump, D.C. Fibrin formation on vessel walls in hyperplastic and malignant prostate tissue. Cancer 1991, 67, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Sierko, E.; Zacharski, L.R.; Zimnoch, L.; Kudryk, B.; Kisiel, B. Tissue factor-dependent coagulation activation and impaired fibrinolysis in situ in gastric cancer. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2003, 29, 291–299. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Rucińska, M.; Zacharski, L.R.; Kozlowski, L.; Zimnoch, L.; Piotrowski, Z.; Kudryk, B.J.; Kisiel, W. Localization of blood coagulation factors in situ in pancreatic carcinoma. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wizigmann-Voos, S.; Plate, K.H. Pathology, genetics and cell biology of hemangioblastomas. Histol. Histopathol. 1996, 11, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Kafri, N.A.; Hafizi, S. Tumour-secreted protein S (ProS1) activates a Tyro3-Erk signalling axis and protects cancer cells from apoptosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.; Gore, M.; Lemke, G. Structure, expression, and activity of Tyro-3, a neural adhesion-related receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar]
- Werling, R.W.; Zacharski, L.R.; Kisiel, W.; Bajaj, S.P.; Memoli, V.A.; Rousseau, S.A. Distribution of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in normal and malignant human tissues. Thromb. Haemost. 1993, 69, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurer, M.A. Protein and mRNA expression of tissue factor pathaway inhibitor-1 (TFPI-1) in breast, pancreatic and colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2007, 34, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageshita, T.; Funasaka, Y.; Ichihashi, M.; Ishichara, T.; Tokuo, H.; Ono, T. Differential expression of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in metastatic melanoma lesions. Pigment Cell Res. 2002, 15, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, W.; Seftor, E.A.; Petrovan, R.J.; Weiss, R.M.; Gruman, L.M.; Margaryan, N.V.; Seftor, R.E.B.; Miyagi, J.; Hendrix, M.J.C. Differential role of tissue factor pathway. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5381–5389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Mysliwiec, M.; Matuszewska, E.; Sulkowski, S.; Zimnoch, L.; Politynska, B.; Wojtukiewicz, A.M.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Heterogeneous expression of proangiogenic and coagulation proteins in gliomas of different histopathological grade. Pathol Onco Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, H.; Nishi, T.; Kuratsu, J.; Kamikubo, Y.; Kochi, M.; Ushio, Y. Suppression of the tissue factor-dependent coagulation cascade: A contributing factor for the development of intratumoral hemorrhage in glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2000, 6, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirkhoshravi, A.; Meyer, T.; Chang, J.-Y.; Amaya, M.; Siddiqui, H.; Francis, J.L. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor reduces experimental lung metastases of B16 melanoma. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 930–936. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, C.N.; Lakka, S.S.; Kin, Y.; Konduri, S.D.; Fuller, G.N.; Mohanam, S.; Rao, J.S. Expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 inversely correlates during the progression of human gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Parker, A.R.; Fukushima, N.; Miyagi, Y.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Eshleman, J.R.; Goggins, M. Epigenetic inactivation of TFPI-2 as a mechanism associated with growth and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2005, 24, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, P.; Gu, W. TFPI-2 suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion through regulation of ERK signaling and interaction with actinin-4 and myosin-9. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.T. Chromosomal deletions and tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2001, 20, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, S.M.; Tullis, C.; Stracner, D.; Song, C.Y.; Gewin, J. Minimal interval defined on 7q in uterine leiomyoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2005, 157, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IzCaccamo, D.V.; Keohane, M.E.; McKeever, P.E. Plasminogen activators and inhibitors in gliomas, an immunohistochemical study. Mod. Pathol. 1994, 7, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kono, S.; Rao, J.S.; Bruner, J.M.; Sawaya, R. Immunohistochemical localization of plazminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in human brain tumors. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1994, 53, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sawaya, R.; Mohanam, S.; Loskutoff, D.J.; Bruner, J.M.; Rao, V.H.; Oka, K.; Tomonga, M.; Nicolson, G.L.; Rao, J.S. Expression of cellular localization of messenger RNA for plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in human astorcytoma in vivo. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 3329–3332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muracciole, X.; Romain, S.; Dufour, H.; Palmari, J.; Chinot, O.; Ouafik, L.; Grisoli, F.; Branger, D.F.; Martin, P.M. PAI-1 and EGFR expression in adult glioma tumors, toward a mole prognostic classification. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 52, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Rama, O.J.; Shi, M.L.; Rayford, A.; Rao, J.S. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in brain tumors, relation to malignancy and necrosis. Neurosurgery 1995, 36, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Coagulation Factors | Localization | Low-Grade Gliomas (n = 13) IHC Score | High-Grade Gliomas (n = 27) IHC Score | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <200 | ≥200 | <200 | ≥200 | |||
| F1+2 | Cancer cells | 9 | 4 | 2 | 25 | <0.001 |
| Tumor stroma in the vicinity of blood vessels | 4 | 9 | 8 | 19 | NS | |
| TFPI | Cancer cells | 9 | 4 | 7 | 20 | <0.01 |
| Endothelial cells | 1 | 12 | 1 | 26 | NS | |
| TFPI-2 | Cancer cells | 0 | 13 | 25 | 2 | <0.001 |
| Endothelial cells | 3 | 10 | 13 | 14 | NS | |
| PAI-1 | Cancer cells | 1 | 12 | 24 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Endothelial cells | 1 | 12 | 23 | 4 | <0.001 | |
| PC | Cancer cells | 5 | 8 | 0 | 27 | <0.001 |
| Endothelial cells | 5 | 8 | 0 | 27 | <0.001 | |
| PS | Cancer cells | 2 | 11 | 23 | 4 | <0.001 |
| Endothelial cells | 2 | 11 | 2 | 25 | NS | |
| TM | Cancer cells | 1 | 12 | 8 | 19 | NS |
| Endothelial cells | 4 | 9 | 26 | 1 | <0.001 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Mysliwiec, M.; Matuszewska, E.; Sulkowski, S.; Zimnoch, L.; Politynska, B.; Wojtukiewicz, A.M.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Imbalance in Coagulation/Fibrinolysis Inhibitors Resulting in Extravascular Thrombin Generation in Gliomas of Varying Levels of Malignancy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050663
Wojtukiewicz MZ, Mysliwiec M, Matuszewska E, Sulkowski S, Zimnoch L, Politynska B, Wojtukiewicz AM, Tucker SC, Honn KV. Imbalance in Coagulation/Fibrinolysis Inhibitors Resulting in Extravascular Thrombin Generation in Gliomas of Varying Levels of Malignancy. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(5):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050663
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtukiewicz, Marek Z., Marta Mysliwiec, Elwira Matuszewska, Stanislaw Sulkowski, Lech Zimnoch, Barbara Politynska, Anna M. Wojtukiewicz, Stephanie C. Tucker, and Kenneth V. Honn. 2021. "Imbalance in Coagulation/Fibrinolysis Inhibitors Resulting in Extravascular Thrombin Generation in Gliomas of Varying Levels of Malignancy" Biomolecules 11, no. 5: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050663
APA StyleWojtukiewicz, M. Z., Mysliwiec, M., Matuszewska, E., Sulkowski, S., Zimnoch, L., Politynska, B., Wojtukiewicz, A. M., Tucker, S. C., & Honn, K. V. (2021). Imbalance in Coagulation/Fibrinolysis Inhibitors Resulting in Extravascular Thrombin Generation in Gliomas of Varying Levels of Malignancy. Biomolecules, 11(5), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050663






