Iridoids, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Cornus mas, C. officinalis, and C. mas × C. officinalis Fruits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Biological Material
2.3. Preparation of Extracts for Analysis of Active Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity
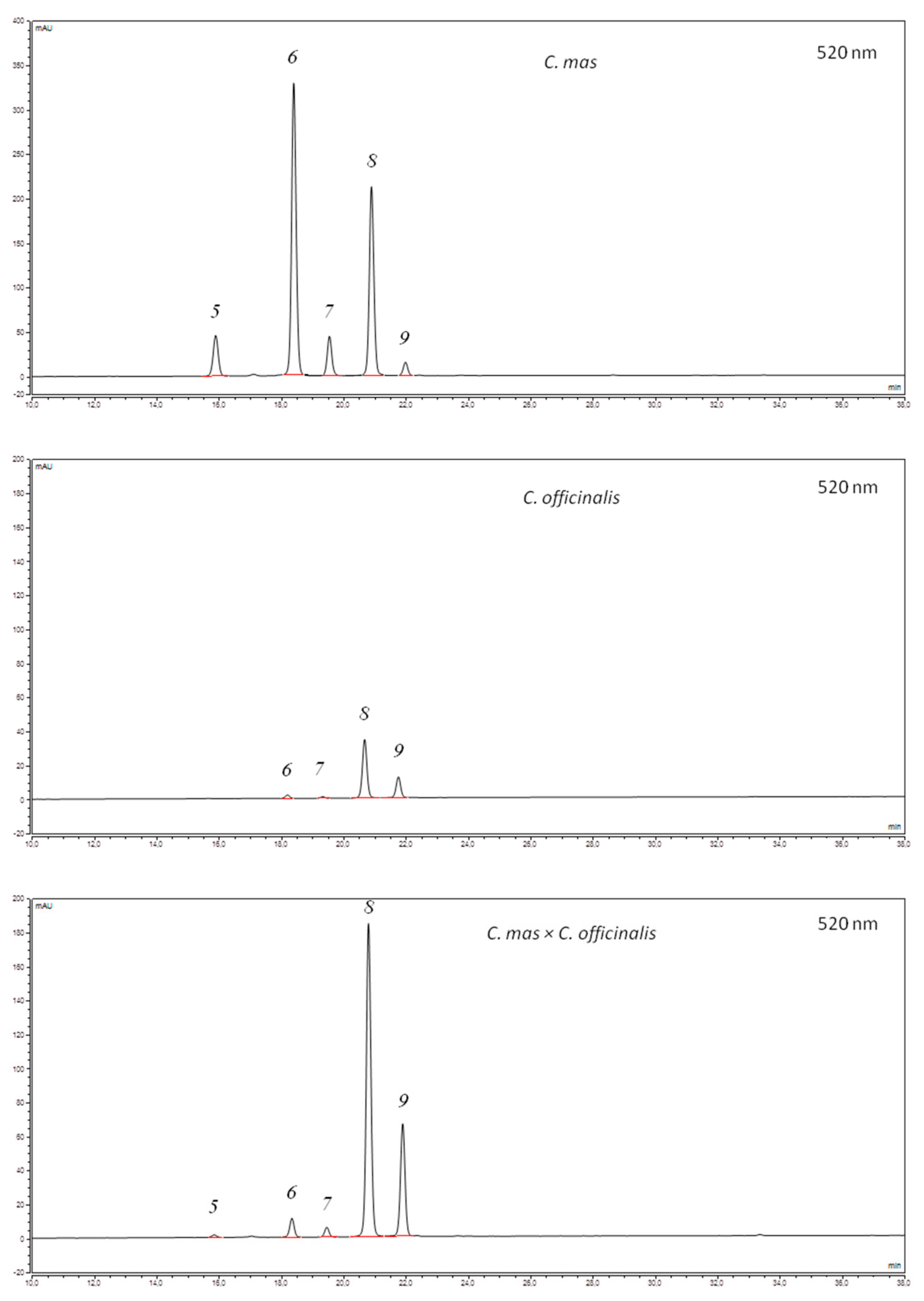
2.4. HPLC Quantification of Iridoids and Flavonoids
2.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC) and Antioxidative Capacity (AC)
2.5.1. Total Phenolic Content
2.5.2. FRAP Assay
2.5.3. DPPH Assay
2.5.4. ABTS Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Iridoids, Anthocyanins, and Flavonols of the Cornus Fruit Extracts
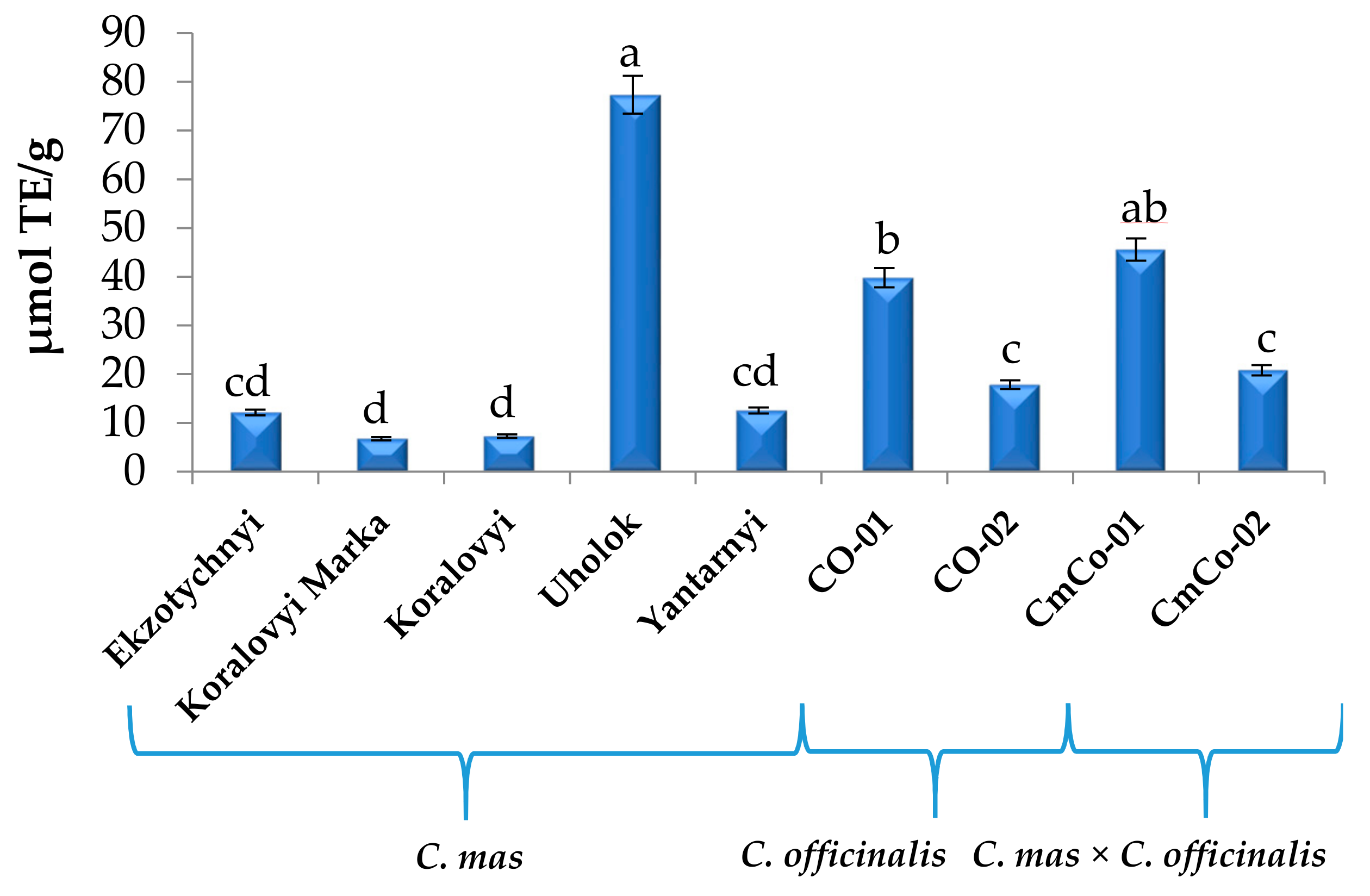
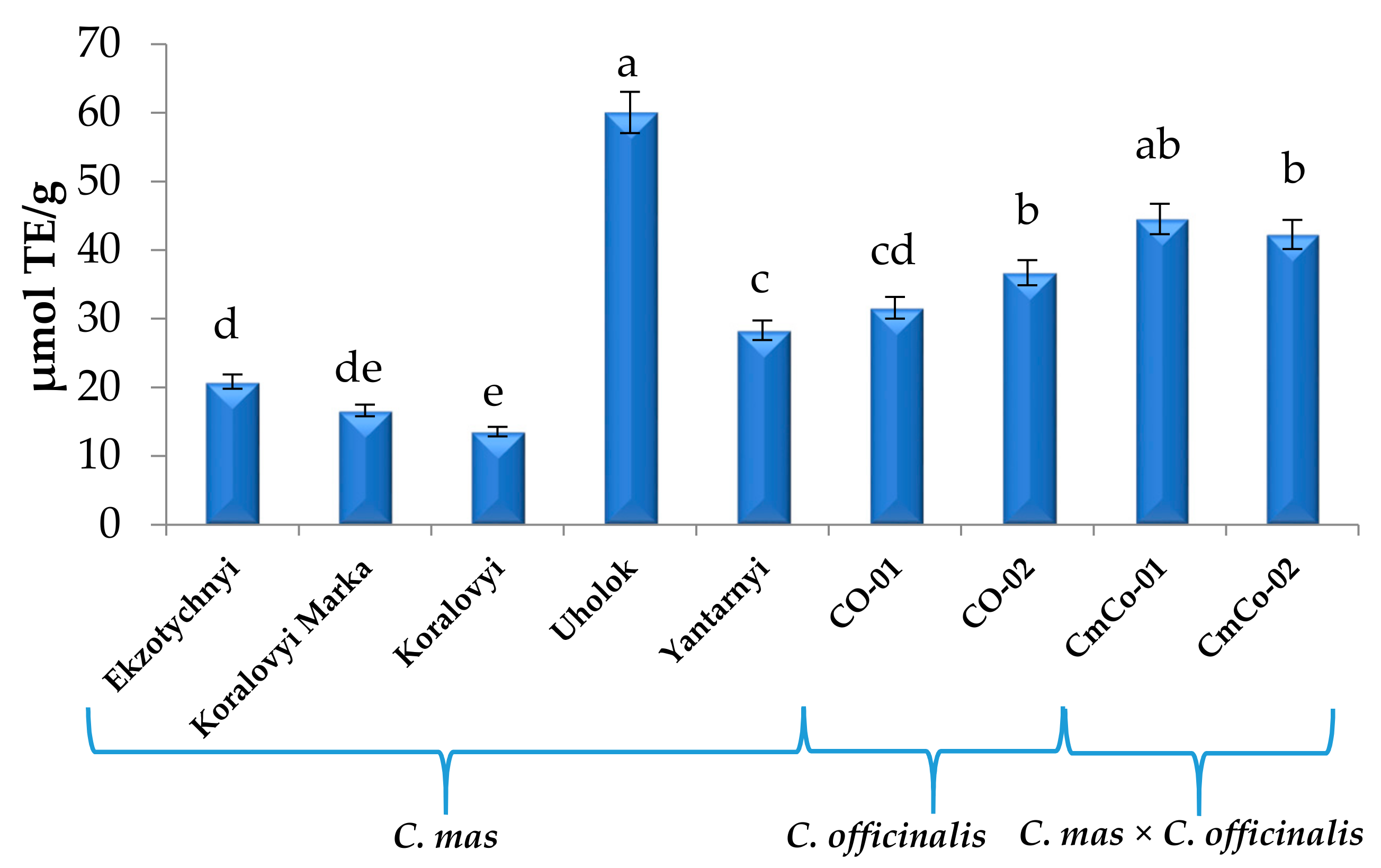
3.2. Antioxidant Capacity (AC) of Cornus Fruit Extracts
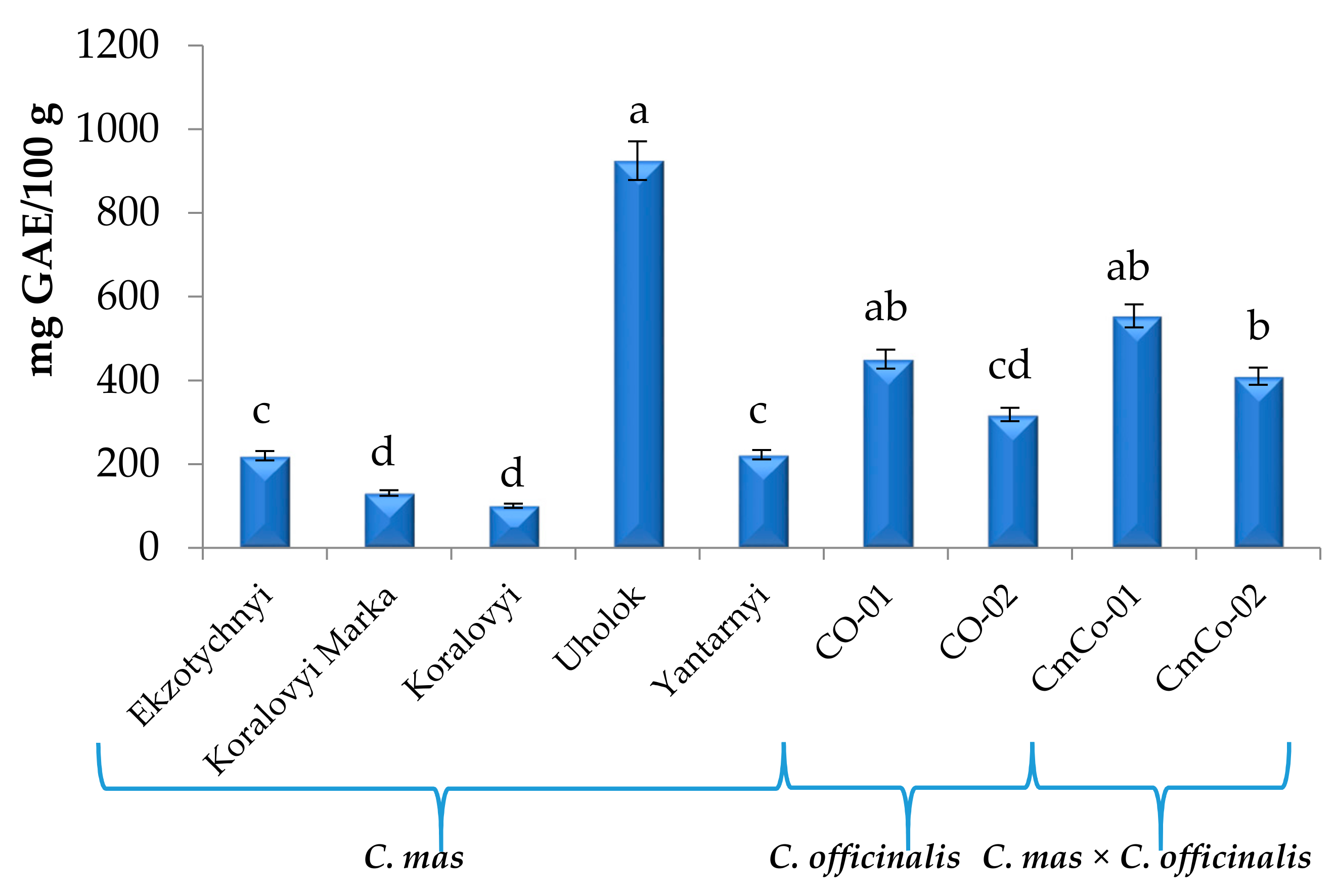
3.3. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) of the Cornus Fruit Extracts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brindza, P.; Brindza, J.; Tóth, D.; Klimenko, S.; Grigorieva, O. Biological and commercial characteristics of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) Population in the Gemer Region of Slovakia. Acta Hortic. 2009, 818, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymenko, S.; Grygorieva, O.; Brindza, J. Less Known Species of fruIt Crops; Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra: Nitra, Slovakia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Piórecki, N. Morphological, physical & chemical, and antioxidant profiles of polish varieties of cornelian cherry fruit (Cornus mas L.). Żywn. Nauka Technol. Jakość 2011, 3, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Pantelidis, G.E.; Vasilakakis, M.; Manganaris, G.A.; Diamantidis, G. Antioxidant capacity, phenol, anthocyanin and ascorbic acid contents in raspberries, blackberries, red currants, gooseberries and cornelian cherries. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, A.Z.; Szumny, A.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Piórecki, N.; Klymenko, S.V. Iridoids and anthocyanins in cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) cultivars. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 40, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tural, S.; Koca, I. Physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of cornelian cherry fruits (Cornus mas L.) grown in Turkey. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 116, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasam, B.; Olson, L.K.; Schutzki, R.E.; Tai, M.-H.; Nair, M.G. Amelioration of obesity and glucose intolerance in High-Fat-Fed C57BL/6 Mice by anthocyanins and ursolic acid in cornelian cherry (Cornus mas). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; West, B.J.; Jensen, C.J. UPLC-TOF-MS characterization and identification of bioactive iridoids in Cornus mas Fruit. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, B.J.; Deng, S.; Jensen, C.J.; Palu, A.K.; Berrio, L.F. Antioxidant, toxicity, and iridoid tests of processed cornelian cherry fruits. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirtzi, C.; Tsatalas, P.; Spanakis, M.; Kokkalou, E. GC-MS analysis of volatile constituents of Cornus mas fruits and pulp. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2013, 16, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Gorji, A.; Asgary, S.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; Siavash, M. Evaluation of the effects of Cornus mas L. fruit extract on glycemic control and insulin level in type 2 diabetic adult patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shishehbor, F.; Azemi, M.E.; Zameni, D.; Saki, A. Inhibitory effect of hydroalcoholic extracts of barberry, sour cherry and cornelian Cherry α-amylase and α-Glucosidase activities. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2016, 5, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, B.M.; Štajner, D.; Slavko, K.; Sandra, B. Antioxidant capacity of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.)–comparison between permanganate reducing antioxidant capacity and other antioxidant methods. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Asgary, S.; Adelnia, A.; Setorki, M.; Khazaei, M.; Kazemi, S. The effects of cornelian cherry on athero-sclerosis and atherogenic factors in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabi, M.; Sadraie, J.; Ghaffarifar, F. Comparative study of the effect of garlic tablet and blueberry extract on Cryptosporidum parvumoocysts in HANK solution. Sci. J. Kurdistan Univ. Med Sci. 2012, 17, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Darbandi, N.; Hashemi, A.; Noori, M.; Momeni, H.R. Effect of Cornus mas fruit flavonoids on memory retention, level of plasma glucose and lipids in an intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced experimental Alzheimer’s disease model in Wistar rats. Environ. Exp. Biol. 2016, 14, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Shokrzadeh, M.; Majd, A.; Nezhadsattari, T. Cytotoxic effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Cornus mas L. fruit on MCF7, HepG2 and CHO cell line by MTT Assay. J. Maz. Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 24, 130–138. [Google Scholar]
- Somi, M.H.; Banihabib, N.; Dehghan, G.; Haghi, M.E.; Panahi, F. Hepatoprotective effect of Cornus mas fruits extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in male albino rats. Thrita 2014, 3, 17625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moldovan, B.; Filip, A.; Clichici, S.; Suharoschi, R.; Bolfa, P.; David, L. Antioxidant activity of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) fruits extract and the in vivo evaluation of its anti-inflammatory effects. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirtzi, C.; Tsatalas, P.; Gabrieli, C.; Plioukas, M.; Kokkalou, E. LC-DAD-MS analysis, antioxidant and biological activities of Cornus mas fruits and pulp. J. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 5, 320–328. [Google Scholar]
- Klimenko, S. The cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.); collection, preservation and utilization of genetic resources. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2004, 12, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Brindza, P.; Brindza, J.; Tóth, D.; Klimenko, S.; Grigorieva, O. Slovakian cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.): Potential for cultivation. Acta Hortic. 2007, 760, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, G.; Turcsi, E.; Molnár, P.; Szabó, L.G.; Deli, J. University of Pécs Institute of Pharmacognosy Pécs Rókus u. Hungary isolation and identification of carotenoids in the fruit of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.). Planta Med. 2007, 73, P_286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovac, A.; Joksić, G.; Jankovic, T.; Šavikin, K.; Menković, N. Radioprotective properties of the phytochemically characterized extracts of Crataegus monogyna, Cornus mas and Gentianella austriaca on human lymphocytes in vitro. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucarska, A.Z.; Szumny, A.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Zając, K. Fatty acid compositions of seed oils of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.). Acta Biochim. Pol. 2009, 56, 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, K.; Ercisli, S.; Zengin, Y.; Sengul, M.; Kafkas, E. Preliminary characterisation of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) genotypes for their physico-chemical properties. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, H.; Yousef, H.; Jafar, H.; Mohammad, A. Antioxidant capacity and phytochemical properties of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) genotypes in Iran. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetkovská, J.; Diviš, P.; Vespalcová, M.; Pořízka, J.; Reznicek, V. Basic nutritional properties of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) cultivars grown in the Czech Republic. Acta Aliment. 2015, 44, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milenkovic-Andjelkovic, A.; Andjelkovic, M.; Radovanovic, A.; Radovanovic, B.; Nikolic, V. Phenol composition, DPPH radical scavenging and antimicrobial activity of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas) fruit and leaf extracts. Chem. Ind. 2015, 69, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przybylska, D.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Cybulska, I.; Sozański, T.; Piórecki, N.; Fecka, I. Cornus mas L. stones: A valuable by-product as an ellagitannin source with high antioxidant potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efenberger-Szmechtyk, M.; Nowak, A.; Czyżowska, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Fecka, I. Composition and antibacterial activity of Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliot, Cornus mas L. and Chaenomeles superba Lindl. leaf extracts. Molecules 2020, 25, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussouni, S.; Karakousi, C.V.; Tsatalas, P.; Lazari, D.; Kokkalou, E. Biological studies with phytochemical analysis of Cornus mas unripe fruits. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, K.-J.; Cheng, C.-S.; Yan, G.-Q.; Lu, W.-L.; Ge, J.-F.; Cheng, Y.-X.; Li, N. Bioactive compounds from Cornus officinalis fruits and their effects on diabetic nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Gao, Q.; Yin, L.; Quan, H.; Chen, R.; Fu, X.; Lin, D. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, M.-Y.; Yu, Z.-L.; Hu, W.; Cai, B.-C. Studies on separation, appraisal and the biological activity of 5-HMF in Cornus officinalis. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2008, 33, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, B.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Park, K.-S.; Chung, K.-H.; Kim, C.-H. Attenuating effect of a traditional korean formulation, Paeng-Jo-Yeon-Nyeon-Baek-Ja-In-Hwan(PJBH), on hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in PC12 cells. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Tain, Y.-L.; Chiang, P.-H. Ba-Wei-Die-Huang-Wan (Hachimi-jio-gan) can ameliorate cyclophosphamide-induced ongoing bladder overactivity and acidic adenosine triphosphate solution-induced hyperactivity on rats prestimulated bladder. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 184, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, X.D.; Cai, H.; Cai, B.C. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Fructus Corni. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 18, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.-H.; Seo, C.-S.; Lee, H.-Y.; Jung, D.-Y.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, J.-A.; Song, K.Y.; Shin, H.-K.; Lee, M.-Y.; Seo, Y.B.; et al. Hepatoprotective and antioxidative activities of Cornus officinalis against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, C.; Cao, B.; Li, G.; Mao, M. Ecological effects on phenotypic, cytological and biochemical diversity of Cornus officinalis germplasm resources in China and USA. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.J.; Kim, T.B.; Yang, H.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Neuroprotective iridoid glycosides from Cornus officinalis fruits against glutamate-induced toxicity in HT22 hippocampal cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quah, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.-B.; Birhanu, B.; Ali, S.; Abbas, M.; Boby, N.; Im, Z.-E.; Park, S.-C. Cornus officinalis ethanolic extract with potential anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Sun, F.; An, Y.; Ai, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Li, L. Morroniside protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 613, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yang, P.; Zhang, L. Mode of action of Shan-Zhu-Yu (Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc.) in the treatment of depression based on network pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Park, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Jeong, I.-Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Seo, K.-I. Apoptotic action of ursolic acid isolated from Corni fructus in RC-58T/h/SA#4 primary human prostate cancer cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6435–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E.; Liu, E.H.; Hui-Jun, L.I.; Ping, L.I. Chemical constituents from the fruit of Cornus officinalis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 7, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-Y.; Wang, R.; Shi, Y.-P. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Cornus officinalis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 45, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ye, X.-S.; Wang, X.-X.; Yang, Y.-N.; Zhang, P.-C.; Ma, B.-Z.; Zhang, W.-K.; Xu, J.-K. Four new iridoid glucosides containing the furan ring from the fruit of Cornus officinalis. Fitoterapia 2017, 120, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Feng, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-B.; Wang, F.-S.; Lu, J.-H. Corni Fructus: A review of chemical constituents and pharmacological activities. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, W.; Zhao, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Akanda, R.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; Choi, Y.-J.; Park, B.-Y. Neuroprotective effects of Cornus officinalis on stress-induced hippocampal deficits in rats and H2O2-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.-I.; Nishioka, I. Sedoheptulose digallate from Cornus officinalis. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 3469–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Yang, J.; Wu, X.-G.; Xu, X.-J.; Fu, Q.-Y. Three new iridoids from leaves of Cornus officinalis. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 17, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analysis of nutritional components of Cornus officianalis. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 32, 785–789. [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. Analysis of fat-soluble components in Cornus officinalis flesh and seeds by GC-MS. Food Sci. 2007, 28, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.S. Galloyl glucoses from the seeds of Cornus officinalis with inhibitory activity against protein glycation, aldose reductase, and cataractogenesis ex vivo. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-C.; Yang, J.; Li, J.-K.; Liang, X.-H.; Sun, J.-L. Two new secoiridoid glucosides from the twigs of Cornus officinalis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozowska, M.; Gawrońska, B.; Woźnicka, A. Morphological, anatomical and genetic differentiation of Cornus mas, Cornus officinalis and their interspecific hybrid. Dendrobiology 2013, 70, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klymenko, S.; Ilyinska, A. Biometric characteristics of fruits and leaves of Cornus officinalis Siebold et Zucc. genotypes in the M.M. Gryshko National Botanical Garden of the NAS of Ukraine. Plant Introd. 2020, 85–86, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ohlander, M.; Jeppsson, N.; Björk, L.; Trajkovski, V. Changes in antioxidant effects and their relationship to phytonutrients in fruits of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) during maturation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.-C.; Chen, H.-Y. Antioxidant activity of various tea extracts in relation to their antimutagenicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymenko, S.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Piórecki, N. Antioxidant activities and phenolic compounds in fruits of cultivars of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.). Agrobiodiversity Improv. Nutr. Health Life Qual. 2019, 3, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Cai, H.; Wang, M.; Ding, X.; Yang, H.; Cai, B. Simultaneous determination of six active components in crude and processed Fructus Corni by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Total saponins of Cornus officinalis Sieb. ameliorates the endothelium dependent relaxation of mesenteric artery by regulating nitric oxide release in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2012, 37, 757–764. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, G.; Chen, X.; Chai, Y. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Fructus Corni using ultrasound assisted microwave extraction and high performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array UV detection and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, X. Simultaneous Determination of 11 high-polarity components from Fructus Corni: A quantitative LC–MS/MS method for improved quality control. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 56, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareed, S.K.; Reddy, M.K.; Schutzki, R.E.; Nair, M.G. Anthocyanins in Cornus alternifolia, Cornus controversa, Cornus kousa and Cornus florida fruits with health benefits. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Wu, X.; Schaich, K. Standardized Methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Hydamaka, A.W.; Lowry, L.; Beta, T. Comparison of antioxidant capacity and phenolic compounds of berries, chokecherry and seabuckthorn. Open Life Sci. 2009, 4, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalaby, A.; Shanab, S.M.M. Antioxidant compounds, assays of determination and mode of action. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Tsao, R. Nomenclature and general classification of antioxidant activity/capacity assays. In Measurement of Antioxidant Activity & Capacity; Apak, R., Capanoglu, E., Shahidi, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorta, E.; Fuentes-Lemus, E.; Speisky, H.; Lissi, E.; López-Alarcón, C. Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of food samples: A chemical examination of the oxygen radical absorbance capacity assay. In Measurement of Antioxidant Activity & Capacity; Apak, R., Capanoglu, E., Shahidi, F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovic-Uzelac, V.; Levaj, B.; Bursa, D.; Pedisi, S.; Radoji, I.; Biško, A. Total phenolics and antioxidant capacity assays of selected fruits. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2007, 72, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, K.-A.; Hwang, Y.-J.; Song, J. Antioxidant activities and oxidative stress inhibitory effects of ethanol extracts from Cornus officinalis on raw 264.7 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeon, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, M.-R. Antioxidative, Antimutagenic, and Cytotoxic Activities of Ethanol Extracts from Cornus officianalis. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.-H.; Choi, S.H.; Oh, Y.I.; Kim, S.-J. Anti-oxidative effects of flavonoids enriched Corni fructus extract and the mechanism. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rop, O.; Mlcek, J.; Kramarova, D.; Jurikova, T. Selected cultivars of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) as a new food source for human nutrition. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Biaggi, M.; Donno, D.; Mellano, M.G.; Riondato, I.; Rakotoniaina, E.N.; Beccaro, G.L. Cornus mas (L.) fruit as a potential source of natural health-promoting compounds: Physico-chemical characterisation of bioactive components. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, F.; Kalyoncu, I.H. Some nutritional, pomological and physical properties of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.). J. Food Eng. 2003, 60, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijelić, S.M.; Gološin, B.R.; Todorović, J.I.N.; Cerović, S.B.; Popović, B.M. Physicochemical fruit characteristics of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) Genotypes from Serbia. HortScience 2011, 46, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ersoy, N.; Bagci, Y.; Gok, V. Antioxidant properties of 12 cornelian cherry fruit types (Cornus mas L.) selected from Turkey. Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Piórecki, N.; Fecka, I. Iridoids, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of edible honeysuckle berries (Lonicera caerulea var. kamtschatica Sevast.). Molecules 2017, 22, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghisalberti, E. Biological and pharmacological activity of naturally occurring iridoids and secoiridoids. Phytomedicine 1998, 5, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound 1 | C. mas | C. officinalis | C. mas × C. officinalis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ekzotychnyi | Koralovyi Marka | Koralovyi | Uholok | Yantarnyi | Co-01 | Co-02 | CmCo-01 | CmCo-02 | |
| Iridoids | |||||||||
| LA | 77.23 ± 0.83 e 2 | 156.31 ± 27.45 d | 192.71 ± 15.00 c | 239.02 ± 1.79 b | 200.72 ± 0.34 c | 70.76 ± 6.32 e,f | 46.15 ± 3.14 f | 269.32 ± 3.68 a | 193.64 ± 16.16 c |
| Mo | nd 3 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 1037.74 ± 87.52 a | 529.52 ± 30.02 b | 9.68 ± 0.32 c | nd |
| S + L | 2.50 ± 0.37 d | nd | nd | 2.84 ± 0.25 d | 6.44 ± 0.66 d | 223.55 ± 18.11 a | 172.16 ± 10.88 b | 38.14 ± 0.72 c | 28.27 ± 1.72 c |
| Co | 9.36 ± 0.56 e | 8.81 ± 1.37 e | 9.04 ± 0.92 e | 27.07 ± 0.86 c | 18.51 ± 0.13 d | 109.17 ± 9.32 a | 44.98 ± 3.49 b | 32.51 ± 0.27 c | 15.38 ± 2.11 d,e |
| Total | 89.09 e | 165.12 d,e | 201.75 d | 268.93 c,d | 225.67 d | 1441.22 a | 792.81 b | 349.65 c | 237.29 d |
| Anthocyanins | |||||||||
| Df-gal | 0.39 ± 0.02 b | 0,26 ± 0.04 b | nd | 32.81 ± 0.58 a | nd | nd | tr 4 | tr | 0.69 ± 0.14 b |
| Cy-gal | 41.04 ± 0.14 b | 6.83 ± 1.18 c | 0.24 ± 0.02 c | 216.28 ± 8.52 a | nd | 0.58 ± 0.03 c | 1.20 ± 0.14 c | 3.43 ± 0.13 c | 1.75 ± 0.21 c |
| Cy-rob | 7.62 ± 0.02 b | 1.08 ± 0.09 c,d | nd | 30.00 ± 1.83 a | nd | 0.28 ± 0.04 c,d | 0.35 ± 0.03 c,d | 1.69 ± 0.02 c | 1.08 ± 0.13 c,d |
| Pg-gal | 23.59 ± 0.12 c | 23.12 ± 3.18 c | 3.82 ± 0.35 e | 138.79 ± 3.16 a | nd | 11.99 ± 1.20 d | 6.59 ± 0.60 e | 58.78 ± 1.53 b | 20.79 ± 3.27 c |
| Pg-rob | 1.86 ± 0.00 d | 1.76 ± 0.17 d | nd | 9.87 ± 0.51 b | nd | 4.33 ± 0.43 c | 2.38 ± 0.12 d | 20.74 ± 0.66 a | 11.24 ± 1.66 b |
| Total | 74.50 b | 33.05 c | 4.06 d | 427.75 a | nd | 17.18 d | 10.52 d | 84.64 b | 35.55 c |
| Flavonols | |||||||||
| Q-glcr | 0.22 ± 0.01 d | 0.48 ± 0.07 d | 0.40 ± 0.02 d | 1.85 ± 0.04 c | 1.90 ± 0.07 c | 10.83 ± 1.28 a | 7.89 ± 0.72 b | 2.39 ± 0.20 c | 0.59 ± 0.05 d |
| Kf-gal | 1.06 ± 0.04 c | 0.48 ± 0.08 d | 0.07 ± 0.01 e,f | 8.82 ± 0.17 a | nd | 1.74 ± 0.13 b | 0.24 ± 0.03 e | 1.23 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.04 e |
| Total | 1.28 e,f | 0.96 e,f | 0.47 f | 10.67 b | 1.90 e | 12.57 a | 8.13 c | 3.62 d | 0.81 e,f |
| Components | DPPH | ABTS | FRAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthocyanins | 0.843 * | 0.716 * | 0.889 * |
| Iridoids | 0.234 | 0.129 | 0.106 |
| Flavonols | 0.707 * | 0.556 | 0.633 |
| TPC | 0.979 * | 0.942 * | 0.981 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klymenko, S.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Piórecki, N.; Przybylska, D.; Grygorieva, O. Iridoids, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Cornus mas, C. officinalis, and C. mas × C. officinalis Fruits. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060776
Klymenko S, Kucharska AZ, Sokół-Łętowska A, Piórecki N, Przybylska D, Grygorieva O. Iridoids, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Cornus mas, C. officinalis, and C. mas × C. officinalis Fruits. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(6):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060776
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlymenko, Svitlana, Alicja Zofia Kucharska, Anna Sokół-Łętowska, Narcyz Piórecki, Dominika Przybylska, and Olga Grygorieva. 2021. "Iridoids, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity of Cornus mas, C. officinalis, and C. mas × C. officinalis Fruits" Biomolecules 11, no. 6: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060776






