Current Perspectives on the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MMPs as Molecular Promoters in Carcinogenesis
| Groups | Substrates and Targets | MMPs as Activators for Other MMPs |
|---|---|---|
| Collagenases [8,9,12,38,39] | ||
| MMP-1 (collagenase-1) | type I, II, III, VII, VIII, X and XI collagens [40,41], gelatin, nidogen [42], casein, aggrecan [43], perlecan, serpins, tenascin-C [44], versican, vitronectin, fibronectin, L-selectin, ovostatin, myelin basic protein, SDF-1 [45], pentraxin-3 [46], IGFBP [47], TNF precursor [48], VEGF-binding ECM proteins [49] | MMP-1 activates pro-MMP-2 [50] and pro- MMP-9 [51] |
| MMP-8 (collagenase-2) | type I, II, III, V, VII, VIII, and X collagens [52], gelatin, aggrecan [53], elastin, laminin [54], nidogen, fibronectin [55], ovostatin | MMP-8 activates pro-MMP-8 |
| MMP-13 (collagenase-3) | type I-IV, IX, X, and XIV collagens [56,57,58], gelatin, plasminogen, fibronectin [58], osteonectin, aggrecan [59], perlecan [35], laminin, tenascin [58], casein | MMP-13 activates pro-MMP-2 and pro-MMP-9 [60] |
| MMP-18 (collagenase-4) | type I-III collagens, gelatin | |
| Gelatinases [8,9,11,12,46,61] | ||
| MMP-2 (gelatinase A) | gelatin, type I-V, VII, X and XI collagens [40,62,63], elastin [63], aggrecan, laminin [64], fibronectin, nidogen, versican [51], tenascin, vitronectin, myelin basic protein, IGFBP-5 [65], follistatin-like 1 protein [66], follistatin-like 3 protein [46], mHB-EGF, CCL7/MCP-3 [67], CX3CL1/fractalkine, galectin-1, galectin-3 [68], transglutaminase [69], osteopontin, big endothelin-1 [70], TNF precursor, TGF beta, thrombospondin-2 and pyruvate kinase M1/M2 [71] | |
| MMP-9 (gelatinase B) | gelatin, type IV, V, VII, X and XIV collagens [40,63,72,73], aggrecan [43], elastin [63], fibronectin, laminin, nidogen, versican [51], decorin, myelin basic protein, casein, vitronectin, cytokines, chemokines, mHB-EGF [74], interleukin-8 [75], galectin-3 [68], interleukin-2 receptor-α [76], GCP-2/LIX [77], IGFBP [71], TNF precursor, TGF beta, VEGF-binding ECM proteins [49], thrombospondin-2 and pyruvate kinase M1/M2 [71] | |
| Stromelysins [8,9,12,26,78,79] | ||
| MMP-3 (stromelysin-1) | type I-V [63] and IX-XI collagens, gelatin, aggrecan [80], ovostatin, nidogen [81], laminin, elastin, casein [82], osteonectin [60], decorin [44], fibronectin, perlecan [35], proteoglycans, versican [51], tenascin, myelin basic protein, osteopontin, plasminogen [83], IGFBP-3 [84], TNF precursor, VEGF-binding ECM proteins [49] | MMP-3 activates pro-MMP-1 [85], pro-MMP-8, pro-MMP-13 [86] and gelatinases [87,88] |
| MMP-10 (stromelysin-2) | type III-V [63,89], IX and X collagens, gelatin [86], aggrecan [80], fibronectin, casein [82], elastin [63], laminin, nidogen, proteoglycans, fibrilin-10 | MMP-10 activates pro-MMP-1 [82], pro-MMP-8 [90] and pro-MMP-10 |
| MMP-11 (stromelysin-3) | gelatin, fibronectin [91,92], aggrecan, laminin receptor [78] | |
| Matrilysins [8,9,12,61] | ||
| MMP-7 (matrilysin-1) | type IV and X collagens [41,93], gelatin [93], aggrecan [43], decorin [94], elastin [63], entactin [73], casein [93], transferrin [95], fibronectin [93], laminin [93], plasminogen [96], vitronectin, tenascin [97], myelin, proteoglycans, β4-integrin, mHB-EGF [98], E-cadherin [19], osteopontin, syndecan [99], FasL [100] | MMP-7 activates pro-MMP-2 [101], pro-MMP-7 and pro-MMP-9 [102] |
| MMP-26 (matrilysin-2) | type IV collagen [103], gelatin [103], fibronectin [103], fibrinogen, vitronectin [104], casein, α2-macroglobulin | MMP-26 activates pro-MMP-2 and pro-MMP-9 |
| Trans-membrane [8,9,12,46,105] | ||
| MMP-14 (MT1-MMP) | type I-III collagens [106,107], gelatin, casein, fibronectin, laminin, nidogen [107], aggrecan, elastin, fibrin, perlecan, tenascin, vitronectin and proteoglycans [106,107,108], fibrilin-1, α2-macroglobulin [106], dickkopf-1 and cysteine-rich motor neuron-1 [109], galectin-1 [110], galectin-3 [111], syndecan-1, follistatin-like 3 protein [46], cyclophilin A [46], transglutaminase [112], pentraxin-3 [46] | MMP-14 activates pro-MMP-2 [113], pro-MMP-8 and pro-MMP-13 [114] |
| MMP-15 (MT2-MMP) | type I collagen, gelatin, fibronectin [107], laminin [107], aggrecan, perlecan [107], nidogen [107], tenascin, vitronectin, transglutaminase [112] | MMP-15 activates pro-MMP-2 [115] and pro-MMP-13 |
| MMP-16 (MT3-MMP) | type I and III collagens [116], gelatin, casein [117], fibronectin, aggrecan, laminin, perlecan, vitronectin, syndecan [118], transglutaminase [112], VEGF-binding ECM proteins [49] | MMP-16 activates pro-MMP-2 [115], pro-MMP-9 and pro-MMP-13 |
| MMP-24 (MT5-MMP) | gelatin, fibronectin [119], proteoglycans [119], N-cadherin [120] | MMP-24 activates pro-MMP-2 [121] and pro-MMP-13 |
| GP1-anchored [8,9,11,12,26,122,123] | ||
| MMP-17 (MT4-MMP) | fibrinogen [124], fibrin [124], gelatin [125], TNF precursor | |
| MMP-25 (MT6-MMP) | type IV collagen, proteoglycans, gelatin [126], fibronectin [127], vimentin [122], cystatin C [122], galectin-1 [122] | MMP-25 activates pro-MMP-2 [128] |
| Other enzymes [8,9,12,38] | ||
| MMP-12 (macrophage metalloelastase) | type I, IV [129] and V collagens, gelatin [129], elastin [130], fibronectin [129], laminin [129], vitronectin [129], proteoglycans [131], elastin, entactin [132], osteonectin, aggrecan, myelin, fibrinogen [131], α1-antitripsin [133], serine protease inhibitor α1-PI, TNF precursor | |
| MMP-19 (RASI-1) | type I and IV collagens, gelatin [134], aggrecan [135], fibronectin, casein, laminin, nidogen [136], tenascin, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein [135] | MMP-19 activates pro-MMP-9 |
| MMP-20 (enamelysin) | type V collagen, aggrecan [135], amelogenin [121] | |
| MMP-21 (Xenopus-MMP) | - | |
| MMP-23 (CA-MMP) | gelatin | |
| MMP-27 (human MMP-22 homolog) | gelatin | |
| MMP-28 (epylisin) | casein |
3. UV Radiation as a Trigger for MMP Production
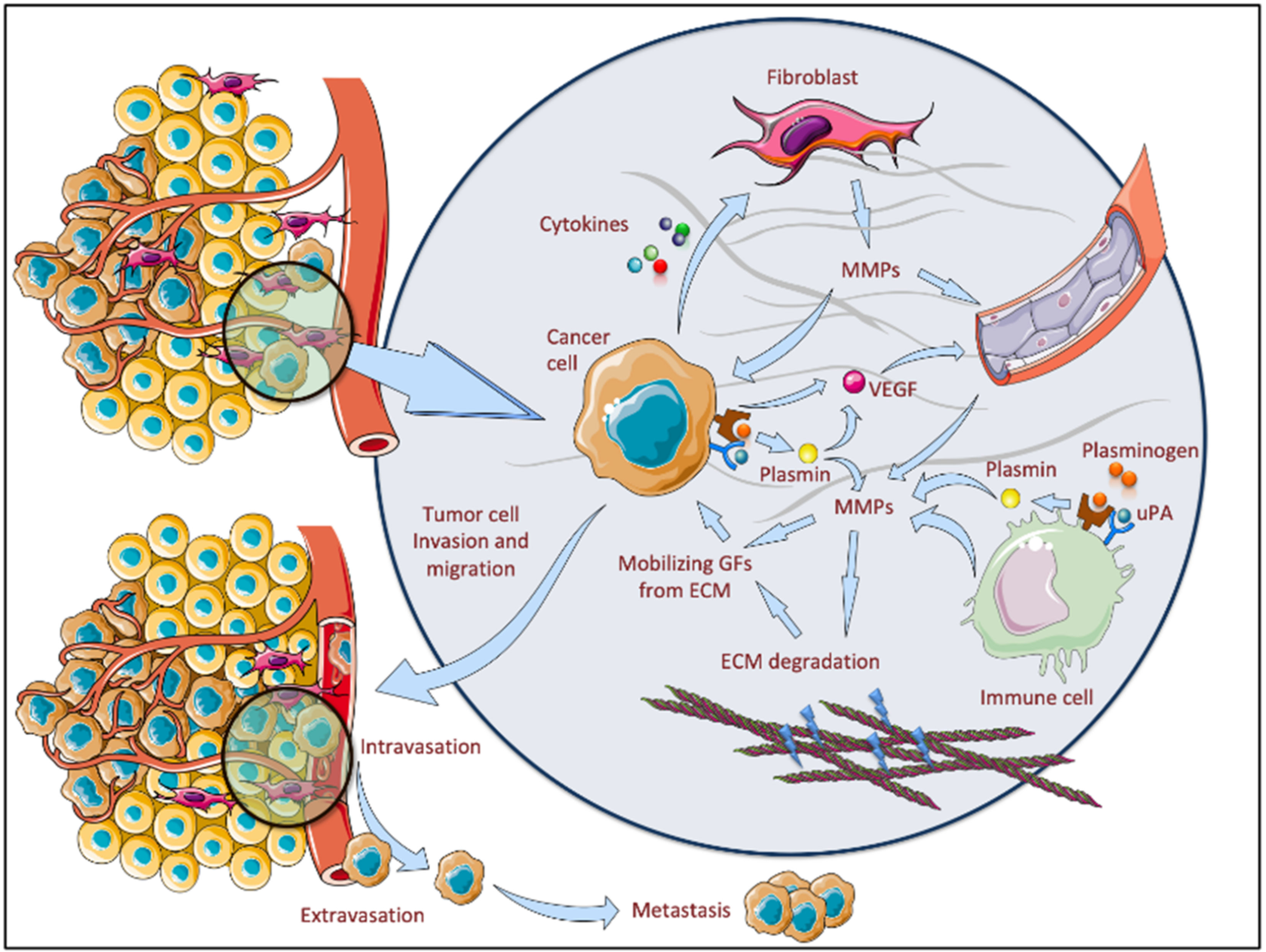
4. Tumor Microenvironment—An Important Source of MMPs in BCC
5. The Role of MMPs in BCC Pathogenesis
5.1. The Expression of MMPs in BCC
5.2. The Link between MMPs and BCC Invasiveness and Recurrence
6. TIMPs—Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases—Potential New Agents in the Management of BCC
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, C.S.; Strange, R.C.; Lear, J.T. Basal cell carcinoma. Bio Med. J. 2003, 327, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.P.; Kus, K.J.; Ruiz, E. Basal Cell Carcinoma Review. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuka, A.G.; Book, S.E. Basal Cell Carcinoma: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Histopathology, and Management. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lupu, M.; Popa, I.M.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Caruntu, A.; Caruntu, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of in VivoReflectance Confocal Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilie, M.A.; Caruntu, C.; Lupu, M.; Lixandru, D.; Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.-R.; Bastian, A.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M.; Zurac, S.A.; et al. Current and Future Applications of Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Imaging in Skin Oncology. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4102–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Photoaging and Photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, D.; Morrison, C.J.; Overall, C.M. Matrix Metalloproteinases: What Do They Not Do? New Substrates and Biological Roles Identified by Murine Models and Proteomics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1803, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laronha, H.; Caldeira, J. Structure and Function of Human Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cells 2020, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, P.G.; Butler, G.S.; Overall, C.M. New Intracellular Activities of Matrix Metalloproteinases Shine in the Moonlight. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Benko, C.; Gill, S.E.; Dufour, A. The Pharmacological TAILS of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Bostan, M.; Caruntu, C.; Ignat, S.R.; Dinescu, S.; Costache, M. Proteomic Technology “Lens” for Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process Identification in Oncology. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 3565970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stawowy, P.; Meyborg, H.; Stibenz, D.; Stawowy, N.B.P.; Roser, M.; Thanabalasingam, U.; Veinot, J.P.; Chrétien, M.; Seidah, N.G.; Fleck, E.; et al. Furin-Like Proprotein Convertases Are Central Regulators of the Membrane Type Matrix Metalloproteinase–Pro-Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Proteolytic Cascade in Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2005, 111, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, Y. Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloproteinases: Their Functions and Regulations. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiouni, W.; Ali, M.A.M.; Schulz, R. Multifunctional Intracellular Matrix Metalloproteinases: Implications in Disease. FEBS J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissinen, L.; Kähäri, V.-M. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounni, N.E.; Roghi, C.; Chabottaux, V.; Janssen, M.; Munaut, C.; Maquoi, E.; Galvez, B.G.; Gilles, C.; Frankenne, F.; Murphy, G.; et al. Up-Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A by Active Membrane-Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase through Activation of Src-Tyrosine Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13564–13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGuire, J.K.; Li, Q.; Parks, W.C. Matrilysin (Matrix Metalloproteinase-7) Mediates E-Cadherin Ectodomain Shedding in Injured Lung Epithelium. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilles, C.; Polette, M.; Coraux, C.; Tournier, J.M.; Meneguzzi, G.; Munaut, C.; Volders, L.; Rousselle, P.; Birembaut, P.; Foidart, J.M. Contribution of MT1-MMP and of Human Laminin-5 Gamma2 Chain Degradation to Mammary Epithelial Cell Migration. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargová, V.; Pytliak, M.; Mechírová, V. Matrix Metalloproteinases. In Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors; Experientia Supplementum; Gupta, S.P., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 103, pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Costache, R.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9423907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badea, M.; Baroş, A.; Bohîlţea, R.E.; Julea, I.E.; Furtunescu, F.; Istrate-Ofiţeru, A.M.; Iovan, L.; Cîrstoiu, M.M.; Burcin, M.R.; Turcan, N.; et al. Modern Interdisciplinary Monitoring of Cervical Cancer Risk. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alaseem, A.; Alhazzani, K.; Dondapati, P.; Alobid, S.; Bishayee, A.; Rathinavelu, A. Matrix Metalloproteinases: A Challenging Paradigm of Cancer Management. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 56, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdiaki, A.; Neagu, M.; Giatagana, E.-M.; Kuskov, A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Nikitovic, D. Glycosaminoglycans: Carriers and Targets for Tailored Anti-Cancer Therapy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Matejczyk, M.; Rosochacki, S. Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs), the Main Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Enzymes in Collagen Degradation, as a Target for Anticancer Drugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rowe, R.G.; Weiss, S.J. Breaching the Basement Membrane: Who, When and How? Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doren, S.R. Matrix Metalloproteinase Interactions with Collagen and Elastin. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, A.; Overall, C.M. Missing the Target: Matrix Metalloproteinase Antitargets in Inflammation and Cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, S.; Ferrari, G.; Cinnante, K.; Scheerer, W.; Galloway, A.C.; Roses, D.F.; Rozanov, D.V.; Remacle, A.G.; Oh, E.-S.; Shiryaev, S.A.; et al. Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-2 Binding to Membrane-Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase Induces MAPK Activation and Cell Growth by a Non-Proteolytic Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialeli, C.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Cancer Progression and Their Pharmacological Targeting. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojilla, C.V.; Kim, I.; Kassiri, Z.; Fata, J.E.; Fang, H.; Khokha, R. Metalloproteinase Axes Increase Beta-Catenin Signaling in Primary Mouse Mammary Epithelial Cells Lacking TIMP3. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sounni, N.E.; Noel, A. Membrane Type-Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tumor Progression. Biochimie 2005, 87, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelock, J.M.; Murdoch, A.D.; Iozzo, R.V.; Underwood, P.A. The Degradation of Human Endothelial Cell-Derived Perlecan and Release of Bound Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor by Stromelysin, Collagenase, Plasmin, and Heparanases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10079–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases Are Essential for the Inflammatory Response in Cancer Cells. J. Signal Transduct. 2010, 2010, 985132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tampa, M.; Caruntu, C.; Mitran, M.; Mitran, C.; Sarbu, I.; Rusu, L.-C.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M.; Georgescu, S.-R. Markers of Oral Lichen Planus Malignant Transformation. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 1959506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herouy, Y.; Simkin, R.; Ulloa, J.; Pearson, I.C.; Mortimer, P.S.; Ciucci, J.L. Metalloproteinases (MMPs) and Their Inhibitors in Venous Leg Ulcer Healing. Phlebo Lymphol. 2004, 44, 231–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kerkelä, E.; Ala-aho, R.; Jeskanen, L.; Lohi, J.; Grénman, R.; Kähäri, M.-V.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Differential Patterns of Stromelysin-2 (MMP-10) and MT1-MMP (MMP-14) Expression in Epithelial Skin Cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welgus, H.G.; Fliszar, C.J.; Seltzer, J.L.; Schmid, T.M.; Jeffrey, J.J. Differential Susceptibility of Type X Collagen to Cleavage by Two Mammalian Interstitial Collagenases and 72-KDa Type IV Collagenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13521–13527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sires, U.I.; Schmid, T.M.; Fliszar, C.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gluck, S.L.; Welgus, H.G. Complete Degradation of Type X Collagen Requires the Combined Action of Interstitial Collagenase and Osteoclast-Derived Cathepsin-B. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 95, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sires, U.I.; Griffin, G.L.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Mecham, R.P.; Murphy, G.; Chung, A.E.; Welgus, H.G.; Senior, R.M. Degradation of Entactin by Matrix Metalloproteinases. Susceptibility to Matrilysin and Identification of Cleavage Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosang, A.J.; Last, K.; Knäuper, V.; Neame, P.; Murphy, G.; Hardingham, T.; Tschesche, H.; Hamilton, J. Fibroblast and Neutrophil Collagenases Cleave at Two Sites in the Cartilage Aggrecan Interglobular Domain. Biochem. J. 1993, 295, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, K.; Kusakabe, M.; Sakakura, T.; Nakanishi, I.; Okada, Y. Susceptibility of tenascin to degradation by matrix metalloproteinases and serine proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1994, 352, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New Functions for the Matrix Metalloproteinases in Cancer Progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, G.S.; Dean, R.A.; Tam, E.M.; Overall, C.M. Pharmacoproteomics of a Metalloproteinase Hydroxamate Inhibitor in Breast Cancer Cells: Dynamics of Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase-Mediated Membrane Protein Shedding. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 4896–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fowlkes, J.L.; Serra, D.M.; Nagase, H.; Thrailkill, K.M. MMPs are IGFBP-degrading proteinases: Implications for cell proliferation and tissue growth. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 878, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearing, A.J.H.; Beckett, P.; Christodoulou, M.; Churchill, M.; Clements, J.; Davidson, A.H.; Drummond, A.H.; Galloway, W.A.; Gilbert, R.; Gordon, J.L.; et al. Processing of Tumour Necrosis Factor-α Precursor by Metalloproteinases. Nature 1994, 370, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jilani, S.M.; Nikolova, G.V.; Carpizo, D.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Processing of VEGF-A by Matrix Metalloproteinases Regulates Bioavailability and Vascular Patterning in Tumors. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crabbe, T.; O’Connell, J.P.; Smith, B.J.; Docherty, A.J. Reciprocated matrix metalloproteinase activation: A process performed by interstitial collagenase and progelatinase A. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 14419–14425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perides, G.; Asher, R.A.; Lark, M.W.; Lane, W.S.; Robinson, R.A.; Bignami, A. Glial Hyaluronate-Binding Protein: A Product of Metalloproteinase Digestion of Versican? Biochem. J. 1995, 312, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visse, R.; Nagase, H. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases: Structure, Function, and Biochemistry. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fosang, A.J.; Last, K.; Neame, P.J.; Murphy, G.; Knäuper, V.; Tschesche, H.; Hughes, C.E.; Caterson, B.; Hardingham, T.E. Neutrophil Collagenase (MMP-8) Cleaves at the Aggrecanase Site E373-A374 in the Interglobular Domain of Cartilage Aggrecan. Biochem. J. 1994, 304, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-Fernández, A.; Fueyo, A.; Folgueras, A.R.; Garabaya, C.; Pennington, C.J.; Pilgrim, S.; Edwards, D.R.; Holliday, D.L.; Jones, J.L.; Span, P.N.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Functions as a Metastasis Suppressor through Modulation of Tumor Cell Adhesion and Invasion. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tschesche, H.; Knäuper, V.; Krämer, S.; Michaelis, J.; Oberhoff, R.; Reinke, H. Latent Collagenase and Gelatinase from Human Neutrophils and Their Activation. Matrix Suppl. 1992, 1, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freije, J.M.; Díez-Itza, I.; Balbín, M.; Sánchez, L.M.; Blasco, R.; Tolivia, J.; López-Otín, C. Molecular Cloning and Expression of Collagenase-3, a Novel Human Matrix Metalloproteinase Produced by Breast Carcinomas. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16766–16773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäuper, V.; López-Otin, C.; Smith, B.; Knight, G.; Murphy, G. Biochemical Characterization of Human Collagenase-3 (∗). J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knäuper, V.; Cowell, S.; Smith, B.; López-Otin, C.; O’Shea, M.; Morris, H.; Zardi, L.; Murphy, G. The Role of the C-Terminal Domain of Human Collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in the Activation of Procollagenase-3, Substrate Specificity, and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase Interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7608–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fosang, A.J.; Last, K.; Knäuper, V.; Murphy, G.; Neame, P.J. Degradation of Cartilage Aggrecan by Collagenase-3 (MMP-13). FEBS Lett. 1996, 380, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, T.; Göhring, W.; Mann, K.; Maurer, P.; Hohenester, E.; Knäuper, V.; Murphy, G.; Timpl, R. Limited Cleavage of Extracellular Matrix Protein BM-40 by Matrix Metalloproteinases Increases Its Affinity for Collagens. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9237–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groblewska, M.; Siewko, M.; Mroczko, B.; Szmitkowski, M. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) and Their Inhibitors (TIMPs) in the Development of Esophageal Cancer. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2012, 50, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aimes, R.T.; Quigley, J.P. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Is an Interstitial Collagenase: Inhibitor-Free Enzyme Catalyzes the Cleavage of Collagen Fibrils and Soluble Native Type I Collagen Generating the Specific ¾-and ¼-Length Fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5872–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, G.; Cockett, M.I.; Ward, R.; Docherty, A.J. Matrix Metalloproteinase Degradation of Elastin, Type IV Collagen and Proteoglycan. A Quantitative Comparison of the Activities of 95 KDa and 72 KDa Gelatinases, Stromelysins-1 and-2 and Punctuated Metalloproteinase (PUMP). Biochem. J. 1991, 277, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannelli, G.; Falk-Marzillier, J.; Schiraldi, O.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Quaranta, V. Induction of Cell Migration by Matrix Metalloprotease-2 Cleavage of Laminin-5. Science 1997, 277, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Quarles, L.D.; Nagase, H.; Suzuki, K.; Serra, D.M.; Fowlkes, J.L. Characterization of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 5-Degrading Proteases Produced throughout Murine Osteoblast Differentiation. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 3527–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, R.A.; Butler, G.S.; Hamma-Kourbali, Y.; Delbé, J.; Brigstock, D.R.; Courty, J.; Overall, C.M. Identification of Candidate Angiogenic Inhibitors Processed by Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) in Cell-Based Proteomic Screens: Disruption of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)/Heparin Affin Regulatory Peptide (Pleiotrophin) and VEGF/Connective Tissue Growth Factor Angiogenic Inhibitory Complexes by MMP-2 Proteolysis. Mol Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McQuibban, G.A.; Gong, J.H.; Tam, E.M.; McCulloch, C.A.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Overall, C.M. Inflammation Dampened by Gelatinase A Cleavage of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-3. Science 2000, 289, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochieng, J.; Fridman, R.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Liotta, L.A.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Raz, A. Galectin-3 Is a Novel Substrate for Human Matrix Metalloproteinases-2 and-9. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 14109–14114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkin, A.M.; Zemskov, E.A.; Hang, J.; Akimov, S.S.; Sikora, S.; Strongin, A.Y. Cell-Surface-Associated Tissue Transglutaminase Is a Target of MMP-2 Proteolysis. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11760–11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Patron, C.; Zouki, C.; Whittal, R.; Chan, J.S.; Davidge, S.T.; Filep, J.G. Matrix Metalloproteinases Regulate Neutrophil-Endothelial Cell Adhesion through Generation of Endothelin-1[1-32]. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudova, A.; auf dem Keller, U.; Butler, G.S.; Overall, C.M. Multiplex N-Terminome Analysis of MMP-2 and MMP-9 Substrate Degradomes by ITRAQ-TAILS Quantitative Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 894–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, G.; Reynolds, J.; Bretz, U.; Baggiolini, M. Partial Purification of Collagenase and Gelatinase from Human Polymorphonuclear Leucocytes. Analysis of Their Actions on Soluble and Insoluble Collagens. Biochem. J. 1982, 203, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sires, U.I.; Dublet, B.; Aubert-Foucher, E.; van der Rest, M.; Welgus, H.G. Degradation of the COL1 Domain of Type XIV Collagen by 92-KDa Gelatinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashiyama, S. Metalloproteinase-Mediated Shedding of Heparin-Binding EGF-like Growth Factor and Its Pathophysiological Roles. Protein Pept. Lett. 2004, 11, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Steen, P.E.; Proost, P.; Wuyts, A.; Van Damme, J.; Opdenakker, G. Neutrophil Gelatinase B Potentiates Interleukin-8 Tenfold by Aminoterminal Processing, Whereas It Degrades CTAP-III, PF-4, and GRO-α and Leaves RANTES and MCP-2 Intact. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2000, 96, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, B.-C.; Hsu, S.-M.; Ho, H.-N.; Lien, H.-C.; Huang, S.-C.; Lin, R.-H. A Novel Role of Metalloproteinase in Cancer-Mediated Immunosuppression. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van den Steen, P.E.; Wuyts, A.; Husson, S.J.; Proost, P.; Van Damme, J.; Opdenakker, G. Gelatinase B/MMP-9 and Neutrophil Collagenase/MMP-8 Process the Chemokines Human GCP-2/CXCL6, ENA-78/CXCL5 and Mouse GCP-2/LIX and Modulate Their Physiological Activities. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, T.; Kwak, O.; Fu, L.; Marshak, A.; Shi, Y.-B. The Matrix Metalloproteinase Stromelysin-3 Cleaves Laminin Receptor at Two Distinct Sites between the Transmembrane Domain and Laminin Binding Sequence within the Extracellular Domain. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Fu, L.; Fiorentino, M.; Matsuda, H.; Das, B.; Shi, Y.-B. Differential Regulation of Cell Type-Specific Apoptosis by Stromelysin-3: A Potential Mechanism via the Cleavage of the Laminin Receptor during Tail Resorption in Xenopus laevis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18545–18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fosang, A.J.; Neame, P.J.; Hardingham, T.E.; Murphy, G.; Hamilton, J.A. Cleavage of Cartilage Proteoglycan between G1 and G2 Domains by Stromelysins. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 15579–15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.M.; Howard, E.W.; Bissell, M.J.; Werb, Z. Rescue of Mammary Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Entactin Degradation by a Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-1 Transgene. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Windsor, L.J.; Grenett, H.; Birkedal-Hansen, B.; Bodden, M.; Engler, J.; Birkedal-Hansen, H. Cell Type-Specific Regulation of SL-1 and SL-2 Genes. Induction of the SL-2 Gene but Not the SL-1 Gene by Human Keratinocytes in Response to Cytokines and Phorbolesters. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17341–17347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijnen, H.R.; Ugwu, F.; Bini, A.; Collen, D. Generation of an Angiostatin-like Fragment from Plasminogen by Stromelysin-1 (MMP-3). Biochemistry 1998, 37, 4699–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowlkes, J.L.; Enghild, J.J.; Suzuki, K.; Nagase, H. Matrix Metalloproteinases Degrade Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 in Dermal Fibroblast Cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 25742–25746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.; Cockett, M.I.; Stephens, P.E.; Smith, B.J.; Docherty, A.J. Stromelysin Is an Activator of Procollagenase. A Study with Natural and Recombinant Enzymes. Biochem. J. 1987, 248, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knäuper, V.; Wilhelm, S.M.; Seperack, P.K.; DeClerck, Y.A.; Langley, K.E.; Osthues, A.; Tschesche, H. Direct Activation of Human Neutrophil Procollagenase by Recombinant Stromelysin. Biochem. J. 1993, 295, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, S.D.; Fliszar, C.J.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Mecham, R.P.; Senior, R.M.; Welgus, H.G. Activation of the 92-KDa Gelatinase by Stromelysin and 4-Aminophenylmercuric Acetate: Differential processing and stabilization of the carboxyl-terminal domain by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6351–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, K.; Umenishi, F.; Funahashi, K.; Koshikawa, N.; Yasumitsu, H.; Umeda, M. Activation of TIMP-2/Progelatinase a Complex by Stromelysin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 185, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.; Murphy, G.; Breathnach, R. Human and rat malignant-tumor-associated mRNAs encode stromelysin-like metalloproteinases. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 5195–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäuper, V.; Murphy, G.; Tschesche, H. Activation of Human Neutrophil Procollagenase by Stromelysin 2. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 235, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matchett, E.F.; Wang, S.; Crawford, B.D. Paralogues of Mmp11 and Timp4 Interact during the Development of the Myotendinous Junction in the Zebrafish Embryo. J. Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, M.H.; Alrowaished, S.S.; Goody, M.F.; Crawford, B.D.; Henry, C.A. Laminin and Matrix Metalloproteinase 11 Regulate Fibronectin Levels in the Zebrafish Myotendinous Junction. Skelet Muscle 2016, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, K.; Hattori, Y.; Umenishi, F.; Yasumitsu, H.; Umeda, M. Purification and Characterization of Extracellular Matrix-Degrading Metalloproteinase, Matrin (Pump-1), Secreted from Human Rectal Carcinoma Cell Line. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 7758–7764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Hiramatsu, A.; Fukushima, D.; Pierschbacher, M.D.; Okada, Y. Degradation of Decorin by Matrix Metalloproteinases: Identification of the Cleavage Sites, Kinetic Analyses and Transforming Growth Factor-B1 Release. Biochem. J. 1997, 322, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, S.R.; Conner, G.E.; Nagase, H.; Neuhaus, I.; Woessner, J.F. Characterization of Rat Uterine Matrilysin and Its cDNA: Relationship To Human Pump-1 And Activation Of Procollagenases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16016–16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, B.C.; Sang, Q.A. Angiostatin-Converting Enzyme Activities of Human Matrilysin (MMP-7) and Gelatinase B/Type IV Collagenase (MMP-9). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28823–28825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siri, A.; Knäuper, V.; Veirana, N.; Caocci, F.; Murphy, G.; Zardi, L. Different Susceptibility of Small and Large Human Tenascin-C Isoforms to Degradation by Matrix Metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 8650–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, L.; Du, M.; Lopez-Campistrous, A.; Fernandez-Patron, C. Agonist-Induced Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Promotes Vasoconstriction through the Epidermal Growth Factor–Receptor Pathway. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Park, P.W.; Wilson, C.L.; Parks, W.C. Matrilysin Shedding of Syndecan-1 Regulates Chemokine Mobilization and Transepithelial Efflux of Neutrophils in Acute Lung Injury. Cell 2002, 111, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strand, S.; Vollmer, P.; van den Abeelen, L.; Gottfried, D.; Alla, V.; Heid, H.; Kuball, J.; Theobald, M.; Galle, P.R.; Strand, D. Cleavage of CD95 by Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Induces Apoptosis Resistance in Tumour Cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3732–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crabbe, T.; Smith, B.; O’Connell, J.; Docherty, A. Human Progelatinase A Can Be Activated by Matrilysin. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, K.; Yokohama, Y.; Nakanishi, I.; Ohuchi, E.; Fujii, Y.; Nakai, N.; Okada, Y. Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 (Matrilysin) from Human Rectal Carcinoma Cells: Activation of the Precursor, Interaction with Other Matrix Metalloproteinases and Enzymic Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6691–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uría, J.A.; López-Otín, C. Matrilysin-2, a New Matrix Metalloproteinase Expressed in Human Tumors and Showing the Minimal Domain Organization Required for Secretion, Latency, and Activity. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4745–4751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, G.N.; Ratnikov, B.I.; Rozanov, D.V.; Godzik, A.; Deryugina, E.I.; Strongin, A.Y. Characterization of Matrix Metalloproteinase-26, a Novel Metalloproteinase Widely Expressed in Cancer Cells of Epithelial Origin. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkelä, E.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Tumor Progression: Focus on Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, E.; Imai, K.; Fujii, Y.; Sato, H.; Seiki, M.; Okada, Y. Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase Digests Interstitial Collagens and Other Extracellular Matrix Macromolecules. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’ortho, M.; Will, H.; Atkinson, S.; Butler, G.; Messent, A.; Gavrilovic, J.; Smith, B.; Timpl, R.; Zardi, L.; Murphy, G. Membrane-type Matrix Metalloproteinases 1 and 2 Exhibit Broad-spectrum Proteolytic Capacities Comparable to Many Matrix Metalloproteinases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 250, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pei, D.; Weiss, S.J. Transmembrane-Deletion Mutants of the Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Process Progelatinase A and Express Intrinsic Matrix-Degrading Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9135–9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinzone, J.J.; Hall, B.M.; Thudi, N.K.; Vonau, M.; Qiang, Y.-W.; Rosol, T.J.; Shaughnessy, J.D. The Role of Dickkopf-1 in Bone Development, Homeostasis, and Disease. Blood 2009, 113, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, R.A.; Overall, C.M. Proteomics Discovery of Metalloproteinase Substrates in the Cellular Context by ITRAQTM Labeling Reveals a Diverse MMP-2 Substrate Degradome. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ochieng, J.; Green, B.; Evans, S.; James, O.; Warfield, P. Modulation of the Biological Functions of Galectin-3 by Matrix Metalloproteinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1379, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, A.M.; Akimov, S.S.; Zaritskaya, L.S.; Ratnikov, B.I.; Deryugina, E.I.; Strongin, A.Y. Matrix-Dependent Proteolysis of Surface Transglutaminase by Membrane-Type Metalloproteinase Regulates Cancer Cell Adhesion and Locomotion. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18415–18422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, H.; Takino, T.; Okada, Y.; Cao, J.; Shinagawa, A.; Yamamoto, E.; Seiki, M. A Matrix Metalloproteinase Expressed on the Surface of Invasive Tumour Cells. Nature 1994, 370, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäuper, V.; Will, H.; López-Otin, C.; Smith, B.; Atkinson, S.J.; Stanton, H.; Hembry, R.M.; Murphy, G. Cellular Mechanisms for Human Procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) Activation: Evidence That MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and Gelatinase A (MMP-2) Are Able to Generate Active Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17124–17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Sato, H.; Takino, T.; Iwata, K.; Inoue, M.; Seiki, M. Isolation of a Mouse MT2-MMP Gene from a Lung CDNA Library and Identification of Its Product. FEBS Lett. 1997, 402, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, S.; Katoh, M.; Saito, S.; Watanabe, T.; Masuho, Y. Identification of Soluble Type of Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Formed by Alternatively Spliced MRNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Struct. Expr. 1997, 1354, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofuda, K.; Yasumitsu, H.; Nishihashi, A.; Miki, K.; Miyazaki, K. Expression of Three Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloproteinases (MT-MMPs) in Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Characterization of MT3-MMPs with and without Transmembrane Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9749–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asundi, V.K.; Erdman, R.; Stahl, R.C.; Carey, D.J. Matrix Metalloproteinase-dependent Shedding of Syndecan-3, a Transmembrane Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan, in Schwann Cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 73, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, J.; Lei, J.; Pei, D. Expression, Purification and Charaterization of Recombinant Mouse MT5-MMP Protein Products. FEBS Lett. 1999, 462, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porlan, E.; Martí-Prado, B.; Morante-Redolat, J.M.; Consiglio, A.; Delgado, A.C.; Kypta, R.; López-Otín, C.; Kirstein, M.; Fariñas, I. MT5-MMP Regulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Functional Quiescence through the Cleavage of N-Cadherin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, E.; Pendás, A.M.; Knäuper, V.; Sorsa, T.; Salo, T.; Salido, E.; Murphy, G.; Simmer, J.P.; Bartlett, J.D.; López-Otín, C. Identification and Structural and Functional Characterization of Human Enamelysin (MMP-20). Biochemistry 1997, 36, 15101–15108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, A.E.; Bellac, C.L.; Dufour, A.; Goebeler, V.; Overall, C.M. Biochemical Characterization and N-Terminomics Analysis of Leukolysin, the Membrane-Type 6 Matrix Metalloprotease (MMP25): Chemokine and Vimentin Cleavages Enhance Cell Migration and Macrophage Phagocytic Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13382–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Avila, G.; Sommer, B.; Mendoza-Posada, D.A.; Ramos, C.; Garcia-Hernandez, A.A.; Falfan-Valencia, R. Matrix Metalloproteinases Participation in the Metastatic Process and Their Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications in Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 137, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, W.R.; Puente, X.S.; Freije, J.M.; Knäuper, V.; Amour, A.; Merryweather, A.; López-Otın, C.; Murphy, G. Membrane Type 4 Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP17) Has Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Convertase Activity but Does Not Activate pro-MMP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14046–14055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Johnson, A.R.; Ye, Q.-Z.; Dyer, R.D. Catalytic Activities and Substrate Specificity of the Human Membrane Type 4 Matrix Metalloproteinase Catalytic Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33043–33049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- English, W.R.; Velasco, G.; Stracke, J.O.; Knäuper, V.; Murphy, G. Catalytic Activities of Membrane-Type 6 Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP25). FEBS Lett. 2001, 491, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, T.; Yi, J.; Guo, A.; Wang, X.; Overall, C.M.; Jiang, W.; Elde, R.; Borregaard, N.; Pei, D. Subcellular Distribution and Cytokine- and Chemokine-Regulated Secretion of Leukolysin/MT6-MMP/MMP-25 in Neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 21960–21968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco, G.; Cal, S.; Merlos-Suárez, A.; Ferrando, A.A.; Alvarez, S.; Nakano, A.; Arribas, J.; López-Otín, C. Human MT6-Matrix Metalloproteinase: Identification, Progelatinase A Activation, and Expression in Brain Tumors. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 877–882. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, S.; Cossins, J.; Lury, J.; Wells, G. Macrophage Metalloelastase Degrades Matrix and Myelin Proteins and Processes a Tumour Necrosis Factor-α Fusion Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 228, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Trubetskoy, O.V.; Gacheru, S.N.; Kagan, H.M. Metalloproteinase Activity Secreted by Fibrogenic Cells in the Processing of Prolysyl Oxidase: Potential Role of Procollagen C-Proteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7113–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banda, M.; Werb, Z. The Role of Macrophage Elastase in the Proteolysis of Fibrinogen, Plasminogen, and Fibronectin. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1980, 39, 1756. [Google Scholar]
- Gronski, T.J., Jr.; Martin, R.L.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Walsh, B.C.; Holman, M.C.; Huber, M.; Van Wart, H.E.; Shapiro, S.D. Hydrolysis of a Broad Spectrum of Extracellular Matrix Proteins by Human Macrophage Elastase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12189–12194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banda, M.; Clark, E.; Sinha, S.; Travis, J. Interaction of Mouse Macrophage Elastase with Native and Oxidized Human Alpha 1-Proteinase Inhibitor. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolb, C.; Mauch, S.; Peter, H.-H.; Krawinkel, U.; Sedlacek, R. The Matrix Metalloproteinase RASI-1 Is Expressed in Synovial Blood Vessels of a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient. Immunol. Lett. 1997, 57, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, J.O.; Fosang, A.J.; Last, K.; Mercuri, F.A.; Pendás, A.M.; Llano, E.; Perris, R.; Di Cesare, P.E.; Murphy, G.; Knäuper, V. Matrix Metalloproteinases 19 and 20 Cleave Aggrecan and Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein (COMP). FEBS Lett. 2000, 478, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Titz, B.; Dietrich, S.; Sadowski, T.; Beck, C.; Petersen, A.; Sedlacek, R. Activity of MMP-19 Inhibits Capillary-like Formation Due to Processing of Nidogen-1. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Smith, F.; Jia, J.; Zheng, Y. UV-Induced Molecular Signaling Differences in Melanoma and Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 996, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruntu, C.; Mirica, A.; Roşca, A.E.; Mirica, R.; Caruntu, A.; Tampa, M.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M.; Badarau, A.I.; et al. The role of estrogens and estrogen receptors in melanoma development and progression. Acta Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Kaur, C.D.; Jangdey, M.; Saraf, S. Matrix Metalloproteinase Enzymes and Their Naturally Derived Inhibitors: Novel Targets in Photocarcinoma Therapy. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 13, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, R.; Philips, N.; Suárez-Pérez, J.; Juarranz, A.; Devmurari, A.; Chalensouk-Khaosaat, J.; González, S. Mechanisms of Photoaging and Cutaneous Photocarcinogenesis, and Photoprotective Strategies with Phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Attenuates MAP Kinase/AP-1 Activation and MMPl Expression in UVA-Irradiated Human Fibroblasts Induced by Culture Medium from UVB-Irradiated Human Skin Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.-C.E.; Hung, Y.-T.; Fang, A.-H.; Ching-Shuang, W. Effects of Irradiance on UVA-Induced Skin Aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 94, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turcan, N.; Bohiltea, R.E.; Ionita-Radu, F.; Furtunescu, F.; Navolan, D.; Berceanu, C.; Nemescu, D.; Cirstoiu, M.M. Unfavorable Influence of Prematurity on the Neonatal Prognostic of Small for Gestational Age Fetuses. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Woo, S.; Choi, W.; Kim, H.; Yi, C.; Kim, K.; Cheng, J.; Yang, S.; Suh, J. Scopoletin Downregulates MMP-1 Expression in Human Fibroblasts via Inhibition of P38 Phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolae, I.; Ene, C.D.; Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Matei, C.; Ceausu, E. Effects of UV Radiation and Oxidative DNA Adduct 8-Hydroxy-2′-Deoxiguanosine on the Skin Diseases. Rev. Chim. 2014, 9, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, S.; Cordella, M.; Tabolacci, C.; Nassa, G.; D’Arcangelo, D.; Senatore, C.; Pagnotto, P.; Magliozzi, R.; Salvati, A.; Weisz, A.; et al. TNF-Alpha and Metalloproteases as Key Players in Melanoma Cells Aggressiveness. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurac, S.; Negroiu, G.; Petrescu, S.; Tudose, I.; Andrei, R.; Caius, S.; Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Staniceanu, F. Matrix Metalloproteinases Underexpression in Melanoma with Regression. In Proceedings of the 24th European Congress of Pathology, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–12 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zurac, S.; Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Cioplea, M.; Nedelcu, R.; Bastian, A.; Popp, C.; Nichita, L.; Andrei, R.; Tebeica, T.; et al. Variations in the Expression of TIMP1, TIMP2 and TIMP3 in Cutaneous Melanoma with Regression and Their Possible Function as Prognostic Predictors. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3354–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, T.; Robinson, S.C.; Schulz, M.; Trümper, L.; Balkwill, F.R.; Binder, C. Enhanced Invasiveness of Breast Cancer Cell Lines upon Co-Cultivation with Macrophages Is Due to TNF-Alpha Dependent up-Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteases. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, S.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Bowden, T.G. Differential Inhibition of UVB-Induced AP-1 and NF-KappaB Transactivation by Components of the Jun BZIP Domain. Mol. Carcinog. 2005, 43, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Caruntu, C.; Dumitru, C.; Surcel, M.; Zurac, S. Inflammation: A Key Process in Skin Tumorigenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4068–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK Signal Pathways in the Regulation of Cell Proliferation in Mammalian Cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelor, M.A.; Bowden, G.T. UVA-Mediated Activation of Signaling Pathways Involved in Skin Tumor Promotion and Progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2004, 14, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.S.; Chen, Z.; Dong, G.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Bancroft, C.C.; Capo, D.E.; Yeh, N.T.; Mukaida, N.; Van Waes, C. (Interleukin)-1alpha Promotes Nuclear Factor-KappaB and AP-1-Induced IL-8 Expression, Cell Survival, and Proliferation in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Tampa, M.; Mitran, M.I.; Mitran, C.I.; Sarbu, M.I.; Matei, C.; Nicolae, I.; Caruntu, A.; Tocut, S.M.; Popa, M.I.; Caruntu, C.; et al. Mediators of Inflammation—A Potential Source of Biomarkers in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1061780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madzharova, E.; Kastl, P.; Sabino, F.; Auf dem Keller, U. Post-Translational Modification-Dependent Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanjul-Fernández, M.; Folgueras, A.R.; Cabrera, S.; López-Otín, C. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Evolution, Gene Regulation and Functional Analysis in Mouse Models. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1803, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean, C.; Bogdanowicz, P.; Haure, M.-J.; Castex-Rizzi, N.; Fournié, J.-J.; Laurent, G. UVA activated Synthesis of Metalloproteinases 1, 3 and 9 Is Prevented by a Broadspectrum Sunscreen. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubissi, F.K.; Yedjou, C.G.; Spiegelman, V.S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cross-Talk between Wnt and Hh Signaling Pathways in the Pathology of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciurea, M.E.; Cernea, D.; Georgescu, C.C.; Cotoi, O.S. Expression of CXCR4, MMP-13 and β-Catenin in Different Histological Subtypes of Facial Basal Cell Carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2013, 54, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Bode, A.M.; Ma, W.-Y.; Chen, N.; Dong, Z. Induction of EGFR-Dependent and EGFR-Independent Signaling Pathways by Ultraviolet A Irradiation. DNA Cell Biol. 2001, 20, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Matei, C.; Scheau, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Recent Advances in Signaling Pathways Comprehension as Carcinogenesis Triggers in Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Avila, G.; Sommer, B.; García-Hernández, A.A.; Ramos, C. Matrix Metalloproteinases’ Role in Tumor Microenvironment. In Tumor Microenvironment; Birbrair, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1245, pp. 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Sakai, R. Direct Interaction between Carcinoma Cells and Cancer Associated Fibroblasts for the Regulation of Cancer Invasion. Cancers 2015, 7, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffek, S.; Schilling, O.; Franzke, C.-W. Series “Matrix Metalloproteinases in Lung Health and Disease”: Biological Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases: A Critical Balance. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallata, A.M.; Wyatt, R.A.; Levesque, J.M.; Dufour, A.; Overall, C.M.; Crawford, B.D. Intracellular Localization in Zebrafish Muscle and Conserved Sequence Features Suggest Roles for Gelatinase A Moonlighting in Sarcomere Maintenance. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limb, G.A.; Matter, K.; Murphy, G.; Cambrey, A.D.; Bishop, P.N.; Morris, G.E.; Khaw, P.T. Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Associates with Intracellular Organelles and Confers Resistance to Lamin A/C Degradation during Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eguchi, T.; Kubota, S.; Kawata, K.; Mukudai, Y.; Uehara, J.; Ohgawara, T.; Ibaragi, S.; Sasaki, A.; Kuboki, T.; Takigawa, M. Novel Transcription-Factor-like Function of Human Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 Regulating the CTGF/CCN2 Gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2391–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, R.N.; Rafii, S.; Lyden, D. Preparing the “Soil”: The Premetastatic Niche. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11089–11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Grady, A.; Dunne, C.; O’Kelly, P.; Murphy, G.M.; Leader, M.; Kay, E. Differential Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Implications for Tumour Progression. Histopathology 2007, 51, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didiasova, M.; Wujak, L.; Wygrecka, M.; Zakrzewicz, D. From Plasminogen to Plasmin: Role of Plasminogen Receptors in Human Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21229–21252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georgescu, S.R.; Tampa, M.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Caruntu, C.; Caruntu, A.; Lupu, M.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Tumour Microenvironment in Skin Carcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1226, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Haass, N.K. Microenvironment-Driven Dynamic Heterogeneity and Phenotypic Plasticity as a Mechanism of Melanoma Therapy Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, U.; Loeffler, K.U.; Nadal, J.; Holz, F.G.; Herwig-Carl, M.C. Polarization and Distribution of Tumor-Associated Macrophages and COX-2 Expression in Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Ocular Adnexae. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjiu, J.-W.; Chen, J.-S.; Shun, C.-T.; Lin, S.-J.; Liao, Y.-H.; Chu, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-F.; Chiu, H.-C.; Dai, Y.-S.; Inoue, H.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophage-Induced Invasion and Angiogenesis of Human Basal Cell Carcinoma Cells by Cyclooxygenase-2 Induction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padoveze, E.H.; Chiacchio, N.D.; Ocampo-Garza, J.; Cernea, S.S.; Belda, W.; Sotto, M.N. Macrophage Subtypes in Recurrent Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma after Mohs Micrographic Surgery. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, M.A.; Satpathy, S.; Cao, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Vasaikar, S.V.; Krug, K.; Petralia, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, W.-W.; Reva, B.; et al. Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium. Proteogenomic Characterization Reveals Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cell 2020, 182, 200–225.e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z. Development and Validation of a Metastasis-Related Gene Signature for Predicting the Overall Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 6299–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, S.H. Local Immune Response in Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma. Dan. Med. J. 2017, 64, B5412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, C.; Orlandi, A.; Costanza, G.; Di Stefani, A.; Piccioni, A.; Di Cesare, A.; Chiricozzi, A.; Ferlosio, A.; Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; et al. Expression of IL-23/Th17-Related Cytokines in Basal Cell Carcinoma and in the Response to Medical Treatments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beksaç, B.; İlter, N.; Erdem, Ö.; Çakmak, P.; Çenetoğlu, S.; Yapar, D. Sparsity of Dendritic Cells and Cytotoxic T Cells in Tumor Microenvironment May Lead to Recurrence in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, C.; Tampa, M.; Caruntu, C.; Ion, R.-M.; Georgescu, S.-R.; Dumitrascu, G.R.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Protein Microarray for Complex Apoptosis Monitoring of Dysplastic Oral Keratinocytes in Experimental Photodynamic Therapy. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amano, T.; Fu, L.; Marshak, A.; Kwak, O.; Shi, Y.-B. Spatio-Temporal Regulation and Cleavage by Matrix Metalloproteinase Stromelysin-3 Implicate a Role for Laminin Receptor in Intestinal Remodeling during Xenopus Laevis Metamorphosis. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 234, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaporis, H.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Lowes, M.A.; Haider, A.S.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Darabi, K.; Whynot-Ertelt, J.; Khatcherian, A.; Cardinale, I.; Novitskaya, I.; et al. Human Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Associated with Foxp3+ T Cells in a Th2 Dominant Microenvironment. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crawford, B.D.; Pilgrim, D.B. Ontogeny and Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in the Zebrafish Embryo by in Vitro and in Vivo Zymography. Dev. Biol. 2005, 286, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keow, J.Y.; Pond, E.D.; Cisar, J.S.; Cravatt, B.F.; Crawford, B.D. Activity-Based Labeling of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Living Vertebrate Embryos. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, E.J.; Crawford, B.D. The Epitope-Mediated MMP Activation Assay: Detection and Quantification of the Activation of Mmp2 in Vivo in the Zebrafish Embryo. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, T.; Mutnal, A.; Fay, K.; Fligiel, S.E.G.; Wang, T.; Johnson, T.; Baker, S.R.; Varani, J. Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression in Basal Cell Carcinoma: Relationship between Enzyme Profile and Collagen Fragmentation Pattern. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2005, 79, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, J.; Hattori, Y.; Chi, Y.; Schmidt, T.; Perone, P.; Zeigler, M.E.; Fader, D.J.; Johnson, T.M. Collagenolytic and Gelatinolytic Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin: Comparison with Normal Skin. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.D.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, G.S.; Han, K.T.; Lim, J.S.; Kang, C.S. Comparative Analysis of Immunohistochemical Markers with Invasiveness and Histologic Differentiation in Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.S.; Lu, M.P.; Wu, M.T. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 by fibroblasts in co-cultures with keratinocytes, basal cell carcinoma and melanoma. J. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monhian, N.; Jewett, B.S.; Baker, S.R.; Varani, J. Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression in Normal Skin Associated with Basal Cell Carcinoma and in Distal Skin from the Same Patients. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2005, 7, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manola, I.; Mataic, A.; Drvar, D.L.; Pezelj, I.; Dzombeta, T.R.; Kruslin, B. Peritumoral Clefting and Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatarova, Z.I.; Softova, E.B.; Dokova, K.G.; Messmer, E.M. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1, -9, -13, and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-1 in Basal Cell Carcinomas of the Eyelid. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, J.S.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Pierson, K.C.; Pitts-Kiefer, A.; Fan, L.; Belkin, D.A.; Wang, C.Q.; Bhuvanendran, S. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in the Cutaneous SCC Microenvironment Are Heterogeneously Activated. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciążyńska, M.; Bednarski, I.A.; Wódz, K.; Kolano, P.; Narbutt, J.; Sobjanek, M.; Woźniacka, A.; Lesiak, A. Proteins Involved in Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma Development. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4064–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hattori, Y.; Nerusu, K.C.; Bhagavathula, N.; Brennan, M.; Hattori, N.; Murphy, H.S.; Su, L.D.; Wang, T.S.; Johnson, T.M.; Varani, J. Vascular Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 (Collagenase-3) in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, A.K.; Yassin, E.; Khater, A.; Abdelgaber, S. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 and Ki-67 in Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer in Xeroderma Pigmentosum and Non-Xeroderma Pigmentosum. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2013, 35, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S.; Tolvanen, K.; Virolainen, S.; Kuivanen, T.; Kyllönen, L.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Differential Expression of Stromal MMP-1, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in Basal Cell Carcinomas of Immunosuppressed Patients and Controls. Virchows Arch. 2008, 452, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, M.A.; Caruntu, C.; Rosca, A.E.; Kaleshi, H.; Caruntu, A.; Moraru, L.; Docea, A.O.; Zurac, S.; Boda, D.; Neagu, M.; et al. Reflectance Confocal Microscopy and Dermoscopy for in Vivo, Non-Invasive Skin Imaging of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poswar, F.O.; Fraga, C.A.C.; Farias, L.C.; Feltenberger, J.D.; Cruz, V.P.D.; Santos, S.H.S.; Silveira, C.M.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Guimarães, A.L.S. Immunohistochemical Analysis of TIMP-3 and MMP-9 in Actinic Keratosis, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin, and Basal Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2013, 209, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U.; Pabst, F.; Krönert, C.; Schorcht, J.; Haroske, G.; Klemm, E.; Kittner, T. High-Risk Basal Cell Carcinoma: An Update. Expert Rev. of Dermatol. 2010, 5, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimovska Nilsson, K.; Neittaanmäki, N.; Zaar, O.; Angerer, T.B.; Paoli, J.; Fletcher, J.S. TOF-SIMS Imaging Reveals Tumor Heterogeneity and Inflammatory Response Markers in the Microenvironment of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 041012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goździalska, A.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Drąg, J.; Brzewski, P.; Jaśkiewicz, J.; Pastuszczak, M. Expression of Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in Basal-Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matei, C.; Tampa, M.; Ion, R.; Neagu, M.; Constantin, C. Photodynamic properties of aluminium sulphonated phthalo-cyanines in human displazic oral keratinocytes experimental model. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2012, 7, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Orimoto, A.M.; Neto, C.F.; Pimentel, E.R.A.; Sanches, J.A.; Sotto, M.N.; Akaishi, E.; Ruiz, I.R.G. High Numbers of Human Skin Cancers Express MMP2 and Several Integrin Genes. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2008, 35, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Kohda, F.; Nakahara, T.; Chiba, T.; Tsuji, G.; Hachisuka, J.; Ito, T.; Tu, Y.; Moroi, Y.; Uchi, H.; et al. Aberrant Expression of S100A6 and Matrix Metalloproteinase 9, but Not S100A2, S100A4, and S100A7, Is Associated with Epidermal Carcinogenesis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 72, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadeh, H.; Saravani, S.; Heydari, F.; Shahraki, S. Differential Immunohistochemical Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers of the Head and Neck. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribier, B.; Noacco, G.; Peltre, B.; Grosshans, E. Expression of Stromelysin 3 in Basal Cell Carcinomas. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2001, 11, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greco, M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Chiefari, E.; Vitagliano, T.; Ciriaco, A.G.; Brunetti, F.S.; Cuda, G.; Brunetti, A. HMGA1 and MMP-11 Are Overexpressed in Human Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.T.; Kim, H.S.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, W.S.; Cho, B.K.; Reichrath, J. Increased Immunoreactivity of Membrane Type-1 Matrix Metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) and β-Catenin in High-Risk Basal Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, T.Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, R.; Wicha, M.S.; Yu, S.M.; Weiss, S.J. Divergent Matrix-Remodeling Strategies Distinguish Developmental from Neoplastic Mammary Epithelial Cell Invasion Programs. Dev. Cell 2018, 47, 145–160.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philips, N.; Auler, S.; Hugo, R.; Gonzalez, S. Beneficial Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases for Skin Health. Enzym. Res. 2011, 2011, 427285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J.; Tan, T.K.; Lee, S.R.; Zhao, Y.; Harris, D.C.H.; Zheng, G. E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Complex and the Epithelial Barrier. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 567305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanjaka-Rogošić, L.; Puizina-Ivić, N.; Mirić, L.; Rogošić, V.; Kuzmić-Prusac, I.; Babić, M.S.; Vuković, D.; Mardešić, S. Matrix Metalloproteinases and E-Cadherin Immunoreactivity in Different Basal Cell Carcinoma Histological Types. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.Y.; Cha, S.T.; Chang, C.C.; Hsiao, C.H.; Tan, C.T.; Lu, Y.C.; Jee, S.H.; Kuo, M.L. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in stromal-cell-derived factor 1 alpha-directed invasion of human basal cell carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2491–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Khalawany, M.A.; Abou-Bakr, A.A. Role of Cyclooxygenase-2, Ezrin and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 as Predictive Markers for Recurrence of Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2013, 9, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, N.; Baspinar, S.; Bozkurt, K.K.; Caloglu, E.; Ciris, I.M.; Kapucuoglu, N. Increased Expression of COX-2 in Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin: A Pilot Study. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2011, 54, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, S.; Scuderi, C.; Gattuso, G.; Di Bella, V.; Candido, S.; Basile, M.S.; Libra, M.; Falzone, L. Functional Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Melanoma. Cells 2020, 9, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Lu, Y.-T.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.-H.; Li, N.-G.; Tang, Y.-P.; Duan, J.-A. Recent Opportunities in Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor Drug Design for Cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, K.; Nagase, H. The Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases (TIMPs): An Ancient Family with Structural and Functional Diversity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2010, 1803, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raeeszadeh-Sarmazdeh, M.; Do, L.D.; Hritz, B.G. Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors: Potential for the Development of New Therapeutics. Cells 2020, 34, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M. Expression and significance of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase in non-melanoma skin cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2012, 34, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-H.; Rapti, M.; Murphy, G. Unveiling the Surface Epitopes That Render Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 Inactive against Membrane Type 1-Matrix Metalloproteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40224–40230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.H.; Atkinson, S.; Rapti, M.; Handsley, M.; Curry, V.; Edwards, D.; Murphy, G. The Activity of a Designer Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases (TIMP)-1 against Native Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in a Cell-Based Environment. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Mitran, M.I.; Mitran, C.I.; Matei, C.; Caruntu, A.; Scheau, C.; Nicolae, I.; Matei, A.; Caruntu, C.; et al. Current Perspectives on the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060903
Tampa M, Georgescu SR, Mitran MI, Mitran CI, Matei C, Caruntu A, Scheau C, Nicolae I, Matei A, Caruntu C, et al. Current Perspectives on the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(6):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060903
Chicago/Turabian StyleTampa, Mircea, Simona Roxana Georgescu, Madalina Irina Mitran, Cristina Iulia Mitran, Clara Matei, Ana Caruntu, Cristian Scheau, Ilinca Nicolae, Andreea Matei, Constantin Caruntu, and et al. 2021. "Current Perspectives on the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Basal Cell Carcinoma" Biomolecules 11, no. 6: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060903
APA StyleTampa, M., Georgescu, S. R., Mitran, M. I., Mitran, C. I., Matei, C., Caruntu, A., Scheau, C., Nicolae, I., Matei, A., Caruntu, C., Constantin, C., & Neagu, M. (2021). Current Perspectives on the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Biomolecules, 11(6), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060903













