Novel Insight of Histamine and Its Receptor Ligands in Glaucoma and Retina Neuroprotection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Damage of Optic Nerve
- Trabecular meshwork obstruction by foreign material (e.g., glycosaminoglycans, pigments, red blood cells);
- Trabecular cell loss of phagocytic activity and death;
- Loss of giant vacuoles from Schlemm’s canal endothelium and reduced pore size and density in the wall of this canal.
3. The Histaminergic System
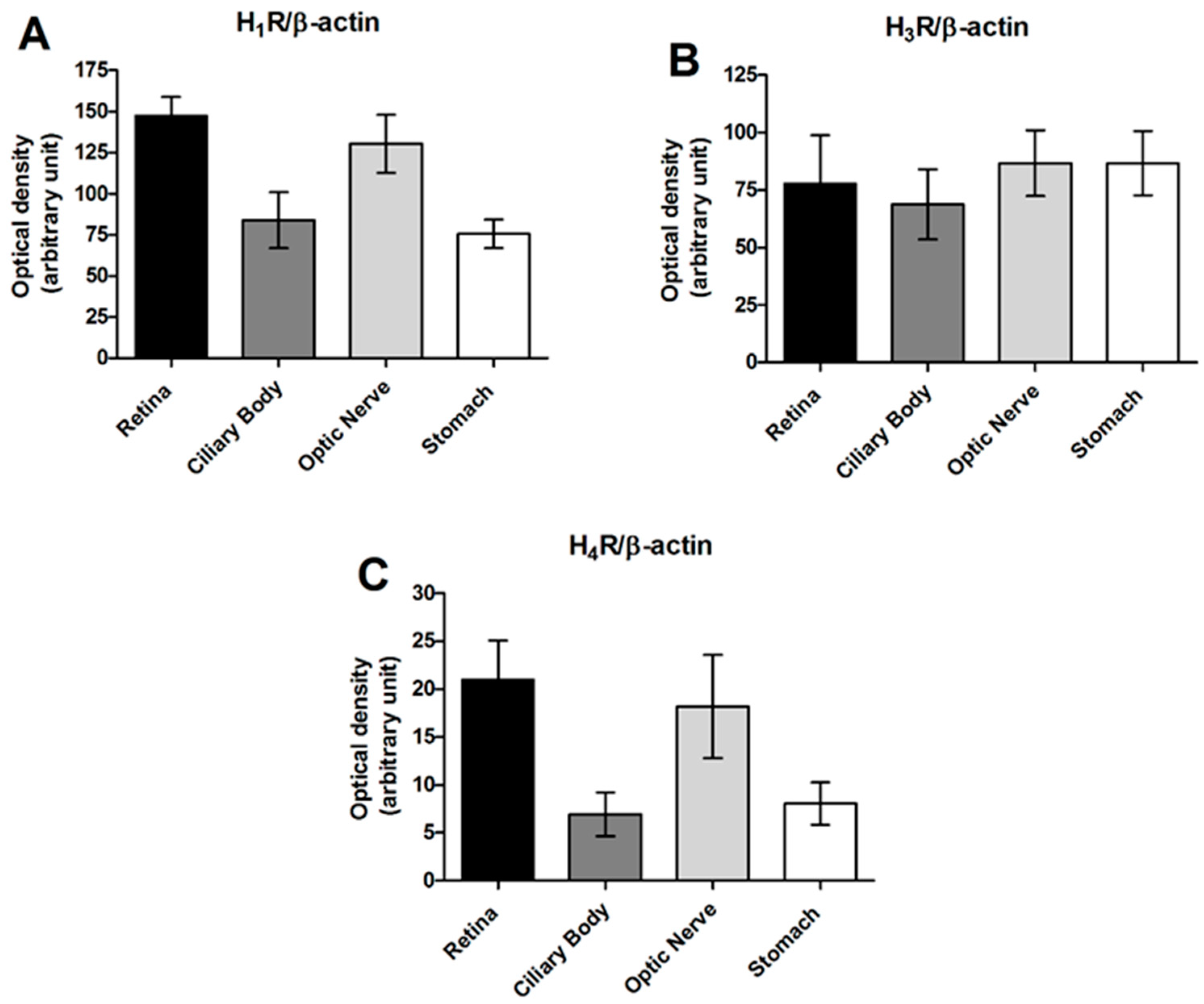
4. The Histaminergic System at Ocular Level
5. The Role of Histamine H3 Receptors in the Control of Intraocular Pressure
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickells, R.W.; Howell, G.R.; Soto, I.; John, S.W.M. Under pressure: Cellular and molecular responses during glaucoma, a common neurodegeneration with axonopathy. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgatroyd, H.; Bembridge, J. Intraocular pressure. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2008, 8, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, R. Autophagy in glaucoma: Crosstalk with apoptosis and its implications. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanay, I.; Tian, B.B.B.; Gabelt, A.T.; Geiger, B.; Kaufman, P.L. Latrunculin B effects on trabecular meshwork and corneal endothelial morphology in monkeys *. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 2236–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamer, W.D.; Acott, T.S. Current understanding of conventional outflow dysfunction in glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saccà, S.C.; Gandolfi, S.; Bagnis, A.; Manni, G.; Damonte, G.; Traverso, C.E.; Izzotti, A. The Outflow Pathway: A Tissue With Morphological and Functional Unity. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 1876–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.V.; Pattabiraman, P.P.; Kopczynski, C. Role of the Rho GTPase/Rho kinase signaling pathway in pathogenesis and treatment of glaucoma: Bench to bedside research. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 158, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quigley, H.A. Glaucoma. In Proceedings of the Lancet; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 377, pp. 1367–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Kersey, J.P.; Broadway, D.C. Corticosteroid-induced glaucoma: A review of the literature. Eye 2006, 20, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.T.; Drack, A.V.; Kwitek, A.E.; Cannon, R.L.; Stone, E.M.; Alward, W.L.M. Clinical Features and Linkage Analysis of a Family with Autosomal Dominant Juvenile Glaucoma. Ophthalmology 1993, 100, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Lu, H.; Arno, M.; Iglesias, A.I.; Bonnemaijer, P.; Broer, L.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Klaver, C.C.W.; van Duijn, C.; Hysi, P.G.; et al. Evaluation of the Myocilin Mutation Gln368Stop Demonstrates Reduced Penetrance for Glaucoma in European Populations. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souma, T.; Tompson, S.W.; Thomson, B.R.; Siggs, O.M.; Kizhatil, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Feng, L.; Limviphuvadh, V.; Whisenhunt, K.N.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; et al. Angiopoietin receptor TEK mutations underlie primary congenital glaucoma with variable expressivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2575–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.F.; Hoying, J.B.; Witte, M.H.; Daniel Stamer, W. Schlemm’s Canal Endothelia, Lymphatic, or Blood Vasculature? J. Glaucoma 2007, 16, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, H.A.; Broman, A.T. The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoyng, P.F.J.; Van Beek, L.M. Pharmacological therapy for glaucoma: A review. Drugs 2000, 59, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgambellone, S.; Durante, M.; Masini, E.; Lucarini, L. Up-To Date of the Pharmacological Therapies for Glaucoma Special Focus on Glaucoma Special Focus on Glaucoma. Spec. Focus Glaucoma 2020, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, L.; Bossers, K.; Luchetti, S.; Balesar, R.; Lethbridge, N.; Chazot, P.L.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations in the histaminergic system in the substantia nigra and striatum of Parkinson’s patients: A postmortem study. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Chen, Z. The roles of histamine and its receptor ligands in central nervous system disorders: An update. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 175, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Nuutinen, S. The histaminergic network in the brain: Basic organization and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P.; Chazot, P.L.; Cowart, M.; Gutzmer, R.; Leurs, R.; Liu, W.L.S.; Stark, H.; Thurmond, R.L.; Haas, H.L. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. XCVIII. histamine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 601–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Histamine and H1-antihistamines: Celebrating a century of progress. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, E.H.; Neumann, D.; Seifert, R. Modulation of behavior by the histaminergic system: Lessons from HDC-, H3R- and H4R-deficient mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.; Schneider, E.H.; Seifert, R. Analysis of histamine receptor knockout mice in models of inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 348, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thangam, E.B.; Jemima, E.A.; Singh, H.; Baig, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mathias, C.B.; Church, M.K.; Saluja, R. The role of histamine and histamine receptors in mast cell-mediated allergy and inflammation: The hunt for new therapeutic targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Schwartz, J.C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature 1983, 302, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Schwartz, J.C. Autoregulation of histamine release in brain by presynaptic H3-receptors. Neuroscience 1985, 15, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Selbach, O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, S.; Panula, P. Histamine in Neurotransmission and Brain Diseases. In Histamine in Inflammation; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Thurmond, R.L., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 709, pp. 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek, B.A.; Ghiabi, B. The other side of the histamine H3 receptor. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Bassetti, C.; Lammers, G.J.; Arnulf, I.; Mayer, G.; Rodenbeck, A.; Lehert, P.; Ding, C.L.; Lecomte, J.M.; Schwartz, J.C. Pitolisant versus placebo or modafinil in patients with narcolepsy: A double-blind, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurmond, R.L.; Kazerouni, K.; Chaplan, S.R.; Greenspan, A.J. Peripheral Neuronal Mechanism of Itch: Histamine and Itch; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781466505438. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, A.C.; Pini, A.; Lucarini, L.; Lanzi, C.; Veglia, E.; Thurmond, R.L.; Stark, H.; Masini, E. Prevention of bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice by naproxen and JNJ7777120 treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucarini, L.; Pini, A.; Rosa, A.C.; Lanzi, C.; Durante, M.; Chazot, P.L.; Krief, S.; Schreeb, A.; Stark, H.; Masini, E. Role of histamine H4 receptor ligands in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connelly, W.M.; Shenton, F.C.; Lethbridge, N.; Leurs, R.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Faull, R.L.M.; Lees, G.; Chazot, P.L. The histamine H 4 receptor is functionally expressed on neurons in the mammalian CNS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanna, M.D.; Ghelardini, C.; Thurmond, R.L.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Behavioural phenotype of histamine H4 receptor knockout mice: Focus on central neuronal functions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 114, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.D.; Stark, H.; Lucarini, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Histamine H 4 receptor activation alleviates neuropathic pain through differential regulation of ERK, JNK, and P38 MAPK phosphorylation. Pain 2015, 156, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellan Baldan, L.; Williams, K.A.; Gallezot, J.D.; Pogorelov, V.; Rapanelli, M.; Crowley, M.; Anderson, G.M.; Loring, E.; Gorczyca, R.; Billingslea, E.; et al. Histidine Decarboxylase Deficiency Causes Tourette Syndrome: Parallel Findings in Humans and Mice. Neuron 2014, 81, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greferath, U.; Kambourakis, M.; Barth, C.; Fletcher, E.L.; Murphy, M. Characterization of histamine projections and their potential cellular targets in the mouse retina. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, A.; Satoh, H.; Rangel, C.; Mills, S.L.; Hoshi, H.; O’Brien, J.; Marshak, D.R.; Macleish, P.R.; Marshak, D.W. Histamine receptors of cones and horizontal cells in Old World monkey retinas. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.C.; Satoh, H.; Wu, S.M.; Marshak, D.W. Histamine enhances voltage-gated potassium currents of on bipolar cells in macaque retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimov, N.P.; Marshak, D.W.; Frishman, L.J.; Glickman, R.D.; Yusupov, R.G. Histamine reduces flash sensitivity of ON ganglion cells in the primate retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3825–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skingsley, D.R.; Laughlin, S.B.; Hardie, R.C. Properties of histamine-activated chloride channels in the large monopolar cells of the dipteran compound eye: A comparative study. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1995, 176, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombe, P.E. The large monopolar cells L1 and L2 are responsible for ERG transients in Drosophila. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1986, 159, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastinger, M.; Tian, N.; Horvath, T.; Marshak, D. Retinopetal axons in mammals: Emphasis on histamine and serotonin. Curr. Eye Res. 2006, 31, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.S.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Haas, H.L. Histamine H3 receptors and sleep-wake regulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markwardt, K.L.; Magnino, P.E.; Pang, I.H. Histamine induced contraction of human ciliary muscle cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1997, 64, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbag, L.; Allbaugh, R.A.; Weaver, A.; Seo, Y.J.; Mochel, J.P. Histamine-Induced Conjunctivitis and Breakdown of Blood–Tear Barrier in Dogs: A Model for Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montan, P.G.; Van Hage-Hamsten, M. Eosinophil cationic protein in tears in allergic conjunctivitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 80, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inada, N.; Shoji, J.; Shiraki, Y.; Aso, H.; Yamagami, S. Histamine H1 and H4 receptor expression on the ocular surface of patients with chronic allergic conjunctival diseases. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luncă, D.-C.; Păunescu, H.; Mușat, O.; Fulga, I. The histaminergic control of the iridal vascular tone in rats and its influencing by topical administration of olopatadine and ranitidine. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachkar, Y.; Bouassida, W. Drug-induced acute angle closure glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2007, 18, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razeghinejad, M.R.; Myers, J.S.; Katz, L.J. Iatrogenic glaucoma secondary to medications. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampeli, E.; Tiligada, E. The role of histamine H 4 receptor in immune and inflammatory disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.; Di Stefano, A.; Vicari, C.; Motterle, L.; Brun, P. Histamine H4 receptors in normal conjunctiva and in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 66, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nau, C.B.; Malihi, M.; McLaren, J.W.; Hodge, D.O.; Sit, A.J. Circadian Variation of Aqueous Humor Dynamics in Older Healthy Adults. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.D.; Gregory, D.S. A Circadian Rhythm of Aqueous Flow Underlies the Circadian Rhythm of IOP in NZW Rabbits. | IOVS | ARVO Journals. Available online: https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2160758 (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Tripathi, R.C.; Tripathi, B.J. Human trabecular endothelium, corneal endothelium, keratocytes, and scleral fibroblasts in primary cell culture. A comparative study of growth characteristics, morphology, and phagocytic activity by light and scanning electron microscopy. Exp. Eye Res. 1982, 35, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzi, C.; Lucarini, L.; Durante, M.; Sgambellone, S.; Pini, A.; Catarinicchia, S.; Łażewska, D.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Stark, H.; Masini, E. Role of Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists on Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Rabbit Models of Transient Ocular Hypertension and Glaucoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Impagnatiello, F.; Giambene, B.; Lanzi, C.; Pini, A.; Somma, T.; Bastia, E.; Ongini, E.; Galassi, F.; Masini, E. The nitric oxide donating triamcinolone acetonide NCX 434 does not increase intraocular pressure and reduces endothelin-1 induced biochemical and functional changes in the rabbit eye. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, D.Y.; Bae, H.; Park, D.Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.K.; Song, S.; Chung, T.Y.; Lim, D.H.; Kubota, Y.; et al. Impaired angiopoietin/Tie2 signaling compromises Schlemm’s canal integrity and induces glaucoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3877–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| A | IOP-Lowering Effect | |||||
| Compound | Basal | After Saline | Post Treatment (60 min) | ΔΔIOP (60 min) | Post Treatment (120 min) | ΔΔIOP (120 min) |
| IOP, mmHg | IOP, mmHg | IOP, mmHg | mmHg | IOP, mmHg | mmHg | |
| Vehicle | 15 ± 0.3 | 36 ± 7.5 | 38 ± 3.9 | 0 ± 3.9 | 28 ± 5.7 | 0 ± 5.7 |
| Ciproxifan | 13 ± 4.3 | 38 ± 6.2 | 22 ± 5.3 | −18.9 ± 5.3 ** | 17 ± 5.5 | −16.4 ± 5.5 ** |
| DL-76 | 15 ± 4.3 | 34 ± 6.2 | 23 ± 7.4 | −15.4 ± 7.5 ** | 20 ± 3.0 | −16.1 ± 3.1 ** |
| GSK189254 | 14 ± 5.6 | 37 ± 5.5 | 32 ± 4.3 | −8.5 ± 4.3 * | 25 ± 6.7 | −9.9 ± 6.7 * |
| Timolol | 14 ± 2.5 | 38 ± 5.7 | 21 ± 3.8 | −16.5 ± 3.8 ** | 19 ± 4.6 | −14.8 ± 4.7 ** |
| B | IOP-Lowering Effect | |||||
| Compound | Basal | After Carbomer | Post-Treatment (7 days) | ΔΔIOP (7 days) | ||
| IOP, mmHg | IOP, mmHg | IOP, mmHg | mmHg | |||
| Vehicle | 15 ± 0.3 | 38 ± 2.8 | 41 ± 7.3 | 0 ± 2.12 | ||
| Ciproxifan | 13 ± 5.1 | 36 ± 4.1 | 20 ± 2.9 | −19 ± 2.9 ** | ||
| DL-76 | 12 ± 3.5 | 34 ± 2.8 | 23 ± 3.8 | −15.7 ± 2.7 * | ||
| GSK189254 | 14 ± 0.0 | 40 ± 1.4 | 26 ± 2.8 | −14.5 ± 3.8 * | ||
| Timolol | 15 ± 0.7 | 41 ± 5.6 | 27 ± 2.1 | −13.5 ± 2.1 * | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sgambellone, S.; Lucarini, L.; Lanzi, C.; Masini, E. Novel Insight of Histamine and Its Receptor Ligands in Glaucoma and Retina Neuroprotection. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081186
Sgambellone S, Lucarini L, Lanzi C, Masini E. Novel Insight of Histamine and Its Receptor Ligands in Glaucoma and Retina Neuroprotection. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(8):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081186
Chicago/Turabian StyleSgambellone, Silvia, Laura Lucarini, Cecilia Lanzi, and Emanuela Masini. 2021. "Novel Insight of Histamine and Its Receptor Ligands in Glaucoma and Retina Neuroprotection" Biomolecules 11, no. 8: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081186
APA StyleSgambellone, S., Lucarini, L., Lanzi, C., & Masini, E. (2021). Novel Insight of Histamine and Its Receptor Ligands in Glaucoma and Retina Neuroprotection. Biomolecules, 11(8), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081186






