The Effects of Low-Level Helium–Neon (He–Ne) Laser Irradiation on Lipids and Fatty Acids, and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome in the Blastula Stage and Underyearlings of the Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar: A Novel Approach in Salmonid Restoration Procedures in the North
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.2. Lipid Extraction and Lipid Classes Analysis
2.3. Certain Phospholipid Fractions Analysis by HPLC
2.4. Fatty Acid Analysis
2.5. Enzyme Analyses
2.6. Proteome Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth and Development of Fish during the Experiment
3.2. Lipid Profile and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes in Mature Eggs (Unfertilized)
3.3. Lipid Profile, the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome at the Blastula Stage
3.4. Lipid Profile and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome in Underyearlings of Atlantic Salmon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jówko, E.; Płaszewski, M.; Cieśliński, M.; Sacewicz, T.; Cieśliński, I.; Jarocka, M. The effect of low level laser irradiation on oxidative stress, muscle damage and function following neuromuscular electrical stimulation. A double blind, randomised, crossover trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohale, B.R.; Agrawal, A.A.; Raut, C.P. Effect of low-level laser therapy on wound healing and patients’ response after scalpel gingivectomy: A randomized clinical split-mouth study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2018, 22, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, S.; Yadollahpour, A.; Mirzaiyan, M. Low level laser therapy for the treatment of chronic wound: Clinical considerations. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2015, 8, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, Z.; Harith, M.A. Laser researches on livestock semen and oocytes: A brief review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dreyer, T.R.; Siqueira, A.F.P.; Magrini, T.D.; Fiorito, P.A.; Assumpção, M.E.O.A.; Nichi, M.; Martinho, H.S.; Milazzotto, M.P. Biochemical and topological analysis of bovine sperm cells induced by low power laser irradiation. In Medical Laser Applications and Laser-Tissue Interactions V, Proceedings of the SPIE-OSA Biomedical Optics (Optical Society of America, 2011), Munich, Germany, 22–26 May 2011; Sroka, R., Lilge, L., Eds.; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 8092, p. 80920V. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmast, N.V.; Milyanchuk, N.P.; Nemova, N.N. Current state of Atlantic salmon populations in Karelia and updating its farm breeding technologies. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference “Arctic: History and Modernity”, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 18–19 March 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 539, p. 012188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bura, M.; Mandzinets’, S.; Temnik, M. Development of embryos and larvae of loach Misgurnus fossilis L. under exposure to low intensity helium neon light. Visn. Lviv. Univ. Ser. Biol. 2010, 54, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Romanyuk, M.S.; Mandzinets’, S.M.; Bura, M.V.; Sanagurs’kii, D.I. Effect of lowintensity laser radiation of varying exposure on the activity of Na, KATPase of loach embryos. Fotobiol. Fotomed. 2011, 1, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk, M.S.; Bura, M.V.; Mandzynets, S.M.; Kulachkovsky, O.R.; Sanagursky, D.I. Influence low-intensity laser irradiation on the ultrastructural organization of loach embryo cells. Cytol. Genet. 2014, 48, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzdensky, A.B.; Gorbacheva, L.T.; Vorob’eva, O.A.; Son, C.G. Helium-neon laser radiation effect on some teratogenic processes in fish embryos. Light Opt. Biomed. 2001, 4515, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Uzdensky, A.B. Helium-neon laser radiation effect on fish embryos and larvae. In Proceedings of the OE/LASE’94, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 23–29 January 1994; Volume 2128, pp. 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Barulin, N.V.; Plavsky, V.Y.; Shumsky, K.L.; Atroshchenko, O.A.; Novikova, E.G.; Rogovtsov, S.V.; Liman, M.S. Recommendations for the Reproduction of Sturgeon Fish in Industrial Fish Breeding Complexes Using Innovative Methods: For Specialists in the Field of Fisheries and Aquaculture, Graduate Students, University Students, Students of the Institute for Advanced Training and Retraining of Personnel; Sadomov, N.A., Kostousov, V.G., Eds.; Gorki: Bgskha, Belarus, 2016; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, A.P.; Pinheiro, A.L.; Mester, A.R.; Franke, R.P.; Whelan, H.T. Biostimulatory windows in low intensity laser activation: Lasers, scanners and NASA’s light-emitting diode array system. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg. 2001, 19, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.P.; Wang, J.J.; Yu, C.L.; Lan, C.C.E.; Chen, G.S.; Yu, H.S. Helium–neon laser irradiation stimulates cell proliferation through photostimulatory effects in mitochondria. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passarella, S.; Karu, T. Absorption of monochromatic and narrow band radiation in the visible and near IR by both mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial photoacceptors results in photobiomodulation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 140, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoseyeva, G.S.; Karu, T.I.; Lyapunova, T.S.; Pomoshnikova, N.A.; Meissel, M.N. The activation of yeast metabolism with He-Ne laser. II. Activityof enzymes of oxidative and phosphorus metabolism. Laser Life Sci. 1988, 2, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, M.; Greco, S.; Passarella, D. Specific helium-neon laser sensitivity of the purified cytochrome c oxidase. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2000, 76, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaffaldano, N.; Paventi, G.; Pizzuto, R.; Di Iorio, M.; Bailey, J.L.; Manchisi, A.; Passarella, S. Helium-neon laser irradiation of cryopreserved ram sperm enhances cytochrome c oxidase activity and ATP levels improving semen quality. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Naim, J.O.; McGowan, M.; Ippolito, K.; Lanzafame, R.J. Photomodulation of oxidative metabolism and electron chain enzymes in rat liver mitochondria. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 66, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liman, M.S.; Barulin, N.V. The effect of low intensity optical radiation on embryos and larvae of rainbow trout. Sci. Notes Petrozavodsk. State Univ. 2018, 3, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, E.K. Effects of Laser Exposure on Fish in Early Ontogenesis; GPZ: Petrozavodsk, Russia, 2004; p. 126. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, E.K.; Ostachkov, O.A. Stimulation of embryogenesis of sturgeon fish species by exposure to electromagnetic radiation in the infrared zone of the spectrum. In Problems of Reproduction, Feeding and Disease Control of Fish When Grown in Artificial Conditions Materials of Scientific Conference; KarRc RAS: Petrozavodsk, Russia, 2002; pp. 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Burlakov, A.B.; Averyanova, O.V.; Sleptsova, L.A.; Pashchenko, V.Z.; Tusov, V.B. The effect of laser irradiation on embryo-genesis of the loach Misgurnus fossilis. In Biologically Active Substances and Factors in Aquaculture; Collection of Scientific Papers; Glubokov, A., Ed.; Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1993; pp. 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Nemova, N.N.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Pekkoeva, S.N.; Voronin, V.P.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Murzina, S.A. Effect of the photoperiod on lipid spectrum of young Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar L. Russ. J. Physiol. 2020, 106, 622–630. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloan-Syanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissue (for brain, liver and muscle). J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzina, S.A.; Pekkoeva, S.N.; Kondakova, E.A.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Filippova, K.A.; Nemova, N.N.; Orlov, A.M.; Berge, J.; Falk-Petersen, S. Tiny but Fatty: Lipids and Fatty acids in the Daubed Shanny (Leptoclinus maculatus), a Small Fish in Svalbard Waters. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, L. Spectrophotometric assay of cytochrome c oxidase. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1955, 2, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassault, A. Lactate dehydrogenase, UV-method with pyruvate and NADH. Methods Enzym. Anal. 1983, 3, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 3rd ed.; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1983; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M. (Ed.) The bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay for protein quantitation. In Basic Protein and Peptide Protocols, 1st ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zgoda, V.G.; Kopylov, A.T.; Tikhonova, O.V.; Moisa, A.A.; Pyndyk, N.V.; Farafonova, T.E.; Novikova, S.E.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Ponomarenko, E.A.; Poverennaya, E.V.; et al. Chromosome 18 transcriptome profiling and targeted proteome mapping in depleted plasma, liver tissue and HepG2 cells. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 23–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakoff, R. R in Action: Data Analysis and Graphics with R; DMK Press: Moscow, Russia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kucherenko, N.E.; Vasiliev, A.N. Lipids; Vischa Shk.: Kiev, Ukraine, 1985; p. 247. [Google Scholar]
- Netyuhaylo, L.G.; Tarasenko, L.M. Features of lung tissue cell membrane lipid composition under acute emotional stress in rats. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2001, 73, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rebl, A.; Goldammer, T. Under control: The innate immunity of fish from the inhibitors’ perspective. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 77, 328–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozernyuk, N.D. Adaptive specific features of energy metabolism in fish ontogenesis. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 42, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, R.A.; Marra, E.; Passarella, S.; Petragallo, V.A.; Greco, M. Increase in cytosolic and mitochondrial protein synthesis in rat hepatocytes irradiated in vitro by He-Ne laser. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1996, 34, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, C.; Campbell, P.; Couture, P. Physiological correlates of growth and condition in the yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A. 2008, 151, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, T.I.; Tiphlova, O.A.; Fedoseyeva, G.E.; Kalendo, G.S.; Letokhov, V.S.; Lobko, V.V.; Lyapunova, T.S.; Pomoshnikova, N.; Meissel, M.N. Biostimulating action of low-intensity monochromatic visible light: Is it possible? Laser Chem. 1984, 5, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treberg, J.R.; Lewis, J.M.; Driedzic, W.R. Comparison of liver enzymes in osmerid fishes: Key differences between a glycerol accumulating species, rainbow smelt (Osmerus mordax) and a species that does not accumulate glycerol, capelin (Mallotus villosus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. 2002, 132, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Yang, L.; Tang, X.; Yang, X.; Bao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, M. Patterns of catabolic capacities and energy metabolism in developing embryos and yolk-sac larvae of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2017, 481, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.N.; Fyhn, H.J. Requirement for amino acids in ontogeny of fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 684–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosvitin plays a critical role in the immunity of zebrafish embryos via acting as a pattern recognition receptor and an antimicrobial effector. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22653–22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovoll, M.; Johnsen, H.; Boshra, H.; Bogwald, J.; Sunyer, J.O.; Dalmo, R.A. The ontogeny and extrahepatic expression of complement factor C3 in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J. CsPTX1, a pentraxin of Cynoglossus semilaevis, is an innate immunity factor with antibacterial effects. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheis, R.; Kircheis, L.; Oshima, H.; Kohchi, C.; Soma, G.; Mizuno, D. Selective lysis of early embryonic cells by the alternative pathway of complement-a possible mechanism for programmed cell death in empryogenesis. In Vivo 1996, 10, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henson, P.M.; Hume, D.A. Apoptotic cell removal in development and tissue homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 1998, 27, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastellos, D.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: More than a ‘guard‘ against invading pathogens. TRENDS Immunol. 2002, 23, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastellos, D.; Andronis, C.; Persidis, A.; Lambris, J.D. Novel biological networks modulated by complement. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemova, N.N.; Sidorov, V.S. Lysosomal Proteases in Embryogenesis of Salmon Salmo salar L. Zhurn. Evolyuts. Biokhim. Fiziol. 1984, 20, 576–580. [Google Scholar]
- Nemova, N.N. Properties and physiological role of intracellular proteinases in fish tissues. Usp. Sovr. Biol. 1991, 3, 947–953. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, M.S. Histone proteomics and the epigenetic regulation of nucleosome mobility. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2007, 4, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrelly, L.A.; Thompson, R.E.; Zhao, S.; Lepack, A.E.; Lyu, Y.; Bhanu, N.V.; Zhang, B.; Loh, Y.E.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Vadodaria, K.C.; et al. Histone serotonylation is a permissive modification that enhances TFIID binding to H3K4me3. Nature 2019, 567, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, M.; Mulugeta, T.; Gellein Blikeng, B.; West, A.C.; Jørgensen, E.H.; Rød Sandven, S.; Hazlerigg, D. RNA profiling identifies novel, photoperiod-history dependent markers associated with enhanced saltwater performance in juvenile Atlantic salmon. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, M.; van Eijk, M.; Haagsman, H.P.; Hartshorn, K.L. Histones as mediators of host defense, inflammation and thrombosis. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikapitiya, C.; Dorrington, T.; Gomez-Chaim, M. The role of histones in the immune responses of aquatic invertebrates. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2013, 10, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
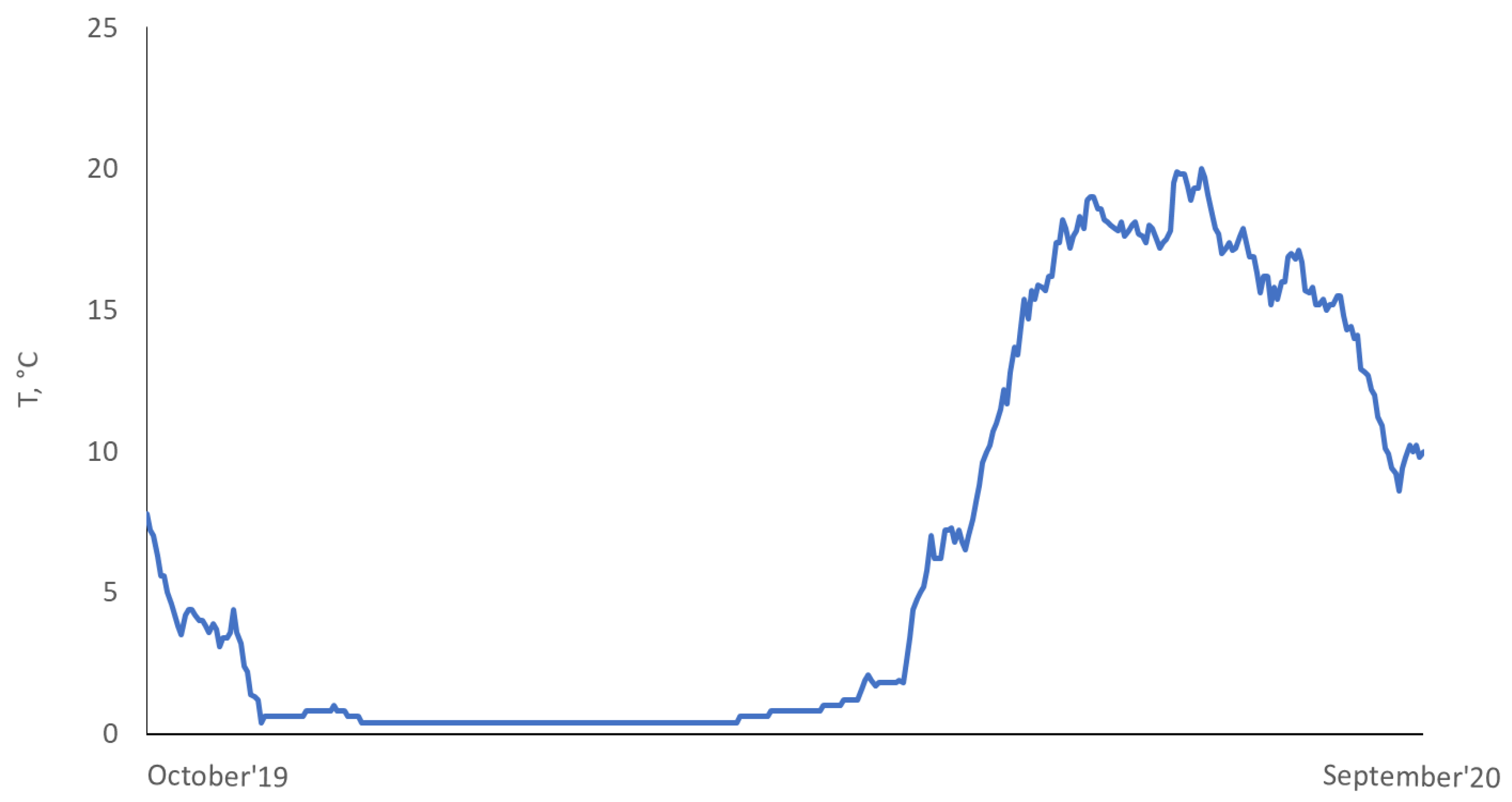

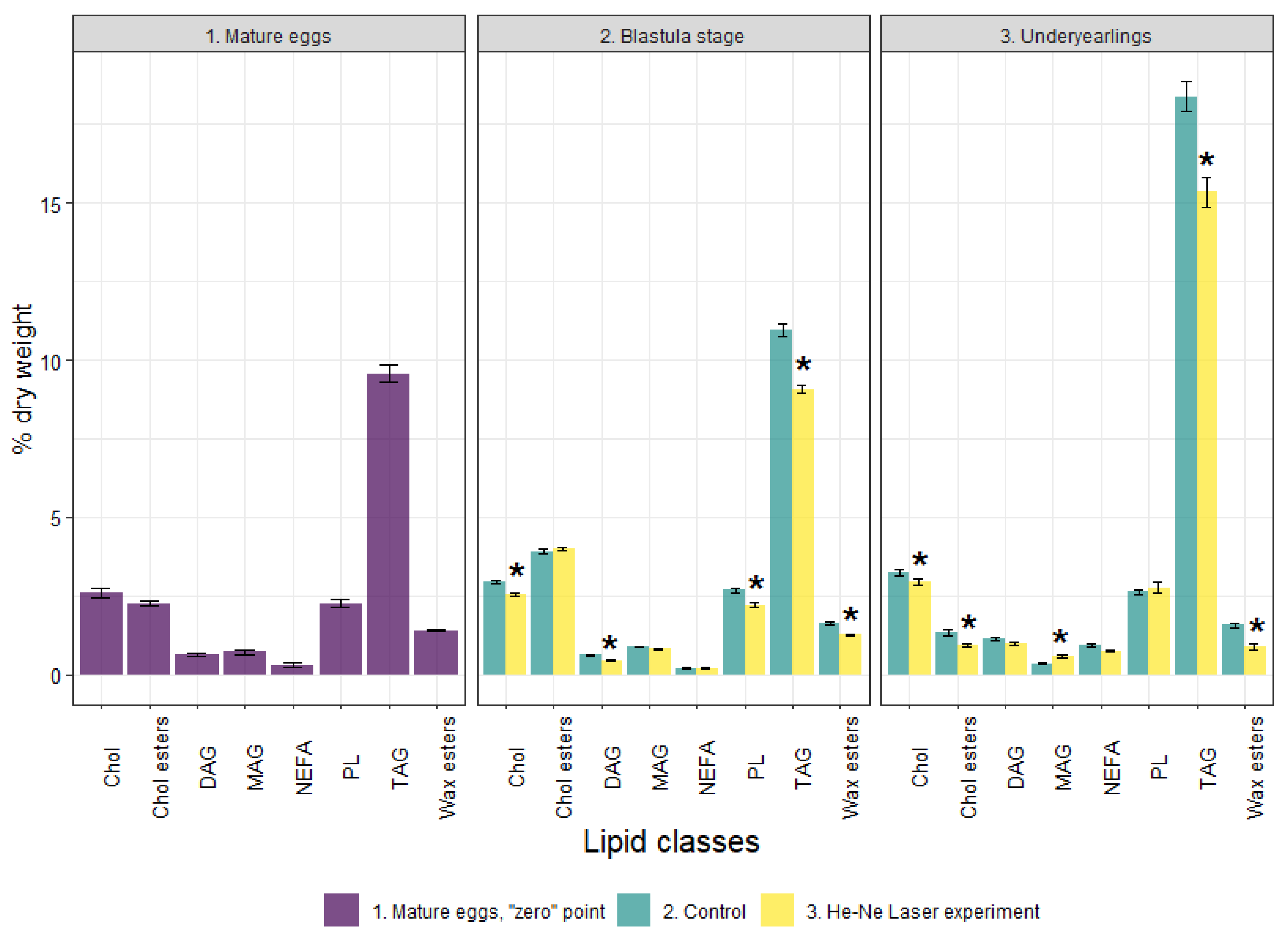










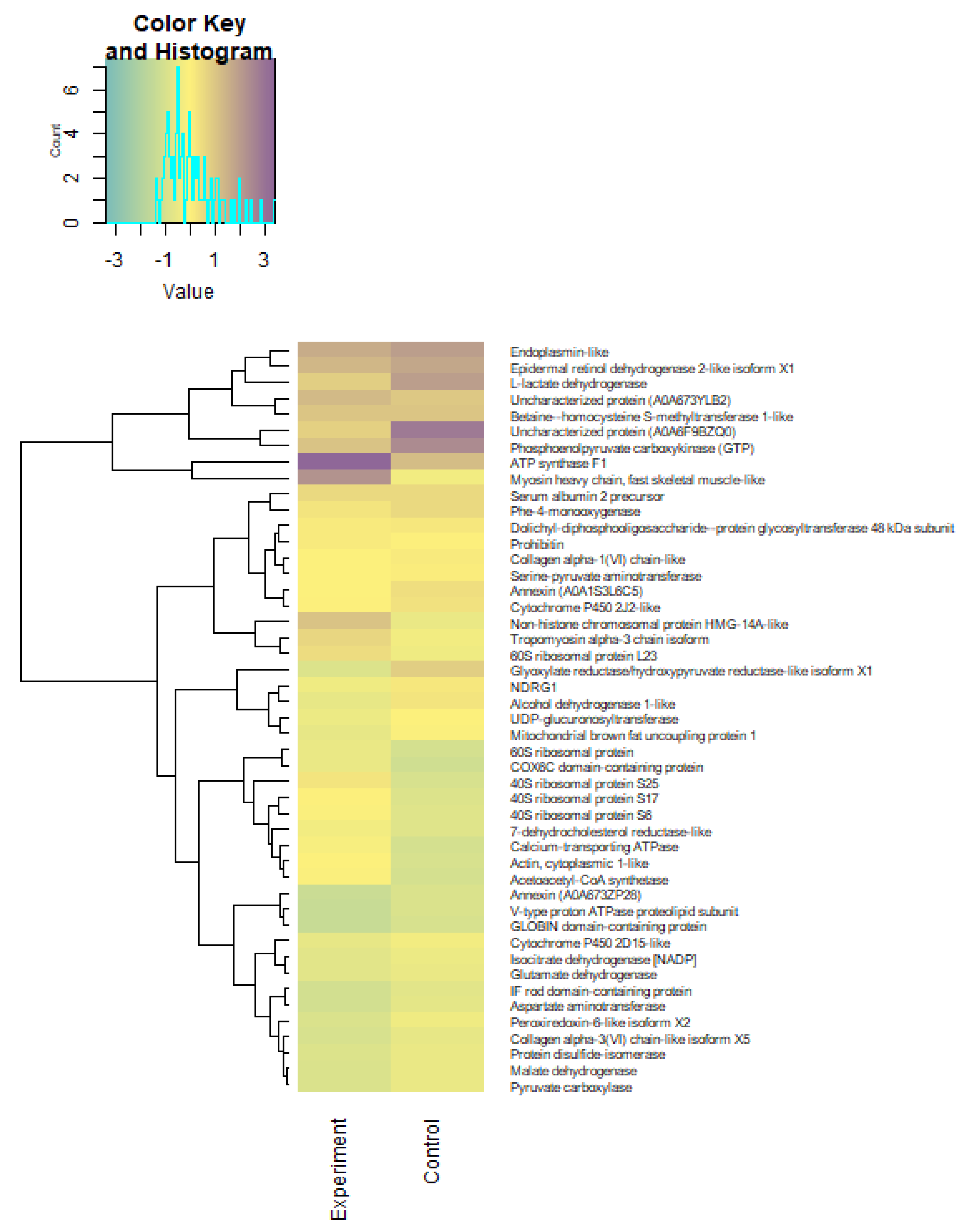

| Group | n | Weight, g | Fork Length, cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mature eggs | |||
| 25 | 0.090 ± 0.001 | - | |
| Blastula stage | |||
| Control | 15 | 0.101 ± 0.007 | - |
| LE | 15 | 0.108 ± 0.003 | - |
| Underyearlings | |||
| Control | 10 | 6.141 ± 0.323 | 8.140 ± 0.114 |
| LE | 10 | 7.394 ± 0.292 | 8.792 ± 0.133 |
| Stage | Mature Eggs | Blastula Stage (Control) | Blastula Stage (Experiment) | Underyearlings (Control) | Underyearlings (Experiment) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n-3)/(n-6) | 13.01 ± 0.16 | 11.99 ± 0.16 | 11.53 ± 0.14 | 3.06 ± 0.01 | 3.06 ± 0.02 |
| 16:0/18:1(n-9) | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.68 ± 0.02 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 1.07 ± 0.01 | 1.04 ± 0.01 |
| 18:1(n-9)/18:1(n-7) | 5.18 ± 0.04 | 5.07 ± 0.22 | 5.39 ± 0.18 | 5.31 ± 0.08 | 5.32 ± 0.07 |
| 18:1(n-9)/18:0 | 2.75 ± 0.01 | 2.89 ± 0.1 | 2.98 ± 0.1 | 4.19 ± 0.03 | 4.15 ± 0.03 |
| 18:3(n-3)/18:2(n-6) | 0.65 ± 0.01 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0 | 0.24 ± 0 |
| 20:4(n-6)/18:2(n-6) | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.03 | 0.6 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0 | 0.12 ± 0 |
| 20:5(n-3)/18:3(n-3) | 12.57 ± 0.07 | 11.32 ± 0.74 | 10.2 ± 0.5 | 3.58 ± 0.06 | 3.78 ± 0.1 * |
| 22:6(n-3)/20:5(n-3) | 1.89 ± 0.01 | 2.22 ± 0.09 | 2.29 ± 0.07 | 2.84 ± 0.06 | 2.62 ± 0.08 * |
| Parameter | Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Mature eggs | ||
| LDH | 3.78 ± 0.23 1.24 ± 0.09 | |
| Aldolase | ||
| Blastula stage | ||
| Control | Experiment | |
| COX | 65.21 ± 7.07 | 92.11 ± 9.43 * |
| LDH | 29.41 ± 1.64 | 28.79 ± 2.71 |
| G6PDH | 14.32 ± 0.91 | 18.69 ± 2.04 * |
| GPDH | 11.61 ± 1.57 | 18.04 ± 1.73 * |
| Aldolase | 0.94 ± 0.08 | 1.01 ± 0.08 |
| LDH/COX | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 0.26 ± 0.03 * |
| Underyearlings | ||
| Control | Experiment | |
| COX | 22.16 ± 2.28 | 22.10 ± 4.01 |
| LDH | 5829.48 ± 364.83 | 5349.20 ± 393.27 |
| Aldolase | 173.20 ± 14.32 | 165.12 ± 8.25 |
| Protein | Code | LOC | Organism | GO Molecular Function | GO Biological Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosvitin | A0A1S3P927 | LOC100136426 | Salmo salar | Lipid transporter activity Nutrient reservoir activity | |
| Cathepsin D-like | A0A1S3QT99 | LOC106596118 | Salmo salar | Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity | |
| Alpha-1-antitrypsin homolog | A0A1S3SAE4 | LOC106608112 | Salmo salar | Extracellular space Cellular component | |
| Pentaxin | A0A1S3SCW1 | LOC106608633 | Salmo salar | Metal ion binding | |
| Coagulation factor XIII B chain-like | A0A1S3QWZ2 | LOC106598077 | Salmo salar | Lacks conserved residue(s) required for the propagation of feature annotation | |
| Serine protease-like protein | M4V2E4 | LOC101448046 | Salmo salar | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | Complement activation Notch signaling pathway |
| L-rhamnose-binding lectin CSL3-like | A0A1S3QXD6 | LOC106597995 | Salmo salar | Carbohydrate binding | |
| Nucleoside diphosphate kinase | B5XCJ8 | NDKA | Salmo salar | ATP binding Nucleoside diphosphate activity | CTP biosynthetic process GTP biosynthetic process UTP biosynthetic process |
| Complement C3 | A0A1S3QRL5 | LOC106595495 | Salmo salar | Endopeptidase inhibitor activity | Complement activation |
| Protein | Mean Decrease Gini |
|---|---|
| Phosvitin | 0.1781333 |
| Cathepsin D-like | 0.3953333 |
| Alpha-1-antitrypsin homolog | 0.1033333 |
| Pentaxin | 0.4060000 |
| Coagulation factor XIII B chain-like | 0.1740000 |
| Serine protease-like protein | 0.3880000 |
| L-rhamnose-binding lectin CSL3-like | 0.4153333 |
| Nucleoside diphosphate kinase | 0.3678667 |
| Complement C3 | 0.1533333 |
| Protein | Code | LOC | Species | GO Molecular Function | GO Biological Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | |||||
| 40S ribosomal protein S26 | B5XBS3 | RS26 | Salmo salar | Structural constituent of ribosome | Translation |
| Extended synaptotagmin-2-B-like isoform X2 | A0A674ALB0 | LOC106599471 | Salmo salar | Lipid binding | Endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane tethering lipid transport |
| Membrane-spanning 4-domains subfamily A member 4A | B5XDT3 | M4A4A | Salmo salar | Membrane | |
| Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase subunit KCP2 | B5X788 | KCP2 | Salmo salar | Membrane | |
| Tubulin beta chain | A0A1S3PR98 | LOC106586934 | Salmo salar | GTPase activity GTP binding structural component of cytoskeleton | Microtubule-based process |
| Gap junction delta-4 protein-like | A0A1S3LVP6 | LOC106568834 | Salmo salar | Cell communication | |
| Cellular nucleic acid-binding protein | B9EQ90 | CNBP | Salmo salar | Nucleic acid binding Zinc ion binding | |
| Collagen alpha-1(XIV) chain-like | A0A1S3MK17 | LOC106573054 | Salmo salar | Collagen trimer | |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 16 member A1 | A0A1S3R7N3 | aldh16a1 | Salmo salar | Oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor | |
| EH domain containing protein 1-like | A0A1S3SVN9 | LOC106612088 | Salmo salar | ATP binding Calcium ion binding GTP binding | |
| Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase 2-like | A0A1S3L9D5 | LOC106565224 | Salmo salar | Metal ion binding Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase activity | Peptide cross-linking |
| Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase | A0A1S3R7W7 | LOC100380640 | Salmo salar | glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase activity | N-terminal protein myristoylation |
| Carnitine O-acetyltransferase-like | A0A1S3M6L2 | LOC106570862 | Salmo salar | transferase activity, transferring acyl groups | |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 | B5X435 | DPP3 | Salmo salar | dipeptidyl-peptidase activity metal ion binding metalloaminopeptidae activity | |
| DNA J homolog subfamily A member 2-like | A0A1S3KQ60 | LOC106561246 | Salmo salar | ATP binding heat shock protein binding metal ion binding unfolded protein binding | Protein folding response to heat |
| Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4-like isoform X4 | A0A1S3RR20 | LOC106604228 | Salmo salar | ATP binding | |
| Heat shock 70 kDa protein-like | A0A1S3R3M8 | LOC106599929 | Salmo salar | ATP binding | |
| H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit | B5XA24 | NOLA1 | Salmo salar | RNA binding | Pseudouridine synthesis rRNA processing |
| Extracellular matrix protein 1-like | A0A1S3MVW9 | LOC106575366 | Salmo salar | signal transduction | |
| Tropomyosin-1 alpha chain | B5X4E8 | TPM1 | Salmo salar | Actin binding | |
| Proactivator polypeptide | B5X4D6 | SAP | Salmo salar | Adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway regulation of lipid metabolic process sphingolipid metabolic process | |
| Complement C2-like | A0A1S3NRD5 | LOC106580826 | Salmo salar | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | complement activation innate immune response |
| Signal recognition particle receptor subunit alpha-like isoform X1 | A0A1S3NSP9 | LOC106581092 | Salmo salar | GTPase activity GTP binding signal recognition particle binding | SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane |
| Collagen alpha-1(I) chain | A0A1S3S6G4 | LOC100286406 | Salmo salar | Extracellular matrix structural Constituent metal ion binding | |
| Anoctamin | A0A1S3PDW1 | ano5 | Salmo salar | protein dimerization activity | |
| N-acetyltransferase 8-like | A0A1S3P7U0 | LOC106583684 | Salmo salar | N-acetyltransferase activity | |
| Spectrin beta chain | A0A1S3RFA5 | LOC106602627 | Salmo salar | Actin binding phospholipid binding structural constituent of cytoskeleton | Actin filament capping |
| CDGSH iron-sulfur domain-containing protein 2A | A0A1S3RH14 | LOC106602754 | Salmo salar | 2 iron, 2 sulfurcluster binding Metal ion binding | Autophagy |
| Calpain-5-like isoform X2 | A0A1S3T047 | LOC106612883 | Salmo salar | calcium-dependent cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | |
| cGMP-dependent protein kinase | A0A1S3N3S1 | LOC106577002 | Salmo salar | ATP binding cGMP binding cGMP-dependent protein kinase activity | |
| Cytochrome P450 3A27-like | A0A1S3QK62 | LOC106593341 | Salmo salar | Heme binding Iron ion binding Monooxygenase activity oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen | |
| Si:ch211-152c8.4 | A0A673XRM9 | LOC100136426 | Salmo trutta | ||
| ER lumen protein-retaining receptor | A0A1S3Q507 | LOC106589518 | Salmo trutta | ER retention sequence binding | Protein retention in ER lumen protein transport |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A674BI77 | LOC115176156 | Salmo trutta | Actin binding Calcium ion binding Microtubule binding | Intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization |
| HATPase_c domain-containing protein | A0A674BXP0 | LOC115174523 | Salmo trutta | ATP binding Unfolded protein binding | Protein folding |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] | A0A673YKU9 | LOC115192436 | Salmo trutta | Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding N,N-dimethylaniline monooxygenase activity NADP binding | |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A674DSP5 | tomm70 | Salmo trutta | Transmembrane | |
| Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 | A0A673VXG8 | LOC115167117 | Salmo trutta | collagen binding extracellular matrix binding Integrin binding | Cell adhesion Cell population proliferation |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A674DP36 | LOC115198253 | Salmo trutta | Zinc ion binding | Endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport intracellular protein transport |
| Ras-associating domain-containing protein | A0A673W873 | LOC115197363 | Salmo trutta | Adherens junction Maintenance signal transduction | |
| RNA helicase | A0A674AWY3 | DDX5 | Salmo trutta | ATP binding Nucleic acid binding RNA helicase activity | |
| Methionine synthase | A0A674BZ74 | LOC115190130 | Salmo trutta | Cobalamin binding Methionine synthase activity Zinc ion binding | Methylation pteridine-containing compound metabolic process |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A6F9C1R4 | CSTEINMANNI _LOCUS3550401 | Coregonus sp. | Lipid transporter activity | |
| Uncharacterized protein (fragment) | A0A6F9AAX4 | CSTEINMANNI _LOCUS1015781 | Coregonus sp. ‘balchen’ | Phosphatidylinositol binding | |
| Protein kinase domain-containing protein | A0A060Y1F8 | GSONMT000 | Oncorhynchus mykiss | ATP binding | |
| Myosin heavy chain | Q8JIP5 | N/A | Oncorhynchus keta | Actin filament binding ATP binding motor activity | |
| Fibrillar collagen NC1 domain-containing protein | A0A4W5M2R8 | N/A | Hucho hucho (huchen) | Extracellular matrix structural constituent | |
| Septin-type G domain-containing protein | A0A4W5N0E8 | N/A | Hucho hucho (huchen) | GTP binding | |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A4W5PNZ1 | N/A | Hucho hucho (huchen) | Actin binding | |
| He–Ne Laser experiment | |||||
| Fructose-bisphosphatealdolase | O73866 | ALDOB | Salmo salar | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase activity | Glycolytic process |
| Enhancer of rudimentary homolog | B5X283 | ERH | Salmo salar | Cell cycle | |
| Outerdense fiber protein 2-like isoform X2 | A0A1S3R511 | LOC106600419 | Salmo salar | Negative regulation of cilium assembly | |
| Lumican | A0A1S3N0X4 | LOC106576454 | Salmo salar | Collagen fibril organization visual perception | |
| Cathepsin M | Q70SU8 | salarin | Salmo salar | Cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity protease binding | |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A1S3QJQ6 | LOC106593464 | Salmo salar | Catalytic activity | |
| Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 36 | A0A1S3NVC8 | ttc36 | Salmo salar | ||
| Erythrocyte band 7 integral membrane protein-like | A0A1S3KZT9 | LOC106563232 | Salmo salar | ||
| SURF1-like protein | B5XGV8 | SURF1 | Salmo salar | Cytochrome-c oxidase activity | Embryonic organ development spinal cord motor neuron differentiation |
| Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain-like isoform X3 | A0A1S3NNW5 | LOC106580396 | Salmo salar | Actin binding | |
| Syntenin-1 | B5X137 | SDCB1 | Salmo salar | ||
| Serine palmitoyl transferase 1 isoform X1 | A0A1S3MCX2 | sptlc1 | Salmo salar | Pyridoxal phosphate binding Transferase activity | Biosynthetic process |
| Cytochrome P450 2F3-like | A0A1S3QRX0 | LOC106595913 | Salmo salar | heme binding iron ion binding oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen | |
| SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily E member 1-like isoform X1 | A0A1S3RAD2 | LOC106601263 | Salmo salar | DNA binding | ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling |
| Myosin heavy chain, fast skeletal muscle-like | A0A1S3QIX9 | LOC106593179 | Salmo salar | Actin filament binding ATP binding motor activity | |
| Probable 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase E1 component DHKTD1, mitochondrial | A0A1S3MIZ7 | LOC106573060 | Salmo salar | oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (succinyl-transferring) activity thiamine pyrophosphate binding | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| Torsin-1A-interacting protein 2-like | A0A1S3KK08 | LOC106560502 | Salmo salar | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | A0A1S3LDJ3 | LOC106565890 | Salmo salar | Alkaline phosphatase activity | |
| LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 | A0A1S3S575 | LOC106607249 | Salmo salar | metal ion binding | Ion transport |
| Peptidase M20 domain-containing protein 2 | A0A1S3S7W2 | pm20d2 | Salmo salar | Hydrolase activity | |
| Putative all-trans-retinol 13,14-reductase | A0A1S3S561 | LOC100196171 | Salmo salar | ||
| Myosin-10-like isoform X12 | A0A1S3L623 | LOC106564681 | Salmo salar | Actin filament binding ATP binding motor activity | |
| Annexin | B5XAE0 | ANXA5 | Salmo salar | Calcium-dependent phospholipid binding calcium ion binding | Negative regulation of coagulation |
| Catenin delta-1-like isoform X7 | A0A1S3RRP7 | LOC106604654 | Salmo salar | Cadherin binding | Cell–cell adhesion |
| Granulins-like isoform X2 | A0A1S3RAE7 | LOC106601556 | Salmo salar | ||
| Utrophin-like isoform X7 | A0A1S3S9Q6 | LOC106608002 | Salmo salar | Actin binding Zinc ion binding | |
| Apolipoprotein B-100-like | A0A1S3M854 | LOC106571178 | Salmo salar | Lipid transporter activity | |
| RNA-binding protein 4B | B5DG79 | LOC106577685 | Salmo salar | RNA binding | |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13-like isoform X2 | A0A1S3L7P6 | LOC106564960 | Salmo salar | Structural molecule activity | |
| Fibrillar collagen NC1 domain-containing protein | A0A673ZWM6 | N/A | Salmo trutta | Extracellular matrix structural constituent | |
| GRIP domain-containing protein | A0A674ABA3 | LOC115199935 | Salmo trutta | ||
| Vacuolar proton pump subunit B | A0A673WHM8 | LOC115193839 | Salmo trutta | ATP binding | ATP metabolic process |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A674BVJ8 | LOC115166471 | Salmo trutta | Calcium ion binding | Endocytosis |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A674DB91 | TPM1 | Salmo trutta | actin binding | |
| SERPIN domain-containing protein | A0A060XBJ0 | GSONMT00058278001 | Oncorhynchus mykiss | Serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity | Negative regulation of complement activation regulation of blood coagulation |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A4W5LNI8 | N/A | Hucho hucho | ||
| Coagulation factor X | A0A4W5JVR3 | F10 | Hucho hucho | Calcium ion binding Serine-type endopeptidase activity | Blood coagulation |
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A4W5MR86 | N/A | Hucho hucho | ||
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial | A0A4W5K6Y5 | N/A | Hucho hucho | 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding electron transfer activity NADH dehydrogenase | ATP synthesis coupled electron transport |
| Protein | Code | Species | GO Molecular Function | GO Biological Process | Control (iBAQ) | He–Ne Laser Experiment (iBAQ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncharacterized protein | A0A674DK55 | Salmo turtta | DNA binding protein heterodimerization activity | 19647000000 | 16077000000 | |
| Histone H4 | A0A674C0Y3 | Salmo trutta | DNA binding protein heterodimerization activity | DNA-templated transcription, initiation | 19301000000 | 12952000000 |
| Histone H2A | C1BEH9 | Oncorhynchus mykiss | DNA binding protein heterodimerization activity | Defense response to Gram-positive bacterium Innate immune response Membrane disruption in other organisms | 14375000000 | 7603900000 |
| Histone H1 | P06350 | Oncorhynchus mykiss | DNA binding | Defense response to bacterium Nucleosome assembly | 8659100000 | 5947400000 |
| Histone H3 | A0A4W5QXQ5 | Hucho hucho | DNA binding protein heterodimerization activity | 8337600000 | 2860100000 | |
| Histone domain-containing protein | A0A060WQS0 | Oncorhynchus mykiss | DNA binding protein heterodimerization activity | 3103700000 | 5338700000 | |
| Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | O42161 | Salmo salar | ATP binding | 2906100000 | 3423800000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murzina, S.A.; Voronin, V.P.; Churova, M.V.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Shulgina, N.S.; Provotorov, D.S.; Tikhonova, O.V.; Nemova, N.N. The Effects of Low-Level Helium–Neon (He–Ne) Laser Irradiation on Lipids and Fatty Acids, and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome in the Blastula Stage and Underyearlings of the Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar: A Novel Approach in Salmonid Restoration Procedures in the North. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010133
Murzina SA, Voronin VP, Churova MV, Ruokolainen TR, Shulgina NS, Provotorov DS, Tikhonova OV, Nemova NN. The Effects of Low-Level Helium–Neon (He–Ne) Laser Irradiation on Lipids and Fatty Acids, and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome in the Blastula Stage and Underyearlings of the Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar: A Novel Approach in Salmonid Restoration Procedures in the North. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(1):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010133
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurzina, Svetlana A., Viktor P. Voronin, Maria V. Churova, Tatiana R. Ruokolainen, Natalia S. Shulgina, Dmitriy S. Provotorov, Olga V. Tikhonova, and Nina N. Nemova. 2022. "The Effects of Low-Level Helium–Neon (He–Ne) Laser Irradiation on Lipids and Fatty Acids, and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome in the Blastula Stage and Underyearlings of the Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar: A Novel Approach in Salmonid Restoration Procedures in the North" Biomolecules 12, no. 1: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010133
APA StyleMurzina, S. A., Voronin, V. P., Churova, M. V., Ruokolainen, T. R., Shulgina, N. S., Provotorov, D. S., Tikhonova, O. V., & Nemova, N. N. (2022). The Effects of Low-Level Helium–Neon (He–Ne) Laser Irradiation on Lipids and Fatty Acids, and the Activity of Energetic Metabolism Enzymes and Proteome in the Blastula Stage and Underyearlings of the Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar: A Novel Approach in Salmonid Restoration Procedures in the North. Biomolecules, 12(1), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010133







