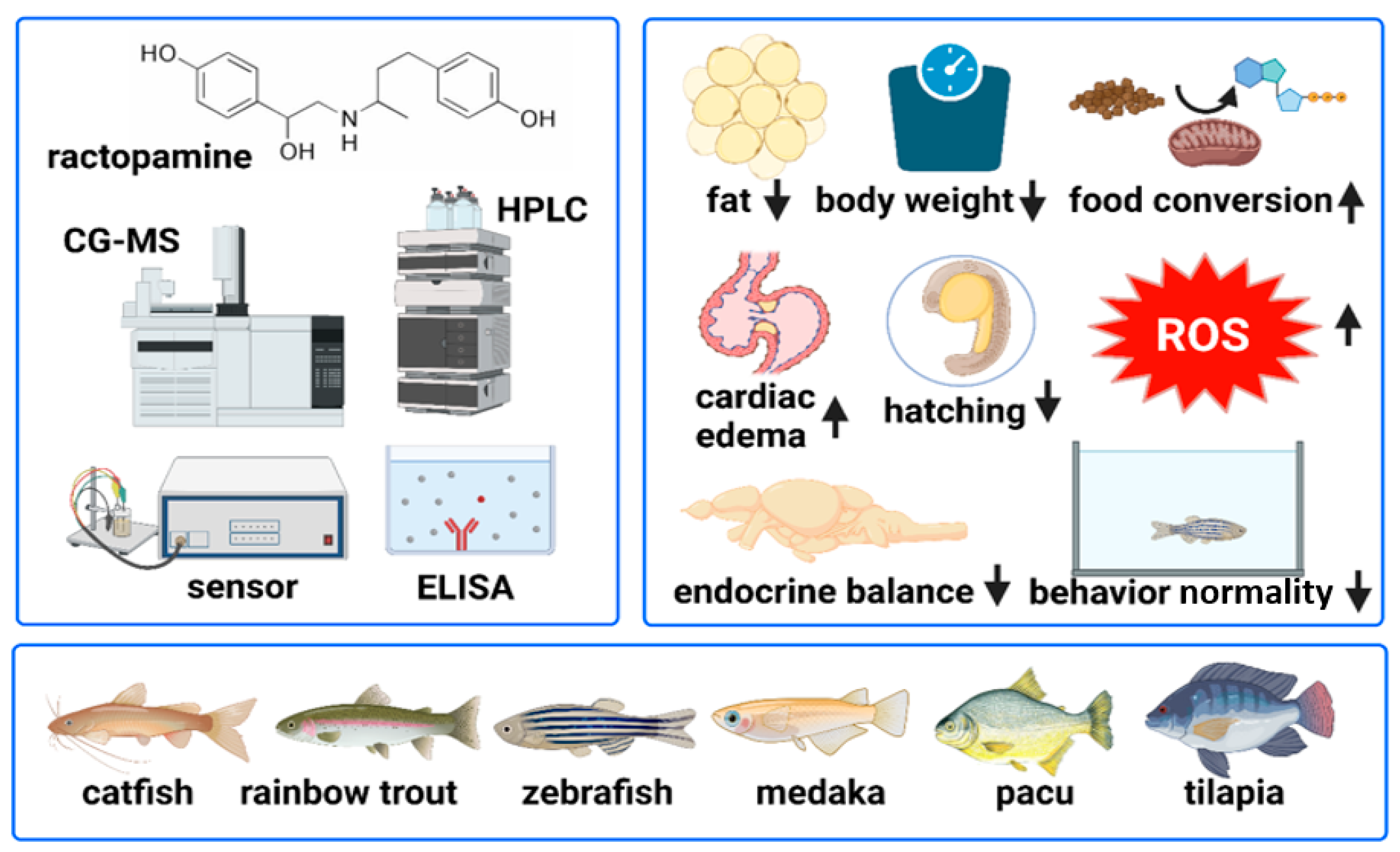
Ractopamine at the Center of Decades-Long Scientific and Legal Disputes: A Lesson on Benefits, Safety Issues, and Conflicts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Applications of RAC in Livestock and Poultry Sectors
| Feed Additives | Animals | Concentration | Physiological Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ractopamine | Crossbred gilts and barrows | 0 and 20 ppm | Improved feed efficiency, average daily gain (ADG), and decreased cooking loss of loin | [27] |
| Ractopamine | Pigs | 20 mg/kg | Increased ADG, decreased feed conversion ratio (FCR), higher carcass lean proportion | [28] |
| Ractopamine | Pigs | 0, 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg | Increased growth (p < 0.001), better efficiency (p < 0.001), and intensified muscular profile (p < 0.001) | [29] |
| Ractopamine | Dogs | 1 mg/kg | Acute myocardial activity | [30] |
| Ractopamine and clenbuterol | Roundworm (Caenorhabditis elegans) | 10 µg/L | Decreased brood size, alteration in locomotion behavior, reduced lifespan | [31] |
| Ractopamine | Cattle | 200 to 350 gm/animal | Increased protein deposition and decreased lipogenesis, increased feed efficiency, increased ADG, and increased carcass weight | [26] |
| Ractopamine | Cattle | 200 mg/animal/day for 28 to 42 days | Increased incidence of death (from 0.59 to 1.129/10,000 cattle) | [32] |
| Ractopamine | Pigs | 0 mg/kg to 7.4 mg/kg | Increased ADG (18.8%), improved gain-to-feed efficiency (23.7%), increased carcass yield (0.7% units), and reduced backfat depths (6.3%) as compared to control (0 mg/kg) | [33] |
| Ractopamine + CON basal diet | Pigs | CON basal diet, CON + 1% ractopamine | Increased lean meat in the RAC group, fecal score, and growth performance was nonsignificant | [34] |
3. Biological Basis of the RAC Response in Animal Tissues
4. Potential Benefits of RAC Feeding on Fishes
5. RAC Level Detection in Wastewater Systems
6. RAC Poses Physiological and Toxicological Effects on Fishes
| Feed Additives | Animals | Concentration | Physiological or Toxicological Effects/Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potential beneficial effects | ||||
| Ractopamine | Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) | 0, 20, and 100 mg/kg | Increased weight gain and reduced fat deposition | [71] |
| Ractopamine and dietary proteins | Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) | RAC = 0 and 20 mg/kg Protein = 240 and 360 g/kg | Increased weight gain and less fat deposition are more functional when surplus protein is ingested | [73] |
| Ractopamine | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) (walbaum) | 0, 5, 10, 20, and 40 ppm | Higher feed efficiency in average treatment weeks No effect of RAC on growth, feed intake, and efficiency after 8–12 weeks of trial. No effect of RAC on hepatosomatic index (HIS) | [74] |
| Ractopamine and dietary proteins | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) (walbaum) | RAC = 0 and 10 ppm CP = 25%, 35%, and 45% | Protein level more significantly affects growth, carcass composition, and pigmentation than ractopamine | [75] |
| Ractopamine and l-carnitine | Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | RAC = 0 and 10 mg/kg l-carnitine = 0, 1, and 2 g/kg−1 | 1 g/kg l-carnitine and 10 mg/kg RAC enhanced the specific growth rate, feed efficiency, FCR, protein efficiency of fish, increased serum albumin level, total protein, and globulin | [76] |
| Ractopamine | Juvenile pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) | RAC = 0, 10, 20, and 40 mg | Feeding RAC for 60 days did not improve growth and body composition at any tested concentration but altered hematology and biochemical parameters | [77] |
| Ractopamine | Pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) | RAC = 11.25, 22.50, 33.75, and 45 ppm | RAC at 11.25 ppm reduced the fat content in fillets of pacu but improved the peroxide formation in samples kept in the freezer for 60 days. At 33.75 ppm, RAC was potent in preventing oxidation during storage in the refrigerator | [78] |
| Ractopamine | Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | RAC = 0, 4, 8, 12, and 16 mg/kg | RAC showed a limited effect in changing body composition, lowering fat contents, and no changes in growth parameters when fed for 31 days | [80] |
| Ractopamine | Tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) | RAC = 0, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg | RAC showed a limited effect on changing metabolism and reducing fat content. However, using a 20 mg/kg RAC dose for 30 days induced a slight decrease in visceral fat | [79] |
| Potential adverse effects | ||||
| Ractopamine | Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) | 5, 25, 125, and 625 ppb | Disruption of the endocrine system and antioxidative/detoxification genes were affected | [87] |
| Ractopamine | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | 0.1, 0.2, 0.85, 8.5, and 85 ppb | Behavioral alteration and oxidative status imbalance | [88] |
| Ractopamine | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | 0.1, 0.2, 0.85, 8.5, and 85 ppb | Increased cardiac rate, induced exploratory behavior, no influence on hatching and survival rate | [89] |
| Ractopamine | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | 250, 350, and 450 ppm for 21 days | Behavioral alteration compromised the reproduction ability of adult zebrafish. Heart edema, granular formation, delayed hatching, and abnormalities in embryos | [90] |
| Ractopamine | Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | 0.1, 1, 2, 4, and 8 ppm for 24 h | Induced hyperactivity in zebrafish larval locomotory behavior, increased cardiac, blood flow, and oxygen consumption rates, beta- blocker (propranolol), after co-incubating with RAC, tends to normalize the induced hyperactivity at 8ppm, lowered the cardiac rate as a “rescue agent” | [91] |
7. RAC Levels Detected in Poultry Animals and Products
| Specimen | Instrumentation | No. of β-agonists/Internal Standards | Linear Range | LOD/LOQ | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine | GC–MS3 (electron impact–ion trap) | Clenbuterol/ methyltestosterone (IS) | 0.5–5 ppb | 0.2 ppb | [93] |
| Pig muscle and human urine | Electrochemical detection | Ractopamine and salbutamol/-- | 1–28 μM (ractopamine) 5–220 μM (salbutamol) | -- | [94] |
| Pig muscle and urine | HPLC-UV | Ractopamine/ephedrine hydrochloride | 0.01–2 ppm | LOD: 0.003 ppm LOQ: 0.01 ppm | [97] |
| Pig samples | HPLC-UV | Ractopamine, clenbuterol, and salbutamol | 0.5–50 ppb 0.5–50 ppb 0.2–20 ppb | LOD: 0.1, 0.1, and 0.05 ppb | [96] |
| Pork | HPLC-UV | Derivatized ractopamine | 0.15–100 μg/g | LOD: 0.078 μg/g | [95] |
| Pork | ELISA | Salbutamol and ractopamine/-- | 0–1.0 ppb | LOD: 0.5 ppb | [98] |
| Swine meat/animal feed | ELISA | Salbutamol/-- | 0.05–1.0 ppb | LOD: 0.3–1.5 ppb LOQ: 0.6–3.0 ppb | [99] |
| Porcine meat | MEKC | Ractopamine | 10–300 ng/g | LOD: 5 ng/g | [100] |
| Animal feeds | HPLC-MS | Ractopamine, clenbuterol, and salbutamol | 0.5–500 mg/kg | LOD: 0.01 mg/kg LOQ: 0.05 mg/kg | [101] |
| Goat, various tissues | UPLC–MS/MS | Salbutamol/SAL-d3 | 0.5–100 ppb | LOD: 0.2 ppb LOQ: 0.5 ppb | [102] |
| Animal feeds | UPLC–MS/MS | Ractopamine, salbutamol, terbutaline, fenoterol, metaproterenol, clenbuterol, formoterol, tulobuterol, phenylethanolamine A/d3-salbutamol, d6-ractopamine, d6-clenbuterol | 5–100 ppb | LOD: 0.01–0.05 ppb LOQ: 0.03–0.20 ppb | [95] |
| Goat, various tissues | UPLC-Q-Orbitrap | RAC/[d6]-RAC | 0.5–500 ppb | LOD: 0.15 ppb LOQ: 0.5 ppb | [103] |
| Pork, beef, mutton, and chicken | UPLC-Q-Orbitrap | Salbutamol, cimaterol, bromchlorbuterol, ractopamine, isoxsuprine, mapenterol, terbutaline, cimbuterol, clenbuterol, brombuterol, mabuterol, clorprenaline/clenbuterol-d9, salbutamol-d3 | 0.01–50 ppb | LOD: 0.0033–0.01 ppb LOQ: 0.01–0.03 ppb | [104] |
8. RAC Regulations and Feed Fights
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castanon, J.I.R. History of the Use of Antibiotic as Growth Promoters in European Poultry Feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Responsible Use of Antibiotics in Aquaculture: FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 469; Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bakharev, A.A.; Sheveleva, O.M.; Fomintsev, K.A.; Grigoryev, K.N.; Koshchaev, A.G.; Amerkhanov, K.A.; Dunin, I.M. Biotechnological characteristics of meat cattle breeds in the Tyumen region. J. Pharm. Sci. and Res. 2018, 10, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Kashaeva, A.; Shakirov, S.; Akhmetzyanova, F.; Khairullin, D. Toxicological safety assessment of ZeolFat energy feed additive. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 27, 00086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Feijoó, C.G.; Navarrete, P. Antibiotics in aquaculture–use, abuse and alternatives. Health Environ. Aquac. 2012, 159, 159–198. [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida, V.V.; Nuñez, A.J.C.; Miyada, V.S. Ractopamine as a metabolic modifier feed additive for finishing pigs: A review. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2012, 55, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, L.R.; Lima, J.A.; Santos, F.A.; Lana, M.A.G.; Ribeiro, A.C.D.S.R.; de Oliveira, E.C. LC–MS/MS quantification of ractopamine in bovine and swine muscle: Stability of matrix-matched calibration solutions. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2017, 22, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Grandy, D.K.; Janowsky, A. Ractopamine, a Livestock Feed Additive, Is a Full Agonist at Trace Amine–Associated Receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang-Fu, W.-G. Simultaneous determination of clenbuterol, salbutamol and ractopamine in milk by reversed-phase liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with isotope dilution. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centner, T.J.; Alvey, J.C.; Stelzleni, A.M. Beta agonists in livestock feed: Status, health concerns, and international trade. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 4234–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, T.J.; Rodewald, J.M.; Brunelle, S.L.; Neeley, M.; Wallace, M.; Connolly, P.; Coleman, M.R. Determination and Confirmation of Parent and Total Ractopamine in Bovine, Swine, and Turkey Tissues by Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry: First Action 2011.23. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1235–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, S.; Bankoğlu, B.; Özkan, A.; Atar, N.; Yola, M.L. Electrochemical sensing of ractopamine by carbon nitride nanotubes/ionic liquid nanohybrid in presence of other β-agonists. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 254, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, C.L.; Rojo, A.; Ellis, M.; Boler, D.D.; McKeith, F.K.; Killefer, J.; Gaines, A.M.; Matzat, P.D.; Schroeder, A.L. Growth performance of immunologically castrated (with Improvest) barrows (with or without ractopamine) compared to gilt, physically castrated barrow, and intact male pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 2289–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsbernd, A.; Stalder, K.; Karriker, L.; Patience, J. Comparison among gilts, physical castrates, entire males, and immunological castrates in terms of growth performance, nitrogen and phosphorus retention, and carcass fat iodine value. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 5702–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, O.A.D.; Feddern, V.; Athayde, N.B.; Manzke, N.E.; Roça, R.D.O.; Lopes, L.D.S.; De Lima, G.J.M.M. Ractopamine supplementation improves leanness and carcass yield, minimally affecting pork quality in immunocastrated pigs. Sci. Agricola 2018, 75, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalhus, J.L.; Jones, S.D.M.; Schaefer, A.L.; Tong, A.K.W.; Robertson, W.M.; Murray, A.C.; Merrill, J.K. The effect of ractopamine on performance, carcass composition and meat quality of finishing pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 70, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Waitt, W.; Mowrey, D.; Anderson, D. Effect of ractopamine hydrochloride on growth performance and carcass composition of finisher pigs fed corn-soy diets with 5% added fat. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 66 (Suppl. S1), 324. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.; Swatland, H.; Young, L. Effect of ractopamine on growth and carcass characteristics of finishing swine. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 67, 1168. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, J.T.; Mersmann, H.J.; Hill, D.A.; Pond, W.G. Effects of ractopamine on genetically obese and lean pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmes, C.A.; Bustamante, O.H.; González, F.G.; Larraín, R.E.; Gandarillas, M. Effects of ractopamine plus amino acids on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality, and ractopamine residues of finishing pigs. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. Rev. Latinoam. Cienc. Agric. 2014, 41, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinckel, A.P.; Li, N.; Richert, B.T.; Preckel, P.V.; Einstein, M.E. Development of a model to describe the compositional growth and dietary lysine requirements of pigs fed ractopamine. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, D.E.; Hancock, D.L.; Anderson, D.B. Phenethanolamine Repartitioning Agents. In Farm Animal Metabolism and Nutrition; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 65–96. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, S.L.; Chung, K.Y.; Hutcheson, J.P.; Nichols, W.T.; Yates, D.A.; Streeter, M.N.; Swingle, R.S.; Galyean, M.L.; Johnson, B.J. Dose and release pattern of anabolic implants affects growth of finishing beef steers across days on feed. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, T.C.; Engle, T.E.; Galyean, M.L.; Wagner, J.J.; Tatum, J.D.; Anthony, R.V.; Laudert, S.B. Effects of ractopamine and trenbolone acetate implants with or without estradiol on growth performance, carcass characteristics, adipogenic enzyme activity, and blood metabolites in feedlot steers and heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 4102–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, I.J.; Thompson, J.M.; Dunshea, F.R. A Meta-Analysis of Zilpaterol and Ractopamine Effects on Feedlot Performance, Carcass Traits and Shear Strength of Meat in Cattle. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttaro, B.E.; Ball, R.O.; Dick, P.; Rae, W.; Vessie, G.; Jeremiah, L.E. Effect of ractopamine and sex on growth, carcass characteristics, processing yield, and meat quality characteristics of crossbred swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1993, 71, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.-J.; Xu, Z.-R.; Chen, H.-L. Effects of ractopamine at different dietary protein levels on growth performance and carcass characteristics in finishing pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1999, 79, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, J.; Rincker, P.; McKeith, F.; Carr, S.; Armstrong, T.; Matzat, P. Meta-Analysis of the Ractopamine Response in Finishing Swine. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2007, 23, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, M.J.; Mullin, K.; Ensley, S.M.; Ware, W.A.; Slavin, R.E. Myocardial Toxicity in a Group of Greyhounds Administered Ractopamine. Veter- Pathol. 2011, 49, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Gao, W.; Wang, D. Adverse Effects from Clenbuterol and Ractopamine on Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and the Underlying Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loneragan, G.H.; Thomson, D.U.; Scott, H.M. Increased Mortality in Groups of Cattle Administered the β-Adrenergic Agonists Ractopamine Hydrochloride and Zilpaterol Hydrochloride. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, J.W.; Allee, G.L.; Rincker, P.J.; Gooding, J.P.; Acheson, R.J.; McKenna, D.R.; Puls, C.L.; Carr, S.N. Effects of ractopamine hydrochloride on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of heavy-weight finishing pigs sent for slaughter using a 3-phase marketing strategy. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2017, 1, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.-R.; Im, Y.-M.; Kim, I.H. Effect of dietary ractopamine supplementation on growth performance, meat quality and fecal score in finishing pigs. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 47, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, T.A.; Ivers, D.J.; Wagner, J.R.; Anderson, D.B.; Weldon, W.C.; Berg, E.P. The effect of dietary ractopamine concentration and duration of feeding on growth performance, carcass characteristics, and meat quality of finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 3245–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunshea, F.R.; King, R.H.; Campbell, R.G. Interrelationships between dietary protein and ractopamine on protein and lipid deposition in finishing gilts. J. Anim. Sci. 1993, 71, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlemann, G.D.; Allee, G.L.; Rincker, P.J.; Ritter, M.J.; Boler, D.D.; Carr, S.N. Impact of ractopamine hydrochloride on growth, efficiency, and carcass traits of finishing pigs in a three-phase marketing strategy. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.H.; Cline, T.R.; Schinckel, A.P.; Jones, D.J. The impact of ractopamine, energy intake, and dietary fat on finisher pig growth performance and carcass merit. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 3152–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, C.T.; Hankins, S.L.; Schinckel, A.P.; Richert, B.T. Evaluation of Three Genetic Populations of Pigs for Response to Increasing Levels of Paylean TM. Available online: https://www.ansc.purdue.edu/pork-archive/pubs/EvalGeneticPopPaylean.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- See, M.T.; Armstrong, T.A.; Matzat, P.D.; Belstra, B.A.; McKeith, F.K.; Rincker, P.J.; Xi, L.; Odle, J.; Culbertson, M.; Herring, W.; et al. Effect of ractopamine feeding level on growth performance and carcass composition. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Stites, C.R.; McKeith, F.K.; Singh, S.D.; Bechtel, P.J.; Mowrey, D.H.; Jones, D.J. The effect of ractopamine hydrochloride on the carcass cutting yields of finishing swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 3094–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.E.; Jones, D.J.; Mowrey, D.H.; Anderson, D.B.; Veenhuizen, E.L. The effect of various levels of ractopamine hydrochloride on the performance and carcass characteristics of finishing swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimbs, K.J.; Pringle, T.D.; Azain, M.; Meers, S.A.; Armstrong, T.A. Effects of ractopamine on performance and composition of pigs phenotypically sorted into fat and lean groups. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.D.; Solomon, M.B.; Steele, N.C. Influence of level of dietary protein or energy on effects of ractopamine in finishing swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4487–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, G.M.; Zerby, H.N.; Moeller, S.J.; Baas, T.J.; Johnson, C.; Watkins, L.E. The effect of feeding ractopamine (Paylean) on muscle quality and sensory characteristics in three diverse genetic lines of swine. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, O.; Darko, E.A.; He, P.; Young, L.G. Manipulation of porcine carcass composition by ractopamine. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 3633–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.T.; Nienaber, J.A.; Klindt, J.; Crouse, J.D. Effect of ractopamine on growth, carcass traits, and fasting heat production of US con-temporary crossbred and Chinese Meishan pure-and crossbred pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4810–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.E. Biological basis of the ractopamine response. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80 (Suppl. S2), E28–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.S. Assessing the Possible Influence of Residues of Ractopamine, a Livestock Feed Additive, in Meat on Alzheimer Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 2021, 11, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.A.; Abu-Hassiba, A.E.-H.G.; ElRouby, M.T.; Abou-Hashim, F.; Omar, H.S. Food adulteration with genetically modified soybeans and maize, meat of animal species and ractopamine residues in different food products. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 55, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, W.J.; González, A. Catecholamine systems in the brain of vertebrates: New perspectives through a comparative approach. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 308–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.M. Current Developments on the Role of α1-Adrenergic Receptors in Cognition, Cardioprotection, and Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 652152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, H.; Webb, E.; Frylinck, L.; Strydom, P. Effects of short and extended fasting periods and cattle breed on glycogenolysis, sarcomere shortening and Warner-Bratzler shear force. South Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 48, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, T.A.; Tucha, O.; Walitza, S.; Lange, K.W. Animal models of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A critical review. ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2010, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, R.D.; Botteron, K.N.; Todd, R.D.; Botteron, K.N. Is attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder an energy deficiency syndrome? Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.B.; Veenhuizen, E.L.; Waitt, W.P.; Paxton, R.E.; Mowrey, D.H. Effect of ractopamine on nitrogen retention, growth performance and carcass composition of finisher pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 65 (Suppl. S1), 130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Boyer, J.L.; Mills, S.E. Acute Effects of Beta-Adrenergic Agonists on Porcine Adipocyte Metabolism In Vitro. J. Anim. Sci. 1989, 67, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, R.; Dickerson, P.; Johnson, S.; Burkett, R.; Burnett, R.; Schroeder, A.; Bergen, W.; Anderson, D. The effect of ractopamine on lipid metabolism in pigs. Federation Proceedings. In Proceedings of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD, USA, 29 April 1987; p. 1177. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, S.; Liu, C.; Gu, Y.; Schinckel, A. Effects of ractopamine on adipose tissue metabolism and insulin binding in finishing hogs. Interaction with genotype and slaughter weight. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 1990, 7, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joost, H.-G.; Weber, T.M.; Cushman, S.W.; Simpson, I.A. Activity and phosphorylation state of glucose transporters in plasma membranes from insulin-, isoproterenol-, and phorbol ester-treated rat adipose cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 11261–11267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; López-Casillas, F.; Bai, D.H.; Luo, X.; Pape, M.E. Role of reversible phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in long-chain fatty acid synthesis. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mabrouk, G.M.; Helmy, I.M.; Thampy, K.G.; Wakil, S.J. Acute hormonal control of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. The roles of insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6330–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, A.G. Dietary Regulation Of Gene Expression: Enzymes Involved In Carbohydrate And Lipid Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1987, 7, 157–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, K.H.; Flores-Riveros, J.R.; McLenithan, J.C.; Janicot, M.; Lane, M.D. Transcriptional repression of the mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter (GLUT4) gene by cAMP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1991, 88, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; García-Sáinz, J.A. Adrenergic regulation of adipocyte metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 1983, 24, 945–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; El-Dakar, A.; Mohsen, M.; Abdelraouf, E.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Effects of using exogenous diges-tive enzymes or natural enhancer mixture on growth, feed utilization, and body composition of rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. J. Agric. Sci. Tech. B 2014, 4, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Tal, Y.; Schreier, H.J.; Sowers, K.R.; Stubblefield, J.D.; Place, A.R.; Zohar, Y. Environmentally sustainable land-based marine aquaculture. Aquaculture 2009, 286, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.; Laudert, S.; Parrott, J.; Mowrey, D.; White, D.; Anderson, D.; Merrill, J. Ractopamine HCL dose titration in feedlot steers: Performance and carcass traits. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68 (Suppl. S1), 294. [Google Scholar]
- Parrott, J.C.P.; Carroll, L.H.; Laudert, S.B.; Merrill, J.K.; Mowrey, D.H.; White, D.R.; Anderson, D.B. Ractopamine HCl dose titration in feedlot steers: Chemical carcass composition. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Cowey, C. Nutrient Requirements of Warmwater Fishes and Shellfishes. Aquaculture 1985, 44, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustin, W.; Lovell, R. Feeding the repartitioning agent, ractopamine, to channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) increases weight gain and reduces fat deposition. Aquaculture 1993, 109, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.B.; Veenhuizen, E.L.; Jones, D.J.; Schroeder, A.L.; Hancock, D.L. The use of phenethanolamines to reduce fat and increase carcass leanness in meat animals. Fat Cholest. Reduc. Foods Technol. Strateg. 1991, 12, 43–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mustin, W.; Lovell, R. Dietary protein concentration and daily feed allowance influence response of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque), to ractopamine. Aquac. Nutr. 1995, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, G.W.; Moccia, R.D. Growth performance and carcass composition of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), fed the (β-agonist ractopamine. Aquac. Res. 1998, 29, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, R.D.; Gurure, R.M.; Atkinson, J.L.; Vandenberg, G.W. Effects of the repartitioning agent ractopamine on the growth and body composition of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), fed three levels of dietary protein. Aquac. Res. 1998, 29, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji-Abadi, S.M.A.J.; Soofiani, N.M.; Sadeghi, A.A.; Chamani, M.; Riazi, G.H. Effects of supplemental dietary l-carnitine and ractopamine on the performance of juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: Dietary l-Carnitine and Ractopamine Supplements in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicudo, A.; Sado, R.; Cyrino, J. Growth, body composition and hematology of juvenile pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) fed increasing levels of ractopamine. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2012, 64, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; Leal, R.; Mesquita, T.; Pimenta, M.E.D.S.G.; Zangerônimo, M.; Sousa, R.; Alvarenga, R. Effect of ractopamine on the chemical and physical characteristics of pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) steaks. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2014, 66, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, I.G.; Souto, C.N.; Faria, T.M.; Mazini, B.S.; Martins, G.P.; Oliveira, S.L.; Oliveira, D.S. The Use of Ractopamine as a Fat-Reducing Feed Additive in Tambaqui Farming: Preliminary Results. World Aquac. 2017, 48, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, A.T.; Bittarello, A.C.; Tovo, R.P.; Meurer, F.; dos Santos, L.D.; Bombardelli, R.A. Effect of ractopamine on Nile tilapia in the end of grow-out period. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2017, 46, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, T.; Nordling, J.; Lagesson, A.; Klaminder, J.; Hellström, G.; Christensen, B.; Fick, J. Environmental relevant levels of a benzodiazepine (oxazepam) alters important behavioral traits in a common planktivorous fish, (Rutilus rutilus). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2017, 80, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, V.; Santos, M.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; Castro, L.F.; Ferreira, M. Simvastatin modulates gene expression of key receptors in zebrafish embryos. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2017, 80, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennigen, J.A.; Stroud, P.; Zamora, J.M.; Moon, T.W.; Trudeau, V.L. Pharmaceuticals as Neuroendocrine Disruptors: Lessons Learned from Fish on Prozac. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2011, 14, 387–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Snow, D.D.; Damon-Powell, T.; Miesbach, D. Occurrence of steroid hormones and antibiotics in shallow groundwater impacted by livestock waste control facilities. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 123, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, C. Determination of 76 pharmaceutical drugs by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry in slaughterhouse wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8312–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.-H.; Lin, A.; Wang, X.-H.; Lin, C.-F. Occurrence of β-blockers and β-agonists in hospital effluents and their receiving rivers in southern Taiwan. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 32, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, S.; Lin, X.; Tan, H.; Fu, Z. Early Life Exposure to Ractopamine Causes Endocrine-Disrupting Effects in Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 96, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachett, A.; Bevilaqua, F.; Chitolina, R.; Garbinato, C.; Gasparetto, H.; Magro, J.D.; Conterato, G.M.; Siebel, A.M. Ractopamine hydrochloride induces behavioral alterations and oxidative status imbalance in zebrafish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2018, 81, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbinato, C.; Schneider, S.E.; Sachett, A.; Decui, L.; Conterato, G.M.; Müller, L.G.; Siebel, A.M. Exposure to ractopamine hydrochloride induces changes in heart rate and behavior in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21468–21475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonare, S.; Sole, S.; Umap, S. Exposure to Ractopamine Induces Behavioural and Reproductive Alterations in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Int. 2018, 25, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, K.; Saputra, F.; Suryanto, M.E.; Lai, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-C.; Yu, W.-H.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Hsiao, C.-D. Evaluation of Effects of Ractopamine on Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Locomotory Physiology in Animal Model Zebrafish Larvae. Cells 2021, 10, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Willett, C.; Fremgen, T. Zebrafish: An Animal Model for Toxicological Studies. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2003, 17, 1.7.1–1.7.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Colamonici, C.; Rossi, F.; Botrè, F. Determination of clenbuterol in human urine by GC–MS–MS–MS: Confirmation analysis in antidoping control. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 773, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, M.; Li, Y.-S.; Chen, S.-M. Electrochemical detection of toxic ractopamine and salbutamol in pig meat and human urine samples by using poly taurine/zirconia nanoparticles modified electrodes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 110, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Li, D.; Qin, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, B.; Geng, Q.; Guo, M.; Punyapitak, D.; Cao, Y. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of ractopamine residue in pork samples by solid phase extraction and pre-column derivatization. Meat Sci. 2015, 106, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Chang, C. Combined Solid-Phase Microextraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultroviolet Detection for Simultaneous Analysis of Clenbuterol, Salbutamol and Ractopamine in Pig Samples: SPME-HPLC for Analysis of Clenbuterol, Salbutamol and Ractopamine. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Zhao, G.; Fu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhou, H.; Chang, C. Combined microextraction by packed sorbent and high-performance liquid chromatography–ultraviolet detection for rapid analysis of ractopamine in porcine muscle and urine samples. Food Chem. 2013, 145, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Wen, K.; Wang, Z. Development and Application of a Gel-Based Immunoassay for the Rapid Screening of Salbutamol and Ractopamine Residues in Pork. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10556–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, S.-Y.; Lei, Y.-C.; Tai, Y.-T.; Chang, T.-H.; Kuo, T.-F. Screening of salbutamol residues in swine meat and animal feed by an enzyme immunoassay in Taiwan. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 654, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Lu, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Cheng, H.-L.; Wu, S.-M. Chemometric optimization of cation-selective exhaustive injection sweeping micellar electrokinetic chromatography for quantification of ractopamine in porcine meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Chang, B.Y.; Dong, T.; He, P.L.; Yang, W.J.; Wang, Z.Y. Simultaneous determination of salbutamol, ractopamine, and clenbuterol in animal feeds by SPE and LC-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gu, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; Ni, H.; Xue, M.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Qin, Y. Determination of Salbutamol Residues in Goat Various Tissues After Exposure to Growth-promoting Doses. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 42, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Junguo, L.; Su, X.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yao, T.; Qin, Y. Distribution and Depletion of Ractopamine in Goat Plasma, Urine and Various Muscle Tissues. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 41, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Shi, F.; Gong, L.; Tan, H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, J. Ultra-trace analysis of 12 β2-agonists in pork, beef, mutton and chicken by ultrahigh-performance liquid-chromatography–quadrupole-orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, K.; Kiebooms, J.A.L.; Claessens, M.; Rappé, K.; Bussche, J.V.; Noppe, H.; Van Praet, N.; De Wulf, E.; Van Caeter, P.; Janssen, C.; et al. Development of analytical strategies using U-HPLC-MS/MS and LC-ToF-MS for the quantification of micropollutants in marine organisms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Trade Organisation WTO|Understanding the Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures Agreement. Available online: https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/sps_e/spsund_e.htm (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Shieh, J.-S.; Yang, S.-G. Statutory safety quarantine and its compensation of consumer’s long-term intake of food additives. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 7, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottemiller, H. Dispute over drug in feed limiting US meat exports. Available online: https://www.nbcnews.com/business/markets/dispute-over-drug-feed-limiting-us-meat-exports-flna174014 (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Bottemiller, H. Codex Adopts Ractopamine Limits for Beef and Pork. Available online: https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2012/07/codex-votes-69-67-to-advance-ractopamine-limits-for-beef-and-pork/ (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Baynes, R.E.; Dedonder, K.; Kissell, L.; Mzyk, D.; Marmulak, T.; Smith, G.; Tell, L.; Gehring, R.; Davis, J.; Riviere, J.E. Health concerns and management of select veterinary drug residues. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 88, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.; Hanrahan, C. The US-EU Beef Hormone Dispute; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Johnson, R. US-EU Poultry Dispute on the Use of Pathogen Reduction Treatments (PRTs); Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Niño, A.M.; Granja, R.H.; Wanschel, A.C.; Salerno, A.G. The challenges of ractopamine use in meat production for export to European Union and Russia. Food Control 2017, 72, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, T.S.; Howard, S.T.; Woerner, D.R.; Scanga, J.A.; McKenna, D.R.; Kolath, W.H.; Chapman, P.L.; Tatum, J.D.; Belk, K.E. Effects of dietary ractopamine hydrochloride and zilpaterol hydrochloride supplementation on performance, carcass traits, and carcass cutability in beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincker, P.J.; Allen, J.B.; Edmonds, M.; Brown, M.S.; Kube, J.C. Effects of voluntary removal of ractopamine hydrochloride (Optaflexx) on live performance and carcass characteristics of beef steers. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2021, 5, txab047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Kim, D.-B.; Nam, T.G.; Seo, D.; Yoo, M. Identification and quantification of multi-class veterinary drugs and their metabolites in beef using LC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, K.; Raza, A.; Vasquez, R.D.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Malhotra, N.; Huang, J.-C.; Buenafe, O.E.M.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Liang, S.-S.; Hsiao, C.-D. Ractopamine at the Center of Decades-Long Scientific and Legal Disputes: A Lesson on Benefits, Safety Issues, and Conflicts. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101342
Abbas K, Raza A, Vasquez RD, Roldan MJM, Malhotra N, Huang J-C, Buenafe OEM, Chen KH-C, Liang S-S, Hsiao C-D. Ractopamine at the Center of Decades-Long Scientific and Legal Disputes: A Lesson on Benefits, Safety Issues, and Conflicts. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(10):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101342
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Kumail, Aqeel Raza, Ross D. Vasquez, Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, Nemi Malhotra, Jong-Chin Huang, Olivia E. M. Buenafe, Kelvin H. -C. Chen, Shih-Shin Liang, and Chung-Der Hsiao. 2022. "Ractopamine at the Center of Decades-Long Scientific and Legal Disputes: A Lesson on Benefits, Safety Issues, and Conflicts" Biomolecules 12, no. 10: 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101342
APA StyleAbbas, K., Raza, A., Vasquez, R. D., Roldan, M. J. M., Malhotra, N., Huang, J.-C., Buenafe, O. E. M., Chen, K. H.-C., Liang, S.-S., & Hsiao, C.-D. (2022). Ractopamine at the Center of Decades-Long Scientific and Legal Disputes: A Lesson on Benefits, Safety Issues, and Conflicts. Biomolecules, 12(10), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101342











