Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmid, and Reagents
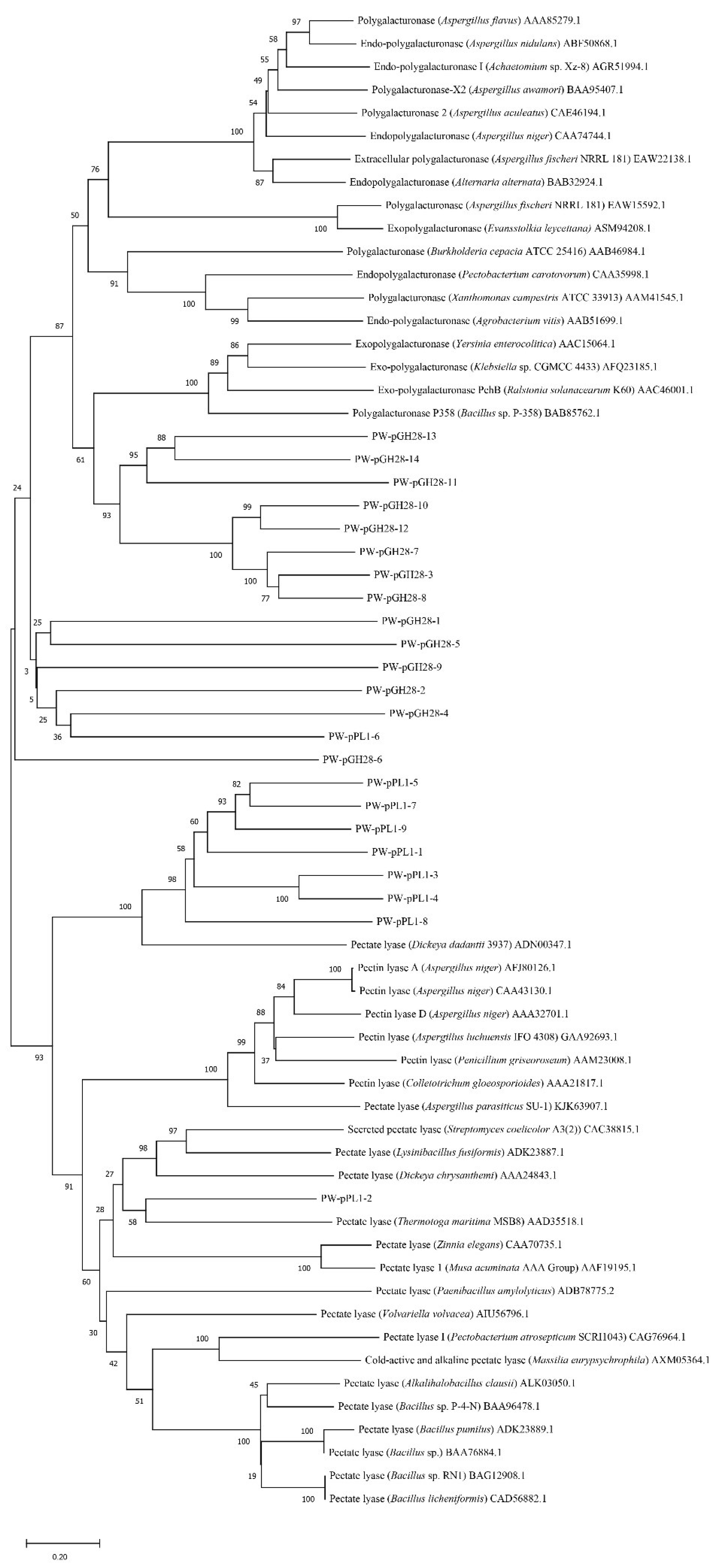
2.2. Screening of Novel Pectinolytic Genes and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Cloning of the Pectinolytic Genes
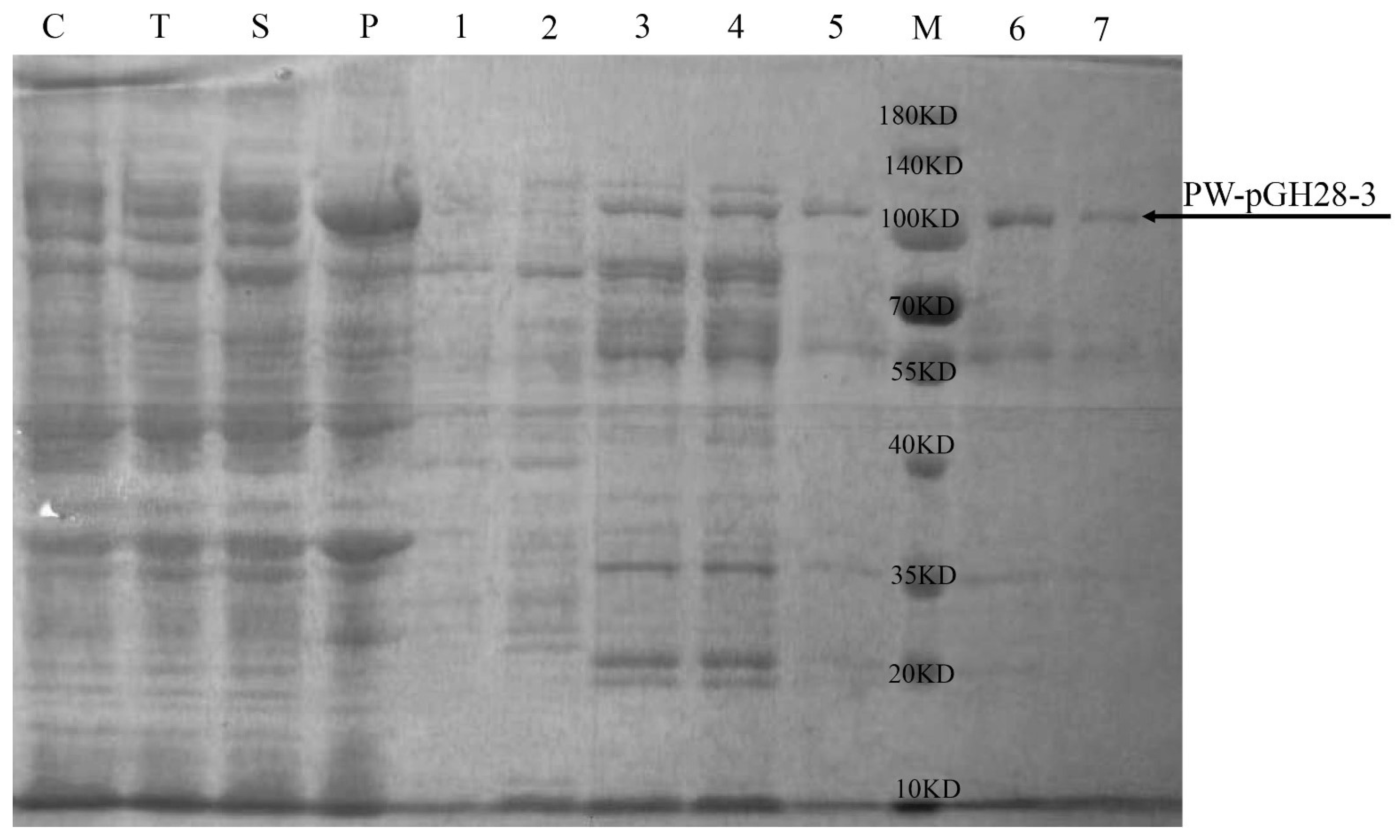
2.4. Expression of the Pectinolytic Genes
2.5. Expression and Purification of PW-pGH28-3 Pectinolytic Enzyme
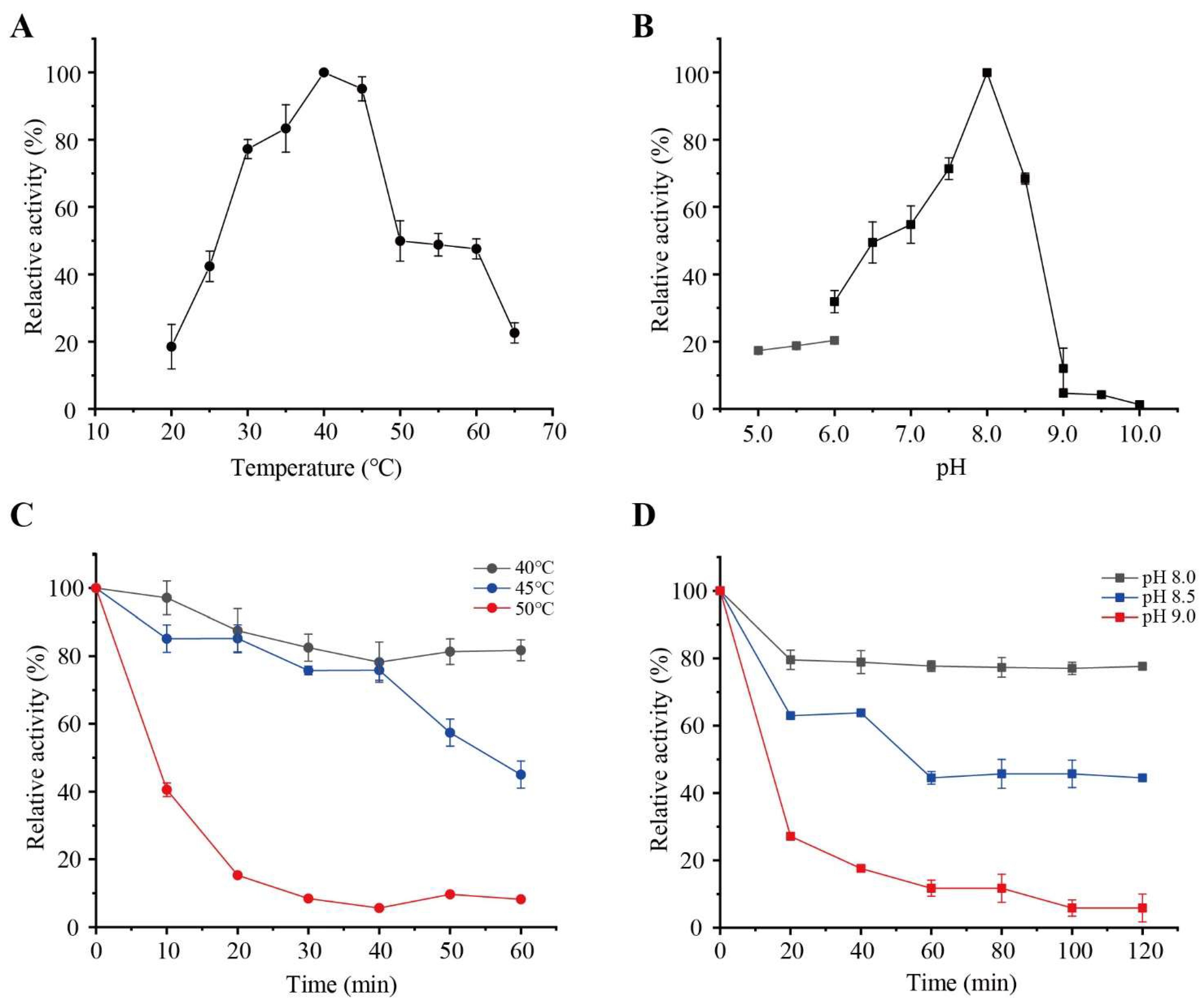
2.6. Effects of Temperature and pH on PW-pGH28-3 Activity
2.7. Detecting the Hydrolysates of PW-pGH28-3 by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)
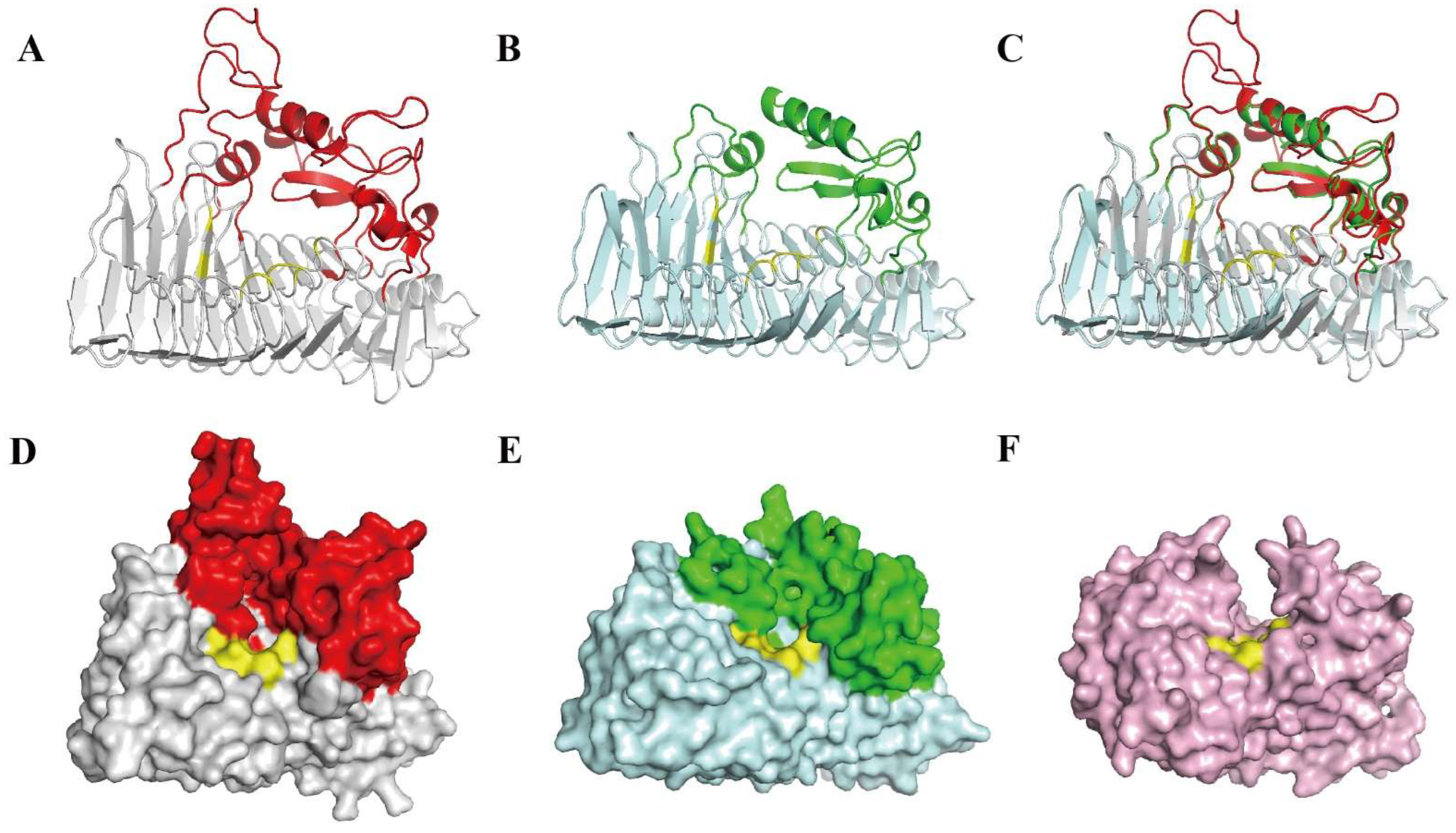
2.8. Bioinformatics Analyses of PW-pGH28-3
3. Results
3.1. Insights into the Pectinolytic Genes Derived from Pulp and Paper Wastewater Treatment Microbiota
3.2. Purification and Characterization of PW-pGH28-3
3.3. Bioinformatics Analysis and Exo-Polygalacturonase Activity Confirmation of PW-pGH28-3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrestha, S.; Kognou, A.L.M.; Zhang, J.; Qin, W. Different facets of lignocellulosic biomass including pectin and its perspectives. Waste Biomass Valori. 2021, 12, 4805–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot-Allain, M.C.N.; Ramasawmy, B.; Emmambux, M.N. Extraction, characterisation, and application of pectin from tropical and sub-tropical fruits: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 282–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayani, R.S.; Saxena, S.; Gupta, R. Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.; Bhatti, H.N.; Bilal, M.; Asgher, M. Multiple parameter optimizations for enhanced biosynthesis of exo-polygalacturonase enzyme and its application in fruit juice clarification. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13, 20160256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.; Bhatti, H.N.; Bilal, M.; Asgher, M. Purification, kinetic, and thermodynamic characteristics of an exo-polygalacturonase from penicillium notatum with industrial perspective. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Qin, W. New insights in pectinase production development and industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 9069–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.; Bhatti, H.N.; Bilal, M. Recent advances in the production strategies of microbial pectinases—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.R.; Vohra, P.K.; Chopra, S.; Tewari, R. Applications of pectinases in the commercial sector: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, G.; Singh, A.; Kaur, A.; Singh, R.; Kaur, J.; Mahajan, R. Microbial pectinases: An ecofriendly tool of nature for industries. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavuthodi, B.; Sebastian, D. Review on bacterial production of alkaline pectinase with special emphasis on Bacillus species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Comm. 2018, 11, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, D. Production optimization of a heat-tolerant alkaline pectinase from Bacillus subtilis ZGL14 and its purification and characterization. Bioengineered 2017, 8, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oumer, O.J.; Abate, D. Characterization of pectinase from Bacillus subtilis strain Btk 27 and its potential application in removal of mucilage from coffee beans. Enzyme Res. 2017, 2017, 7686904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoondal, G.S.; Tiwari, R.P.; Tewari, R.; Dahiya, N.; Beg, Q.K. Microbial alkaline pectinases and their industrial applications: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Sahoo, D.; Rai, A.K.; Singh, S.P. A highly alkaline pectate lyase from the Himalayan hot spring metagenome and its bioscouring applications. Process Biochem. 2022, 115, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, P.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Yin, H.; Cai, C.; Gu, J.; Lü, X. Metagenomic mining pectinolytic microbes and enzymes from an apple pomace-adapted compost microbial community. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Lu, P.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; He, W.; Long, T. Metagenomic insight into the microbial degradation of organic compounds in fermented plant leaves. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Mai, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Su, M.; Du, J.; Wu, Y.; Dai, J.; Tang, Q.; Gao, J.; et al. Performance and microbial communities of a novel integrated industrial-scale pulp and paper wastewater treatment plant. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 278, 123896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Wei, Y. Characterization of efficient xylanases from industrial-scale pulp and paper wastewater treatment microbiota. AMB Express 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Geng, A.; Liu, F.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, X. Insight into dominant cellulolytic bacteria from two biogas digesters and their glycoside hydrolase genes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Geng, A.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qian, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z. Discovery of (hemi-) cellulase genes in a metagenomic library from a biogas digester using 454 pyrosequencing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8173–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Gou, X. TLC to fleetly analyze monosaccharide composition of polysaccharide. Food Sci. 2006, 12, 603–607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yohe, T.; Huang, L.; Entwistle, S.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Busk, P.K.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y. dbCAN2: A meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W95–W101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonivento, D.; Pontiggia, D.; Matteo, A.D.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Salvi, G.; Tsernoglou, D.; Cervone, F.; Lorenzo, G.D.; Federici, L. Crystal structure of the endopolygalacturonase from the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum lupini and its interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins. Proteins 2008, 70, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijning, T.; van Pouderoyen, G.; Kluskens, L.; van der Oost, J.; Dijkstra, B.W. The crystal structure of a hyperthermoactive exopolygalacturonase from Thermotoga maritima reveals a unique tetramer. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3665–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, D.W.; Boraston, A.B. The structural basis for exopolygalacturonase activity in a family 28 glycoside hydrolase. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickersgill, R.; Smith, D.; Worboys, K.; Jenkins, J. Crystal structure of polygalacturonase from Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24660–24664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kester, H.C.; Kusters-van Someren, M.A.; Müller, Y.; Visser, J. Primary structure and characterization of an exopolygalacturonase from Aspergillus tubingensis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 240, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, H.; Chevrette, M.G.; Zhang, L.; Cao, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Pope, P.B.; Currie, C.R.; et al. Functional metagenomics reveals abundant polysaccharide-degrading gene clusters and cellobiose utilization pathways within gut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. ISME J. 2019, 13, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Vahidi, M.F.; Bahram, M.; Han, J.; Ding, X.; Salekdeh, G.H. Metagenomic analysis reveals a dynamic microbiome with diversified adaptive functions to utilize high lignocellulosic forages in the cattle rumen. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.D.; Auffret, M.D.; Warr, A.; Walker, A.W.; Roehe, R.; Watson, M. Compendium of 4941 rumen metagenome-assembled genomes for rumen microbiome biology and enzyme discovery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, M.; Sczyrba, A.; Egan, R.; Kim, T.-W.; Chokhawala, H.; Schroth, G.; Luo, S.; Clark, D.S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science 2011, 331, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista-García, R.A.; del Rayo Sánchez-Carbente, M.; Talia, P.; Jackson, S.A.; O’Leary, N.D.; Dobson, A.D.; Folch-Mallol, J.L. From lignocellulosic metagenomes to lignocellulolytic genes: Trends, challenges and future prospects. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2016, 10, 864–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.L.; Yu, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Baez-Magana, M.; Arutyunova, E.; O’Hara, E.; McAllister, T.; Ominski, K.H.; Lemieux, M.J.; Guan, L.L. Accelerated discovery of novel glycoside hydrolases using targeted functional profiling and selective pressure on the rumen microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozandeh Shahraki, M.; Farhadyar, K.; Kavousi, K.; Azarabad, M.H.; Boroomand, A.; Ariaeenejad, S.; Hosseini Salekdeh, G. A generalized machine-learning aided method for targeted identification of industrial enzymes from metagenome: A xylanase temperature dependence case study. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Somerville, C.; Anderson, C.T. POLYGALACTURONASE INVOLVED IN EXPANSION1 functions in cell elongation and flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1018–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.; Ahn, Y.; Kumar, R.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, B.H. Lignocellulolytic microbiomes for augmenting lignocellulose degradation in anaerobic digestion. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, M.V.; Fernández-Arrojo, L.; Gil-Martínez, J.; Montesinos, A.; Chernikova, T.N.; Nechitaylo, T.Y.; Waliszek, A.; Tortajada, M.; Rojas, A.; Huws, S.A. Microbial β-glucosidases from cow rumen metagenome enhance the saccharification of lignocellulose in combination with commercial cellulase cocktail. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Gong, M.; Shang, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Bao, D. Efficient conversion of spent mushroom substrate into a high value-added anticancer drug pentostatin with engineered Cordyceps militaris. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 10030–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qu, Y. Engineering of filamentous fungi for efficient conversion of lignocellulose: Tools, recent advances and prospects. Biotechnol. adv. 2019, 37, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Closest Genes | Accession Numbers |
Sequence Identity | Endo- or Exo-Polygalacturonase Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW-pGH28-1 | Hypothetical protein [Chloroflexi bacterium] | NLG99247.1 | 45.2% | |
| PW-pGH28-2 | Hypothetical protein [Dehalococcoidia bacterium] | NLE96346.1 | 69.9% | |
| PW-pGH28-3 | Exo- polygalacturonase [Aquipluma nitroreducens] | BBE19954.1 | 58.4% | ✓ |
| PW-pGH28-4 | Right-handed parallel beta-helix repeat-containing protein [Methanobacterium sp.] | MBI4813419.1 | 66.9% | |
| PW-pGH28-5 | Right-handed parallel beta-helix repeat-containing protein [Lentisphaerae bacterium] | NLC83012.1 | 94.8% | |
| PW-pGH28-6 | S-layer homology domain-containing protein [Armatimonadetes bacterium] | MBN1461142.1 | 49.5% | |
| PW-pGH28-7 | Glycoside hydrolase family 28 protein [Bacteroidales bacterium] | NLX28859.1 | 99.8% | |
| PW-pGH28-8 | Glycoside hydrolase family 28 protein [Bacteroidales bacterium] | MBN1107786.1 | 80.1% | ✓ |
| PW-pGH28-9 | Disaggregatase related [Methanomethylovorans sp. PtaU1.Bin073] | OPY19182.1 | 79.0% | |
| PW-pGH28-10 | Exo-poly-alpha-D-galacturonosidase [Bacteroidetes bacterium] | MBP1676534.1 | 76.4% | ✓ |
| PW-pGH28-11 | Right-handed parallel beta-helix repeat-containing protein [Bacteroidales bacterium] | MBG0861178.1 | 81.0% | ✓ |
| PW-pGH28-12 | Glycoside hydrolase family 28 protein [Paludibacter sp.] | MBP6662256.1 | 72.1% | |
| PW-pGH28-13 | TPA: hypothetical protein [Chloroflexi bacterium] | HFI27235.1 | 54.8% | |
| PW-pGH28-14 | Glycoside hydrolase family 28 protein [Bacteroidales bacterium] | MBK7713019.1 | 57.4% | |
| PW-pPL1-1 | T9SS type A sorting domain-containing protein [Catalinimonas alkaloidigena] | WP_089687757.1 | 52.1% | |
| PW-pPL1-2 | Pectate trisaccharide-lyase precursor [Bacteroidetes bacterium A Durb.BinA395] | OPZ03270.1 | 73.6% | ✓ |
| PW-pPL1-3 | Polysaccharide lyase [Bacteroides sp. 51] | WP_163173617.1 | 82.6% | |
| PW-pPL1-4 | Polysaccharide lyase [Paludibacter sp. SCN 50-10] | ODT57447.1 | 83.9% | |
| PW-pPL1-5 | Hypothetical protein BGP01_06875 [Paludibacter sp. 47-17] | OJX91998.1 | 57.5% | |
| PW-pPL1-6 | Pectate lyase [Phycisphaerae bacterium] | MBN2560505.1 | 80.7% | |
| PW-pPL1-7 | Hypothetical protein [Bacteroidetes bacterium] | MBP1676284.1 | 61.5% | |
| PW-pPL1-8 | Pectate lyase precursor [Deltaproteobacteria bacterium ] | MBM4340551.1 | 69.6% | |
| PW-pPL1-9 | Pectate lyase [Bacteroidales bacterium] | NLD63827.1 | 80.6% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L.; Qu, L.; Wei, Y. Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101388
Miao Q, Zhang X, Wang Y, Li X, Wang Z, Tian L, Qu L, Wei Y. Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(10):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101388
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Qin, Xiaoling Zhang, Yitong Wang, Xiaoqi Li, Zheng Wang, Lingmin Tian, Lingbo Qu, and Yongjun Wei. 2022. "Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota" Biomolecules 12, no. 10: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101388
APA StyleMiao, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Li, X., Wang, Z., Tian, L., Qu, L., & Wei, Y. (2022). Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota. Biomolecules, 12(10), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101388









