Discovery of MAO-B Inhibitor with Machine Learning, Topomer CoMFA, Molecular Docking and Multi-Spectroscopy Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Preparation
2.2. Topomer CoMFA
2.3. Molecular Docking
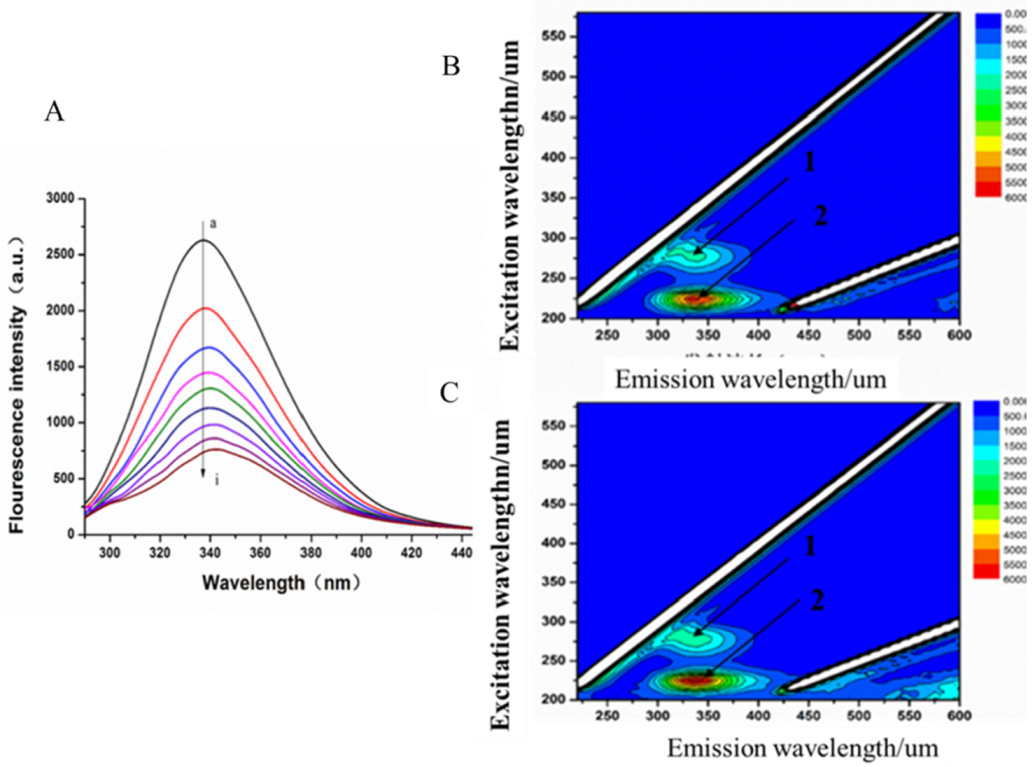
2.4. Fluorescence Spectra
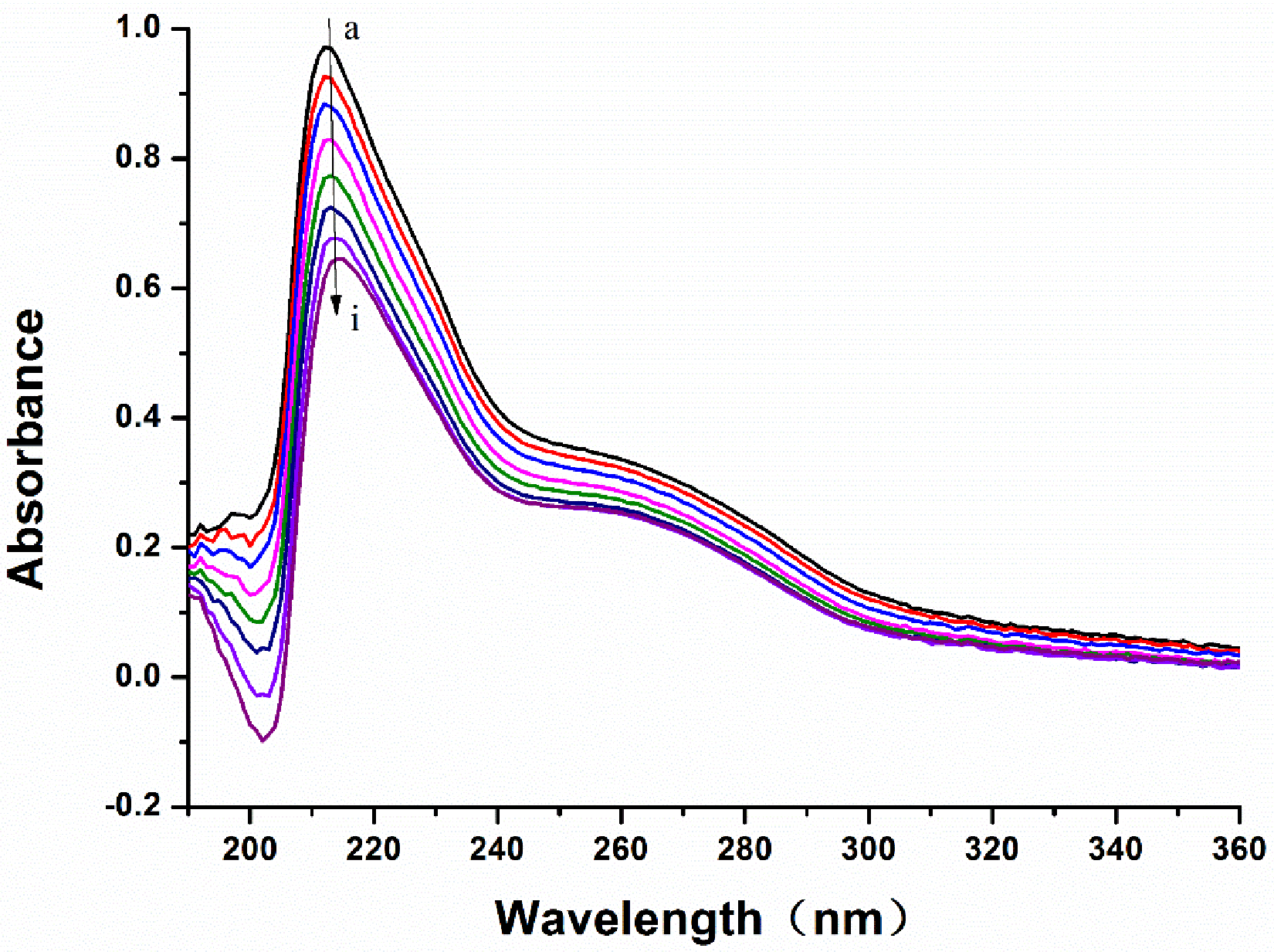
2.5. UV-Vis Absorption Spectra
2.6. Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry
3. Results
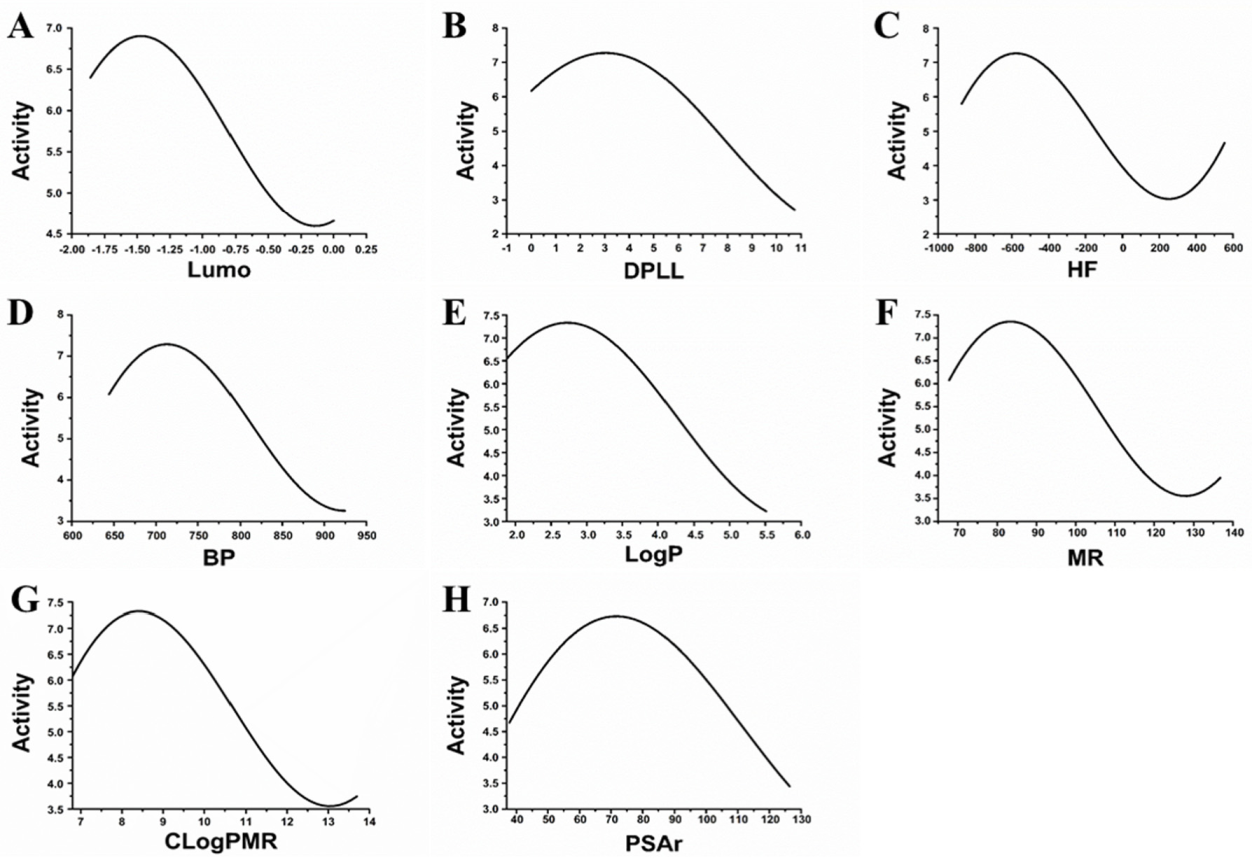
3.1. Feature Selection and Construction of MAO-B Inhibitor Prediction Model
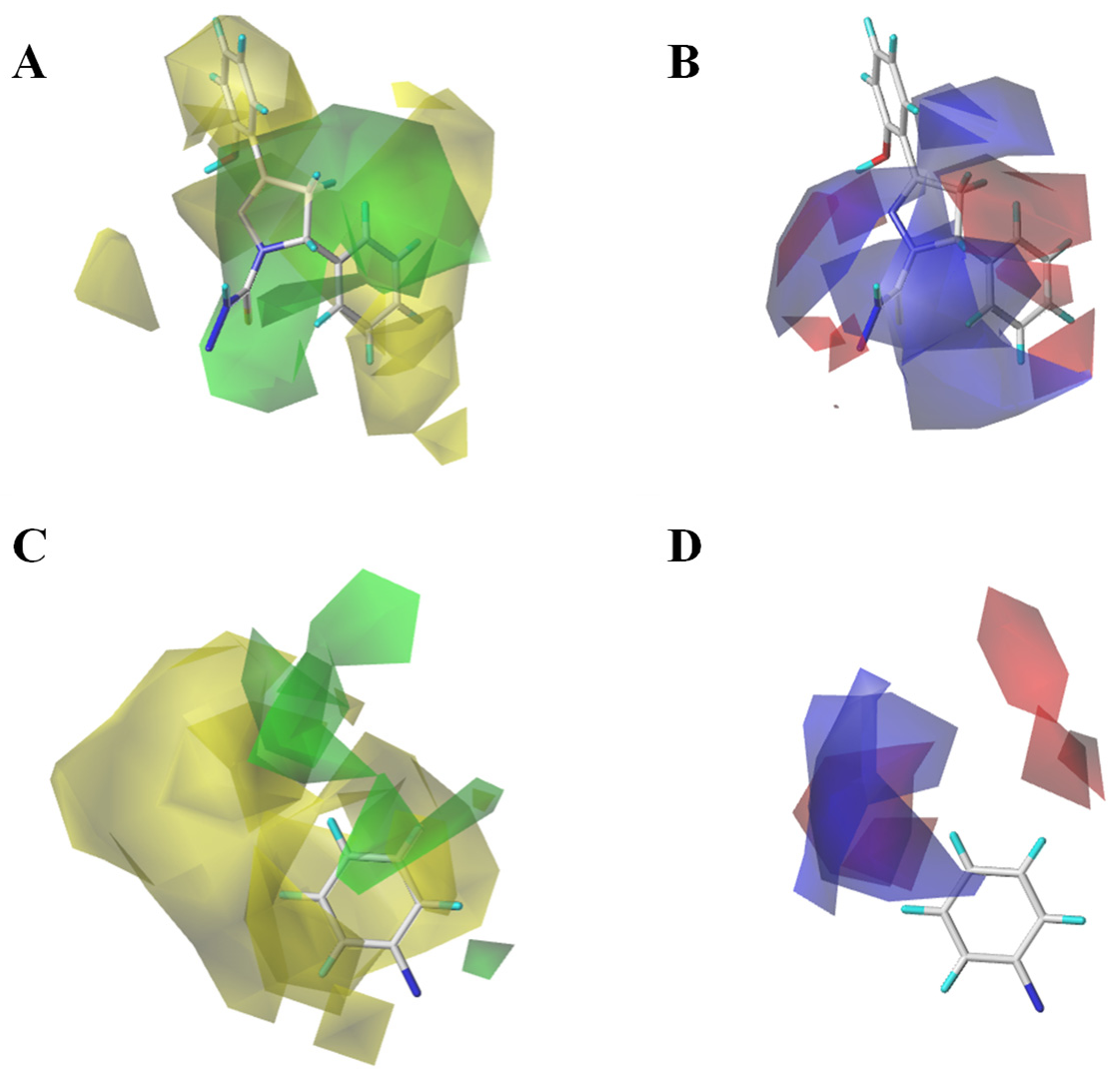
3.2. Topomer CoMFA Prediction Model
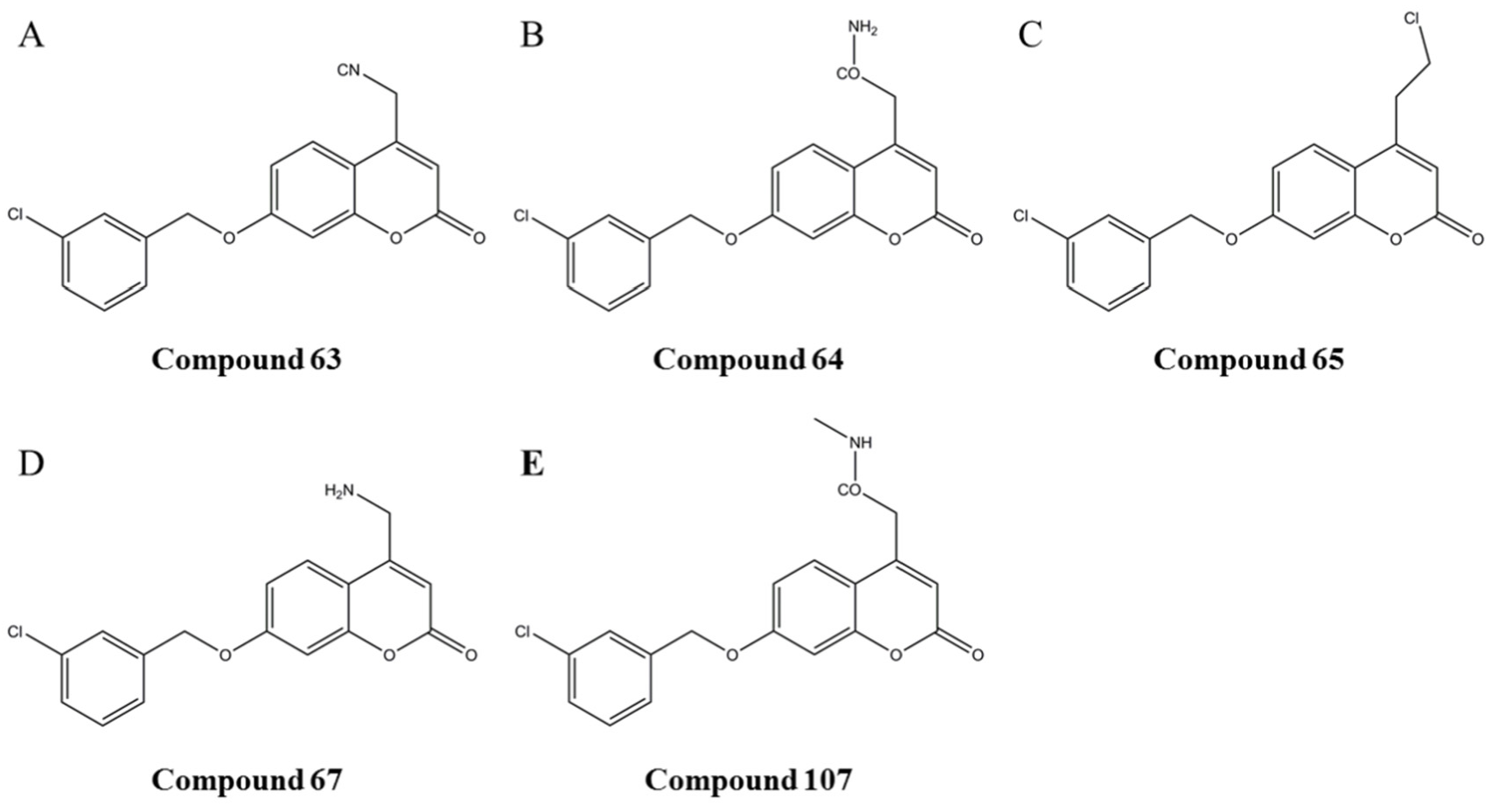
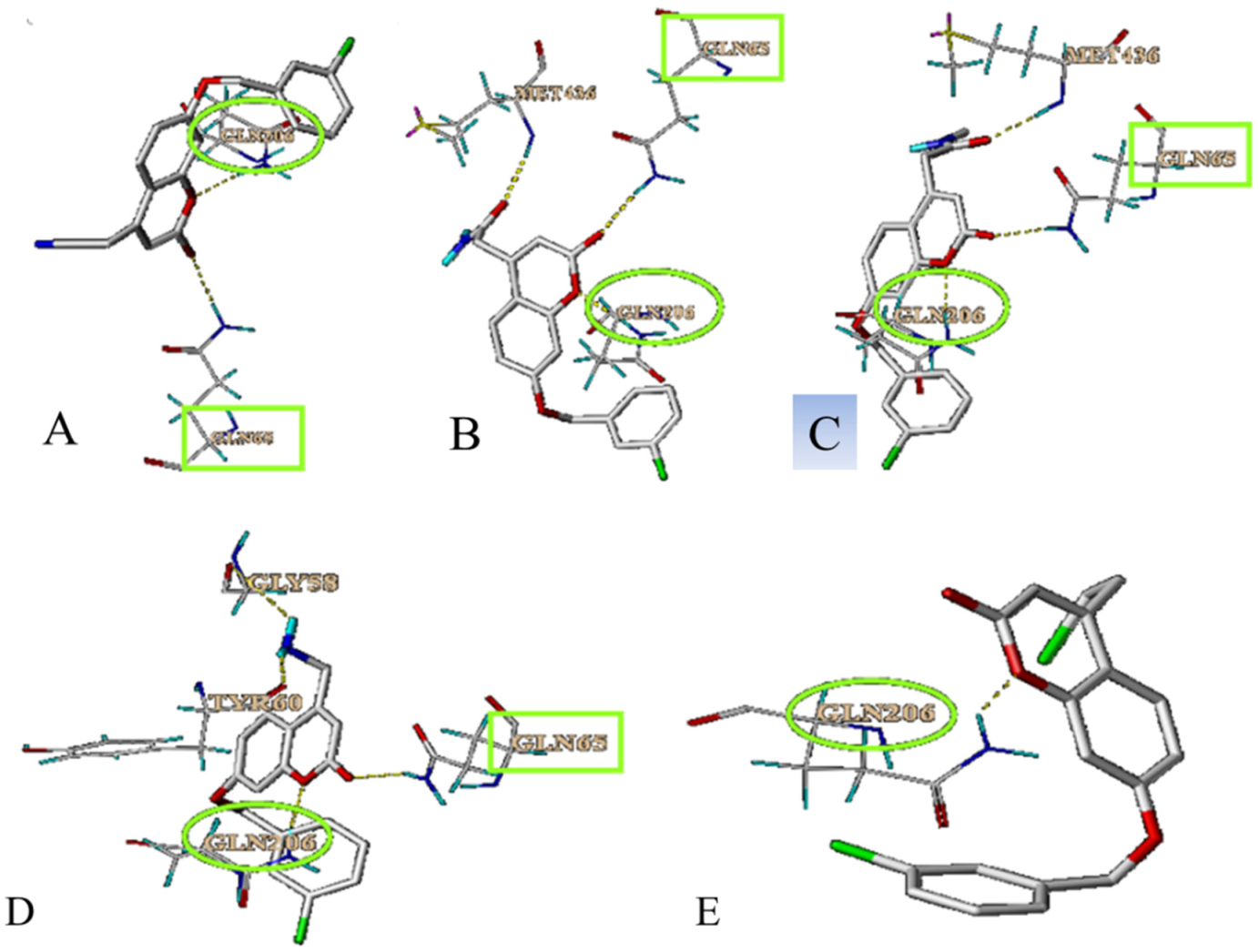
3.3. Simulation of the Interaction between Compounds and MAO-B
3.4. Prediction and Validation of the Interaction between Potential Compounds and MAO-B
3.4.1. Predicting and Activity Evaluation of LB
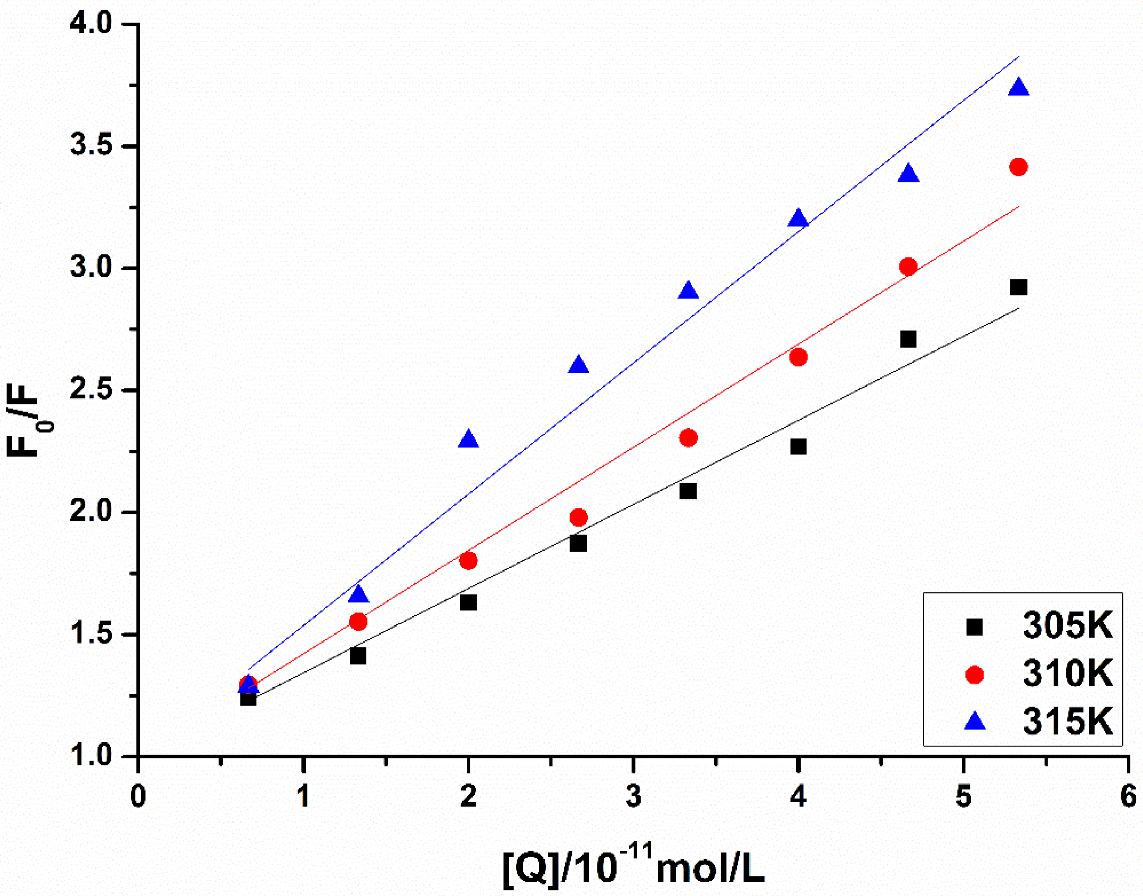
3.4.2. Fluorescence Quenching of MAO-B
3.5. Calculation of the Binding Constant and Binding Point
3.6. The UV-Vis Absorption Spectra of the LB and MAO-B System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, C.O.; Dougherty, J. What’s new in Alzheimer’s disease? Home Healthc Nurse 2003, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.E.; Hensley, K.; Butterfield, D.A.; Leedle, R.A.; Carney, J.M. Direct evidence of oxidative injury produced by the Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide (1-40) in cultured hippocampal neurons. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 131, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wärmländer, S.K.T.S.; Gräslund, A.; Abrahams, J.P. Cross-interactions between the Alzheimer Disease Amyloid-β Peptide and Other Amyloid Proteins: A Further Aspect of the Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16485–16493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fotiou, D.; Kaltsatou, A.; Tsiptsios, D.; Nakou, M. Evaluation of the cholinergic hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease with neuropsychological methods. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 27, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotr, L.; Hermann, E.; Mirko, B.; Georg, B.; Manuel, M.J.; Markus, O.; Johannes, K.; Jens, W. Tau Protein Phosphorylated at Threonine 181 in CSF as a Neurochemical Biomarker in Alzheimer’s Disease: Original Data and Review of the Literature. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 23, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, Y.; Darwish, M.; Hishikawa, N.; Yamashita, T.; Sato, K.; Takemoto, M.; Abe, K. Therapeutic effects of drug switching between acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greig, N.H.; Sambamurti, K.; Lahiri, D.K.; Becker, R.E. Amyloid-β precursor protein synthesis inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafii, M.S. Targeting tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 2842–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Manju, S.L.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Mathew, B. Identification of Indole-Based Chalcones: Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Reversible Class of MAO-B Inhibitors. Arch. Der Pharm. 2016, 349, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chadha, N.; Tiwari, A.K.; Sehgal, N.; Mishra, A.K. Prospective atom-based 3D-QSAR model prediction, pharmacophore generation, and molecular docking study of carbamate derivatives as dual inhibitors of AChE and MAO-B for Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, P.; Lachenmayer, L.; Laux, G. Clinical Applications of MAO-Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Schedin-Weiss, S.; Inoue, M.; Hromadkova, L.; Teranishi, Y.; Yamamoto, N.G.; Wiehager, B.; Bogdanovic, N.; Winblad, B.; Sandebring-Matton, A.; Frykman, S.; et al. Monoamine oxidase B is elevated in Alzheimer disease neurons, is associated with gamma-secretase and regulates neuronal amyloid beta-peptide levels. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Yarishkin, O.; Hwang, Y.J.; Chun, Y.E.; Park, M.; Woo, D.H.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Chun, H.; et al. GABA from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Su, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Synthesis and evaluation of selegiline derivatives as monoamine oxidase inhibitor, antioxidant and metal chelator against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3722–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, B.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Green, C.; Fine, E.; Schmeïdler, J. Selegiline in the treatment of behavioural disturbance in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1997, 12, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, O.; Mandel, S.; Bar-Am, O.; Yogev-Falach, M.; Avramovich-Tirosh, Y.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M.B.H. Multifunctional neuroprotective derivatives of rasagiline as anti-alzheimer’s disease drugs. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelhafez, O.M.; Amin, K.M.; Ali, H.I.; Abdalla, M.M.; Batran, R.Z. Monoamine oxidase A and B inhibiting effect and molecular modeling of some synthesized coumarin derivatives. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, V.; Sinha, B.N.; Ucar, G.; Ercan, A. Pyrazoline-based mycobactin analogues as MAO-inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6362–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Esteban, G.; Ojima, M.; Bautistaaguilera, O.M.; Inokuchi, T.; Moraleda, I.; Iriepa, I.; Samadi, A.; Youdim, M.B.; Romero, A. Donepezil + propargylamine + 8-hydroxyquinoline hybrids as new multifunctional metal-chelators, ChE and MAO inhibitors for the potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisani, L.; Farina, R.; Nicolotti, O.; Gadaleta, D.; Soto-Otero, R.; Catto, M.; Di, B.M.; Mendez-Alvarez, E.; Carotti, A. In silico design of novel 2H-chromen-2-one derivatives as potent and selective MAO-B inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, R.D. Topomer CoMFA: A design methodology for rapid lead optimization. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ding, H.; He, M.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Niu, B.; Zhong, X. Comparison of Early Changes in Ocular Surface and Inflammatory Mediators between Femtosecond Lenticule Extraction and Small-Incision Lenticule Extraction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong-jin, T.; Lin, Y.; Jia-huang, L.; Jun, C. Molecular modelling studies of 3,5-dipyridyl-1,2,4-triazole derivatives as xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitors using 3D-QSAR, Topomer CoMFA, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.D.; More, U.A.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Badiger, A.M. Two- and three-dimensional QSAR studies on a set of antimycobacterial pyrroles: CoMFA, Topomer CoMFA, and HQSAR. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 23, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilewar, S.S.; Kathiravan, M.K. 3D CoMFA, CoMSIA, topomer CoMFA and HQSAR studies on aromatic acid esters for carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity. J. Chemom. 2014, 28, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.N. Surflex: Fully Automatic Flexible Molecular Docking Using a Molecular Similarity-Based Search Engine. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Newton-Vinson, P.; Hubálek, F.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structure of human monoamine oxidase B, a drug target for the treatment of neurological disorders. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J. Software Review:ChemOffice 2005 Pro by CambridgeSoft. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2005, 45, 1468–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Terán, C.; Pérez-Castillo, Y.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Via, D. Synthesis and Study of a Series of 3-Arylcoumarins as Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7127–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, P.; Dubeau, S.; Maharvi, G.M.; Fauq, A.H.; Thomas, T.J.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Binding of antitumor tamoxifen and its metabolites 4-hydroxytamoxifen and endoxifen to human serum albumin. Biochimie, 2011; 93, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, F.; Bordbar, A.-K.; Divsalar, A.; Mohammadi, K.; Saboury, A.A. Interaction of Curcumin and Diacetylcurcumin with the Lipocalin Member β-Lactoglobulin. Protein J. 2009, 28, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Masters, B.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Third Edition. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 029901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-X.; Xu, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-D. Interaction between hesperetin and human serum albumin revealed by spectroscopic methods. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2005, 1724, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Song, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Molecular spectroscopic study on the interaction of tetracyclines with serum albumins. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandagal, P.B.; Ashoka, S.; Seetharamappa, J.; Shaikh, S.M.T.; Jadegoud, Y.; Ijare, O.B. Study of the interaction of an anticancer drug with human and bovine serum albumin: Spectroscopic approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Binda, C.; Mattevi, A. Structural insights into the mechanism of amine oxidation by monoamine oxidases A and B. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 464, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidari, A.; Fatemi, M. CoMFA, topomer CoMFA and HQSAR studies on a series of novel HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Albijanic, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, X. Using 3D-QSAR to predict the separation efficiencies of flotation collectors: Implications for rational design of non-polar side chains. Miner. Eng. 2018, 129, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristam, R.; Rao, S.N.; D’Cruz, A.S.; Mahadevan, V.; Viswanadhan, V.N. TRPV1 antagonism by piperazinyl-aryl compounds: A Topomer-CoMFA study and its use in virtual screening for identification of novel antagonists. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2017, 72, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Methods | 10-Fold Cross-Validation Test | Independent Set Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SN (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | SN (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | |
| Naïve Bayes | 90.5 | 67.3 | 81.7 | 96.3 | 53.6 | 67.5 |
| SVM | 95.2 | 66.0 | 83.9 | 100 | 53.6 | 68.7 |
| KNN | 94.8 | 93.1 | 94.1 | 100 | 82.1 | 88.0 |
| C4.5 | 96.0 | 87.4 | 92.7 | 100 | 82.1 | 88.0 |
| Random Forest | 96.4 | 87.4 | 92.9 | 96.3 | 76.8 | 83.1 |
| Random Tree | 92.0 | 89.9 | 91.2 | 96.3 | 76.8 | 83.1 |
| AdaBoost | 97.2 | 89.3 | 94.1 | 96.3 | 75.0 | 81.9 |
| Bagging | 98.0 | 81.8 | 91.7 | 96.3 | 75.0 | 81.9 |
| Dataset | Topomer CoMFA Model 1 | Topomer CoMFA Model 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting model | 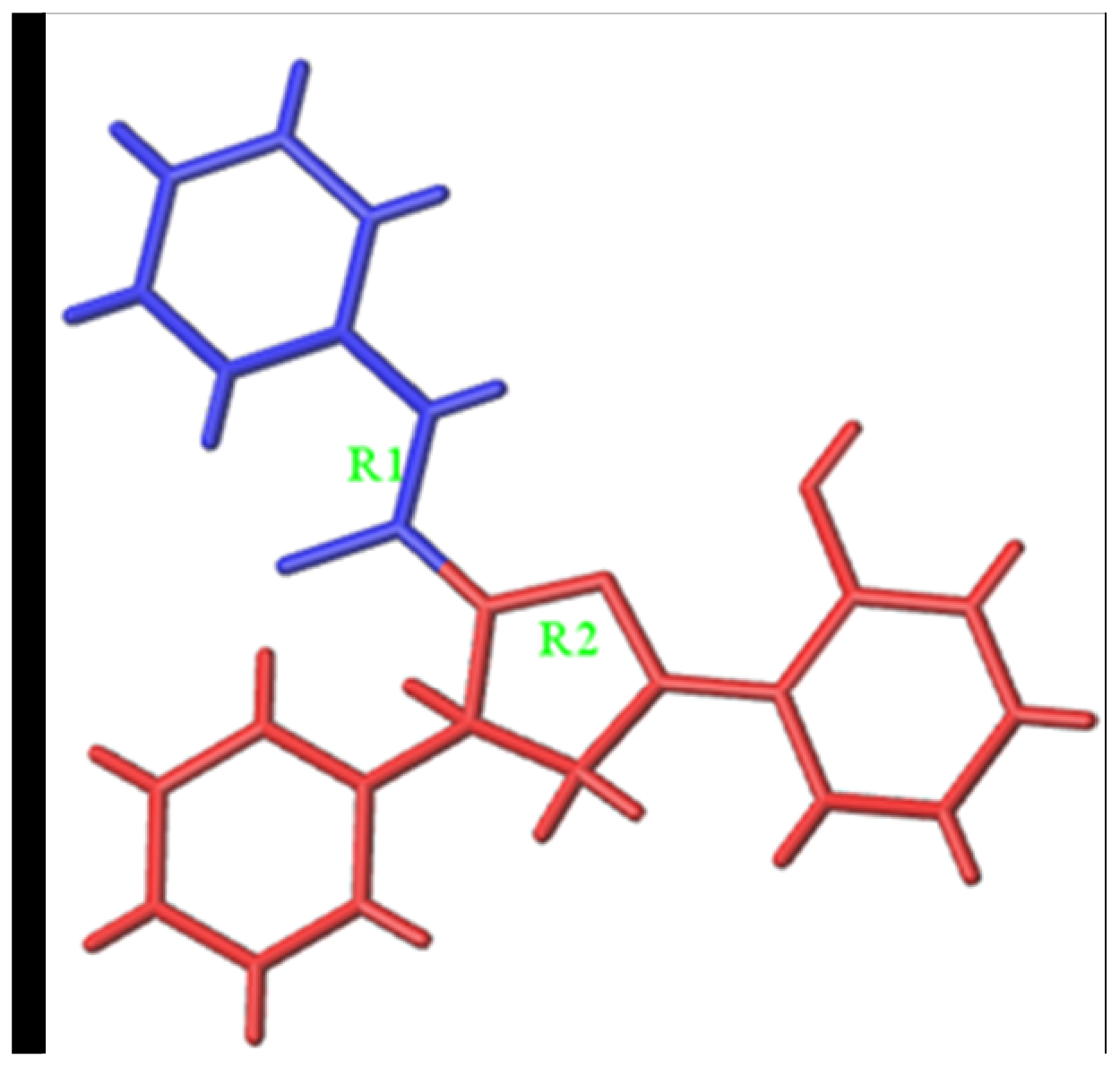 | 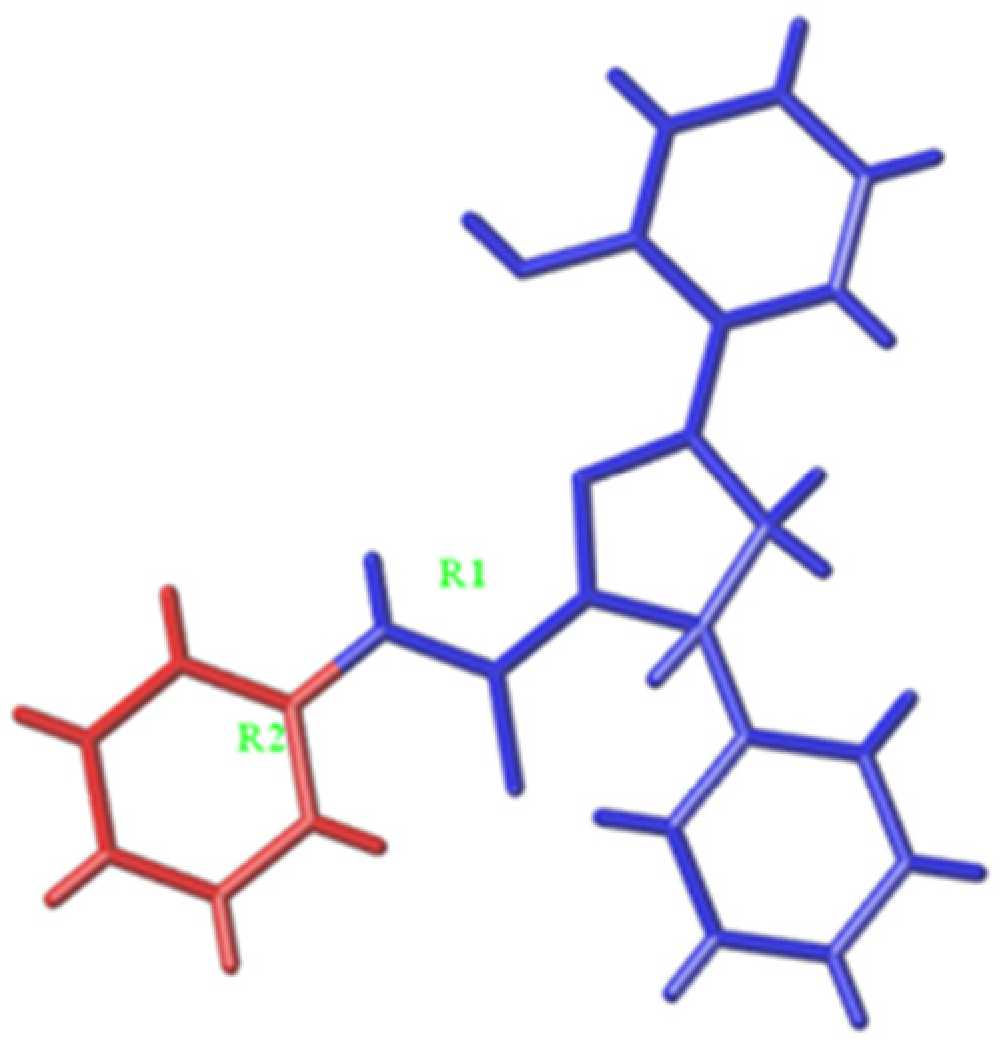 |
| q2 | 0.579 | 0.612 |
| r2 | 0.752 | 0.824 |
| r2test set | 0.856 | 0.809 |
| Compound | Exp | Pre | Compound | Exp | Pre |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | |||||
| 1 | 3.32 | 3.76 | 132 | 6.64 | 7.48 |
| 2 | 3.33 | 3.50 | 133 | 6.64 | 6.55 |
| 3 | 3.35 | 3.69 | 134 | 6.62 | 7.24 |
| 5 | 3.30 | 3.27 | 135 | 6.59 | 6.33 |
| 6 | 3.37 | 3.73 | 136 | 6.57 | 6.35 |
| 7 | 3.31 | 3.15 | 137 | 6.54 | 6.47 |
| 10 | 3.31 | 3.71 | 138 | 6.52 | 6.91 |
| 12 | 4.11 | 4.09 | 139 | 6.52 | 6.83 |
| 13 | 4.05 | 3.97 | 140 | 6.49 | 6.43 |
| 15 | 4.15 | 3.94 | 141 | 6.47 | 6.54 |
| 16 | 4.11 | 3.69 | 142 | 6.46 | 6.40 |
| 17 | 4.09 | 3.44 | 143 | 6.42 | 5.84 |
| 19 | 3.32 | 3.86 | 144 | 6.40 | 6.68 |
| 20 | 3.31 | 3.35 | 145 | 6.39 | 6.32 |
| 21 | 3.30 | 3.06 | 146 | 6.35 | 6.99 |
| 23 | 3.32 | 3.08 | 147 | 6.10 | 6.82 |
| 24 | 3.32 | 3.75 | 148 | 6.10 | 6.28 |
| 25 | 3.70 | 3.73 | 149 | 6.07 | 6.10 |
| 27 | 3.54 | 3.64 | 150 | 6.05 | 7.23 |
| 28 | 3.65 | 3.54 | 151 | 6.02 | 5.02 |
| 29 | 3.70 | 3.52 | 152 | 5.96 | 6.09 |
| 31 | 3.65 | 3.64 | 153 | 5.90 | 6.35 |
| 32 | 3.61 | 3.31 | 154 | 5.89 | 6.46 |
| 33 | 4.40 | 4.43 | 155 | 5.72 | 5.11 |
| 35 | 4.91 | 4.64 | 156 | 5.70 | 5.65 |
| 36 | 4.30 | 4.37 | 157 | 5.66 | 6.10 |
| 37 | 4.99 | 4.80 | 158 | 5.59 | 5.82 |
| 39 | 4.82 | 4.43 | 159 | 5.58 | 5.56 |
| 40 | 5.82 | 5.33 | 160 | 5.52 | 7.48 |
| 41 | 7.77 | 6.74 | 161 | 5.50 | 6.05 |
| 43 | 7.54 | 7.65 | 162 | 5.40 | 4.25 |
| 44 | 6.06 | 5.62 | 163 | 5.33 | 5.71 |
| 45 | 7.68 | 6.78 | 164 | 5.17 | 5.00 |
| 47 | 6.68 | 7.78 | 165 | 5.16 | 5.00 |
| 48 | 5.04 | 5.83 | 166 | 5.15 | 5.16 |
| 49 | 5.68 | 6.09 | 167 | 5.14 | 4.97 |
| 51 | 6.31 | 6.34 | 168 | 5.10 | 6.05 |
| 52 | 7.32 | 6.88 | 169 | 5.05 | 6.42 |
| 53 | 7.28 | 7.60 | 170 | 5.04 | 5.01 |
| 55 | 4.00 | 5.71 | 171 | 5.02 | 4.91 |
| 56 | 6.38 | 5.38 | 172 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 57 | 6.63 | 6.16 | 173 | 5.00 | 4.68 |
| 59 | 6.66 | 7.27 | 174 | 5.00 | 4.83 |
| 60 | 8.28 | 7.79 | 175 | 4.96 | 4.90 |
| 61 | 7.85 | 7.83 | 176 | 4.92 | 4.31 |
| 63 | 7.80 | 7.03 | 177 | 4.88 | 4.98 |
| 64 | 7.52 | 7.17 | 178 | 4.88 | 4.60 |
| 65 | 7.62 | 7.74 | 179 | 4.82 | 4.43 |
| 67 | 7.82 | 7.68 | 180 | 4.82 | 4.43 |
| 68 | 7.89 | 7.25 | 181 | 4.82 | 4.43 |
| 69 | 7.96 | 7.30 | 182 | 4.79 | 4.44 |
| 71 | 6.35 | 6.70 | 183 | 4.76 | 4.43 |
| 72 | 5.95 | 6.59 | 184 | 4.75 | 4.99 |
| 75 | 7.00 | 6.86 | 185 | 4.72 | 5.04 |
| 77 | 8.11 | 7.32 | 186 | 4.64 | 6.19 |
| 78 | 8.24 | 7.36 | 187 | 4.42 | 4.65 |
| 79 | 6.12 | 6.48 | 188 | 4.35 | 4.39 |
| 81 | 6.94 | 6.95 | 189 | 4.33 | 4.51 |
| 82 | 6.90 | 6.99 | 190 | 4.32 | 4.25 |
| 83 | 6.24 | 6.34 | 191 | 4.30 | 4.42 |
| 85 | 7.21 | 6.81 | 192 | 4.25 | 4.57 |
| 86 | 7.13 | 6.85 | 193 | 4.25 | 4.86 |
| 87 | 4.61 | 6.32 | 194 | 4.13 | 4.35 |
| 89 | 6.50 | 6.89 | 195 | 4.13 | 3.34 |
| 90 | 7.34 | 7.65 | 196 | 4.07 | 4.15 |
| 91 | 5.39 | 5.47 | 197 | 4.07 | 3.67 |
| 93 | 7.55 | 7.26 | 198 | 4.05 | 5.05 |
| 94 | 5.11 | 6.57 | 199 | 3.92 | 3.86 |
| 95 | 5.01 | 4.77 | 200 | 3.82 | 3.99 |
| 97 | 6.23 | 5.70 | 201 | 3.82 | 3.70 |
| 98 | 4.50 | 5.83 | 202 | 3.52 | 6.03 |
| 99 | 7.57 | 7.55 | 203 | 3.30 | 5.14 |
| 101 | 5.74 | 6.68 | 204 | 3.24 | 2.99 |
| 102 | 8.48 | 7.78 | 205 | 2.08 | 3.13 |
| 103 | 8.05 | 7.82 | 206 | 1.81 | 4.43 |
| 105 | 6.30 | 6.45 | 207 | 8.37 | 7.48 |
| 106 | 8.13 | 7.55 | 208 | 8.36 | 7.48 |
| 107 | 7.89 | 7.75 | 209 | 8.36 | 7.48 |
| 109 | 5.92 | 7.51 | 210 | 8.36 | 7.48 |
| 110 | 7.82 | 7.92 | 211 | 8.00 | 7.48 |
| 111 | 7.54 | 8.08 | 212 | 7.82 | 7.67 |
| 113 | 6.40 | 5.74 | 213 | 7.82 | 7.27 |
| 114 | 7.37 | 6.81 | 214 | 7.77 | 7.24 |
| 115 | 7.30 | 7.12 | 215 | 7.74 | 7.00 |
| 116 | 7.15 | 7.35 | 216 | 7.70 | 6.19 |
| 117 | 7.11 | 6.11 | 217 | 7.66 | 6.35 |
| 118 | 7.05 | 7.42 | 218 | 7.62 | 7.74 |
| 119 | 7.01 | 6.99 | 219 | 7.62 | 7.74 |
| 120 | 7.01 | 6.99 | 220 | 7.62 | 7.74 |
| 121 | 7.00 | 6.99 | 221 | 7.59 | 6.99 |
| 122 | 7.00 | 6.82 | 222 | 7.52 | 6.63 |
| 123 | 7.00 | 6.62 | 223 | 7.52 | 7.17 |
| 124 | 6.96 | 6.81 | 224 | 7.52 | 7.37 |
| 125 | 6.92 | 5.14 | 225 | 7.52 | 7.17 |
| 126 | 6.85 | 6.98 | 226 | 7.52 | 7.17 |
| 127 | 6.74 | 6.86 | 227 | 7.48 | 6.82 |
| 128 | 6.70 | 6.70 | 228 | 7.40 | 6.96 |
| 129 | 6.70 | 7.09 | 229 | 7.40 | 7.14 |
| 130 | 6.64 | 6.03 | 230 | 7.40 | 7.14 |
| 131 | 6.64 | 6.56 | 231 | 7.40 | 7.14 |
| Test set | |||||
| 4 | 3.32 | 3.52 | 62 | 7.11 | 6.74 |
| 9 | 3.35 | 3.82 | 66 | 7.40 | 7.14 |
| 14 | 4.12 | 4.19 | 70 | 6.69 | 6.80 |
| 18 | 3.34 | 3.19 | 76 | 7.44 | 7.11 |
| 22 | 3.31 | 3.74 | 80 | 6.58 | 6.74 |
| 26 | 3.66 | 3.97 | 84 | 6.39 | 6.60 |
| 30 | 3.68 | 3.40 | 88 | 7.00 | 7.03 |
| 34 | 4.71 | 4.22 | 92 | 8.06 | 7.60 |
| 38 | 4.46 | 4.59 | 96 | 7.41 | 5.77 |
| 42 | 8.13 | 7.38 | 100 | 4.50 | 7.28 |
| 46 | 7.36 | 7.74 | 104 | 7.47 | 7.37 |
| 50 | 6.32 | 6.29 | 108 | 7.49 | 7.73 |
| 54 | 7.40 | 6.33 | 112 | 7.31 | 7.85 |
| 58 | 6.99 | 6.05 | |||
| [Q] (×10−11 mol/L) | 305 K | 310 K | 315 K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | F0/F | F | F0/F | F | F0/F | |
| 0.00 | 2836 | / | 2636 | / | 2344 | / |
| 0.67 | 2282 | 1.24 | 2034 | 1.30 | 1819 | 1.29 |
| 1.33 | 2006 | 1.41 | 1697 | 1.55 | 1414 | 1.66 |
| 2.00 | 1739 | 1.63 | 1462 | 1.80 | 1136 | 2.29 |
| 2.67 | 1514 | 1.87 | 1332 | 1.98 | 1003 | 2.60 |
| 3.33 | 1360 | 2.09 | 1143 | 2.31 | 897.8 | 2.90 |
| 4.00 | 1249 | 2.27 | 999.8 | 2.64 | 814.3 | 3.20 |
| 4.67 | 1047 | 2.71 | 876.6 | 3.01 | 770.2 | 3.38 |
| 5.33 | 970.4 | 2.92 | 771.7 | 3.42 | 697.4 | 3.74 |
| T(K) | Ksv (×102 L/mol) | Kq (×1010 L/mol s−1) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| 305 | 2.79 | 2.79 | 0.874 |
| 310 | 3.38 | 3.38 | 0.902 |
| 315 | 4.55 | 4.55 | 0.932 |
| T(K) | Ka (×1010 L/mol) | n | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| 305 | 2.8834 | 1.0080 | 0.995 |
| 310 | 2.3267 | 0.9930 | 0.995 |
| 315 | 2.1500 | 1.0767 | 0.989 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Qin, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; An, Q.; Xu, J.; Qu, X.; Cao, X.; Niu, B. Discovery of MAO-B Inhibitor with Machine Learning, Topomer CoMFA, Molecular Docking and Multi-Spectroscopy Approaches. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101470
Zheng L, Qin X, Wang J, Zhang M, An Q, Xu J, Qu X, Cao X, Niu B. Discovery of MAO-B Inhibitor with Machine Learning, Topomer CoMFA, Molecular Docking and Multi-Spectroscopy Approaches. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(10):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101470
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Linfeng, Xiangyang Qin, Jiao Wang, Mengying Zhang, Quanlin An, Jinzhi Xu, Xiaosheng Qu, Xin Cao, and Bing Niu. 2022. "Discovery of MAO-B Inhibitor with Machine Learning, Topomer CoMFA, Molecular Docking and Multi-Spectroscopy Approaches" Biomolecules 12, no. 10: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101470
APA StyleZheng, L., Qin, X., Wang, J., Zhang, M., An, Q., Xu, J., Qu, X., Cao, X., & Niu, B. (2022). Discovery of MAO-B Inhibitor with Machine Learning, Topomer CoMFA, Molecular Docking and Multi-Spectroscopy Approaches. Biomolecules, 12(10), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101470








