Blood Transcript Biomarkers Selected by Machine Learning Algorithm Classify Neurodegenerative Diseases including Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Aquisition
2.2. Dataset Normalization
2.3. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
2.4. Random Forest Classification (RF)
3. Results
3.1. Literature-Based Transcript Selection for Stress Response Classifies Disease
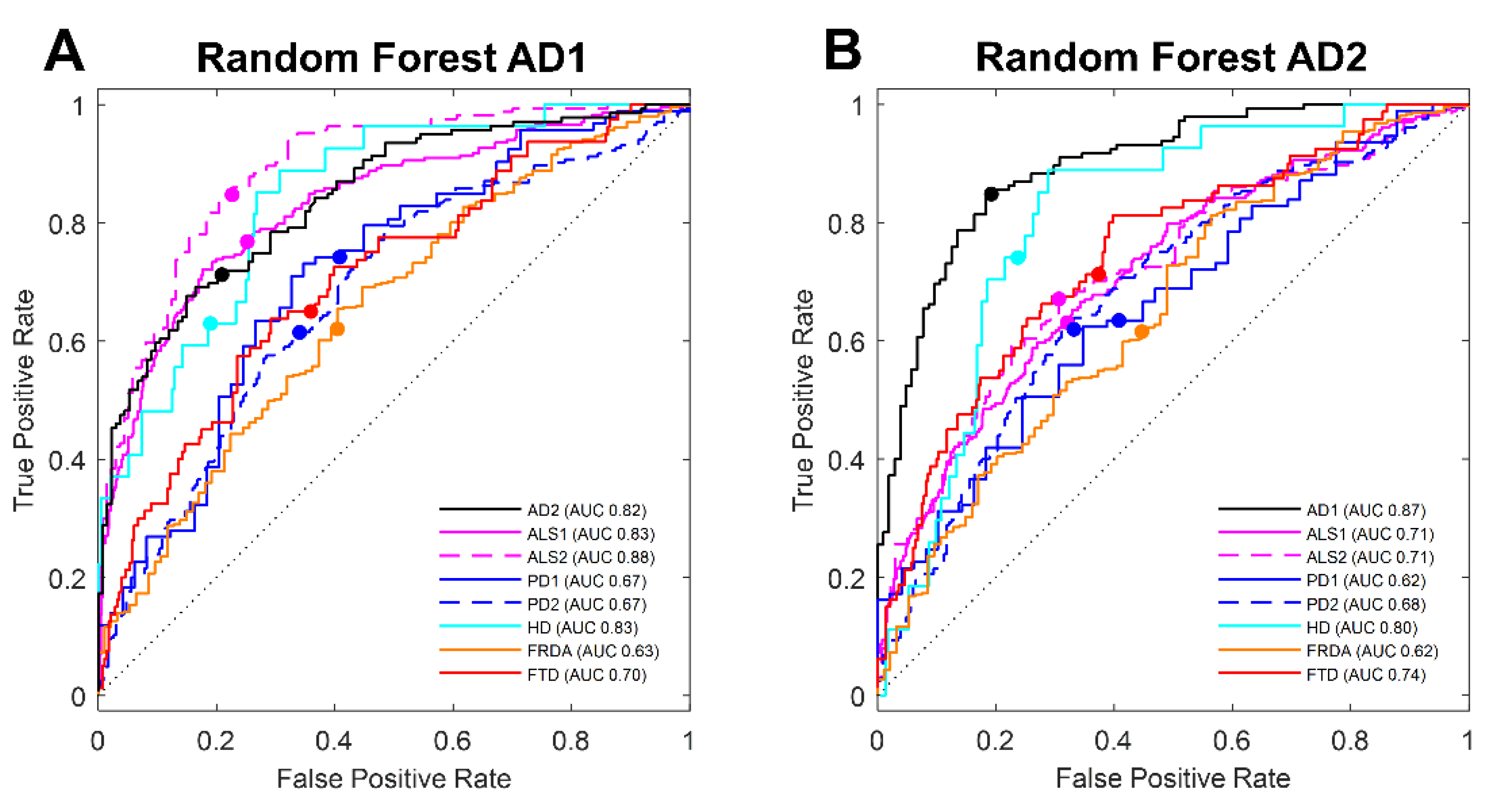
3.2. Machine Learning Selection of Transcripts in Blood Classifies AD
3.3. Machine Learning Selection of Blood Transcript Classifiers for other Neurodegenerative Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patent Applications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beach, T.G.; Monsell, S.E.; Phillips, L.E.; Kukull, W. Accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer disease at National Institute on Aging Alzheimer Disease Centers, 2005-2010. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Wilde, A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Pelkmans, W.; Bouwman, F.; Verwer, J.; Groot, C.; van Buchem, M.M.; Zwan, M.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Yaqub, M.; et al. Association of Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography With Changes in Diagnosis and Patient Treatment in an Unselected Memory Clinic Cohort: The ABIDE Project. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikari, T.K.; Emeršič, A.; Vrillon, A.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Ashton, N.J.; Kramberger, M.G.; Dumurgier, J.; Hourregue, C.; Čučnik, S.; Brinkmalm, G.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of clinical performance of CSF phospho-tau T181 and T217 biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 17, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikari, T.K.; Pascoal, T.A.; Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Benedet, A.L.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Chamoun, M.; Savard, M.; Kang, M.S.; Therriault, J.; et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: A diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (CMS), C.f.M.M.S. Decision Memo for Beta Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography in Dementia and Neurodegenerative Disease (CAG-00431N). Available online: https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=N&NCAId=265 (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Huang, Y.; Mucke, L. Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 2012, 148, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehman, C.D.; Arao, R.F.; Sprague, B.L.; Lee, J.M.; Buist, D.S.M.; Kerlikowske, K.; Henderson, L.M.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; Rauscher, G.H.; et al. National Performance Benchmarks for Modern Screening Digital Mammography: Update from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. Radiology 2017, 283, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, L.C.; Pignone, M.P. Screening accuracy for late-life depression in primary care: A systematic review. J. Fam. Pract. 2003, 52, 956–964. [Google Scholar]
- Elsafi, S.H.; Alqahtani, N.I.; Zakary, N.Y.; Al Zahrani, E.M. The sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, and likelihood ratios of fecal occult blood test for the detection of colorectal cancer in hospital settings. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhavadharini, B.; Mahalakshmi, M.M.; Maheswari, K.; Kalaiyarasi, G.; Anjana, R.M.; Deepa, M.; Ranjani, H.; Priya, M.; Kumar, M.; Usha, S.; et al. Use of capillary blood glucose for screening for gestational diabetes mellitus in resource-constrained settings. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Bryant, S.E.; Edwards, M.; Johnson, L.; Hall, J.; Villarreal, A.E.; Britton, G.B.; Quiceno, M.; Cullum, C.M.; Graff-Radford, N.R. A blood screening test for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 3, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O′Bryant, S.E.; Lista, S.; Rissman, R.A.; Edwards, M.; Zhang, F.; Hall, J.; Zetterberg, H.; Lovestone, S.; Gupta, V.; Graff-Radford, N.; et al. Comparing biological markers of Alzheimer’s disease across blood fraction and platforms: Comparing apples to oranges. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 3, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyse, M.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Andre, F.; Jiang, Z.; Burris, H.A.; Toi, M.; Eiermann, W.; Lindsay, M.-A.; Slamon, D. Statistical controversies in clinical research: Statistical significance-too much of a good thing. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyse, M.; Molenberghs, G.; Paoletti, X.; Oba, K.; Alonso, A.; Van Der Elst, W.; Burzykowski, T. Statistical evaluation of surrogate endpoints with examples from cancer clinical trials. Biom. J. 2016, 58, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvaux, E.; Mastroeni, D.; Nolz, J.; Chow, N.; Sabbagh, M.; Caselli, R.J.; Reiman, E.M.; Marshall, F.J.; Coleman, P.D. Multivariate analyses of peripheral blood leukocyte transcripts distinguish Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, control, and those at risk for developing Alzheimer’s. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 58, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, M.; Najafi, A.; Shakeri, M.T. Classification and Biomarker Genes Selection for Cancer Gene Expression Data Using Random Forest. Iran. J. Pathol. 2017, 12, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Wei, J.S.; Ringnér, M.; Saal, L.H.; Ladanyi, M.; Westermann, F.; Berthold, F.; Schwab, M.; Antonescu, C.R.; Peterson, C.; et al. Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyle, N.; Keohane, A.; Newhouse, S.; Lunnon, K.; Johnston, C.; Soininen, H.; Kloszewska, I.; Mecocci, P.; Tsolaki, M.; Vellas, B.; et al. A Pathway Based Classification Method for Analyzing Gene Expression for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 49, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Rheenen, W.; Diekstra, F.P.; Harschnitz, O.; Westeneng, H.J.; van Eijk, K.R.; Saris, C.G.; Groen, E.J.; Van Es, M.A.; Blauw, H.M.; Van Vught, P.W.; et al. Whole blood transcriptome analysis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A biomarker study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sood, S.; Gallagher, I.J.; Lunnon, K.; Rullman, E.; Keohane, A.; Crossland, H.; Phillips, B.E.; Cederholm, T.; Jensen, T.; van Loon, L.J.; et al. A novel multi-tissue RNA diagnostic of healthy ageing relates to cognitive health status. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachun, D.; Gao, F.; Isaacs, C.; Strawser, C.; Yang, Z.; Dokuru, D.; Van Berlo, V.; Sears, R.; Farmer, J.; Perlman, S.; et al. Peripheral blood gene expression reveals an inflammatory transcriptomic signature in Friedreich’s ataxia patients. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2965–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locascio, J.J.; Eberly, S.; Liao, Z.; Liu, G.; Hoesing, A.N.; Duong, K.; Trisini-Lipsanopoulos, A.; Dhima, K.; Hung, A.Y.; Flaherty, A.W.; et al. Association between alpha-synuclein blood transcripts and early, neuroimaging-supported Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2015, 138 Pt 9, 2659–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Kruse, C.P.S.; List, E.O.; Berryman, D.E.; Kopchick, J.J. ALS blood expression profiling identifies new biomarkers, patient subgroups, and evidence for neutrophilia and hypoxia. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamir, R.; Klein, C.; Amar, D.; Vollstedt, E.-J.; Bonin, M.; Usenovic, M.; Wong, Y.C.; Maver, A.; Poths, S.; Safer, H.; et al. Analysis of blood-based gene expression in idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology 2017, 89, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunnon, K.; Ibrahim, Z.; Proitsi, P.; Lourdusamy, A.; Newhouse, S.; Sattlecker, M.; Furney, S.; Saleem, M.; Soininen, H.; Kłoszewska, I.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and immune activation are detectable in early Alzheimer’s disease blood. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 30, 685–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, J.-I.; Nachun, D.; Petrosyan, L.; Throesch, B.; Campau, E.; Gao, F.; Baldwin, K.K.; Coppola, G.; Gottesfeld, J.M.; Soragni, E. Transcriptional profiling of isogenic Friedreich ataxia neurons and effect of an HDAC inhibitor on disease signatures. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, P.; Kibbe, W.A.; Lin, S.M. nuID: A universal naming scheme of oligonucleotides for illumina, affymetrix, and other microarrays. Biol. Direct 2007, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Ishibashi, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Sugitani, M.; Takayama, T.; Esumi, M. beta-Glucuronidase is a suitable internal control gene for mRNA quantitation in pathophysiological and non-pathological livers. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 95, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, M.; Ciccarone, F.; Guastafierro, T.; Bacalini, M.; Calabrese, R.; Moreno-Villanueva, M.; Reale, A.; Chevanne, M.; Bürkle, A.; Caiafa, P. Validation of suitable internal control genes for expression studies in aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2010, 131, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, J.D.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, G. Probe mapping across multiple microarray platforms. Brief Bioinform. 2012, 13, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawar, S.; Mouazen, A.M. Comparison between Random Forests, Artificial Neural Networks and Gradient Boosted Machines Methods of On-Line Vis-NIR Spectroscopy Measurements of Soil Total Nitrogen and Total Carbon. Sensors 2017, 17, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Classification and regression trees. In The Wadsworth Statistics/Probability Series; Wadsworth International Group: Belmont, CA, USA, 1984; p. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, A.; Stevens, J.R. Random forests for microarrays. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 411, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.J.; Zhu, M.; Pyun, E.I.; Brooks, A.I.; Therianos, S.; Meyers, V.E.; Coleman, P.D. Defects in expression of genes related to synaptic vesicle trafficking in frontal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2003, 12, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lunnon, K.; Sattlecker, M.; Furney, S.J.; Coppola, G.; Simmons, A.; Proitsi, P.; Lupton, M.K.; Lourdusamy, A.; Johnston, C.; Soininen, H.; et al. A blood gene expression marker of early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 33, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummings, J. Drug Development for Psychotropic, Cognitive-Enhancing, and Disease-Modifying Treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 33, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabers, A.; Perna, L.; Lange, J.; Mons, U.; Schartner, J.; Güldenhaupt, J.; Saum, K.U.; Janelidze, S.; Holleczek, B.; Rujescu, D.; et al. Amyloid blood biomarker detects Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, L.; Witteveen, A.; Beumer, I.; Delahaye, L.; Wehkamp, D.; Akker, J.V.D.; Snel, M.; Chan, B.; Floore, A.; Bakx, N.; et al. Controlling technical variation amongst 6693 patient microarrays of the randomized MINDACT trial. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Uriarte, R.; Alvarez de Andres, S. Gene selection and classification of microarray data using random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donohue, D.E.; Gautam, A.; Miller, S.-A.; Srinivasan, S.; Abu-Amara, D.; Campbell, R.; Marmar, C.R.; Hammamieh, R.; Jett, M. Gene expression profiling of whole blood: A comparative assessment of RNA-stabilizing collection methods. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.S.; Shaw, L.M.; Vemuri, P.; Wiste, H.J.; Weigand, S.D.; et al. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: An updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

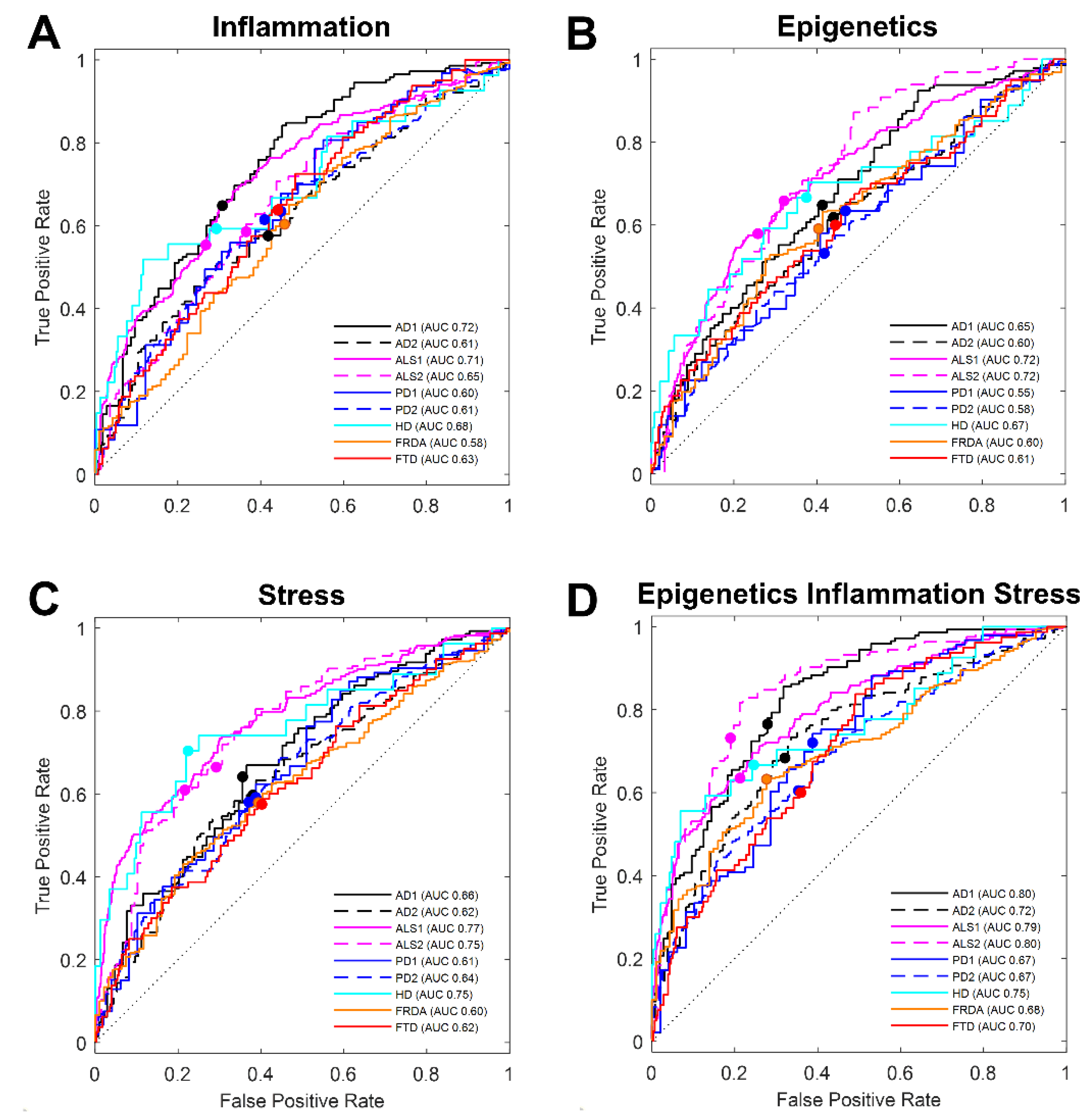
| Inflammation | Epigenetics | Stress |
|---|---|---|
| C5 | DNMT1 | CRYAB |
| IL10RA | DNMT3A | FTH1 |
| IL17RA | HDAC1 | FTL |
| IL8 | HDAC6 | GAPDH |
| LIF | MBD2 | HSP90AB1 |
| SERPING1 | SIRT1 | HSPB1 |
| TNF | PTGS1 | |
| PTGS2 | ||
| TFRC |
| GSE63060 AD1 | GSE63061 AD2 | GSE57475 PD1 | GSE99039 PD2 | GSE99039 HD | GSE112676 ALS1 | GSE112680 ALS2 | GSE140830 bvFTD | GSE102008 FRDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFDP1 | RPS25 | ELOVL4 | MRPS15 | FNDC1 | ATP5I | ACAA1 | PET100 | ABCA1 |
| ATP5I | UFC1 | CECR1 | CIRBP | SOCS6 | ABCA1 | ARHGAP30 | KLF6 | HLA-DRB1 |
| CMTM2 | HLA-A/ HLA-A29 allele | PITHD1/ C1orf128 | HELZ2/ PRIC285 | ANXA2 | QPCT | IKBIP/IKIP | SNURF | FKBP1A |
| DDIT4 | HFE/HLA-H | LDLR | MRVI1 | FYN | CNPY3 | AIF1 | UPK3BL | SULT1A1 |
| RPL36AL | CD72 | CENPV/ PRR6 | SLC35A2 | CRK | VIM | SPECC1L/ CYTSA | LCN2 | SERPINE2 |
| APBB3 | RPL36AL | DHRS4L2 | ASXL1 | UBE2D3 | CTSZ | BRMS1 | NGFRAP1 | TUBB1 |
| NDUFS5 | MS4A7 | PPP1R13L | KIR3DL3 | DCBLD2 | C5AR1 | ISG15 | DEFA3 | NDUFAF3 |
| ING3 | UQCRH | MFN2 | PTK2B | SESN3 | HNRNPUL2 | RNF44 | POLR1D | NUDT3 |
| GRAP | RPS27A | MEAF6/ C1orf149 | FAM102A | HIVEP3 | CHKB | HIST1H4C | FYN | RARRES3 |
| SNTB2 | DCAF5/ WDR22 | SIAH2 | SIK3 | MCM3 | ARF4 | PPP3R1 | PRDX6 | OSCAR |
| STIP1 | NDUFS5 | OR51S1 | PTGDS | SEPSECS | SLC40A1 | MYLPF/ MRLC2 | MS4A7 | VSTM1 |
| MED16 | NDUFA1 | TSC22D1 | BHLHE40 | FECH | CREBBP | ZFP36L2 | RUFY1 | MRPL2 |
| NDUFA1 | C19orf12 | HPSE | UBE3A | FANCD2 | PPP2R5A | CX3CR1 | KLF2 | NUDT18 |
| AATF | COTL1 | DAPK2 | EPB41L2 | LONP2 | CAPZA2 | ATP2B4 | ATF6 | TAPBP |
| CDK10 | MRPL51 | GPR34 | LILRB1 | DDX42 | VPS13C | TMEM131 | DUSP1 | ZFP36L2 |
| SHFM1 | KIAA0907/ KHDC4 | GEMIN6 | PTGDS | UBFD1 | NRIP1 | NIN | PPM1F | HPSE |
| CETN2 | RPS25P6 | OVCA2 | PTGDS | FBXL20 | CD82 | S100A4 | PTCRA | IGFBP3 |
| TPM3 | LOC646200 | NSUN7 | LOC100510080 | COL4A3 | BRI3 | RPS15A | METRNL | VARS2 |
| MRPL51 | RPS23P8 | THRA | LOC100510377 | CENPK | LAMTOR1/ C11orf59 | HLA-DRA | FBP1 | SASH1 |
| LOC646200 | RPL36AL | ENTPD4 | IGHG1 | CLPTM1 | RORA | ZMIZ1 | DEFA1B | OSCAR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huseby, C.J.; Delvaux, E.; Brokaw, D.L.; Coleman, P.D. Blood Transcript Biomarkers Selected by Machine Learning Algorithm Classify Neurodegenerative Diseases including Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111592
Huseby CJ, Delvaux E, Brokaw DL, Coleman PD. Blood Transcript Biomarkers Selected by Machine Learning Algorithm Classify Neurodegenerative Diseases including Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111592
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuseby, Carol J., Elaine Delvaux, Danielle L. Brokaw, and Paul D. Coleman. 2022. "Blood Transcript Biomarkers Selected by Machine Learning Algorithm Classify Neurodegenerative Diseases including Alzheimer’s Disease" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111592
APA StyleHuseby, C. J., Delvaux, E., Brokaw, D. L., & Coleman, P. D. (2022). Blood Transcript Biomarkers Selected by Machine Learning Algorithm Classify Neurodegenerative Diseases including Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111592







