Spexin Regulates Hypothalamic Leptin Action on Feeding Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Intracerebroventricular (icv) Cannulation and Material Administration
2.3. Measurement of Body Temperature and Locomotor Activity
2.4. Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotide Administration
2.5. Ribo-Tag System
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Cell Culture and Luciferase Assay
2.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assays
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Central SPX Induces Anorexia in Mice
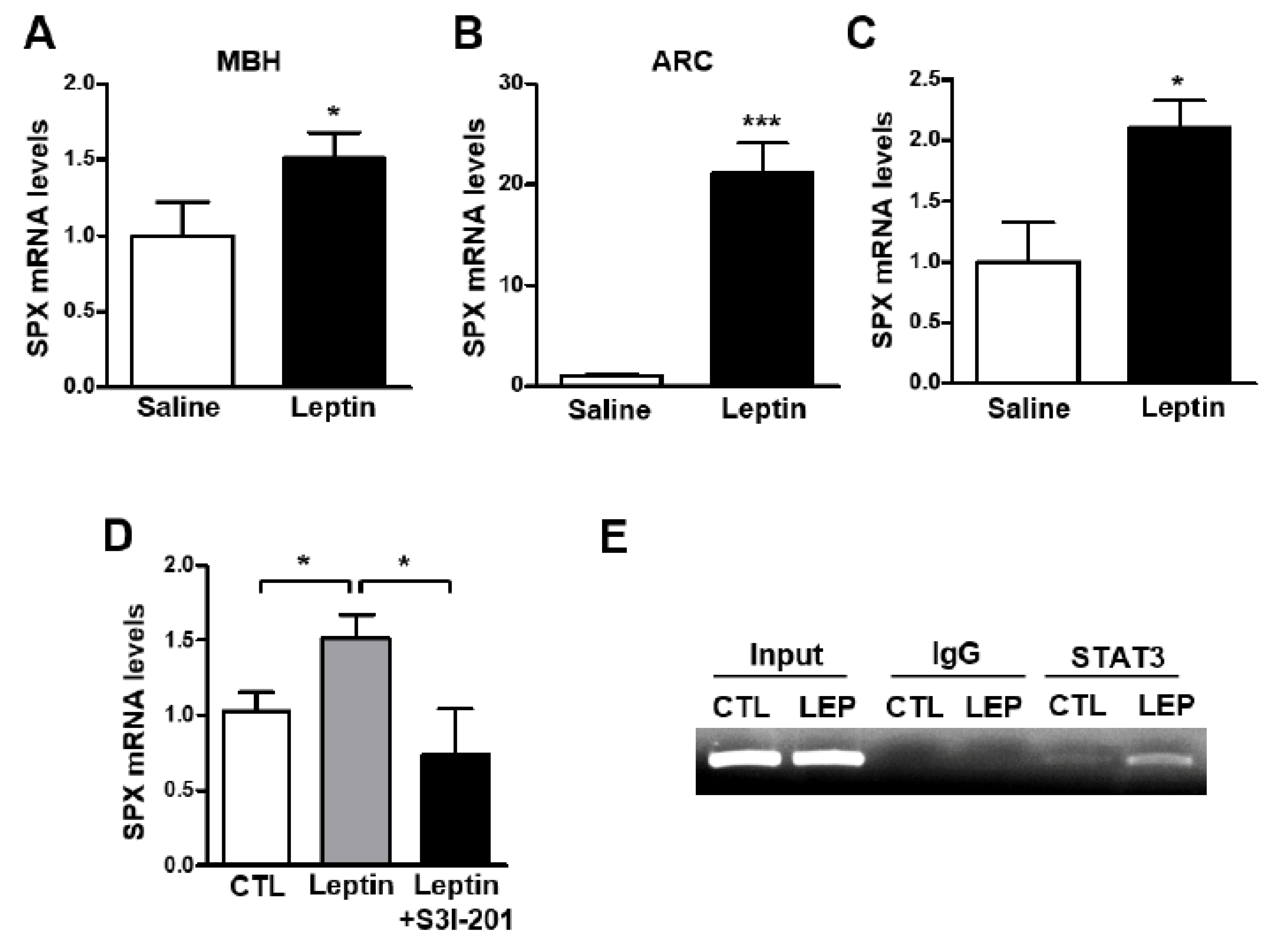
3.2. Leptin Increases SPX Expression via STAT3 Activation in the Mouse Hypothalamus
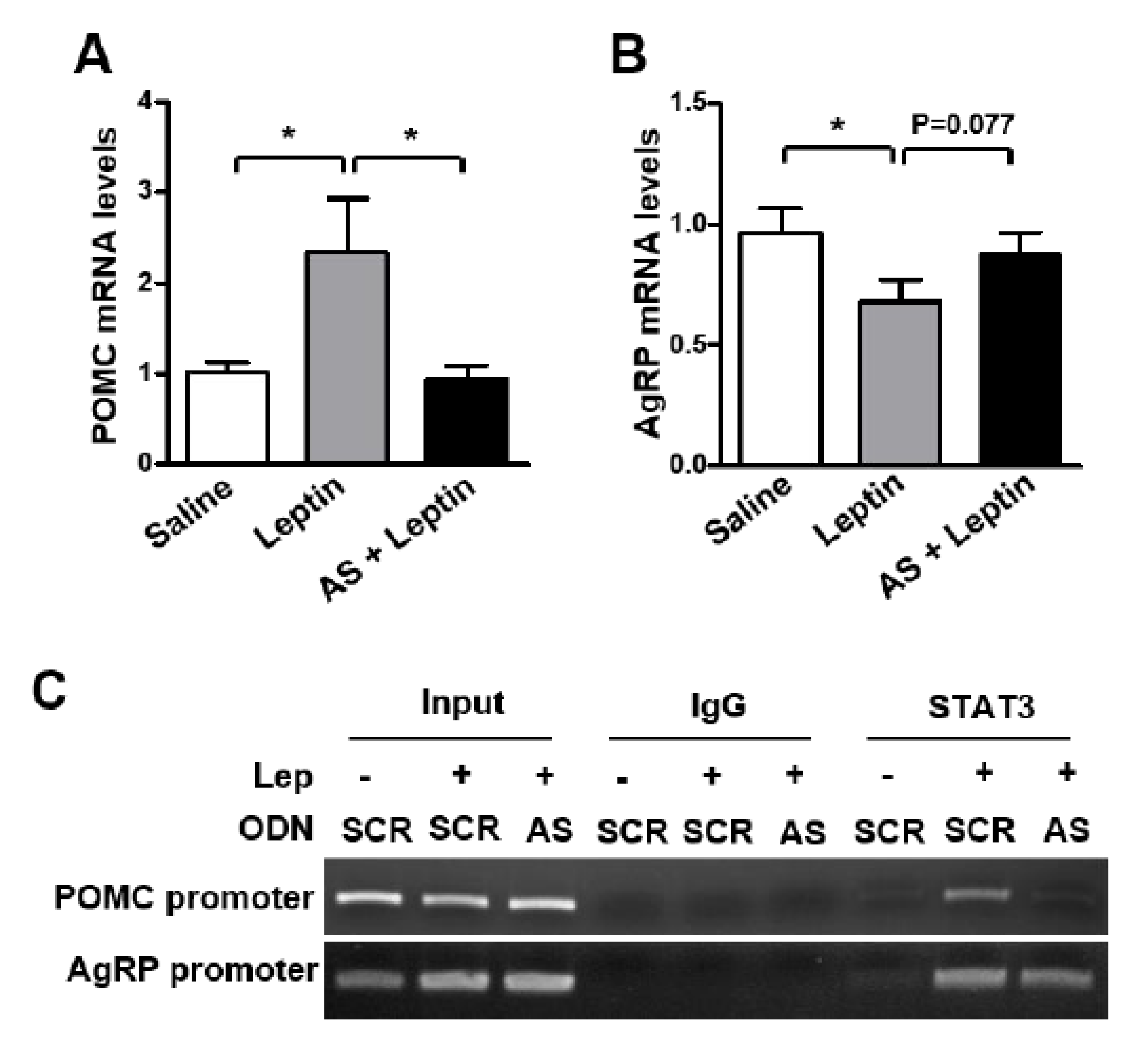
3.3. SPX Inhibition Blocks Leptin’s Anorexigenic Action
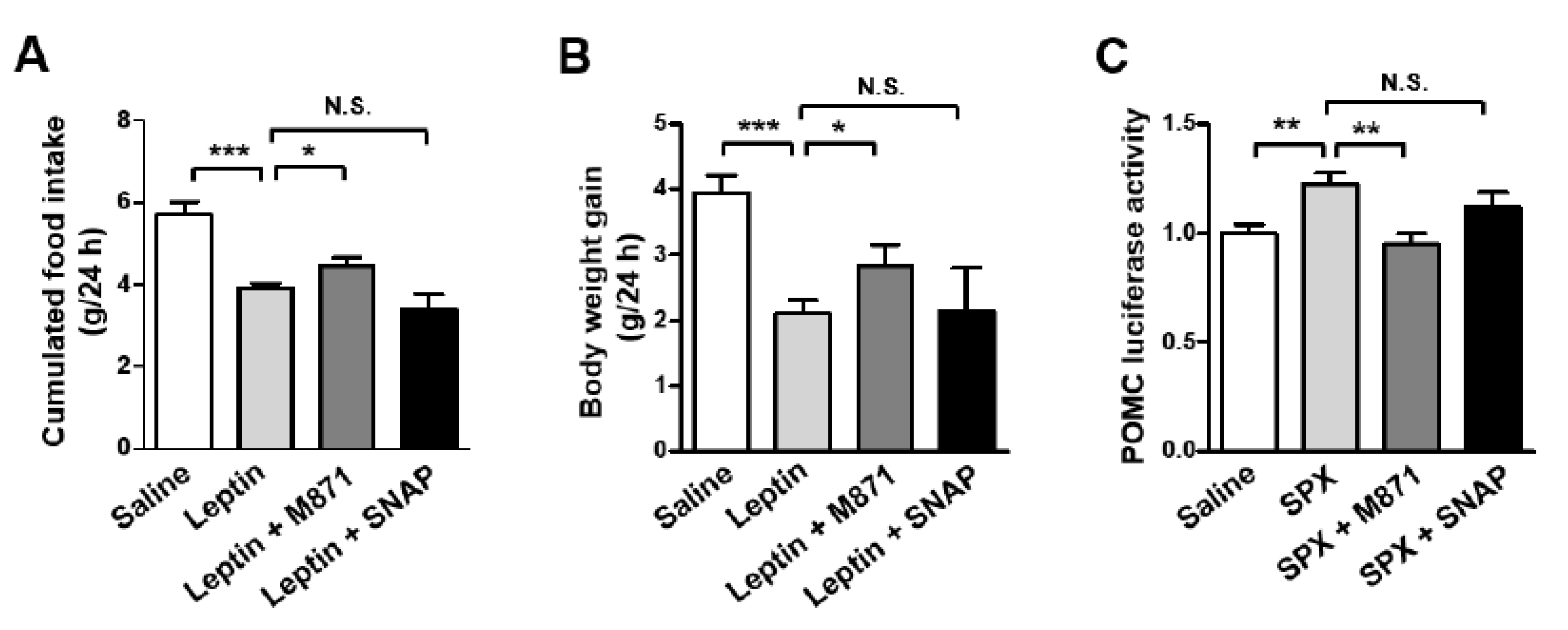
3.4. GALR2 Is Important in the Anorexigenic Action of Leptin-Induced SPX
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirabeau, O.; Perlas, E.; Severini, C.; Audero, E.; Gascuel, O.; Possenti, R.; Birney, E.; Rosenthal, N.; Gross, C. Identification of novel peptide hormones in the human proteome by hidden Markov model screening. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmez, K.; Zaveri, N.T.; Kerman, I.A.; Burke, S.; Neal, C.R.; Xie, X.; Watson, S.J.; Toll, L. Evolutionary sequence modeling for discovery of peptide hormones. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, L.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of spexin in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 196, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.K.; Sze, K.H.; Chen, T.; Cho, C.K.; Law, H.C.; Chu, I.K.; Wong, A.O. Goldfish spexin: Solution structure and novel function as a satiety factor in feeding control. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E348–E366. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Lin, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Chen, D.; Yuan, D.; Wang, T.; et al. Ya-fish (Schizothorax prenanti) spexin: Identification, tissue distribution and mRNA expression responses to periprandial and fasting. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Yun, S.; Son, G.H.; Hwang, J.I.; Park, C.R.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, K.; Vaudry, H.; Seong, J.Y. Coevolution of the spexin/galanin/kisspeptin family: Spexin activates galanin receptor type II and III. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzionato, A.; Rucinski, M.; Macchi, V.; Stecco, C.; Malendowicz, L.K.; De Caro, R. Spexin expression in normal rat tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2010, 58, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.H. A novel neuropeptide in suppressing luteinizing hormone release in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 374, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucinski, M.; Porzionato, A.; Ziolkowska, A.; Szyszka, M.; Macchi, V.; De Caro, R.; Malendowicz, L.K. Expression of the spexin gene in the rat adrenal gland and evidences suggesting that spexin inhibits adrenocortical cell proliferation. Peptides 2010, 31, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll, L.; Khroyan, T.V.; Sonmez, K.; Ozawa, A.; Lindberg, I.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Eans, S.O.; Shahien, A.A.; Kapusta, D.R. Peptides derived from the prohormone proNPQ/spexin are potent central modulators of cardiovascular and renal function and nociception. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walewski, J.L.; Ge, F.; Lobdell, H.t.; Levin, N.; Schwartz, G.J.; Vasselli, J.R.; Pomp, A.; Dakin, G.; Berk, P.D. Spexin is a novel human peptide that reduces adipocyte uptake of long chain fatty acids and causes weight loss in rodents with diet-induced obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrooz, M.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Ostadrahimi, A. Different spexin level in obese vs normal weight children and its relationship with obesity related risk factors. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Hossain, J.; Nader, N.; Aguirre, R.; Sriram, S.; Balagopal, P.B. Decreased Circulating Levels of Spexin in Obese Children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2931–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitarafan, V.; Esteghamati, A.; Azam, K.; Yosaee, S.; Djafarian, K. Comparing serum concentration of spexin among patients with metabolic syndrome, healthy overweight/obese, and normal-weight individuals. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2019, 33, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.H.K. Spexin Suppress Food Intake in Zebrafish: Evidence from Gene Knockout Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.K.H.; Chen, Y.; He, M.; Lin, C.; Bian, Z.; Wong, A.O.L. Mouse Spexin: (II) Functional Role as a Satiety Factor inhibiting Food Intake by Regulatory Actions within the Hypothalamus. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 681647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmquist, J.K.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Saper, C.B.; Flier, J.S. Unraveling the central nervous system pathways underlying responses to leptin. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.P.; Dube, M.G.; Pu, S.; Xu, B.; Horvath, T.L.; Kalra, P.S. Interacting appetite-regulating pathways in the hypothalamic regulation of body weight. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 68–100. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Woods, S.C.; Porte, D., Jr.; Seeley, R.J.; Baskin, D.G. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 2000, 404, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J.; Porte, D., Jr.; Schwartz, M.W. Signals that regulate food intake and energy homeostasis. Science 1998, 280, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A. The leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6093–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A.; Dembski, M.; Weng, X.; Deng, N.; Culpepper, J.; Devos, R.; Richards, G.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Clark, F.T.; Deeds, J.; et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 1995, 83, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Charlat, O.; Tartaglia, L.A.; Woolf, E.A.; Weng, X.; Ellis, S.J.; Lakey, N.D.; Culpepper, J.; Moore, K.J.; Breitbart, R.E.; et al. Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: Identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell 1996, 84, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Proenca, R.; Montez, J.M.; Carroll, K.M.; Darvishzadeh, J.G.; Lee, J.I.; Friedman, J.M. Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 1996, 379, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, N.; Skoda, R.C. The leptin receptor activates janus kinase 2 and signals for proliferation in a factor-dependent cell line. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisse, C.; Halaas, J.L.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Stoffel, M.; Friedman, J.M. Leptin activation of Stat3 in the hypothalamus of wild-type and ob/ob mice but not db/db mice. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, C.I.; Tota, M.; Cully, D.; Smith, T.; Collum, R.; Qureshi, S.; Hess, J.F.; Phillips, M.S.; Hey, P.J.; Vongs, A.; et al. Functional STAT 1 and 3 signaling by the leptin receptor (OB-R); reduced expression of the rat fatty leptin receptor in transfected cells. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5178–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Katsuura, G.; Hayase, M.; Tsuji, T.; Imagawa, K.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Nishi, S.; Hosoda, K.; Nakao, K. The arcuate nucleus as a primary site of satiety effect of leptin in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 224, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Kalra, S.P. Neuropeptidergic regulation of feeding behavior Neuropeptide, Y. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzberg, H.; Huo, L.; Nillni, E.A.; Hollenberg, A.N.; Bjorbaek, C. Role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in regulation of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin gene expression by leptin. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaros, A.; Koralov, S.B.; Rother, E.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Ernst, M.B.; Barsh, G.S.; Rajewsky, K.; Bruning, J.C. Activation of Stat3 signaling in AgRP neurons promotes locomotor activity. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, M.B.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Hess, S.; Paehler, M.; Mesaros, A.; Koralov, S.B.; Kleinridders, A.; Husch, A.; Munzberg, H.; Hampel, B.; et al. Enhanced Stat3 activation in POMC neurons provokes negative feedback inhibition of leptin and insulin signaling in obesity. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11582–11593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.S.; Jin, S.H.; Park, J.J.; Park, J.W.; Namgoong, I.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, J.G. Visfatin induces sickness responses in the brain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, E.; Yang, L.; Su, T.; Morris, D.R.; McKnight, G.S.; Amieux, P.S. Cell-type-specific isolation of ribosome-associated mRNA from complex tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13939–13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.S.; Ebbert, M.T.W.; Baker, K.E.; Cook, C.; Wang, X.; Sens, J.P.; Kocher, J.P.; Petrucelli, L.; Fryer, J.D. Microglial translational profiling reveals a convergent APOE pathway from aging, amyloid, and tau. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Park, B.S.; Yun, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.S.; D’Elia, A.V.; Damante, G.; Lee, K.U.; Park, J.W.; Kim, E.S.; et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1 regulates feeding behavior via melanocortin pathway in the hypothalamus. Diabetes 2011, 60, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Ma, Y.; Gu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Yin, J.; Fan, N.; et al. Spexin peptide is expressed in human endocrine and epithelial tissues and reduced after glucose load in type 2 diabetes. Peptides 2015, 71, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Peripheral Spexin Inhibited Food Intake in Mice. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 4913785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.K.H.; He, M.; Sze, K.H.; Huang, T.; Ko, W.K.W.; Bian, Z.X.; Wong, A.O.L. Mouse Spexin: (I) NMR Solution Structure, Docking Models for Receptor Binding, and Histological Expression at Tissue Level. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 681646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.M.; Lachey, J.L.; Sternson, S.M.; Lee, C.E.; Elias, C.F.; Friedman, J.M.; Elmquist, J.K. Leptin targets in the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 514, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.F.; Koutcherov, I.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.Q.; Storlien, L. Localization of leptin receptor mRNA expression in mouse brain. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 2635–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, H.; Zigman, J.M.; Ye, C.; Lee, C.E.; McGovern, R.A.; Tang, V.; Kenny, C.D.; Christiansen, L.M.; White, R.D.; Edelstein, E.A.; et al. Leptin directly activates SF1 neurons in the VMH, and this action by leptin is required for normal body-weight homeostasis. Neuron 2006, 49, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, C.L.; Deem, J.D.; Phan, B.A.; Doan, T.P.; Ogimoto, K.; Mirzadeh, Z.; Schwartz, M.W.; Morton, G.J. Leptin receptor neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus regulate diurnal patterns of feeding, locomotion, and metabolism. eLife 2021, 10, e63671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinninger, G.M.; Jo, Y.H.; Leshan, R.L.; Louis, G.W.; Yang, H.; Barrera, J.G.; Wilson, H.; Opland, D.M.; Faouzi, M.A.; Gong, Y.; et al. Leptin acts via leptin receptor-expressing lateral hypothalamic neurons to modulate the mesolimbic dopamine system and suppress feeding. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, A.; Dungan Lemko, H.M.; Castorena, C.M.; Fujikawa, T.; Lee, S.; Lord, C.C.; Ahmed, N.; Lee, C.E.; Holland, W.L.; Liu, C.; et al. POMC neurons expressing leptin receptors coordinate metabolic responses to fasting via suppression of leptin levels. eLife 2018, 7, e33710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppari, R.; Ichinose, M.; Lee, C.E.; Pullen, A.E.; Kenny, C.D.; McGovern, R.A.; Tang, V.; Liu, S.M.; Ludwig, T.; Chua, S.C., Jr.; et al. The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: A key site for mediating leptin’s effects on glucose homeostasis and locomotor activity. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Suyama, S.; Koch, M.; Jin, S.; Argente-Arizon, P.; Argente, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Zimmer, M.R.; Jeong, J.K.; Szigeti-Buck, K.; et al. Leptin signaling in astrocytes regulates hypothalamic neuronal circuits and feeding. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Morrill, J.C.; Cai, J.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xue, M.; et al. A neural basis for brain leptin action on reducing type 1 diabetic hyperglycemia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, J., Jr.; Cravo, R.M.; Frazao, R.; Elias, C.F. Hypothalamic sites of leptin action linking metabolism and reproduction. Neuroendocrinology 2011, 93, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.A.; Leinninger, G.M.; Myers, M.G., Jr. Molecular and neural mediators of leptin action. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seamon, M.; Ahn, W.; Li, A.J.; Ritter, S.; Harris, R.B.S. Leptin receptor-expressing neurons in ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus contribute to weight loss caused by fourth ventricle leptin infusions. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E586–E596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, B.N.; Harris, R.B. Leptin in the hindbrain facilitates phosphorylation of STAT3 in the hypothalamus. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E351–E361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B.; Desai, B.N. Fourth-ventricle leptin infusions dose-dependently activate hypothalamic signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E939–E948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommel, J.D.; Trinko, R.; Sears, R.M.; Georgescu, D.; Liu, Z.W.; Gao, X.B.; Thurmon, J.J.; Marinelli, M.; DiLeone, R.J. Leptin receptor signaling in midbrain dopamine neurons regulates feeding. Neuron 2006, 51, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Bello, N.T.; Pang, Z.P. Presynaptic Regulation of Leptin in a Defined Lateral Hypothalamus-Ventral Tegmental Area Neurocircuitry Depends on Energy State. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11854–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.W.; Williams, K.W. Functional heterogeneity of arcuate nucleus pro-opiomelanocortin neurons: Implications for diverging melanocortin pathways. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, B.; Kim, K.-K.; Lee, T.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Park, B.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Jeong, J.-K.; Seong, J.-Y.; Lee, B.-J. Spexin Regulates Hypothalamic Leptin Action on Feeding Behavior. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020236
Jeong B, Kim K-K, Lee T-H, Kim H-R, Park B-S, Park J-W, Jeong J-K, Seong J-Y, Lee B-J. Spexin Regulates Hypothalamic Leptin Action on Feeding Behavior. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Bora, Kwang-Kon Kim, Tae-Hwan Lee, Han-Rae Kim, Byong-Seo Park, Jeong-Woo Park, Jin-Kwon Jeong, Jae-Young Seong, and Byung-Ju Lee. 2022. "Spexin Regulates Hypothalamic Leptin Action on Feeding Behavior" Biomolecules 12, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020236
APA StyleJeong, B., Kim, K.-K., Lee, T.-H., Kim, H.-R., Park, B.-S., Park, J.-W., Jeong, J.-K., Seong, J.-Y., & Lee, B.-J. (2022). Spexin Regulates Hypothalamic Leptin Action on Feeding Behavior. Biomolecules, 12(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020236







