Mechanistic Investigation of GHS-R Mediated Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS) In Vivo
2.3. Immunohistochemistry of Pancreas
2.4. Islet Isolation
2.5. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS)
2.6. Insulin Content of Pancreas and Islets
2.7. Respirometry of Islets
2.8. ATP/ADP Ratio
2.9. Glucose-6-Phosphate Measurement
2.10. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.11. Western Blot
2.12. Extraction and Quantification of Mitochondrial DNA
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
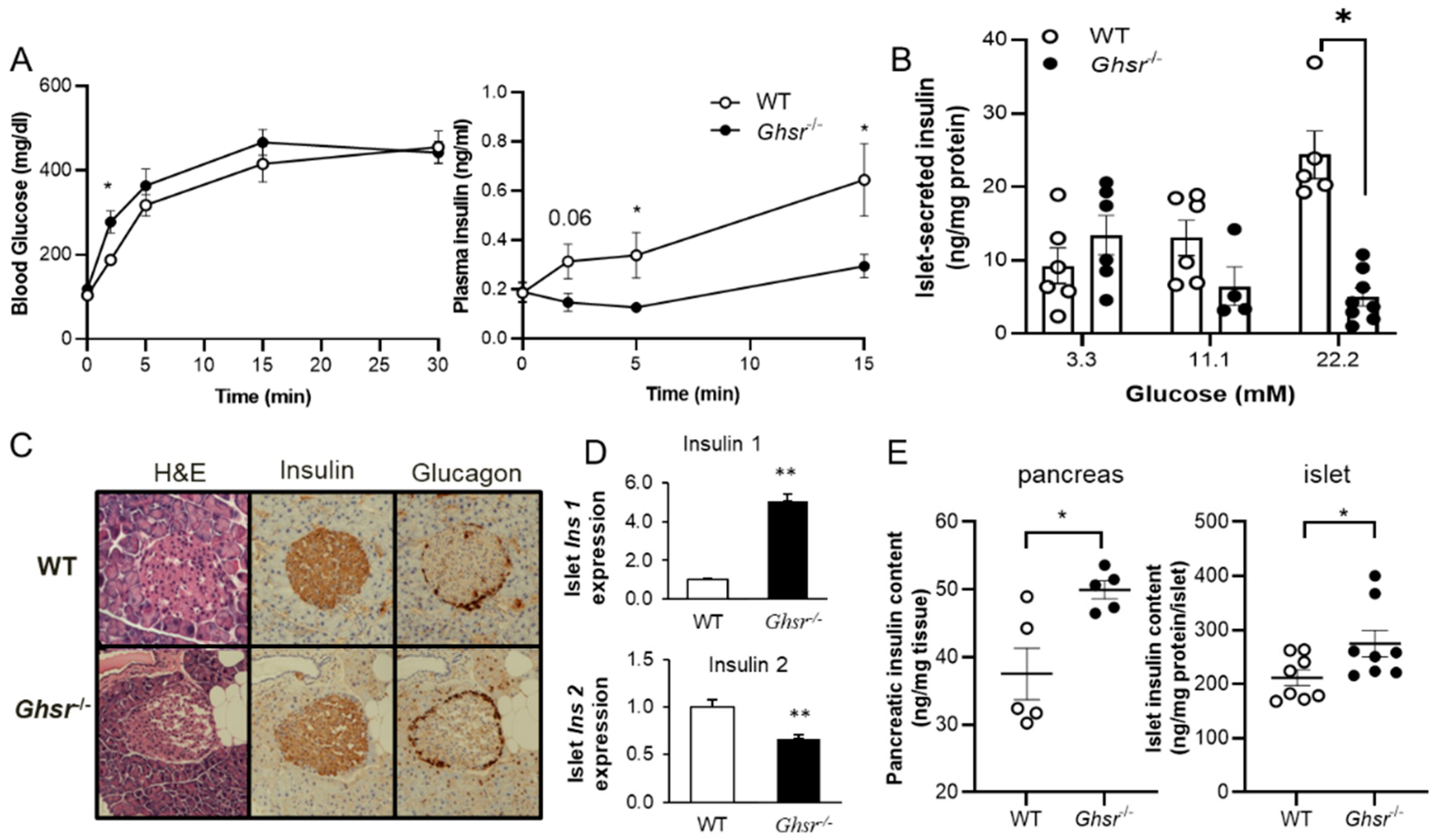
3.1. GHS-R Ablation Decreases Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS)
3.2. Ghsr−/− Islets Exhibit Lower ATP/ADP Ratio
3.3. Glucose Uptake Is Reduced in Ghsr-Ablated Islets
3.4. Identification of Molecular Mediators Governing GHS-R Induced GSIS
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Sawaguchi, A.; Mondal, M.S.; Suganuma, T.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin, a Novel Growth Hormone-Releasing Acylated Peptide, Is Synthesized in a Distinct Endocrine Cell Type in the Gastrointestinal Tracts of Rats and Humans. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.L.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Elghazi, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B.; Sussel, L. Ghrelin cells replace insulin-producing cells in two mouse models of pancreas development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Gallo, D.; Trovato, L.; Biancone, L.; Cantaluppi, V.; Nano, R.; Annunziata, M.; Campiglia, P.; Arnoletti, E.; et al. Obestatin Promotes Survival of Pancreatic Beta-Cells and Human Islets and Induces Expression of Genes Involved in the Regulation of -Cell Mass and Function. Diabetes 2007, 57, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volante, M.; Allìa, E.; Gugliotta, P.; Funaro, A.; Broglio, F.; Deghenghi, R.; Muccioli, G.; Ghigo, E.; Papotti, M. Expression of Ghrelin and of the GH Secretagogue Receptor by Pancreatic Islet Cells and Related Endocrine Tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierup, N.; Yang, S.; McEvilly, R.J.; Mulder, H.; Sundler, F. Ghrelin Is Expressed in a Novel Endocrine Cell Type in Developing Rat Islets and Inhibits Insulin Secretion from INS-1 (832/13) Cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Dezaki, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Arima, T.; Matsuo, H.; et al. Ghrelin Is Present in Pancreatic α-Cells of Humans and Rats and Stimulates Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K. The autonomic nervous system regulates gastric ghrelin secretion in rats. Regul. Pept. 2008, 146, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezaki, K.; Hosoda, H.; Kakei, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Endogenous ghrelin in pancreatic islets restricts insulin release by attenuating Ca2+ signaling in beta-cells: Implication in the glycemic control in rodents. Diabetes 2004, 53, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, M.K.; Pacini, G.; Ahrén, B. Dose-Dependent Inhibition by Ghrelin of Insulin Secretion in the Mouse. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röder, P.V.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Takei, M.; Ishii, H.; Sato, Y. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: A newer perspective. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 4, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, H.; Smith, R.G. Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone release and appetite is mediated through the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4679–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGruccio, M.R.; Mawla, A.M.; Donaldson, C.J.; Noguchi, G.M.; Vaughan, J.; Cowing-Zitron, C.; van der Meulen, T.; Huising, M.O. Comprehensive alpha, beta and delta cell transcriptomes reveal that ghrelin selectively activates delta cells and promotes somatostatin release from pancreatic islets. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanapavan, S.; Kola, B.; Bustin, S.A.; Morris, D.G.; McGee, P.; Fairclough, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carpenter, R.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, R.; Baragli, A.; Settanni, F.; Scarlatti, F.; Ghigo, E. Unraveling the role of the ghrelin gene peptides in the endocrine pancreas. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderwald-Stadler, M.; Krebs, M.; Promintzer, M.; Mandl, M.; Bischof, M.G.; Nowotny, P.; Kästenbauer, T.; Luger, A.; Prager, R.; Anderwald, C. Plasma obestatin is lower at fasting and not suppressed by insulin in insulin-resistant humans. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1393–E1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Dowsett, G.K.C.; Mani, B.K.; Shankar, K.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Metzger, N.P.; Lam, B.Y.H.; Yeo, G.S.H.; Zigman, J.M. High Coexpression of the Ghrelin and LEAP2 Receptor GHSR With Pancreatic Polypeptide in Mouse and Human Islets. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-X.; Qiu, W.-L.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.-C.; He, M.-Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.-C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Sequential progenitor states mark the generation of pancreatic endocrine lineages in mice and humans. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; Nagai, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Blockade of Pancreatic Islet–Derived Ghrelin Enhances Insulin Secretion to Prevent High-Fat Diet–Induced Glucose Intolerance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.-C.; Sakata, I.; Kohno, D.; Perello, M.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Repa, J.J.; Zigman, J.M. Ghrelin Directly Stimulates Glucagon Secretion from Pancreatic α-Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Svendsen, B.Y.; Lam, B.; Yeo, G.S.H.; Holst, J.J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Transcriptomic profiling of pancreatic alpha, beta and delta cell populations identifies delta cells as a principal target for ghrelin in mouse islets. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezaki, K.; Kakei, M.; Yada, T. Ghrelin uses Galphai2 and activates voltage-dependent K+ channels to attenuate glucose-induced Ca2+ signaling and insulin release in islet beta-cells: Novel signal transduction of ghrelin. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Smith, R.G. Modification of ghrelin receptor signaling by somatostatin receptor-5 regulates insulin release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19003–19008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurashina, T.; Dezaki, K.; Yoshida, M.; Rita, R.S.; Ito, K.; Taguchi, M.; Miura, R.; Tominaga, M.; Ishibashi, S.; Kakei, M.; et al. The β-cell GHSR and downstream cAMP/TRPM2 signaling account for insulinostatic and glycemic effects of ghrelin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Asnicar, M.; Saha, P.K.; Chan, L.; Smith, R.G. Ablation of ghrelin improves the diabetic but not obese phenotype of ob/ob mice. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Saha, P.K.; Ma, X.; Henshaw, I.O.; Shao, L.; Chang, B.H.J.; Buras, E.D.; Tong, Q.; Chan, L.; McGuinness, O.P.; et al. Ablation of ghrelin receptor reduces adiposity and improves insulin sensitivity during aging by regulating fat metabolism in white and brown adipose tissues. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, Y.; Lin, L.; Qin, G.; Pereira, F.A.; Haymond, M.W.; Butte, N.F.; Sun, Y. Ablation of ghrelin receptor in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice has paradoxical effects on glucose homeostasis when compared with ablation of ghrelin in ob/ob mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E422–E431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.F.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin action at a molecular level—100 years of progress. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinwall, C.A.; Lakey, J.R.T.; Kennedy, R.T. Insulin-stimulated Insulin Secretion in Single Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6360–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, A.; Hinault, C.; Kulkarni, R.N. Growth factor control of pancreatic islet regeneration and function. Pediatr. Diabetes 2009, 10, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouche, C.; Lopez, X.; Fleischman, A.; Cypess, A.M.; O’Shea, S.; Stefanovski, D.; Bergman, R.N.; Rogatsky, E.; Stein, D.T.; Kahn, C.R.; et al. Insulin enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in healthy humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4770–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, F.; Lopez, X.; Manning, R.; Kahn, C.R.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Goldfine, A.B. Insulin Augmentation of Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Is Impaired in Insulin-Resistant Humans. Diabetes 2012, 61, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderwald, C.; Tura, A.; Grassi, A.; Krebs, M.; Szendroedi, J.; Roden, M.; Bischof, M.G.; Luger, A.; Pacini, G. Insulin Infusion During Normoglycemia Modulates Insulin Secretion According to Whole-Body Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Brüning, J.C.; Winnay, J.N.; Postic, C.; Magnuson, M.; Kahn, C. Tissue-Specific Knockout of the Insulin Receptor in Pancreatic β Cells Creates an Insulin Secretory Defect Similar to that in Type 2 Diabetes. Cell 1999, 96, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Winnay, J.N.; Daniels, M.; Brüning, J.C.; Flier, S.N.; Hanahan, D.; Kahn, C.R. Altered function of insulin receptor substrate-1–deficient mouse islets and cultured β-cell lines. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, R69–R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, D.; Gutierrez, J.S.; Towery, H.; Burks, D.J.; Ren, J.-M.; Previs, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bernal, D.; Pons, S.; Shulman, G.; et al. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 1998, 391, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Mu, J.; Kim, J.K.; Thorvaldsen, J.L.; Chu, Q.; Crenshaw, E.B.; Kaestner, K.H.; Bartolomei, M.S.; Shulman, G.I.; Birnbaum, M.J. Insulin Resistance and a Diabetes Mellitus-Like Syndrome in Mice Lacking the Protein Kinase Akt2 (PKBβ). Science 2001, 292, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Ueki, K.; Takahashi, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Okamoto, M.; Awazawa, M.; Okazaki, Y.; Ohsugi, M.; Inabe, K.; Umehara, T.; et al. Class IA Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase in Pancreatic β Cells Controls Insulin Secretion by Multiple Mechanisms. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillam, M.T.; Hummler, E.; Schaerer, E.; Yeh, J.I.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Beermann, F.; Schmidt, A.; Deriaz, N.; Thorens, B. Early diabetes and abnormal postnatal pancreatic islet development in mice lacking Glut-2. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poykko, S.M.; Kellokoski, E.; Horkko, S.; Kauma, H.; Kesaniemi, Y.A.; Ukkola, O. Low Plasma Ghrelin Is Associated With Insulin Resistance, Hypertension, and the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2546–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purnell, J.Q.; Weigle, D.S.; Breen, P.; Cummings, D.E. Ghrelin Levels Correlate with Insulin Levels, Insulin Resistance, and High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, But Not with Gender, Menopausal Status, or Cortisol Levels in Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5747–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezaki, A.; Hosoda, H.; Ito, K.; Iwama, S.; Miura, N.; Matsuoka, H.; Kondo, C.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Sugihara, S. Fasting Plasma Ghrelin Levels Are Negatively Correlated With Insulin Resistance and PAI-1, but Not With Leptin, in Obese Children and Adolescents. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3408–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, G.; Samson, S.L.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin: Much more than a hunger hormone. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Yoon, C.Y.; Jang, P.G.; Park, Y.J.; Shin, C.S.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, J.W.; Pak, Y.K.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; et al. The Mitogenic and Antiapoptotic Actions of Ghrelin in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. The Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor: Its Intracellular Signaling and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4837–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Okimura, Y.; Iida, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Sowa, H.; Kaji, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Chihara, K. Ghrelin Modulates the Downstream Molecules of Insulin Signaling in Hepatoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5667–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, E.; Zhang, C.; Mumford, S.; Ye, A.; Trevisan, M.; Chen, L.; Browne, R.W.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Schisterman, E. Longitudinal Study of Insulin Resistance and Sex Hormones over the Menstrual Cycle: The BioCycle Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 5435–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-S.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Tu, H.-J.; Liang, Q.-L.; Dai, L.-J. A protocol for islet isolation from mouse pancreas. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, D.; Pradhan, G.; Wu, C.S.; Allred, C.D.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y. A Simple High Efficiency Protocol for Pancreatic Islet Isolation from Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 150, e57048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmeier, H.E.; Mulder, H.; Chen, G.; Henkel-Rieger, R.; Prentki, M.; Newgard, C.B. Isolation of INS-1-derived cell lines with robust ATP-sensitive K+ channel-dependent and -independent glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 2000, 49, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, K.; Kopchick, J.J.; Liu, J.-L. Growth hormone receptor gene deficiency causes delayed insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscles without affecting compensatory islet cell overgrowth in obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2006, 291, E491–E498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, L.; Qin, G.; Lu, X.; Fiorotto, M.; Dixit, V.D.; Sun, Y. Ablations of Ghrelin and Ghrelin Receptor Exhibit Differential Metabolic Phenotypes and Thermogenic Capacity during Aging. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Butte, N.F.; Garcia, J.M.; Smith, R.G. Characterization of Adult Ghrelin and Ghrelin Receptor Knockout Mice under Positive and Negative Energy Balance. Endocrinology 2007, 149, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, B.M.; Schaefer, I.M.; Villa-Komaroff, L.; Chirgwin, J.M. Characterization of the two nonallelic genes encoding mouse preproinsulin. J. Mol. Evol. 1986, 23, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiao, M.-S.; Liao, B.-Y.; Long, M.; Yu, H.-T. Adaptive Evolution of the Insulin Two-Gene System in Mouse. Genet. 2008, 178, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, K.; Ma, X.; Chang, X.; Shi, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, K.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; et al. Knockin of Cre Gene at Ins2 Locus Reveals No Cre Activity in Mouse Hypothalamic Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.V.; Joseph, J.W.; Ronnebaum, S.M.; Burgess, S.C.; Sherry, A.D.; Newgard, C.B. Metabolic cycling in control of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1287–E1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Almaça, J.; Dadi, P.K.; Hong, H.; Sakamoto, W.; Rossi, M.; Lee, R.; Vierra, N.C.; Lu, H.; Cui, Y.; et al. β-arrestin-2 is an essential regulator of pancreatic β-cell function under physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, D.; Reckers, K.; Drain, P.; Rustenbeck, I. Glucose but not KCl diminishes submembrane granule turnover in mouse beta-cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 59, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Koshkin, V.; Allister, E.M.; Gyulkhandanyan, A.V.; Wheeler, M.B. Molecular and Metabolic Evidence for Mitochondrial Defects Associated with β-Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 59, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B. GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 2014, 58, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. The sweet trap in tumors: Aerobic glycolysis and potential targets for therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38908–38926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gu, W.; Chen, C. Knocking down Insulin Receptor in Pancreatic Beta Cell lines with Lentiviral-Small Hairpin RNA Reduces Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion via Decreasing the Gene Expression of Insulin, GLUT2 and Pdx1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watada, H.; Kajimoto, Y.; Miyagawa, J.-I.; Hanafusa, T.; Hamaguchi, K.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Kawamori, R.; Yamasaki, Y. PDX-1 Induces Insulin and Glucokinase Gene Expressions in αTC1 Clone 6 Cells in the Presence of Betacellulin. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Maechler, P.; Ritz-Laser, B.; Hagenfeldt, K.A.; Ishihara, H.; Philippe, J.; Wollheim, C.B. Pdx1 Level Defines Pancreatic Gene Expression Pattern and Cell Lineage Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25279–25286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Brun, T.; Kataoka, K.; Sharma, A.J.; Wollheim, C.B. MAFA controls genes implicated in insulin biosynthesis and secretion. Diabetologia 2006, 50, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.-A.; Kaneto, H.; Stein, R.; Miyatsuka, T.; Kawamori, D.; Henderson, E.; Kojima, I.; Matsuhisa, M.; Hori, M.; Yamasaki, Y. MafA Regulates Expression of Genes Important to Islet β-Cell Function. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2764–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, G.; Wu, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kanikarla, P.; Guo, S.; Yechoor, V.K.; Samson, S.L.; Sun, Y. Obestatin stimulates glucose-induced insulin secretion through ghrelin receptor GHS-R. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Bongmba, O.Y.N.; Lee, J.H.; Tuchaai, E.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.-P.; Xue, B.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin receptor in agouti-related peptide neurones regulates metabolic adaptation to calorie restriction. J. Neuroendocr. 2019, 31, e12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Nakano, Y.; Coppari, R.; Balthasar, N.; Marcus, J.N.; Lee, C.E.; Jones, J.E.; Deysher, A.E.; Waxman, A.R.; White, R.D.; et al. Mice lacking ghrelin receptors resist the development of diet-induced obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3564–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, G.; Wu, C.-S.; Villarreal, D.; Lee, J.; Han, H.; Gaharwar, A.; Tian, Y.; Fu, W.; Guo, S.; Smith, R.; et al. β Cell GHS-R Regulates Insulin Secretion and Sensitivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.M.; Niu, J.; Zhang, A.; Svendsen, B.; Campbell, J.E.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Tong, J. Intraislet Ghrelin Signaling Does Not Regulate Insulin Secretion From Adult Mice. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, L.; Desbois, P.; Lamotte, L.; Duvillié, B.; Cordonnier, N.; Jackerott, M.; Jami, J.; Bucchini, D.; Joshi, R.L. Compensatory responses in mice carrying a null mutation for Ins1 or Ins2. Diabetes 2001, 50 (Suppl. 1), 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderigo-Milne, H.; Hauge-Evans, A.C.; Persaud, S.; Jones, P. Differential expression of insulin genes 1 and 2 in MIN6 cells and pseudoislets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haythorne, E.; Rohm, M.; Van De Bunt, M.; Brereton, M.F.; Tarasov, A.I.; Blacker, T.S.; Sachse, G.; Dos Santos, M.S.; Exposito, R.T.; Davis, S.; et al. Diabetes causes marked inhibition of mitochondrial metabolism in pancreatic β-cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Upshaw, L.; Strong, D.M.; Robertson, R.P.; Reems, J. Increased oxygen consumption rates in response to high glucose detected by a novel oxygen biosensor system in non-human primate and human islets. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, L.J.; van de Bunt, M.; Braun, M.; Frayn, K.N.; Clark, A.; Gloyn, A.L. GLUT2 (SLC2A2) is not the principal glucose transporter in human pancreatic beta cells: Implications for understanding genetic association signals at this locus. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, K.; Takamatsu, S.; Minowa, M.T.; Yoshida, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Marth, J.D. Dietary and Genetic Control of Glucose Transporter 2 Glycosylation Promotes Insulin Secretion in Suppressing Diabetes. Cell 2005, 123, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raum, J.C.; Gerrish, K.; Artner, I.; Henderson, E.; Guo, M.; Sussel, L.; Schisler, J.; Newgard, C.B.; Stein, R. FoxA2, Nkx2.2, and PDX-1 Regulate Islet β-Cell-Specific mafA Expression through Conserved Sequences Located between Base Pairs −8118 and −7750 Upstream from the Transcription Start Site. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 5735–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, G.C.; Sharma, A.; Zangen, D.H.; Bonner-Weir, S. Transcription factor abnormalities as a cause of beta cell dysfunction in diabetes: A hypothesis. Acta Diabetol. 1997, 34, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, U.; Jonsson, J.; Jonsson, L.; Simu, K.; Edlund, H. β-Cell-specific inactivation of the mouseIpf1/Pdx1 gene results in loss of the β-cell phenotype and maturity onset diabetes. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, T.-A.; Artner, I.; Henderson, E.; Means, A.; Sander, M.; Stein, R. The MafA transcription factor appears to be responsible for tissue-specific expression of insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2930–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.-A.; Zhao, L.; Artner, I.; Jarrett, H.W.; Friedman, D.; Means, A.; Stein, R. Members of the Large Maf Transcription Family Regulate Insulin Gene Transcription in Islet β Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 6049–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaras, S.E.; Zhao, L.; Means, A.; Henderson, E.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Stein, R. The Islet beta Cell-enriched RIPE3b1/Maf Transcription Factor Regulates pdx-1 Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12263–12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunton, J.E.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Yim, S.; Okada, T.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Roberson, R.S.; Ricordi, C.; O’Connell, P.J.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. Loss of ARNT/HIF1β Mediates Altered Gene Expression and Pancreatic-Islet Dysfunction in Human Type 2 Diabetes. Cell 2005, 122, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norquay, L.D.; D’Aquino, K.E.; Opare-Addo, L.M.; Kuznetsova, A.; Haas, M.; Bluestone, J.A.; White, M.F. Insulin Receptor Substrate-2 in β-Cells Decreases Diabetes in Nonobese Diabetic Mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4531–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Alejandro, E.; Han, Z.; Kalynyak, T.B.; Li, H.; Beith, J.L.; Gross, J.; Warnock, G.L.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Insulin protects islets from apoptosis via Pdx1 and specific changes in the human islet proteome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19575–19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, Ó.; Gomez-Hernandez, A.; Diaz-Castroverde, S.; Nevado, C.; García, G.; Otero, Y.F.; Perdomo, L.; Beneit, N.; Benito, M. Insulin receptor isoform A confers a higher proliferative capability to pancreatic beta cells enabling glucose availability and IGF-I signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 409, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin Receptor Signaling in Normal and Insulin-Resistant States. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.D.; Dula, S.B.; Corbin, K.L.; Wu, R.; Nunemaker, C.S. A Practical Guide to Rodent Islet Isolation and Assessment. Biol. Proced. Online 2009, 11, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardooz, H.; Asl, S.Z.; Naseri, M.G. Effect of chronic psychological stress on insulin release from rat isolated pancreatic islets. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardooz, H.; Zahediasl, S.; Rostamkhani, F.; Farrokhi, B.; Nasiraei, S.; Kazeminezhad, B.; Gholampour, R. Effects of acute and chronic psychological stress on isolated islets’ insulin release. EXCLI J. 2012, 11, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, S.M.; Page, L.C.; Tong, J. Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. J. Neuroendocr. 2019, 31, e12705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Fiori, J.L.; Shin, Y.-K.; Okun, E.; Kim, J.S.; Rapp, P.R.; Egan, J.M. Pancreatic polypeptide inhibits somatostatin secretion. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3233–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, Y.L.; Kwon, H.Y. Effects of pancreatic polypeptide on insulin action in exocrine secretion of isolated rat pancreas. J. Physiol. 1993, 463, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egido, E.M.; Rodriguez-Gallardo, J.; Silvestre, R.A.; Marco, J. Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on insulin and pancreatic somatostatin secretion. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 146, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, B.K.; Shankar, K.; Zigman, J.M. Ghrelin’s Relationship to Blood Glucose. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, A.M.; Small, C.J.; Ward, H.L.; Murphy, K.G.; Dakin, C.L.; Taheri, S.; Kennedy, A.R.; Roberts, G.H.; Morgan, D.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. The novel hypothalamic peptide ghrelin stimulates food intake and growth hormone secretion. Endocrinology 2020, 14, 4325–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, M.; Ronchi, C.L.; Gebbia, C.; Cappiello, V.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; Peracchi, M. Stimulatory Effects of Ghrelin on Circulating Somatostatin and Pancreatic Polypeptide Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.C.; Bauchle, C.J.; Rouault, A.A.; Stephens, S.B.; Sebag, J.A. The Insulinostatic Effect of Ghrelin Requires MRAP2 Expression in δ Cells. Iscience 2020, 23, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldanzi, G.; Filigheddu, N.; Cutrupi, S.; Catapano, F.; Bonissoni, S.; Fubini, A.; Malan, D.; Baj, G.; Granata, R.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.; Gill, D.A.S.; Davies, R.; Loveridge, N.; Houston, P.A.; Robinson, I.C.A.F.; Wells, T. Ghrelin and Des-Octanoyl Ghrelin Promote Adipogenesis Directly in Vivo by a Mechanism Independent of the Type 1a Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhanty, P.J.D.; van der Eerden, B.; Van Der Velde, M.; Gauna, C.; Pols, H.A.P.; Jahr, H.; Chiba, H.; Van Der Lely, A.J.; Van Leeuwen, J.P.T.M. Ghrelin and unacylated ghrelin stimulate human osteoblast growth via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways in the absence of GHS-R1a. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 188, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meulen, T.; Donaldson, C.J.; Caceres, E.; Hunter, A.E.; Cowing-Zitron, C.; Pound, L.D.; Adams, M.W.; Zembrzycki, A.; Grove, K.L.; Huising, M.O. Urocortin3 mediates somatostatin-dependent negative feedback control of insulin secretion. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K.; Takemi, S.; Gupta, D.; Varshney, S.; Mani, B.K.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Metzger, N.P.; Richard, C.P.; Berglund, E.D.; Zigman, J.M. Ghrelin cell-expressed insulin receptors mediate meal- and obesity-induced declines in plasma ghrelin. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e146983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pradhan, G.; Lee, J.H.; Wu, C.-S.; Wang, H.; Lin, L.; Donti, T.; Graham, B.H.; Rajan, A.S.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Samson, S.L.; et al. Mechanistic Investigation of GHS-R Mediated Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030407
Pradhan G, Lee JH, Wu C-S, Wang H, Lin L, Donti T, Graham BH, Rajan AS, Balasubramanyam A, Samson SL, et al. Mechanistic Investigation of GHS-R Mediated Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(3):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030407
Chicago/Turabian StylePradhan, Geetali, Jong Han Lee, Chia-Shan Wu, Hongying Wang, Ligen Lin, Taraka Donti, Brett H. Graham, Arun S. Rajan, Ashok Balasubramanyam, Susan L. Samson, and et al. 2022. "Mechanistic Investigation of GHS-R Mediated Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets" Biomolecules 12, no. 3: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030407
APA StylePradhan, G., Lee, J. H., Wu, C.-S., Wang, H., Lin, L., Donti, T., Graham, B. H., Rajan, A. S., Balasubramanyam, A., Samson, S. L., Guo, S., & Sun, Y. (2022). Mechanistic Investigation of GHS-R Mediated Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets. Biomolecules, 12(3), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030407







