RT-QuIC and Related Assays for Detecting and Quantifying Prion-like Pathological Seeds of α-Synuclein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Potential of αSynD
3. SAAs for Detecting Pathological Prion Aggregates
4. SAAs for Detecting αSyn Aggregates
5. Detection of αSynD Seeds in Peripheral Tissues
6. Prodromal and Early-Stage Detection of αSynD Seeds by RT-QuIC
7. Detecting αSynD Seeds in MSA Biospecimens
8. Detection of αSynD in Familial Variants of Synucleinopathy
9. Attempts to Correlate αSyn SAA Results with Clinical Measures
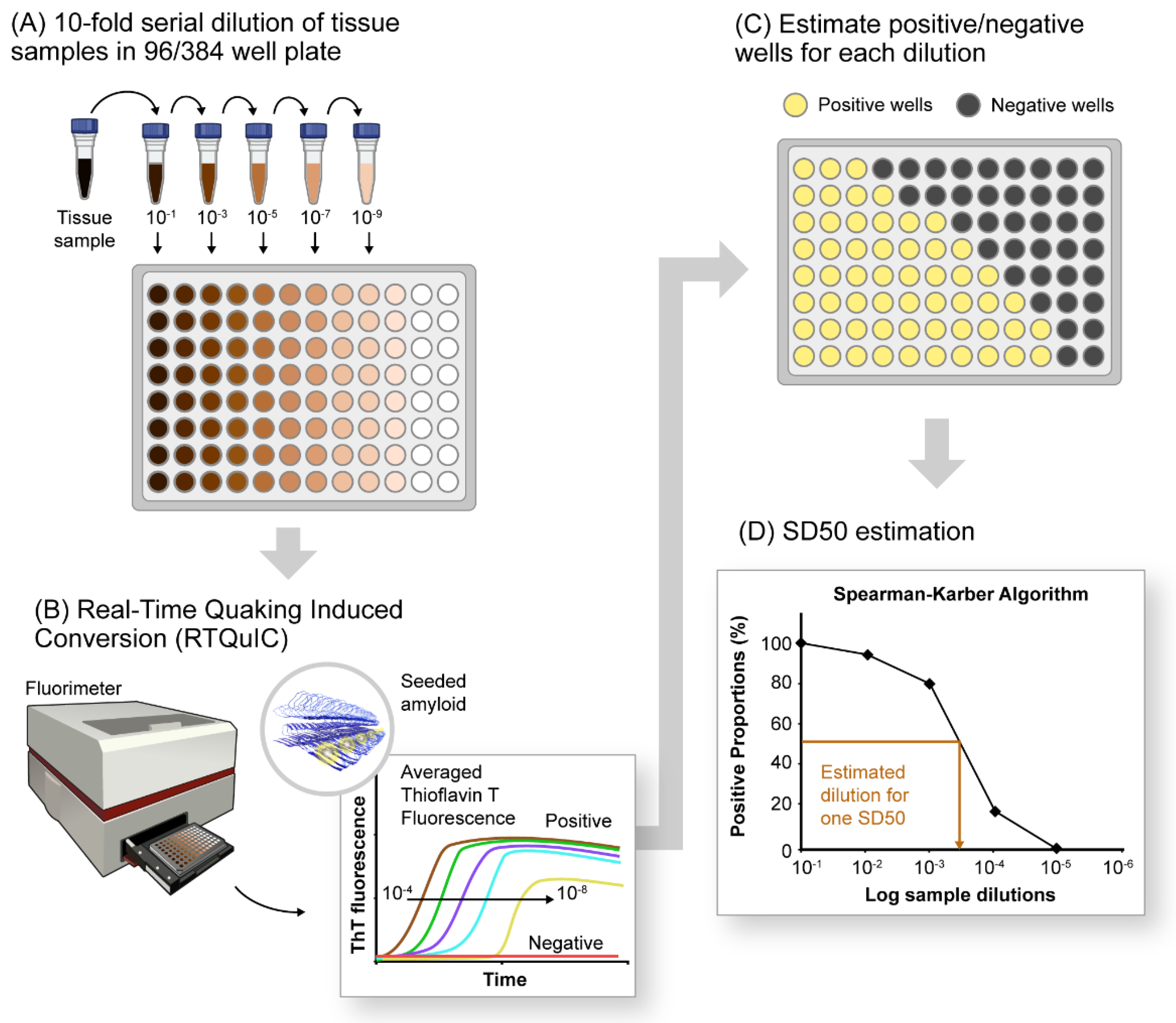
10. Quantification of αSynD Seeds Using RT-QuIC
11. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koga, S.; Sekiya, H.; Kondru, N.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of Synucleinopathies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burre, J.; Vivona, S.; Diao, J.; Sharma, M.; Brunger, A.T.; Sudhof, T.C. Properties of native brain α-synuclein. Nature 2013, 498, E4–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, S.; Sahay, S.; Maji, S.K. α-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation: Implications in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 890–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullman, O.; Fisher, C.K.; Stultz, C.M. Explaining the structural plasticity of α-synuclein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19536–19546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulic, S.; Le, T.T.; Moda, F.; Abounit, S.; Corvaglia, S.; Casalis, L.; Gustincich, S.; Zurzolo, C.; Tagliavini, F.; Legname, G. Defined α-synuclein prion-like molecular assemblies spreading in cell culture. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarutani, A.; Arai, T.; Murayama, S.; Hisanaga, S.I.; Hasegawa, M. Potent prion-like behaviors of pathogenic α-synuclein and evaluation of inactivation methods. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundin, P.; Melki, R.; Kopito, R. Prion-like transmission of protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Rub, U.; Bratzke, H.; Del Tredici, K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, Z.; Englund, E.; Widner, H.; Lindvall, O.; Li, J.Y.; Brundin, P. Signs of degeneration in 12–22-year old grafts of mesencephalic dopamine neurons in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2011, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angot, E.; Steiner, J.A.; Lema Tome, C.M.; Ekstrom, P.; Mattsson, B.; Bjorklund, A.; Brundin, P. α-Synuclein cell-to-cell transfer and seeding in grafted dopaminergic neurons in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Luk, K.C.; Patel, T.P.; Tanik, S.A.; Riddle, D.M.; Stieber, A.; Meaney, D.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 2011, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luk, K.C.; Kehm, V.; Carroll, J.; Zhang, B.; O’Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 2012, 338, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Covell, D.J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R.M.; Olufemi, M.F.; Luk, K.C.; et al. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, S.H.; Kam, T.I.; Panicker, N.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.R.; Kook, M.; Foss, C.A.; et al. Transneuronal Propagation of Pathologic α-synuclein from the Gut to the Brain Models Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron 2019, 103, 627–641.e627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, S.; Chutna, O.; Bousset, L.; Aldrin-Kirk, P.; Li, W.; Bjorklund, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Roybon, L.; Melki, R.; Li, J.Y. Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uemura, N.; Yagi, H.; Uemura, M.T.; Hatanaka, Y.; Yamakado, H.; Takahashi, R. Inoculation of α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces Lewy body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Challis, C.; Hori, A.; Sampson, T.R.; Yoo, B.B.; Challis, R.C.; Hamilton, A.M.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Gradinaru, V. Gut-seeded α-synuclein fibrils promote gut dysfunction and brain pathology specifically in aged mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerman, A.L.; Stohr, J.; Aoyagi, A.; Rampersaud, R.; Krejciova, Z.; Watts, J.C.; Ohyama, T.; Patel, S.; Widjaja, K.; Oehler, A.; et al. Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2015, 112, E4949–E4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for α-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woerman, A.L.; Patel, S.; Kazmi, S.A.; Oehler, A.; Lee, J.; Mordes, D.A.; Olson, S.H.; Prusiner, S.B. Kinetics of α-synuclein prions preceding neuropathological inclusions in multiple system atrophy. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woerman, A.L.; Oehler, A.; Kazmi, S.A.; Lee, J.; Halliday, G.M.; Middleton, L.T.; Gentleman, S.M.; Mordes, D.A.; Spina, S.; Grinberg, L.T.; et al. Multiple system atrophy prions retain strain specificity after serial propagation in two different Tg(SNCA*A53T) mouse lines. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, M.D.; Comellas, G.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Covell, D.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Kloepper, K.D.; Courtney, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Barclay, A.M.; Kendall, A.; et al. Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human α-synuclein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, D.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Stahlberg, H.; Melki, R. Cryo-EM structure of α-synuclein fibrils amplified by PMCA from PD and MSA patient brains. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Lauer, M.E.; Riek, R.; Britschgi, M.; Stahlberg, H. Cryo-EM structure of α-synuclein fibrils. Elife 2018, 7, e36402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec, S.A.M.; Woerman, A.L. Evidence of distinct α-synuclein strains underlying disease heterogeneity. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohaker, T.; Jung, B.C.; Liou, S.H.; Fernandez, C.O.; Riedel, D.; Becker, S.; Halliday, G.M.; Bennati, M.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Structural heterogeneity of α-synuclein fibrils amplified from patient brain extracts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, M.J.; Orru, C.D.; Concha-Marambio, L.; Giaisi, S.; Groveman, B.R.; Farris, C.M.; Holguin, B.; Hughson, A.G.; LaFontant, D.E.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; et al. High diagnostic performance of independent α-synuclein seed amplification assays for detection of early Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfoul, G.; McGuire, L.I.; Pal, S.; Ironside, J.W.; Neumann, J.; Christie, S.; Joachim, C.; Esiri, M.; Evetts, S.G.; Rolinski, M.; et al. α-Synuclein RT-QuIC in the CSF of patients with α-synucleinopathies. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groveman, B.R.; Orru, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Raymond, L.D.; Zanusso, G.; Ghetti, B.; Campbell, K.J.; Safar, J.; Galasko, D.; Caughey, B. Rapid and ultra-sensitive quantitation of disease-associated α-synuclein seeds in brain and cerebrospinal fluid by alphaSyn RT-QuIC. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Tokuda, T.; Waragai, M.; Mendez, N.; Ishii, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Soto, C. Development of a Biochemical Diagnosis of Parkinson Disease by Detection of α-Synuclein Misfolded Aggregates in Cerebrospinal Fluid. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.K.; Low, P.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.W.; Colosimo, C.; Durr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucetti, C.; Logi, C.; Del Dotto, P.; Berti, C.; Ceravolo, R.; Baldacci, F.; Dolciotti, C.; Gambaccini, G.; Rossi, G.; Bonuccelli, U. Levodopa response in dementia with lewy bodies: A 1-year follow-up study. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Dickson, D.W.; Lowe, J.; Emre, M.; O’Brien, J.T.; Feldman, H.; Cummings, J.; Duda, J.E.; Lippa, C.; Perry, E.K.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2005, 65, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Muller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geschwind, M.D.; Murray, K. Differential diagnosis with other rapid progressive dementias in human prion diseases. Handb Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerr, I.; Hermann, P. Diagnostic challenges in rapidly progressive dementia. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2018, 18, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, G.; Fabbrini, A.; Suppa, A. Progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple system atrophy and corticobasal degeneration. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 165, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, M.B.; Esselink, R.A.; Abdo, W.F.; Meijer, F.J.; Drost, G.; Norgren, N.; Janssen, M.J.; Borm, G.F.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. Ancillary investigations to diagnose parkinsonism: A prospective clinical study. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, A.; Fairfoul, G.; Ayudhaya, A.C.N.; Serradell, M.; Gelpi, E.; Vilaseca, I.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Gaig, C.; Santamaria, J.; Tolosa, E.; et al. Detection of α-synuclein in CSF by RT-QuIC in patients with isolated rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: A longitudinal observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, U.J.; Boehme, A.K.; Fairfoul, G.; Shahnawaz, M.; Ma, T.C.; Hutten, S.J.; Green, A.; Soto, C. Comparative study of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein seeding aggregation assays for diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rumund, A.; Green, A.J.E.; Fairfoul, G.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. α-Synuclein real-time quaking-induced conversion in the cerebrospinal fluid of uncertain cases of parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bongianni, M.; Ladogana, A.; Capaldi, S.; Klotz, S.; Baiardi, S.; Cagnin, A.; Perra, D.; Fiorini, M.; Poleggi, A.; Legname, G.; et al. α-Synuclein RT-QuIC assay in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.M.G.; Elia, A.E.; Portaleone, S.M.; Cazzaniga, F.A.; Rossi, M.; Bistaffa, E.; De Cecco, E.; Narkiewicz, J.; Salzano, G.; Carletta, O.; et al. Efficient RT-QuIC seeding activity for α-synuclein in olfactory mucosa samples of patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Baiardi, S.; Teunissen, C.E.; Quadalti, C.; van de Beek, M.; Mammana, A.; Maserati, M.S.; Van der Flier, W.M.; Sambati, L.; Zenesini, C.; et al. Diagnostic Value of the CSF α-Synuclein Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion Assay at the Prodromal MCI Stage of Dementia With Lewy Bodies. Neurology 2021, 97, e930–e940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, G.J.; Hope, J.; Kocisko, D.A.; Priola, S.A.; Raymond, L.D.; Bossers, A.; Ironside, J.; Will, R.G.; Chen, S.G.; Petersen, R.B.; et al. Molecular assessment of the transmissibilities of BSE and scrapie to humans. Nature 1997, 388, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocisko, D.A.; Priola, S.A.; Raymond, G.J.; Chesebro, B.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr.; Caughey, B. Species specificity in the cell-free conversion of prion protein to protease-resistant forms: A model for the scrapie species barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3923–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessen, R.A.; Kocisko, D.A.; Raymond, G.J.; Nandan, S.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr.; Caughey, B. Nongenetic propagation of strain-specific phenotypes of scrapie prion protein. Nature 1995, 375, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocisko, D.A.; Come, J.H.; Priola, S.A.; Chesebro, B.; Raymond, G.J.; Lansbury, P.T.; Caughey, B. Cell-free formation of protease-resistant prion protein. Nature 1994, 370, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, G.J.; Bossers, A.; Raymond, L.D.; O’Rourke, K.I.; McHolland, L.E.; Bryant, P.K., III; Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S.; Smits, M.; Caughey, B. Evidence of a molecular barrier limiting susceptibility of humans, cattle and sheep to chronic wasting disease. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4425–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bossers, A.; Belt, P.B.G.M.; Raymond, G.J.; Caughey, B.; de Vries, R.; Smits, M.A. Scrapie susceptibility-linked polymorphisms modulate the in vitro conversion of sheep prion protein to protease-resistant forms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4931–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castilla, J.; Saa, P.; Hetz, C.; Soto, C. In vitro generation of infectious scrapie prions. Cell 2005, 121, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saborio, G.P.; Permanne, B.; Soto, C. Sensitive detection of pathological prion protein by cyclic amplification of protein misfolding. Nature 2001, 411, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saa, P.; Castilla, J.; Soto, C. Ultra-efficient replication of infectious prions by automated protein misfolding cyclic amplification. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35245–35252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colby, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Groth, D.; Legname, G.; Riesner, D.; Prusiner, S.B. Prion detection by an amyloid seeding assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20914–20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atarashi, R.; Satoh, K.; Sano, K.; Fuse, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ishibashi, D.; Matsubara, T.; Nakagaki, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Shirabe, S.; et al. Ultrasensitive human prion detection in cerebrospinal fluid by real-time quaking-induced conversion. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilham, J.M.; Orrú, C.D.; Bessen, R.A.; Atarashi, R.; Sano, K.; Race, B.; Meade-White, K.D.; Taubner, L.M.; Timmes, A.; Caughey, B. Rapid End-Point Quantitation of Prion Seeding Activity with Sensitivity Comparable to Bioassays. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raymond, G.J.; Race, B.; Orru, C.D.; Raymond, L.D.; Bongianni, M.; Fiorini, M.; Groveman, B.R.; Ferrari, S.; Sacchetto, L.; Hughson, A.G.; et al. Transmission of CJD from nasal brushings but not spinal fluid or RT-QuIC product. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Raymond, L.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Nonno, R.; Zou, W.; Ghetti, B.; Gambetti, P.; Caughey, B. Bank Vole Prion Protein As an Apparently Universal Substrate for RT-QuIC-Based Detection and Discrimination of Prion Strains. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, R.; Wilham, J.M.; Christensen, L.; Hughson, A.G.; Moore, R.A.; Johnson, L.M.; Onwubiko, H.A.; Priola, S.A.; Caughey, B. Simplified ultrasensitive prion detection by recombinant PrP conversion with shaking. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, R.; Moore, R.A.; Sim, V.L.; Hughson, A.G.; Dorward, D.W.; Onwubiko, H.A.; Priola, S.A.; Caughey, B. Ultrasensitive detection of scrapie prion protein using seeded conversion of recombinant prion protein. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, L.I.; Peden, A.H.; Orru, C.D.; Wilham, J.M.; Appleford, N.E.; Mallinson, G.; Andrews, M.; Head, M.W.; Caughey, B.; Will, R.G.; et al. RT-QuIC analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orru, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Hughson, A.G.; Zanusso, G.; Coulthart, M.B.; Caughey, B. Rapid and sensitive RT-QuIC detection of human Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease using cerebrospinal fluid. MBio 2015, 6, e02451-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foutz, A.; Appleby, B.S.; Hamlin, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Cohen, Y.; Chen, W.; Blevins, J.; Fausett, C.; Wang, H.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of human prion detection in cerebrospinal fluid. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Baiardi, S.; Hughson, A.G.; McKenzie, N.; Moda, F.; Rossi, M.; Capellari, S.; Green, A.; Giaccone, G.; Caughey, B.; et al. High diagnostic value of second generation CSF RT-QuIC across the wide spectrum of CJD prions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Manca, M.; Foutz, A.; Camacho, M.V.; Raymond, G.J.; Race, B.; Orru, C.D.; Yuan, J.; Shen, P.; Li, B.; et al. Early preclinical detection of prions in the skin of prion-infected animals. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, C.D.; Yuan, J.; Appleby, B.S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Winner, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, Y.A.; Rodgers, M.; Rarick, J.; et al. Prion seeding activity and infectivity in skin samples from patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mammana, A.; Baiardi, S.; Rossi, M.; Franceschini, A.; Donadio, V.; Capellari, S.; Caughey, B.; Parchi, P. Detection of prions in skin punch biopsies of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, C.D.; Soldau, K.; Cordano, C.; Llibre-Guerra, J.; Green, A.J.; Sanchez, H.; Groveman, B.R.; Edland, S.D.; Safar, J.G.; Lin, J.H.; et al. Prion Seeds Distribute throughout the Eyes of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Patients. MBio 2018, 9, e02095-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orru, C.D.; Bongianni, M.; Tonoli, G.; Ferrari, S.; Hughson, A.G.; Groveman, B.R.; Fiorini, M.; Pocchiari, M.; Monaco, S.; Caughey, B.; et al. A test for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease using nasal brushings. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bongianni, M.; Orrù, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Sacchetto, L.; Fiorini, M.; Tonoli, G.; Triva, G.; Capaldi, S.; Testi, S.; Ferrari, S.; et al. Diagnosis of Human Prion Disease Using Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion Testing of Olfactory Mucosa and Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orru, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Foutz, A.; Bongianni, M.; Cardone, F.; McKenzie, N.; Culeux, A.; Poleggi, A.; Grznarova, K.; Perra, D.; et al. Ring trial of 2nd generation RT-QuIC diagnostic tests for sporadic CJD. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, A.V.; McNulty, E.E.; Mayfield, A.; Crum, J.M.; Keel, M.K.; Hoover, E.A.; Ruder, M.G.; Mathiason, C.K. Detection of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions in Fetal Tissues of Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer. Viruses 2021, 13, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, A.V.; McNulty, E.; Hoover, C.E.; Pulscher, L.A.; Hoover, E.A.; Mathiason, C.K. Infectious Prions in the Pregnancy Microenvironment of Chronic Wasting Disease-Infected Reeves’ Muntjac Deer. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00501-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selariu, A.; Powers, J.G.; Nalls, A.; Brandhuber, M.; Mayfield, A.; Fullaway, S.; Wyckoff, C.A.; Goldmann, W.; Zabel, M.M.; Wild, M.A.; et al. In utero transmission and tissue distribution of chronic wasting disease-associated prions in free-ranging Rocky Mountain elk. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3444–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Morales, R.; Barria, M.A.; Soto, C. Estimating prion concentration in fluids and tissues by quantitative PMCA. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orru, C.D.; Wilham, J.M.; Raymond, L.D.; Kuhn, F.; Schroeder, B.; Raeber, A.J.; Caughey, B. Prion disease blood test using immunoprecipitation and improved quaking-induced conversion. mBio 2011, 2, e00078-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, R.; Duran-Aniotz, C.; Diaz-Espinoza, R.; Camacho, M.V.; Soto, C. Protein misfolding cyclic amplification of infectious prions. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha-Marambio, L.; Pritzkow, S.; Moda, F.; Tagliavini, F.; Ironside, J.W.; Schulz, P.E.; Soto, C. Detection of prions in blood from patients with variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 370ra183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, B.C.; Lim, Y.J.; Bae, E.J.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.J. Amplification of distinct α-synuclein fibril conformers through protein misfolding cyclic amplification. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herva, M.E.; Zibaee, S.; Fraser, G.; Barker, R.A.; Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. Anti-amyloid compounds inhibit α-synuclein aggregation induced by protein misfolding cyclic amplification (PMCA). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11897–11905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, M.; Candelise, N.; Baiardi, S.; Capellari, S.; Giannini, G.; Orru, C.D.; Antelmi, E.; Mammana, A.; Hughson, A.G.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; et al. Ultrasensitive RT-QuIC assay with high sensitivity and specificity for Lewy body-associated synucleinopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargar, C.; Wang, W.; Gunzler, S.A.; LeFevre, A.; Wang, Z.; Lerner, A.J.; Singh, N.; Tatsuoka, C.; Appleby, B.; Zhu, X.; et al. Streamlined α-synuclein RT-QuIC assay for various biospecimens in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelise, N.; Schmitz, M.; Llorens, F.; Villar-Pique, A.; Cramm, M.; Thom, T.; da Silva Correia, S.M.; da Cunha, J.E.G.; Mobius, W.; Outeiro, T.F.; et al. Seeding variability of different alpha synuclein strains in synucleinopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggiolini, I.; Erskine, D.; Vaikath, N.N.; Ponraj, J.; Mansour, S.; Morris, C.M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. RT-QuIC Using C-Terminally Truncated α-Synuclein Forms Detects Differences in Seeding Propensity of Different Brain Regions from Synucleinopathies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.I.; Lee, J.; Monteiro, O.; Woerman, A.L.; Lazar, A.A.; Condello, C.; Paras, N.A.; Prusiner, S.B. Different α-synuclein prion strains cause dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113489119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweighauser, M.; Shi, Y.; Tarutani, A.; Kametani, F.; Murzin, A.G.; Ghetti, B.; Matsubara, T.; Tomita, T.; Ando, T.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 585, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Luo, F.; Liu, Z.; Gui, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Li, X. Amyloid fibril structure of α-synuclein determined by cryo-electron microscopy. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Ge, P.; Murray, K.A.; Sheth, P.; Zhang, M.; Nair, G.; Sawaya, M.R.; Shin, W.S.; Boyer, D.R.; Ye, S.; et al. Cryo-EM of full-length α-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, D.R.; Li, B.; Sun, C.; Fan, W.; Sawaya, M.R.; Jiang, L.; Eisenberg, D.S. Structures of fibrils formed by α-synuclein hereditary disease mutant H50Q reveal new polymorphs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, S.; Uchihara, T.; Nakamura, A.; Mori, F.; Kakita, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H. Axonal α-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2008, 131, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donadio, V.; Incensi, A.; Del Sorbo, F.; Rizzo, G.; Infante, R.; Scaglione, C.; Modugno, N.; Fileccia, E.; Elia, A.E.; Cencini, F.; et al. Skin Nerve Phosphorylated α-synuclein Deposits in Parkinson Disease With Orthostatic Hypotension. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Vedders, L.; Lue, L.; White Iii, C.L.; Akiyama, H.; Caviness, J.N.; Shill, H.A.; Sabbagh, M.N.; et al. Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated α-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Gibbons, C.H.; Lafo, J.; Freeman, R. α-Synuclein in cutaneous autonomic nerves. Neurology 2013, 81, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stokholm, M.G.; Danielsen, E.H.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.J.; Borghammer, P. Pathological α-synuclein in gastrointestinal tissues from prodromal Parkinson disease patients. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, F.; Carletti, R.; Fusconi, M.; Pellicano, C.; Pontieri, F.E.; Di Gioia, C.R.; de Vincentiis, M. α-Synuclein in salivary gland as biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manne, S.; Kondru, N.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Huang, X.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. α-Synuclein real-time quaking-induced conversion in the submandibular glands of Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, S.; Kondru, N.; Jin, H.; Serrano, G.E.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.; Adler, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Blinded RT-QuIC Analysis of α-Synuclein Biomarker in Skin Tissue From Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 2230–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Becker, K.; Donadio, V.; Siedlak, S.; Yuan, J.; Rezaee, M.; Incensi, A.; Kuzkina, A.; Orru, C.D.; Tatsuoka, C.; et al. Skin α-Synuclein Aggregation Seeding Activity as a Novel Biomarker for Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammana, A.; Baiardi, S.; Quadalti, C.; Rossi, M.; Donadio, V.; Capellari, S.; Liguori, R.; Parchi, P. RT-QuIC Detection of Pathological α-Synuclein in Skin Punches of Patients with Lewy Body Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2173–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzkina, A.; Bargar, C.; Schmitt, D.; Rossle, J.; Wang, W.; Schubert, A.L.; Tatsuoka, C.; Gunzler, S.A.; Zou, W.Q.; Volkmann, J.; et al. Diagnostic value of skin RT-QuIC in Parkinson’s disease: A two-laboratory study. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadio, V.; Wang, Z.; Incensi, A.; Rizzo, G.; Fileccia, E.; Vacchiano, V.; Capellari, S.; Magnani, M.; Scaglione, C.; Stanzani Maserati, M.; et al. In Vivo Diagnosis of Synucleinopathies: A Comparative Study of Skin Biopsy and RT-QuIC. Neurology 2021, 96, e2513–e2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerstad, M.D.; Boeve, B.; Wentzel-Larsen, T.; Aarsland, D.; Larsen, J.P. Occurrence and clinical correlates of REM sleep behaviour disorder in patients with Parkinson’s disease over time. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeve, B.F.; Silber, M.H.; Ferman, T.J.; Lucas, J.A.; Parisi, J.E. Association of REM sleep behavior disorder and neurodegenerative disease may reflect an underlying synucleinopathy. Mov. Disord. 2001, 16, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.A.; Fernandez-Cordon, C.; Coon, E.A.; Low, P.A.; Miglis, M.G.; Jaradeh, S.; Bhaumik, A.K.; Dayalu, P.; Urrestarazu, E.; Iriarte, J.; et al. Prevalence of REM sleep behavior disorder in multiple system atrophy: A multicenter study and meta-analysis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2015, 25, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazzi, G.; Corsini, R.; Provini, F.; Pierangeli, G.; Martinelli, P.; Montagna, P.; Lugaresi, E.; Cortelli, P. REM sleep behavior disorders in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 1997, 48, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, D.; Bindman, D.; Nesbitt, A.D.; Cash, D.; Milosevic, M.; Francis, P.T.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Leschziner, G.D.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Ballard, C.; et al. Striatal Dopaminergic Deficit and Sleep in Idiopathic Rapid Eye Movement Behaviour Disorder: An Explorative Study. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2021, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, M.; Zucchella, C.; Rustioni, V.; Sinforiani, E.; Manni, R. Cognitive performances and mild cognitive impairment in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: Results of a longitudinal follow-up study. Sleep 2013, 36, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youn, S.; Kim, T.; Yoon, I.Y.; Jeong, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, K.W. Progression of cognitive impairments in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coon, E.A.; Singer, W.; Low, P.A. Pure Autonomic Failure. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-Velasquez, J.J.; Flores-Vazquez, J.F.; Barron-Velazquez, E.; Sosa-Ortiz, A.L.; Illigens, B.W.; Siepmann, T. Autonomic Dysfunction in α-Synucleinopathies. Front Neurol. 2019, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barone, D.A.; Henchcliffe, C. Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and the link to α-synucleinopathies. Clin. Neurophysiol 2018, 129, 1551–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coon, E.A.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Berini, S.E.; Benarroch, E.E.; Sandroni, P.; Low, P.A.; Singer, W. Predicting phenoconversion in pure autonomic failure. Neurology 2020, 95, e889–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, A.; Iranzo, A.; Holzknecht, E.; Perra, D.; Bongianni, M.; Gaig, C.; Heim, B.; Serradell, M.; Sacchetto, L.; Garrido, A.; et al. α-Synuclein seeds in olfactory mucosa of patients with isolated REM sleep behaviour disorder. Brain 2021, 144, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perra, D.; Bongianni, M.; Novi, G.; Janes, F.; Bessi, V.; Capaldi, S.; Sacchetto, L.; Tagliapietra, M.; Schenone, G.; Morbelli, S.; et al. α-Synuclein seeds in olfactory mucosa and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, C.D.; Ma, T.C.; Hughson, A.G.; Groveman, B.R.; Srivastava, A.; Galasko, D.; Angers, R.; Downey, P.; Crawford, K.; Hutten, S.J.; et al. A rapid α-synuclein seed assay of Parkinson’s disease CSF panel shows high diagnostic accuracy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadalti, C.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; Baiardi, S.; Mastrangelo, A.; Rossi, M.; Zenesini, C.; Giannini, G.; Candelise, N.; Sambati, L.; Polischi, B.; et al. Neurofilament light chain and α-synuclein RT-QuIC as differential diagnostic biomarkers in parkinsonisms and related syndromes. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, B.; Constantinescu, R.; Freeman, R.; Gerhard, A.; Jellinger, K.; Jeromin, A.; Krismer, F.; Mollenhauer, B.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Shaw, L.M.; et al. Fluid biomarkers in multiple system atrophy: A review of the MSA Biomarker Initiative. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 80, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Potential clinical utility of multiple system atrophy biomarkers. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 1189–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia Guedes, L.; Mestre, T.; Outeiro, T.F.; Ferreira, J.J. Are genetic and idiopathic forms of Parkinson’s disease the same disease? J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orme, T.; Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J. The Genetics of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Koss, D.J.; Erskine, D.; Walker, L.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Burn, D.; Donaghy, P.; Morris, C.; Taylor, J.P.; Thomas, A.; et al. Dementia with Lewy bodies: An update and outlook. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.; Fairfoul, G.; Tolosa, E.S.; Marti, M.J.; Green, A.; Barcelona, L.S.G. α-Synuclein RT-QuIC in cerebrospinal fluid of LRRK2-linked Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brockmann, K.; Quadalti, C.; Lerche, S.; Rossi, M.; Wurster, I.; Baiardi, S.; Roeben, B.; Mammana, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Hauser, A.K.; et al. Association between CSF α-Synuclein seeding activity and genetic status in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlmutter, J.S. Assessment of Parkinson disease manifestations. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2009, 49, 10.1.1–10.1.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manne, S.; Kondru, N.; Hepker, M.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Lewis, M.; Huang, X.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Ultrasensitive Detection of Aggregated α-Synuclein in Glial Cells, Human Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Brain Tissue Using the RT-QuIC Assay: New High-Throughput Neuroimmune Biomarker Assay for Parkinsonian Disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, R.M. Animal virus titration techniques. In Techniques in Experimental Virology; Harris, R.J.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, K.; Atarashi, R.; Satoh, K.; Ishibashi, D.; Nakagaki, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Murayama, S.; Mishima, K.; Nishida, N. Prion-Like Seeding of Misfolded α-Synuclein in the Brains of Dementia with Lewy Body Patients in RT-QUIC. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 55, 3916–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokratian, A.; Ziaee, J.; Kelly, K.; Chang, A.; Bryant, N.; Wang, S.; Xu, E.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Ervin, J.; et al. Heterogeneity in α-synuclein fibril activity correlates to disease phenotypes in Lewy body dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srivastava, A.; Alam, P.; Caughey, B. RT-QuIC and Related Assays for Detecting and Quantifying Prion-like Pathological Seeds of α-Synuclein. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040576
Srivastava A, Alam P, Caughey B. RT-QuIC and Related Assays for Detecting and Quantifying Prion-like Pathological Seeds of α-Synuclein. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrivastava, Ankit, Parvez Alam, and Byron Caughey. 2022. "RT-QuIC and Related Assays for Detecting and Quantifying Prion-like Pathological Seeds of α-Synuclein" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040576
APA StyleSrivastava, A., Alam, P., & Caughey, B. (2022). RT-QuIC and Related Assays for Detecting and Quantifying Prion-like Pathological Seeds of α-Synuclein. Biomolecules, 12(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040576





