Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Anti-Pyroglu3 Abeta Antibody Delivery and Immune Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
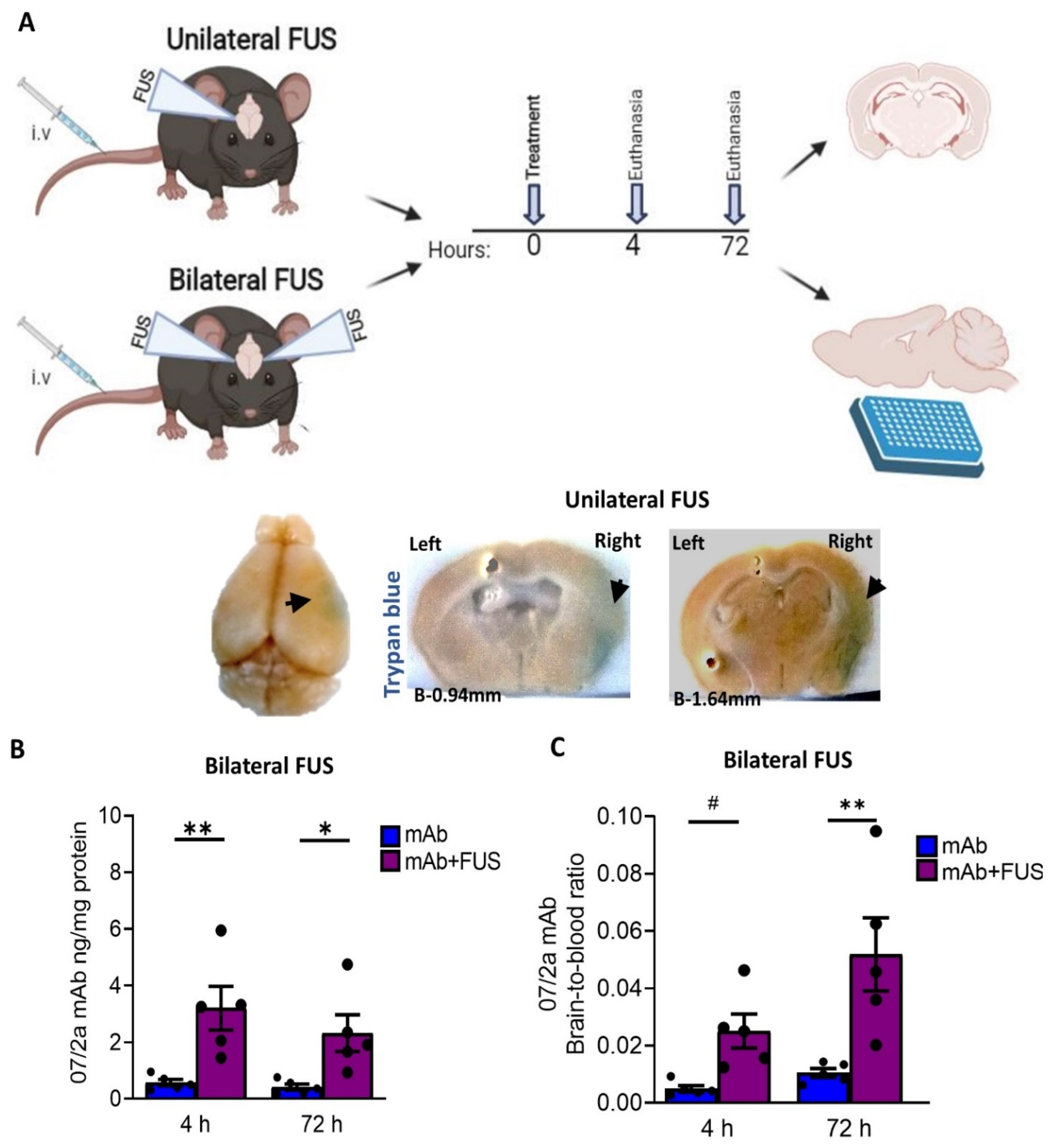
2.2. Treatment
2.3. ELISA
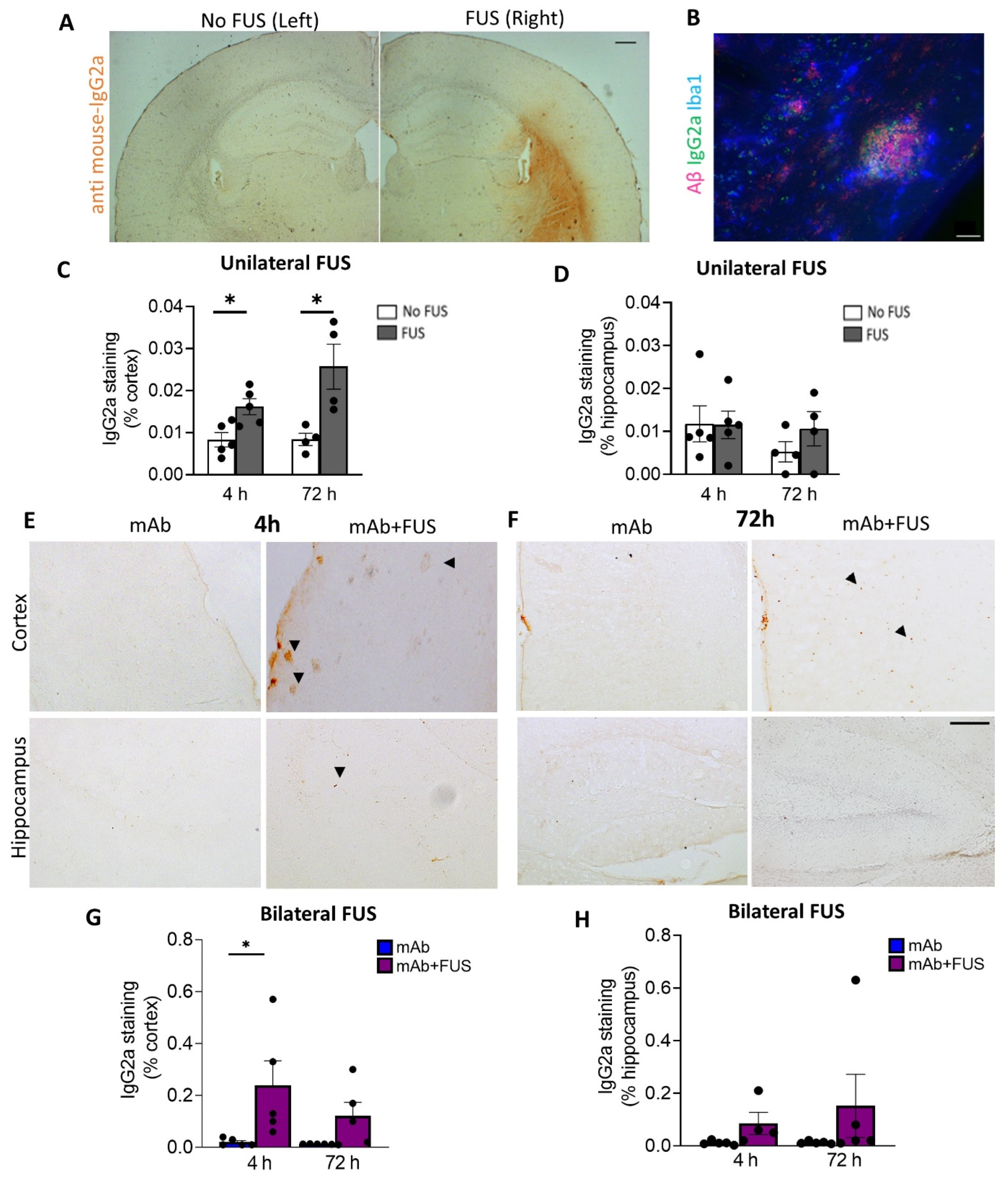
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
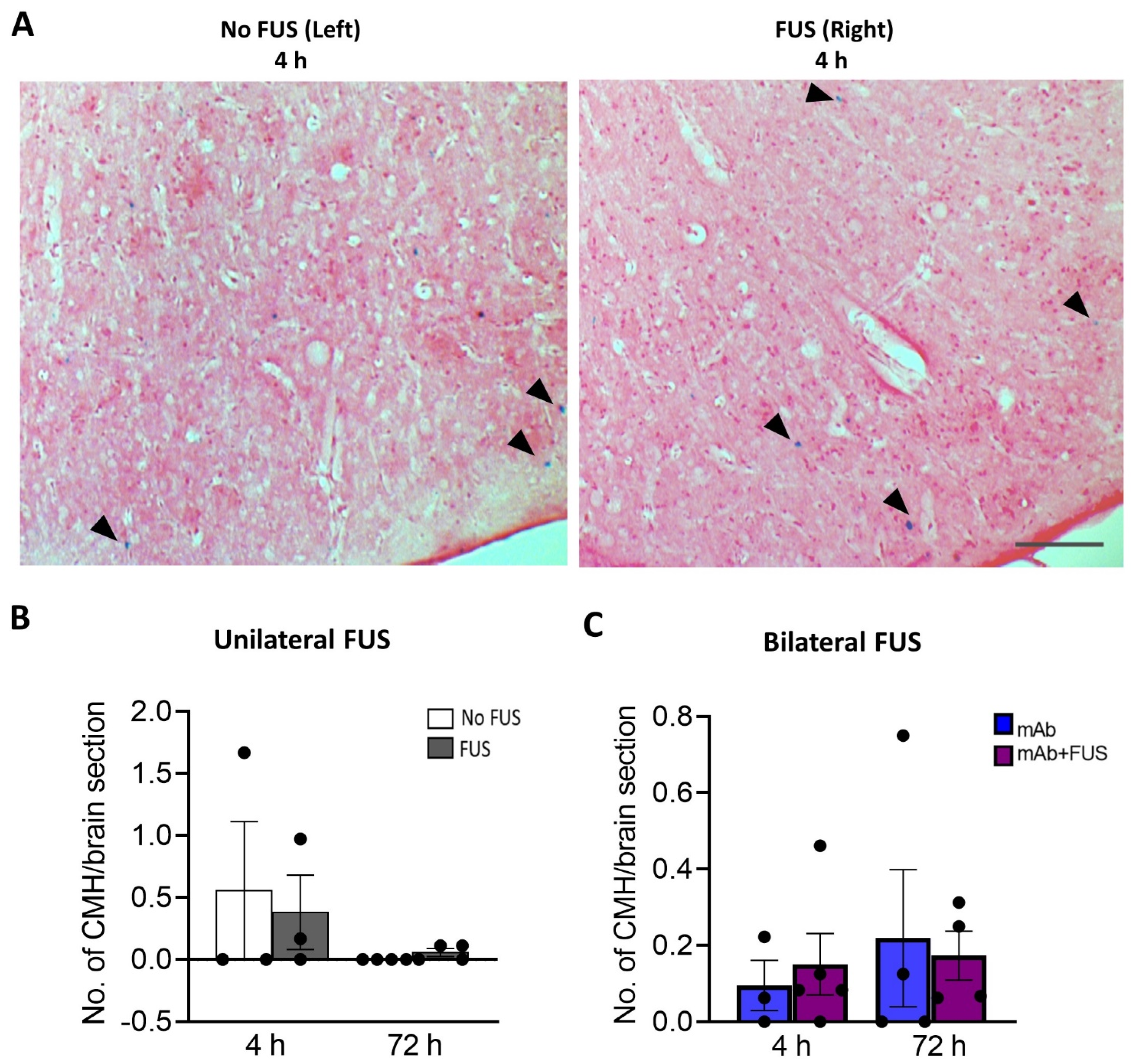
2.5. Microhemorrhage Detection
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. FUS Enhanced Targeted Delivery of 07/2a mAb
3.2. FUS Increased Antibody Immunoreactivity in Brain
3.3. FUS Increased the Microglial Immunoreactivity and Neutrophil/Monocyte Infiltration after Anti-pGlu3Aβ Treatment
3.4. 07/2a + FUS Combination Treatment Does Not Increase the Number of Cerebral Microhemorrhages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrari, C.; Sorbi, S. The Complexity of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Evolving Puzzle. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1047–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, J.; Selkoe, J.H. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease at 25 Years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo, J.T.; Kelly, L.; Verma, A.; Carare, R.O.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Dodart, J.-C. Amyloid-β and α-Synuclein Immunotherapy: From Experimental Studies to Clinical Trials. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 733857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. Addendum: The Antibody Aducanumab Reduces Aβ Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2017, 546, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahase, E. Aducanumab: 4 in 10 High Dose Trial Participants Experienced Brain Swelling or Bleeding. BMJ 2021, 375, n2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakos, J.; Purcell, D.; Suhy, J.; Chalkias, S.; Burkett, P.; Marsica Grassi, C.; Castrillo-Viguera, C.; Rubino, I.; Vijverberg, E. Detection and Management of Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Treated with Anti-Amyloid Beta Therapy. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 9, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloway, S.; Chalkias, S.; Barkhof, F.; Burkett, P.; Barakos, J.; Purcell, D.; Suhy, J.; Forrestal, F.; Tian, Y.; Umans, K.; et al. Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities in 2 Phase 3 Studies Evaluating Aducanumab in Patients with Early Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberlein, S.B.; Budd Haeberlein, S.; Aisen, P.S.; Barkhof, F.; Chalkias, S.; Chen, T.; Cohen, S.; Dent, G.; Hansson, O.; Harrison, K.; et al. Two Randomized Phase 3 Studies of Aducanumab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 9, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammers, C.; Schwarten, M.; Buell, A.K.; Willbold, D. Pyroglutamate-Modified Aβ(3–42) Affects Aggregation Kinetics of Aβ(1–42) by Accelerating Primary and Secondary Pathways. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4996–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cynis, H.; Frost, J.L.; Crehan, H.; Lemere, C.A. Immunotherapy Targeting Pyroglutamate-3 Aβ: Prospects and Challenges. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alawode, D.O.T.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Fox, N.C.; Zetterberg, H. Donanemab Removes Alzheimer’s Plaques: What Is Special about Its Target? Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e395–e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, C.H. Anti-Amyloid-β Monoclonal Antibodies for Alzheimer’s Disease: Pitfalls and Promise. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kouhi, A.; Pachipulusu, V.; Kapenstein, T.; Hu, P.; Epstein, A.L.; Khawli, L.A. Brain Disposition of Antibody-Based Therapeutics: Dogma, Approaches and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemere, C.A. Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Hoops and Hurdles. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golde, T.E. Open Questions for Alzheimer’s Disease Immunotherapy. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-T.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Wong, H.L.; Cai, J.; Peng, L.; Tian, X.-Q. Current Approaches to Enhance CNS Delivery of Drugs across the Brain Barriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikitsh, J.L.; Chacko, A.-M. Pathways for Small Molecule Delivery to the Central Nervous System across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2014, 6, PMC.S13384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, A.; Hynynen, K. Drug Delivery across the Blood–brain Barrier Using Focused Ultrasound. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagai, N.; Yamakawa, K.; Muranaka, Y.; Hokamura, K.; Umemura, K. Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Transiently Enhances Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability During Cerebral Ischemia through Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Mediated Endothelial Endocytosis in Mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhou, L.; Alanis, K.; Hou, J.; Baker, L.A. Imaging Effects of Hyperosmolality on Individual Tricellular Junctions. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tung, Y.-S.; Vlachos, F.; Choi, J.J.; Deffieux, T.; Selert, K.; Konofagou, E.E. In Vivo Transcranial Cavitation Threshold Detection during Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Mice. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 6141–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helfield, B.; Chen, X.; Watkins, S.C.; Villanueva, F.S. Biophysical Insight into Mechanisms of Sonoporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9983–9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chen, W.-S.; Inserra, C.; Wei, K.-C.; Liu, H.-L. Safety Evaluation of Frequent Application of Microbubble-Enhanced Focused Ultrasound Blood-Brain-Barrier Opening. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epelbaum, S.; Burgos, N.; Canney, M.; Matthews, D.; Houot, M.; Santin, M.D.; Desseaux, C.; Bouchoux, G.; Stroer, S.; Martin, C.; et al. Pilot Study of Repeated Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Patients with Mild Alzheimer’s Disease with an Implantable Ultrasound Device. Alzheimer’s Res. 2022, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahao, A.; Meng, Y.; Llinas, M.; Huang, Y.; Hamani, C.; Mainprize, T.; Aubert, I.; Heyn, C.; Black, S.E.; Hynynen, K.; et al. First-in-Human Trial of Blood–brain Barrier Opening in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinenga, G.; Götz, J. Scanning Ultrasound Removes Amyloid-β and Restores Memory in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 278ra33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinenga, G.; Koh, W.K.; Götz, J. A Comparative Study of the Effects of Aducanumab and Scanning Ultrasound on Amyloid Plaques and Behavior in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chung, Y.-H.; Lin, K.-J.; Yang, L.-Y.; Yen, T.-C.; Liu, H.-L. Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening Enhances GSK-3 Inhibitor Delivery for Amyloid-Beta Plaque Reduction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Heinen, S.; Krantic, S.; McLaurin, J.; Branch, D.R.; Hynynen, K.; Aubert, I. Clinically Approved IVIg Delivered to the Hippocampus with Focused Ultrasound Promotes Neurogenesis in a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32691–32700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xhima, K.; Markham-Coultes, K.; Nedev, H.; Heinen, S.; Saragovi, H.U.; Hynynen, K.; Aubert, I. Focused Ultrasound Delivery of a Selective TrkA Agonist Rescues Cholinergic Function in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackmore, D.G.; Turpin, F.; Palliyaguru, T.; Evans, H.T.; Chicoteau, A.; Lee, W.; Pelekanos, M.; Nguyen, N.; Song, J.; Sullivan, R.K.P.; et al. Low-Intensity Ultrasound Restores Long-Term Potentiation and Memory in Senescent Mice through Pleiotropic Mechanisms Including NMDAR Signaling. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6975–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crehan, H.; Liu, B.; Kleinschmidt, M.; Rahfeld, J.-U.; Le, K.X.; Caldarone, B.J.; Frost, J.L.; Hettmann, T.; Hutter-Paier, B.; O’Nuallain, B.; et al. Effector Function of Anti-Pyroglutamate-3 Aβ Antibodies Affects Cognitive Benefit, Glial Activation and Amyloid Clearance in Alzheimer’s-like Mice. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Qiaoqiao, S.; Yongzhi, Z.; Chanikarn, P.; Camilla, H.; Shawna, A.; Maren, K.S. Focused Ultrasound with Anti-pGlu3 Aβ Enhances Efficacy in Alzheimer’s Disease-like Mice via Recruitment of Peripheral Immune Cells. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS: A Historical Viewpoint. Fluids Barriers CNS 2011, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wisniewski, T.; Goñi, F. Immunotherapeutic Approaches for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2015, 85, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemere, C.A.; Masliah, E. Can Alzheimer Disease Be Prevented by Amyloid-β Immunotherapy? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spencer, B.; Masliah, E. Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Past, Present and Future. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardridge, W.M. Blood-Brain Barrier and Delivery of Protein and Gene Therapeutics to Brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.I.; Carpenter, J.S.; Mehta, R.I.; Haut, M.W.; Ranjan, M.; Najib, U.; Lockman, P.; Wang, P.; D’haese, P.-F.; Rezai, A.R. Blood-Brain Barrier Opening with MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound Elicits Meningeal Venous Permeability in Humans with Early Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 2021, 298, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.L.; Liu, B.; Kleinschmidt, M.; Schilling, S.; Demuth, H.-U.; Lemere, C.A. Passive Immunization against Pyroglutamate-3 Amyloid-β Reduces Plaque Burden in Alzheimer-like Transgenic Mice: A Pilot Study. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 10, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demattos, R.B.; Lu, J.; Tang, Y.; Racke, M.M.; Delong, C.A.; Tzaferis, J.A.; Hole, J.T.; Forster, B.M.; McDonnell, P.C.; Liu, F.; et al. A Plaque-Specific Antibody Clears Existing β-Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Neuron 2012, 76, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayer, T.A. Pyroglutamate Aβ Cascade as Drug Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Garmendia, R.; Gevorkian, G. Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta Peptides: Emerging Targets for Alzheimer´s Disease Immunotherapy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMahon, D.; Bendayan, R.; Hynynen, K. Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Increases in Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability on Rat Microvascular Transcriptome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, Z.I.; Kim, S.; Jikaria, N.; Qureshi, F.; Milo, B.; Lewis, B.K.; Bresler, M.; Burks, S.R.; Frank, J.A. Disrupting the Blood–brain Barrier by Focused Ultrasound Induces Sterile Inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E75–E84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schregel, K.; Baufeld, C.; Palotai, M.; Meroni, R.; Fiorina, P.; Wuerfel, J.; Sinkus, R.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; McDannold, N.; White, P.J.; et al. Targeted Blood Brain Barrier Opening with Focused Ultrasound Induces Focal Macrophage/Microglial Activation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 665722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordão, J.F.; Thévenot, E.; Markham-Coultes, K.; Scarcelli, T.; Weng, Y.-Q.; Xhima, K.; O’Reilly, M.; Huang, Y.; McLaurin, J.; Hynynen, K.; et al. Amyloid-β Plaque Reduction, Endogenous Antibody Delivery and Glial Activation by Brain-Targeted, Transcranial Focused Ultrasound. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 248, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daley, J.M.; Thomay, A.A.; Connolly, M.D.; Reichner, J.S.; Albina, J.E. Use of Ly6G-Specific Monoclonal Antibody to Deplete Neutrophils in Mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillay, J.; den Braber, I.; Vrisekoop, N.; Kwast, L.M.; de Boer, R.J.; Borghans, J.A.M.; Tesselaar, K.; Koenderman, L. In Vivo Labeling with 2H2O Reveals a Human Neutrophil Lifespan of 5.4 Days. Blood 2010, 116, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.-P.; Bellavance, M.-A.; Préfontaine, P.; Rivest, S. Real-Time in Vivo Imaging Reveals the Ability of Monocytes to Clear Vascular Amyloid Beta. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poon, C.; Pellow, C.; Hynynen, K. Neutrophil Recruitment and Leukocyte Response Following Focused Ultrasound and Microbubble Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Treatments. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1655–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikov, N.; McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Jolesz, F.; Hynynen, K. Cellular Mechanisms of the Blood-Brain Barrier Opening Induced by Ultrasound in Presence of Microbubbles. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2004, 30, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Raymond, S.; Jolesz, F.A.; Hynynen, K. MRI-Guided Targeted Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption with Focused Ultrasound: Histological Findings in Rabbits. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2005, 31, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.M.; Clyne, A.M. Sex Differences in the Blood–brain Barrier and Neurodegenerative Diseases. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 011509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bathini, P.; Sun, T.; Schenk, M.; Schilling, S.; McDannold, N.J.; Lemere, C.A. Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Anti-Pyroglu3 Abeta Antibody Delivery and Immune Responses. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070951
Bathini P, Sun T, Schenk M, Schilling S, McDannold NJ, Lemere CA. Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Anti-Pyroglu3 Abeta Antibody Delivery and Immune Responses. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(7):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070951
Chicago/Turabian StyleBathini, Praveen, Tao Sun, Mathias Schenk, Stephan Schilling, Nathan J. McDannold, and Cynthia A. Lemere. 2022. "Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Anti-Pyroglu3 Abeta Antibody Delivery and Immune Responses" Biomolecules 12, no. 7: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070951
APA StyleBathini, P., Sun, T., Schenk, M., Schilling, S., McDannold, N. J., & Lemere, C. A. (2022). Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Anti-Pyroglu3 Abeta Antibody Delivery and Immune Responses. Biomolecules, 12(7), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070951






