Abstract
Cisplatin (cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II), DDP) is an antineoplastic agent widely used in the treatment of solid tumors because of its extensive cytotoxic activity. However, the main limiting side effect of DDP use is nephrotoxicity, a rapid deterioration in kidney function due to toxic chemicals. Several studies have shown that epigenetic processes are involved in DDP-induced nephrotoxicity. Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), a class of epigenetic processes, are molecules that regulate gene expression under physiological and pathological conditions. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are the most characterized class of ncRNAs and are engaged in many cellular processes. In this review, we describe how different miRNAs regulate some pathways leading to cell death by apoptosis, specifically the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Accordingly, many classes of natural products have been tested for their ability to prevent DDP-induced apoptosis. The study of epigenetic regulation for underlying cell death is still being studied, which will allow new strategies for the diagnosis and therapy of this unwanted disease, which is presented as a side effect of antineoplastic treatment.
1. Introduction
Globally, cancer is the second leading cause of death. In 2020, 19.3 million new cases of cancer and almost 10 million people died from this disease [1,2]. In 2022, 1,918,030 new cancer cases and 609,360 cancer deaths are projected to occur in the United States [3]. Cisplatin (cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II), DDP) is an antineoplastic agent widely used in the treatment of solid tumors because of its extensive cytotoxic activity [4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Despite tremendous advances in oncology, DDP remains a much sought-after chemotherapeutic agent. However, its application has been limited due to several side effects such as nephrotoxicity [11]. Nephrotoxicity is defined as the rapid deterioration in kidney function due to the toxic effect of medications and chemicals [12]. For this to occur, DDP is concentrated and reabsorbed by renal tubular cells (five times more than in the blood), which triggers a rapid decline in renal function [13].
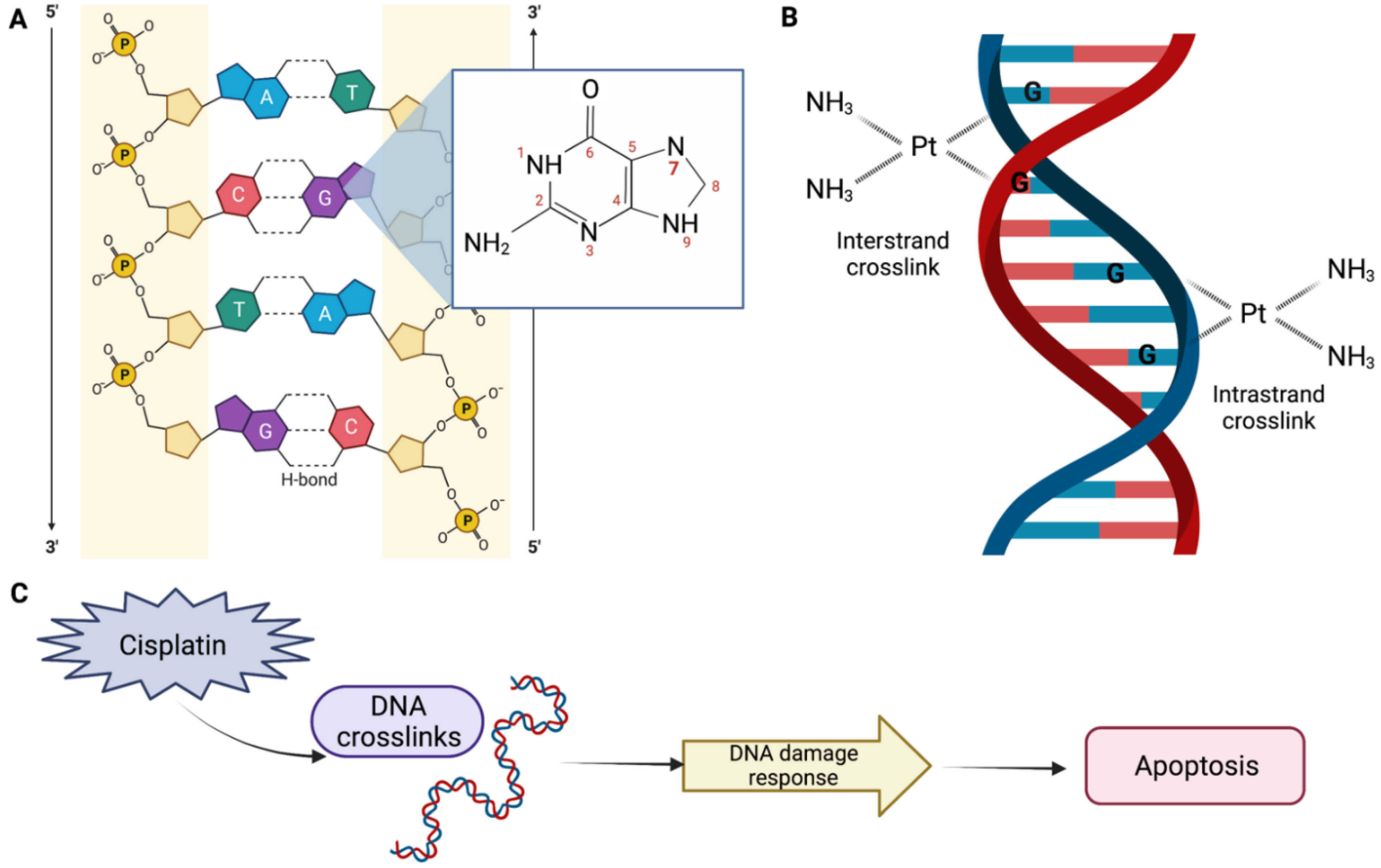
DDP-induced nephrotoxicity can present in a several ways, but the most common and serious presentation is acute kidney injury (AKI), which occurs in 20–30% of patients. The mechanism of the DDP action is not completely understood. However, it is known that DDP interacts primarily with genomic DNA, specifically the N7 position of guanine bases (Figure 1A), causing inter- and intrastrand DNA crosslinks (Figure 1B), which perturbs DNA synthesis, replication, and transcription, thereby inducing replication stress and DNA damage response. This results in defective DNA strands, which may eventually result in cell apoptosis (Figure 1C) [14,15].
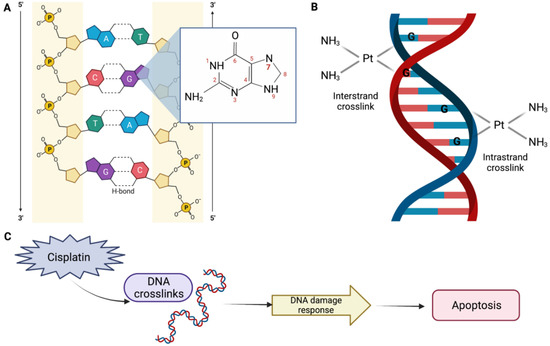
Figure 1.
Mechanism of the cisplatin (DDP) action. (A) The platinum atom of DDP binds covalently to the N7 position of guanine. (B) An interstrand crosslink is formed when DDP binds to two bases from different strands. On the other hand, an intrastrand adduct is formed when DDP binds to two bases of the same strand. (C) DDP perturbs genomic DNA, inducing DNA damage response, which may result in apoptosis, DNA repair, and/or cell cycle arrest. Created with BioRender.com.
The nephrotoxic effect produced by DDP is due to it accumulation in the kidney, mainly in the S3 segment of the proximal tubules, determined by the high density of negatively charged mitochondria in the proximal tubular cells, which attracts positively charged DDP hydrolyzed complexes [16] and contributes critically to sublethal and lethal injury of kidney tubules and the consequent loss of renal function.
Several studies have shown that epigenetic processes are involved in DDP-induced nephrotoxicity in recent years. In 2001, Wu and Morris defined the term “epigenetics” as the study of the changes in gene expression, which occur in organisms with differentiated cells, and the mitotic inheritance of given patterns of gene expression [17]. These modifications result from changes in chromatin structural/activation states without altering the DNA primary nucleotide sequence, triggering the activation of transcription or gene silencing [18]. Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), a class of epigenetic processes, are molecules that regulate gene expression under physiological and pathological conditions [19]. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small ncRNAs, with an average of 22 bp in length, which have been extensively studied. The latest release of the miRbase database (v22) contains 2654 human mature miRNAs sequences [20], which confirms their importance in gene expression regulation.
Therefore, understanding the importance of miRNAs during the action of DDP, specifically upon the induction of apoptosis during nephrotoxicity, is of great scientific interest.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
A comprehensive search in Google Scholar, Scopus, Pubmed, and Web of Knowledge databases was carried out, to identify studies published from 1st January 1966 until May 2022, concerning the contribution of microRNAs in DDP-induced apoptosis related to nephrotoxicity. Keyword combinations were used using the following words: cisplatin, AKI, nephrotoxicity, renal cells, microRNA, miR, apoptosis, cell death, and natural products.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Original articles fulfilling the following search criteria were selected: (1) related to apoptosis, (2) using DDP as the nephrotoxic agent, (3) written in English, (4) fully accessible for the authors (through journal subscriptions, request to authors, open access, among others), and (5) in peer-reviewed journals. Review articles and studies where the primary outcome was DDP resistance or sensitization in cancer were excluded. In addition, all those papers that did not meet the five inclusion criteria previously described were excluded from this study.
3. Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway during DDP-Induced Nephrotoxicity
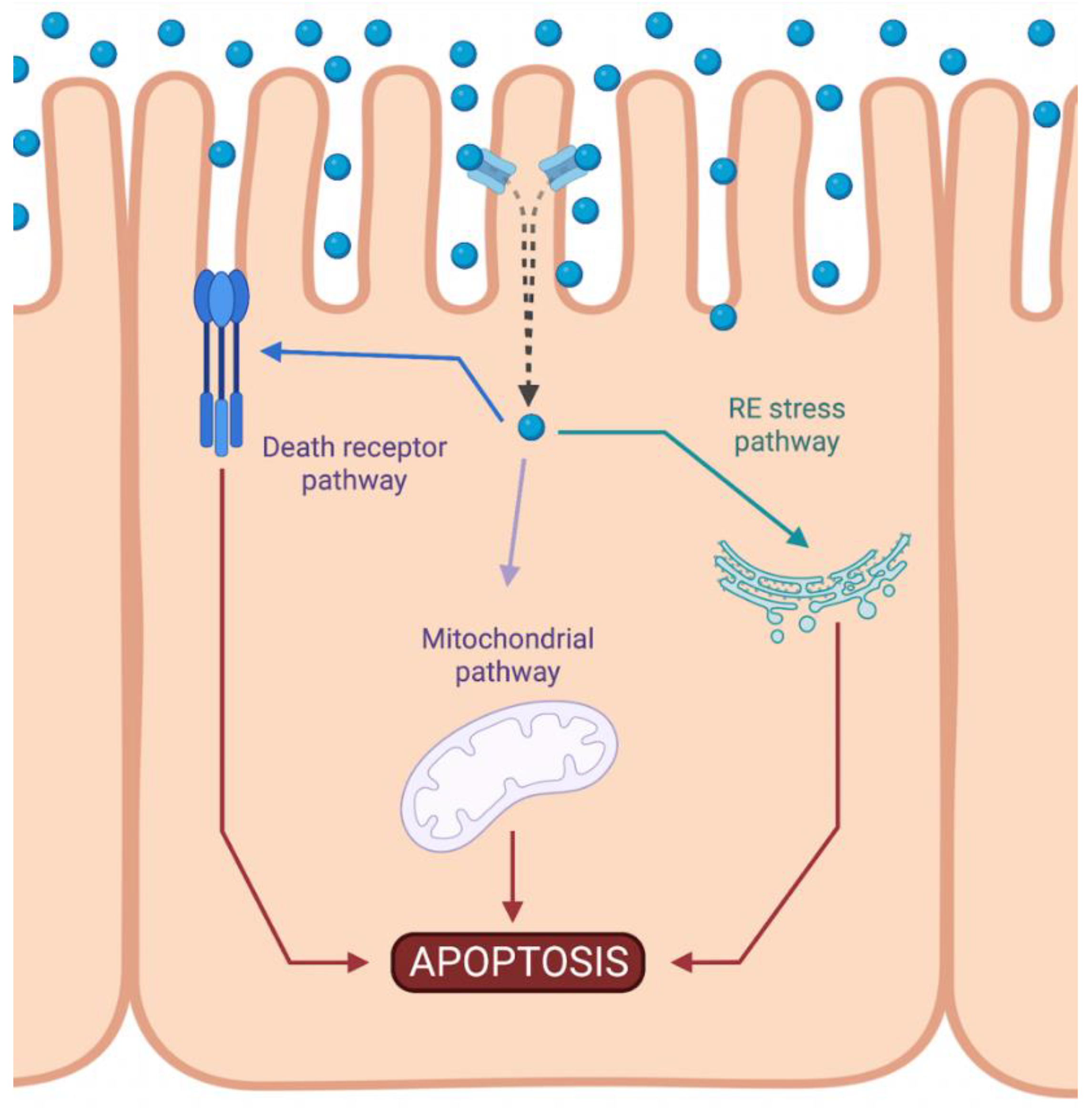
Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is an adverse side effect of this antineoplastic drug therapy and involves several types of cellular death, such as the necrosis (also called uncontrolled cell death) [21,22,23], apoptosis (programmed cell death) [24,25,26,27,28,29], and necroptosis (regulated inflammatory cell death) [30,31] of renal cells. Concerning programmed apoptosis cell death, the three pathways that have been described are called intrinsic, extrinsic, and endoplasmic reticulum stress (Figure 2). In this review, we focus specifically on the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
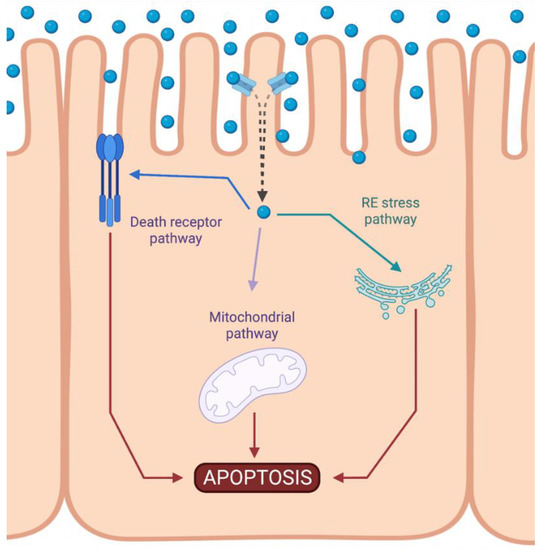
Figure 2.
Activation of apoptotic pathways during cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Cisplatin (blue circle) can activate both mitochondrial (purple) and death receptor (blue) pathways of apoptosis. Likewise, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress may also be induced (green). Created with BioRender.com.
The intrinsic pathway refers to a primarily mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic pathway that results in cell damage. The intrinsic mitochondrial pathway is the main apoptotic pathway prompted during DDP-induced nephrotoxicity. In this pathway, cellular stress leads to the activation of the proapoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) proteins, Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), and Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer (Bak) [32], and the reduction of antiapoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2, Bcl-extra-large (Bcl-XL), and myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1) [33,34]. This triggers mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization (MOMP), releasing apoptotic factors, such as apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) [35], cytochrome c [36], endonuclease G [37], HtrA2/Omi [38], Smac/DIABLO [39], and others. Chipuk et al. also showed that p53 directly activated Bax and triggered apoptosis [40].
Cytochrome c is a crucial mediator of the mitochondrial pathway. Once in the cytosol, cytochrome c induces a dATP-mediate oligomerization of apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 (Apaf-1) in a 2:1 ratio. This complex then recruits the initiator caspase of this pathway, procaspase-9, and induces its autoactivation [41]. Finally, caspase-9, in turn, activates downstream caspases, such as caspase-3, and initiates the process of caspase-dependent apoptosis [42]. In normal conditions, the second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (Smac), a protein located in the mitochondria, however, is released into the cytosol when cells undergo apoptosis [43]. Some studies have shown that inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), such as XIAP, cIAP1, and cIAP2, are group proteins that negatively regulate both caspases and cell death [44]. Thus, Smac is able to promote caspase-9 activation by binding to IAPs and removing their inhibitory activity [43].
The involvement of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in DDP-induced nephrotoxicity has been reported. On in vitro cultured cells, DDP treatment led to a reduction of proapoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression, which was accompanied with an increase of antiapoptotic protein Bax and Bak [33,34,36,45,46,47,48], leading to apoptosis. In the same way, in the rodent model, a reduced Bcl-2 protein expression was also observed after a single dose of DDP [45]. After DDP treatment, the translocation of endogenous Bax from the cytosolic to the membrane fractions was observed and, subsequently, the release of cytochrome c. In addition, using adult Wistar rats, a single dose of DDP triggered severe kidney tissue damage, accompanied by an increase in cytochrome c activity [49].
Endonuclease G has also been observed to be induced during DDP injury in mice [50]. Furthermore, using primary mouse proximal tubule cells, Cilenti et al. showed that the level of Omi protein was also upregulated after DDP treatment, and this upregulation was followed by the release of Omi from mitochondria to the cytoplasm, and the subsequent degradation of XIAP [51]. Cisplatin also increases the expression of Apaf-1 [52] and then activates caspase-9/-3 [53], leading to cell death.
4. Involvement of microRNAs upon Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathway during DDP-Induced Nephrotoxicity
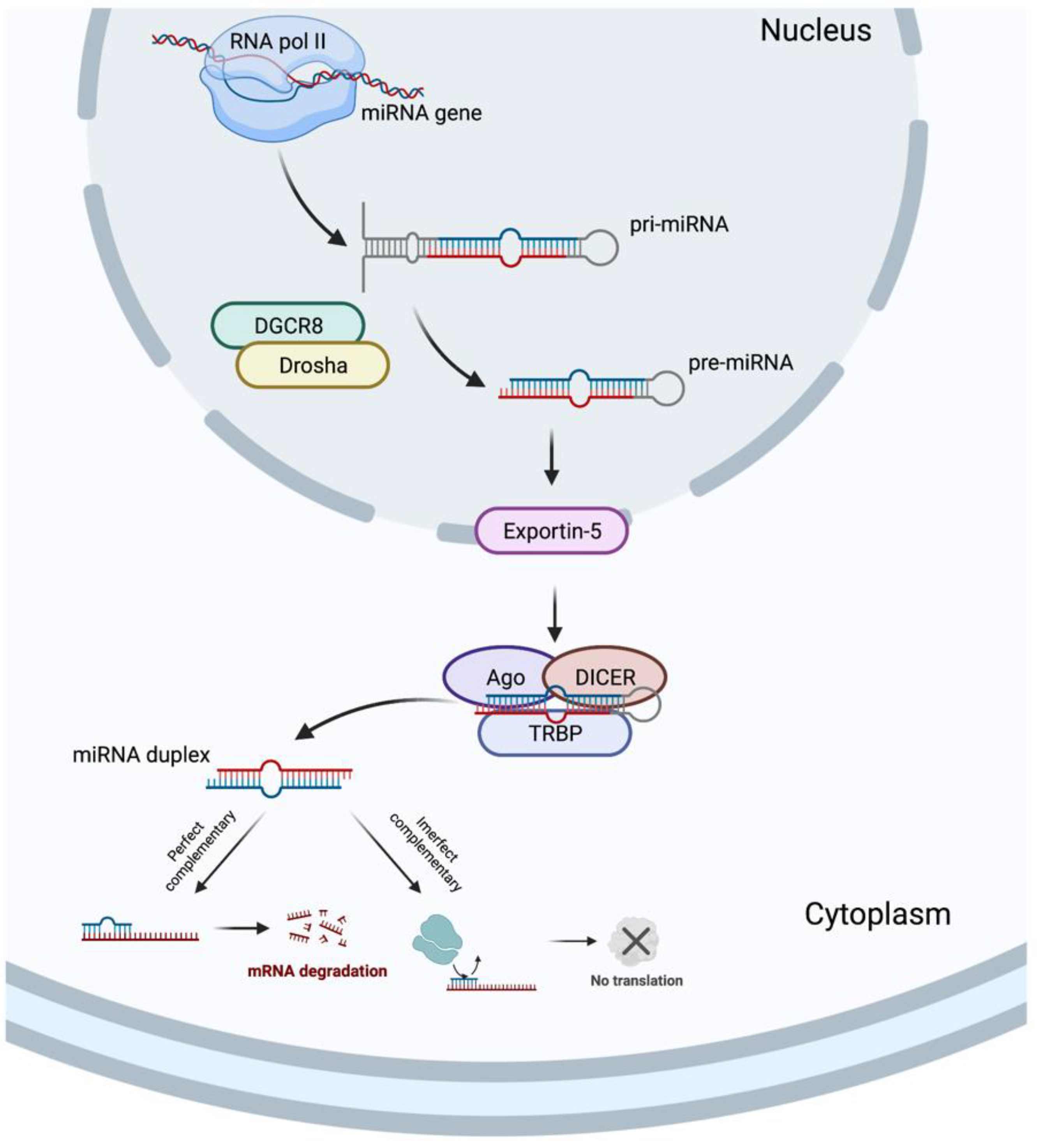
In 1993, two different studies, by Lee et al. [54] and Wightman et al. [55], discovered the miRNAs, which revolutionized the field of molecular biology. MicroRNAs are a class of ncRNAs of approximately 22 bp in length that recognize target sites, most commonly found in the 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of mRNAs, through imperfect base-pairing, with one or more mismatches in sequence complementarity [56]. Briefly, the miRNAs biogenesis is started when a pri-miRNA is transcribed from its miRNA gene and then recognized and cleaved into pre-miRNA by RNA binding protein DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8 (DGCR8) and a ribonuclease III enzyme, Drosha [57], resulting in the formation of a pre-miRNA, which is exported to the cytoplasm by an Exportin-5 and then processed by the RNase III endonuclease, DICER, in collaboration with the transactivation response RNA binding protein (TRBP) and Argonaute (Ago), which remove the terminal loop, resulting in a mature miRNA duplex [58]. Both 5p or 3p strands originated from the 5′ or 3′ end of the pre-miRNA harping, respectively, are derived from the mature miRNA duplex. Thus, the final result is the generation of a miRNA, which can negatively regulate gene targets at the post-transcriptional level by perfect complementarity of their “seed” region to the 3′-UTR of its target mRNA, inducing their degradation, or by an imperfect complementarity, resulting in translational repression [59] (Figure 3).
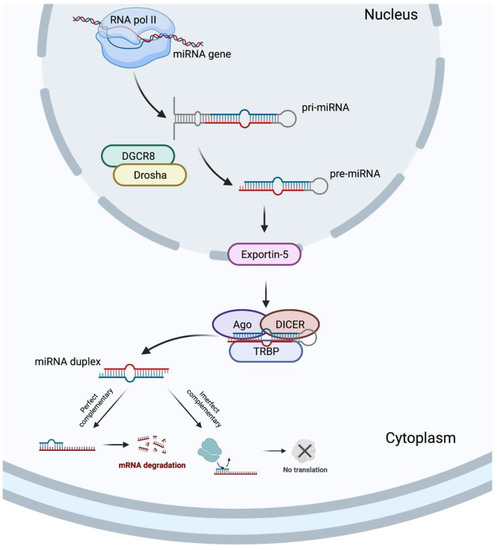
Figure 3.
MicroRNA biogenesis. Created with BioRender.com.
In the following, recent progress of miRNA-targeted therapeutics is described, and potential applications in the treatment of DDP-induced nephrotoxicity are discussed. Related to the intrinsic pathway, several miRNAs have been described to regulate apoptosis-related signaling molecules, which are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) involved in cisplatin (DDP)-induced apoptosis-related signaling molecules.
Using a gene microarray analysis, Zhu et al. [60] demonstrated that renal tissues from the acute kidney injury (AKI) rats caused an upregulation in 36 miRNAs and downregulation in 8 miRNAs. They selected miR-146b for its pronounced changes and verified the increase of miR-146b in the kidneys of AKI rats and in NRK-52E cells treated with DDP. Moreover, transfection with the miR-146b inhibitor reduced the apoptotic rate of NRK-52E cells by directly targeting ErbB4. In DDP-induced apoptosis, restoring the in vitro inhibition of miR-377 expression in tubular epithelial cells after DDP-induced kidney injury in mice was restored by using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), since they promoted an increase in the expression of cytoprotective genes, such as Bcl-2 [48]. Mesenchymal stem cells are stromal cells that can self-renew and that also exhibit a multilineage differentiation [61]; they have been verified to be a safe and effective delivery vehicle for therapeutic miRNA treatment [62]. Another bioinformatic research study also demonstrated that miR-1184 was downregulated in AKI. To obtain this, exosomal-miR-1184-derived MSCs alleviated DDP-induced HK-2 cell injury, observed by the downregulation of the expression levels of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 and the upregulation of the protein expression level of Bcl-2 [63]. In the same way, bone marrow MSCs also downregulated miR-107 expression induced after the DDP stimulus, which increased the level of RPS19, and finally inhibited DDP-induced apoptosis by reducing Bcl-2 protein expression [64]. Another study demonstrated that the treatment with urinary exosomes from premature infants alleviated DDP-induced AKI in mice and inhibited the apoptosis of HK-2 cells by reducing the expression of Bax and increasing the expression of Bcl-2 via miR-30a-5p and targeting MAPK8 [45].
The ability of DDP to induce cell death requires the sequential activation of the p53/ROS/p38a MAPK cascade [77]. On this basis, a microarray analysis identified 47 differentially expressed miRNAs during DDP-cytotoxicity of HK-2 cells. Moreover, a pathway analysis indicated that the top upregulated pathways included the MAPK and p53 signaling pathways. A further network analysis showed that the MAPK signaling pathway and apoptosis were identified as core pathways and miR-9-3p and miR-371b-5p as the most critical miRNAs during DDP-induced cytotoxicity [65]. In rat renal proximal tubular cells, DDP-induced miR-449 upregulation was able to inhibit SIRT1 expression, which further elevated acetylated p53 and BAX levels, leading to the p53/BAX signaling of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Nevertheless, inhibiting miR-449 expression in DDP-treated cells suppressed cell apoptosis [33]. After sequencing and a subsequent qRT-PCR, Han et al. [69] revealed that miR-132-3p was upregulated after DDP treatment in mouse and HK-2 cells. Moreover, they also found that apoptosis was suppressed by inhibiting the miR-132-3p expression in DDP-stimulated HK-2 cells, and this suppression was blocked by miR-132-3p mimics and exacerbated DDP-induced AKI by negatively regulating SIRT1 and activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Yang et al. [75] also demonstrated that p53 was upregulated in DDP-induced AKI mice. They also observed that pifithrin-α inhibited the p53 expression and attenuated renal injury in vivo and cell apoptosis in vitro in mice and HK-2 cells, respectively. In addition, they identified that p53 regulated miR-199a-3p expression and blocking miR-199a-3p reduced DDP-induced apoptosis in HK-2 cells. In addition, the treatment of NRK-52E cells with this antineoplastic demonstrated that DDP facilitated the association of FOXO3 and p53 and was parallel with the accumulation of Bax. Furthermore, the overexpression of miR-122 diminished p53 and Bax levels in NRK-52E cells treated with DDP, while the overexpression of miR-34a promoted both the basal and the inducible expression of p53 and Bax [67].
p53 mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubular cells, and p53 can activate caspase-3 [78]. Related to this, Li et al. [76] described that HRPTEp cells treated with DDP for 48 h showed that DDP led to significantly upregulated miR-449a. In the same way, the overexpression of miR-449a led to an increased apoptotic rate of HRPTEpCs after DDP insult, while antagomir-449a reversed it. Another study demonstrated that HK-2 cells stimulated with DDP showed that the downregulation of miR-205-5p promoted cell apoptosis, observed by an enhanced caspase-3 activity and apoptosis rate of in vitro cultured cells. However, enhancing miR-205-5p expression suppressed apoptotic rate [72]. The levels of miR-144-5p were also downregulated in DDP-stimulated HK-2 cells, and the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins showed that enhancing miR-144-5p expression was able to increase the expression levels of caspase-3/-9, and Bax, and to decrease the expression levels of Bcl-2, by regulating PKM2 expression [71]. Opposite results were observed by Zhang et al. [70], since they demonstrated that remote ischemic preconditioning, a strategy to induce resistance in a target organ, exerted a protective effect on DDP-induced AKI in mice by reversing the downregulation of miR-144 and the dysregulation of caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 expression in renal tissues of DDP-induced AKI in mice and NRK-52 cells. A similar study also showed that an enhanced miR-182-5p expression could reduce renal epithelial Bcl-2 levels and promote Bax and cleaved caspase-3 after in vitro DDP insult, and inhibiting its expression attenuated the damage of DDP in HK-2 cells [74]. Zhu et al. [34] found that miR-181a expression downregulated after DDP-induced apoptosis. They also found that Bcl-2 was upregulated and Bax was downregulated after the transient transfection of the miR-181a inhibitor in HK-2 cells, suggesting that miR-181a was directly involved in the apoptotic process. Using qRT-PCR analysis, Zhang et al. [73] observed a downregulation of miR-205 in HK-2 cells treated with DDP. The transient overexpression of miR-205 using mimics demonstrated that HK-2 cells were more resistant to DDP-induced apoptosis, by modulating CMTM4 protein expression. In another study, qPCR was performed to evaluate the miR-125b expression in in vitro and in vivo DDP-induced damage, and the results showed the upregulation of miR-125b after DDP injection and in cultured tubular epithelial cells treated with DDP. Moreover, DDP-induced apoptosis was decreased by using a miR-125b inhibitor, as shown by the TUNEL assay and the reduced Bax expression [68]. Another study demonstrated that DDP notably increased miR-31 expression and apoptosis-associated proteins (caspase-3 and Bax), while decreasing the antiapoptotic factor, Bcl-2, in kidney samples [66].
Thus, it is evident that many miRNAs exert a fundamental role in activating or inhibiting critical molecules in the progression of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis.
5. Potential Utility of Natural Products in DDP-Induced Apoptosis
Cisplatin is an effective chemotherapeutic drug whose clinical use and efficacy are limited by its nephrotoxicity, which affects mainly the renal tubular cells. It accumulates in proximal and distal epithelial tubule cells and causes cell death. Consequently, various classes of natural products have been tested for their capacity to prevent DDP-induced nephrotoxicity. Furthermore, natural products also overcome resistance, sensitizing cancer cells to DDP [79].
Currently, there is no effective drug to avoid or treat DDP-induced nephrotoxicity. As a result, multiple drugs from natural products have been developed to protect against DDP-induced side effects. All the following natural products we describe have been shown to reduce, alleviate, or mitigate DDP-induced nephrotoxicity by regulating DDP-induced mouse tubular epithelial cells apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of p53, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3/-9 and activating the expression of Bcl-2 both in in vitro cultured HEK-293, HK-2 and/or LLC-PK1 cells and in in vivo DDP-induced AKI mice and/or rats.
Alkaloids are a class of natural compound. Alkaloids represent a vast group of naturally occurring compounds which contain at least one nitrogen atom (amino or amido in some cases). Some alkaloids shown to prevent DDP-induced apoptosis include the berberine [80,81], betaine [49,82], boldine [83], and ligustrazine [84,85].
Flavonoids are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants. Several studies have shown that the use of certain flavonoids prevent DDP-induced apoptosis, most notably the use of astilbin [86], cyanidin [87], epicatechin gallate [88], farrerol [89], galangin [90,91], hespertin [92], icariin [93,94], isoliquiritin [95], isoorientin [96], isoquercitrin [97], luteolin [98,99], morin [100], naringin [101], puerarin [66], quercetin [102,103], rutin [104], scutellarin [105], silybin [106], silymarin [107,108], and wogonin [109,110].
Another class of natural product consists of phenolic compounds. They are secondary metabolites produced in the shikimic acid of plants, which contain benzene rings, with one or more hydroxyl substituents. Phenolic compounds with research related to this side effect include curcumin [111,112,113,114,115], ellagic acid [116], epigallocatechin gallate [117,118], ferulic acid [115], honokiol [119], hydroxytyrosol [120], oleuropein [121], punicalagin [122], rosmarinic acid [123], sinapic acid [124], and zingerone [125].
Likewise, terpenoids are a large and diverse group of lipids resulting from five-carbon isoprene units assembled in thousands of combinations and are isolated from plants and microbial sources. The following terpenoids have shown potential in some studies: anemoside B4 [126], carnosic acid [127], carvacrol [128,129], dioscin [130], germacrone [131], ginsenoside 20 (S)-RG3/Re/RG5/Rk1/Rh2 [132,133,134,135,136], linalool [137], Panax quinquefolius saponins [138], Panax notoginseng saponins [139,140], platycodin D [141,142], pseudoginsengenin DQ [53], red ginseng [143], saikosaponin D [144], and Terminalia arjuna triterpenoid saponins [145].
However, only a few studies have shown the use of antioxidants in epigenetic regulation, specifically on miRNAs, during DDP-induced apoptosis. For example, betanin, a natural red glycoside food dye obtained from beets, has been shown to reduce organ damage induced by DDP by reducing miRNA-34a expression and enhancing the SIRT1/PGC-α pathway [146]. Moreover, puerarin, another natural flavonoid extracted from the Chinese medical herb Radix puerariae, alleviated DDP-induced AKI by suppressing miR-31 expression, enhancing Numb activation, thereby inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway [66]. Finally, dioscin, a steroid saponin commonly found in various herbs, protected against DDP-induced injury to NRK-52E and HK-2 cells by decreasing miR-34a expression, which was accompanied by increased levels of SIRT1, and thus, cell damage [130].
Therefore, natural products could be developed as a new candidate to alleviate DDP-induced cell injury. In addition, they could be used as an ncRNA-based therapy to counteract apoptosis and other pathways induced during nephrotoxicity.
6. Conclusions
Nephrotoxicity is the main side effect of DDP treatment. Therefore, understanding the epigenetic mechanisms underlying the side effect of nephrotoxicity may contribute to implementing therapeutic strategies to alleviate this side effect of chemotherapeutic treatment. This review revealed the complexity of the interactions between miRNAs with their respective targets, how this contributed to the induction of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway, and some natural strategies for overcoming this side effect. Thus, it provided a starting point for developing ncRNA-based therapies to accelerate the resolution of apoptosis induced during nephrotoxicity, thus improving the quality of life of patients treated with DPP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.L. and L.A.S.; methodology, P.L.; software, P.L.; validation, P.L., K.S., N.S. and P.M.; formal analysis, P.L. and N.S.; investigation, P.L.; resources, L.A.S.; data curation, P.L.; writing—original draft preparation, P.L., Y.L., N.R. and I.P.; writing—review and editing, P.L., P.M. and L.A.S.; visualization, L.A.S.; supervision, L.A.S.; project administration, P.M. and L.A.S.; funding acquisition, N.S., K.S., P.M. and L.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ANID-FAPESP (grant no. 19/13250-1), FONDECYT (grant no. 1171765) and FONDECYT postdoctoral grant no. 3220404 awarded to P.L.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Remenar, E.; van Herpen, C.; Gorlia, T.; Mesia, R.; Degardin, M.; Stewart, J.S.; Jelic, S.; Betka, J.; Preiss, J.H.; et al. Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Sheinfeld, J.; Mazumdar, M.; Bajorin, D.F.; Bosl, G.J.; Herr, H.; Lyn, P.; Vlamis, V. Etoposide and cisplatin adjuvant therapy for patients with pathologic stage II germ cell tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 2700–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J. Enhanced tumor suppression by adenoviral PTEN gene therapy combined with cisplatin chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magali, L.; Pascal, F.; Serge, A.; Mathieu, B.; Ayoube, Z.; Claire, T.; Christiane, M. Better survival in impaired renal function patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer treated by cisplatin-pemetrexed. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Bundy, B.; Wenzel, L.; Huang, H.Q.; Baergen, R.; Lele, S.; Copeland, L.J.; Walker, J.L.; Burger, R.A.; Gynecologic Oncology, G. Intraperitoneal cisplatin and paclitaxel in ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.N.; Herzog, T.J.; Lewin, S.; Giuntoli, R.L.; Armstrong, D.K.; Rocconi, R.P.; Spannuth, W.A.; Gold, M.A. A comparison of cisplatin/paclitaxel and carboplatin/paclitaxel in stage IVB, recurrent or persistent cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 105, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, C.M.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; James, K.; Tannock, I.F.; Zee, B.; Carson, J.; Pater, J.; Sullivan, L.D. Improved local control of invasive bladder cancer by concurrent cisplatin and preoperative or definitive radiation. The National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, M.H.; Devarajan, P. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Molecular mechanisms. Cancer Ther. 2003, 1, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Naimi, M.S.; Rasheed, H.A.; Hussien, N.R.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I. Nephrotoxicity: Role and significance of renal biomarkers in the early detection of acute renal injury. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.R.; Faubel, S.; Edelstein, C.L. Biomarkers of Drug-Induced Kidney Toxicity. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Pabla, N.; Tang, C.; He, L.; Dong, Z. DNA damage response in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, A.B.; Cubeddu, L.X. Role of NK1 receptors on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 361, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Nishikawa, M.; Haque, A.M.; Hirose, M.; Mashimo, M.; Sato, E.; Inoue, M. Mitochondrial density determines the cellular sensitivity to cisplatin-induced cell death. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, C1466–C1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Morris, J.R. Genes, genetics, and epigenetics: A correspondence. Science 2001, 293, 1103–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, D.Q.; Gigek, C.O.; Chen, E.S.; Burbano, R.R.; Smith Mde, A. DNA and histone methylation in gastric carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand-Lehouillier, V.; Legault, L.-M.; McGraw, S. Endocrine Epigenetics, Epigenetic Profiling and Biomarker Identification. In Encyclopedia of Endocrine Diseases (Second Edition); Huhtaniemi, I., Martini, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Lei, L.; Wu, X.; Li, Y. Numb ameliorates necrosis and inflammation in acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin. Chem Biol. Interact. 2020, 330, 109251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. TNFR2-mediated apoptosis and necrosis in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2003, 285, F610–F618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, S.I.; Guo, X.; Velazquez, H.; Torres, R.; Olson, E.; Garcia-Milian, R.; Moeckel, G.W.; Desir, G.V.; Safirstein, R. Regulated necrosis and failed repair in cisplatin-induced chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.; Zhou, L.; Mi, Q.S.; Huang, S.; She, J.X.; Dong, Z. MicroRNA-34a is induced via p53 during cisplatin nephrotoxicity and contributes to cell survival. Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Dai, X.M.; Li, S.; Qi, G.L.; Cao, G.X.; Zhong, Y.; Yin, P.D.; Yang, X.S. MiR-30c regulates cisplatin-induced apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting Bnip3L and Hspa5. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ni, J.; Chen, S.; Bai, M.; Lin, J.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jia, Z.; Huang, S.; et al. MicroRNA-709 Mediates Acute Tubular Injury through Effects on Mitochondrial Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Ganugula, R.; Arora, M.; Nabity, M.B.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Kumar, M. Oral delivery of nanoparticle urolithin A normalizes cellular stress and improves survival in mouse model of cisplatin-induced AKI. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F1255–F1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, F.M.; Tang, R.N.; Tu, Y.; Liu, H. MicroRNA26a inhibits cisplatin-induced renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis through suppressing the expression of transient receptor potential channel 6 mediated dynamin-related protein 1. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrill, A.H.; Lin, H.; Tobacyk, J.; Seely, J.C. Mouse population-based evaluation of urinary protein and miRNA biomarker performance associated with cisplatin renal injury. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Kong, W.; Zhang, B. Functional role of microRNA-500a-3P-loaded liposomes in the treatment of cisplatin-induced AKI. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Q.; Gao, L.; Li, H.D.; Wang, J.N.; Wei, B.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; et al. hsa-miR-500a-3P alleviates kidney injury by targeting MLKL-mediated necroptosis in renal epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 3523–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Dong, G.; Franklin, J.; Dong, Z. The pathological role of Bax in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, W.; Xie, W.; Yang, X.; Xia, N.; Yang, K. Inhibiting microRNA-449 Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Injury in NRK-52E Cells Possibly via Regulating the SIRT1/P53/BAX Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Hong, Q.; Zhang, D.; Geng, W.J.; Xie, Y.S.; Chen, X.M. Role of microRNA-181a in the apoptosis of tubular epithelial cell induced by cisplatin. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candé, C.; Cohen, I.; Daugas, E.; Ravagnan, L.; Larochette, N.; Zamzami, N.; Kroemer, G. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): A novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie 2002, 84, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa Lee, R.; Mi Song, J.; Young Park, M.; Kyung Kang, S.; Keun Kim, Y.; Sup Jung, J. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis by translocation of endogenous Bax in mouse collecting duct cells11Abbreviations: ROS, reactive oxygen species; SAPK/JNK, stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; ECL, enhanced chemiluminescence; LDH, lactic dehydrogenase; DPPD, diphenyl-p-phenylene-diamine; DFO, deferoxamine; DMTU, dimethylthiourea; and BHA, butylated hydroxyanisole. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 62, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, X. Endonuclease G is an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nature 2001, 412, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Wassell, R.; Mukattash, R.; Cilenti, L.; DuBois, G.; Lazebnik, Y.; Zervos, A.S.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; et al. Identification of Omi/HtrA2 as a mitochondrial apoptotic serine protease that disrupts inhibitor of apoptosis protein-caspase interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrain, C.; Creagh, E.M.; Martin, S.J. Apoptosis-associated release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria requires active caspases and is blocked by Bcl-2. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6627–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Kuwana, T.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Droin, N.M.; Newmeyer, D.D.; Schuler, M.; Green, D.R. Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 2004, 303, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11549–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Acharya, S.; Fishel, R.; Alnemri, E.S. Cytochrome c and dATP-mediated oligomerization of Apaf-1 is a prerequisite for procaspase-9 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17941–17945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, C.; Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Smac, a Mitochondrial Protein that Promotes Cytochrome c–Dependent Caspase Activation by Eliminating IAP Inhibition. Cell 2000, 102, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Reed, J.C. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Luo, Q.; Fan, L.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Meng, Y.; Yun, C.; Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Cui, S.; et al. The urinary exosomes derived from premature infants attenuate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice via microRNA-30a-5p/mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8). Bioengineered 2022, 13, 1650–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.S.; De Leon, M.; Devarajan, P. Cisplatin induces apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells via activation of mitochondrial pathways. J. Am. Soc.Nephrol. 2002, 13, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Liao, J.W.; Hu, O.Y.; Pao, L.H. Blockade of KCa3.1 potassium channels protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, D.C.; Bassi, E.J.; Azevedo, H.; Anderson, L.; Origassa, C.S.; Cenedeze, M.A.; de Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Felizardo, R.J.; da Silva, R.C.; Hiyane, M.I.; et al. A Regulatory miRNA-mRNA Network Is Associated with Tissue Repair Induced by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.M.; Al-Dalain, S.M. Betaine downregulates microRNA 34a expression via a p53-dependent manner in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Apostolov, E.O.; Shah, S.V.; Wang, X.; Bogdanov, K.V.; Buzder, T.; Stewart, A.G.; Basnakian, A.G. Induction of renal endonuclease G by cisplatin is reduced in DNase I-deficient mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2544–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilenti, L.; Kyriazis, G.A.; Soundarapandian, M.M.; Stratico, V.; Yerkes, A.; Park, K.M.; Sheridan, A.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Bonventre, J.V.; Zervos, A.S. Omi/HtrA2 protease mediates cisplatin-induced cell death in renal cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2005, 288, F371–F379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzaez, M.; Sancho, M.; Marchan, S.; Mondragon, L.; Montava, R.; Valero, J.G.; Landeta, O.; Basanez, G.; Carbajo, R.J.; Pineda-Lucena, A.; et al. Apaf-1 inhibitors protect from unwanted cell death in in vivo models of kidney ischemia and chemotherapy induced ototoxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.; Li, P. Pseudoginsengenin DQ Exhibits Therapeutic Effects in Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Sirt1/NF-kappaB and Caspase Signaling Pathway without Compromising Its Antitumor Activity in Mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivdasani, R.A. MicroRNAs: Regulators of gene expression and cell differentiation. Blood 2006, 108, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denli, A.M.; Tops, B.B.; Plasterk, R.H.; Ketting, R.F.; Hannon, G.J. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 2004, 432, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chendrimada, T.P.; Gregory, R.I.; Kumaraswamy, E.; Norman, J.; Cooch, N.; Nishikura, K.; Shiekhattar, R. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature 2005, 436, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Dong, G.; Liang, X.; Dong, Z. Epigenetic regulation in AKI and kidney repair: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, J.; Yin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jia, H.; Tao, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; et al. MicroRNA-146b, a Sensitive Indicator of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Repair of Acute Renal Injury. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.C.; Shyu, W.C.; Lin, S.Z. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transpl. 2011, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.D.; Pollock, K.; Kambal, A.; Cary, W.; Mitchell, G.-M.; Tempkin, J.; Stewart, H.; McGee, J.; Bauer, G.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Genetically Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Proposed Therapeutic for Huntington’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; He, W.; Zheng, D.; He, Q.; Tan, M.; Jin, J. Exosomal-miR1184 derived from mesenchymal stem cells alleviates cisplatin-associated acute kidney injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, L.; Shao, F. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute kidney injury via miR-107-mediated regulation of ribosomal protein S19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, D.D.; Li, J.Y.; Yin, Y.C.; Li, P.C.; Qiu, L.; Chen, L.M. Identification of microRNA-mRNA networks involved in cisplatin-induced renal tubular epithelial cells injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 851, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, X. Puerarin alleviates cisplatin-induced acute renal damage and upregulates microRNA-31-related signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3122–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, H.K.; Cho, I.J.; Choi, D.W.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, W.D.; Hwang, S.J.; Choi, S.; et al. Discovery of an integrative network of microRNAs and transcriptomics changes for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liang, S.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z. miR-125b Disrupts Mitochondrial Dynamics via Targeting Mitofusin 1 in Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Dis. 2022, 8, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lin, F.; Ruan, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, R.; Ning, J.; Jiang, K.; Xie, J.; Li, H.; Li, C.; et al. miR-132-3p promotes the cisplatin-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response of renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting SIRT1 via the NF-kappaB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 108022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Jing, R.; Liu, T.; Liu, B. Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Protects Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury through the PTEN/AKT Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 7629396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Chang, M.; Liu, G.; Xu, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, R.; Feng, M. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 reduces renal epithelial cell apoptosis in cisplatin-induced AKI by regulating the miR-144-5p/PKM2 axis. Biomed. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bi, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 aggravate renal epithelial cell apoptosis in cisplatin-induced AKI by regulating miR-205-5p. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y. MicroRNA-205 inhibits renal cells apoptosis via targeting CMTM4. Iran, J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Gong, Y.; Guo, L. Long Noncoding RNA PRNCR1 Reduces Renal Epithelial Cell Apoptosis in Cisplatin-Induced AKI by Regulating miR-182-5p/EZH1. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2021, 46, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Liu, F.; Guan, B.; Luo, Z.; Lin, J.; Fang, W.; Liu, L.; Zuo, W. p53 induces miR-199a-3p to suppress mechanistic target of rapamycin activation in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 17625–17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hou, G. LincRNA-p21 Inhibits Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis of Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Sponging miR-449a. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2021, 46, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragado, P.; Armesilla, A.; Silva, A.; Porras, A. Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38alpha MAPK activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, B.S.; Schnellmann, R.G. Cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis: Caspase 3-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Zheng, G.-J.; Feng, B. Phytochemicals: Current strategy to sensitize cancer cells to cisplatin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.K.; Malik, S.; Mutneja, E.; Sahu, A.K.; Rupashi, K.; Dinda, A.K.; Arya, D.S.; Bhatia, J. Mechanism involved in fortification by berberine in cddp-induced nephrotoxicity. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domitrović, R.; Cvijanović, O.; Pernjak-Pugel, E.; Škoda, M.; Mikelić, L.; Crnčević-Orlić, T. Berberine exerts nephroprotective effect against cisplatin-induced kidney damage through inhibition of oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation, autophagy and apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, H.; El Medany, A.E.; Salam, R.; El Medany, G.E.; Nayal, O.A. Betaine supplementation mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative/nitrosative stress and suppression of inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 67, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, N.H.; Gungor, H.; Ekici, M.; Erdogan, M.A.; Karayigit, M.O.; Kara, H. Boldine provides protective effect against nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin in Wistar rats: Role of oxidative stress, inflammation and caspase-3. Biocell 2022, 46, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Li, J.; Li, Q.X.; Ai, Y.X.; Zhang, L. Protective effects of ligustrazine on cisplatin-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and nephrotoxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Li, Q.X. Effects of ligustrazine on renal cell apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-related proteins in rats with cisplatin-induced renal injury. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 19, 352–356. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-W.; Xu, Y.; Weng, Y.-Y.; Fan, X.-Y.; Bai, Y.-F.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Lou, L.-J.; Zhang, F. Astilbin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, T.; Choi, M.Y.; Liang, Y.; Xue, J.; Wong, Y.S. Cyanidin reverses cisplatin-induced apoptosis in HK-2 proximal tubular cells through inhibition of ROS-mediated DNA damage and modulation of the ERK and AKT pathways. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Suchal, K.; Bhatia, J.; Gamad, N.; Dinda, A.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Arya, D.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying attenuation of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by epicatechin gallate. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wei, W.; Fan, X.; Ci, X. Farrerol Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibiting the Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Oxidation, Inflammation, and Apoptotic Signaling Pathways. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, A.; Vasisth, S.; Khan, S.I.; Malik, S.; Nag, T.C.; Arya, D.S.; Bhatia, J. Galangin ameliorates cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in vivo by modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation through interplay of MAPK signaling cascade. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Tsai, M.S.; Hsieh, P.C.; Shih, J.H.; Wang, T.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, T.H.; Wang, S.H. Galangin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death in mice through inhibition of ERK and NF-kappaB signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Ci, X. Hesperetin relieves cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by mitigating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, S.; Su, X.; Qiu, G.; Wu, Z. Protective effects of icariin on cisplatin-induced acute renal injury in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.D.; Hou, J.G.; Yang, G.; Jiang, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ren, S.; Li, W. Icariin ameliorates cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human embryonic kidney 293 cells by suppressing ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Wu, M.; Yu, H.; Long, G.; Gui, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Jia, Z.; Xia, W. Isoliquiritin Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Renal Proximal Tubular Cell Injury by Antagonizing Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 873739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wei, W.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Ci, X. Isoorientin Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through the Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Activating the SIRT1/SIRT6/Nrf-2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xia, W.; Long, G.; Pei, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Chen, H. Isoquercitrin Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Via the Inhibition of Apoptosis, In fl ammation, and Oxidative Stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 599416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domitrovic, R.; Cvijanovic, O.; Pugel, E.P.; Zagorac, G.B.; Mahmutefendic, H.; Skoda, M. Luteolin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibition of platinum accumulation, inflammation and apoptosis in the kidney. Toxicology 2013, 310, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.P.; Park, S.K.; Kim, D.H.; Sung, M.J.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, A.S.; Lee, J.E.; Ramkumar, K.M.; Lee, S.; Park, M.H.; et al. Luteolin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice by regulation of p53-dependent renal tubular apoptosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Alvarez, C.; Moreno-Londoño, Á.P.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Effect of Pretreatment of Morin on the Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity on LLC-PK1 and T24 Cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1934578X1801300416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, Y.; Aouey, B.; Aroui, S.; Kebieche, M.; Fetoui, H. Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of naringin on cisplatin-induced renal injury in the rat. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 243, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, A.G.; Hernandez-Sanchez, M.T.; Martinez-Salgado, C.; Morales, A.I.; Vicente-Vicente, L.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J. A meta-analysis of preclinical studies using antioxidants for the prevention of cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Implications for clinical application. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 780–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, A.G.; Prieto, M.; Colino, C.I.; Gutierrez-Millan, C.; Ruszkowska-Ciastek, B.; de Paz, E.; Martin, A.; Morales, A.I.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J. A Micellar Formulation of Quercetin Prevents Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, R.R.; Abdel Fattah, S.M. Mechanisms involved in the possible nephroprotective effect of rutin and low dose gamma irradiation against cisplatin-induced nephropathy in rats. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 169, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Nie, J.; Zheng, Z.L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, L.M.; Zhu, Y.; Su, Z.Q.; Zheng, G.J.; Feng, B. Renoprotective effect of scutellarin on cisplatin-induced renal injury in mice: Impact on inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lai, W.; Rao, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Z.; Lou, T. Activation of Sirtuin 3 by Silybin Attenuates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cisplatin-induced Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninsontia, C.; Pongjit, K.; Chaotham, C.; Chanvorachote, P. Silymarin selectively protects human renal cells from cisplatin-induced cell death. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantituvanont, A.; Jiamchaisri, P.; Chunhacha, P.; Pongjit, K.; Ninsontia, C.; Meksawan, K.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Silymarin inhibits cisplatin-mediated apoptosis via inhibition of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical generation. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 37, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, A.M.; El-Naga, R.N.; Gad, A.M.; Tadros, M.G.; Fawzy, H.M. Wogonin pre-treatment attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Impact on PPAR-gamma, inflammation, apoptosis and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Li, H.D.; Wu, W.F.; Ming-Kuen Tang, P.; Ren, G.L.; Gao, L.; Li, X.F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Ma, T.T.; et al. Wogonin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by targeting RIPK1-mediated necroptosis. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Abdelrahman, A.; Al Suleimani, Y.; Manoj, P.; Ali, H.; Nemmar, A.; Al Za’abi, M. Effect of concomitant treatment of curcumin and melatonin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Fayi, M.; Otifi, H.; Alshyarba, M.; Dera, A.A.; Rajagopalan, P. Thymoquinone and curcumin combination protects cisplatin-induced kidney injury, nephrotoxicity by attenuating NFκB, KIM-1 and ameliorating Nrf2/HO-1 signalling. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Kader, M.; Taha, R.I. Comparative nephroprotective effects of curcumin and etoricoxib against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topcu-Tarladacalisir, Y.; Sapmaz-Metin, M.; Karaca, T. Curcumin counteracts cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by preventing renal tubular cell apoptosis. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bami, E.; Ozakpınar, O.B.; Ozdemir-Kumral, Z.N.; Köroglu, K.; Ercan, F.; Cirakli, Z.; Sekerler, T.; Izzettin, F.V.; Sancar, M.; Okuyan, B. Protective effect of ferulic acid on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 54, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guada, M.; Ganugula, R.; Vadhanam, M.; Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. Urolithin A Mitigates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibiting Renal Inflammation and Apoptosis in an Experimental Rat Model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 363, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatima, S.; Al-Mohaimeed, N.; Al-Shaikh, Y.; Tyagi, P.; Banu, N.; Hasan, S.; Arjumand, S. Combined treatment of epigallocatechin gallate and Coenzyme Q10 attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via suppression of oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation and cellular damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 94, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Song, J.; Jiang, B.; Pei, F.; Chen, B.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects against cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting the apoptosis in mouse. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4607–4616. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, R.W.; He, S.P.; Lan, J.G.; Zhu, W.Z. Honokiol ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via inhibition of mitochondrial fission. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3886–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ai, Q.; Wei, Y. Hydroxytyrosol protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via attenuating CKLF1 mediated inflammation, and inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potočnjak, I.; Škoda, M.; Pernjak-Pugel, E.; Peršić, M.P.; Domitrović, R. Oral administration of oleuropein attenuates cisplatin-induced acute renal injury in mice through inhibition of ERK signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladaileh, S.H.; Al-Swailmi, F.K.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Ahmeda, A.F.; Mahmoud, A.M. Punicalagin prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis in rats. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domitrović, R.; Potočnjak, I.; Crnčević-Orlić, T.; Škoda, M. Nephroprotective activities of rosmarinic acid against cisplatin-induced kidney injury in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.A. Sinapic acid modulates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandemir, F.M.; Yildirim, S.; Caglayan, C.; Kucukler, S.; Eser, G. Protective effects of zingerone on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in female rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22562–22574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y. Anemoside B4 attenuates nephrotoxicity of cisplatin without reducing anti-tumor activity of cisplatin. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.D.; Rentam, K.K.R.; Putcha, U.K.; Kuncha, M.; Vegi, G.M.N.; Sistla, R. Carnosic acid attenuates renal injury in an experimental model of rat cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-sayed, E.S.M.; Ar, A.A.; Am, M.; Aa, E.A. Thymol and carvacrol prevent cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potočnjak, I.; Domitrović, R. Carvacrol attenuates acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin through suppression of ERK and PI3K/Akt activation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 98, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, X.; Yin, L.; Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Protective effects of dioscin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2512–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soodvilai, S.; Meetam, P.; Siangjong, L.; Chokchaisiri, R.; Suksamrarn, A.; Soodvilai, S. Germacrone reduces cisplatin-induced toxicity of renal proximal tubular cells via inhibition of organic cation transporter. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.N.; Xu, X.Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Gong, X.J.; Li, K.K.; Ren, S.; Li, W. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rk1, a major rare saponin from black ginseng, on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in HEK-293 cells. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Li, W.; Tan, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Li, P. Effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on renal apoptosis in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in vivo. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.-S.; Han, I.-H.; Lee, D.; An, J.M.; Kim, S.-N.; Shin, M.-S.; Yamabe, N.; Hwang, G.S.; Yoo, H.H.; Choi, S.-J.; et al. Beneficial effects of fermented black ginseng and its ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in LLC-PK1 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yan, M.H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.S. Ginsenoside Rg5 Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Mice through Inhibition of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.F.; Han, X.Y.; Sun, Y.S.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.X.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.Y. Kidney Protection Effect of Ginsenoside Re and Its Underlying Mechanisms on Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Injury. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Abduldaium, Y.S.; Younis, N.S. Ameliorative effect of linalool in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: The role of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and NRF2/HO1 pathways. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.N.; Li, Y.Z.; Li, W.; Yan, X.T.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.C.; Yang, L.M. Nephroprotective effects of saponins from leaves of panax quinquefolius against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Zou, X.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wen, Y. Panax notoginseng saponins attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via inhibiting the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8391–8400. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, B.; Liu, Z.; Xie, L.; Lv, L.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J.; Dai, Y.; She, W. Panax notoginseng Saponins protect auditory cells against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by inducing the AKT/Nrf2 signaling-mediated redox pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3533–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.N.; Leng, J.; Shen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.D.; Wang, S.H.; Li, H.P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Li, W. Platycodin D suppresses cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity by suppressing ROS-mediated oxidative damage, apoptosis, and inflammation in HEK-293 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Song, I.B.; Lee, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Cho, E.S.; Son, H.Y.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.W.; Yun, H.I. Platycodin D, a triterpenoid sapoinin from Platycodon grandiflorum, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4254–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Son, H.Y.; Park, B.K.; Ryu, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y. Red ginseng ameliorates acute cisplatin-induced nephropathy. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Dang, C.; Kang, H.; Dai, Z.; Lin, S.; Guan, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hui, W. Saikosaponin-D reduces cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by repressing ROS-mediated activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB signalling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, I.O. Amelioration of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats by triterpenoid saponin of Terminalia arjuna. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shaffei, I.; Abdel-Latif, G.A.; Farag, D.B.; Schaalan, M.; Salama, R.M. Ameliorative effect of betanin on experimental cisplatin-induced liver injury; the novel impact of miRNA-34a on the SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).