Norlobaridone Inhibits Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Some Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Disrupting Its Transcriptional Activator Protein LasR Dimerization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Buffers
2.2. Growth Curve Analysis
2.3. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effect on the Formation of Virulence Factors
2.3.1. Inhibitory Effect on the Biofilm Formation
2.3.2. Inhibitory Effect on Pyocyanin Production
2.3.3. Inhibitory Effect on Rhamnolipids Production
2.4. Standard Curve for L-Rhamnose by Orcinol Reagent
2.5. LasR, RhlR, and QscR Reporter In Vitro Assays
2.6. Production and Purification of LasR Protein
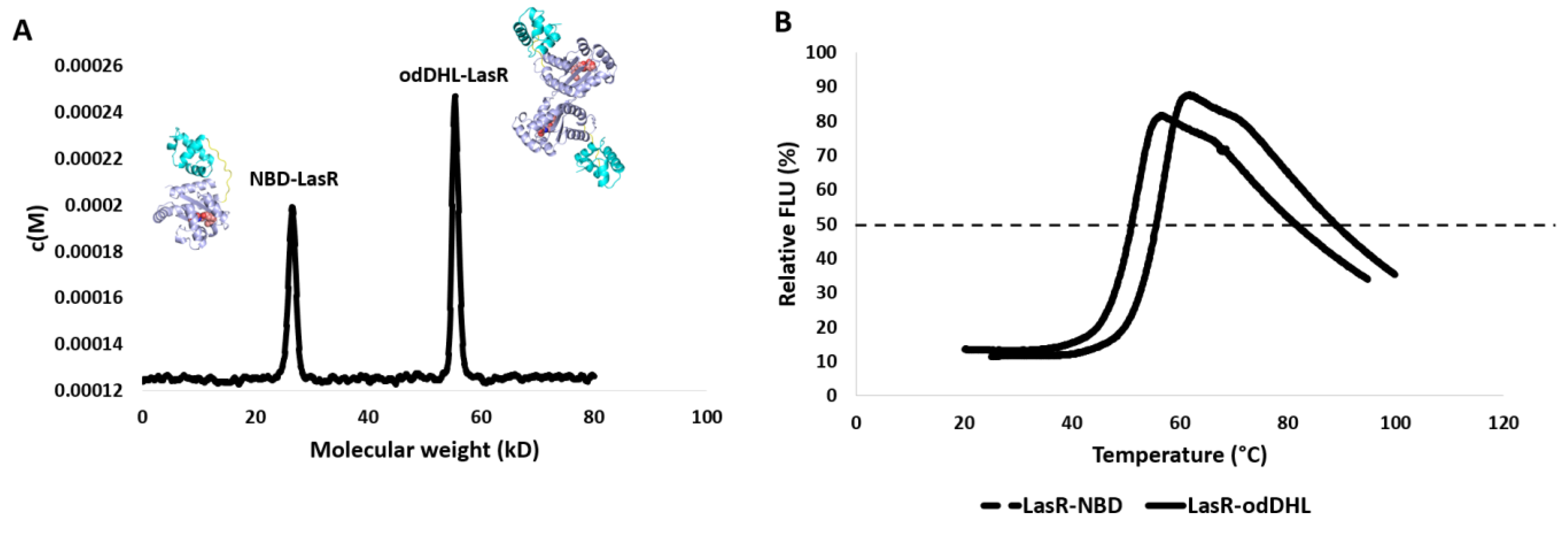
2.7. Sedimentation Velocity Analysis
2.8. Thermal Shift Assay
2.9. In Silico Study
2.9.1. Molecular Docking
2.9.2. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.9.3. Absolute Binding Free Energy Calculation
3. Results
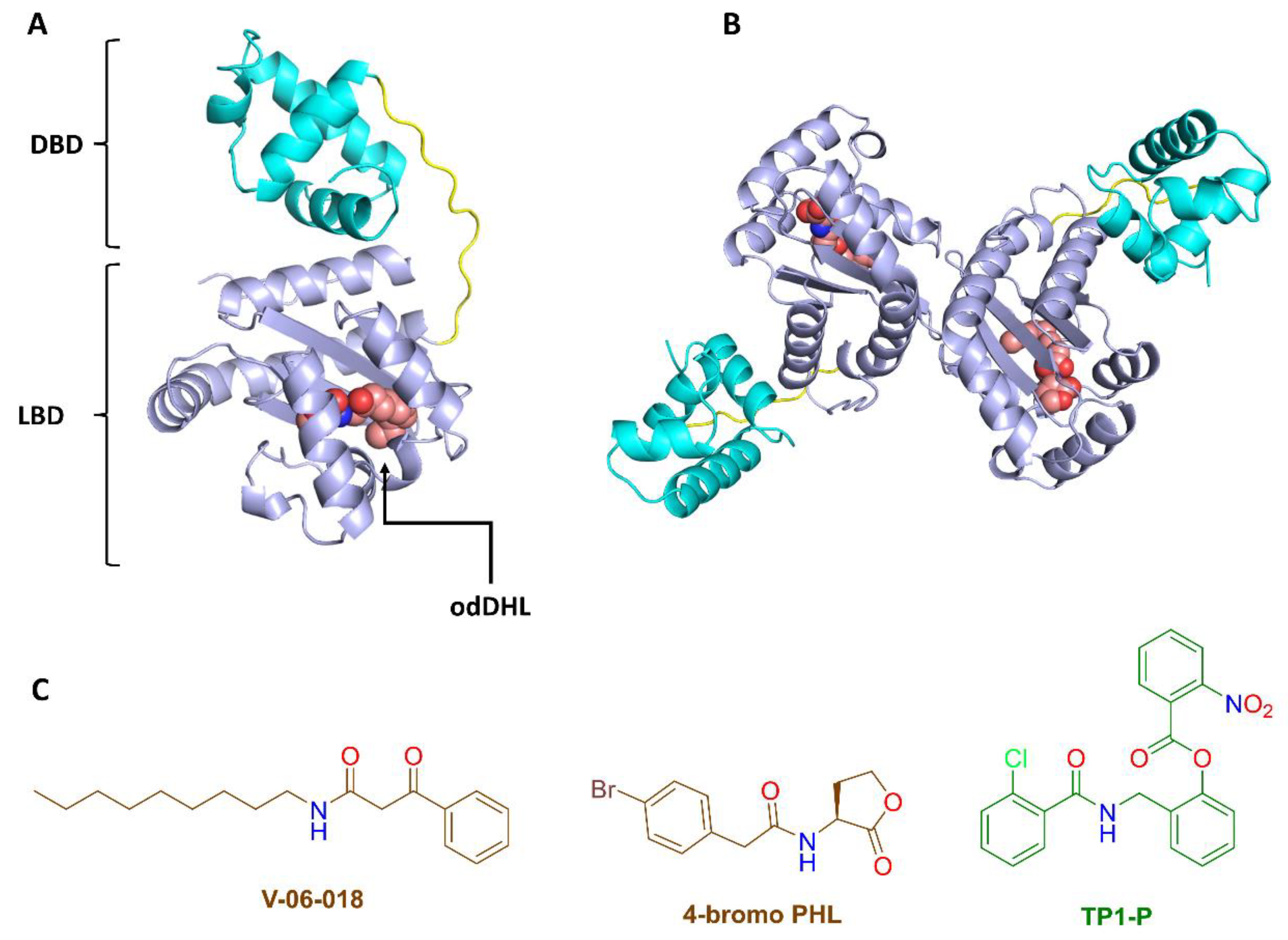
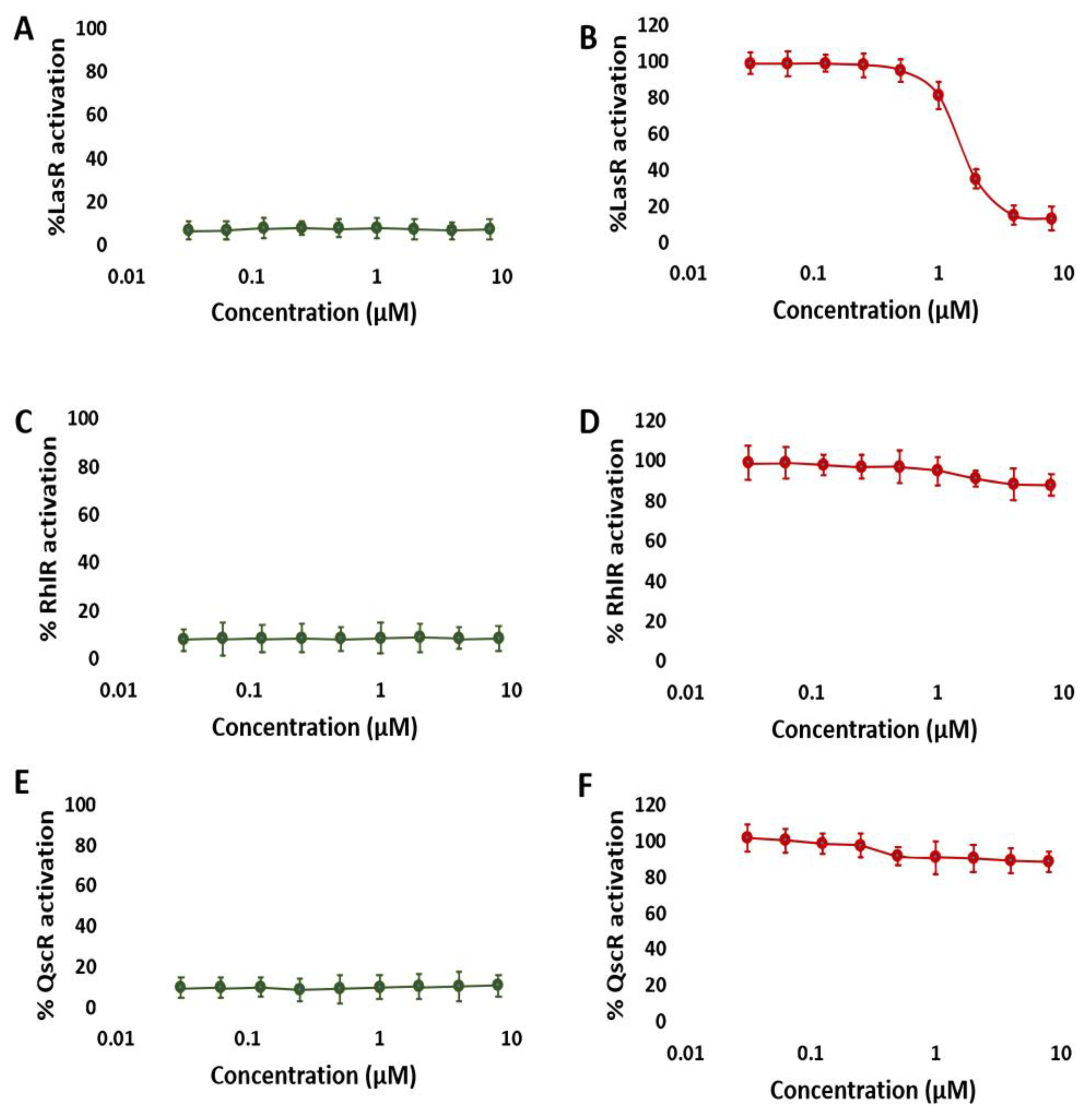
3.1. NBD Exhibits Selectivity for LasR in P. aeruginosa
3.2. NBD Interferes with LasR Dimerization
3.3. NBD Induces Destabilization of LasR
3.4. NBD Reduced the Production of P. aeruginosa Virulence Factors
3.5. In Silico Study
3.5.1. NBD Binds Similarly to odDHL Inside the LasR Ligand Binding Site
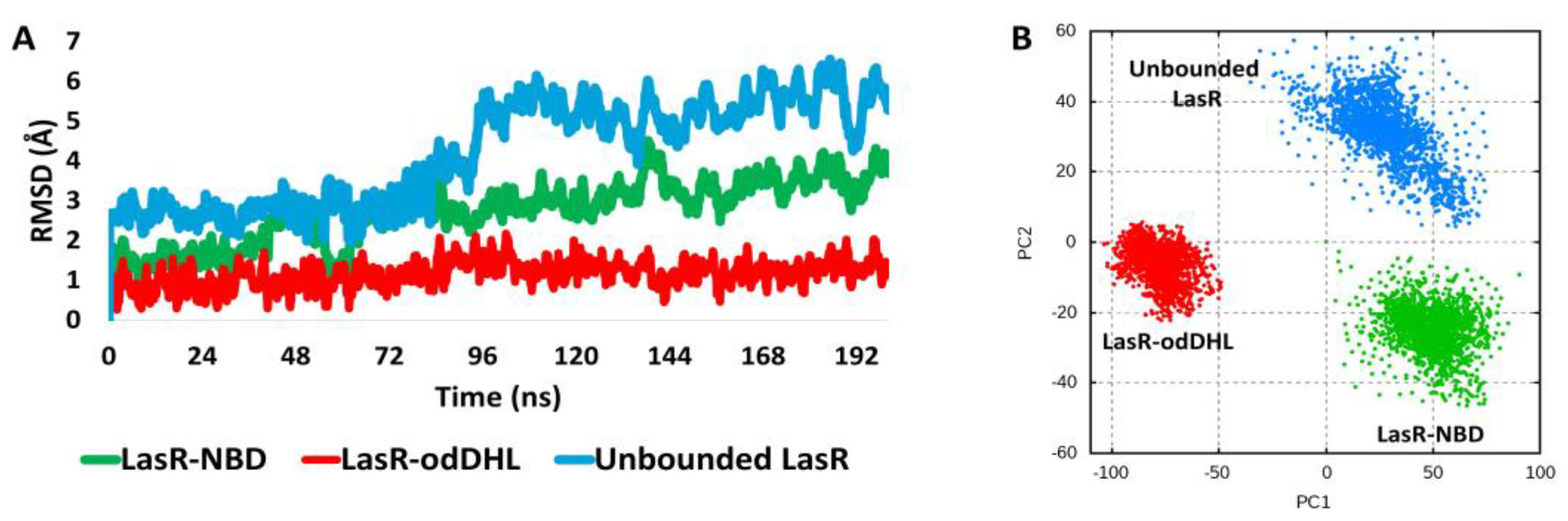
3.5.2. NBD Destabilizes LasR
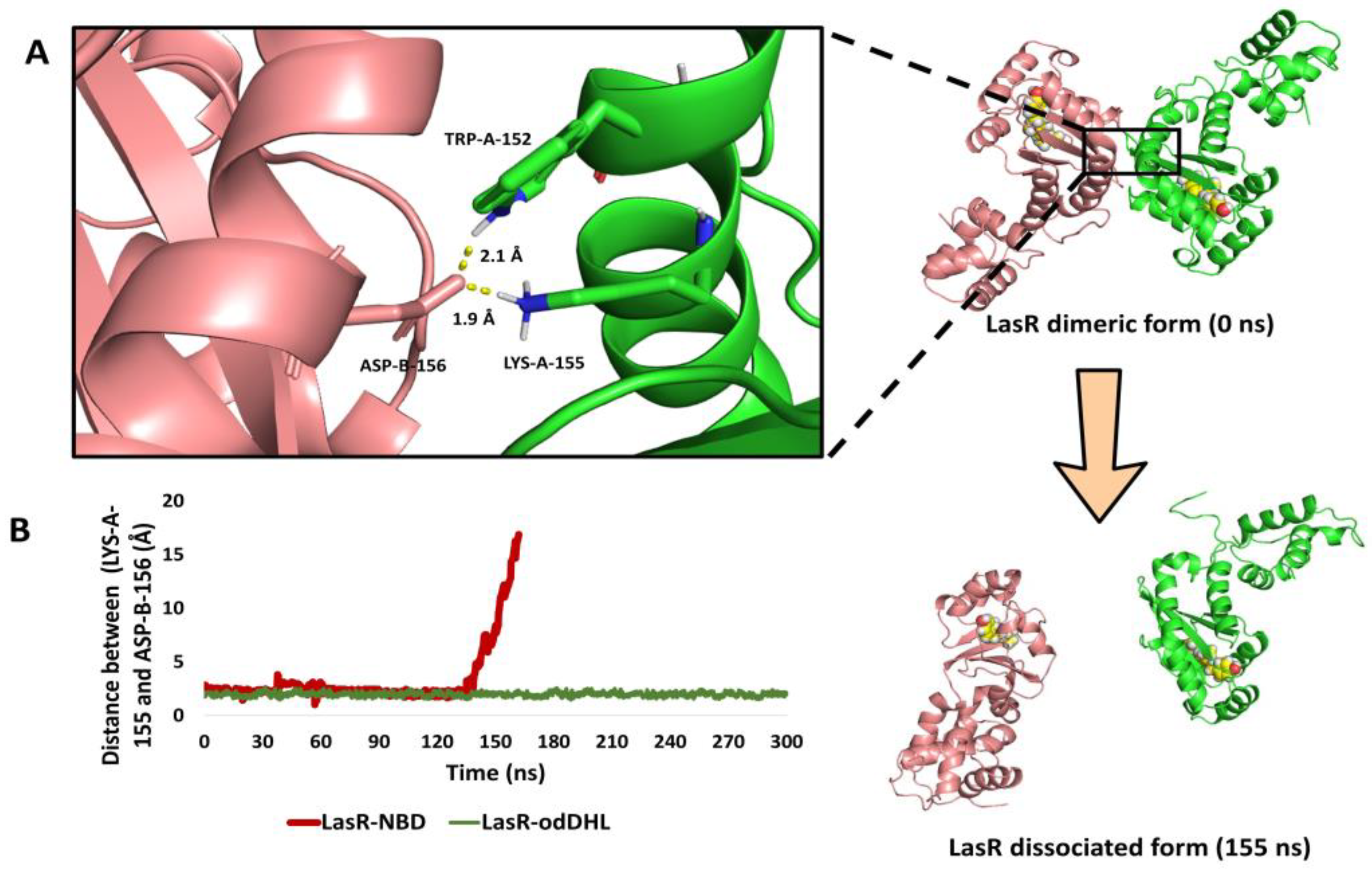
3.5.3. NBD Induces LasR Complex Dissociation upon MD Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forschner-Dancause, S.; Poulin, E.; Meschwitz, S. Quorum Sensing Inhibition and Structure–Activity Relationships of β-Keto Esters. Molecules 2016, 21, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; WHO Librrary Catalog Data; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, P.; Sivaraman, S.; Chandy, S. Communication strategies for improving public awareness on appropriate antibiotic use: Bridging a vital gap for action on antibiotic resistance. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1867–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Speert, D.P. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and impact on treatment. Drug Resist. Update 2000, 3, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, L.S.; Hill, J.M.; Caballero, A.R.; Green, L.C.; O’Callaghan, R.J. Protease IV, a unique extracellular protease and virulence factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16792–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegretta, G.; Maurer, C.K.; Eberhard, J.; Maura, D.; Hartmann, R.W.; Rahme, L.; Maura, M. In-depth profiling of MvfR-regulated small molecules in Pseudomonas aeruginosa after quorum sensing inhibitor treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitwalli, H.; Alsahafi, R.; Balhaddad, A.A.; Weir, M.D.; Xu, H.H.; Melo, M.A. Emerging contact-killing antibacterial strategies for developing anti-biofilm dental polymeric restorative materials. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyi, T.D.; Adetutu, A. In silico anti-quorum sensing activities of phytocompounds of Psidium guajava in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2023, 9, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Kadam, P.; Jain, T.; Bhargava, A.; Marick, A.; Saiya, B.; Maiti, S.; Pandya, S.; Patel, R.; Jadhav, N. Investigation of physico-chemical properties and evaluation of the biological potential of essential oil extracted from Artemisia pallens. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Albetran, H.M.; Alheshibri, M.H.; Timoumi, A.; Algarou, N.A.; Akhtar, S.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.A.; Alahmari, F.S.; Baykal, A.; et al. Synthesis of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers and characterization of their antibacterial and antibiofilm potential against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; McDermott, C.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; McFarland, A.J.; Forbes, A.; Perkins, A.V.; Grant, G.D. Cellular effects of pyocyanin, a secreted virulence factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaros, N.; Nordmann, P.; Plesiat, P.; Roussel-Delvallez, M.; Van Eldere, J.; Glupczynski, Y.; van Laethem, Y.; Jacobs, F.; Lebecque, P.; Malfroot, A.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Resistance and therapeutic options at the turn of the new millennium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipnis, E.; Sawa, T.; Wiener-Kronish, J. Targeting mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2006, 36, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strateva, T.; Mitov, I. Contribution of an arsenal of virulence factors to pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Pierson, E.; Hung, D.T. Targeting virulence: A new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczak, A.K.; Hung, D.T. Productive steps toward an antimicrobial targeting virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, W.R.J.D.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; Bovvden, S.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Applications of small molecule activators and inhibitors of quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Chaudhary, U.; Gupta, V. Quorum sensing and Bacterial Pathogenicity: From Molecules to Disease. J. Lab. Physicians 2011, 3, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, N.A.; Byers, J.T.; Commander, P.; Corbett, M.J.; Coulthurst, S.J.; Everson, L.; Harris, A.K.; Pemberton, C.L.; Simpson, N.J.; Slater, H.; et al. The regulation of virulence in phytopathogenic Erwinia species: Quorum sensing, antibiotics and ecological considerations. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 81, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradal, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekimpe, V.; Deziel, E. Revisiting the quorum-sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The transcriptional regulator RhlR regulates LasR-specific factors. Microbiology 2009, 155, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukatzki, S.; Kessin, R.H.; Mekalanos, J.J. The human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa utilizes conserved virulence pathways to infect the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3159–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Miller, D.M.; Wezeman, R.J.; Mattmann, M.E.; Lin, Q.; Blackwell, H.E. Comparative analyses of N-acylated homoserine lactones reveal unique structural features that dictate their ability to activate or inhibit quorum sensing. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, K.; Steinbach, A.; Helms, V. Interfering with bacterial quorum sensing. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2016, 8, PMC-S13209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowski, J.E.; McCready, A.R.; Cong, J.-P.; Li, Z.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Smith, C.D.; Henke, B.R.; Hughson, F.M.; Bassler, B.L. An autoinducer analogue reveals an alternative mode of ligand binding for the LasR quorum-sensing receptor. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, S.M.; Dunlap, P.V. LuxR-and acyl-homoserine-lactone-controlled non-lux genes define a quorum-sensing regulon in Vibrio fischeri. J. Bacteriol. Res. 2000, 182, 2811–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, C.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of abiotic, non-lactone modulators of LuxR-type quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4812–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Winzer, K.; Chan, W.C.; Camara, M. Look who’s talking: Communication and quorum sensing in the bacterial world. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, J.T.; Galloway, W.R.J.D.; Saraf, S.; Baxendale, I.R.; Ley, S.V.; Ladlow, M.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Microwave and flow syntheses of Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) and analogues. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, C.; Pu, Q.; Deng, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenesis, virulence factors; antibiotic resistance; interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G.; Parsek, M.R.; Pearson, J.P.; Iglewski, B.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Greenberg, E.P. The involvement of cell to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 1998, 280, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.O.; Burmolle, M.; Hentzer, M.; Haagensen, J.A.; Hougen, H.P.; Calum, H.; Madsen, K.G.; Moser, C.; Molin, S.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolerance to tobramycin, hydrogen peroxide and polymorphonuclear leukocytes is quorum sensing dependent. Microbiology 2005, 151, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Hentzer, M.; Kote, P.K.M.; Nielsen, J.; Eberl, L.; Givskov, M. Screening for quorum-sensing inhibitors (QSI) by use of a novel genetic system, the QSI selector. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Hentzer, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Hoiby, N. Synthetic furanones inhibit quorum-sensing and enhance bacterial clearance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintim, H.O.; Smith, J.A.; Wang, J.; Nakayama, S.; Yan, L. Paradigm shift in discovering next-generation anti-infective agents: Targeting quorum sensing, cdi-GMP signaling and biofilm formation in bacteria with small molecules. Future Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 1005–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Nussbaum, F.; Brands, M.; Hinzen, B.; Weigand, S.; Habich, D. Antibacterial natural products in medicinal chemistry–exodus or revival? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 5072–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K. The science of antibiotic discovery. Cell 2020, 181, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfour, H.Z. Anti-Quorum Sensing Natural Compounds. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardot, M.; Millot, M.; Hamion, G.; Billard, J.L.; Juin, C.; Ntoutoume, G.N.; Sol, V.; Mambu, L.; Imbert, C. Lichen polyphenolic compounds for the eradication of Candida albicans biofilms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 698883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompilio, A.; Pomponio, S.; Di Vincenzo, V.; Crocetta, V.; Nicoletti, M.; Piovano, M.; Garbarino, J.A.; Di Bonaventura, G. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of secondary metabolites of lichens against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from cystic fibrosis patients. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, A.; Millot, M.; Pinon, A.; Liagre, B.; Girardot, M.; Imbert, C.; Ouk, T.S.; Jargeat, P.; Mambu, L. Antiproliferative and antibiofilm potentials of endolichenic fungi associated with the lichen Nephroma laevigatum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithyanand, P.; Beema Shafreen, R.M.; Muthamil, S.; Karutha Pandian, S. Usnic acid, a lichen secondary metabolite inhibits Group A Streptococcus biofilms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendili, M.; Khadhri, A.; Mediouni-Ben Jemâa, J.; Andolfi, A.; Tufano, I.; Aschi-Smiti, S.; DellaGreca, M. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Compounds Isolated from Tunisian Lichens Species. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Agarwal, P.; Khatana, K.; Khan, S.A. Biomedical Aspects of Lichen-Derived Products: Roadmap to Alternative Sources for Synthetic Drugs. In Lichen-Derived Products: Extraction and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Roy, S.; Tayung, K.; Yasmin, F. Assessment of antibacterial potential of different solvent extract of foliose lichens against human pathogenic bacteria. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan Kumar, P.; Siva, B.; Anand, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Vekata Rao, C.; Boustie, J.; Suresh Babu, K. Isolation, semi-synthesis, free-radicals scavenging, and advanced glycation end products formation inhibitory constituents from Parmotrema tinctorum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 22, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packiavathy, A.; Sasikumar, P.; Pandian, S.K.; Veeraravi, A. Prevention of quorum-sensing-mediated biofilm development and virulence factors production in Vibrio spp. by curcumin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 10177–10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Bonaventura, G.D.I.; Djukić, S.; Ćirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. APMIS 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Tomida, J. Responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Quercetin is an effective inhibitor of quorum sensing, biofilm formation and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essar, D.W.; Eberly, L.; Hadero, A.; Crawford, I.P. Identification and Characterization of Genesfora Second Anthranilate Synthasein Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Interchange ability of the Two Anthranilate Synthases and Evolutionary Implications. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mawgoud, A.M.; Hausmann, R.; Lepine, F.; Muller, M.M.; Deziel, E. Rhamnolipids: Detection, analysis, biosynthesis, genetic regulation, and bioengineering of production. In Biosurfactants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 13–55. [Google Scholar]
- Deziel, E.; Lepine, F.; Milot, S.; Villemur, R. Mass spectrometry monitoring of rhamnolipids from a growing culture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 57RP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1485, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Nie, Y. Synthesis and inhibitory effect of 4-Br-PHL derivatives on the biofilm of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 42, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, M.C.; Blackwell, H.E. Structure-based design and biological evaluation of triphenyl scaffold-based hybrid compounds as hydrolytically stable modulators of a LuxR-type quorum sensing receptor. ACS Infect. Dis. 2016, 2, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lequette, Y. Activity of purified QscR, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum-sensing transcription factor. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibergen, N.R.; Moore, J.D.; Mattmann, M.E. Potent and Selective Modulation of the RhlR Quorum Sensing Receptor by Using Non-native Ligands: An Emerging Target for Virulence Control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugani, S.A.; Whiteley, M.; Lee, K.M.; D’Argenio, D.; Manoil, C.; Greenberg, E.P. QscR, a modulator of quorum-sensing signal synthesis and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2752–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck, P. Size-distribution analysis of macromolecules by sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation and lamm equation modeling. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 1606–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2. 0: New docking methods, expanded force field. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabash, A.; Chuk, O. Using of PyMOL Program in the Educational Process. Ph.D. Thesis, National Aviation University, Kyiv, Ukraine, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bergdorf, M.; Robinson-Mosher, A.; Guo, X.; Law, K.H.; Shaw, D.E. Desmond/GPU Performance as of April 2021; Technical Report DESRES/TR–2021-01; DE Shaw Research: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, S.T.; Tam, N.M.; Pham, M.Q.; Nguyen, T.H. Benchmark of popular free energy approaches revealing the inhibitors binding to SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Chen, H.; Blazhynska, M.; de Lacam, E.G.C.; Szczepaniak, F.; Pavlova, A.; Shao, X.; Gumbart, J.C.; Dehez, F.; Roux, B.; et al. Accurate determination of protein: Ligand standard binding free energies from molecular dynamics simulations. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 1114–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, M.E.; Chen, L. Structural basis of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent signaling. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, D.E.; O’Reilly, M.C.; Nyffeler, K.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Design, synthesis, and biochemical characterization of non-native antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing receptor LasR with nanomolar IC50 values. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysoczynski-Horita, C.L.; Boursier, M.E.; Hill, R.; Hansen, K.; Blackwell, H.E.; Churchill, M.E. Mechanism of agonism and antagonism of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator QscR with non-native ligands. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 108, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suneby, E.G.; Herndon, L.R.; Schneider, T.L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR DNA binding is directly inhibited by quorum sensing antagonists. ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkunas, B.; Galloway, W.R.; Wright, M.; Ibbeson, B.M.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; O’Connell, K.M.; Bartolucci, N.; Valle, M.D.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Inhibition of the production of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor pyocyanin in wild-type cells by quorum sensing autoinducer-mimics. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8452–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aleam, R.H.A.; Sayed, A.M.; Taha, M.N.; George, R.F.; Georgey, H.H.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M. Design and synthesis of novel benzimidazole derivatives as potential Pseudomonas aeruginosa anti-biofilm agents inhibiting LasR: Evidence from comprehensive molecular dynamics simulation and in vitro investigation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowski, J.E.; Mukherjee, S.; McCready, A.R.; Cong, J.P.; Aquino, C.J.; Kim, H.; Henke, B.R.; Smith, C.D.; Bassler, B.L. Flavonoids suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence through allosteric inhibition of quorum-sensing receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4064–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Dong, Y.; Wu, D.; Bowler, M.W.; Zhang, L.; Song, H. QsIA disrupts LasR dimerization in antiactivation of bacterial quorum sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20765–20770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.T.; Noto, J.G.; Nichols-O’Neill, L.; Perez, L.J. Potent irreversible inhibitors of LasR quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.R.; Ma, Y.K.; Shi, Q.S.; Xie, X.B.; Sun, T.L.; Peng, H.; Huang, X.M. Diallyl disulfide from garlic oil inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors by inactivating key quorum sensing genes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7555–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soltane, R.; Alasiri, A.; Taha, M.N.; Abd El-Aleam, R.H.; Alghamdi, K.S.; Ghareeb, M.A.; Keshek, D.E.-G.; Cardoso, S.M.; Sayed, A.M. Norlobaridone Inhibits Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Some Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Disrupting Its Transcriptional Activator Protein LasR Dimerization. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111573
Soltane R, Alasiri A, Taha MN, Abd El-Aleam RH, Alghamdi KS, Ghareeb MA, Keshek DE-G, Cardoso SM, Sayed AM. Norlobaridone Inhibits Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Some Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Disrupting Its Transcriptional Activator Protein LasR Dimerization. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(11):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111573
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoltane, Raya, Ahlam Alasiri, Mostafa N. Taha, Rehab H. Abd El-Aleam, Kawthar Saad Alghamdi, Mosad A. Ghareeb, Doaa El-Ghareeb Keshek, Susana M. Cardoso, and Ahmed M. Sayed. 2023. "Norlobaridone Inhibits Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Some Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Disrupting Its Transcriptional Activator Protein LasR Dimerization" Biomolecules 13, no. 11: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111573
APA StyleSoltane, R., Alasiri, A., Taha, M. N., Abd El-Aleam, R. H., Alghamdi, K. S., Ghareeb, M. A., Keshek, D. E.-G., Cardoso, S. M., & Sayed, A. M. (2023). Norlobaridone Inhibits Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Some Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Disrupting Its Transcriptional Activator Protein LasR Dimerization. Biomolecules, 13(11), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111573










