Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha (FAPα) in Fibrosis: Beyond a Perspective Marker for Activated Stromal Cells?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Overview of “Activated Stromal Cells” and FAPα as Their Marker
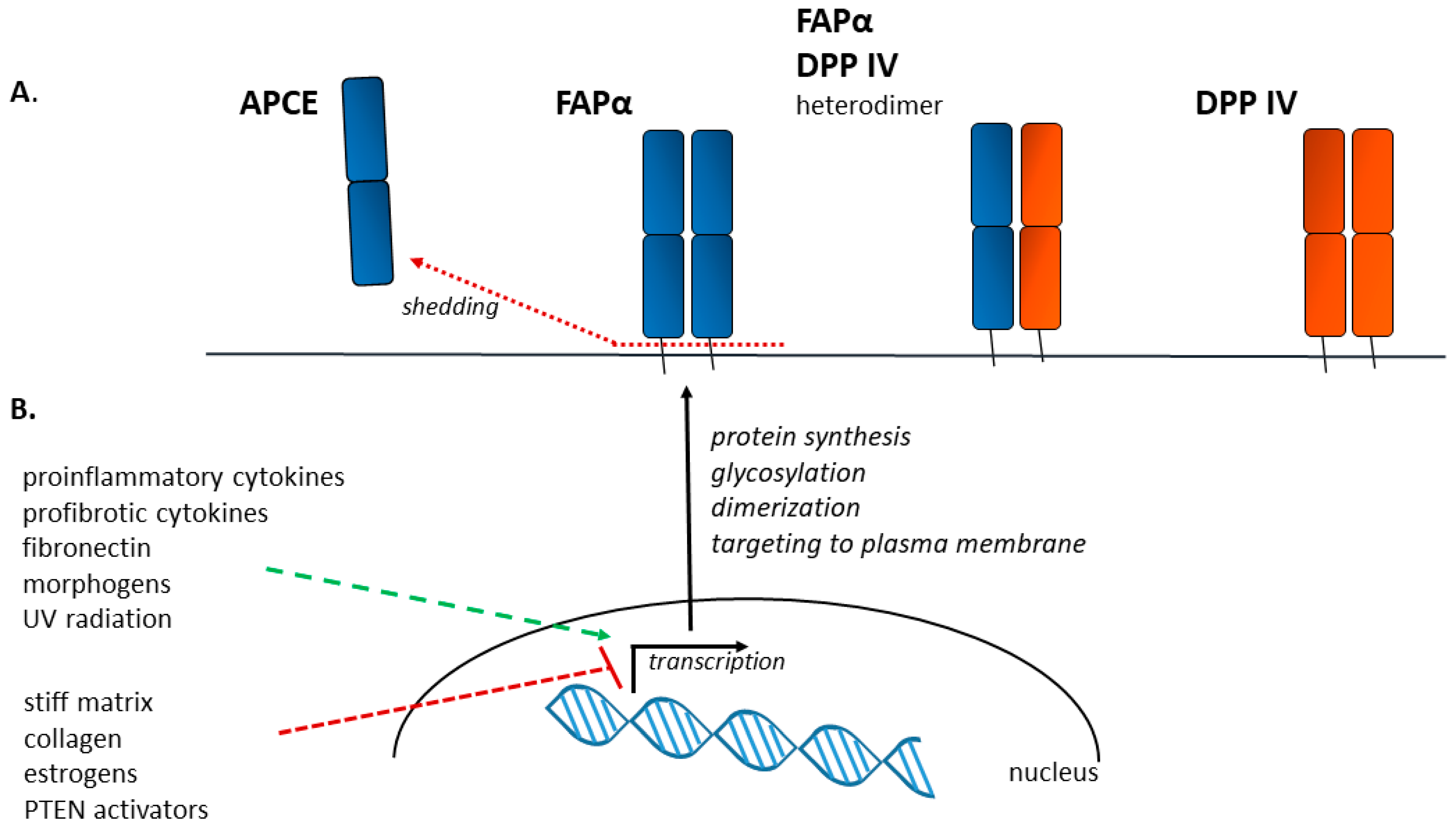
3. FAPα as a Protein—Structure, Activity, Localization
4. Factors Influencing FAPα Expression
5. Functions of FAPα- and FAPα-Positive Cells in Fibrosis
5.1. Paracrine Activity
5.2. ECM Remodeling
5.3. Migration and Invasion
5.4. Myofibroblast Differentiation
5.5. Immune Response
6. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) and FAPα-Positive Fibrosis-Associated Cells (FAFs)—Obvious Similarity to Transfer the Conceptions from Cancer to Fibrosis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reinke, J.M.; Sorg, H. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound Repair and Regeneration: Mechanisms, Signaling, and Translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Tamaki, Z.; Wang, W.; Hinchcliff, M.; Hoover, P.; Getsios, S.; White, E.S.; Varga, J. Fibronectin EDA Promotes Chronic Cutaneous Fibrosis Through Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 232ra50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demura, S.A.; Kogan, E.A.; Paukov, V.S. Pathologic reparation of the stem cell niche zones of respiratory acini in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulʹmonologiâ 2015, 25, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakshir, P.; Hinz, B. The Big Five in Fibrosis: Macrophages, Myofibroblasts, Matrix, Mechanics, and Miscommunication. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68–69, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Common and Unique Mechanisms Regulate Fibrosis in Various Fibroproliferative Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Kalluri, R. Cellular Mechanisms of Tissue Fibrosis. 1. Common and Organ-Specific Mechanisms Associated with Tissue Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C216–C225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B. Formation and Function of the Myofibroblast during Tissue Repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochaton-Piallat, M.-L.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B. The Myofibroblast in Wound Healing and Fibrosis: Answered and Unanswered Questions. F1000Res 2016, 5, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Fibroblasts in Fibrosis: Novel Roles and Mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.W.; Mifflin, R.C.; Valentich, J.D.; Crowe, S.E.; Saada, J.I.; West, A.B. Myofibroblasts. I. Paracrine Cells Important in Health and Disease. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1999, 277, C1–C19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldi, R.; Hiltbrunner, A.; Dugina, V.; Tille, J.-C.; Chaponnier, C. Smooth Muscle Actin Isoforms: A Tug of War between Contraction and Compliance. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 92, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Talele, N.P.; Boo, S.; Koehler, A.; Knee-Walden, E.; Balestrini, J.L.; Speight, P.; Kapus, A.; Hinz, B. MicroRNA-21 Preserves the Fibrotic Mechanical Memory of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, A.V.; Kelsh, R.; Peters, J.H.; Sekiguchi, K.; Van De Water, L.; McKeown-Longo, P.J. The A4β1 Integrin and the EDA Domain of Fibronectin Regulate a Profibrotic Phenotype in Dermal Fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2015, 41, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinejad-Farsangi, S.; Farazmand, A.; Gharibdoost, F.; Karimizadeh, E.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Faridani, H.; Mahmoudi, M.; Jamshidi, A.R. Inhibition of MicroRNA-21 Induces Apoptosis in Dermal Fibroblasts of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, D.; He, M.; Hong, C.; Gao, S.; Rane, S.; Yang, Z.; Abdellatif, M. MicroRNA-21 Is a Downstream Effector of AKT That Mediates Its Antiapoptotic Effects via Suppression of Fas Ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20281–20290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Dang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, M.; Hua, H. MicroRNA-98 Inhibits TGF-Β1-Induced Differentiation and Collagen Production of Cardiac Fibroblasts by Targeting TGFBR1. Hum. Cell 2017, 30, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, S.; Bone, N.B.; Zmijewska, A.A.; Jiang, S.; Park, D.W.; Bernard, K.; Locy, M.L.; Ravi, S.; Deshane, J.; Mannon, R.B.; et al. Metformin Reverses Established Lung Fibrosis in a Bleomycin Model. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reverse EMT via TGF-Β1/Smad Pathway and Promote Repair of Damaged Endometrium. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwanpura, S.M.; Thomas, B.J.; Bardin, P.G. Pirfenidone: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Clinical Applications in Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagares, D.; Santos, A.; Grasberger, P.E.; Liu, F.; Probst, C.K.; Rahimi, R.A.; Sakai, N.; Kuehl, T.; Ryan, J.; Bhola, P.; et al. Targeted Apoptosis of Myofibroblasts with the BH3 Mimetic ABT-263 Reverses Established Fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Li, M.-Y.; Nakamura, T. HGF Reduces Advancing Lung Fibrosis in Mice: A Potential Role for MMP-dependent Myofibroblast Apoptosis. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Lin, S.; Mao, C.; Wang, B.; Song, X.; Lv, C. Astaxanthin Prevents Pulmonary Fibrosis by Promoting Myofibroblast Apoptosis Dependent on Drp1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2215–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataliya, B.; Mikhail, A.; Vladimir, P.; Olga, G.; Maksim, V.; Ivan, Z.; Ekaterina, N.; Georgy, S.; Natalia, D.; Pavel, M.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Facilitate Resolution of Pulmonary Fibrosis by miR-29c and miR-129 Intercellular Transfer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, V.D.; Hsia, H.C.; Schwarzbauer, J.E. Reversible Modulation of Myofibroblast Differentiation in Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, L.; Jagirdar, R.; Jin, T.; Thannickal, V.J. Reversible Differentiation of Myofibroblasts by MyoD. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toblli, J.E.; Ferrini, M.G.; Cao, G.; Vernet, D.; Angerosa, M.; Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F. Antifibrotic Effects of Pioglitazone on the Kidney in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Mohamed, M.Z.; El-Tahawy, N.F.; Abdelrahman, A.M. Antifibrotic Effects of Bezafibrate and Pioglitazone against Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Albino Rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Varone, F.; Bergna, M.; de Andrade, J.; Falk, J.; Hallowell, R.; Jouneau, S.; Kondoh, Y.; Morrow, L.; Randerath, W.; et al. Pharmacological Management of Progressive-Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Review of the Current Evidence. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyts, W.A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Borensztajn, K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Crestani, B.; Grutters, J.C.; Maher, T.M.; Poletti, V.; Richeldi, L.; et al. Combination Therapy: The Future of Management for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of Fibrosis: Therapeutic Translation for Fibrotic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHutchison, J.; Goodman, Z.; Patel, K.; Makhlouf, H.; Rodriguez–Torres, M.; Shiffman, M.; Rockey, D.; Husa, P.; Chuang, W.; Levine, R.; et al. Farglitazar Lacks Antifibrotic Activity in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1365–1373.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.E.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A Phase 3 Trial of Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.W.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kardatzke, D.; King, T.E.; Lancaster, L.; Sahn, S.A.; Szwarcberg, J.; et al. Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (CAPACITY): Two Randomised Trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Pinzani, M. Anti-Fibrotic Therapy: Lost in Translation? J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, S66–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Prasse, A.; Kreuter, M.; Johow, J.; Rabe, K.F.; Bonella, F.; Bonnet, R.; Grohe, C.; Held, M.; Wilkens, H.; et al. Pirfenidone in Patients with Progressive Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases Other than Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (RELIEF): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2b Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilberg, F.; Tontsch-Grunt, U.; Baum, A.; Le, A.T.; Doebele, R.C.; Lieb, S.; Gianni, D.; Voss, T.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Haslinger, C.; et al. Triple Angiokinase Inhibitor Nintedanib Directly Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth and Induces Tumor Shrinkage via Blocking Oncogenic Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.H.; Fine, A. Fibrotic Reactions in the Lung: The Activation of the Lung Fibroblast. Exp. Lung Res. 1986, 11, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorio, T.K.; Kähäri, V.-M.; Lehtonen, A.; Vuorio, E.I. Fibroblast Activation in Scleroderma. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1984, 13, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E. Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1990, 259, L159–L184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, C.; Boldt, J.; King, T.E.; Crouch, E.; Vartio, T.; McDonald, J.A. An Immunohistochemical Study of Architectural Remodeling and Connective Tissue Synthesis in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 140, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, J.J.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B.; Chaponnier, C.; Brown, R.A. Myofibroblasts and Mechano-Regulation of Connective Tissue Remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbiani, G. 50 Years of Myofibroblasts: How the Myofibroblast Concept Evolved. In Myofibroblasts; Hinz, B., Lagares, D., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2299, pp. 1–5. ISBN 978-1-07-161381-8. [Google Scholar]
- van Caam, A.; Vonk, M.; van den Hoogen, F.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P. Unraveling SSc Pathophysiology; The Myofibroblast. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Blockade of PDGF Receptor Signaling Reduces Myofibroblast Number and Attenuates Renal Fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugina, V.; Fontao, L.; Chaponnier, C.; Vasiliev, J.; Gabbiani, G. Focal Adhesion Features during Myofibroblastic Differentiation Are Controlled by Intracellular and Extracellular Factors. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, C.A.; Finato, N.; Rocco, M.; Feruglio, G.A.; Puricelli, C.; Cigola, E.; Quaini, F.; Sonnenblick, E.H.; Olivetti, G.; Anversa, P. Structural Basis of End-Stage Failure in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy in Humans. Circulation 1994, 89, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detlefsen, S.; Sipos, B.; Feyerabend, B.; Klöppel, G. Pancreatic Fibrosis Associated with Age and Ductal Papillary Hyperplasia. Virchows Arch. 2005, 447, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasebe, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Akashi-Tanaka, S.; Hojo, T.; Shibata, T.; Sasajima, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Tsuda, H. P53 Expression in Tumor-Stromal Fibroblasts Forming and Not Forming Fibrotic Foci in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.M.; Chu, E.; Lau, K.H.V.; Kwong, A.J. Liver Fibrosis in Elderly Cadavers: Localization of Collagen Types I, III, and IV, α-Smooth Muscle Actin, and Elastic Fibers. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.; Henke, C.A.; Bitterman, P.B. Extracellular Matrix as a Driver of Progressive Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.; Forster, C.; Pengo, T.; Montero, A.; Swift, J.; Schwartz, M.A.; Henke, C.A.; Bitterman, P.B. Registration of the Extracellular Matrix Components Constituting the Fibroblastic Focus in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e125185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.S.; Zukas, A.; Chandan, V.; Katzenstein, A.-L.A.; Puré, E. Fibroblast Activation Protein: A Serine Protease Expressed at the Remodeling Interface in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Meltzer, E.B.; Gray, A.; Miura, R.; Wogensen, L.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Noble, P.W. Severe Lung Fibrosis Requires an Invasive Fibroblast Phenotype Regulated by Hyaluronan and CD44. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, O.; Winkler, J.; Minasyan, M.; Herzog, E.L. The Role of Immune and Inflammatory Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, C.; McDonald, J.A. The Roles of the Myofibroblast in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ultrastructural and Immunohistochemical Features of Sites of Active Extracellular Matrix Synthesis. Am. J. Pathol. 1991, 138, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Röhrich, M.; Leitz, D.; Glatting, F.M.; Wefers, A.K.; Weinheimer, O.; Flechsig, P.; Kahn, N.; Mall, M.A.; Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein–Specific PET/CT Imaging in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Translational Exploratory Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-T. Proteolytic Activity of Specialized Surface Protrusions Formed at Rosette Contact Sites of Transformed Cells. J. Exp. Zool. 1989, 251, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Fang, Q.; Fu, Z.; Li, J.; Lai, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Peng, X.; Hu, K.; Nie, X.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Expression in Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsky, W.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Aoyama, A.; Kelly, T.; Akiyama, S.K.; Mueller, S.C.; Chen, W.T. A Potential Marker Protease of Invasiveness, Seprase, Is Localized on Invadopodia of Human Malignant Melanoma Cells. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 5702–5710. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, P.; O’Connor, B.F. Seprase: An Overview of an Important Matrix Serine Protease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2008, 1784, 1130–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Albright, C.F.; Fish, B.H.; George, H.J.; Selling, B.H.; Hollis, G.F.; Wynn, R. Expression, Purification, and Kinetic Characterization of Full-Length Human Fibroblast Activation Protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 24, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.N.; Jackson, K.W.; Christiansen, V.J.; Lee, C.S.; Chun, J.-G.; McKee, P.A. Antiplasmin-Cleaving Enzyme Is a Soluble Form of Fibroblast Activation Protein. Blood 2006, 107, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.E.; Hamson, E.J.; Koczorowska, M.M.; Tholen, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Bailey, C.G.; Lay, A.J.; Twigg, S.M.; Lee, Q.; Roediger, B.; et al. Identification of Novel Natural Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Alpha by Differential Degradomics and Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, F.M.; Nadvi, N.A.; Yao, T.-W.; Gorrell, M.D. Neuropeptide Y, B-Type Natriuretic Peptide, Substance P and Peptide YY Are Novel Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α: Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1316–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, L.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R. Fibroblast Activation Protein-α as a Target in the Bench-to-Bedside Diagnosis and Treatment of Tumors: A Narrative Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 648187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, M.J.; Raj, B.K.; Calvo, B.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Sanz-Moncasi, M.P.; Healey, J.H.; Old, L.J.; Rettig, W.J. Molecular Cloning of Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha, a Member of the Serine Protease Family Selectively Expressed in Stromal Fibroblasts of Epithelial Cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5657–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Scanlan, M.J.; Mohan Raj, B.K.; Murty, V.V.V.S.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Old, L.J.; Rettig, W.J.; Chaganti, R.S.K. The Gene for Fibroblast Activation Protein α (FAP), a Putative Cell Surface-Bound Serine Protease Expressed in Cancer Stroma and Wound Healing, Maps to Chromosome Band 2q23. Genomics 1995, 25, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrell, M.D.; Gysbers, V.; McCaughan, G.W. CD26: A Multifunctional Integral Membrane and Secreted Protein of Activated Lymphocytes: CD26: Receptor and Peptidase. Scand. J. Immunol. 2001, 54, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, W.J.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Beresford, H.R.; Oettgen, H.F.; Melamed, M.R.; Old, L.J. Cell-Surface Glycoproteins of Human Sarcomas: Differential Expression in Normal and Malignant Tissues and Cultured Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3110–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, J.; Kriz, M.; Hilberg, F.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Bamberger, U.; Lenter, M.C.; Park, J.; Viertel, B.; Püschner, H.; Mauz, M.; et al. Targeted Disruption of Mouse Fibroblast Activation Protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, J.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Kriz, M.; Hilberg, F.; Mueller, E.; Bamberger, U.; Rettig, W.J.; Schnapp, A. Expression of the Fibroblast Activation Protein during Mouse Embryo Development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2001, 45, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Parkhurst, S.M. Parallels between Tissue Repair and Embryo Morphogenesis. Development 2004, 131, 3021–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.W.; Deonarine, A.; Jones, J.O.; Denton, A.E.; Feig, C.; Lyons, S.K.; Espeli, M.; Kraman, M.; McKenna, B.; Wells, R.J.B.; et al. Depletion of Stromal Cells Expressing Fibroblast Activation Protein-α from Skeletal Muscle and Bone Marrow Results in Cachexia and Anemia. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolznig, H.; Schweifer, N.; Puri, C.; Kraut, N.; Rettig, W.J.; Kerjaschki, D.; Garin-Chesa, P. Characterization of Cancer Stroma Markers: In Silico Analysis of an mRNA Expression Database for Fibroblast Activation Protein and Endosialin. Cancer Immun. 2005, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Croft, A.P.; Campos, J.; Jansen, K.; Turner, J.D.; Marshall, J.; Attar, M.; Savary, L.; Wehmeyer, C.; Naylor, A.J.; Kemble, S.; et al. Distinct Fibroblast Subsets Drive Inflammation and Damage in Arthritis. Nature 2019, 570, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monslow, J.; Todd, L.; Chojnowski, J.E.; Govindaraju, P.K.; Assoian, R.K.; Puré, E. Fibroblast Activation Protein Regulates Lesion Burden and the Fibroinflammatory Response in Apoe-Deficient Mice in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1118–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmanns, J.; Hoffmann, D.; Habbaba, Y.; Schmitto, J.D.; Sedding, D.; Fraccarollo, D.; Galuppo, P.; Bauersachs, J. Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha Expression Identifies Activated Fibroblasts after Myocardial Infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 87, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettig, W.J.; Su, S.L.; Fortunato, S.R.; Scanlan, M.J.; Mohan Raj, B.K.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Healey, J.H.; Old, L.J. Fibroblast Activation Protein: Purification, Epitope Mapping and Induction by Growth Factors. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 58, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, W.-W.; Wen, Q.-T.; Xu, L.; Chen, M. TGF-β-Induced Fibroblast Activation Protein Expression, Fibroblast Activation Protein Expression Increases the Proliferation, Adhesion, and Migration of HO-8910PM. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 87, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokopp, C.E.; Schoenauer, R.; Richards, P.; Bauer, S.; Lohmann, C.; Emmert, M.Y.; Weber, B.; Winnik, S.; Aikawa, E.; Graves, K.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Is Induced by Inflammation and Degrades Type I Collagen in Thin-Cap Fibroatheromata. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.; Govindaraju, P.; Jacob, M.; Todd, L.; Monslow, J.; Puré, E. Extracellular Matrix Directs Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Activated Fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2018, 67, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Xie, B.; Lu, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Z. microRNA-30a Attenuates TGF-β1–Induced Activation of Pulmonary Fibroblast Cell by Targeting FAP-α. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 3745–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, M.J.; Farhadi, E.; Vodjgani, M.; Karami, J.; Tahmasebi, M.N.; Sharafat Vaziri, A.; Asgari, M.; Rezaei, N.; Mostafaei, S.; Jamshidi, A.; et al. Role of Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes of Rheumatoid Arthritis. IJAAI 2021, 20, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, O. Ultraviolet Exposure of Melanoma Cells Induces Fibroblast Activation Protein-α in Fibroblasts: Implications for Melanoma Invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2011 39, 193–202. [CrossRef]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Tafelmeyer, P.; Golshayan, D. Regulation of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α Expression: Focus on Intracellular Protein Interactions. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 14028–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Guan, Q.; Zheng, L.; Qu, X.; Dai, H.; Cheng, Z. Estrogen-Mediated Activation of Fibroblasts and Its Effects on the Fibroid Cell Proliferation. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GeneCards. Available online: https://Www.Genecards.Org/Cgi-Bin/Carddisp.Pl?gene=FAP (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Higashino, N.; Koma, Y.; Hosono, M.; Takase, N.; Okamoto, M.; Kodaira, H.; Nishio, M.; Shigeoka, M.; Kakeji, Y.; Yokozaki, H. Fibroblast Activation Protein-Positive Fibroblasts Promote Tumor Progression through Secretion of CCL2 and Interleukin-6 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L. Vocal Fold Fibroblasts Promote Angiogenesis in Vocal Fold Leukoplakia by Secreting Pro-Angiogenic Factors. Auris Nasus Larynx 2022, 49, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segerer, S.E.; Bartmann, C.; Schwab, M.; Kämmerer, U. Expression of the Peptidase “Fibroblast Activation Protein” on Decidual Stromal Cells Facilitating Tissue Remodeling. Gynecol. Obs. Investig. 2020, 85, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Kelly, T. Seprase Promotes Rapid Tumor Growth and Increased Microvessel Density in a Mouse Model of Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2712–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto-Llerena, M.; Ercan, C.; Kancherla, V.; Taha-Mehlitz, S.; Eppenberger-Castori, S.; Soysal, S.D.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Bolli, M.; Von Flüe, M.; Nicolas, G.P.; et al. High Expression of FAP in Colorectal Cancer Is Associated with Angiogenesis and Immunoregulation Processes. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghersi, G.; Zhao, Q.; Salamone, M.; Yeh, Y.; Zucker, S.; Chen, W.-T. The Protease Complex Consisting of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV and Seprase Plays a Role in the Migration and Invasion of Human Endothelial Cells in Collagenous Matrices. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4652–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-O.; Mullins, S.R.; Franco-Barraza, J.; Valianou, M.; Cukierman, E.; Cheng, J.D. FAP-Overexpressing Fibroblasts Produce an Extracellular Matrix That Enhances Invasive Velocity and Directionality of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, V.J.; Jackson, K.W.; Lee, K.N.; McKee, P.A. Effect of Fibroblast Activation Protein and A2-Antiplasmin Cleaving Enzyme on Collagen Types I, III, and IV. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 457, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Lenter, M.C.; Zimmermann, R.N.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Old, L.J.; Rettig, W.J. Fibroblast Activation Protein, a Dual Specificity Serine Protease Expressed in Reactive Human Tumor Stromal Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 36505–36512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.-H.; Zhu, Q.; Li, H.-H.; Ra, H.-J.; Majumdar, S.; Gulick, D.L.; Jerome, J.A.; Madsen, D.H.; Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Speicher, D.W.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Accelerates Collagen Degradation and Clearance from Lungs in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8070–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Monslow, J.; Klampatsa, A.; Leibowitz, M.; Sun, J.; Liousia, M.; Woodruff, P.; Moon, E.; Todd, L.; Puré, E.; et al. Loss of Cells Expressing Fibroblast Activation Protein Has Variable Effects in Models of TGF-β and Chronic Bleomycin-Induced Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2019, 317, L271–L282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Yu, D.M.T.; McCaughan, G.W.; Gorrell, M.D. Fibroblast Activation Protein Increases Apoptosis, Cell Adhesion, and Migration by the LX-2 Human Stellate Cell Line. Hepatology 2005, 42, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Li, L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Rong, Y.; Li, Y. Mechanism of Regulation of Stem Cell Differentiation by Matrix Stiffness. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffi, M.; Sorrentino, L.; Monieri, M.; Fociani, P.; Mazzucchelli, S.; Bonzini, M.; Zerbi, P.; Sampietro, G.M.; Di Sabatino, A.; Corsi, F. Inhibition of Fibroblast Activation Protein Restores a Balanced Extracellular Matrix and Reduces Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease Strictures Ex Vivo. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, C.K.; Dries, E.; Popovic, N.; Singh, A.A.; Haemers, P.; Roderick, H.L.; Claus, P.; Sipido, K.R.; Driesen, R.B. Global Fibroblast Activation throughout the Left Ventricle but Localized Fibrosis after Myocardial Infarction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.-T.; Kim, Y.-O.; Yan, X.-Z.; Abe, H.; Aslam, M.; Park, K.-S.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Jia, J.-D.; Klein, T.; You, H.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Activates Macrophages and Promotes Parenchymal Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 841–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Jendro, M.C.; Wadle, A.; Kleber, S.; Stenner, F.; Dinser, R.; Reich, A.; Faccin, E.; Gödde, S.; Dinges, H.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Is Expressed by Rheumatoid Myofibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Missotten, L.; Geboes, K. Expression of Myofibroblast Activation Molecules in Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy Epiretinal Membranes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011, 89, e115–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D.B.; Fraccarollo, D.; Galuppo, P.; Frantz, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Tillmanns, J. Genetic Ablation of Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha Attenuates Left Ventricular Dilation after Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovgren, A.K.; Kovacs, J.J.; Xie, T.; Potts, E.N.; Li, Y.; Foster, W.M.; Liang, J.; Meltzer, E.B.; Jiang, D.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; et al. β-Arrestin Deficiency Protects Against Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice and Prevents Fibroblast Invasion of Extracellular Matrix. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 74ra23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbayianni, I.; Kanellopoulou, P.; Fanidis, D.; Nastos, D.; Ntouskou, E.-D.; Galaris, A.; Harokopos, V.; Hatzis, P.; Tsitoura, E.; Homer, R.; et al. SRC and TKS5 Mediated Podosome Formation in Fibroblasts Promotes Extracellular Matrix Invasion and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Habiel, D.M.; Vrishika, K.; Coelho, A.L.; Deng, N.; Xie, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; et al. PD-L1 on Invasive Fibroblasts Drives Fibrosis in a Humanized Model of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e125326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svee, K.; White, J.; Vaillant, P.; Jessurun, J.; Roongta, U.; Krumwiede, M.; Johnson, D.; Henke, C. Acute Lung Injury Fibroblast Migration and Invasion of a Fibrin Matrix Is Mediated by CD44. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1713–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qu, J.; Huang, X.; Kurundkar, A.; Zhu, L.; Yang, N.; Venado, A.; Ding, Q.; Liu, G.; Antony, V.B.; et al. Mechanosensing by the A6-Integrin Confers an Invasive Fibroblast Phenotype and Mediates Lung Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.S.; Thannickal, V.J.; Carskadon, S.L.; Dickie, E.G.; Livant, D.L.; Markwart, S.; Toews, G.B.; Arenberg, D.A. Integrin α 4β1 Regulates Migration across Basement Membranes by Lung Fibroblasts: A Role for Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Deleted on Chromosome 10. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.W.; Rossi, D.; Peterson, M.; Smith, K.; Sikström, K.; White, E.S.; Connett, J.E.; Henke, C.A.; Larsson, O.; Bitterman, P.B. Fibrotic Extracellular Matrix Activates a Profibrotic Positive Feedback Loop. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimes, R.; Zijlstra, A.; Hooper, J.; Ogbourne, S.; Sit, M.-L.; Fuchs, S.; Gotley, D.; Quigley, J.; Antalis, T. Endothelial Cell Serine Proteases Expressed during Vascular Morphogenesis and Angiogenesis. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 89, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, X.; Dai, Y.; Yang, T.; Chen, K. Radiation-Induced FAP + Fibroblasts Are Involved in Keloid Recurrence after Radiotherapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 957363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienus, K.; Bayat, A.; Gilmore, B.F.; Seifert, O. Increased Expression of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Alpha in Keloid Fibroblasts: Implications for Development of a Novel Treatment Option. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovedatti, L.; Di Sabatino, A.; Knowles, C.H.; Sengupta, N.; Biancheri, P.; Corazza, G.R.; MacDonald, T.T. Fibroblast Activation Protein Expression in Crohn’s Disease Strictures. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, S.; Maarek, M.; Coumel, P.; Guize, L.; Lekieffre, J.; Medvedowsky, J.-L.; Sebaoun, A. Characterization of Different Subsets of Atrial Fibrillation in General Practice in France: The ALFA Study. Circulation 1999, 99, 3028–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, D.; Handly-Santana, A.; Biffi, G.; Elyada, E.; Almeida, A.S.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Corbo, V.; Oni, T.E.; Hearn, S.A.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Distinct Populations of Inflammatory Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilvaer, T.K.; Rakaee, M.; Hellevik, T.; Østman, A.; Strell, C.; Bremnes, R.M.; Busund, L.-T.; Dønnem, T.; Martinez-Zubiaurre, I. Tissue Analyses Reveal a Potential Immune-Adjuvant Function of FAP-1 Positive Fibroblasts in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, D.N.; van Caam, A.P.M.; Vitters, E.L.; Walgreen, B.; Helsen, M.M.A.; Klein, C.; Gudi, S.; Wubs, T.; Kumari, J.; Vonk, M.C.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Targeted Photodynamic Therapy Selectively Kills Activated Skin Fibroblasts from Systemic Sclerosis Patients and Prevents Tissue Contraction. IJMS 2021, 22, 12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppage, A.L.; Heard, K.R.; DiMare, M.T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Lai, J.H.; Bachovchin, W.W. Human FGF-21 Is a Substrate of Fibroblast Activation Protein. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ye, S.; Chen, X.; Gong, F.; Lu, W.; Li, X. Rush to the Fire: FGF21 Extinguishes Metabolic Stress, Metaflammation and Tissue Damage. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2017, 38, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, E.Y.; Jin, Z.; Ackermann, B.L.; Thomas, M.K.; Gutierrez, J.A. Circulating FGF21 Proteolytic Processing Mediated by Fibroblast Activation Protein. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picke, A.-K.; Campbell, G.M.; Blüher, M.; Krügel, U.; Schmidt, F.N.; Tsourdi, E.; Winzer, M.; Rauner, M.; Vukicevic, V.; Busse, B.; et al. Thy-1 (CD90) Promotes Bone Formation and Protects against Obesity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes: Key Effector Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, D.N.; Rijpkema, M.; Buitinga, M.; Walgreen, B.; Helsen, M.M.A.; Brennan, E.; Klein, C.; Laverman, P.; Ramming, A.; Schmidkonz, C.; et al. Targeting of Fibroblast Activation Protein in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Imaging and Ex. Vivo Photodynamic Therapy. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, D.N.; Rijpkema, M.; Boss, M.; Walgreen, B.; Helsen, M.M.A.; Bos, D.L.; Brom, M.; Klein, C.; Laverman, P.; Van Der Kraan, P.M.; et al. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy Selectively Kills Activated Fibroblasts in Experimental Arthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3952–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, C.; Cannet, C.; Gérard, C.; Suply, T.; Ksiazek, I.; Jarman, E.; Beckmann, N. Effects of the Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor, PT100, in a Murine Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 809, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y. Allograft Inflammatory Factor-1 and Its Immune Regulation. Autoimmunity 2007, 40, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The Biology and Function of Fibroblasts in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, Y.; Knops, N.; Elmonem, M.A.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Arcolino, F.O.; Van Den Heuvel, L.; Levtchenko, E.; Kuypers, D.; Goldschmeding, R. Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) from Basics to Clinics. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68–69, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fukui, H.; Hara, K.; Zhang, X.; Kitayama, Y.; Eda, H.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; Kikuchi, S.; Watari, J.; et al. FGF9 from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Is a Possible Mediator of Invasion and Anti-Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopf, J.D.; Tholen, S.; Koczorowska, M.M.; De Wever, O.; Biniossek, M.L.; Schilling, O. The Stromal Cell-Surface Protease Fibroblast Activation Protein-α Localizes to Lipid Rafts and Is Recruited to Invadopodia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Simms, A.E.; Mazur, A.; Wang, S.; León, N.R.; Jones, B.; Aziz, N.; Kelly, T. Fibroblast Activation Protein-α Promotes Tumor Growth and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells through Non-Enzymatic Functions. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.C.; Ghersi, G.; Akiyama, S.K.; Sang, Q.-X.A.; Howard, L.; Pineiro-Sanchez, M.; Nakahara, H.; Yeh, Y.; Chen, W.-T. A Novel Protease-Docking Function of Integrin at Invadopodia. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24947–24952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.M.; Jung, J.; Aziz, N.; Kissil, J.L.; Puré, E. Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibits Tumor Stromagenesis and Growth in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3613–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yu, S.-Y.; Bao, X.; Ohyama, C.; Khoo, K.-H.; Fukuda, M.N.; Fukuda, M. Core3 O-Glycan Synthase Suppresses Tumor Formation and Metastasis of Prostate Carcinoma PC3 and LNCaP Cells through Down-Regulation of A2β1 Integrin Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17157–17169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artym, V.V.; Zhang, Y.; Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, F.; Yamada, K.M.; Mueller, S.C. Dynamic Interactions of Cortactin and Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase at Invadopodia: Defining the Stages of Invadopodia Formation and Function. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3034–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanian, H.; Kimura, T.; Rurik, J.G.; Hancock, A.S.; Leibowitz, M.S.; Li, L.; Scholler, J.; Monslow, J.; Lo, A.; Han, W.; et al. Targeting Cardiac Fibrosis with Engineered T Cells. Nature 2019, 573, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Byun, J.; Shim, G.; Oh, Y.-K. Fibroblast Activation Protein Activated Antifibrotic Peptide Delivery Attenuates Fibrosis in Mouse Models of Liver Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichgräber, V.; Monasterio, C.; Chaitanya, K.; Boger, R.; Gordon, K.; Dieterle, T.; Jäger, D.; Bauer, S. Specific Inhibition of Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)-Alpha Prevents Tumor Progression in Vitro. Adv. Med. Sci. 2015, 60, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Dendl, K.; Cardinale, J.; Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Haberkorn, U. FAPI PET: Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor Use in Oncologic and Nononcologic Disease. Radiology 2023, 306, e220749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.; Heirbaut, L.; Cheng, J.D.; Joossens, J.; Ryabtsova, O.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Lambeir, A.-M.; De Meester, I.; Augustyns, K.; et al. Selective Inhibitors of Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) with a (4-Quinolinoyl)-Glycyl-2-Cyanopyrrolidine Scaffold. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, E.; Chinnasamy, D.; Yu, Z.; Morgan, R.A.; Lee, C.-C.R.; Restifo, N.P.; Rosenberg, S.A. Immune Targeting of Fibroblast Activation Protein Triggers Recognition of Multipotent Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Cachexia. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, R.-Z.; Ruan, J.; Zhu, X.-B.; Yang, Y. Up-Regulation of THY1 Attenuates Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis and Promotes Lung Fibroblast Apoptosis during Acute Interstitial Pneumonia by Blockade of the WNT Signaling Pathway. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagood, J.S.; Prabhakaran, P.; Kumbla, P.; Salazar, L.; MacEwen, M.W.; Barker, T.H.; Ortiz, L.A.; Schoeb, T.; Siegal, G.P.; Alexander, C.B.; et al. Loss of Fibroblast Thy-1 Expression Correlates with Lung Fibrogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hagood, J.S.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E. Thy-1 Expression Regulates the Ability of Rat Lung Fibroblasts to Activate Transforming Growth Factor-β in Response to Fibrogenic Stimuli. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagood, J.S.; Mangalwadi, A.; Guo, B.; MacEwen, M.W.; Salazar, L.; Fuller, G.M. Concordant and Discordant Interleukin-1–Mediated Signaling in Lung Fibroblast Thy-1 Subpopulations. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 26, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, T.H.; Grenett, H.E.; MacEwen, M.W.; Tilden, S.G.; Fuller, G.M.; Settleman, J.; Woods, A.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.; Hagood, J.S. Thy-1 Regulates Fibroblast Focal Adhesions, Cytoskeletal Organization and Migration through Modulation of P190 RhoGAP and Rho GTPase Activity. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 295, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.F.; Strane, P.W.; Bryksin, A.V.; White, E.S.; Hagood, J.S.; Barker, T.H. Conformational Coupling of Integrin and Thy-1 Regulates Fyn Priming and Fibroblast Mechanotransduction. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 211, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shentu, T.-P.; Huang, T.-S.; Cernelc-Kohan, M.; Chan, J.; Wong, S.S.; Espinoza, C.R.; Tan, C.; Gramaglia, I.; van der Heyde, H.; Chien, S.; et al. Thy-1 Dependent Uptake of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Blocks Myofibroblastic Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipman, W.D.; Sandoval, M.J.; Veiga, K.; Donlin, L.T.; Lu, T.T. Fibroblast Subtypes in Tissues Affected by Autoimmunity: With Lessons from Lymph Node Fibroblasts. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 64, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein Shochet, G.; Brook, E.; Israeli-Shani, L.; Edelstein, E.; Shitrit, D. Fibroblast Paracrine TNF-α Signaling Elevates Integrin A5 Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinek, A. Adhesion Molecules and Cell Surface Receptors in the Heart Transplant-Associated Arteriosclerosis. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 1996, 34, 3–19. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basalova, N.; Alexandrushkina, N.; Grigorieva, O.; Kulebyakina, M.; Efimenko, A. Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha (FAPα) in Fibrosis: Beyond a Perspective Marker for Activated Stromal Cells? Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121718
Basalova N, Alexandrushkina N, Grigorieva O, Kulebyakina M, Efimenko A. Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha (FAPα) in Fibrosis: Beyond a Perspective Marker for Activated Stromal Cells? Biomolecules. 2023; 13(12):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121718
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasalova, Nataliya, Natalya Alexandrushkina, Olga Grigorieva, Maria Kulebyakina, and Anastasia Efimenko. 2023. "Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha (FAPα) in Fibrosis: Beyond a Perspective Marker for Activated Stromal Cells?" Biomolecules 13, no. 12: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121718
APA StyleBasalova, N., Alexandrushkina, N., Grigorieva, O., Kulebyakina, M., & Efimenko, A. (2023). Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha (FAPα) in Fibrosis: Beyond a Perspective Marker for Activated Stromal Cells? Biomolecules, 13(12), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121718






