Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist GAC0001E5 Impedes Glutaminolysis and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TCGA Gene Expression Data
2.2. Treatments, Cell Lines, and Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assays
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.5. Western Analysis of LXRβ Expression
2.6. Glutamine Dependency Assays
2.7. Intracellular Glutamate Measurements
2.8. Intracellular GSH/GSSG Assay
2.9. ROS Levels
3. Results
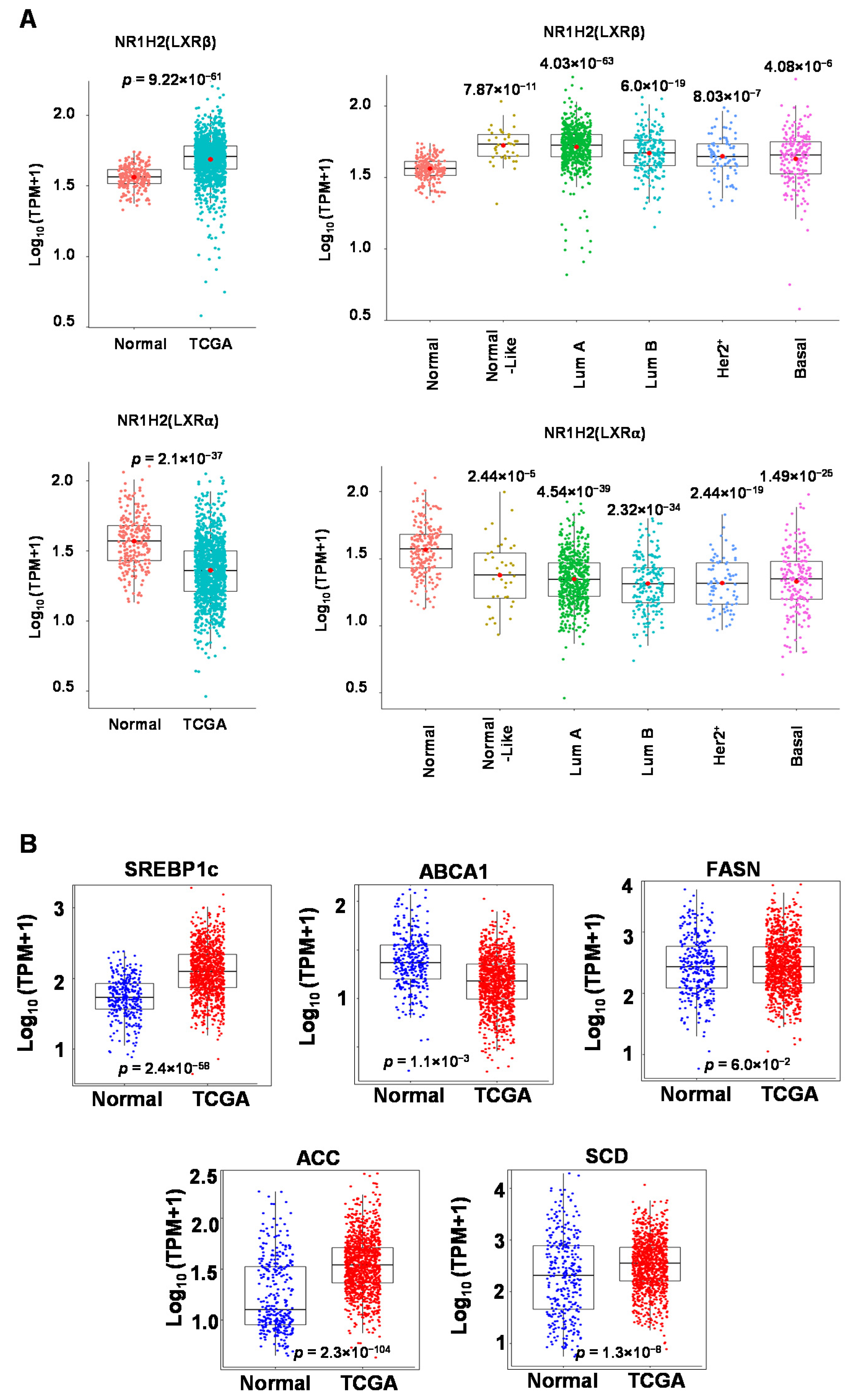
3.1. Expression of LXR and LXR Target Genes in Clinical Samples
3.2. Treatments with 1E5 Reduced Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation/Survival
3.3. Novel LXR Ligand 1E5 Functions as an Inverse Agonist and Disrupts LXRβ Protein Expression
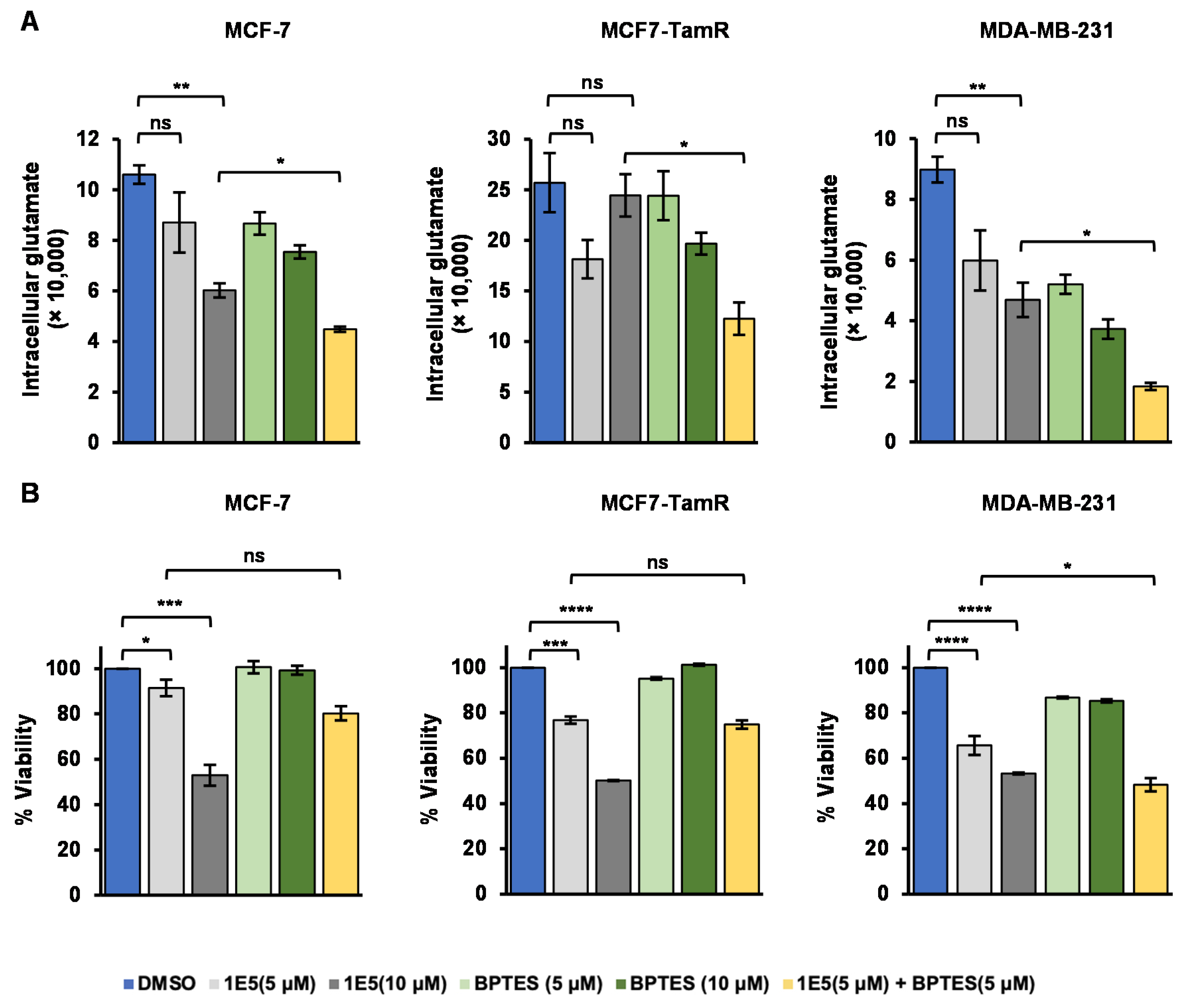
3.4. Glutamate Metabolism Is Disrupted by LXR Ligand 1E5
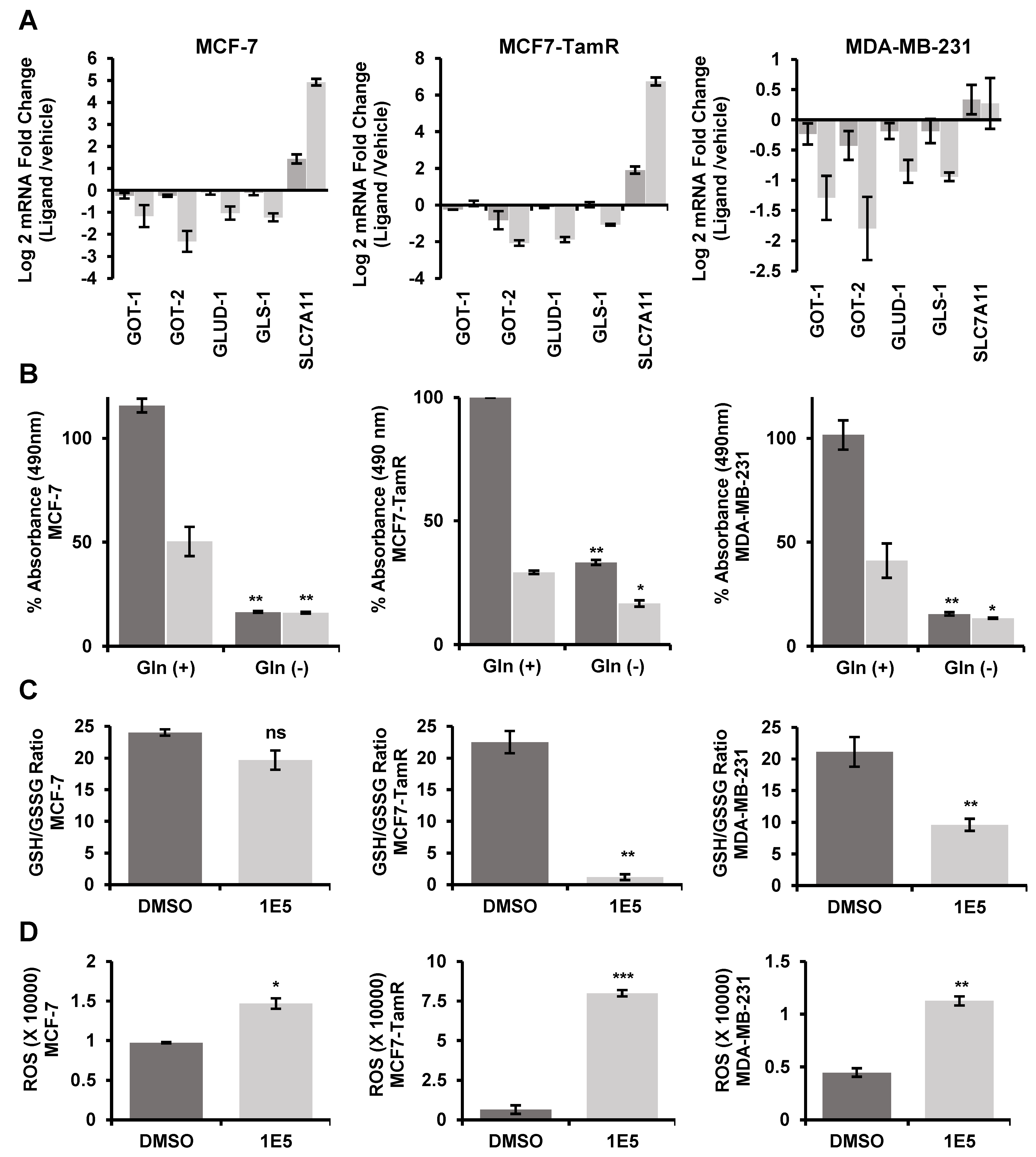
3.5. Expression of Glutaminolysis Genes and Redox Homeostasis Are Disrupted by 1E5
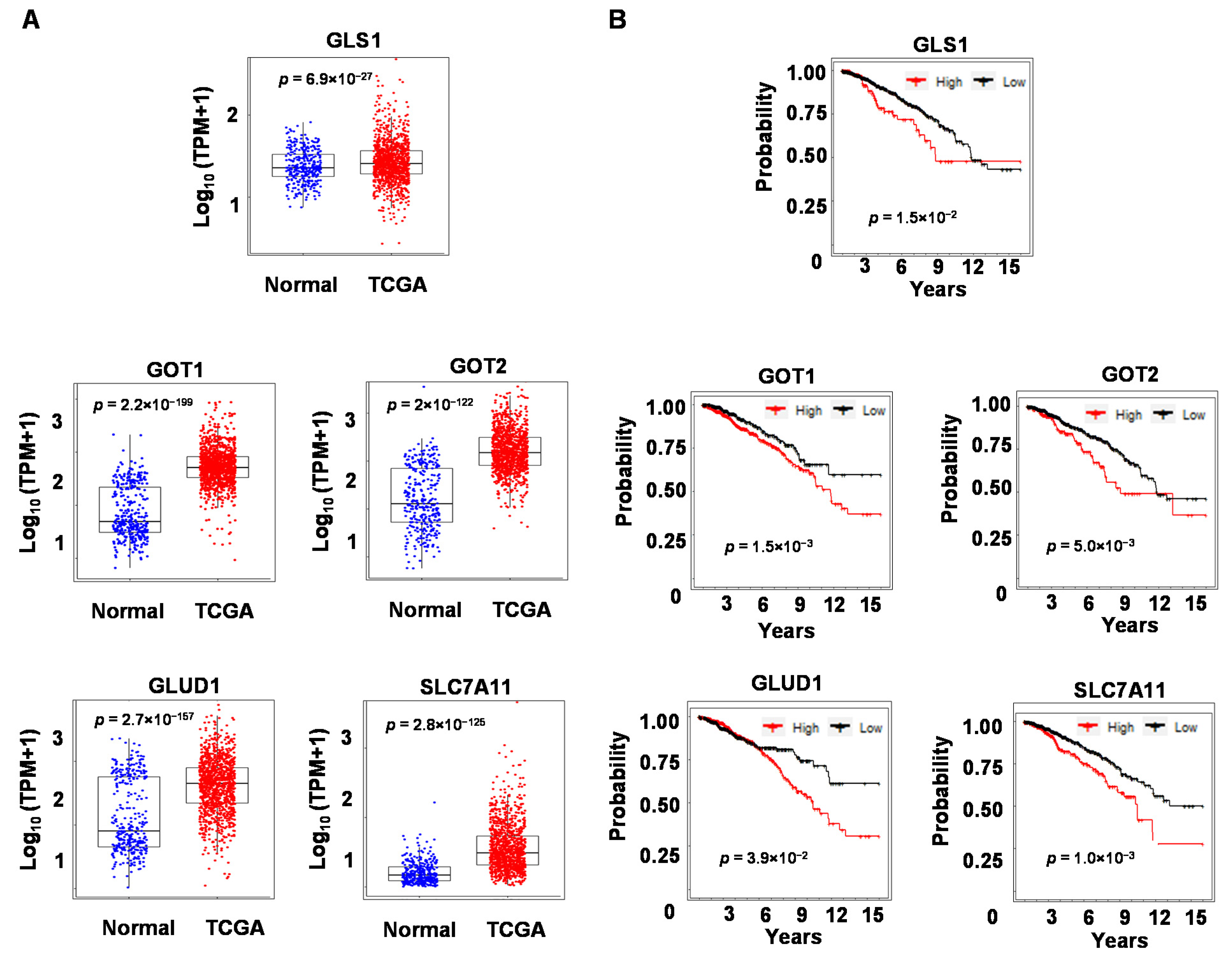
3.6. Expression Levels of Glutaminolysis Genes Are Elevated in Breast Tumors and Are Associated with Breast Cancer Patient Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jakobsson, T.; Treuter, E.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Steffensen, K.R. Liver X receptor biology and pharmacology: New pathways, challenges and opportunities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelcer, N. Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.B.; McKilligin, E.; Pei, L.; Watson, M.A.; Collins, A.R.; Laffitte, B.A.; Chen, M.; Noh, G.; Goodman, J.; Hagger, G.N.; et al. Synthetic LXR ligand inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7604–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffett, K.; Welch, R.D.; Flaveny, C.A.; Kolar, G.R.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Burris, T.P. The LXR inverse agonist SR9238 suppresses fibrosis in a model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Targeting liver X receptors in cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Vedin, L.-L.; Steffensen, K.R. The emerging roles of liver X receptors and their ligands in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Vu, T.; Vedin, L.-L.; Liu, K.; Jonsson, P.; Lin, J.Z.; Candelaria, N.R.; Candelaria, L.P.; Addanki, S.; Williams, C.; Gustafsson, J.; et al. Liver × receptor ligands disrupt breast cancer cell proliferation through an E2F-mediated mechanism. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelaria, N.R.; Addanki, S.; Zheng, J.; Nguyen-Vu, T.; Karaboga, H.; Dey, P.; Gabbi, C.; Vedin, L.-L.; Liu, K.; Wu, W.; et al. Antiproliferative Effects and Mechanisms of Liver X Receptor Ligands in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, H.; Huang, W.; Srivastava, S.; Widmann, S.; Addanki, S.; Gamage, K.T.; Mazhar, Z.; Ebalunode, J.O.; Briggs, J.M.; Gustafsson, J.; et al. Screening of Focused Compound Library Targeting Liver X Receptors in Pancreatic Cancer Identified Ligands with Inverse Agonist and Degrader Activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 2916–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaveny, C.A.; Griffett, K.; El-Gendy, B.E.-D.M.; Kazantzis, M.; Sengupta, M.; Amelio, A.L.; Chatterjee, A.; Walker, J.; Solt, L.A.; Kamenecka, T.M.; et al. Broad Anti-tumor Activity of a Small Molecule that Selectively Targets the Warburg Effect and Lipogenesis. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Widmann, S.; Ho, C.; Nguyen, D.; Nguyen, A.; Premaratne, A.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Lin, C.-Y. Novel Liver X Receptor Ligand GAC0001E5 Disrupts Glutamine Metabolism and Induces Oxidative Stress in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic Reprogramming: A Cancer Hallmark Even Warburg Did Not Anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, D.R.; Thompson, C.B. Glutamine addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluntun, A.A.; Lukey, M.J.; Cerione, R.A.; Locasale, J.W. Glutamine Metabolism in Cancer: Understanding the Heterogeneity. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ansari, R.; McIntyre, A.; Craze, M.L.; Ellis, I.O.; Rakha, E.A.; Green, A.R. Altered glutamine metabolism in breast cancer; subtype dependencies and alternative adaptations. Histopathology 2018, 72, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampa, M.; Arlt, H.; He, T.; Ospina, B.; Reeves, J.; Zhang, B.; Murtie, J.; Deng, G.; Barberis, C.; Hoffmann, D.; et al. Glutaminase is essential for the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells with a deregulated glutamine metabolism pathway and its suppression synergizes with mTOR inhibition. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.D.; Lamichhane, S.; Lundgren, S.; Bofin, A.; Fjøsne, H.; Giskeødegård, G.F.; Bathen, T.F. Metabolic characterization of triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnassy, S.; Thangavel, H.; Quttina, M.; Khan, A.F.; Dhanyalayam, D.; Ritho, J.; Karami, S.; Ren, J.; Bawa-Khalfe, T. Constitutively active androgen receptor supports the metastatic phenotype of endocrine-resistant hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Venneti, S.; Nagrath, D. Glutaminolysis: A Hallmark of Cancer Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Talmon, G.; Wang, J. Glutamate in cancers: From metabolism to signaling. J. Biomed. Res. 2020, 34, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ko, B.; Hensley, C.T.; Jiang, L.; Wasti, A.T.; Kim, J.; Sudderth, J.; Calvaruso, M.A.; Lumata, L.; Mitsche, M.; et al. Glutamine Oxidation Maintains the TCA Cycle and Cell Survival during Impaired Mitochondrial Pyruvate Transport. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J. The amino acid transporter SLC7A11-mediated crosstalk implicated in cancer therapy and the tumor microenvironment. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 205, 115241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, P.K.; Roy, R.G.; Samkaria, A. Oxidative Stress: Glutathione and Its Potential to Protect Methionine-35 of Aβ Peptide from Oxidation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27052–27061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.H.; Cha, H.-J.; Lee, H.; Hong, S.-H.; Park, C.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-S.; Hwang, H.-J.; et al. Protective Effect of Glutathione against Oxidative Stress-induced Cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 Macrophages through Activating the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor-2/Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Sung, Y.; Han, J.M. Glutamine reliance in cell metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1496–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Srivastava, S.; Zhang, J. Starve Cancer Cells of Glutamine: Break the Spell or Make a Hungry Monster? Cancers 2019, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.-C.; Han, J.-M. Amino Acid Metabolism in Cancer Drug Resistance. Cells 2022, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, L.-E.; van Geldermalsen, M.; Guan, Y.F.; Wahi, K.; Mayoh, C.; Balaban, S.; Pang, A.; Wang, Q.; Cowley, M.J.; Brown, K.K.; et al. Glutamine addiction promotes glucose oxidation in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4066–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro-Lizcano, M.; López-Rivas, A. Glutamine metabolism regulates FLIP expression and sensitivity to TRAIL in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Qin, T.; Yin, X.; Ma, X. Therapeutic progress and challenges for triple negative breast cancer: Targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirke, V.M. Tamoxifen from Failed Contraceptive Pill to Best-Selling Breast Cancer Medicine: A Case-Study in Pharmaceutical Innovation. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-S. Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Premaratne, A.; Ho, C.; Basu, S.; Khan, A.F.; Bawa-Khalfe, T.; Lin, C.-Y. Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist GAC0001E5 Impedes Glutaminolysis and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020345
Premaratne A, Ho C, Basu S, Khan AF, Bawa-Khalfe T, Lin C-Y. Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist GAC0001E5 Impedes Glutaminolysis and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(2):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020345
Chicago/Turabian StylePremaratne, Asitha, Charles Ho, Shinjini Basu, Ashfia Fatima Khan, Tasneem Bawa-Khalfe, and Chin-Yo Lin. 2023. "Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist GAC0001E5 Impedes Glutaminolysis and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Breast Cancer Cells" Biomolecules 13, no. 2: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020345
APA StylePremaratne, A., Ho, C., Basu, S., Khan, A. F., Bawa-Khalfe, T., & Lin, C.-Y. (2023). Liver X Receptor Inverse Agonist GAC0001E5 Impedes Glutaminolysis and Disrupts Redox Homeostasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules, 13(2), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020345






