The Roles of Exosomes in Metastasis of Sarcoma: From Biomarkers to Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
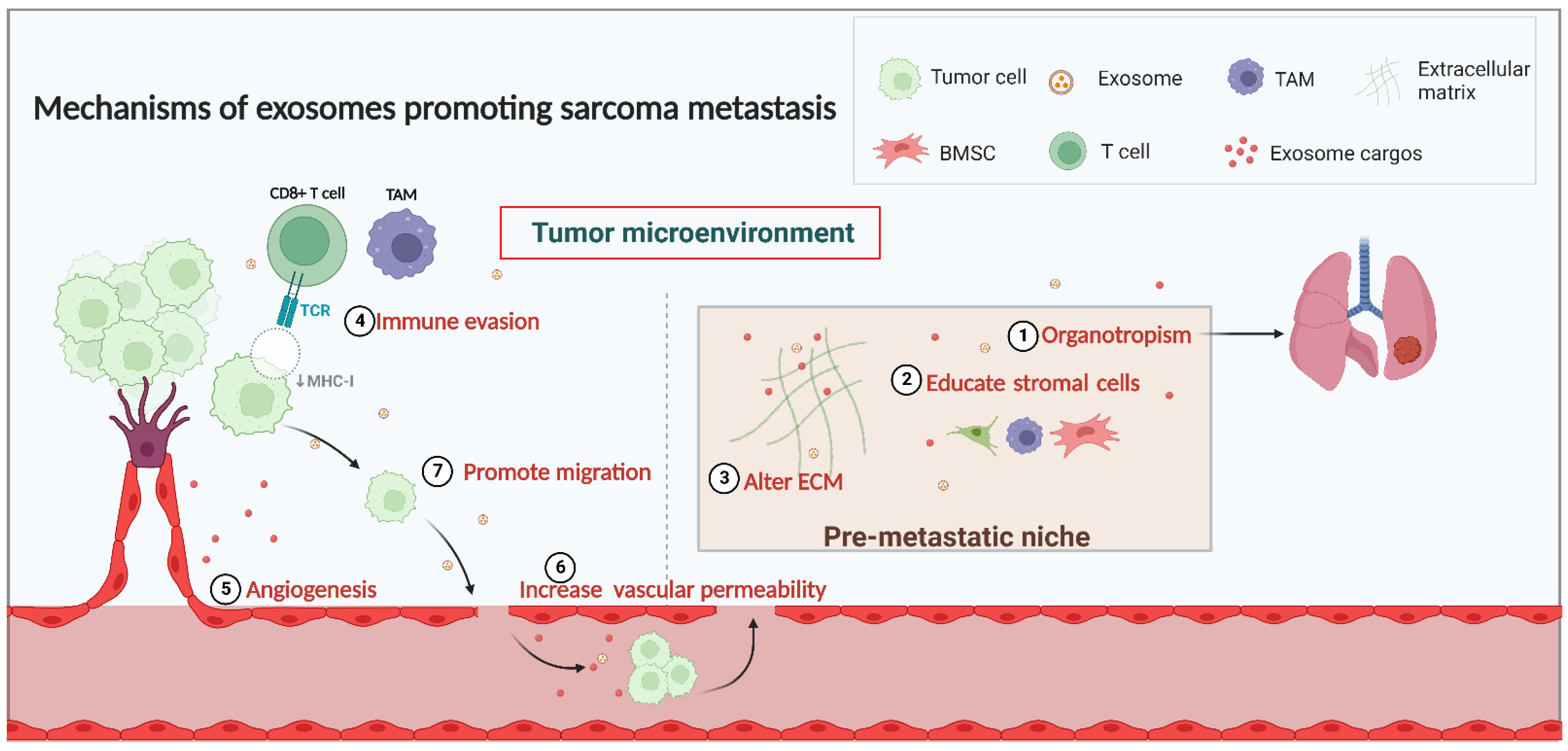
2. The Mechanisms of Exosome Involvement in Sarcoma Metastasis
2.1. Exosomes and the TME in Sarcoma Metastasis
2.2. Exosome and PMN Formation in Sarcoma Metastasis
2.2.1. Organotropism in PMN Formation
2.2.2. Interaction with Stromal Cells in PMN Formation
2.2.3. Alterations in the ECM in PMN Formation
2.3. Regulation of Immunity
2.4. Angiogenesis and Vascular Permeability
2.5. Migration of Sarcoma Cells
3. Exosomes as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Sarcoma Metastasis
3.1. Osteosarcoma
3.1.1. Exosomal Proteins as Biomarkers in OS
3.1.2. Exosomal miRNAs as Biomarkers in OS
3.1.3. Exosomal lncRNAs as Biomarkers in OS
3.2. Chondrosarcoma
3.3. Rhabdomyosarcoma
3.4. Liposarcoma
4. Therapeutic Strategies Based on Exosome for Sarcoma Metastasis
4.1. Inhibition of Exosome Release
4.2. Blocking Downstream Pathway of Exosome
4.3. Harnessing Exosomes as Delivery Systems to Treat Sarcoma Metastasis
5. Clinical Experience of Exosomes in Sarcoma Metastasis
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dancsok, A.R.; Asleh-Aburaya, K.; Nielsen, T.O. Advances in sarcoma diagnostics and treatment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 7068–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.M.; Ro, J.Y.M. The 2020 WHO Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue: Selected Changes and New Entities. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2021, 28, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakoff, M.S.; Bielack, S.S.; Meltzer, P.; Gorlick, R. Osteosarcoma: Current Treatment and a Collaborative Pathway to Success. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, M.; Tawbi, H. Immunotherapeutic approaches to sarcoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Trufero, J.; Jurado, J.C.; Gómez-Mateo, M.; Bernabeu, D.; Floría, L.J.; Lavernia, J.; Sebio, A.; del Muro, X.G.; Álvarez, R.; Correa, R.; et al. Uncommon and peculiar soft tissue sarcomas: Multidisciplinary review and practical recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Spanish group for Sarcoma research (GEIS—GROUP). Part I. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 99, 102259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeland, S.; Bielack, S.S.; Whelan, J.; Bernstein, M.; Hogendoorn, P.; Krailo, M.D.; Gorlick, R.; Janeway, K.A.; Ingleby, F.C.; Anninga, J.; et al. Survival and prognosis with osteosarcoma: Outcomes in more than 2000 patients in the EURAMOS-1 (European and American Osteosarcoma Study) cohort. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 109, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabello, L.; Troisi, R.J.; Savage, S.A. Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer 2009, 115, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, K.; Johannesen, T.B.; Berner, A.; Haugland, H.K.; Bjerkehagen, B.; Bøhler, P.J.; Bruland, S. Time-trends on incidence and survival in a nationwide and unselected cohort of patients with skeletal osteosarcoma. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Dirksen, U.; Bielack, S. Sarcomas of Soft Tissue and Bone. Prog. Tumor Res. 2016, 43, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SKachare, S.D.; Brinkley, J.; Vohra, N.A.; Zervos, E.E.; Wong, J.H.; Fitzgerald, T.L. Radiotherapy associated with improved survival for high-grade sarcoma of the extremity. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 112, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Gorlick, R. Advancing therapy for osteosarcoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, I.J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Kuo, S.-J.; Su, C.-M.; Tang, C.-H. An update on current and future treatment options for chondrosarcoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2019, 19, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, Y.; Zhou, C.D.; Jones, R.L. Systemic Therapy in Metastatic or Unresectable Well-Differentiated/Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SMiwa, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Igarashi, K.; Tsuchiya, H. Recent Advances and Challenges in the Treatment of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetouni, N.C.; Sergi, C.M. Metastasis; Sergi, C.M., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Hu, X.; Wen, Y.; Tu, C.; Hornicek, F.; Duan, Z.; Min, L. Exosomes in the tumor microenvironment of sarcoma: From biological functions to clinical applications. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Shen, J.; Tu, C.; Hornicek, F.; Duan, Z. The roles and implications of exosomes in sarcoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaoutis, C.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Theocharis, S. Exosomes in sarcomas: Tiny messengers with broad implications in diagnosis, surveillance, prognosis and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2019, 449, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.V.; Grünewald, T.G.P. Tumour-derived exosomes: Tiny envelopes for big stories. Biol. Cell 2015, 107, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaziha, P.; Ceder, S.; Li, Q.; Panaretakis, T. Tumor cell-derived exosomes: A message in a bottle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Record, M.; Subra, C.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; Poirot, M. Exosomes as intercellular signalosomes and pharmacological effectors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, B.; Wu, L.; Hvam, M.L.; Aslan, H.; Dong, M.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Moghimi, S.M.; Howard, K.A. Tumour exosomes display differential mechanical and complement activation properties dependent on malignant state: Implications in endothelial leakiness. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 29685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chengalvala, V.; Hu, H.; Sun, D. Tumor-derived exosomes: Nanovesicles made by cancer cells to promote cancer metastasis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2136–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wang, G.; Hu, W.; Yao, Y.; Yu, X.-F. Emerging roles and therapeutic value of exosomes in cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Na Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Wang, H. Tumor-associated exosomes promote lung cancer metastasis through multiple mechanisms. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, R.; Robertson, B.M.; Iyer, S.; Barry, J.; Dinavahi, S.S.; Robertson, G.P. The role of exosomes in metastasis and progression of melanoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 85, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, T.; Saini, S. Role of Exosomes in Prostate Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, X. The potential roles of exosomes in pancreatic cancer initiation and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, M.; Cilibrasi, C.; Papanastasopoulos, P.; Giamas, G. Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Therapy Resistance in the Breast Cancer Microenvironment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghabozorgi, A.S.; Ahangari, N.; Eftekhaari, T.E.; Torbati, P.N.; Bahiraee, A.; Ebrahimi, R.; Pasdar, A. Circulating exosomal miRNAs in cardiovascular disease pathogenesis: New emerging hopes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21796–21809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, X. The potential roles of exosomal noncoding RNAs in osteosarcoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 236, 3354–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka, A.; Kornek, M.; Cho, W.C. Small Extracellular Vesicles and Their Involvement in Cancer Resistance: An Up-to-Date Review. Cells 2022, 11, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, A.; Urdinez, J.; Boro, A.; Arlt, M.J.E.; Egli, F.E.; Niederöst, B.; Jaeger, P.K.; Moschini, G.; Muff, R.; Fuchs, B.; et al. Exploring the Role of Osteosarcoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation and Metastasis in the 143-B Xenograft Mouse Osteosarcoma Model. Cancers 2020, 12, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortzel, I.; Dror, S.; Kenific, C.M.; Lyden, D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: Communication from a distance. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guise, T. Examining the metastatic niche: Targeting the microenvironment. Semin. Oncol. 2010, 37 (Suppl. S2), S2–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X. Immunosuppressive cells in tumor immune escape and metastasis. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, F.; Shao, Z. Exosomal lncRNA RAMP2-AS1 Derived from Chondrosarcoma Cells Promotes Angiogenesis Through miR-2355-5p/VEGFR2 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 3291–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicón-Bosch, M.; Tirado, O.M. Exosomes in Bone Sarcomas: Key Players in Metastasis. Cells 2020, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.K.; Schiavone, K.; Gouin, F.; Heymann, M.-F.; Heymann, D. Biology of Bone Sarcomas and New Therapeutic Developments. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 174–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehnman, M.; Chaabane, W.; Haglund, F.; Tsagkozis, P. The Tumor Microenvironment of Pediatric Sarcoma: Mesenchymal Mechanisms Regulating Cell Migration and Metastasis. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamuth, N.J.; Womer, R.B. Ewing’s sarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Haider, A.; Rashid, S.; Al-Nabet, A.D.M. Paget’s “Seed and Soil” Theory of Cancer Metastasis: An Idea Whose Time has Come. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2019, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, I.; Syn, N.; Sethi, G.; Goh, B.C.; Wang, L. Role of tumor-derived exosomes in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaila, B.; Lyden, D. The metastatic niche: Adapting the foreign soil. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Z.; Su, P.; Li, Y.; Qian, A. Bone Microenvironment and Osteosarcoma Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massague, J. Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczanowska, S.; Kaplan, R.N. Mapping the switch that drives the pre-metastatic niche. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, R.; Wang, H.; Loo, D.; Martin, S.; Cumming, A.; Cai, N.; Lane, R.; Ponce, N.S.; Topkas, E.; Inder, K.; et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by highly metastatic clonal variants of osteosarcoma preferentially localize to the lungs and induce metastatic behaviour in poorly metastatic clones. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43570–43587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S. Integrins and Exosomes, a Dangerous Liaison in Cancer Progression. Cancers 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.A.; Horwitz, A.F. Integrin, a transmembrane glycoprotein complex mediating cell-substratum adhesion. J. Cell. Sci. Suppl. 1987, 8, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Lai, Y.-Y.; Hsu, H.-C.; Fong, Y.-C.; Lien, M.-Y.; Tang, C.-H. CCL4 Stimulates Cell Migration in Human Osteosarcoma via the mir-3927-3p/Integrin αvβ3 Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.K.; Pouliot, N.; Stanley, K.L.; Chia, J.; Moseley, J.M.; Hards, D.K.; Anderson, R.L. Tumor-specific expression of alphavbeta3 integrin promotes spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer to bone. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 8, R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickarski, M.; Gleason, A.; Bednar, B.; Duong, L.T. Orally active αvβ3 integrin inhibitor MK-0429 reduces melanoma metastasis. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Wu, X.F.; Gu, X.J.; Jiang, X.H. Exosomal miR-1228 From Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma by Directly Targeting SCAI. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, S.; Yun, J.-P. H3K27 acetylation activated-COL6A1 promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis by repressing STAT1 and activating pulmonary cancer-associated fibroblasts. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhadi, V.K.; Daddali, R.; Seppänen-Kaijansinkko, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Osteosarcoma Pathogenesis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Long, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, D.; Hu, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, L. miRNA-221-3p derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage exosomes aggravates the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma through SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 axis. Aging 2021, 13, 19760–19775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-T.; Bian, Z.-Y.; Fan, Q.-M.; Li, G.; Tang, T. Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) target osteosarcoma and promote its growth and pulmonary metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2009, 281, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, W.; Cui, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Xue, H.; Wu, L.; et al. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma by transferring exosomal LncRNA SNHG17. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 10094–10111. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskar, B.; Mekala, N.; Baadhe, R.R.; Rao, P. Role of signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 9, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, R.; Roth, M.; Piperdi, S.; Zhang, W.; Dorfman, H.; Rao, P.; Park, A.; Tripathi, S.; Freeman, C.; et al. Genetically transforming human osteoblasts to sarcoma: Development of an osteosarcoma model. Genes Cancer 2017, 8, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, R.; Gutierrez-Aranda, I.; Sáez-Castillo, A.I.; Labarga, A.; Rosu-Myles, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, S.; Toribio, M.L.; Menendez, P.; Rodriguez, R. The differentiation stage of p53-Rb-deficient bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells imposes the phenotype of in vivo sarcoma development. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4970–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; He, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Shu, H.; Sun, L. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote osteosarcoma development by activating oncogenic autophagy. J. Bone Oncol. 2020, 21, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- XChang, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, G.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J. New perspective into mesenchymal stem cells: Molecular mechanisms regulating osteosarcoma. J. Bone Oncol. 2021, 29, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhaneni, K.C.; Hassler, M.-Y.; Abraham, A.; Whitt, J.; Mo, Y.-Y.; Atfi, A.; Pochampally, R. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells under Stress Increase Osteosarcoma Migration and Apoptosis Resistance via Extracellular Vesicle Mediated Communication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, B.P.; Mi, J. Metabolic reprogramming of the tumour microenvironment. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 3892–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, J.P. The metastatic niche and stromal progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, I.G.; Sood, A.K.; Mok, S.; Liu, J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their putative role in potentiating the initiation and development of epithelial ovarian cancer. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Larghi, P.; Mancino, A.; Rubino, L.; Porta, C.; Totaro, M.G.; Rimoldi, M.; Biswas, S.K.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, F.; Parolini, I.; Coscia, C.; Camerini, S.; Zanetti, C.; Cardarelli, S.; Poiana, G.; Sargiacomo, M. Scientific Program 2012 ISEV meeting Wednesday 18th April. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1, 18182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.; Das, A.; Sagi, I. Emerging roles of ECM remodeling processes in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 62, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S. Extracellular Matrix Alterations in Metastatic Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, D.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Yuan, W.; et al. Effects of exosomes on pre-metastatic niche formation in tumors. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes and tumor-mediated immune suppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugeratski, F.G.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes as mediators of immune regulation and immunotherapy in cancer. FEBS J. 2020, 288, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachva, M.C.; Lai, H.; Jia, A.; Rouleau, M.; Sorensen, P.H. Extracellular Vesicles in Reprogramming of the Ewing Sarcoma Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 726205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.; Akiyoshi, K.; Shiku, H. Exosome-mediated regulation of tumor immunology. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Cai, Z.; Sun, W.; Hua, Y.; Xu, J. Immune Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma: Components, Therapeutic Strategies and Clinical Applications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 907550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; He, J.; Feng, C.; Tu, C. Exosomal MiRNAs in Osteosarcoma: Biogenesis and Biological Functions. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 902049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.V.; Troyer, R.M.; Ramsey, S.A.; Leeper, H.; Yang, L.; Maier, C.S.; Goodall, C.P.; Ruby, C.E.; Albarqi, H.A.; Taratula, O.; et al. A Preliminary Proteomic Investigation of Circulating Exosomes and Discovery of Biomarkers Associated with the Progression of Osteosarcoma in a Clinical Model of Spontaneous Disease. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, L.; Ruan, Y.; Xue, W. Tumor-derived Exosomes Induced M2 Macrophage Polarization and Promoted the Metastasis of Osteosarcoma Cells Through Tim-3. Arch. Med Res. 2021, 52, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-G.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Fang, S.-X.; Zhang, Q.; Xin, H.-W.; Ma, Z. Long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs in tumor angiogenesis: From mechanisms to clinical significance. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2021, 22, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspriţoiu, V.M.; Stoica, I.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C. Epigenetic Regulation of Angiogenesis in Development and Tumors Progression: Potential Implications for Cancer Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 689962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Zent, R. Regulation of endothelial cell functions by basement membrane- and arachidonic acid-derived products. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2009, 1, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, N.; Liao, S.; Rothzerg, E.; Yao, F.; Li, Y.; Wood, D.; Xu, J. Current research progress in targeted anti-angiogenesis therapy for osteosarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Gurevich, D.B. Macrophage regulation of angiogenesis in health and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 119, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.M.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Sun, R.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C. Exosome: A Novel Approach to Stimulate Bone Regeneration through Regulation of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Román, J.; Zentella-Dehesa, A. Vascular permeability changes involved in tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.F.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Bao, Q.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, L.; Tong, L.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Exosomal miR-675 from metastatic osteosarcoma promotes cell migration and invasion by targeting CALN1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Yangbin, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Tumor Growth Through Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmicheal, J.; Hayashi, C.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.; Lushnikov, A.; Kshirsagar, P.G.; Patel, A.; Jain, M.; et al. Label-free characterization of exosome via surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the early detection of pancreatic cancer. Nanomedicine 2018, 16, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, W.; Feng, S.; Duan, A.; Ji, C.; Shen, K.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, D.; et al. Exosomal Transfer of LCP1 Promotes Osteosarcoma Cell Tumorigenesis and Metastasis by Activating the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Liao, D.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Zeng, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, M.; et al. Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis through its secretion into exosomes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, B.; Guo, W. Exosomal PD-L1 and N-cadherin predict pulmonary metastasis progression for osteosarcoma patients. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Song, S.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, J. Plasma Exosome-Derived Sentrin SUMO-Specific Protease 1: A Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With Osteosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 625109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Pu, P.; Wang, C.; Ding, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xiang, W.; Wang, W. Osteosarcoma Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-1307 Promotes Tumorgenesis via Targeting AGAP1. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7358153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, B.; Duan, A.; Shen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, X.; Wei, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, S. Exosomal transfer of miR-769-5p promotes osteosarcoma proliferation and metastasis by targeting DUSP16. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, P.; Zhu, J. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-208a promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 235, 4734–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting PIK3R1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 11016–11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Uotani, K.; Yoshida, A.; Morita, T.; Nezu, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Yoshida, A.; Uehara, T.; Omori, T.; Sugiu, K.; et al. Clinical significance of circulating miR-25-3p as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in osteosarcoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33375–33392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei, L.; Calore, F.; Creighton, C.J.; Guescini, M.; Batte, K.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Zewdu, A.; Braggio, D.A.; Bill, K.L.; Fadda, P.; et al. Exosome-Derived miR-25-3p and miR-92a-3p Stimulate Liposarcoma Progression. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 3846–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamloush, F.; Ghayad, S.E.; Rammal, G.; Fahs, A.; Ayoub, A.J.; Merabi, Z.; Harajly, M.; Zalzali, H.; Saab, R. The PAX3-FOXO1 oncogene alters exosome miRNA content and leads to paracrine effects mediated by exosomal miR-486. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, N.; Xie, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Peng, T. Exosome-transmitted linc00852 associated with receptor tyrosine kinase AXL dysregulates the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6354–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Huang, Q.; Guo, W. LncRNA CASC15 is Upregulated in Osteosarcoma Plasma Exosomes and CASC15 Knockdown Inhibits Osteosarcoma Progression by Regulating miR-338-3p/RAB14 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 12055–12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Qin, P.; Zhang, D.; Cui, X.; Gao, J.; Yu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 encapsulated in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by stabilizing ERG and sponging miR-183-5p. Aging 2019, 11, 9581–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, W.; Niu, J.; et al. Macrophages-derived exosomal lncRNA LIFR-AS1 promotes osteosarcoma cell progression via miR-29a/NFIA axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannerström, B.; Kornilov, R.; Abu-Shahba, A.G.; Chowdhury, I.M.; Sinha, S.; Seppänen-Kaijansinkko, R.; Kaur, S. Epigenetic alterations in mesenchymal stem cells by osteosarcoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Zhong, L.; Yin, J.; Zeng, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Guan, X.-Y.; et al. Chromosomal translocation-derived aberrant Rab22a drives metastasis of osteosarcoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, A.; Ullrich, P.V.; Heinz, J.; Pfeifer, D.; Scholber, J.; Herget, G.W.; Hauschild, O.; Bronsert, P.; Stark, G.B.; Bannasch, H.; et al. Identification of a blood-borne miRNA signature of synovial sarcoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Zeisberg, M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J. Curcumol Synergizes with Cisplatin in Osteosarcoma by Inhibiting M2-like Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Molecules 2022, 27, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Xiao, B.; Ma, Z.; Huo, H.; Li, W. A seven-lncRNA signature for predicting Ewing’s sarcoma. Peerj 2021, 9, e11599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.-Q.; Wei, Q.-J.; Tang, R.-X.; Chen, W.-J.; Yang, X.; Peng, Z.-G.; Hu, X.-H.; Ma, J.; Chen, G. Prediction of clinical outcome and survival in soft-tissue sarcoma using a ten-lncRNA signature. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80336–80347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; Gordon, A.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Shipley, J. Genes, chromosomes, and rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1999, 26, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.L.; Sandstrom, D.J.; Law, K.; Fiore, C.; Sicinska, E.; Brito, J.; Bailey, D.; Fletcher, J.A.; Loda, M.; Rodig, S.J.; et al. c-Jun amplification and overexpression are oncogenic in liposarcoma but not always sufficient to inhibit the adipocytic differentiation programme. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, A.; Ortiz, A. Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Tool in Nanomedicine and Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, S.R.; Lagerweij, T.; Pérez-Lanzón, M.; Ho, X.D.; Léveillé, N.; Melo, S.A.; Cleton-Jansen, A.-M.; Jordanova, E.S.; Roncuzzi, L.; Greco, M.; et al. Blocking Tumor-Educated MSC Paracrine Activity Halts Osteosarcoma Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Munoz, L.; Cai, N.; Cumming, A.; Macklin, R.; Merida de Long, L.; Topkas, E.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Hill, M.; Saunders, N.A. Progression of Osteosarcoma from a Non-Metastatic to a Metastatic Phenotype Is Causally Associated with Activation of an Autocrine and Paracrine uPA Axis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Dong, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of miR-101 inhibits lung metastasis in osteosarcoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimbo, K.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Kato, Y.; Kubo, T.; Shimose, S.; Ochi, M. Exosome-formed synthetic microRNA-143 is transferred to osteosarcoma cells and inhibits their migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-150 suppresses the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells via targeting IGF2BP1. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 5323–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, P.; Lu, Y.; Lin, S.; Yuan, G. The exosomal transfer of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived miR-1913 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting NRSN2. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 10178–10192. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Li, Z.; Feng, G.; Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, S. Tumor suppressing role of serum-derived exosomal microRNA-15a in osteosarcoma cells through the GATA binding protein 2/murine double minute 2 axis and the p53 signaling pathway. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 8378–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, G.; Cai, W.; Millard, R.W.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J.; Peng, T.; Fan, G.-C. Cardiomyocytes mediate anti-angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic rats through the exosomal transfer of miR-320 into endothelial cells. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 74, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, E.; Presutti, D.; Favoriti, P.; Santini, S.; Papoff, G.; Tuccilli, C.; Carletti, R.; Di Gioia, C.; Lori, E.; Ferent, I.C.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of the Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor WX-340 on Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Brennan, M.Á.; Lötvall, J.; Breakefield, X.O.; EL Andaloussi, S. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Albero, M.; Medel-Martínez, A.; Martín-Duque, P. Use of exosomes as vectors to carry advanced therapies. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23975–23987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kim, M.S. Using exosomes, naturally-equipped nanocarriers, for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cao, G.; Lan, H.; Liao, H.; Hu, Y.; Feng, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, P. Chondrocyte-derived Exosomal miR-195 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation and Anti-Apoptotic by Targeting KIF4A in vitro and in vivo. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 16, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
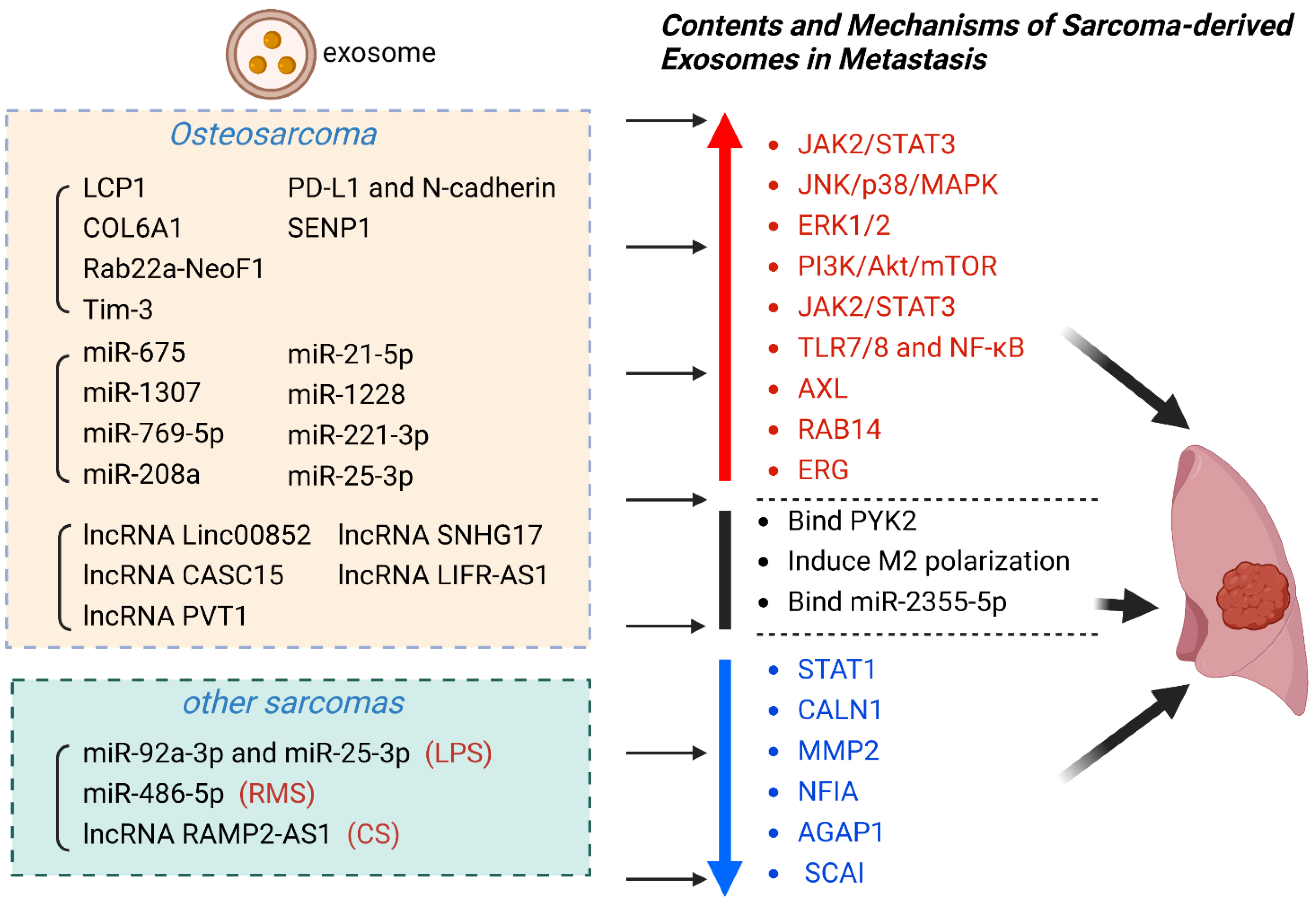

| Exosomal Contents | Sarcoma | Exosome Source | Exosomal Cargo | Effect | Clinical Significance | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| proteins | OS | Serum | LCP1 | Activate JAK2/STAT3 | promote metastasis | [106] |
| OS | Serum | COL6A1 | Downregulate STAT1 | promote metastasis | [65] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | Rab22a-NeoF1 | Bind PYK2 | promote metastasis | [107] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | Tim-3 | Induce macrophage polarization | promote metastasis | [93] | |
| OS | Serum | PD-L1 and N-cadherin | Not mentioned | promote metastasis | [108] | |
| OS | Plasma | SENP1 | Not mentioned | promote metastasis | [109] | |
| miRNA | OS | Serum | miR-675 | Downregulate CALN1 | promote metastasis | [103] |
| OS | Serum | miR-1307 | Inhibit AGAP1 | promote metastasis | [110] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | miR-769-5p | Activate JNK/p38/MAPK | promote metastasis | [111] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | miR-208a | Activate ERK1/2 | promote metastasis | [112] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | miR-21-5p | Activate PI3K/Akt/mTOR;Express VEGF | promote metastasis | [113] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | miR-1228 | Inhibit SCAI | promote metastasis | [64] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | miR-221-3p | Activate JAK2/STAT3 | promote metastasis | [67] | |
| OS | Serum | miR-25-3p | Not mentioned | promote metastasis | [114] | |
| LPS | Plasma | miR-92a-3p and miR-25-3p | Activate TLR7/8 and NF-κB | promote metastasis | [115] | |
| RMS | Serum | miR-486-5p | Mediate PAX3-FOXO1 | promote metastasis | [116] | |
| lncRNA | CS | Serum | lncRNA RAMP2-AS1 | Competitively bind miR-2355-5p | promote metastasis | [46,115] |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | lncRNA Linc00852 | Upregulate AXL | promote metastasis | [117] | |
| OS | Slasma | lncRNA CASC15 | Upregulate RAB14 | promote metastasis | [118] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | lncRNA PVT1 | Upregulate ERG | promote metastasis | [119] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | lncRNA SNHG17 | Downregulate MMP2 | promote metastasis | [69] | |
| OS | Cell culture fluid | lncRNA LIFR-AS1 | Downregulate NFIA | promote metastasis | [120] |
| Strategy | Sarcoma | Experiment | Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibiting exosome release | OS | In vitro | Inhibit LncRNA SNHG17 | [69] |
| OS | In vitro | Inhibit miR-769-5p | [111] | |
| LPS | In vitro | Inhibit miR-25-3p and miR-92a-3p | [115] | |
| Blocking exosome interactions with recipient cells | OS | In vivo | Block IL-6 or TGF-β | [132] |
| OS | In vivo and in vitro | Block the uPA/uPAR axis | [133] | |
| OS | In vitro | Block Hedgehog signaling | [104] | |
| OS | In vivo and in vitro | Block the Rab22a-NeoF1/PYK2 axis | [107] | |
| OS | In vitro | Block the miR-2861 axis | [69] | |
| OS | In vitro | Block the miR-1307/AGAP1axis | [110] | |
| OS | In vitro | Block the miR-1228/SCAI axis | [64] | |
| Harnessing exosomes as delivery systems to treat metastatic sarcoma | OS | In vivo and in vitro | miR-101 | [134] |
| OS | In vitro | miR-143 | [135] | |
| OS | In vivo and in vitro | miR-150 | [136] | |
| OS | In vitro | miR-1913 | [137] | |
| OS | In vitro | miR-15a | [138] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Min, L. The Roles of Exosomes in Metastasis of Sarcoma: From Biomarkers to Therapeutic Targets. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030456
Tan L, Wang Y, Hu X, Min L. The Roles of Exosomes in Metastasis of Sarcoma: From Biomarkers to Therapeutic Targets. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Linyun, Yitian Wang, Xin Hu, and Li Min. 2023. "The Roles of Exosomes in Metastasis of Sarcoma: From Biomarkers to Therapeutic Targets" Biomolecules 13, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030456
APA StyleTan, L., Wang, Y., Hu, X., & Min, L. (2023). The Roles of Exosomes in Metastasis of Sarcoma: From Biomarkers to Therapeutic Targets. Biomolecules, 13(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030456





