The N-Glycosylation of Total Plasma Proteins and IgG in Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Isolation of IgG from Human Plasma
2.3. Enzymatic Release and Fluorescent Labeling of N-Glycans from IgG and Total Plasma Proteins
2.4. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography of Labeled N-Glycans
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
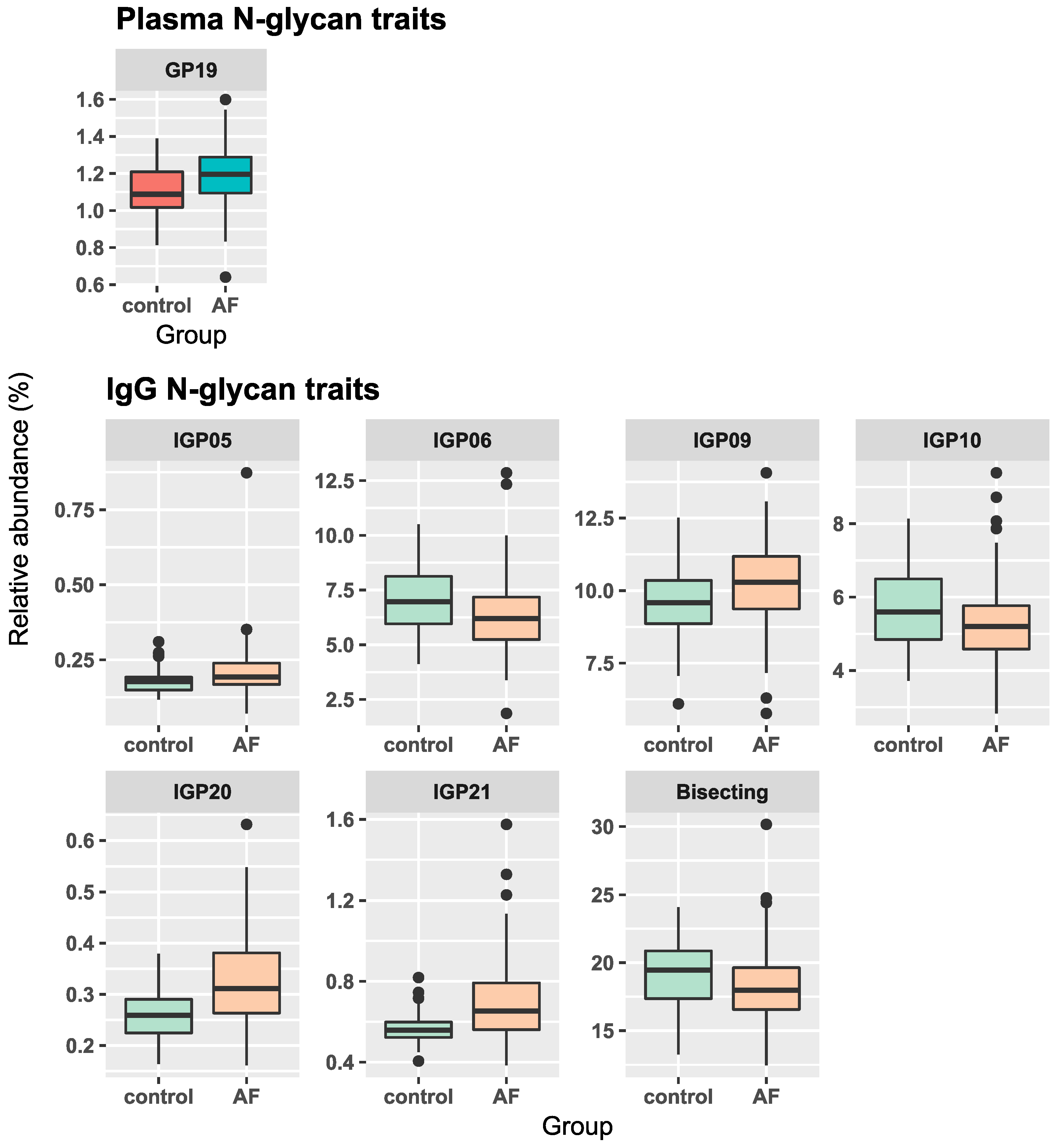
3.1. Associations of Plasma and IgG N-Glycans with AF
3.2. Associations of Total Plasma Protein N-Glycans with AF Recurrence after Catheter Ablation
3.3. Differences in IgG N-Glycome following Catheter Ablation
3.4. Association of IgG N-Glycans with the CHA2DS2-VASc Score
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Go, A.S.; Hylek, E.M.; Phillips, K.A.; Chang, Y.; Henault, L.E.; Selby, J.V.; Singer, D.E. Prevalence of Diagnosed Atrial Fibrillation in Adults: National Implications for Rhythm Management and Stroke Prevention: The AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA 2001, 285, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krijthe, B.P.; Kunst, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Stricker, B.H.; Heeringa, J. Projections on the Number of Individuals with Atrial Fibrillation in the European Union, from 2000 to 2060. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilaveris, P.E.; Kennedy, H.L. Silent Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Clinical Impact. Clin. Cardiol. 2017, 40, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markides, V.; Schilling, R.J. Atrial Fibrillation: Classification, Pathophysiology, Mechanisms and Drug Treatment. Heart 2003, 89, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vaziri, S.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Wolf, P.A. Independent Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation in a Population-Based Cohort: The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA 1994, 271, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.H.; Nattel, S.; Kalman, J.M.; Sanders, P. Modifiable Risk Factors and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2017, 136, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, J.M.; Gallagher, C.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Lau, D.H.; Sanders, P. Risk Factor Management and Atrial Fibrillation. EP Eur. 2021, 23, ii52–ii60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating in the Pulmonary Veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Qu, Z.; Weiss, J.N. Cardiac Fibrosis and Arrhythmogenesis: The Road to Repair Is Paved with Perils. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 70, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Nattel, S. Implications of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviles, R.J.; Martin, D.O.; Apperson-Hansen, C.; Houghtaling, P.L.; Rautaharju, P.; Kronmal, R.A.; Tracy, R.P.; Van Wagoner, D.R.; Psaty, B.M.; Lauer, M.S.; et al. Inflammation as a Risk Factor for Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2003, 108, 3006–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.; Zografos, T.; Papamikroulis, G.-A.; Siasos, G.; Vogiatzi, G.; Theofilis, P.; Briasoulis, A.; Papaioannou, S.; Vavuranakis, M.; Gennimata, V.; et al. Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovani, B.; Gudelj, I. N-Glycosylation and Inflammation; the Not-So-Sweet Relation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 893365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, R.; Hermjakob, H.; Sharon, N. On the Frequency of Protein Glycosylation, as Deduced from Analysis of the SWISS-PROT Database. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1473, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagneux, P.; Hennet, T.; Varki, A. Biological Functions of Glycans. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-62182-421-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Takahashi, M.; Gu, J.-G.; Miyoshi, E.; Matsumoto, A.; Kitazume, S.; Taniguchi, N. Functional Roles of N-Glycans in Cell Signaling and Cell Adhesion in Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novokmet, M.; Lukić, E.; Vučković, F.; Ðurić, Ž.; Keser, T.; Rajšl, K.; Remondini, D.; Castellani, G.; Gašparović, H.; Gornik, O.; et al. Changes in IgG and Total Plasma Protein Glycomes in Acute Systemic Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.J.; Kronewitter, S.R.; de Leoz, M.L.A.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycomics and Disease Markers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, H.; Pabon Porras, M.A.; Mora, S. Glycosylation and Cardiovascular Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1325, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ząbczyńska, M.; Link-Lenczowski, P.; Pocheć, E. Glycosylation in Autoimmune Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1325, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, I.; Peschke, B.; Lünemann, J.D. Regulation of Antibody Effector Functions through IgG Fc N-Glycosylation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2017, 74, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Nimmerjahn, F. The Role of Differential IgG Glycosylation in the Interaction of Antibodies with FcγRs in Vivo. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2011, 16, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinkuolie, A.O.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Mora, S. A Novel Protein Glycan Biomarker and Future Cardiovascular Disease Events. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 3, e001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birukov, A.; Plavša, B.; Eichelmann, F.; Kuxhaus, O.; Hoshi, R.A.; Rudman, N.; Štambuk, T.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Schiborn, C.; Morze, J.; et al. Immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation Signatures in Incident Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittenbecher, C.; Štambuk, T.; Kuxhaus, O.; Rudman, N.; Vučković, F.; Štambuk, J.; Schiborn, C.; Rahelić, D.; Dietrich, S.; Gornik, O.; et al. Plasma N-Glycans as Emerging Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Risk: A Prospective Investigation in the EPIC-Potsdam Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, C.; Gudelj, I.; Macdonald-Dunlop, E.; Mangino, M.; Zierer, J.; Bešić, E.; Joshi, P.K.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Glycosylation Profile of Immunoglobulin G Is Cross-Sectionally Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Two Independent Cohorts. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifer, D.; Louca, P.; Cvetko, A.; Deriš, H.; Cindrić, A.; Grallert, H.; Peters, A.; Polašek, O.; Gornik, O.; Mangino, M.; et al. N-Glycosylation of Immunoglobulin G Predicts Incident Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudman, N.; Kifer, D.; Kaur, S.; Simunović, V.; Cvetko, A.; Pociot, F.; Morahan, G.; Gornik, O. Children at Onset of Type 1 Diabetes Show Altered N-Glycosylation of Plasma Proteins and IgG. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmers, R.F.H.; Vilaj, M.; Urda, D.; Agakov, F.; Šimurina, M.; Klaric, L.; Rudan, I.; Campbell, H.; Hayward, C.; Wilson, J.F.; et al. IgG Glycan Patterns Are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Independent European Populations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetko, A.; Mangino, M.; Tijardović, M.; Kifer, D.; Falchi, M.; Keser, T.; Perola, M.; Spector, T.D.; Lauc, G.; Menni, C.; et al. Plasma N-Glycome Shows Continuous Deterioration as the Diagnosis of Insulin Resistance Approaches. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossan, J.S.; Šesto, I.; Štambuk, K.; Šipić, T.; Bernat, R.; Gudelj, I.; Rotkvić, L.; Žulj, M.; Mirat, J. Is the Extent of Left Atrial Fibrosis Associated with Body Mass Index in Patients Undergoing Pulmonary Vein Isolation for Atrial Fibrillation? Kardiol. Pol. 2021, 79, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucić, M.; Knezević, A.; Vidic, J.; Adamczyk, B.; Novokmet, M.; Polasek, O.; Gornik, O.; Supraha-Goreta, S.; Wormald, M.R.; Redzić, I.; et al. High Throughput Isolation and Glycosylation Analysis of IgG-Variability and Heritability of the IgG Glycome in Three Isolated Human Populations. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2011, 10, M111.010090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmačić, I.T.; Ugrina, I.; Štambuk, J.; Gudelj, I.; Vučković, F.; Lauc, G.; Pučić-Baković, M. High-Throughput Glycomics: Optimization of Sample Preparation. Biochem. Biokhimiia 2015, 80, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldova, R.; Asadi Shehni, A.; Haakensen, V.D.; Steinfeld, I.; Hilliard, M.; Kifer, I.; Helland, A.; Yakhini, Z.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L.; Rudd, P.M. Association of N-Glycosylation with Breast Carcinoma and Systemic Features Using High-Resolution Quantitative UPLC. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 2314–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, A.; Gornik, O.; Polasek, O.; Pucic, M.; Redzic, I.; Novokmet, M.; Rudd, P.M.; Wright, A.F.; Campbell, H.; Rudan, I.; et al. Effects of Aging, Body Mass Index, Plasma Lipid Profiles, and Smoking on Human Plasma N-Glycans. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotz, V.; Wuhrer, M. N-Glycome Signatures in Human Plasma: Associations with Physiology and Major Diseases. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 2966–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J.G.M. Refining Clinical Risk Stratification for Predicting Stroke and Thromboembolism in Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Risk Factor-Based Approach: The Euro Heart Survey on Atrial Fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ji, L. Adjusting Multiple Testing in Multilocus Analyses Using the Eigenvalues of a Correlation Matrix. Heredity 2005, 95, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, R.R.; Alonso, A.; Lopez, F.L.; Filion, K.B.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.R.; Soliman, E.Z.; Pankow, J.S.; Selvin, E. Type 2 Diabetes, Glucose Homeostasis and Incident Atrial Fibrillation: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2012, 98, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, F.; Reiding, K.R.; Jansen, B.C.; Kammeijer, G.S.M.; Bondt, A.; Wuhrer, M. Human Plasma Protein N-Glycosylation. Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 309–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šoić, D.; Keser, T.; Štambuk, J.; Kifer, D.; Pociot, F.; Lauc, G.; Morahan, G.; Novokmet, M.; Gornik, O. High-Throughput Human Complement C3 N-Glycoprofiling Identifies Markers of Early Onset Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Children. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2022, 21, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Patel, R.P. Endothelial Heterogeneity and Adhesion Molecules N-Glycosylation: Implications in Leukocyte Trafficking in Inflammation. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Jiao, H.; Zhao, D.; Teng, J. Association between Serum Apolipoprotein B and Atrial Fibrillation: A Case–Control Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Jiang, L.; Pan, L.-Z.; LaBarre, M.J.; Anderson, D.; Reff, M. Expression of GnTIII in a Recombinant Anti-CD20 CHO Production Cell Line: Expression of Antibodies with Altered Glycoforms Leads to an Increase in ADCC through Higher Affinity for FCγRIII. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 74, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljičanin, T.; Metelko, Ž. Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus in Croatia and Worldwide. Medix Spec. Med. Dvomjesečnik 2009, 80–81, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Korantzopoulos, P. Association between C-Reactive Protein and Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation after Successful Electrical Cardioversion: A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Immunoglobulin G Resulting from Fc Sialylation. Science 2006, 313, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Wormald, M.R.; Rudd, P.M.; Fischer, P.B.; Dwek, R.A.; Sim, R.B. Glycosylation Changes of IgG Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Can Activate Complement via the Mannose-Binding Protein. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsten, C.M.; Pandey, M.K.; Figge, J.; Kilchenstein, R.; Taylor, P.R.; Rosas, M.; McDonald, J.U.; Orr, S.J.; Berger, M.; Petzold, D.; et al. Galactosylated IgG1 Links FcγRIIB and Dectin-1 to Block Complement-Mediated Inflammation. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Atrial Fibrillation | Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 172 | 54 | |
| Age (years) | 64 (57–69) | 64 (57–69) | |
| Female sex | 63 (36%) | 19 (35%) | |
| BMI | 28.9 (4.37) | ||
| AF classification | |||
| Paroxysmal | 135 (78%) | ||
| Persistent | 37 (22%) | ||
| CHA2DS2-VASc | |||
| 0 | 33 (19%) | ||
| 1 | 48 (28%) | ||
| 2 | 45 (26%) | ||
| 3 | 36 (21%) | ||
| <4 | 10 (6%) | ||
| Hypertension | |||
| No | 58 (34%) | ||
| Yes | 114 (66%) | ||
| Diabetes melitus | |||
| No | 159 (92%) | ||
| Yes | 13 (8%) | ||
| Coronary disease | |||
| No | 153 (89%) | ||
| Yes | 19 (11%) | ||
| Stroke or TIA | |||
| No | 165 (96%) | ||
| Yes | 7 (4%) | ||
| AF recurrence (6 months) | |||
| No | 120 (70%) | ||
| Yes | 50 (29%) | ||
| N/A | 2 (1%) | ||
| Atrial fibrosis # | |||
| No | 21 (12%) | ||
| Mild | 43 (25%) | ||
| Extensive | 103 (60%) | ||
| N/A | 5 (3%) |
| Sample | Glycan Trait | β-Coefficient (95% Confidence Interval) * | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | GP19 | 0.075 (0.036, 0.114) | 0.0002 | 0.004 |
| IgG | IGP5 | 0.123 (0.042, 0.204) | 0.003 | 0.012 |
| IGP6 | −0.093 (−0.167, −0.019) | 0.0134 | 0.022 | |
| IGP9 | 0.065 (0.02, 0.109) | 0.0048 | 0.047 | |
| IGP10 | −0.083 (−0.143, −0.024) | 0.0062 | 0.029 | |
| IGP20 | 0.221 (0.149, 0.294) | 8 × 10−9 | 1 × 10−7 | |
| IGP21 | 0.166 (0.095, 0.237) | 6 × 10−6 | 6 × 10−5 | |
| Bisecting | −0.055 (−0.096, −0.014) | 0.0084 | 0.037 |
| Sample | Association | Glycan Trait | β-Coefficient (95% Confidence Interval) * | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | AF recurrence | GP2 | 0.117 (0.038, 0.196) | 0.0041 | 0.034 |
| GP7 | 0.094 (0.028, 0.159) | 0.0053 | 0.037 | ||
| GP9 | 0.123 (0.039, 0.207) | 0.0043 | 0.034 | ||
| GP15 | 0.12 (0.046, 0.195) | 0.0017 | 0.024 | ||
| OligoMan | 0.069 (0.03, 0.107) | 0.0006 | 0.012 | ||
| IgG | Pre- and post-procedure | IGP05 | −0.108 (−0.166, −0.05) | 0.0003 | 0.002 |
| IGP17 | −0.086 (−0.143, −0.029) | 0.0031 | 0.018 | ||
| IGP20 | −0.19 (−0.249, −0.13) | 2 × 10−9 | 2 × 10−8 | ||
| IGP21 | −0.172 (−0.227, −0.118) | 2 × 10−9 | 2 × 10−8 |
| Glycan Trait | Linear β-Coefficient (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value # |
|---|---|---|---|
| IGP4 | 0.179 (0.04, 0.319) | 0.0118 | 0.034 |
| IGP6 | 0.355 (0.201, 0.508) | 1 × 10−5 | 1 × 10−4 |
| IGP8 | −0.067 (−0.119, −0.015) | 0.0123 | 0.034 |
| IGP14 | −0.213 (−0.352, −0.074) | 0.0028 | 0.014 |
| IGP18 | −0.186 (−0.323, −0.048) | 0.0086 | 0.029 |
| IGP23 | −0.275 (−0.475, −0.076) | 0.007 | 0.027 |
| Bisecting | 0.132 (0.049, 0.215) | 0.0019 | 0.013 |
| G0 | 0.214 (0.087, 0.341) | 0.0011 | 0.011 |
| G2 | -0.184 (−0.315, −0.053) | 0.006 | 0.026 |
| S | -0.152 (−0.248, −0.055) | 0.0023 | 0.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plavša, B.; Szavits-Nossan, J.; Blivajs, A.; Rapčan, B.; Radovani, B.; Šesto, I.; Štambuk, K.; Mustapić, V.; Đerek, L.; Rudan, D.; et al. The N-Glycosylation of Total Plasma Proteins and IgG in Atrial Fibrillation. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040605
Plavša B, Szavits-Nossan J, Blivajs A, Rapčan B, Radovani B, Šesto I, Štambuk K, Mustapić V, Đerek L, Rudan D, et al. The N-Glycosylation of Total Plasma Proteins and IgG in Atrial Fibrillation. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(4):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040605
Chicago/Turabian StylePlavša, Branimir, Janko Szavits-Nossan, Aleksandar Blivajs, Borna Rapčan, Barbara Radovani, Igor Šesto, Krešimir Štambuk, Vito Mustapić, Lovorka Đerek, Diana Rudan, and et al. 2023. "The N-Glycosylation of Total Plasma Proteins and IgG in Atrial Fibrillation" Biomolecules 13, no. 4: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040605
APA StylePlavša, B., Szavits-Nossan, J., Blivajs, A., Rapčan, B., Radovani, B., Šesto, I., Štambuk, K., Mustapić, V., Đerek, L., Rudan, D., Lauc, G., & Gudelj, I. (2023). The N-Glycosylation of Total Plasma Proteins and IgG in Atrial Fibrillation. Biomolecules, 13(4), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040605







