Adenosine A2A Receptors Shut Down Adenosine A1 Receptor-Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition to Promote Implementation of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Dugs
2.3. Adenosine Release from Mouse Hippocampal Synaptosomes
2.4. Electrophysiological Recordings
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
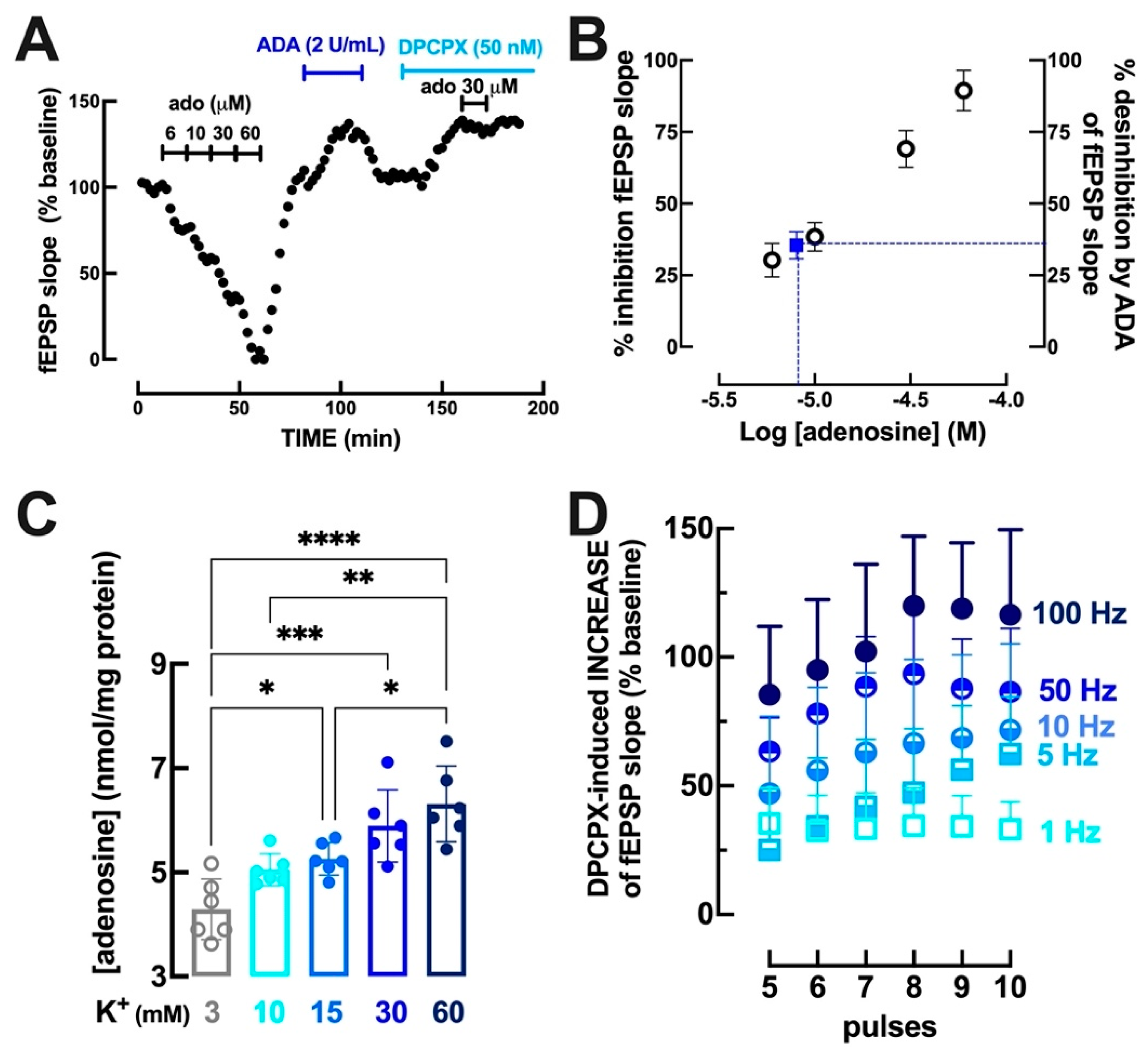
3.1. Intensity- and Frequency-Dependent Increase of Extracellular Adenosine in Hippocampal Synapses
3.2. A2AR Blockade Untethers an A1R-Mediated Inhibition of Hippocampal LTP
3.3. A2AR Activation Dampens A1R-Mediated Inhibition of Hippocampal Transmission
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cunha, R.A. Different cellular sources and different roles of adenosine: A1 receptor-mediated inhibition through astrocytic-driven volume transmission and synapse-restricted A2A receptor-mediated facilitation of plasticity. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Chen, J.F.; Cunha, R.A.; Svenningsson, P.; Vaugeois, J.M. Adenosine and brain function. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2005, 63, 191–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunwiddie, T.V.; Masino, S.A. The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebola, N.; Pinheiro, P.C.; Oliveira, C.R.; Malva, J.O.; Cunha, R.A. Subcellular localization of adenosine A1 receptors in nerve terminals and synapses of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2003, 987, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.M.; Haas, H.L.; Gähwiler, B.H. Comparison of the actions of adenosine at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J. Physiol. 1992, 451, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastião, A.M.; Cunha, R.A.; de Mendonça, A.; Ribeiro, J.A. Modification of adenosine modulation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus of aged rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 131, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.B.; Lupica, C.R.; Dunwiddie, T.V. Activity-dependent release of endogenous adenosine modulates synaptic responses in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A.; Vizi, E.S.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Sebastião, A.M. Preferential release of ATP and its extracellular catabolism as a source of adenosine upon high- but not low-frequency stimulation of rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovatt, D.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Takano, T.; Smith, N.A.; Schnermann, J.; Tieu, K.; Nedergaard, M. Neuronal adenosine release, and not astrocytic ATP release, mediates feedback inhibition of excitatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6265–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, O.; Casper, K.B.; Kubera, C.; Zhang, J.; Revilla-Sanchez, R.; Sul, J.Y.; Takano, H.; Moss, S.J.; McCarthy, K.; Haydon, P.G. Astrocytic purinergic signaling coordinates synaptic networks. Science 2005, 310, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, A.; Haddjeri, N.; Lacaille, J.C.; Robitaille, R. GABAergic network activation of glial cells underlies hippocampal heterosynaptic depression. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5370–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannon, N.M.; Chistiakova, M.; Chen, J.Y.; Bazhenov, M.; Volgushev, M. Adenosine shifts plasticity regimes between associative and homeostatic by modulating heterosynaptic changes. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinho, P.; Madeira, D.; Dias, L.; Simões, A.P.; Cunha, R.A.; Canas, P.M. Purinergic signaling orchestrating neuron-glia communication. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, M.J.; Richardson, M.J. Localized adenosine signaling provides fine-tuned negative feedback over a wide dynamic range of neocortical network activities. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, M.F.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1994, 4, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, C.L.; Garthwaite, J. Adenosine acting on A1 receptors protects NO-triggered rebound potentiation and LTP in rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costenla, A.R.; Diógenes, M.J.; Canas, P.M.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Nogueira, C.; Maroco, J.; Agostinho, P.M.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Cunha, R.A.; de Mendonça, A. Enhanced role of adenosine A2A receptors in the modulation of LTP in the rat hippocampus upon ageing. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.V.; Cunha, R.A.; Ribeiro, J.A. Cross talk between A1 and A2A adenosine receptors in the hippocampus and cortex of young adult and old rats. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 82, 3196–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.V.; Cunha, R.A.; Kull, B.; Fredholm, B.B.; Ribeiro, J.A. Adenosine A2A receptor facilitation of hippocampal synaptic transmission is dependent on tonic A1 receptor inhibition. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciruela, F.; Casadó, V.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Luján, R.; Burgueño, J.; Canals, M.; Borycz, J.; Rebola, N.; Goldberg, S.R.; Mallol, J.; et al. Presynaptic control of striatal glutamatergic neurotransmission by adenosine A1-A2A receptor heteromers. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, N.M.; Zhang, P.; Ilin, V.; Chistiakova, M.; Volgushev, M. Modulation of synaptic transmission by adenosine in layer 2/3 of the rat visual cortex in vitro. Neuroscience 2014, 260, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, N.; Lujan, R.; Cunha, R.A.; Mulle, C. Adenosine A2A receptors are essential for long-term potentiation of NMDA-EPSCs at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Neuron 2008, 57, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temido-Ferreira, M.; Ferreira, D.G.; Batalha, V.L.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Coelho, J.E.; Pereira, P.; Gomes, R.; Pinto, A.; Carvalho, S.; Canas, P.M.; et al. Age-related shift in LTD is dependent on neuronal adenosine A2A receptors interplay with mGluR5 and NMDA receptors. Mol. Psychiatry. 2020, 25, 1876–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, A.P.; Machado, N.J.; Gonçalves, N.; Kaster, M.P.; Simões, A.T.; Nunes, A.; Pereira de Almeida, L.; Goosens, K.A.; Rial, D.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine A2A receptors in the amygdala control synaptic plasticity and contextual fear memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhofs, A.; Canas, P.M.; Timmerman, A.J.; Heistek, T.S.; Real, J.I.; Xavier, C.; Cunha, R.A.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Ferreira, S.G. Adenosine A2A receptors control glutamatergic synaptic plasticity in fast spiking interneurons of the prefrontal cortex. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.Q.; Matheus, F.C.; Silva, H.B.; Real, J.I.; Rial, D.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Oses, J.P.; Silva, A.C.; Gonçalves, N.; Prediger, R.D.; et al. Increased ATP release and higher impact of adenosine A2A receptors on corticostriatal plasticity in a rat model of presymptomatic Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieraszko, A.; Goldsmith, G.; Seyfried, T.N. Stimulation-dependent release of adenosine triphosphate from hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989, 485, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A. Regulation of the ecto-nucleotidase pathway in rat hippocampal nerve terminals. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, E.; Matos, M.; Sévigny, J.; El-Tayeb, A.; Bynoe, M.S.; Müller, C.E.; Cunha, R.A.; Chen, J.F. Ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73)-mediated formation of adenosine is critical for the striatal adenosine A2A receptor functions. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 11390–11399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Canas, P.M.; Oses, J.P.; Fernandes, F.D.; Duarte, F.V.; Palmeira, C.M.; Tomé, A.R.; Agostinho, P.; Andrade, G.M.; et al. Enhanced ATP release and CD73-mediated adenosine formation sustain adenosine A2A receptor over-activation in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3666–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.Q.; Lopes, J.P.; Silva, H.B.; Lemos, C.; Silva, A.C.; Gonçalves, N.; Tomé, Â.R.; Ferreira, S.G.; Canas, P.M.; Rial, D.; et al. Synaptic and memory dysfunction in a β-amyloid model of early Alzheimer’s disease depends on increased formation of ATP-derived extracellular adenosine. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, E.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Real, J.E.; Silva, H.B.; Pochmann, D.; Silva, T.S.; Matos, M.; Gonçalves, N.; Tomé, Â.R.; Chen, J.F.; et al. Increased ATP release and CD73-mediated adenosine A2A receptor activation mediate convulsion-associated neuronal damage and hippocampal dysfunction. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 157, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, A.P.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Rial, D.; Ferreira, S.G.; Lopes, J.P.; Canas, P.M.; Cunha, R.A. CD73-mediated formation of extracellular adenosine is responsible for adenosine A2A receptor-mediated control of fear memory and amygdala plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.; Pochmann, D.; Lemos, C.; Silva, H.B.; Real, J.I.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Rial, D.; Gonçalves, N.; Simões, A.P.; Ferreira, S.G.; et al. Increased synaptic ATP release and CD73-mediated formation of extracellular adenosine in the control of behavioral and electrophysiological modifications caused by chronic stress. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A. Release of ATP and adenosine and formation of extracellular adenosine in the hippocampus. In The Role of Adenosine in the Nervous System; Okada, Y., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, L.V.; Halldner, L.; Rebola, N.; Johansson, B.; Ledent, C.; Chen, J.F.; Fredholm, B.B.; Cunha, R.A. Binding of the prototypical adenosine A2A receptor agonist CGS 21680 to the cerebral cortex of adenosine A1 and A2A receptor knockout mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A.; Constantino, M.D.; Ribeiro, J.A. ZM241385 is an antagonist of the facilitatory responses produced by the A2A adenosine receptor agonists CGS21680 and HENECA in the rat hippocampus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garção, P.; Szabó, E.C.; Wopereis, S.; Castro, A.A.; Tomé, Â.R.; Prediger, R.D.; Cunha, R.A.; Agostinho, P.; Köfalvi, A. Functional interaction between pre-synaptic α6β2-containing nicotinic and adenosine A2A receptors in the control of dopamine release in the rat striatum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, R.A.; Sebastião, A.M.; Ribeiro, J.A. Ecto-5′-nucleotidase is associated with cholinergic nerve terminals in the hippocampus but not in the cerebral cortex of the rat. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, R.A.; Sebastião, A.M. Adenosine and adenine nucleotides are independently released from both the nerve terminals and the muscle fibres upon electrical stimulation of the innervated skeletal muscle of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 1993, 424, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.P.; Pliássova, A.; Cunha, R.A. The physiological effects of caffeine on synaptic transmission and plasticity in the mouse hippocampus selectively depend on adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 166, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.W.; Collingridge, G.L. Capabilities of the WinLTP data acquisition program extending beyond basic LTP experimental functions. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 162, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaleonidopoulos, V.; Trompoukis, G.; Koutsoumpa, A.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. A gradient of frequency-dependent synaptic properties along the longitudinal hippocampal axis. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Fernández, V.; Andrew, R.D.; Barajas-López, C. ATP inhibits glutamate synaptic release by acting at P2Y receptors in pyramidal neurons of hippocampal slices. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaustein, M.P.; Goldring, J.M. Membrane potentials in pinched-off presynaptic nerve ternimals monitored with a fluorescent probe: Evidence that synaptosomes have potassium diffusion potentials. J. Physiol. 1975, 247, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, H.T.; Nicholls, D.G. The relationship between cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and the release of glutamate from synaptosomes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1990, 18, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meder, W.; Fink, K.; Göthert, M. Involvement of different calcium channels in K+- and veratridine-induced increases of cytosolic calcium concentration in rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 356, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A. How does adenosine control neuronal dysfunction and neurodegeneration? J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 1019–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaife-Lopes, N.; Sousa, V.C.; Pereira, D.B.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Chao, M.V.; Sebastião, A.M. Activation of adenosine A2A receptors induces TrkB translocation and increases BDNF-mediated phospho-TrkB localization in lipid rafts: Implications for neuromodulation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8468–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantis, K.; Tsiamaki, E.; Kouvaros, S.; Papatheodoropoulos, C.; Angelatou, F. Adenosine A2A receptors permit mGluR5-evoked tyrosine phosphorylation of NR2B (Tyr1472) in rat hippocampus: A possible key mechanism in NMDA receptor modulation. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, N.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Lopes, L.V.; Richardson, P.J.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine A1 and A2A receptors are co-expressed in pyramidal neurons and co-localized in glutamatergic nerve terminals of the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2005, 133, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, N.; Canas, P.M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, R.A. Different synaptic and subsynaptic localization of adenosine A2A receptors in the hippocampus and striatum of the rat. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canas, P.M.; Porciúncula, L.O.; Cunha, G.M.; Silva, C.G.; Machado, N.J.; Oliveira, J.M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine A2A receptor blockade prevents synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction caused by beta-amyloid peptides via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14741–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana da Silva, S.; Haberl, M.G.; Zhang, P.; Bethge, P.; Lemos, C.; Gonçalves, N.; Gorlewicz, A.; Malezieux, M.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Grosjean, N.; et al. Early synaptic deficits in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease involve neuronal adenosine A2A receptors. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köfalvi, A.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Ledent, C.; Mackie, K.; Vizi, E.S.; Cunha, R.A.; Sperlágh, B. Involvement of cannabinoid receptors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release in the rodent striatum: A combined immunochemical and pharmacological analysis. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Cruz, A.; Carlström, M.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Sebastião, A.M. Dual influence of endocannabinoids on long-term potentiation of synaptic transmission. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.G.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Marques, J.M.; Tomé, Â.R.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Nunes-Correia, I.; Ledent, C.; Harkany, T.; Venance, L.; Cunha, R.A.; et al. Presynaptic adenosine A2A receptors dampen cannabinoid CB1 receptor-mediated inhibition of corticostriatal glutamatergic transmission. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köfalvi, A.; Moreno, E.; Cordomí, A.; Cai, N.S.; Fernández-Dueñas, V.; Ferreira, S.G.; Guixà-González, R.; Sánchez-Soto, M.; Yano, H.; Casadó-Anguera, V.; et al. Control of glutamate release by complexes of adenosine and cannabinoid receptors. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martire, A.; Tebano, M.T.; Chiodi, V.; Ferreira, S.G.; Cunha, R.A.; Köfalvi, A.; Popoli, P. Pre-synaptic adenosine A2A receptors control cannabinoid CB1 receptor-mediated inhibition of striatal glutamatergic neurotransmission. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, E.; Fernández-Dueñas, V.; López-Cano, M.; Taura, J.; Watanabe, M.; Ferrer, I.; Luján, R.; Ciruela, F. Adenosine A2A-cannabinoid CB1 receptor heteromers in the hippocampus: Cannabidiol blunts Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced cognitive impairment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5382–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviv, T.; Riven, I.; Dolev, I.; Vertkin, I.; Balana, B.; Slesinger, P.A.; Slutsky, I. Basal GABA regulates GABABR conformation and release probability at single hippocampal synapses. Neuron 2010, 67, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.J.; Almeida, T.; Richardson, P.J.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, R.A. Dual presynaptic control by ATP of glutamate release via facilitatory P2X1, P2X2/3, and P2X3 and inhibitory P2Y1, P2Y2, and/or P2Y4 receptors in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6286–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, L.; Lopes, C.R.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Nunes, A.; Pochmann, D.; Machado, N.J.; Tomé, A.R.; Agostinho, P.; Cunha, R.A. Crosstalk between ATP-P2X7 and adenosine A2A receptors controlling neuroinflammation in rats subject to repeated restraint stress. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 639322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, R.A.; Johansson, B.; Constantino, M.D.; Sebastião, A.M.; Fredholm, B.B. Evidence for high-affinity binding sites for the adenosine A2A receptor agonist [3H]CGS21680 in the rat hippocampus and cerebral cortex that are different from striatal A2A receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1996, 353, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.A.; Constantino, M.D.; Ribeiro, J.A. G protein coupling of CGS 21680 binding sites in the rat hippocampus and cortex is different from that of adenosine A1 and striatal A2A receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1999, 359, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldner, L.; Lopes, L.V.; Daré, E.; Lindström, K.; Johansson, B.; Ledent, C.; Cunha, R.A.; Fredholm, B.B. Binding of adenosine receptor ligands to brain of adenosine receptor knock-out mice: Evidence that CGS 21680 binds to A1 receptors in hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 370, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, M.; Shen, H.Y.; Augusto, E.; Wang, Y.; Wei, C.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Agostinho, P.; Boison, D.; Cunha, R.A.; Chen, J.F. Deletion of adenosine A2A receptors from astrocytes disrupts glutamate homeostasis leading to psychomotor and cognitive impairment: Relevance to schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry. 2015, 78, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.Y.; Coelho, J.E.; Ohtsuka, N.; Canas, P.M.; Day, Y.J.; Huang, Q.Y.; Rebola, N.; Yu, L.; Boison, D.; Cunha, R.A.; et al. A critical role of the adenosine A2A receptor in extrastriatal neurons in modulating psychomotor activity as revealed by opposite phenotypes of striatum and forebrain A2A receptor knock-outs. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2970–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.Y.; Canas, P.M.; Garcia-Sanz, P.; Lan, J.Q.; Boison, D.; Moratalla, R.; Cunha, R.A.; Chen, J.F. Adenosine A2A receptors in striatal glutamatergic terminals and GABAergic neurons oppositely modulate psychostimulant action and DARPP-32 phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.J.; Augusto, E.; Gomes, C.A.; Singer, P.; Wang, Y.; Boison, D.; Cunha, R.A.; Yee, B.K.; Chen, J.F. Regulation of fear responses by striatal and extrastriatal adenosine A2A receptors in forebrain. Biol. Psychiatry. 2014, 75, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, M.J.; Dale, N. Neuronal transporter and astrocytic ATP exocytosis underlie activity-dependent adenosine release in the hippocampus. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 3853–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Wan, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Pan, S.; Peng, W.; Dong, A.; et al. Neuronal activity-induced, equilibrative nucleoside transporter-dependent, somatodendritic adenosine release revealed by a GRAB sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2212387120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimon, A.; Strasburger, H.J.; Ayata, P.; Chen, X.; Nair, A.; Ikegami, A.; Hwang, P.; Chan, A.T.; Graves, S.M.; Uweru, J.O.; et al. Negative feedback control of neuronal activity by microglia. Nature 2020, 586, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- zur Nedden, S.; Hawley, S.; Pentland, N.; Hardie, D.G.; Doney, A.S.; Frenguelli, B.G. Intracellular ATP influences synaptic plasticity in area CA1 of rat hippocampus via metabolism to adenosine and activity-dependent activation of adenosine A1 receptors. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6221–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Stockwell, J.; Cayabyab, F.S. Adenosine A1 receptor-mediated endocytosis of AMPA receptors contributes to impairments in long-term potentiation (LTP) in the middle-aged rat hippocampus. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mendonça, A.; Ribeiro, J.A. Long-term potentiation observed upon blockade of adenosine A1 receptors in rat hippocampus is N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 291, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, C.S.; Kramár, E.A.; Colgin, L.L.; Lin, B.; Gall, C.M.; Lynch, G. Long-term potentiation is impaired in middle-aged rats: Regional specificity and reversal by adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5956–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Llort, L.; Masino, S.A.; Diao, L.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Tobeña, A.; Halldner, L.; Fredholm, B.B. Mice lacking the adenosine A1 receptor have normal spatial learning and plasticity in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, but they habituate more slowly. Synapse 2005, 57, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuch, B.P.; Dale, N.; Wall, M.J. Deletion of ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) reveals direct action potential-dependent adenosine release. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3842–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andiné, P.; Rudolphi, K.A.; Fredholm, B.B.; Hagberg, H. Effect of propentofylline (HWA 285) on extracellular purines and excitatory amino acids in CA1 of rat hippocampus during transient ischaemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 100, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Graham, D.I.; Stone, T.W. Release of endogenous adenosine and its metabolites by the activation of NMDA receptors in the rat hippocampus in vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 106, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diógenes, M.J.; Neves-Tomé, R.; Fucile, S.; Martinello, K.; Scianni, M.; Theofilas, P.; Lopatár, J.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Maggi, L.; Frenguelli, B.G.; et al. Homeostatic control of synaptic activity by endogenous adenosine is mediated by adenosine kinase. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T.; Venton, B.J. Regional variations of spontaneous, transient adenosine release in brain slices. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashiro, K.; Fujii, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Morita, M. Multiple pathways for elevating extracellular adenosine in the rat hippocampal CA1 region characterized by adenosine sensor cells. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankratov, Y.; Lalo, U.; Verkhratsky, A.; North, R.A. Vesicular release of ATP at central synapses. Pflugers Arch. 2006, 452, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes, C.R.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Olaio, S.; Tomé, A.R.; Cunha, R.A.; Lopes, J.P. Adenosine A2A Receptors Shut Down Adenosine A1 Receptor-Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition to Promote Implementation of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040715
Lopes CR, Gonçalves FQ, Olaio S, Tomé AR, Cunha RA, Lopes JP. Adenosine A2A Receptors Shut Down Adenosine A1 Receptor-Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition to Promote Implementation of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(4):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040715
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes, Cátia R., Francisco Q. Gonçalves, Simão Olaio, Angelo R. Tomé, Rodrigo A. Cunha, and João Pedro Lopes. 2023. "Adenosine A2A Receptors Shut Down Adenosine A1 Receptor-Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition to Promote Implementation of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation" Biomolecules 13, no. 4: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040715
APA StyleLopes, C. R., Gonçalves, F. Q., Olaio, S., Tomé, A. R., Cunha, R. A., & Lopes, J. P. (2023). Adenosine A2A Receptors Shut Down Adenosine A1 Receptor-Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition to Promote Implementation of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Biomolecules, 13(4), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040715









