The Functional Role of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Asthma
Abstract
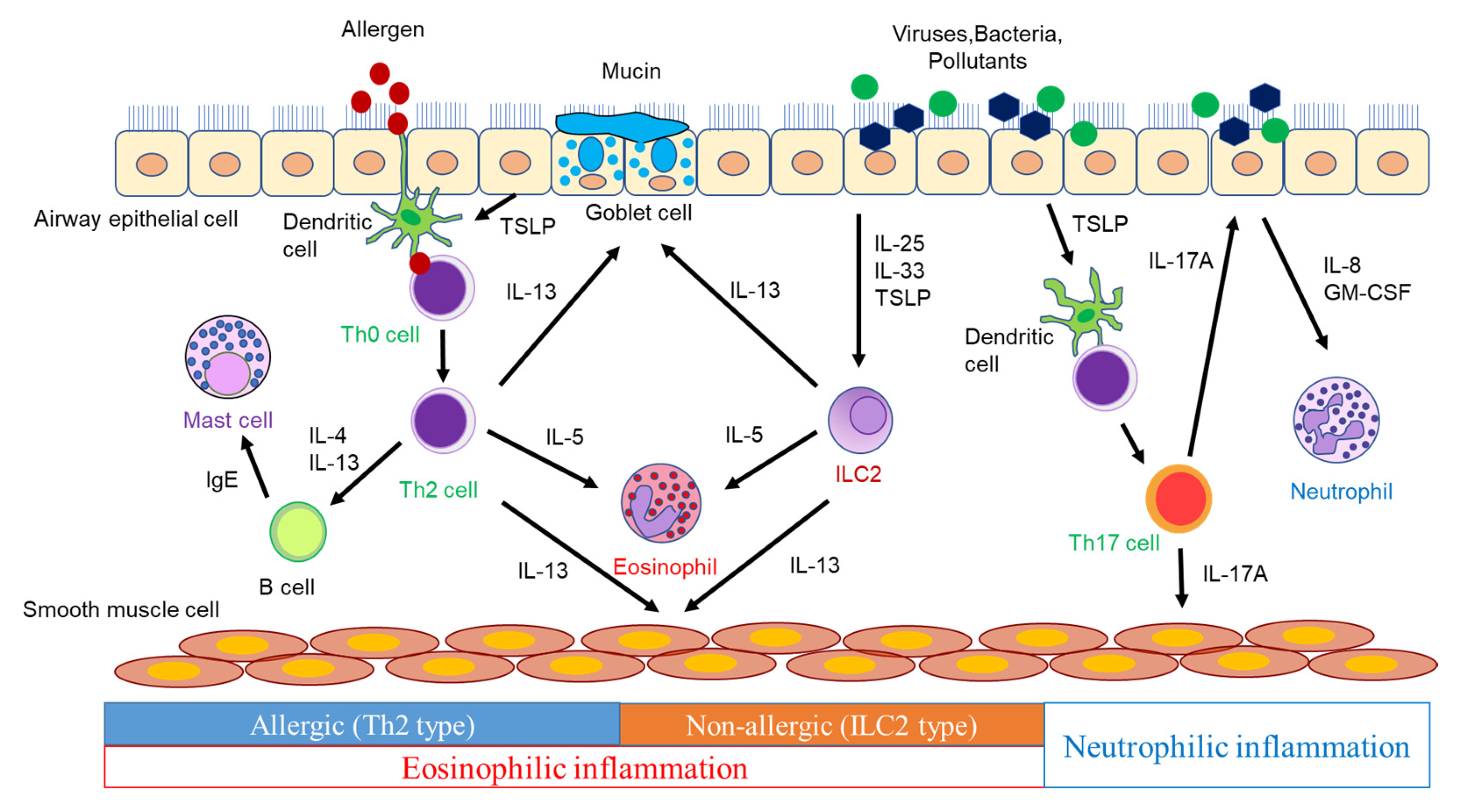
:1. Introduction
2. Airway Inflammation in Asthma Pathogenesis
3. Interaction of ILC2 with Other Immune Cells
3.1. ILC2s and T Cells
3.2. ILC2s and DCs
3.3. ILC2s and Macrophages
3.4. ILC2s and Mast Cells
3.5. ILC2s and Basophils
4. Modulators of ILC2 Function in Asthma
4.1. Cytokines
4.2. Lipid Mediators
4.3. Neuropeptides and Neurotransmitters
4.4. Hormones
5. Impact and Functional Role of ILC2 in Asthma
5.1. Impact of ILC2 in Asthma
5.2. Functional Role of ILC2s in Asthma Pathogenesis
5.2.1. Steroid Resistance
5.2.2. Viral-Induced Asthma Exacerbation
6. Impact of ILC2 on Asthma Comorbidities
6.1. Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease
6.2. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
6.3. Allergic Rhinitis
6.4. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention 2022; GINA: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022; Available online: http://ginasthma.org (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Brusselle, G.; Bracke, K. Targeting immune pathways for therapy in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, S322–S328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsbjerg, C.; Lund, T.K.; Pedersen, L.; Backer, V. Inflammatory subtypes in asthma are related to airway hyperresponsiveness to mannitol and exhaled NO. J. Asthma 2009, 46, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artis, D.; Spits, H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature 2015, 517, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, K.; Yamada, T.; Tanabe, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Ikawa, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Furusawa, J.; Ohtani, M.; Fujii, H.; Koyasu, S. Innate production of TH2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit+Sca-1+ lymphoid cells. Nature 2010, 463, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata, H.; Moro, K.; Koyasu, S.; Asano, K. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells and asthma. Allergol. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Allergol. 2015, 64, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neill, D.R.; Wong, S.H.; Bellosi, A.; Flynn, R.J.; Daly, M.; Langford, T.K.; Bucks, C.; Kane, C.M.; Fallon, P.G.; Pannell, R.; et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature 2010, 464, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.E.; Liang, H.E.; Sullivan, B.M.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Eisley, C.J.; Erle, D.J.; Locksley, R.M. Systemically dispersed innate IL-13-expressing cells in type 2 immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11489–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, Y.; Nagano, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells and the House Dust Mite-Induced Asthma Mouse Model. Cells 2020, 9, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainge, C.L.; Lau, L.C.; Ward, J.A.; Dulay, V.; Lahiff, G.; Wilson, S.; Holgate, S.; Davies, D.E.; Howarth, P.H. Effect of bronchoconstriction on airway remodeling in asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2006–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, T.; Joos, G.F.; Brusselle, G.G. Targeting interleukin-4 in asthma: Lost in translation? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusselle, G.G.; Koppelman, G.H. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, Y.; Nakazawa, S.; Todoroki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Sakai, H.; Misawa, M. Interleukin-13 augments bronchial smooth muscle contractility with an up-regulation of RhoA protein. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.C.; Wenzel, S.E. Intersection of biology and therapeutics: Type 2 targeted therapeutics for adult asthma. Lancet 2020, 395, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Anderson, D.E.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Hastings, W.D.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Hafler, D.A. IL-21 and TGF-beta are required for differentiation of human TH17 cells. Nature 2008, 454, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinley, L.; Alcorn, J.F.; Peterson, A.; Dupont, R.B.; Kapadia, S.; Logar, A.; Henry, A.; Irvin, C.G.; Piganelli, J.D.; Ray, A.; et al. TH17 cells mediate steroid-resistant airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4089–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, G.M.; Hinks, T.S.C. The role of interleukin-17 in asthma: A protective response? ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00364–02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Holgate, S.; Kerwin, E.; Chon, Y.; Feng, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, S.L. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab, a human anti-IL-17 receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, T.Y.; Krauss, R.H.; Sun, A.C.; Takei, F. Lung natural helper cells are a critical source of Th2 cell-type cytokines in protease allergen-induced airway inflammation. Immunity 2012, 36, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.T.; Gottschalk, T.A.; Tsantikos, E.; Hibbs, M.L. The Role of Innate Lymphoid Cells in Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 733324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.J.; Antignano, F.; Halim, T.Y.; Hirota, J.A.; Blanchet, M.R.; Zaph, C.; Takei, F.; McNagny, K.M. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells facilitate sensitization to local, but not systemic, TH2-inducing allergen exposures. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliphant, C.J.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Walker, J.A.; Salimi, M.; Wong, S.H.; Brewer, J.M.; Englezakis, A.; Barlow, J.L.; Hams, E.; Scanlon, S.T.; et al. MHCII-mediated dialog between group 2 innate lymphoid cells and CD4+ T cells potentiates type 2 immunity and promotes parasitic helminth expulsion. Immunity 2014, 41, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symowski, C.; Voehringer, D. Th2 cell-derived IL-4/IL-13 promote ILC2 accumulation in the lung by ILC2-intrinsic STAT6 signaling in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, T.Y.; Steer, C.A.; Matha, L.; Gold, M.J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, I.; McNagny, K.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Takei, F. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are critical for the initiation of adaptive T helper 2 cell-mediated allergic lung inflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Huang, L.; Ji, X.; Yao, S.; Hamed Abdelaziz, M.; Cai, W.; Wang, H.; Cheng, J.; Dineshkumar, K.; Aparna, V.; et al. HMGB1-induced ILC2s activate dendritic cells by producing IL-9 in asthmatic mouse model. Cell. Immunol. 2020, 352, 104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirchandani, A.S.; Besnard, A.G.; Yip, E.; Scott, C.; Bain, C.C.; Cerovic, V.; Salmond, R.J.; Liew, F.Y. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells drive CD4+ Th2 cell responses. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, F.; Davidson, T.S.; Kahle, E.; Kinder, M.; Acharya, K.; Jankovic, D.; Bundoc, V.; Hodges, M.; Shevach, E.M.; Keane-Myers, A.; et al. The TNF-family receptor DR3 is essential for diverse T cell-mediated inflammatory diseases. Immunity 2008, 29, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.D.; Li, R.; Huang, A.F. Role of TL1A in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 891328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Pappu, R.; Ramirez-Carrozzi, V.; Ota, N.; Caplazi, P.; Zhang, J.; Yan, D.; Xu, M.; Lee, W.P.; Grogan, J.L. TNF superfamily member TL1A elicits type 2 innate lymphoid cells at mucosal barriers. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maazi, H.; Banie, H.; Aleman Muench, G.R.; Patel, N.; Wang, B.; Sankaranarayanan, I.; Bhargava, V.; Sato, T.; Lewis, G.; Cesaroni, M.; et al. Activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells regulate type 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated airway hyperreactivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 893–905.e896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchery, T.; Kyle, R.; Camberis, M.; Shepherd, A.; Filbey, K.; Smith, A.; Harvie, M.; Painter, G.; Johnston, K.; Ferguson, P.; et al. ILC2s and T cells cooperate to ensure maintenance of M2 macrophages for lung immunity against hookworms. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Breckenridge, H.A.; Kuo, S.; Singh, S.; Goldsmith, A.G.; Li, Y.; Kreger, J.E.; Bentley, J.K.; Hershenson, M.B. M2 Macrophages promote IL-33 expression, ILC2 expansion and mucous metaplasia in response to early life rhinovirus infections. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 952509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Albacker, L.A.; Baumgarth, N.; McKenzie, A.N.; Smith, D.E.; Dekruyff, R.H.; Umetsu, D.T. Innate lymphoid cells mediate influenza-induced airway hyper-reactivity independently of adaptive immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuzumi, S.; Miyata, J.; Kabata, H.; Mochimaru, T.; Kagawa, S.; Masaki, K.; Irie, M.; Morita, H.; Fukunaga, K. TLR7 Agonist Suppresses Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-mediated Inflammation via IL-27-Producing Interstitial Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 65, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Salimi, M.; Panse, I.; Mjösberg, J.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Spits, H.; Klenerman, P.; Ogg, G. Prostaglandin D2 activates group 2 innate lymphoid cells through chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on TH2 cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, H.; Arae, K.; Unno, H.; Miyauchi, K.; Toyama, S.; Nambu, A.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Motomura, K.; Matsuda, A.; et al. An Interleukin-33-Mast Cell-Interleukin-2 Axis Suppresses Papain-Induced Allergic Inflammation by Promoting Regulatory T Cell Numbers. Immunity 2015, 43, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.E.; Morrison, P.J.; Wilhelm, C.; Wilson, M.; Ahlfors, H.; Renauld, J.C.; Panzer, U.; Helmby, H.; Stockinger, B. IL-9-mediated survival of type 2 innate lymphoid cells promotes damage control in helminth-induced lung inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2951–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, K.; Shibata, S.; Yoshikawa, S.; Karasuyama, H. Basophils and their effector molecules in allergic disorders. Allergy 2021, 76, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.R.; van Dalen, C.J.; Hermans, I.F.; Gibson, P.G.; Simpson, J.L.; Douwes, J. Sputum basophils are increased in eosinophilic asthma compared with non-eosinophilic asthma phenotypes. Allergy 2017, 72, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Wakahara, K.; Nishio, T.; Ito, S.; Hasegawa, Y. Airway basophils are increased and activated in eosinophilic asthma. Allergy 2017, 72, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, Y.; Morita, H.; Moro, K.; Nakae, S.; Artis, D.; Endo, T.A.; Kuroki, Y.; Ohara, O.; Koyasu, S.; Kubo, M. Basophil-derived interleukin-4 controls the function of natural helper cells, a member of ILC2s, in lung inflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Wang, K.; Siracusa, M.C.; Saenz, S.A.; Brestoff, J.R.; Monticelli, L.A.; Noti, M.; Tait Wojno, E.D.; Fung, T.C.; Kubo, M.; et al. Basophils promote innate lymphoid cell responses in inflamed skin. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3717–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, T.; Machida, K.; Motomura, Y.; Takagi, K.; Doutake, Y.; Tanoue-Hamu, A.; Kondo, K.; Mizuno, K.; Moro, K.; Inoue, H. Long-acting muscarinic antagonist regulates group 2 innate lymphoid cell-dependent airway eosinophilic inflammation. Allergy 2021, 76, 2785–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, B.P.; Shafiei Jahani, P.; Akbari, O. Social Networking of Group Two Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergy and Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roediger, B.; Kyle, R.; Tay, S.S.; Mitchell, A.J.; Bolton, H.A.; Guy, T.V.; Tan, S.Y.; Forbes-Blom, E.; Tong, P.L.; Köller, Y.; et al. IL-2 is a critical regulator of group 2 innate lymphoid cell function during pulmonary inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1653–1663.e1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata, H.; Moro, K.; Koyasu, S. The group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) regulatory network and its underlying mechanisms. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 286, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, S.M.; Bernink, J.H.; Nagasawa, M.; Groot, J.; Shikhagaie, M.M.; Golebski, K.; van Drunen, C.M.; Lutter, R.; Jonkers, R.E.; Hombrink, P.; et al. IL-1β, IL-4 and IL-12 control the fate of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in human airway inflammation in the lungs. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.A.; Khorram, N.; Lund, S.; Mehta, A.K.; Croft, M.; Broide, D.H. Lung type 2 innate lymphoid cells express cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1, which regulates TH2 cytokine production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, M. IL-33-driven ILC2/eosinophil axis in fat is induced by sympathetic tone and suppressed by obesity. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 231, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelly, V.S.; Kannan, Y.; Coomes, S.M.; Entwistle, L.J.; Rückerl, D.; Seddon, B.; MacDonald, A.S.; McKenzie, A.; Wilson, M.S. IL-4-producing ILC2s are required for the differentiation of T(H)2 cells following Heligmosomoides polygyrus infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M. Innate and adaptive type 2 immunity in lung allergic inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, K.; Kabata, H.; Tanabe, M.; Koga, S.; Takeno, N.; Mochizuki, M.; Fukunaga, K.; Asano, K.; Betsuyaku, T.; Koyasu, S. Interferon and IL-27 antagonize the function of group 2 innate lymphoid cells and type 2 innate immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHedlidze, T.; Kindermann, M.; Neves, A.T.; Voehringer, D.; Neurath, M.F.; Wirtz, S. IL-27 suppresses type 2 immune responses in vivo via direct effects on group 2 innate lymphoid cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerr, C.U.; McCarthy, C.D.; Mindt, B.C.; Rubio, M.; Meli, A.P.; Pothlichet, J.; Eva, M.M.; Gauchat, J.F.; Qureshi, S.T.; Mazer, B.D.; et al. Type I interferon restricts type 2 immunopathology through the regulation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tei, R.; Iijima, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Lama, J.; Jacobsen, E.A.; Kita, H. TLR3-driven IFN-β antagonizes STAT5-activating cytokines and suppresses innate type 2 response in the lung. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1044–1059.e1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, S.J.; Portillo, A.; Cavagnero, K.; Baum, R.E.; Naji, L.H.; Badrani, J.H.; Mehta, A.; Croft, M.; Broide, D.H.; Doherty, T.A. Leukotriene C4 Potentiates IL-33-Induced Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Activation and Lung Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, W.; Lv, J.; Du, L.; Mi, W.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Leng, Q.; Zhou, H.; et al. BLT1 signaling in epithelial cells mediates allergic sensitization via promotion of IL-33 production. Allergy 2019, 74, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojno, E.D.; Monticelli, L.A.; Tran, S.V.; Alenghat, T.; Osborne, L.C.; Thome, J.J.; Willis, C.; Budelsky, A.; Farber, D.L.; Artis, D. The prostaglandin D2 receptor CRTH2 regulates accumulation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the inflamed lung. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Prostaglandin EInhibits Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Activation and Allergic Airway Inflammation Through E-Prostanoid 4-Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maric, J.; Ravindran, A.; Mazzurana, L.; Björklund, Å.K.; Van Acker, A.; Rao, A.; Friberg, D.; Dahlén, S.E.; Heinemann, A.; Konya, V.; et al. Prostaglandin Esuppresses human group 2 innate lymphoid cell function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1761–1773.e1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Toki, S.; Zhang, J.; Goleniewksa, K.; Newcomb, D.C.; Cephus, J.Y.; Dulek, D.E.; Bloodworth, M.H.; Stier, M.T.; Polosuhkin, V.; et al. Prostaglandin I2 Signaling and Inhibition of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallrapp, A.; Riesenfeld, S.J.; Burkett, P.R.; Abdulnour, R.E.; Nyman, J.; Dionne, D.; Hofree, M.; Cuoco, M.S.; Rodman, C.; Farouq, D.; et al. The neuropeptide NMU amplifies ILC2-driven allergic lung inflammation. Nature 2017, 549, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, R.; Wang, D.; Yu, R.; Liu, B. Neuromedin U Induces Pulmonary ILC2 Activation via the NMUR1 Pathway during Acute Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 68, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Luo, J.; Zeng, N.; Jiang, S.; Chen, W.; Hoyle, R.D.; Klenerman, P.; Pavord, I.D.; Xue, L. Neuromedin U promotes human type 2 immune responses. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, P.; Wiesner, D.L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, J.; Van Dyken, S.; Lashua, A.; Yu, C.; Klein, B.S.; Locksley, R.M.; et al. Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells amplify allergic asthma responses. Science 2018, 360, eaan8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Shih, H.Y.; Davis, F.P.; Meylan, F.; Huang, Y.; Harrison, O.J.; Yao, C.; Mikami, Y.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; et al. Neuropeptide CGRP Limits Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses and Constrains Type 2 Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 51, 682–695.e686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallrapp, A.; Burkett, P.R.; Riesenfeld, S.J.; Kim, S.-J.; Christian, E.; Abdulnour, R.-E.E.; Thakore, P.I.; Schnell, A.; Lambden, C.; Herbst, R.H.; et al. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Negatively Regulates Alarmin-Driven Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses. Immunity 2019, 51, 709–723.e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, S.; Brestoff, J.R.; Flamar, A.L.; Moeller, J.B.; Klose, C.S.N.; Rankin, L.C.; Yudanin, N.A.; Monticelli, L.A.; Putzel, G.G.; Rodewald, H.R.; et al. beta2-adrenergic receptor-mediated negative regulation of group 2 innate lymphoid cell responses. Science 2018, 359, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle-Treger, L.; Suzuki, Y.; Patel, N.; Sankaranarayanan, I.; Aron, J.L.; Maazi, H.; Chen, L.; Akbari, O. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist attenuates ILC2-dependent airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Parkhurst, C.N.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Yano, H.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Artis, D. The ChAT-acetylcholine pathway promotes group 2 innate lymphoid cell responses and anti-helminth immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabe3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, M.; Nair, P.; Salter, B.; Chen, R.; Machida, K.; Inman, M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Sehmi, R. Effect of sex on group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of mild and severe asthmatics. Allergy 2019, 74, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cephus, J.Y.; Stier, M.T.; Fuseini, H.; Yung, J.A.; Toki, S.; Bloodworth, M.H.; Zhou, W.; Goleniewska, K.; Zhang, J.; Garon, S.L.; et al. Testosterone Attenuates Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Mediated Airway Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2487–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffont, S.; Blanquart, E.; Savignac, M.; Cénac, C.; Laverny, G.; Metzger, D.; Girard, J.P.; Belz, G.T.; Pelletier, L.; Seillet, C.; et al. Androgen signaling negatively controls group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cephus, J.Y.; Gandhi, V.D.; Shah, R.; Brooke Davis, J.; Fuseini, H.; Yung, J.A.; Zhang, J.; Kita, H.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Zhou, W.; et al. Estrogen receptor-α signaling increases allergen-induced IL-33 release and airway inflammation. Allergy 2021, 76, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foer, D.; Beeler, P.E.; Cui, J.; Karlson, E.W.; Bates, D.W.; Cahill, K.N. Asthma Exacerbations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Asthma on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, S.; Goleniewska, K.; Reiss, S.; Zhang, J.; Bloodworth, M.H.; Stier, M.T.; Zhou, W.; Newcomb, D.C.; Ware, L.B.; Stanwood, G.D.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 signaling inhibits allergen-induced lung IL-33 release and reduces group 2 innate lymphoid cell cytokine production in vivo. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1515–1528.e1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Stöckli, M.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C. GLP-1 receptor expression in human tumors and human normal tissues: Potential for in vivo targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, S.; Newcomb, D.C.; Printz, R.L.; Cahill, K.N.; Boyd, K.L.; Niswender, K.D.; Peebles, R.S., Jr. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist inhibits aeroallergen-induced activation of ILC2 and neutrophilic airway inflammation in obese mice. Allergy 2021, 76, 3433–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells: A novel biomarker of eosinophilic airway inflammation in patients with mild to moderate asthma. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.N.; Tan, W.P.; Fan, X.L.; Guo, Y.B.; Qin, Z.L.; Li, C.L.; Chen, D.; Lin, Z.B.; Wen, W.; Fu, Q.L. Increased Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Are Correlated with Eosinophilic Granulocytes in Patients with Allergic Airway Inflammation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartemes, K.R.; Kephart, G.M.; Fox, S.J.; Kita, H. Enhanced innate type 2 immune response in peripheral blood from patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 671–678.e674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhu, X.; Bai, C.; Zhu, L.; Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Tang, R.; Chen, Z. IL-13(+) Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Correlate with Asthma Control Status and Treatment Response. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, C.A.; Goplen, N.P.; Zafar, I.; Irvin, C.; Good, J.T., Jr.; Rollins, D.R.; Gorentla, B.; Liu, W.; Gorska, M.M.; Chu, H.; et al. Persistence of asthma requires multiple feedback circuits involving type 2 innate lymphoid cells and IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 59–68.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Smith, S.G.; Salter, B.; El-Gammal, A.; Oliveria, J.P.; Obminski, C.; Watson, R.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Sehmi, R. Allergen-induced Increases in Sputum Levels of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Subjects with Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.G.; Chen, R.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Huang, C.; Oliveria, J.P.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Boulet, L.P.; Lemiere, C.; Martin, J.; et al. Increased numbers of activated group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of patients with severe asthma and persistent airway eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 75–86.e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, Y.J.; Pichavant, M.; Shore, S.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Iwakura, Y.; Israel, E.; Bolger, K.; Faul, J.; et al. Interleukin-17-producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3 inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.U.; Guntur, V.P.; Newcomb, D.C.; Wechsler, M.E. Sex and gender in asthma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Van Dyken, S.J.; Schneider, C.; Lee, J.; Nussbaum, J.C.; Liang, H.E.; Vaka, D.; Eckalbar, W.L.; Molofsky, A.B.; Erle, D.J.; et al. Tissue signals imprint ILC2 identity with anticipatory function. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata, H.; Moro, K.; Fukunaga, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyata, J.; Masaki, K.; Betsuyaku, T.; Koyasu, S.; Asano, K. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces corticosteroid resistance in natural helper cells during airway inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikotra, A.; Choy, D.F.; Ohri, C.M.; Doran, E.; Butler, C.; Hargadon, B.; Shelley, M.; Abbas, A.R.; Austin, C.D.; Jackman, J.; et al. Increased expression of immunoreactive thymic stromal lymphopoietin in patients with severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, e101–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Verma, M.; Michalec, L.; Liu, W.; Sripada, A.; Rollins, D.; Good, J.; Ito, Y.; Chu, H.; Gorska, M.M.; et al. Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 257–268.e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, K.; Aw, M.; Salter, B.M.A.; Ju, X.; Mukherjee, M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Nair, P.; Sehmi, R. The Role of the TL1A/DR3 Axis in the Activation of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Subjects with Eosinophilic Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ploeg, E.K.; Golebski, K.; van Nimwegen, M.; Fergusson, J.R.; Heesters, B.A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, I.; Kradolfer, C.M.A.; van Tol, S.; Scicluna, B.P.; de Bruijn, M.J.W.; et al. Steroid-resistant human inflammatory ILC2s are marked by CD45RO and elevated in type 2 respiratory diseases. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabd3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.J.; Johnston, S.L. The role of viruses in acute exacerbations of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravia, J.; You, D.; Shrestha, B.; Jaligama, S.; Siefker, D.; Lee, G.I.; Harding, J.N.; Jones, T.L.; Rovnaghi, C.; Bagga, B.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease Is Mediated by Age-Variable IL-33. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stier, M.T.; Bloodworth, M.H.; Toki, S.; Newcomb, D.C.; Goleniewska, K.; Boyd, K.L.; Quitalig, M.; Hotard, A.L.; Moore, M.L.; Hartert, T.V.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus infection activates IL-13-producing group 2 innate lymphoid cells through thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 814–824.e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.D.; Siefker, D.; Jones, T.L.; You, D.; Taylor, R.; DeVincenzo, J.; Cormier, S.A. Elevated Levels of Type 2 Respiratory Innate Lymphoid Cells in Human Infants with Severe Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanetti, L.; Dijkhuis, A.; Dekker, T.; Sabogal Pineros, Y.S.; Ravi, A.; Dierdorp, B.S.; Erjefält, J.S.; Mori, M.; Pavlidis, S.; Adcock, I.M.; et al. IL-33 drives influenza-induced asthma exacerbations by halting innate and adaptive antiviral immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1355–1370.e1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.J.; Makrinioti, H.; Rana, B.M.; Shamji, B.W.; Trujillo-Torralbo, M.B.; Footitt, J.; Jerico, D.-R.; Telcian, A.G.; Nikonova, A.; Zhu, J.; et al. IL-33-dependent type 2 inflammation during rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations in vivo. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhariwal, J.; Cameron, A.; Wong, E.; Paulsen, M.; Trujillo-Torralbo, M.B.; Del Rosario, A.; Bakhsoliani, E.; Kebadze, T.; Almond, M.; Farne, H.; et al. Pulmonary Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses during Rhinovirus-induced Asthma Exacerbations In Vivo: A Clinical Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Du, T.; Zhi, Y. Prevalence of Comorbid Asthma and Related Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. The Association of Asthma With COVID-19 Mortality: An Updated Meta-Analysis Based on Adjusted Effect Estimates. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3944–3968.e3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferastraoaru, D.; Hudes, G.; Jerschow, E.; Jariwala, S.; Karagic, M.; de Vos, G.; Rosenstreich, D.; Ramesh, M. Eosinophilia in Asthma Patients Is Protective Against Severe COVID-19 Illness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1152–1162.e1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, L.E.; He, Z.; Collins, W.; Lee, A.S.; Dhondalay, G.; Jiang, S.Y.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Snow, T.T.; Pinsky, B.A.; Artandi, M.; et al. Asthma phenotypes, associated comorbidities, and long-term symptoms in COVID-19. Allergy 2022, 77, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Cadena, A.; Spehner, L.; Kroemer, M.; Khelil, M.B.; Bouiller, K.; Verdeil, G.; Trabanelli, S.; Borg, C.; Loyon, R.; Jandus, C. Severe COVID-19 patients exhibit an ILC2 NKG2D+ population in their impaired ILC compartment. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.; Kokkinou, E.; Carrasco García, A.; Parrot, T.; Palma Medina, L.M.; Maleki, K.T.; Christ, W.; Varnaitė, R.; Filipovic, I.; Ljunggren, H.G.; et al. Innate lymphoid cell composition associates with COVID-19 disease severity. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Mitsui, C.; Hayashi, H.; Ono, E.; Kajiwara, K.; Mita, H.; Watai, K.; Kamide, Y.; Fukutomi, Y.; Sekiya, K.; et al. Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD): Current understanding of AERD. Allergol. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Allergol. 2019, 68, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.J.; Cavagnero, K.J.; Deconde, A.S.; Kim, A.S.; Karta, M.R.; Broide, D.H.; Zuraw, B.L.; White, A.A.; Christiansen, S.C.; Doherty, T.A. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are recruited to the nasal mucosa in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 101–108.e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermwatanachai, T.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Holtappels, G.; Lacoere, T.; Jáuregui, R.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Pieper, D.H.; Van de Wiele, T.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Van Zele, T.; et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by dysbacteriosis of the nasal microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Bailey, M.; Zaunders, J.; Mrad, N.; Sacks, R.; Sewell, W.; Harvey, R.J. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are increased in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps or eosinophilia. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Liu, N.; Qin, Y.; Qiu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, T. The Role of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 586078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, T.A.; Scott, D.; Walford, H.H.; Khorram, N.; Lund, S.; Baum, R.; Chang, J.; Rosenthal, P.; Beppu, A.; Miller, M.; et al. Allergen challenge in allergic rhinitis rapidly induces increased peripheral blood type 2 innate lymphoid cells that express CD84. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Q.; Qin, Z.L.; Fang, S.B.; Xu, Z.B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Bellanti, J.A.; Zheng, S.G.; Fu, Q.L. Effects of myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells on ILC2s in patients with allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 855–867.e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Akasaki, S.; Muto-Haenuki, Y.; Fujieda, S.; Matsushita, K.; Yoshimoto, T. Nasal sensitization with ragweed pollen induces local-allergic-rhinitis-like symptoms in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Dubey, S. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurikisawa, N.; Oshikata, C.; Watanabe, M.; Tsuburai, T.; Kaneko, T.; Saito, H. Innate immune response reflects disease activity in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleich, F.; Brusselle, G.; Louis, R.; Vandenplas, O.; Michils, A.; Pilette, C.; Peche, R.; Manise, M.; Joos, G. Heterogeneity of phenotypes in severe asthmatics. The Belgian Severe Asthma Registry (BSAR). Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, G.; Pan, J.; Ye, L.; Shen, X.; Rosloff, D.; D’Souza, S.S.; Fung, I.T.H.; Celstin, J.; Sun, W.; Sankar, P.; et al. Blockade of IL-4Rα inhibits group 2 innate lymphoid cell responses in asthma patients. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Agache, I.O.; Soong, W.; Israel, E.; Chupp, G.L.; Cheung, D.S.; Theess, W.; Yang, X.; Staton, T.L.; Choy, D.F.; et al. Astegolimab (anti-ST2) efficacy and safety in adults with severe asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Ruddy, M.K.; Pavord, I.D.; Israel, E.; Rabe, K.F.; Ford, L.B.; Maspero, J.F.; Abdulai, R.M.; Hu, C.C.; Martincova, R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Itepekimab in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1656–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ligand | Receptor | Ligand | Receptor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation | Inhibition | ||||
| Epithelial-derived cytokine | IL-25 | IL-25R | Cytokines | IL-10 | IL-10R |
| IL-33 | IL-33R (T1/ST2) | IL-27 | IL-27R | ||
| TSLP | TSLPR | IFN-α | IFN-α/βR | ||
| Co-stimulatory cytokines | IL-2 | IL-2R | IFN-β | IFN-α/βR | |
| IL-4 | IL-4R | IFN-γ | IFN-γR | ||
| IL-7 | IL-7R | ||||
| IL-9 | IL-9R | ||||
| TL1A | DR3 | ||||
| Lipid mediators | CysLTs (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) | CysLTR | Lipid mediators | PGE2 | EP |
| LTB4 | BLT1 | PGI2 | IP | ||
| PGD2 | CRTH2 | LXA4 | ALX/FPR2 | ||
| Neuropeptide Neurotransmitter | NMU | NMUR1 | Neuropeptide Neurotransmitter | VIP | VPAC2 |
| CGRP | CALCRL/RAMP1 | Nicotine | α7nAChR | ||
| ACh | Chrm4 | Adrenaline | β2 AR | ||
| Hormones | Hormones | Androgen | Androgen R | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuyama, T.; Machida, K.; Mizuno, K.; Matsuyama, H.; Dotake, Y.; Shinmura, M.; Takagi, K.; Inoue, H. The Functional Role of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Asthma. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060893
Matsuyama T, Machida K, Mizuno K, Matsuyama H, Dotake Y, Shinmura M, Takagi K, Inoue H. The Functional Role of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Asthma. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(6):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060893
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuyama, Takahiro, Kentaro Machida, Keiko Mizuno, Hiromi Matsuyama, Yoichi Dotake, Masahiro Shinmura, Koichi Takagi, and Hiromasa Inoue. 2023. "The Functional Role of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Asthma" Biomolecules 13, no. 6: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060893
APA StyleMatsuyama, T., Machida, K., Mizuno, K., Matsuyama, H., Dotake, Y., Shinmura, M., Takagi, K., & Inoue, H. (2023). The Functional Role of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Asthma. Biomolecules, 13(6), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060893





