Sex and Age Differences in a Progressive Synucleinopathy Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
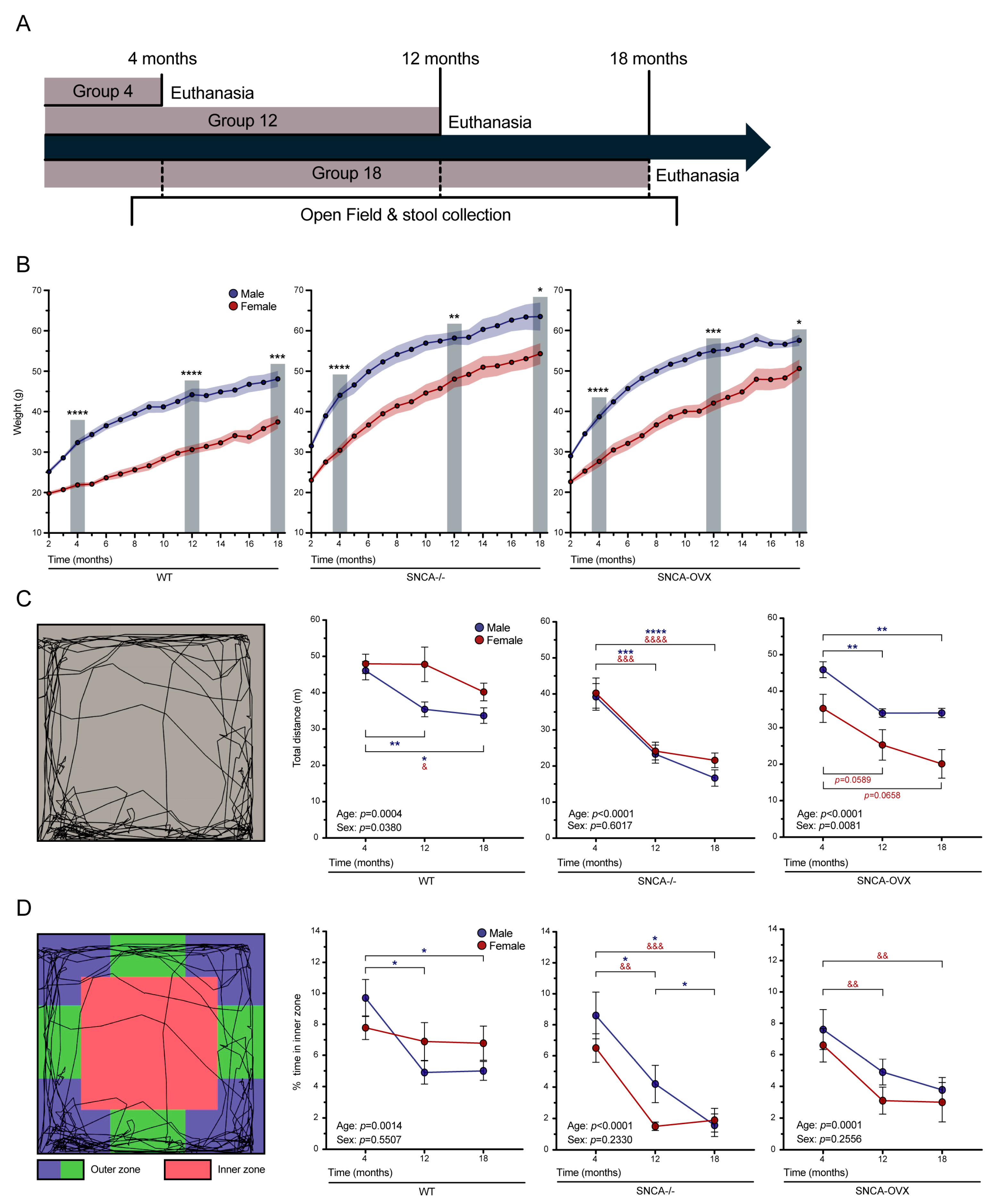
2.2. Weight, Open Field Analysis, and Stool Collection
2.3. Tissue Preparation
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Striatal Biogenic Amine Assay
2.6. Cytokine Immunoassay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Age and Sex on Mouse Weights
3.2. Effects of Age and Sex on Motor and Non-Motor Deficits
3.3. Accumulation of Human αSyn and Loss of Nigral DA Neurons in the SNCA-OVX Mice
3.4. Aging of SNCA-OVX Mice g Resulted in a Progressive Sex-Dependent Loss of Striatal Biogenic Amines
3.5. Effects of Aging, Sex, and Accumulation of Human αSyn in Brain Inflammation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Higgins, J.J.; Golbe, L.I.; Johnson, W.G.; Ide, S.E.; Di Iorio, G.; Sanges, G.; Stenroos, E.S.; Pho, L.T.; Schaffer, A.A.; et al. Mapping of a Gene for Parkinson’s Disease to Chromosome 4q21-q23. Science 1996, 274, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; et al. Mutation in the α-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, T.-B.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.-S.; Lee, D.S.; Min, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Cho, J.; Jeon, B.S. α-Synuclein gene duplication is present in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 2008, 70, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, A.B.; Farrer, M.; Johnson, J.; Singleton, A.; Hague, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Peuralinna, T.; Dutra, A.; Nussbaum, R.; et al. alpha-Synuclein Locus Triplication Causes Parkinson’s Disease. Science 2003, 302, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J. The Synaptic Function of α-Synuclein. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Overk, C.R.; Oueslati, A.; Masliah, E. The many faces of α-synuclein: From structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 14, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein Promotes SNARE-Complex Assembly in Vivo and in Vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reitboeck, P.G.; Anichtchik, O.; Bellucci, A.; Iovino, M.; Ballini, C.; Fineberg, E.; Ghetti, B.; Della Corte, L.; Spano, P.; Tofaris, G.; et al. SNARE protein redistribution and synaptic failure in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2010, 133, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzer, D.; Edwards, R.H. The physiological role of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundt, E.C.; Maynard, N.; Clancy, E.K.; Roy, S.; Bousset, L.; Sourigues, Y.; Covert, M.; Melki, R.; Kirkegaard, K.; Brahic, M. Neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-synuclein fibrils through axonal transport. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-J.; Desplats, P.; Lee, H.-J.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E. Cell-to-Cell Transmission of α-Synuclein Aggregates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 849, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Luk, K.C.; Patel, T.P.; Tanik, S.A.; Riddle, D.M.; Stieber, A.; Meaney, D.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Exogenous α-Synuclein Fibrils Induce Lewy Body Pathology Leading to Synaptic Dysfunction and Neuron Death. Neuron 2011, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordower, J.H.; Chu, Y.; Hauser, R.A.; Freeman, T.B.; Olanow, C.W. Lewy body–like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Englund, E.; Holton, J.L.; Soulet, D.; Hagell, P.; Lees, A.J.; Lashley, T.; Quinn, N.P.; Rehncrona, S.; Björklund, A.; et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanow, C.W.; Prusiner, S.B. Is Parkinson’s disease a prion disorder? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12571–12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordower, J.H.; Olanow, C.W.; Dodiya, H.B.; Chu, Y.; Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Halliday, G.M.; Bartus, R.T. Disease duration and the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2013, 136, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaugler, M.N.; Genc, O.; Bobela, W.; Mohanna, S.; Ardah, M.T.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Cantoni, M.; Bensadoun, J.-C.; Schneggenburger, R.; Knott, G.W.; et al. Nigrostriatal overabundance of α-synuclein leads to decreased vesicle density and deficits in dopamine release that correlate with reduced motor activity. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singaram, C.; Ashraf, W.; Gaumnitz, E.A.; Torbey, C.; Sengupta, A.; Pfeiffer, R.; Quigley, E.M. Dopaminergic defect of enteric nervous system in Parkinson’s disease patients with chronic constipation. Lancet 1995, 346, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesselet, M.-F.; Richter, F.; Zhu, C.; Magen, I.; Watson, M.B.; Subramaniam, S.R. A Progressive Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease: The Thy1-aSyn (“Line 61”) Mice. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2012, 9, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoenen, C.; Gustin, A.; Birck, C.; Kirchmeyer, M.; Beaume, N.; Felten, P.; Grandbarbe, L.; Heuschling, P.; Heurtaux, T. Alpha-Synuclein Proteins Promote Pro-Inflammatory Cascades in Microglia: Stronger Effects of the A53T Mutant. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reish, H.E.A.; Standaert, D.G. Role of α-Synuclein in Inducing Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Parkinson Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajsombath, M.M.; Nam, A.Y.; Ericsson, M.; Nuber, S. Female Sex and Brain-Selective Estrogen Benefit α-Synuclein Tetramerization and the PD-like Motor Syndrome in 3K Transgenic Mice. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7628–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanamsagar, R.; Bilbo, S.D. Sex differences in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders: Focus on microglial function and neuroinflammation during development. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 160, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moisan, F.; Kab, S.; Mohamed, F.; Canonico, M.; Le Guern, M.; Quintin, C.; Carcaillon, L.; Nicolau, J.; Duport, N.; Singh-Manoux, A.; et al. Parkinson disease male-to-female ratios increase with age: French nationwide study and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, K.S.M.; Cook, A.J.; Counsell, C.E. Heterogeneity in male to female risk for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wooten, G.F.; Currie, L.J.; Bovbjerg, V.E.; Lee, J.K.; Patrie, J. Are Men at Greater Risk for Parkinson’s Disease than Women? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaxma, C.A.; Bloem, B.R.; Borm, G.F.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Leenders, K.L.; Eshuis, S.; Booij, J.; Dluzen, D.E.; Horstink, M.W.I.M. Gender differences in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Pecurariu, C.F.; Odin, P.; van Hilten, J.J.; Antonini, A.; Rojo-Abuin, J.M.; Borges, V.; Trenkwalder, C.; Aarsland, D.; Brooks, D.J.; et al. Gender-related differences in the burden of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitkowska, M.; Czyżyk, M.; Friedman, A. Reproductive life characteristics in females affected with Parkinson’s disease and in healthy control subjects—A comparative study on Polish population. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2014, 48, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusters, C.D.; Paul, K.C.; Folle, A.D.; Keener, A.M.; Bronstein, J.M.; Bertram, L.; Hansen, J.; Horvath, S.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Lill, C.M.; et al. Increased Menopausal Age Reduces the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Approach. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, A.-A.; Côté, M.; Bourque, M.; Morissette, M.; Di Paolo, T.; Soulet, D. Neuroprotective and immunomodulatory effects of raloxifene in the myenteric plexus of a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 48, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litim, N.; Morissette, M.; Di Paolo, T. Neuroactive gonadal drugs for neuroprotection in male and female models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 67, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, V.; Echeverria, F.; Barreto, G.E.; Echeverría, J.; Mendoza, C. Estrogenic Plants: To Prevent Neurodegeneration and Memory Loss and Other Symptoms in Women After Menopause. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 644103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, G.E.; Pienaar, I.S.; Vohra, S.; Qamhawi, Z. Sex differences in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 35, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janezic, S.; Threlfell, S.; Dodson, P.D.; Dowie, M.J.; Taylor, T.N.; Potgieter, D.; Parkkinen, L.; Senior, S.L.; Anwar, S.; Ryan, B.; et al. Deficits in dopaminergic transmission precede neuron loss and dysfunction in a new Parkinson model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4016–E4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barone, P.; Antonini, A.; Colosimo, C.; Marconi, R.; Morgante, L.; Avarello, T.P.; Bottacchi, E.; Cannas, A.; Ceravolo, G.; Ceravolo, R.; et al. The PRIAMO study: A multicenter assessment of nonmotor symptoms and their impact on quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.L.; Carvalho, M.M.; Cristóvão, A.; Eje, G.; Baltazar, G.; Salgado, A.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Sousa, N. Rodent models of Parkinson’s disease: Beyond the motor symptomatology. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, K.; Krogh, K.; Østergaard, K.; Borghammer, P. Constipation in Parkinson’s disease: Subjective symptoms, objective markers, and new perspectives. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenbrandt, A.; Morissette, M.; Bourque, M.; Lamontagne-Proulx, J.; Coulombe, K.; Soulet, D.; Di Paolo, T. Effect of sex and gonadectomy on brain MPTP toxicity and response to dutasteride treatment in mice. Neuropharmacology 2021, 201, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Lewis, V.; Przedborski, S. Protocol for the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, J.R.; Tapias, V.; Na, H.M.; Honick, A.S.; Drolet, R.E.; Greenamyre, J.T. A highly reproducible rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coulombe, K.; Kerdiles, O.; Tremblay, C.; Emond, V.; Lebel, M.; Boulianne, A.-S.; Plourde, M.; Cicchetti, F.; Calon, F. Impact of DHA intake in a mouse model of synucleinopathy. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 301, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damier, P.; Hirsch, E.C.; Agid, Y.; Graybiel, A.M. The Substantia Nigra of the Human Brain. II. Patterns of Loss of Dopamine-Containing Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain J. Neurol. 1999, 122 Pt 8, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Ulane, C.M.; Burke, R. Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, A.; Météreau, E.; Tremblay, L.; Favre, E.; Klinger, H.; Lhommée, E.; Le Bars, D.; Castrioto, A.; Prange, S.; Sgambato, V.; et al. Serotonergic and Dopaminergic Lesions Underlying Parkinsonian Neuropsychiatric Signs. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2888–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deusser, J.; Schmidt, S.; Ettle, B.; Plötz, S.; Huber, S.; Müller, C.P.; Masliah, E.; Winkler, J.; Kohl, Z. Serotonergic dysfunction in the A53T alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Standaert, D.G.; Harms, A.S. The gamma chain subunit of Fc receptors is required for α-synuclein-induced pro-inflammatory signaling in microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinale, A.; Calabrese, V.; de Iure, A.; Picconi, B. Alpha-Synuclein as a Prominent Actor in the Inflammatory Synaptopathy of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, L.; Bruckmeier, S.; Burbano, S.D.; Finnell, J.E.; Gorny, N.; Klett, J.; Wood, S.K.; Kelly, M.P. Aging triggers an upregulation of a multitude of cytokines in the male and especially the female rodent hippocampus but more discrete changes in other brain regions. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, V.; Huang, E.Y.-K.; Chou, Y.-C.; Kuo, T.-T.; Olson, L.; Hoffer, B.J. Delayed Dopamine Dysfunction and Motor Deficits in Female Parkinson Model Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, e52434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chartier-Harlin, M.-C.; Kachergus, J.; Roumier, C.; Mouroux, V.; Douay, X.; Lincoln, S.; Levecque, C.; Larvor, L.; Andrieux, J.; Hulihan, M.; et al. α-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuns, J.; Van Broeckhoven, C. alpha-Synuclein gene duplications in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 2008, 70, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlfell, S.; Mohammadi, A.S.; Ryan, B.J.; Connor-Robson, N.; Platt, N.J.; Anand, R.; Serres, F.; Sharp, T.; Bengoa-Vergniory, N.; Wade-Martins, R.; et al. Striatal Dopamine Transporter Function Is Facilitated by Converging Biology of α-Synuclein and Cholesterol. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 658244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’lone, R.; Knorr, K.; Jaffe, I.Z.; Schaffer, M.E.; Martini, P.G.V.; Karas, R.H.; Bienkowska, J.; Mendelsohn, M.E.; Hansen, U. Estrogen Receptors α and β Mediate Distinct Pathways of Vascular Gene Expression, Including Genes Involved in Mitochondrial Electron Transport and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1281–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, A.C.; Meurer, Y.S.R.; Bioni, V.S.; Cunha, D.M.G.; Gonçalves, N.; Lopes-Silva, L.B.; Becegato, M.; Soares, M.B.L.; Marinho, G.F.; Santos, J.R.; et al. Female Rats Are Resistant to Cognitive, Motor and Dopaminergic Deficits in the Reserpine-Induced Progressive Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 757714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.; Pillai, A.; McArthur, S.; Razvi, N.; Datla, K.; Dexter, D.; Gillies, G. Dose- and sex-dependent effects of the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine on the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway of adult rats: Differential actions of estrogen in males and females. Neuroscience 2003, 116, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourque, M.; Liu, B.; Dluzen, D.E.; Di Paolo, T. Sex differences in methamphetamine toxicity in mice: Effect on brain dopamine signaling pathways. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litim, N.; Morissette, M.; Caruso, D.; Melcangi, R.C.; Di Paolo, T. Effect of the 5α-reductase enzyme inhibitor dutasteride in the brain of intact and parkinsonian mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 174, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, M.; Ishii, A.; Iwata, S.; Sakagami, J.; Ukai, Y.; Ono, M.; Kanbe, D.; Muramatsu, S.-I.; Kobayashi, K.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. Selective loss of nigral dopamine neurons induced by overexpression of truncated human α-synuclein in mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirik, D.; Rosenblad, C.; Burger, C.; Lundberg, C.; Johansen, T.E.; Muzyczka, N.; Mandel, R.J.; Björklund, A. Parkinson-like Neurodegeneration Induced by Targeted Overexpression of α-Synuclein in the Nigrostriatal System. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, J.F.; Felicio, L.S.; Osterburg, H.H.; Finch, C.E. Altered Profiles of Estradiol and Progesterone Associated with Prolonged Estrous Cycles and Persistent Vaginal Cornification in Aging C578L/6J Mice. Biol. Reprod. 1981, 24, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, J.F.; Felicio, L.S.; Randall, P.K.; Sims, C.; Finch, C.E. A Longitudinal Study of Estrous Cyclicity in Aging C57BL/6J Mice: I. Cycle Frequency, Length and Vaginal Cytology. Biol. Reprod. 1982, 27, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lofrumento, D.D.; Saponaro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; De Nuccio, F.; Mitolo, V.; Nicolardi, G.; Panaro, M.A. MPTP-Induced Neuroinflammation Increases the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Their Receptors in Mouse Brain. Neuroimmunomodulation 2011, 18, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Breger, L.S.; Lundblad, M.; Wan, O.W.; Mattsson, B.; Luk, K.C.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Björklund, A. Modeling Parkinson’s disease pathology by combination of fibril seeds and α-synuclein overexpression in the rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8284–E8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Boyes, B.E.; McGeer, E.G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 1988, 38, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanow, C.W.; Savolainen, M.; Chu, Y.; Halliday, G.M.; Kordower, J.H. Temporal evolution of microglia and α-synuclein accumulation following foetal grafting in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2019, 142, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Manda, G.; Boscá, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, P.R.; Long, J.M.; Lei, D.-L.; Howard, V.; Jucker, M.; Calhoun, M.E.; Ingram, D.K. Age and gender effects on microglia and astrocyte numbers in brains of mice. Brain Res. 2002, 956, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne-Proulx, J.; Coulombe, K.; Dahhani, F.; Côté, M.; Guyaz, C.; Tremblay, C.; Di Marzo, V.; Flamand, N.; Calon, F.; Soulet, D. Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) at the Enteric Level in a Synucleinopathy Mouse Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellner, L.; Irschick, R.B.; Schanda, K.; Reindl, M.; Klimaschewski, L.; Poewe, W.; Wenning, G.K.; Stefanova, N. Toll-like receptor 4 is required for α-synuclein dependent activation of microglia and astroglia. Glia 2013, 61, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-J.; Suk, J.-E.; Patrick, C.; Bae, E.-J.; Cho, J.-H.; Rho, S.; Hwang, D.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Direct Transfer of α-Synuclein from Neuron to Astroglia Causes Inflammatory Responses in Synucleinopathies. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9262–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sznejder-Pachołek, A.; Joniec-Maciejak, I.; Wawer, A.; Ciesielska, A.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The effect of α-synuclein on gliosis and IL-1α, TNFα, IFNγ, TGFβ expression in murine brain. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenbrandt, A.; Coulombe, K.; Morissette, M.; Bourque, M.; Lamontagne-Proulx, J.; Di Paolo, T.; Soulet, D. Three-Dimensional Analysis of Sex- and Gonadal Status- Dependent Microglial Activation in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamontagne-Proulx, J.; Coulombe, K.; Morissette, M.; Rieux, M.; Calon, F.; Di Paolo, T.; Soulet, D. Sex and Age Differences in a Progressive Synucleinopathy Mouse Model. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060977
Lamontagne-Proulx J, Coulombe K, Morissette M, Rieux M, Calon F, Di Paolo T, Soulet D. Sex and Age Differences in a Progressive Synucleinopathy Mouse Model. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(6):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060977
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamontagne-Proulx, Jérôme, Katherine Coulombe, Marc Morissette, Marie Rieux, Frédéric Calon, Thérèse Di Paolo, and Denis Soulet. 2023. "Sex and Age Differences in a Progressive Synucleinopathy Mouse Model" Biomolecules 13, no. 6: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060977
APA StyleLamontagne-Proulx, J., Coulombe, K., Morissette, M., Rieux, M., Calon, F., Di Paolo, T., & Soulet, D. (2023). Sex and Age Differences in a Progressive Synucleinopathy Mouse Model. Biomolecules, 13(6), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060977






