Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism: Evidence from Epidemiological and Experimental Studies
Abstract
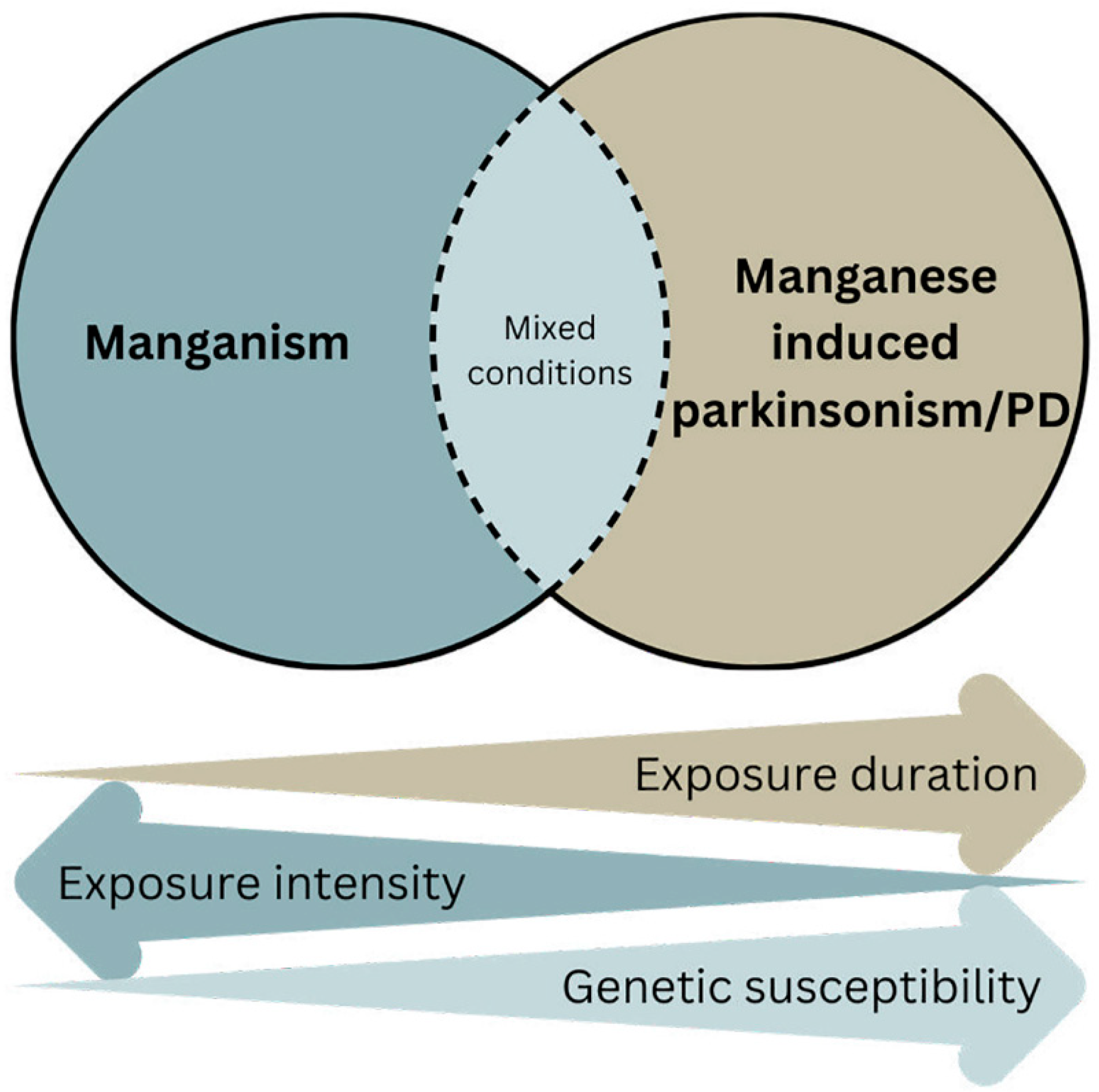
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Human Studies
3.1. Occupational Studies
3.2. Environmental Studies
3.3. Diagnostic Criteria
4. Experimental Studies
4.1. SNCA
4.2. Parkin
4.3. DJ-1
4.4. ATP13A2
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couper, J. On the effects of black oxide of manganese when inhaled into the lungs. Br. Ann. Med. Pharmacol. 1837, 1, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Blanc, P.D. The early history of manganese and the recognition of its neurotoxicity, 1837–1936. Neurotoxicology 2018, 64, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peli, M.; Bostick, B.C.; Barontini, S.; Lucchini, R.G.; Ranzi, R. Profiles and species of Mn, Fe and trace metals in soils near a ferromanganese plant in Bagnolo Mella (Brescia, IT). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndon, E.M.; Jin, L.; Brantley, S.L. Soils reveal widespread manganese enrichment from industrial inputs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Zhou, Y. Trace Metal Pollution in Topsoil Surrounding the Xiangtan Manganese Mine Area (South-Central China): Source Identification, Spatial Distribution and Assessment of Potential Ecological Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, M.R.; Gaudet, B.J.; Stauffer, D.R.; White, T.S.; Brantley, S.L. Using soil records with atmospheric dispersion modeling to investigate the effects of clean air regulations on 60 years of manganese deposition in Marietta, Ohio (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 515–516, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Belitz, K.; Reddy, J.E.; Johnson, T.D. Elevated Manganese Concentrations in United States Groundwater, Role of Land Surface-Soil-Aquifer Connections. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmucci, W.; Rusi, S.; Di Curzio, D. Mobilisation processes responsible for iron and manganese contamination of groundwater in Central Adriatic Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 11790–11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Aschner, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Cranmer, J.M. Neurotoxicity of manganese: Indications for future research and public health intervention from the Manganese 2016 conference. Neurotoxicology 2018, 64, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Sherer, T.; Okun, M.S.; Bloem, B.R. The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson Pandemic. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2018, 8, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marras, C.; Beck, J.C.; Bower, J.H.; Roberts, E.; Ritz, B.; Ross, G.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Savica, R.; Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Willis, A.W.; et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease across North America. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2018, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willis, A.W.; Roberts, E.; Beck, J.C.; Fiske, B.; Ross, W.; Savica, R.; Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Marras, C. Incidence of Parkinson disease in North America. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Martin, C.J.; Doney, B.C. From manganism to manganese-induced parkinsonism: A conceptual model based on the evolution of exposure. Neuromolecular Med. 2009, 11, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racette, B.A.; McGee-Minnich, L.; Moerlein, S.M.; Mink, J.W.; Videen, T.O.; Perlmutter, J.S. Welding-related parkinsonism: Clinical features, treatment, and pathophysiology. Neurology 2001, 56, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Racette, B.A.; Criswell, S.R.; Lundin, J.I.; Hobson, A.; Seixas, N.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Evanoff, B.A.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Zhang, J.; Sheppard, L.; et al. Increased risk of parkinsonism associated with welding exposure. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andruska, K.M.; Racette, A.B. Neuromythology of Manganism. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, M.; Federico, A.; Zhao, T.; Breedveld, G.J.; Battisti, C.; Delnooz, C.; Severijnen, L.A.; Di Toro Mammarella, L.; Mignarri, A.; Monti, L.; et al. Mutations in SLC30A10 cause parkinsonism and dystonia with hypermanganesemia, polycythemia, and chronic liver disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuschl, K.; Meyer, E.; Valdivia, L.E.; Zhao, N.; Dadswell, C.; Abdul-Sada, A.; Hung, C.Y.; Simpson, M.A.; Chong, W.K.; Jacques, T.S.; et al. Mutations in SLC39A14 disrupt manganese homeostasis and cause childhood-onset parkinsonism-dystonia. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuschl, K.; Clayton, P.T.; Gospe, S.M.; Gulab, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Singhi, P.; Aulakh, R.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Barsottini, O.G.; Zaki, M.S.; et al. Syndrome of hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythemia, and hypermanganesemia caused by mutations in SLC30A10, a manganese transporter in man. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamelou, M.; Tuschl, K.; Chong, W.K.; Burroughs, A.K.; Mills, P.B.; Bhatia, K.P.; Clayton, P.T. Dystonia with brain manganese accumulation resulting from SLC30A10 mutations: A new treatable disorder. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boycott, K.M.; Beaulieu, C.L.; Kernohan, K.D.; Gebril, O.H.; Mhanni, A.; Chudley, A.E.; Redl, D.; Qin, W.; Hampson, S.; Küry, S.; et al. Autosomal-Recessive Intellectual Disability with Cerebellar Atrophy Syndrome Caused by Mutation of the Manganese and Zinc Transporter Gene SLC39A8. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elbaz, A.; Bower, J.H.; Maraganore, D.M.; McDonnell, S.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Schaid, D.J.; Rocca, W.A. Risk tables for parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2002, 55, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Guazzetti, S.; Zoni, S.; Benedetti, C.; Fedrighi, C.; Peli, M.; Donna, F.; Bontempi, E.; Borgese, L.; Micheletti, S.; et al. Neurofunctional dopaminergic impairment in elderly after lifetime exposure to manganese. Neurotoxicology 2014, 45, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Environmental Health Criteria 17; Manganese; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981.
- Rodier, J. Manganese poisoning in Moroccan miners. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1955, 12, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miranda, M.; Bustamante, M.L.; Mena, F.; Lees, A. Original footage of the Chilean miners with manganism published in Neurology in 1967. Neurology 2015, 85, 2166–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuler, P.; Oyanguren, H.; Maturana, V.; Valenzuela, A.; Cruz, E.; Plaza, V.; Schmidt, E.; Haddad, R. Manganese poisoning; environmental and medical study at a Chilean mine. Ind. Med. Surg. 1957, 26, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ansola Jimenez, J.; Uiberall, E.; Escudero, E. Manganese poisoning in Chile; study on 64 cases; clinical aspects, disability and medical-legal repair. Prensa Med. Argent. 1946, 33, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Cheng, S.; Ding, Y.; He, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, X.; Xia, Y. The relationship between manganism and the workplace environment in China. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2012, 25, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Huang, C.C.; Hwang, Y.H.; Chiang, J.R.; Lin, J.M.; Chen, J.S. Manganese induced parkinsonism: An outbreak due to an unrepaired ventilation control system in a ferromanganese smelter. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1989, 46, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, A.C.; Ruella Oliveira, S.; Barbosa, F.; Tinkov, A.A.; V Skalny, A.; Santamaría, A.; Lee, E.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Evaluating the risk of manganese-induced neurotoxicity of parenteral nutrition: Review of the current literature. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, I.; Al-Rouqi, R.; Alnuwaysir, H.; Aldhalaan, H.; Alismail, E.; Binmanee, A.; Hawari, A.; Alhazzani, F.; Bin Jabr, M. Exposure of preterm neonates to toxic metals during their stay in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and its impact on neurodevelopment at 2 months of age. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 78, 127173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauberan, J.; Mercier, M.; Katheria, A. Sources of unintentional manganese delivery in neonatal parenteral nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordak, M.; Sloniewicz, N.; Nasierowski, T.; Muszynska, E.; Bujalska-Zadrozny, M. Manganese concentration in patients with encephalopathy following ephedrone use: A narrative review and analysis of case reports. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanotsky, Y.; Selikhova, M.; Fedoryshyn, L.; Kuzyk, P.; Matviyenko, Y.; Semeryak, O.; Dziewulska, D.; Holton, J.L.; Lees, A.J. Neuropathological Findings in Ephedrone Encephalopathy. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisky, I.; Maor, Y.; Goldstein, L.; Inbar, Y.; Ben-Ari, Z. Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration: A Case Series of a Rare Condition. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2023, 25, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Mo, X.A.; Du, F.Q.; Fu, X.; Zhu, X.Y.; Gao, H.Y.; Xie, J.L.; Liao, F.L.; Pira, E.; Zheng, W. Effective treatment of manganese-induced occupational Parkinsonism with p-aminosalicylic acid: A case of 17-year follow-up study. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ky, S.Q.; Deng, H.S.; Xie, P.Y.; Hu, W. A report of two cases of chronic serious manganese poisoning treated with sodium para-aminosalicylic acid. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1992, 49, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, P.; Padhani, Z.A.; Akbar, R.; Arain, F. Hypermanganesaemia with dystonia polycythemia and cirrhosis. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2022, 72, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavasoli, A.; Arjmandi Rafsanjani, K.; Hemmati, S.; Mojbafan, M.; Zarei, E.; Hosseini, S. A case of dystonia with polycythemia and hypermanganesemia caused by SLC30A10 mutation: A treatable inborn error of manganese metabolism. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, M.S.; Issa, M.Y.; Elbendary, H.M.; El-Karaksy, H.; Hosny, H.; Ghobrial, C.; El Safty, A.; El-Hennawy, A.; Oraby, A.; Selim, L.; et al. Hypermanganesemia with dystonia, polycythemia and cirrhosis in 10 patients: Six novel SLC30A10 mutations and further phenotype delineation. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fored, C.M.; Fryzek, J.P.; Brandt, L.; Nise, G.; Sjögren, B.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Blot, W.J.; Ekbom, A. Parkinson’s disease and other basal ganglia or movement disorders in a large nationwide cohort of Swedish welders. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 63, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fryzek, J.P.; Hansen, J.; Cohen, S.; Bonde, J.P.; Llambias, M.T.; Kolstad, H.A.; Skytthe, A.; Lipworth, L.; Blot, W.J.; Olsen, J.H. A cohort study of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders in Danish welders. J. Occup. Environ. Med. Am. Coll. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 47, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenborg, L.; Lassen, C.F.; Hansen, J.; Olsen, J.H. Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders among welders: A Danish cohort study. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.A.; Borenstein, A.R.; Nelson, L.M. Associations of welding and manganese exposure with Parkinson disease: Review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2012, 79, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, S.R.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Videen, T.O.; Moerlein, S.M.; Flores, H.P.; Birke, A.M.; Racette, B.A. Reduced uptake of [18F]FDOPA PET in asymptomatic welders with occupational manganese exposure. Neurology 2011, 76, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Criswell, S.R.; Nielsen, S.S.; Warden, M.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Moerlein, S.M.; Flores, H.P.; Huang, J.; Sheppard, L.; Seixas, N.; Checkoway, H.; et al. [18F]FDOPA positron emission tomography in manganese-exposed workers. Neurotoxicology 2018, 64, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, G. Is electric arc welding linked to manganism or Parkinson’s disease? Toxicol. Rev. 2005, 24, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, W.W.; Nelson, G.; Racette, B.A. 1367 The association between parkinsonism and quality of life in south african manganese mine workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, A506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohani, M.; Kassiri, N.; Emamikhah Abarghouei, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Labbafinejad, Y. Prevalence of Parkinsonism Among Foundry Workers in an Automobile Manufacturing Factory in Tehran. Cureus 2022, 14, e28685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Albini, E.; Benedetti, L.; Borghesi, S.; Coccaglio, R.; Malara, E.C.; Parrinello, G.; Garattini, S.; Resola, S.; Alessio, L. High prevalence of Parkinsonian disorders associated to manganese exposure in the vicinities of ferroalloy industries. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2007, 50, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Guazzetti, S.; Renzetti, S.; Broberg, K.; Caci, M.; Covolo, L.; Crippa, P.; Gelatti, U.; Hashim, D.; Oppini, M.; et al. Metal Exposure and SNCA rs356219 Polymorphism Associated with Parkinson Disease and Parkinsonism. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 556337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squitti, R.; Gorgone, G.; Panetta, V.; Lucchini, R.; Bucossi, S.; Albini, E.; Alessio, L.; Alberici, A.; Melgari, J.M.; Benussi, L.; et al. Implications of metal exposure and liver function in Parkinsonian patients resident in the vicinities of ferroalloy plants. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidelin, A.S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Yaghootkar, H.; Stender, S. A rare genetic variant in the manganese transporter SLC30A10 and elevated liver enzymes in the general population. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Bao, X. A novel homozygous SLC39A14 variant in an infant with hypermanganesemia and a review of the literature. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 949651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Yoganathan, S.; Shamim, U.; Mankad, K.; Gulati, P.; Bonifati, V.; Botre, A.; Kalane, U.; Saini, A.G.; Sankhyan, N.; et al. Clinical Profile and Treatment Outcomes of Hypermanganesemia with Dystonia 1 and 2 among 27 Indian Children. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuschl, K.; Clayton, P.T.; Gospe, S.M., Jr.; Mills, P.B. Hypermanganesemia with Dystonia 1. In GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rodichkin, A.N.; Guilarte, T.R. Hereditary Disorders of Manganese Metabolism: Pathophysiology of Childhood-Onset Dystonia-Parkinsonism in SLC39A14 Mutation Carriers and Genetic Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, A.; Priya, L.; Divya, K.P. “Cock-walk” gait and “horseshoe moustache” sign on MRI in inherited hypermanganesemia. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlberg, K.; Kippler, M.; Alhamdow, A.; Rahman, S.M.; Smith, D.R.; Vahter, M.; Lucchini, R.G.; Broberg, K. Common Polymorphisms in the Solute Carrier SLC30A10 are Associated with Blood Manganese and Neurological Function. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 149, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahlberg, K.E.; Guazzetti, S.; Pineda, D.; Larsson, S.C.; Fedrighi, C.; Cagna, G.; Zoni, S.; Placidi, D.; Wright, R.O.; Smith, D.R.; et al. Polymorphisms in Manganese Transporters SLC30A10 and SLC39A8 Are Associated with Children’s Neurodevelopment by Influencing Manganese Homeostasis. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broberg, K.; Taj, T.; Guazzetti, S.; Peli, M.; Cagna, G.; Pineda, D.; Placidi, D.; Wright, R.O.; Smith, D.R.; Lucchini, R.G.; et al. Manganese transporter genetics and sex modify the association between environmental manganese exposure and neurobehavioral outcomes in children. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgese, L.; Federici, S.; Zacco, A.; Gianoncelli, A.; Rizzo, L.; Smith, D.R.; Donna, F.; Lucchini, R.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Metal fractionation in soils and assessment of environmental contamination in Vallecamonica, Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 5067–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavilonis, B.T.; Lioy, P.J.; Guazzetti, S.; Bostick, B.C.; Donna, F.; Peli, M.; Zimmerman, N.J.; Bertrand, P.; Lucas, E.; Smith, D.R.; et al. Manganese concentrations in soil and settled dust in an area with historic ferroalloy production. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zacco, A.; Resola, S.; Lucchini, R.; Albini, E.; Zimmerman, N.; Guazzetti, S.; Bontempi, E. Analysis of settled dust with X-ray Fluorescence for exposure assessment of metals in the province of Brescia, Italy. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, R.; Donna, F.; Smith, D.R.; Guazzetti, S.; Zacco, A.; Rizzo, L.; Bontempi, E.; Zimmerman, N.J.; Lucchini, R.G. Heavy Metals in Soil and Salad in the Proximity of Historical Ferroalloy Emission. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 3, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferri, R.; Hashim, D.; Smith, D.R.; Guazzetti, S.; Donna, F.; Ferretti, E.; Curatolo, M.; Moneta, C.; Beone, G.M.; Lucchini, R.G. Metal contamination of home garden soils and cultivated vegetables in the province of Brescia, Italy: Implications for human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butler, L.; Gennings, C.; Peli, M.; Borgese, L.; Placidi, D.; Zimmerman, N.; Hsu, H.L.; Coull, B.A.; Wright, R.O.; Smith, D.R.; et al. Assessing the contributions of metals in environmental media to exposure biomarkers in a region of ferroalloy industry. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, E.L.; Bertrand, P.; Guazzetti, S.; Donna, F.; Peli, M.; Jursa, T.P.; Lucchini, R.; Smith, D.R. Impact of ferromanganese alloy plants on household dust manganese levels: Implications for childhood exposure. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgese, L.; Zacco, A.; Pal, S.; Bontempi, E.; Lucchini, R.; Zimmerman, N.; Depero, L.E. A new non-destructive method for chemical analysis of particulate matter filters: The case of manganese air pollution in Vallecamonica (Italy). Talanta 2011, 84, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgese, L.; Salmistraro, M.; Gianoncelli, A.; Zacco, A.; Lucchini, R.; Zimmerman, N.; Pisani, L.; Siviero, G.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Airborne particulate matter (PM) filter analysis and modeling by total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) and X-ray standing wave (XSW). Talanta 2012, 89, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutchik, J.S.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, Y.; Mo, X. How does an occupational neurologist assess welders and steelworkers for a manganese-induced movement disorder? An international team’s experiences in Guanxi, China Part II. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 54, 1562–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, G.R.; Masullo, L.N. Manganese Toxicity, StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Rokad, D.; Neal, M.L.; Ghaisas, S.; Manne, S.; Sarkar, S.; Panicker, N.; Zenitsky, G.; Jin, H.; Lewis, M.; et al. Manganese promotes the aggregation and prion-like cell-to-cell exosomal transmission of alpha-synuclein. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaau4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnell, J.R.; Cui, M.; Tieu, K. Exosomes in Parkinson disease. J. Neurochem. 2020, 157, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutchik, J.; Ratner, M.H. Should Age at Onset of Parkinsonism be the End Point of Interest in Investigations of the Link between Exosomal α-Synuclein and Manganese Exposure in Welders? J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 61, e530–e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamache, P.L.; Haj Salem, I.; Roux-Dubois, N.; Le Bouthillier, J.; Gan-Or, Z.; Dupré, N. Exposure to Pesticides and Welding Hastens the Age-at-Onset of Parkinson’s Disease. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 46, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calne, D.B.; Chu, N.S.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, C.S.; Olanow, W. Manganism and idiopathic parkinsonism: Similarities and differences. Neurology 1994, 44, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakye, G.F.; Paoliello, M.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism and Parkinson’s Disease: Shared and Distinguishable Features. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7519–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guilarte, T.R.; Gonzales, K.K. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism Is Not Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: Environmental and Genetic Evidence. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budinger, D.; Barral, S.; Soo, A.K.S.; Kurian, M.A. The role of manganese dysregulation in neurological disease: Emerging evidence. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Ghaisas, S.; Zenitsky, G.; Jin, H.; Kanthasamy, A.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity: New Insights Into the Triad of Protein Misfolding, Mitochondrial Impairment, and Neuroinflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, J.A. Correlation between the biochemical pathways altered by mutated parkinson-related genes and chronic exposure to manganese. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Parmalee, N.; Aschner, M. Genetic factors and manganese-induced neurotoxicity. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appel-Cresswell, S.; Vilarino-Guell, C.; Encarnacion, M.; Sherman, H.; Yu, I.; Shah, B.; Weir, D.; Thompson, C.; Szu-Tu, C.; Trinh, J.; et al. Alpha-synuclein p.H50Q, a novel pathogenic mutation for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, R.; Kuhn, W.; Muller, T.; Woitalla, D.; Graeber, M.; Kosel, S.; Pzuntek, H.; Epplen, J.T.; Schols, L.; Riess, O. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, S.; Anheim, M.; Letournel, F.; Bousset, L.; Honore, A.; Rozas, N.; Pieri, L.; Madiona, K.; Durr, A.; Melki, R.; et al. G51D alpha-synuclein mutation causes a novel parkinsonian-pyramidal syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.B.; Farrer, M.; Johnson, J.; Singleton, A.; Hague, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Peuralinna, T.; Dutra, A.; Nussbaum, R.; et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 2003, 302, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarranz, J.J.; Alegre, J.; Gomez-Esteban, J.C.; Lezcano, E.; Ros, R.; Ampuero, I.; Vidal, L.; Hoenicka, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Atares, B.; et al. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Roos, J.; Goedert, M. a-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Lewis, A.J.; Genoud, C.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castano-Diez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.L.; Lee, V.M. Cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binolfi, A.; Rasia, R.M.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Ceolin, M.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Fernández, C.O. Interaction of alpha-synuclein with divalent metal ions reveals key differences: A link between structure, binding specificity and fibrillation enhancement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9893–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Metal-triggered structural transformations, aggregation, and fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein. A possible molecular NK between Parkinson’s disease and heavy metal exposure. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44284–44296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peres, T.V.; Parmalee, N.L.; Martinez-Finley, E.J.; Aschner, M. Untangling the Manganese-alpha-Synuclein Web. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhakaran, K.; Chapman, G.D.; Gunasekar, P.G. Alpha-Synuclein overexpression enhances manganese-induced neurotoxicity through the NF-kB-mediated pathway. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducic, T.; Carboni, E.; Lai, B.; Chen, S.; Michalke, B.; Lázaro, D.F.; Outeiro, T.F.; Bähr, M.; Barski, E.; Lingor, P. Alpha-Synuclein Regulates Neuronal Levels of Manganese and Calcium. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. alpha-Synuclein protects against manganese neurotoxic insult during the early stages of exposure in a dopaminergic cell model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Schapira, A.H.; Gardiner, C.; Sargent, I.L.; Wood, M.J.; Cooper, J.M. Lysosomal dysfunction increases exosome-mediated alpha-synuclein release and transmission. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desplats, P.; Lee, H.J.; Bae, E.J.; Patrick, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Crews, L.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.J. Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13010–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Angot, E.; Bergstrom, A.L.; Steiner, J.A.; Pieri, L.; Paul, G.; Outeiro, T.F.; Melki, R.; Kallunki, P.; Fog, K.; et al. alpha-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danzer, K.M.; Kranich, L.R.; Ruf, W.P.; Cagsal-Getkin, O.; Winslow, A.R.; Zhu, L.; Vanderburg, C.R.; McLean, P.J. Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verina, T.; Schneider, J.S.; Guilarte, T.R.; Guilarte, T.R. Manganese exposure induces alpha-synuclein aggregation in the frontal cortex of non-human primates. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 13, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsumine, H.; Saito, M.; Shimoda-Matsubayashi, S.; Tanaka, H.; Ishikawa, A.; Nakagawa-Hattori, Y.; Yokochi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Igarashi, S.; Takano, H.; et al. Localization of a gene for an autosomal recessive form of juvenile Parkinsonism to chromosome 6q25.2-27. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 60, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitada, T.; Asakawa, S.; Hattori, N.; Matsumine, H.; Yamamura, Y.; Minoshima, S.; Yokochi, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Shimizu, N. Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 1998, 392, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Shirata, A.; Yamane, K.; Iwata, M. Parkin-positive autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinsonism with alpha-synuclein-positive inclusions. Neurology 2004, 63, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Lohmann-Hedrich, K. Impact of recent genetic findings in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2007, 20, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Westenberger, A. Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a008888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilarski, L.L.; Pearson, J.P.; Newsway, V.; Majounie, E.; Knipe, M.D.; Misbahuddin, A.; Chinnery, P.F.; Burn, D.J.; Clarke, C.E.; Marion, M.H.; et al. Systematic review and UK-based study of PARK2 (parkin), PINK1, PARK7 (DJ-1) and LRRK2 in early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Singleton, S.; Feng, J.; Garrick, M.; Paradkar, P.N. Parkin regulates metal transport via proteasomal degradation of the 1B isoforms of divalent metal transporter 1. J. Neurochem. 2010, 113, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifati, V.; Rizzu, P.; Van Baren, M.J.; Schaap, O.; Breedveld, G.J.; Krieger, E.; Dekker, M.C.; Squitieri, F.; Ibanez, P.; Joosse, M.; et al. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 2003, 299, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canet-Aviles, R.M.; Wilson, M.A.; Miller, D.W.; Ahmad, R.; McLendon, C.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Baptista, M.J.; Ringe, D.; Petsko, G.A.; Cookson, M.R. The Parkinson’s disease protein DJ-1 is neuroprotective due to cysteine-sulfinic acid-driven mitochondrial localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9103–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Niki, T.; Taira, T.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.; Ariga, H. Association of DJ-1 with chaperones and enhanced association and colocalization with mitochondrial Hsp70 by oxidative stress. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junn, E.; Jang, W.H.; Zhao, X.; Jeong, B.S.; Mouradian, M.M. Mitochondrial localization of DJ-1 leads to enhanced neuroprotection. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taira, T.; Saito, Y.; Niki, T.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.; Takahashi, K.; Ariga, H. DJ-1 has a role in antioxidative stress to prevent cell death. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.; Yin, Z.; Sidoryk-Węgrzynowicz, M.; Jiang, H.; Aschner, M. 15-Deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2‚‚ modulates manganese-induced activation of the NF-kB, Nrf2, and PI3K pathways in astrocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; DeWitt, M.R.; Bornhorst, J.; Soares, F.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Age- and manganese-dependent modulation of dopaminergic phenotypes in a C. elegans DJ-1 genetic model of Parkinson’s disease. Metallomics 2015, 7, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, A.; Heimbach, A.; Gründemann, J.; Stiller, B.; Hampshire, D.; Cid, L.P.; Goebel, I.; Mubaidin, A.F.; Wriekat, A.L.; Roeper, J.; et al. Hereditary parkinsonism with dementia is caused by mutations in ATP13A2, encoding a lysosomal type 5 P-type ATPase. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fonzo, A.; Chien, H.F.; Socal, M.; Giraudo, S.; Tassorelli, C.; Iliceto, G.; Fabbrini, G.; Marconi, R.; Fincati, E.; Abbruzzese, G.; et al. ATP13A2 missense mutations in juvenile parkinsonism and young onset Parkinson disease. Neurology 2007, 68, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usenovic, M.; Tresse, E.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Taylor, J.P.; Krainc, D. Deficiency of ATP13A2 leads to lysosomal dysfunction, alpha-synuclein accumulation, and neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4240–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehay, B.; Ramirez, A.; Martinez-Vicente, M.; Perier, C.; Canron, M.H.; Doudnikoff, E.; Vital, A.; Vila, M.; Klein, C.; Bezard, E. Loss of P-type ATPase ATP13A2/PARK9 function induces general lysosomal deficiency and leads to Parkinson disease neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9611–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitler, A.D.; Chesi, A.; Geddie, M.L.; Strathearn, K.E.; Hamamichi, S.; Hill, K.J.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Cooper, A.A.; Rochet, J.C.; et al. Alpha-synuclein is part of a diverse and highly conserved interaction network that includes PARK9 and manganese toxicity. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rentschler, G.; Covolo, L.; Haddad, A.A.; Lucchini, R.G.; Zoni, S.; Broberg, K. ATP13A2 (PARK9) polymorphisms influence the neurotoxic effects of manganese. Neurotoxicology 2012, 20, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobb, J.F.; Valeri, L.; Claus Henn, B.; Christiani, D.C.; Wright, R.O.; Mazumdar, M.; Godleski, J.J.; Coull, B.A. Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 2015, 16, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czarnota, J.; Gennings, C.; Wheeler, D.C. Assessment of weighted quantile sum regression for modeling chemical mixtures and cancer risk. Cancer Inform. 2015, 14, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, E.B.; Bryan, M.R.; Morcillo, P.; Hardeman, K.N.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. Manganese-induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction Is Not Detectable at Exposures Below the Acute Cytotoxic Threshold in Neuronal Cell Types. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 176, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Rokad, D.; Malovic, E.; Luo, J.; Harischandra, D.S.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Huang, X.; Lewis, M.; Kanthasamy, A.; et al. Manganese activates NLRP3 inflammasome signaling and propagates exosomal release of ASC in microglial cells. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaat9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robison, G.; Sullivan, B.; Cannon, J.R.; Pushkar, Y. Identification of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta as a target of manganese accumulation. Metallomics 2015, 7, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucchini, R.; Tieu, K. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism: Evidence from Epidemiological and Experimental Studies. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081190
Lucchini R, Tieu K. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism: Evidence from Epidemiological and Experimental Studies. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(8):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081190
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucchini, Roberto, and Kim Tieu. 2023. "Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism: Evidence from Epidemiological and Experimental Studies" Biomolecules 13, no. 8: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081190
APA StyleLucchini, R., & Tieu, K. (2023). Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism: Evidence from Epidemiological and Experimental Studies. Biomolecules, 13(8), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081190






