Monitoring Immune Modulation in Season Population: Identifying Effects and Markers Related to Apis mellifera ligustica Honey Bee Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Bees
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.4. Molecular Detection of SBV and DWV to Exclude Data from Diseased Honey Bees
2.5. Statistical Analysis
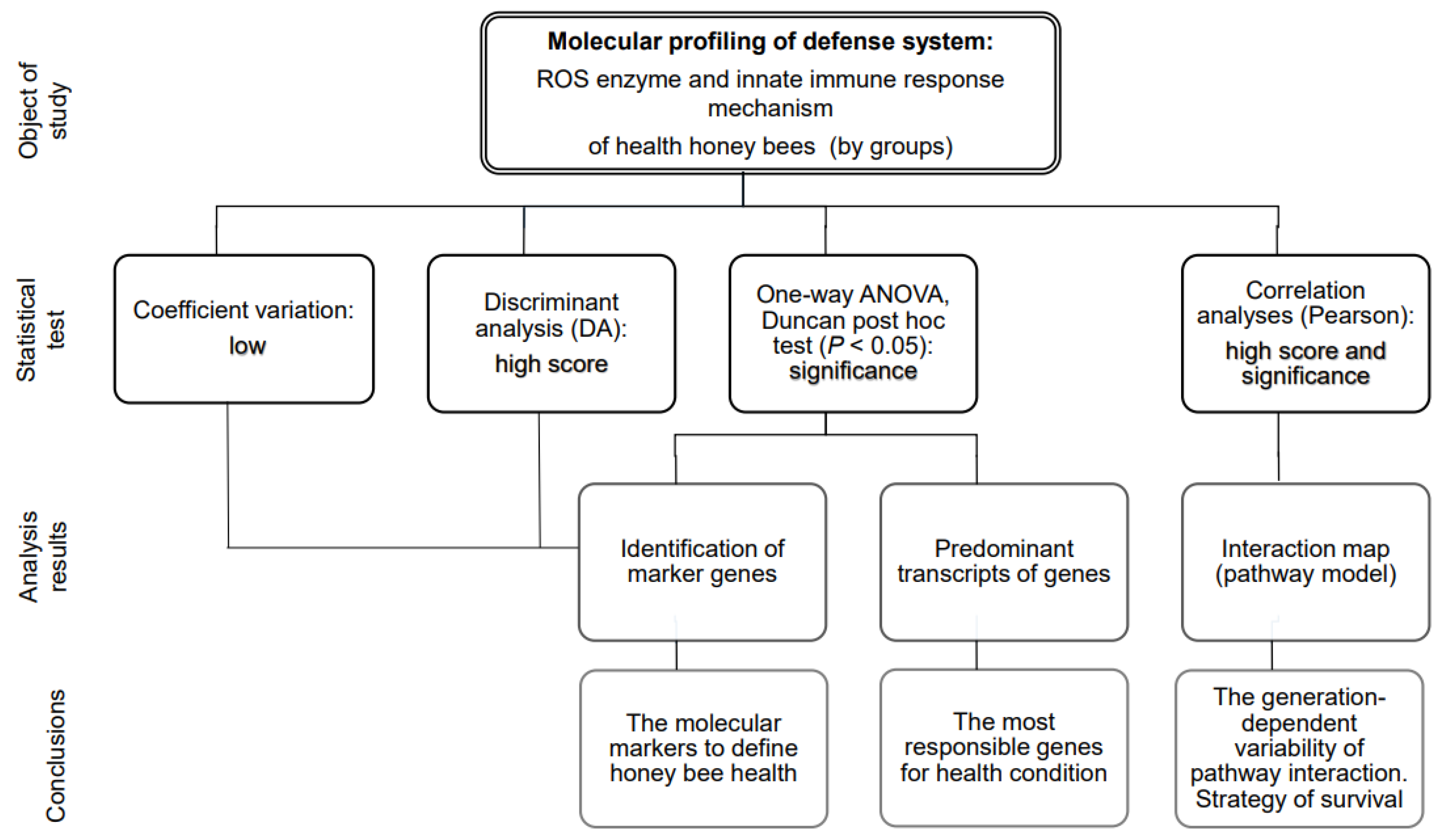
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Profiling with Defense Gene Expressions
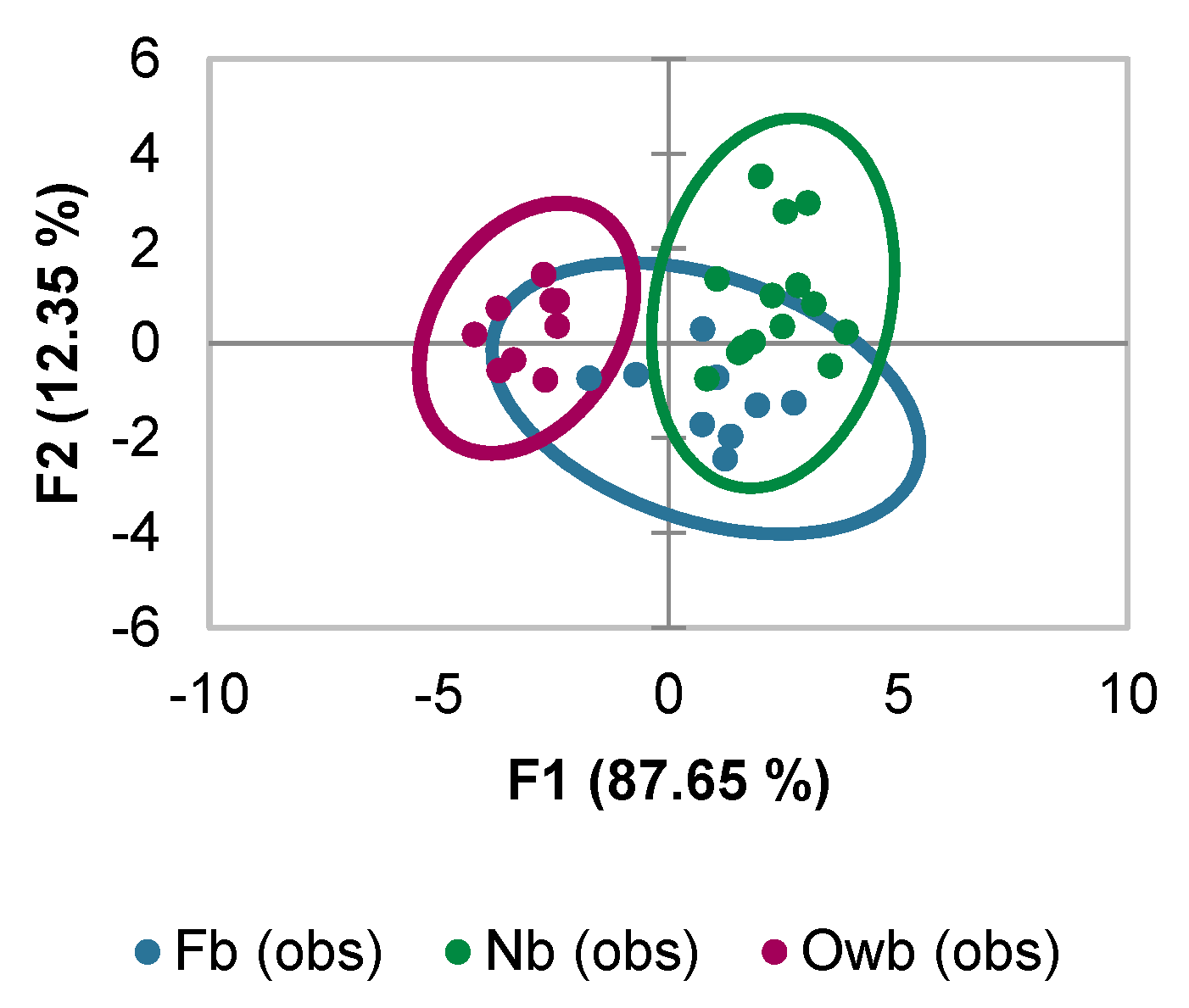
3.1.1. Selection of the Markers Based on Discriminant Analysis Scores
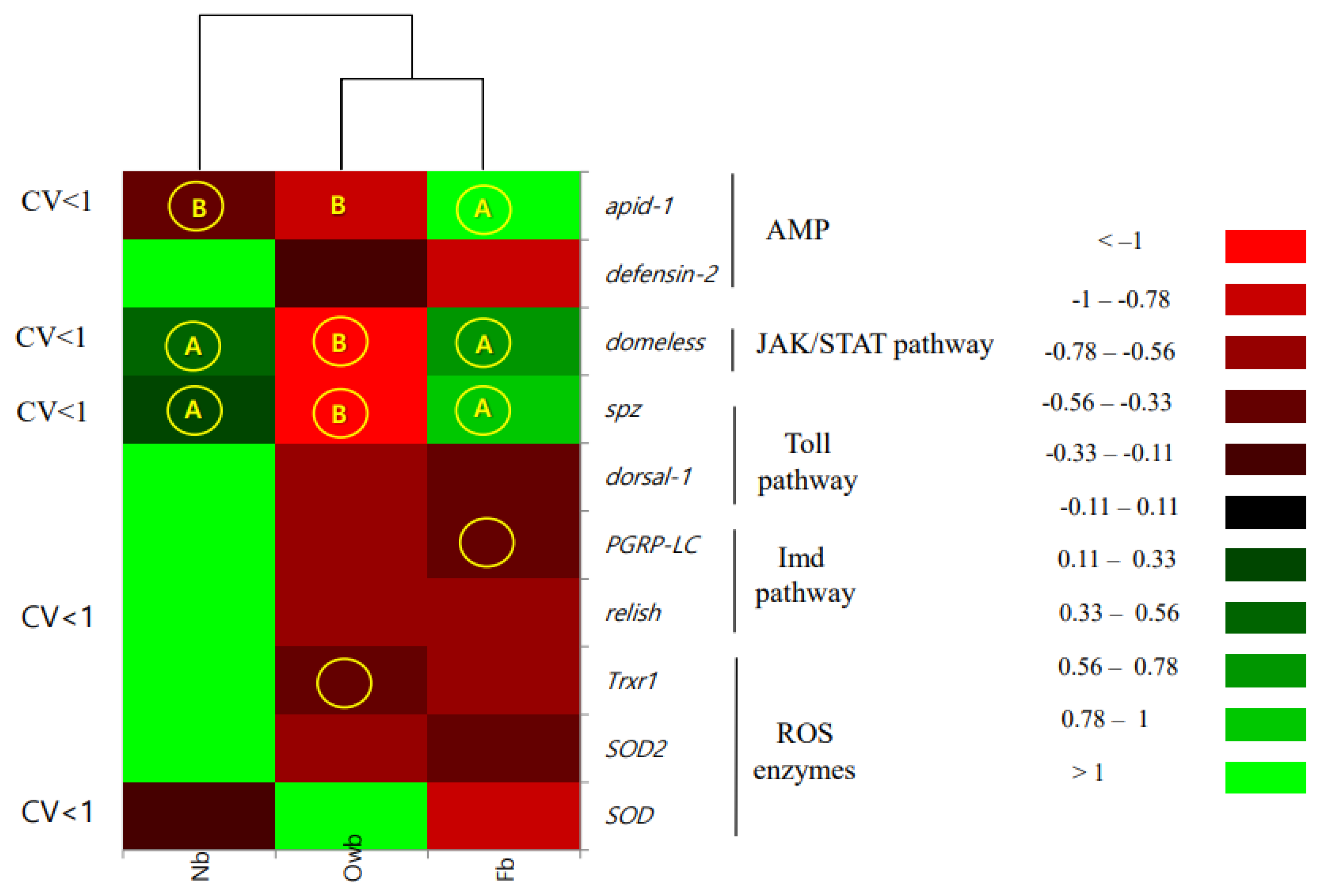
3.1.2. Effect of Variation on Marker Selection
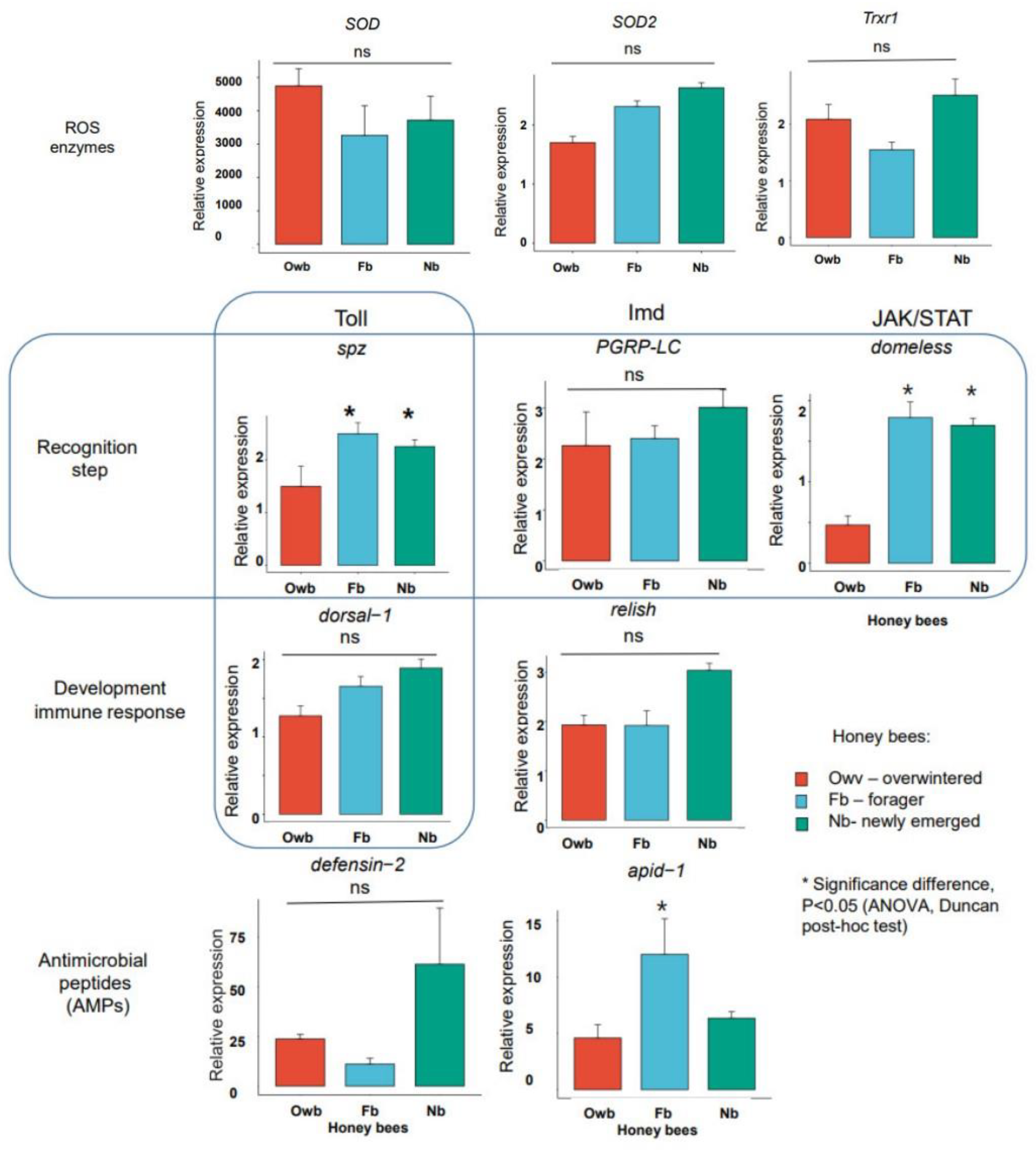
3.1.3. Selection of the Markers Based on Gene Expression
3.2. Molecular Profiling of Defense System Based on Correlation Analysis
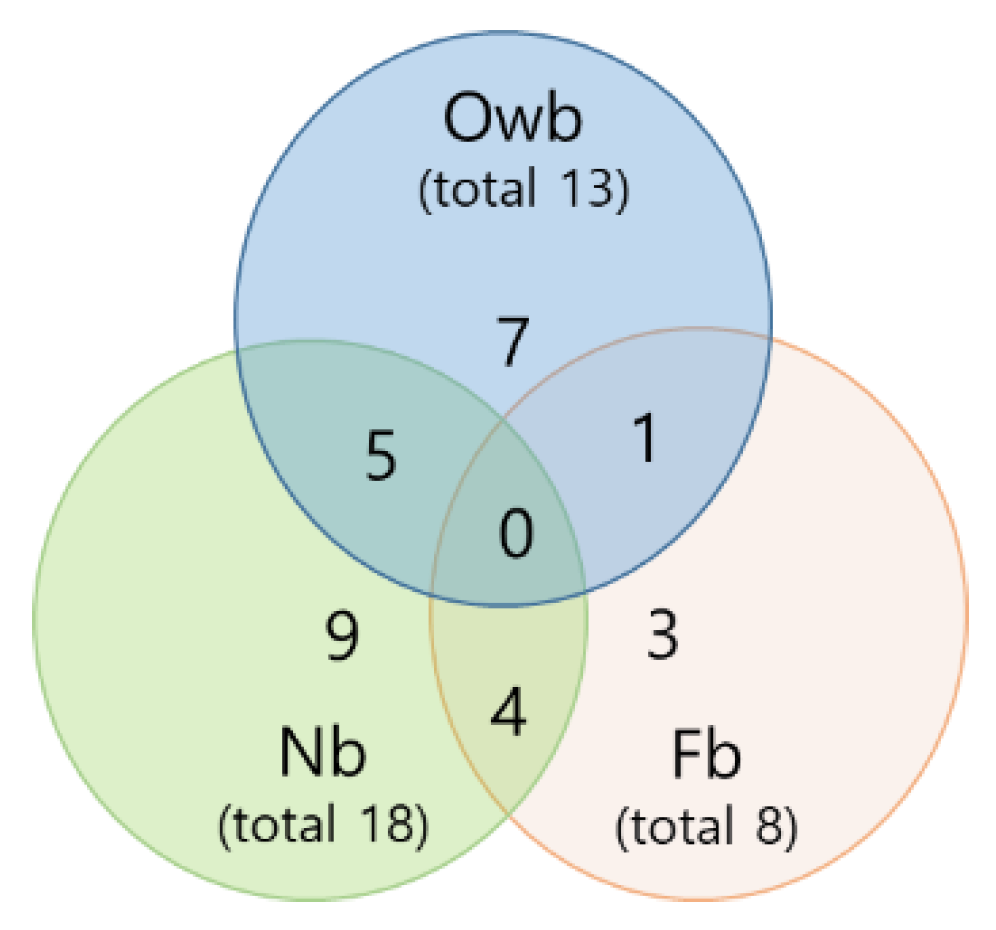
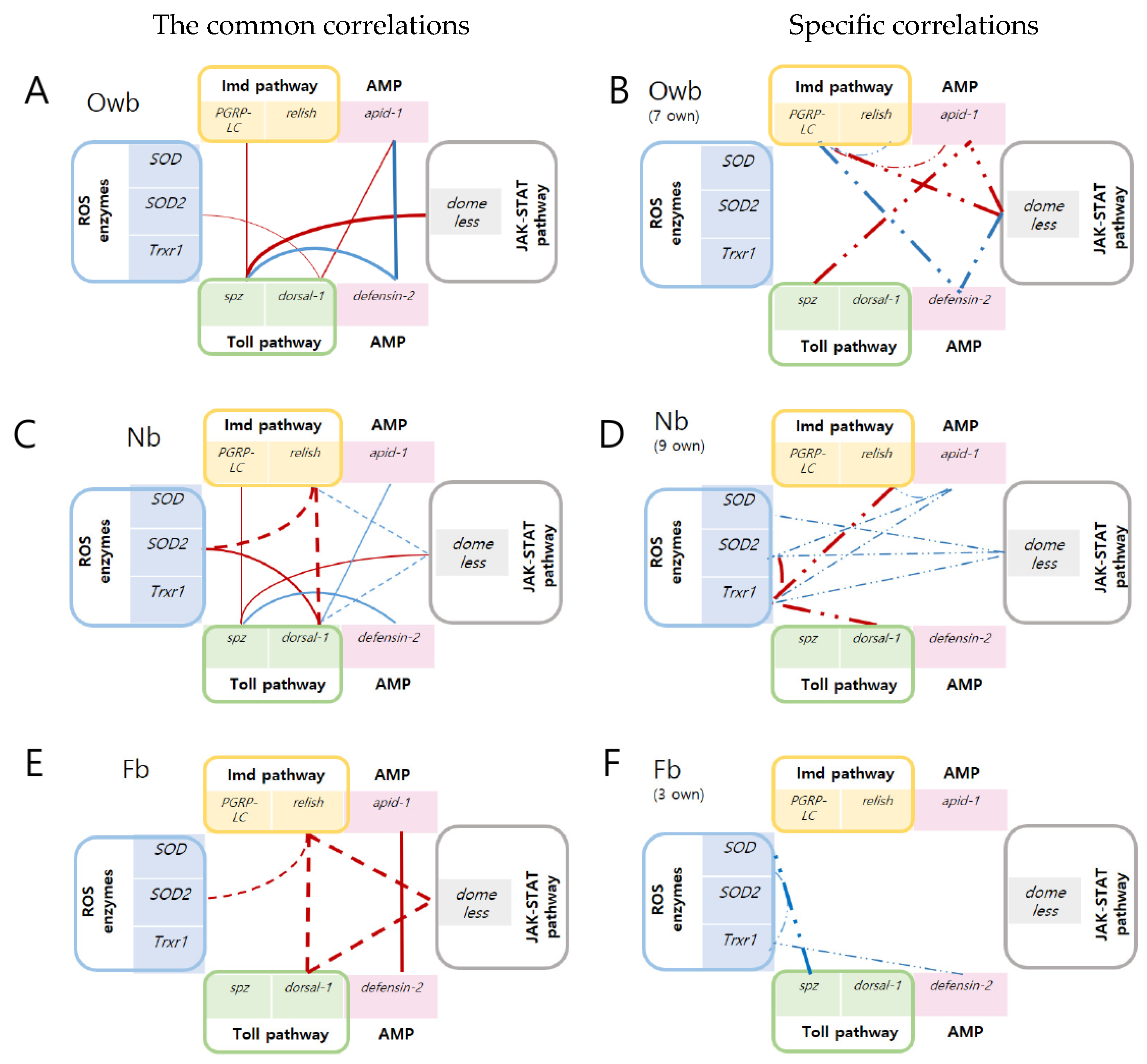
3.2.1. The Common Correlations between Defense Genes in Honey Bees
3.2.2. The Specific Correlations between Defense Genes in Honey Bees
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cilia, G.; Nanetti, A. Honey Bee Health. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byhrø, E.M.H.; Salmela, H.; Vitlic, A.; Wang, Y.; Munch, D.; Amdam, G.V. Different activation of immune-related genes in honey bee nurses and foragers (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 2019, 50, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleolog, J.; Wilde, J.; Miszczak, A.; Gancarz, M.; Strachecka, A. Antioxidation Defenses of Apis mellifera Queens and Workers Respond to Imidacloprid in Different Age-Dependent Ways: Old Queens Are Resistant, Foragers Are Not. Animals 2021, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostálková, S.; Dobeš, P.; Kunc, M.; Hurychová, J.; Škrabišová, M.; Petřivalský, M.; Titěra, D.; Havlík, J.; Hyršl, P.; Danihlík, J. Winter honeybee (Apis mellifera) populations show greater potential to induce immune responses than summer populations after immune stimuli. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, N.; Corona, M.; Neumann, P.; Dainat, B. Overwintering Is Associated with Reduced Expression of Immune Genes and Higher Susceptibility to Virus Infection in Honey Bees. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.E. Regulation of division of labor in insects’ societies. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 637–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, M.L. The Biology of the Honey Bee; Havard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; p. 294. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, A.; Reynaldi, F.; Guzman-Novoa, E. Fundaments of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) immune system. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2019, 10, 705–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, P.; Maggi, M.; Ramirez, L.; Nicolas, S.; Leonardo, F.; Lorenzo, L.; Martin, E. Cellular immunity in Apis mellifera: Studying hemocytes brings light about bees skills to confront threats. Apidologie 2016, 47, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Aronstein, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Hetru, C.; Imler, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.; Thompson, G.J.; Zou, Z.; Hultmark, D. Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orčić, S.; Nikolić, T.; Purać, J.; Šikoparija, B.; Blagojević, D.P.; Vukašinović, E.; Plavša, N.; Stevanović, J.; Kojić, D. Seasonal variation in the activity of selected antioxidant enzymes and malondialdehyde level in worker honey bees. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2017, 165, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, T.V. Peripheral Nervous System Toxicity Biomarkers. In Biomarkers in Toxicology, 1st ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Lexington, KY, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 169–198. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, W.J.; Ulrich, R. Molecular profiling approaches for identifying novel biomarkers. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2004, 3, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.D.; Küng, E.; Boess, F.; Certa, U.; Ebeling, M. Pathway reporter genes define molecular phenotypes of human cells. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharwat, A.; Gaber, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Linear discriminant analysis: A detailed tutorial. AI Commun. 2017, 30, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.A.; Ghanim, M.F. Comprehensive Study and Evaluation of Commonly used Dimensionality Reduction Techniques in Biometrics Field. Al-Rafidain Eng. J. 2020, 25, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, I.; Zeng, J.; Park, T.; Yi, S.V. DNA methylation and transcriptional noise. Epigenetics Chromatin 2013, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.R.; Oliva, M.; Sabatini, P.J.B.; Stockley, T.L.; Siu, L.L. Molecular profiling for precision cancer therapies. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, G.; Arbulu, A.A.; González, N.; Jurado, J.M.L.; Bermejo, J.V.D.; Vallejo, M.E.C. Data mining-based discriminant analysis as a tool for the study of egg quality in native hen breeds. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Kim, Y.J. Epigenetic regulation and the variability of gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, S.; Haesbroeck, G.; Ruwet, C. Multivariate coefficients of variation: Comparison and influence functions. J. Multivar. Anal. 2015, 142, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.B.; Kupelian, V.; Visser, M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Rubin, S.M.; Harris, T.B. Strength, But Not Muscle Mass, Is Associated with Mortality in the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study Cohort. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Arévalo, S.; Vicente-Rubiano, M.; Puerta, F.; Molero, F.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Immune related genes as markers for monitoring health status of honey bee colonies. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonovsky, E.; Schuster, R.; Yeger-Lotem, E. Large-scale analysis of human gene expression variability associates highly variable drug targets with lower drug effectiveness and safety. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3028–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaux, C.; Dantec, C.; Parrinello, H.; Conte, Y.L. Nutrigenomics in honey bees: Digital gene expression analysis of pollen’s nutritive effects on healthy and varroa-parasitized bees. BMC Genom. 2011, 496, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritschler, M.; Vollmann, J.J.; Yañez, O.; Chejanovsky, N.; Crailsheim, K.; Neumann, P. Protein nutrition governs within-host race of honey bee pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korayem, A.M.; Khodiary, M.M.; Abdel-Aal, A.A.A.; El-Sonbaty, A.A.M. The protective strategy of antioxidant enzymes against hydrogen peroxide in honey bee, Apis mellifera during two different seasons. J. Biol. Earth Sci. 2012, 2, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyasov, R.; Gaifullina, L.; Saltykova, E.; Poskryakov, A.; Nikolenko, A. Review of the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptide Defensin in Honey Bees Apis mellifera L. J. Apic. Sci. 2012, 56, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortezza, M.L.; Schenk, M.; Cosolo, A.; Kolybaba, A.; Grass, I.; Classen, A.-K. JAK/STAT signalling mediates cell survival in response to tissue stress. Development 2016, 143, 2907–2919. [Google Scholar]
- Santorelli, L.A.; Wilkinson, T.; Abdulmalik, R.; Rai, Y.; Creevey, C.J.; Huws, S.; Gutierrez-Merino, J. Beehives possess their own distinct microbiomes. Environ. Microbiome 2023, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Tang, J.; Tang, M.; Luo, S.; Zhou, X. Reactive oxygen species are regulated by immune deficiency and Toll pathways in determining the host specificity of honeybee gut bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219634120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Locus | 5′-3′ | Primers | Amplicon Length, bp | NCBI Reference Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | defensin-2 | F | ACCGCTGCTACCACTACGACA | 139 | NM_001011638.1 |
| 2 | R | GCCATTTCTGCAACTACCGCCT | |||
| 3 | relish | F | TCCATTGCATGCAGCACTTCG | 264 | XM_026444175.1 |
| 4 | R | ACACATGCACCAGCTTCAGGA | |||
| 5 | dorsal-1 | F | TGCAGCAAGTGGAACAACCAGT | 114 | XM_006566999.3 |
| 6 | R | CAGGCCTACCTGCACCGAGA | |||
| 7 | domeless | F | GCCGCTGCTCTTTGGCATCT | 238 | XM_006567690.3 |
| 8 | R | GCCAAATTGTTGTTCCAACAGCCC | |||
| 9 | apid-1 | F | TTGTTGTTACCTTTGTAGTCGCGGT | 70 | NM_001011642.1 |
| 10 | R | AGGCGCGTAGGTCGAGTAGG | |||
| 11 | PGRP-LC | F | TGCAATGCGATGGCGACACA | 105 | XM_026441962.1 |
| 12 | R | AGCGACTTGAGCACACCACAC | |||
| 13 | spz (spaetzle) | F | TGGACGACAGCCCTCTTTGTCA | 371 | XM_006565534.3 |
| 14 | R | GCGCCTTCGACGTGACGATT | |||
| 15 | SBV | F | GTGGAACCCGAGTGTTTTGTAACCC | 156 | KY273489.1 |
| 16 | R | AAGCTAAAAGCGTCCACTCTGTACTCT | |||
| 17 | DWV | F | TGT GAA GTG GCG GAC GTT ACA GA | 211 | KT215904.1 |
| 18 | R | GTA TTC TGG ACC CCA TCC GAA TGC | |||
| 19 | β-actin | F | GGATTCCTATGTTGGTGATGAAGCCC | 177 | NM_001185145.1 |
| 20 | R | GGTGCCTCAGTAAGAAGTACCGGATG | |||
| 21 | SOD | F | GCAGTGTGCGTTCTTCAGGGT | 86 | NM_001178027.1 |
| 22 | R | TGACCGGTGACCTTCACGGA | |||
| 23 | SOD2 | F | GGCGGTAAACCAGACGCTGC | 126 | NM_001178048.2 |
| 24 | R | TCCAAGCCAACCCCAACCAGA | |||
| 25 | Trxr-1 | F | CCTGTTGCTATACATGCGGGTCG | 141 | XM_006563201.3 |
| 26 | R | TGCTGCTTCTTCGCTAAGGCCA |
| Name of Gene/Honey Bee Group | SOD | SOD2 | Trxr1 | spz | dorsal−1 | defensin−2 | domeless | apid−1 | PGRP-LC | relish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Owb | 0.304 | 0.175 | 0.353 | 0.722 | 0.286 | 0.269 | 0.671 | 0.821 | 0.286 | 0.717 |
| Nb | 0.720 | 1.713 | 1.289 | 0.216 | 1.770 | 1.716 | 0.192 | 0.436 | 1.711 | 0.342 |
| Fb | 0.771 | 0.116 | 0.241 | 0.235 | 0.214 | 0.741 | 0.306 | 0.293 | 0.437 | 0.738 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frunze, O.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.-j.; Lee, J.-H.; Bilal, M.; Kwon, H.-W. Monitoring Immune Modulation in Season Population: Identifying Effects and Markers Related to Apis mellifera ligustica Honey Bee Health. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010019
Frunze O, Kim H, Kim B-j, Lee J-H, Bilal M, Kwon H-W. Monitoring Immune Modulation in Season Population: Identifying Effects and Markers Related to Apis mellifera ligustica Honey Bee Health. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrunze, Olga, Hyunjee Kim, Byung-ju Kim, Jeong-Hyeon Lee, Mustafa Bilal, and Hyung-Wook Kwon. 2024. "Monitoring Immune Modulation in Season Population: Identifying Effects and Markers Related to Apis mellifera ligustica Honey Bee Health" Biomolecules 14, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010019
APA StyleFrunze, O., Kim, H., Kim, B.-j., Lee, J.-H., Bilal, M., & Kwon, H.-W. (2024). Monitoring Immune Modulation in Season Population: Identifying Effects and Markers Related to Apis mellifera ligustica Honey Bee Health. Biomolecules, 14(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010019






