Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Concentration-Independent Fluorescent Chloride Indicator, ABP-Dextran, Optimized for Extracellular Chloride Measurement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Synthesis of Candidate Fluorescent Compounds
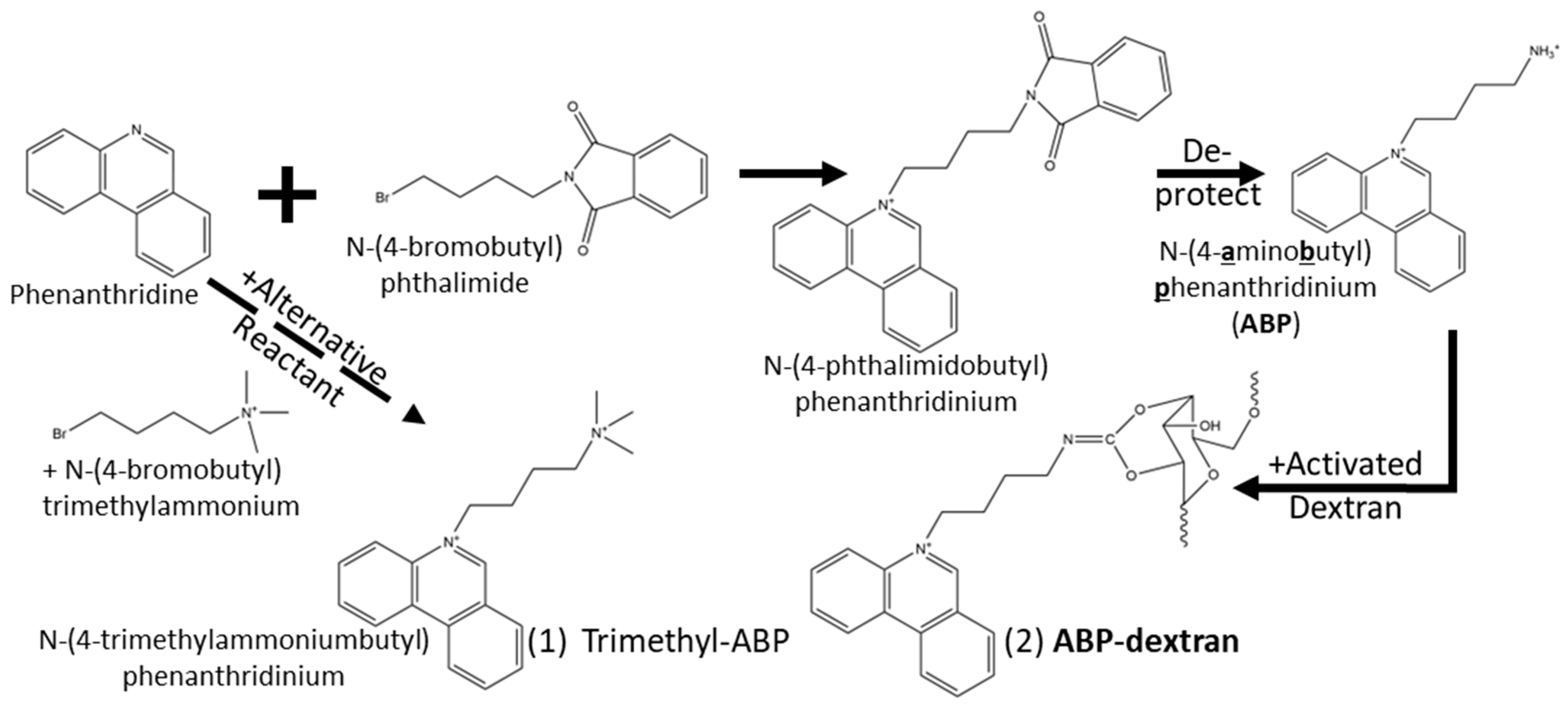
2.3. Synthesis of N(4-aminobutyl)phenantridinium (ABP)
2.4. Conjugation of ABP to Dextran
2.5. Dual-Labeled Dextran
2.6. Spectrophotometry
2.7. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM)
2.8. Calibration of ABP-Dextran
2.9. Animals
2.10. In Vitro Organotypic Slice Cultures and Imaging
2.11. In Vivo Murine Cortical Window Imaging
2.12. Image Processing in ImageJ and Matlab
2.13. Statistics
2.14. Comaprative Brightness and kSV Assay
3. Results
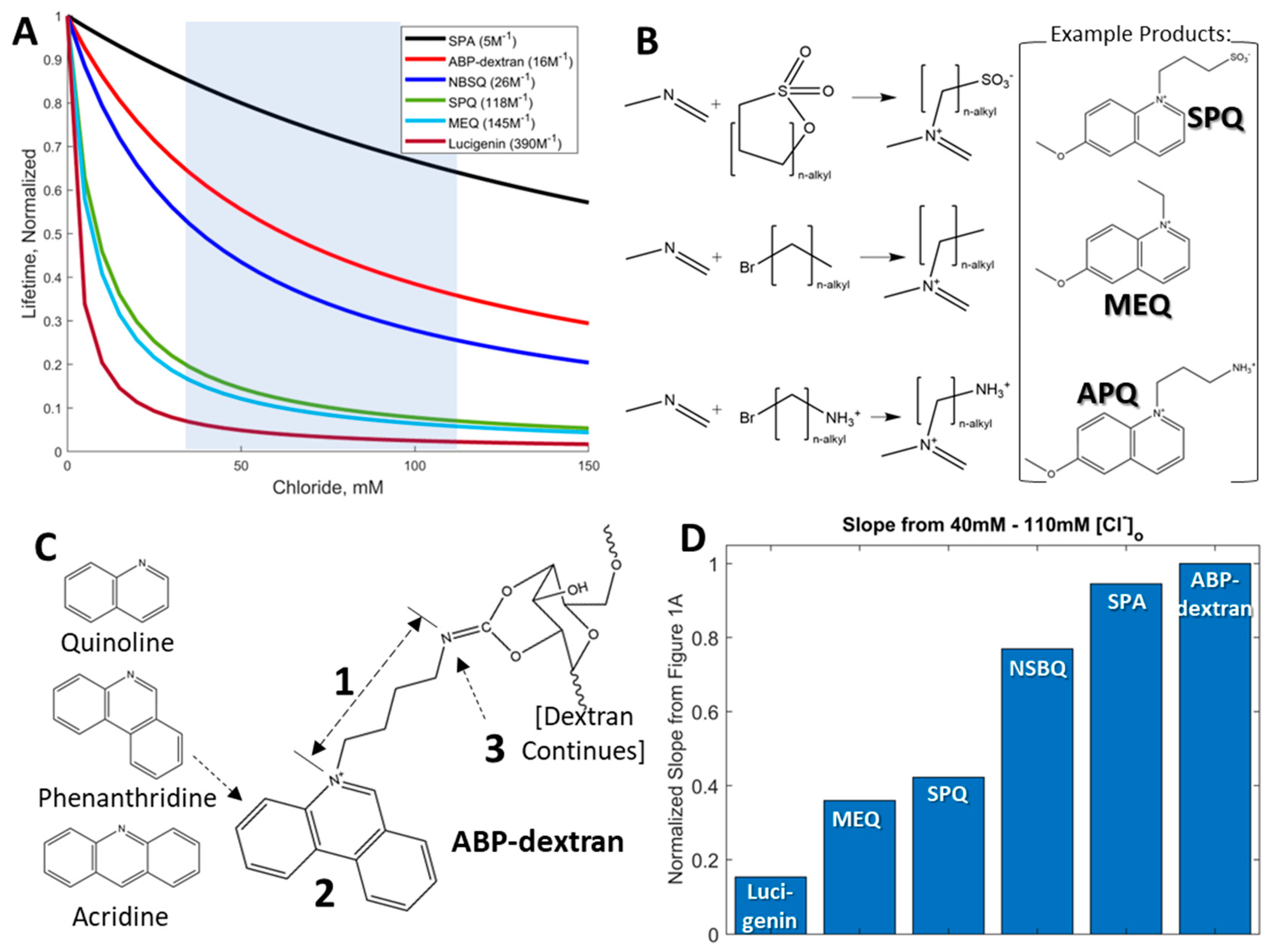
3.1. Development of a Fluorescent Probe for Clo
3.2. Initial Characterization of ABP and ABP-Dextran
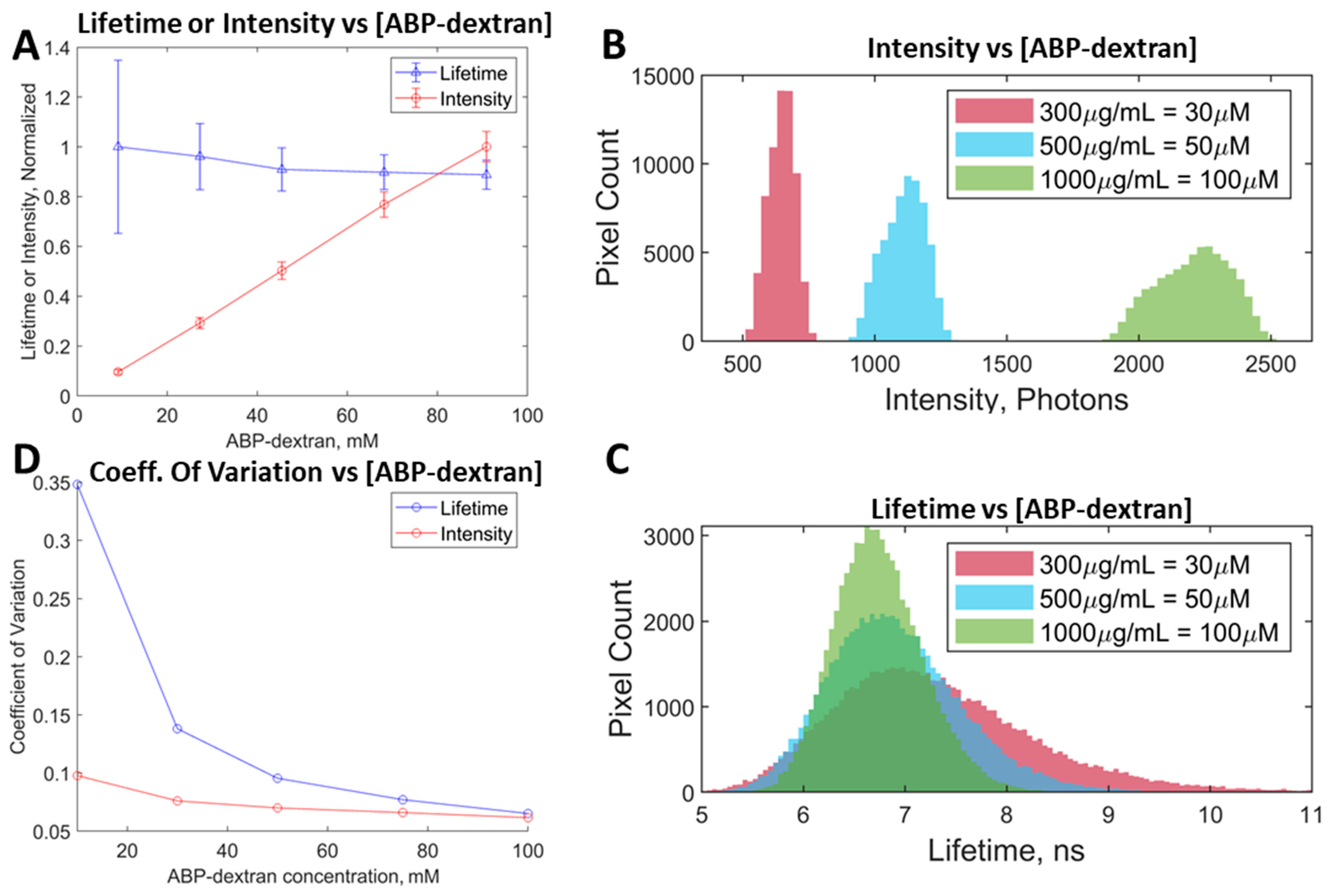
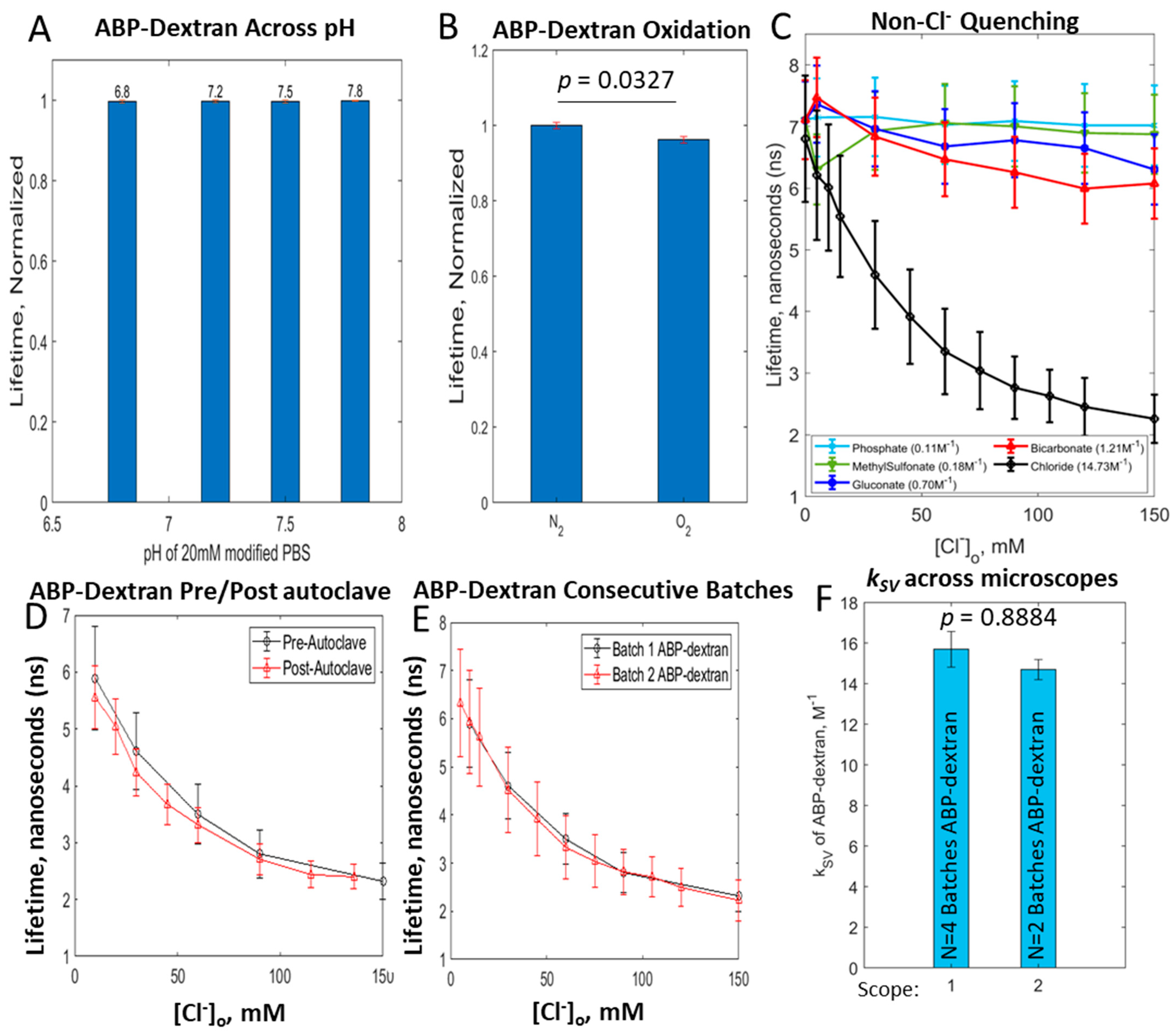
3.3. Optimization of ABP-Dextran
3.4. ABP-Dextran Performance as a Clo Probe
3.5. Performance In Vitro and In Vivo Mouse Tissue
3.6. Exploring a Ratiometric Clo Probe
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glykys, J.; Dzhala, V.; Egawa, K.; Balena, T.; Saponjian, Y.; Kuchibhotla, K.V.; Bacskai, B.J.; Kahle, K.T.; Zeuthen, T.; Staley, K.J. Local impermeant anions establish the neuronal chloride concentration. Science 2014, 343, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glykys, J.; Dzhala, V.; Egawa, K.; Kahle, K.T.; Delpire, E.; Staley, K. Chloride dysregulation, seizures, and cerebral edema: A relationship with therapeutic potential. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biwersi, J.; Verkman, A.S. Cell-permeable fluorescent indicator for cytosolic chloride. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 7879–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, K.; Schleich, W.; Krieger, P.; Loo, L.S.; Wang, D.; Cant, N.B.; Feng, G.; Augustine, G.J.; Kuner, T. Imaging synaptic inhibition in transgenic mice expressing the chloride indicator, Clomeleon. Brain Cell Biol. 2006, 35, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuner, T.; Augustine, G.J. A genetically encoded ratiometric indicator for chloride: Capturing chloride transients in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron 2000, 27, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimley, J.S.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Wen, L.; Beese, L.S.; Hellinga, H.W.; Augustine, G.J. Visualization of synaptic inhibition with an optogenetic sensor developed by cell-free protein engineering automation. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 16297–16309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.S.; Artoni, P.; Landi, S.; Cozzolino, O.; Parra, R.; Pracucci, E.; Trovato, F.; Szczurkowska, J.; Luin, S.; Arosio, D. Simultaneous two-photon imaging of intracellular chloride concentration and pH in mouse pyramidal neurons in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8770–E8779. [Google Scholar]
- Illsley, N.P.; Verkman, A.S. Membrane chloride transport measured using a chloride-sensitive fluorescent probe. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapf, R.; Berry, C.; Verkman, A. Estimation of intracellular chloride activity in isolated perfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubules using a fluorescent indicator. Biophys. J. 1988, 53, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.; Sellers, M.; Chao, A.; Leung, T.; Ketcham, R. Synthesis and characterization of improved chloride-sensitive fluorescent indicators for biological applications. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 178, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biwersi, J.; Farah, N.; Wang, Y.X.; Ketcham, R.; Verkman, A.S. Synthesis of cell-impermeable Cl-sensitive fluorescent indicators with improved sensitivity and optical properties. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, C242–C250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biwersi, J.; Tulk, B.; Verkman, A.S. Long-wavelength chloride-sensitive fluorescent indicators. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 219, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Agulian, S.; Haddad, G.G. Cl- and Na+ homeostasis during anoxia in rat hypoglossal neurons: Intracellular and extracellular in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 1992, 448, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroeger, D.; Tamburri, A.; Amzica, F.; Sík, A. Activity-dependent layer-specific changes in the extracellular chloride concentration and chloride driving force in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krapf, R.; Illsley, N.P.; Tseng, H.C.; Verkman, A.S. Structure-activity relationships of chloride-sensitive fluorescent indicators for biological application. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 169, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birks, J.B. Fluorescence Quantum Yield Measurements. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. A Phys. Chem. 1976, 80A, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehlen, M.H. The centenary of the Stern-Volmer equation of fluorescence quenching: From the single line plot to the SV quenching map. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2020, 42, 100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdichevsky, Y.; Saponjian, Y.; Park, K.I.; Roach, B.; Pouliot, W.; Lu, K.; Swiercz, W.; Dudek, F.E.; Staley, K.J. Staged anticonvulsant screening for chronic epilepsy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 908–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppini, L.; Buchs, P.A.; Muller, D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 37, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, A.; De Marco García, N.V. An in vivo Calcium Imaging Approach for the Identification of Cell-Type Specific Patterns in the Developing Cortex. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 747724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, E.; Offenbacher, H.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical sensor for continuous determination of halides. Ann. Chem. 1984, 56, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S. Development and biological applications of chloride-sensitive fluorescent indicators. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, C375–C388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrasate, M.; Finkbeiner, S. Automated microscope system for determining factors that predict neuronal fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3840–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balena, T.; Lillis, K.; Rahmati, N.; Bahari, F.; Dzhala, V.; Berdichevsky, E.; Staley, K. A Dynamic Balance between Neuronal Death and Clearance in an. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 6084–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S.; Biwersi, J.; Verkman, A.S. Synthesis and characterization of dual-wavelength Cl−-sensitive fluorescent indicators for ratio imaging. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, C747–C757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, K. Ionic mechanisms of ictogenic disinhibition. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Tsien, R.Y. Very long-term memories may be stored in the pattern of holes in the perineuronal net. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12456–12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normoyle, K.P.; Lillis, K.P.; Egawa, K.; McNally, M.A.; Paulchakrabarti, M.; Coudhury, B.P.; Staley, K.J. Displacement of extracellular chloride by sulfated glycosaminoglycans of the brain’s extracellular matrix. J. Physiol. 2023. in revision. [Google Scholar]
- Karamanos, N.K.; Theocharis, A.D.; Piperigkou, Z.; Manou, D.; Passi, A.; Skandalis, S.S.; Vynios, D.H.; Orian-Rousseau, V.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Schmelzer, C.E.H.; et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6850–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, M.; Reinert, T.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Wagner, F.E.; Tröger, W.; Reinert, A.; Jäger, C.; Brückner, G.; Arendt, T. Ion exchanger in the brain: Quantitative analysis of perineuronally fixed anionic binding sites suggests diffusion barriers with ion sorting properties. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kojic, L.; Tsang, M.; Grewal, P.; Liu, J.; Namjoshi, D.; Wellington, C.L.; Tetzlaff, W.; Cynader, M.S.; Jia, W. Distinct roles for metalloproteinases during traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 96, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hartman, R.; Ayer, R.; Marcantonio, S.; Kamper, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Matrix metalloproteinases inhibition provides neuroprotection against hypoxia-ischemia in the developing brain. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; McRae, P.A.; Rankin-Gee, E.K.; Baranov, E.; Wandrey, L.; Rogers, S.; Porter, B.E. Increased metalloproteinase activity in the hippocampus following status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 132, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijet, B.; Stefaniuk, M.; Kostrzewska-Ksiezyk, A.; Tsilibary, P.E.; Tzinia, A.; Kaczmarek, L. Elevation of MMP-9 Levels Promotes Epileptogenesis After Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 9294–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijet, B.; Konopka, A.; Rejmak, E.; Stefaniuk, M.; Khomiak, D.; Bulska, E.; Pikul, S.; Kaczmarek, L. The matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor marimastat inhibits seizures in a model of kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin-Gee, E.K.; McRae, P.A.; Baranov, E.; Rogers, S.; Wandrey, L.; Porter, B.E. Perineuronal net degradation in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Brightness a | QY | kSV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEQ | 1.00 | 0.70 b | 145 b |
| 3TMAPP | 0.29 | 0.74 | 41 |
| 5TMAPP | 0.27 | 0.84 | 32 |
| 1° ABP | 0.37 | 0.75 | 34 |
| ABP-dextran c | 0.24 | 0.54 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Normoyle, K.P.; Lillis, K.P.; Staley, K.J. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Concentration-Independent Fluorescent Chloride Indicator, ABP-Dextran, Optimized for Extracellular Chloride Measurement. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010077
Normoyle KP, Lillis KP, Staley KJ. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Concentration-Independent Fluorescent Chloride Indicator, ABP-Dextran, Optimized for Extracellular Chloride Measurement. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010077
Chicago/Turabian StyleNormoyle, Kieran P., Kyle P. Lillis, and Kevin J. Staley. 2024. "Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Concentration-Independent Fluorescent Chloride Indicator, ABP-Dextran, Optimized for Extracellular Chloride Measurement" Biomolecules 14, no. 1: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010077
APA StyleNormoyle, K. P., Lillis, K. P., & Staley, K. J. (2024). Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Concentration-Independent Fluorescent Chloride Indicator, ABP-Dextran, Optimized for Extracellular Chloride Measurement. Biomolecules, 14(1), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010077







