Conjunctive Analysis of BSA-Seq and SSR Markers Unveil the Candidate Genes for Resistance to Rice False Smut
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Material
2.1. Plant Materials and Pathogen Culture
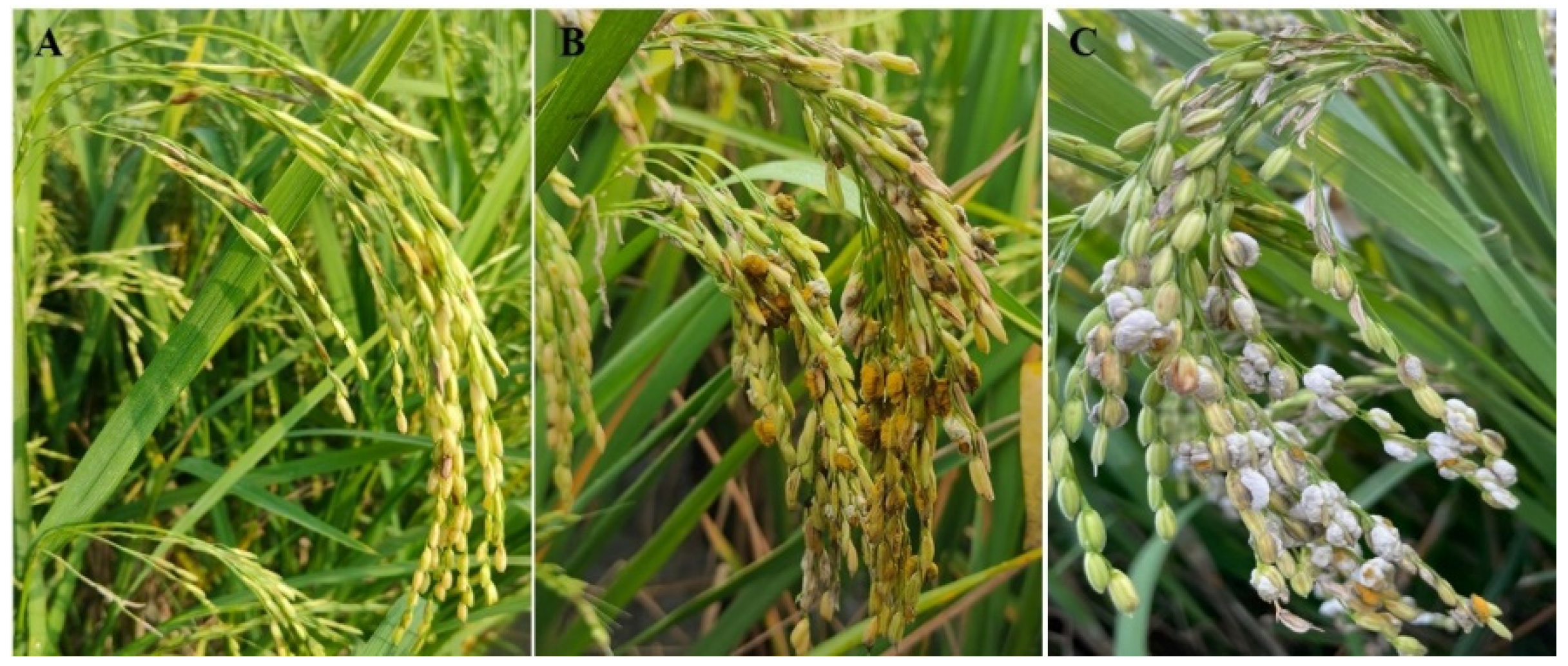
2.2. RFS Inoculation and Disease Scoring
2.3. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction and Construction of Segregating Pools
2.4. Bulk Segregant Analysis Sequencing
2.5. Construction of SSR-Based Genetic Linkage Maps and QTL Analysis
2.6. Candidate Gene Identification
2.7. Expression Analysis of Putative-Resistant Genes by RT-qPCR
3. Results
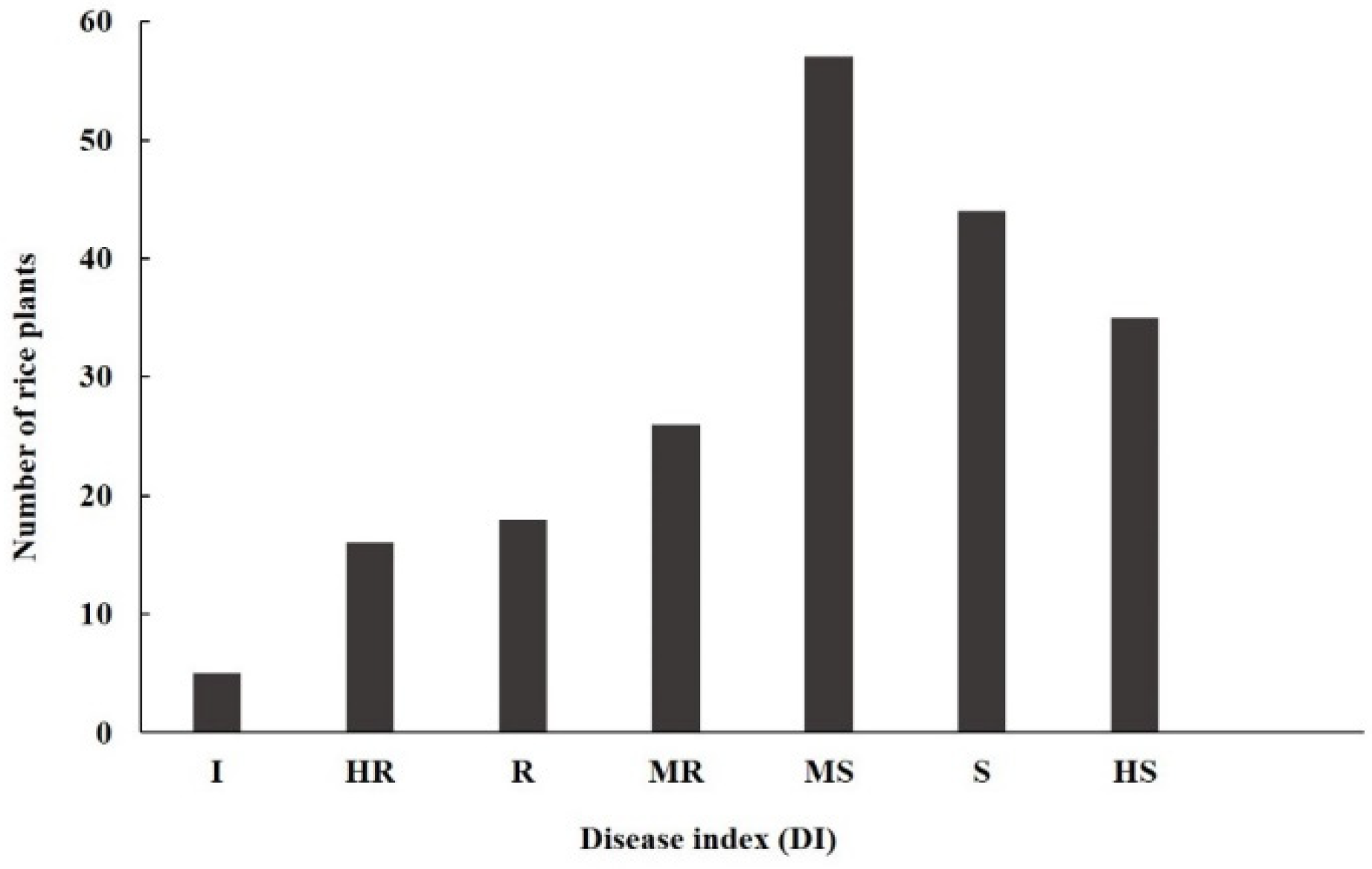
3.1. Genetic Characteristics of Resistance of IR77298-14-1-2::IRGC117374-1 to U. virens
3.2. Mapping QTL for Resistance to RFS Based on the BSA-Seq Technique
3.2.1. Sequencing Data and Quality Assessment
3.2.2. Variation Detection of BSA-Seq Data
3.2.3. Annotation of SNPs and Indels
3.2.4. Association Analysis of BSA-Seq Data
3.3. QTL Identification for RFS Resistance Based on SSR Markers
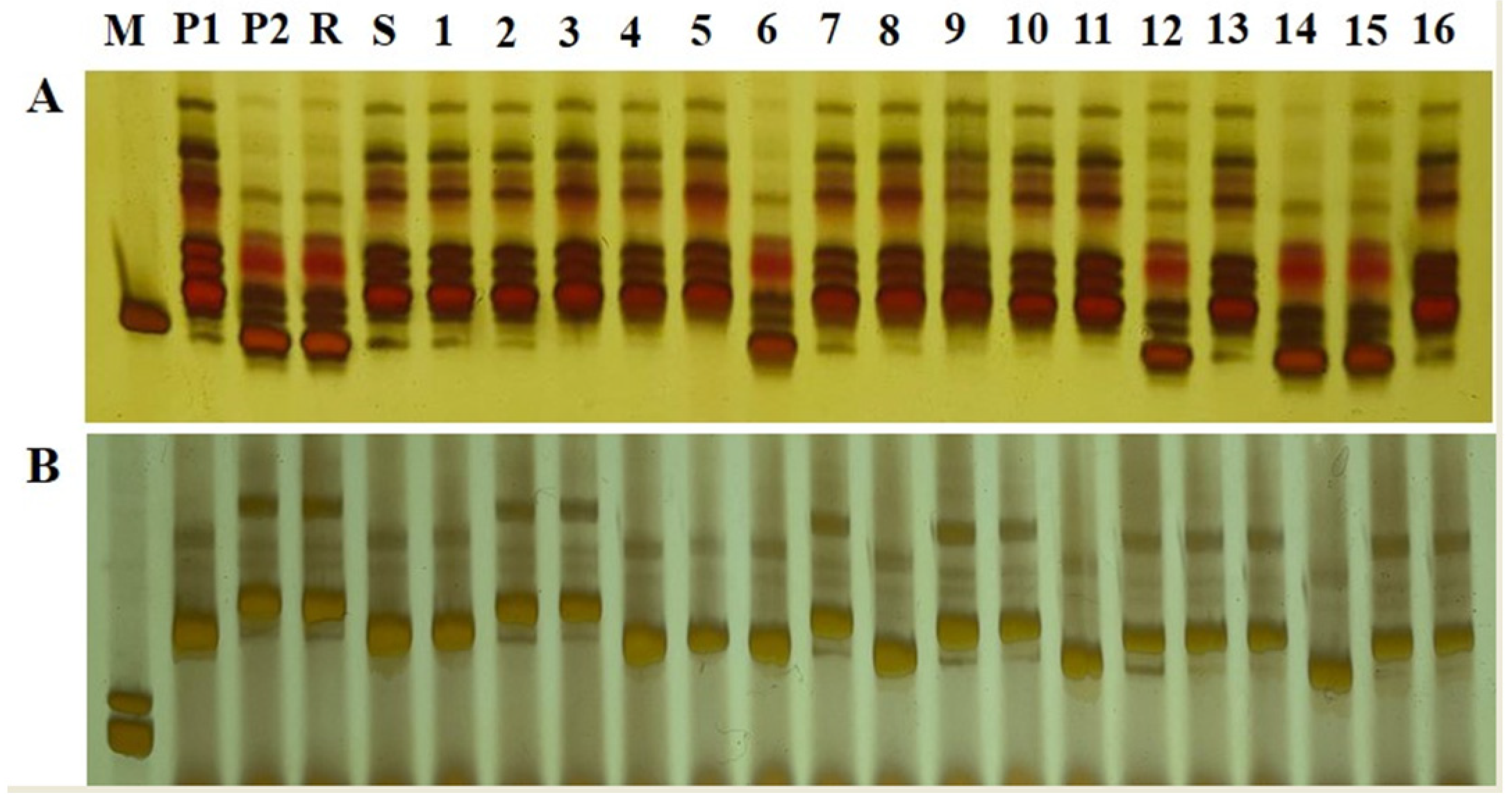
3.3.1. Screening of SSR Molecular Markers for Resistance to RFS
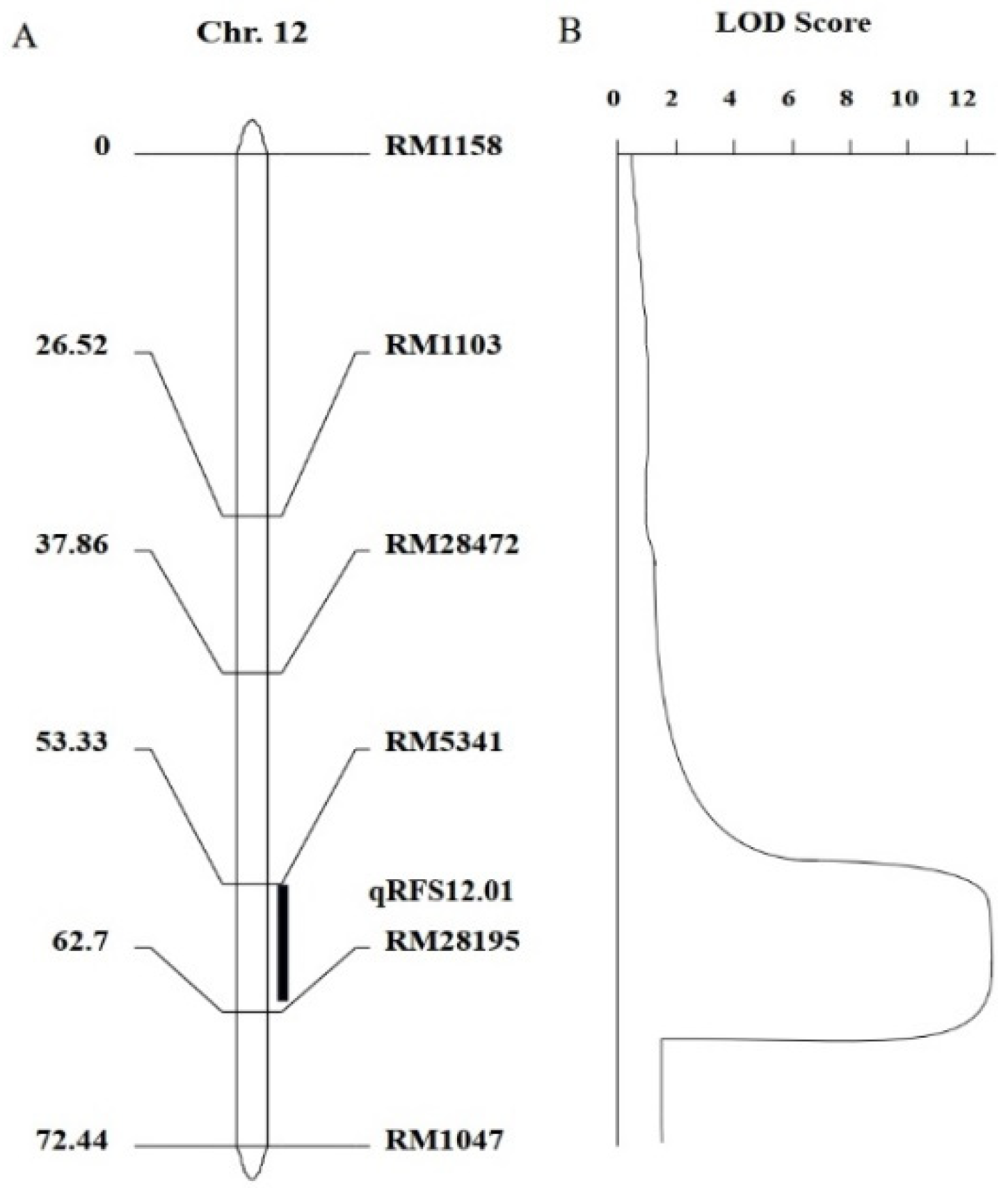
3.3.2. Construction of Genetic Map and QTL Mapping
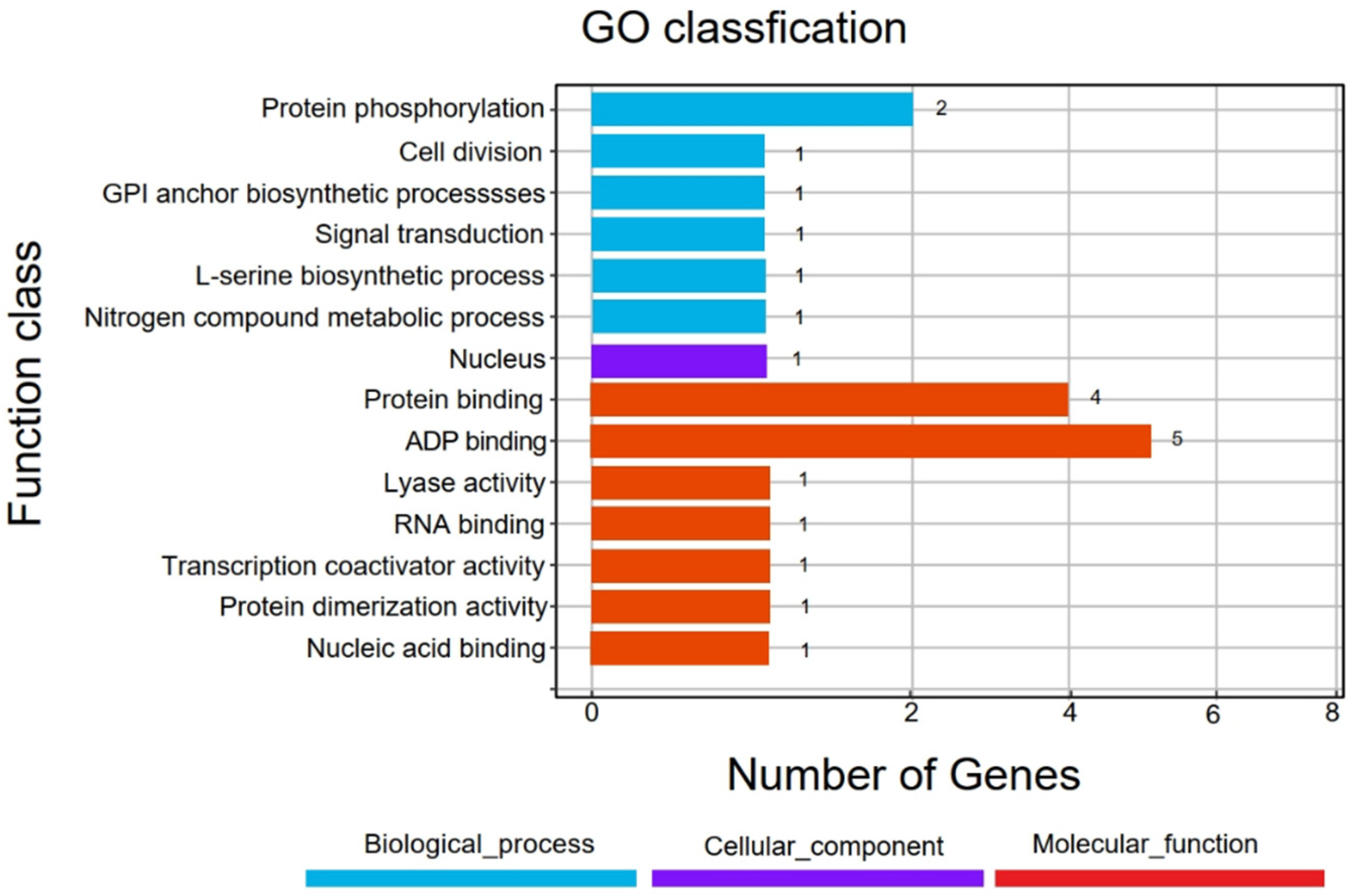
3.4. Identification of Candidate Genes in Final Association Regions
3.5. Expression Profile Analysis of the Candidate Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, T.; Ashizawa, T.; Sonoda, R.; Tanaka, C. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., com. nov., teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens, the causal agent of rice false smut. Mycotaxon 2008, 106, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, S.H. Rice Disease; CAB/CMI: Surrey, UK, 1985; pp. 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.I.; Izumiyama, N. Lupiosis in rice caused by ustiloxin and crude extract of fungal culture of Ustilaginoidea virens. Proc. Jpn. Assoc. Mycotoxicol. 1992, 35, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kois, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Ustiloxins, new antimitotic cycli peptides: Interaction with porcine brain tublin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.J.; Sun, W.B.; Wang, X.H.; Fu, X.X.; Sun, W.X.; Zhou, L.G. Purification of ustiloxins A and B from rice false smut balls by macroporous resins. Molecules 2013, 18, 8181–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y. Identification of rice resistance to RFS, management and prospection of RFS. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, J.; Pan, X.; Yu, M.; Du, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, R.; Song, T.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y. Characterization of propiconazole field-resistant isolates of Ustilaginoidea virens. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 153, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Xue, Q.Z.; Luo, L.J.; Li, Z.K. Preliminary report on quantitative trait loci mapping of false smut resistance using near-isogenic introgression lines in rice. Acta Agric. Zhejiang 2002, 14, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.L. Genetic analysis of rice false smut resistance using mixed major genes and polygenes inheritance model. Acta Agron. Sin. 2008, 34, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andargie, M.; Li, L.; Feng, A.; Zhu, X.; Li, J. Mapping of the quantitative trait locus (QTL) conferring resistance to rice false smut disease. Curr. Plant Biol. 2018, 15, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Meng, S.; Shi, H.; Shen, X.; Kou, Y. A candidate gene for the determination of rice resistant to rice false smut. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Huang, F.; Sheng, H.; Sun, W. Mapping quantitative trait loci for disease resistance to false smut of rice. Phytopathol. Res. 2020, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Yuan, Z.; Fan, F.; Dan, D.; Pan, G.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Li, S. Genome-wide association analysis of resistance to rice false smut. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, S.S.; Bhatia, D.; Jain, J.; Hunjan, M.S.; Kaur, R.; Zaidi, N.W.; Singh, U.S.; Zhou, B.; Lore, J.S. Identification of potential donors and QTLs for resistance to false smut in a subset of rice diversity panel. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 159, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, K.; Kumar, K.; Kaur, A.; Kishore, A.; Kaur, P.; Babbar, A.; Kaur, G.; Kamboj, I.; Lore, J.S.; Vikal, Y.; et al. High-resolution mapping of the quantitative trait locus (QTLs) conferring resistance to false smut disease in rice. J. Appl. Genet. 2022, 63, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Cai, K.X.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, R.Y.; Xie, H.G.; Shou, J.Y.; Fu, J.R.; Li, G.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Wu, S.Q.; et al. Identification and fine-mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring rice false smut resistance in rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2023, 4, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Mackon, E.; Mackon, G.C.J.D.E.; Zhao, Y.T.; Li, Q.F.; Dai, X.G.; Yao, Y.H.; Xia, X.Z.; Nong, B.X.; Liu, P.Q. Combined Analysis of BSA-Seq Based Mapping, RNA-Seq, and metabolomic unraveled candidate genes associated with panicle grain number in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biomolecules 2022, 12, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, X.B.; Yan, D.; Yu, W.J.; Miao, Y.F.; Xu, B. Conjunctive analyses of BSA-Seq and BSR-seq unveil the Msb-GAL and MsJMT as key candidate genes for cytoplasmic male sterility in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Luo, J.J.; Liang, Y.T.; Cai, Z.Q. QTLs mapping of rice grain aging tolerance based on BSA-seq. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023, 21, 5337–5347. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, G.; LaPlant, K.E.; Mazourek, M.; Gore, M.A.; Smart, C.D. A combined BSA-Seq and linkage mapping approach identifies genomic regions associated with Phytophthora root and crown rot resistance in squash. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, N.J.; Beissinger, T.; Hirsch, C.N.; Vaillancourt, B.; Deshpande, S.; Barry, K.; Buell, C.R.; Kaeppler, S.M.; de Leon, N. Shared genomic regions between derivatives of a large segregating population of maize identified using bulked segregant analysis sequencing and traditional linkage analysis. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelmore, R.W.; Paran, I.; Kesseli, R.V. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9828–9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.T.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Lu, D.H. Evaluation and screening of rice germplasm resources resistant to rice false smut. J. South. Agric. 2022, 53, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.T.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.Y.; Lu, D.H. Diversity analysis of the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in Southwest China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Yao, X.; Zhu, L.; Hou, Q. Identification and Molecular Mapping of a Gummy Stem Blight Resistance Gene in Wild Watermelon (Citrullus amarus) Germplasm PI 189225. Plant Dis. 2019, 104, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from next generation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.T.; Demarest, B.L.; Bisgrove, B.W.; Gorsi, B.; Su, Y.C.; Yost, H.J. MMAPPR: Mutation mapping analysis pipeline for pooled RNA-seq. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.E.; Sa, J.K.; Lee, J.K. Bulk segregant analysis identifies SSR markers associated with leaf-and seed-related traits in Perilla crop (Perilla frutescens L.). Genes. Genom. 2021, 43, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, J.K. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Jang, Y.H.; Farooq, M.; Park, J.R.; Kim, E.G.; Du, X.X.; Jan, R.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.I.; Lee, G.S.; et al. Identification of a Major QTL and validation of related genes for tiller angle in rice based on QTL Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCough, S.R.; Doerge, R.W. QTL mapping in rice. Trends Genet. 1995, 11, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Fan, J.; Fang, A.; Li, Y.; Tariqjaveed, M.; Li, D.; Hu, D.; Wang, W.M. Ustilaginoidea virens: Insights into an emerging rice pathogen. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Guo, X.R.; Yan, J.W.; Tian, D.G.; Li, G.; Wang, F. BSA-Seq identification of blast-resistance genes in Gufeng B rice. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 6, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- van Ooijen, G.; Mayr, G.; Kasiem, M.M.; Albrecht, M.; Cornelissen, B.J.; Takken, F.L. Structure–function analysis of the NB-ARC domain of plant disease resistance proteins. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.F.C.; Hughes, R.K.; Banfield, M.J. Structural and biochemical studies of an NB-ARC domain from a plant NLR immune receptor. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhwal, M.K.; Li, P.C.; Lam, I.; Wang, X.U.; Cloutier, S.; You, F.M. Disease resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19248–19290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillet, C.; Travella, S.; Stein, N.; Albar, L.; Nublat, A.; Keller, B. Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15253–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Lin, F.; Dong, Z.Q.; He, X.Y.; Yuan, B.; Zeng, X.S.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q.H. The isolation and characterization of Pik, a rice blast resistance gene which emerged after rice domestication. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Lin, F.; Pan, Q. Characterization of rice blast resistance genes in the Pik cluster and fine mapping of the Pik-p locus. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornero, P.; Chao, R.A.; Luthin, W.N.; Goff, S.A.; Dang, J.L. Large-scale structure–function analysis of the arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance protein. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Shahid, M.Q.; Li, R.B.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Ghouri, F.; Liu, X.D. Genome-wide analysis of genetic variations and the detection of rich variants of NBS-LRR encoding genes in common wild rice lines. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2018, 36, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Mapped Rate (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) | Average Depth | Coverage Ratio 1× (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9311 | 49,872,668 | 49,349,016 | 98.25% | 93.95 | 44.43 | 23.3 | 91.13 |
| IR77298-14-1-2::IRGC117374-1 | 52,778,094 | 50,273,734 | 98.45% | 94.05 | 44.81 | 22.64 | 95.57 |
| R-pool | 79,854,494 | 79,044,776 | 98.52% | 93.59 | 44.9 | 23.37 | 97.21 |
| S-pool | 75,774,592 | 75,139,598 | 98.52% | 93.96 | 44.63 | 25.19 | 90.84 |
| Total | 258,279,848 | 253,807,124 |
| Sample | Total SNPs | HET | HOM_ALT | Het Rate | Ts | Tv | Ts/Tv |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9311 | 2,954,310 | 583,954 | 2,370,356 | 19.77% | 2,184,841 | 903,425 | 2.4184 |
| IR77298-14-1-2::IRGC117374-1 | 2,913,481 | 614,673 | 2,298,808 | 21.10% | 2,156,436 | 893,710 | 2.4129 |
| R-pool | 3,482,716 | 2,355,884 | 1,126,832 | 67.65% | 2,637,543 | 1,098,054 | 2.402 |
| S-pool | 3,504,278 | 1,960,376 | 1,543,902 | 55.94% | 2,699,874 | 1,121,715 | 2.4069 |
| Sample | Total Indels | HET | HOM_ALT | Insertions | Deletions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9311 | 462,940 | 66,304 | 396,636 | 227,374 | 257,169 |
| IR77298-14-1-2::IRGC117374-1 | 454,802 | 71,566 | 383,236 | 222,583 | 252,521 |
| R-pool | 542,475 | 360,446 | 182,029 | 276,475 | 316,251 |
| S-pool | 543,968 | 290,830 | 253,138 | 271,429 | 309,933 |
| Chromosome | Start-Position | End-Position | Size (Mb) | Number of Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 (NC_029267.1) | 10,575,821 | 11,148,578 | 0.57 | 26 |
| 12 (NC_029267.1) | 16,557,521 | 19,631,478 | 3.07 | 109 |
| 12 (NC_029267.1) | 21,494,927 | 23,703,456 | 2.21 | 125 |
| 6 (NC_029261.1) | 25,365 | 805,366 | 0.78 | 64 |
| Total | — | — | 6.63 | 324 |
| Gene ID | Protein Length | Gene Product Name | Expression Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os12g30570 | 385 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY13-like, partial | Pre-emergence inflorescence, leaves, anther, pistil |
| LOC_Os12g30590 | 426 | Disease resistance protein RGA2, NB-ARC domain-containing protein, expressed | Leaves, inflorescence, anther, pistil, endosperm, shoots |
| LOC_Os12g30760 | 1056 | Putative disease resistance protein At4g10780, NB-ARC domain-containing protein | Leaves, inflorescence, anther, pistil |
| LOC_Os12g31160 | 936 | Disease resistance protein Pik-2-like, NB-ARC domain-containing protein, expressed | Leaves, inflorescence, anther, pistil |
| LOC_Os12g31200 | 1009 | Disease resistance protein RGA4-like, NB-ARC domain-containing protein, expressed | Leaves, inflorescence, anther, pistil |
| LOC_Os12g31620 | 902 | Disease resistance protein RPM1, NB-ARC domain-containing protein, expressed | Leaves, inflorescence, anther, pistil |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, R.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Lu, D. Conjunctive Analysis of BSA-Seq and SSR Markers Unveil the Candidate Genes for Resistance to Rice False Smut. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010079
Fu R, Zhao L, Chen C, Wang J, Lu D. Conjunctive Analysis of BSA-Seq and SSR Markers Unveil the Candidate Genes for Resistance to Rice False Smut. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Rongtao, Liyu Zhao, Cheng Chen, Jian Wang, and Daihua Lu. 2024. "Conjunctive Analysis of BSA-Seq and SSR Markers Unveil the Candidate Genes for Resistance to Rice False Smut" Biomolecules 14, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010079
APA StyleFu, R., Zhao, L., Chen, C., Wang, J., & Lu, D. (2024). Conjunctive Analysis of BSA-Seq and SSR Markers Unveil the Candidate Genes for Resistance to Rice False Smut. Biomolecules, 14(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010079





