MicroRNA-503 Suppresses Oral Mucosal Fibroblast Differentiation by Regulating RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Grouping and Processing
2.2. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Experiment
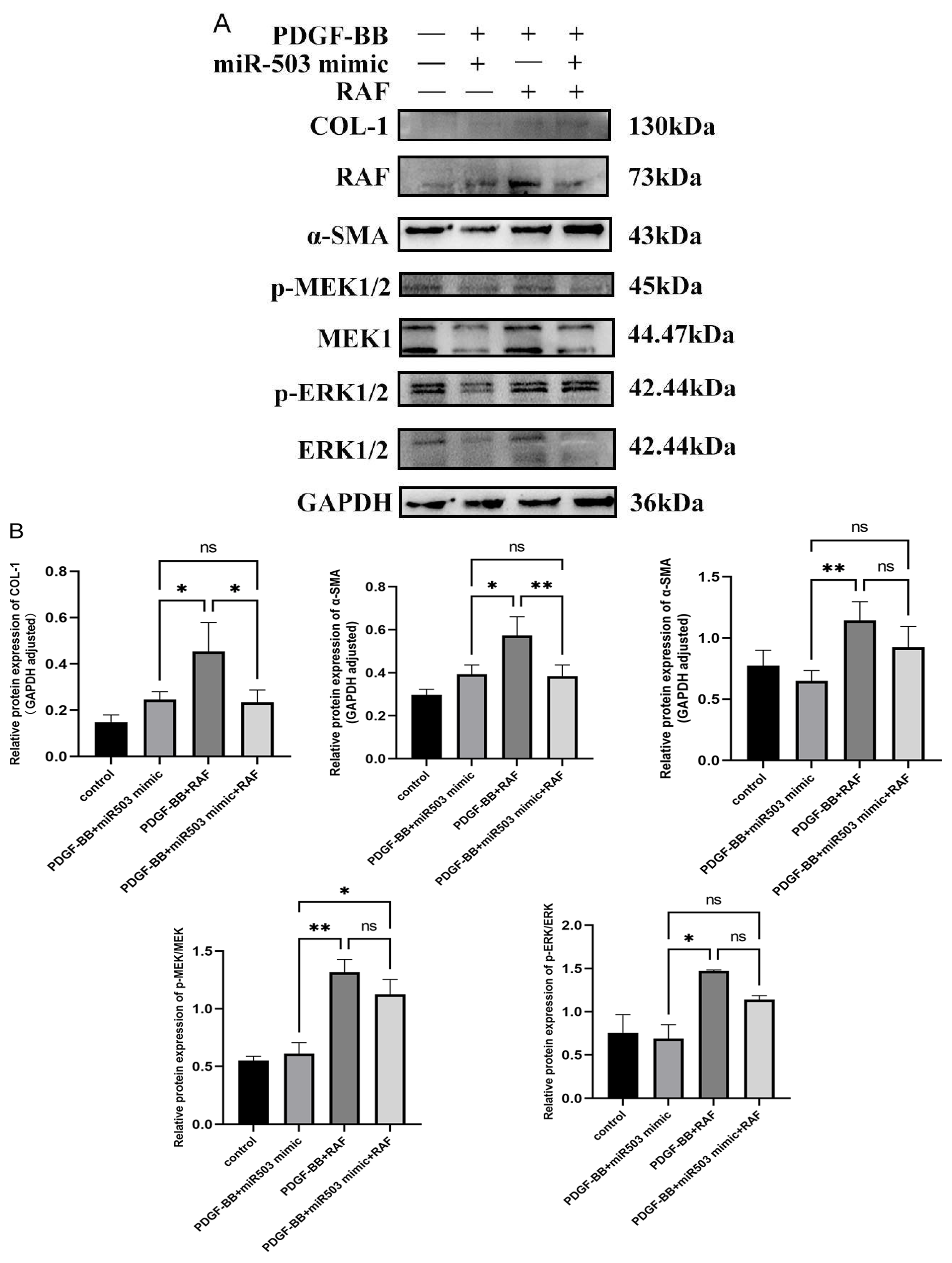
2.3. Western Blot Test
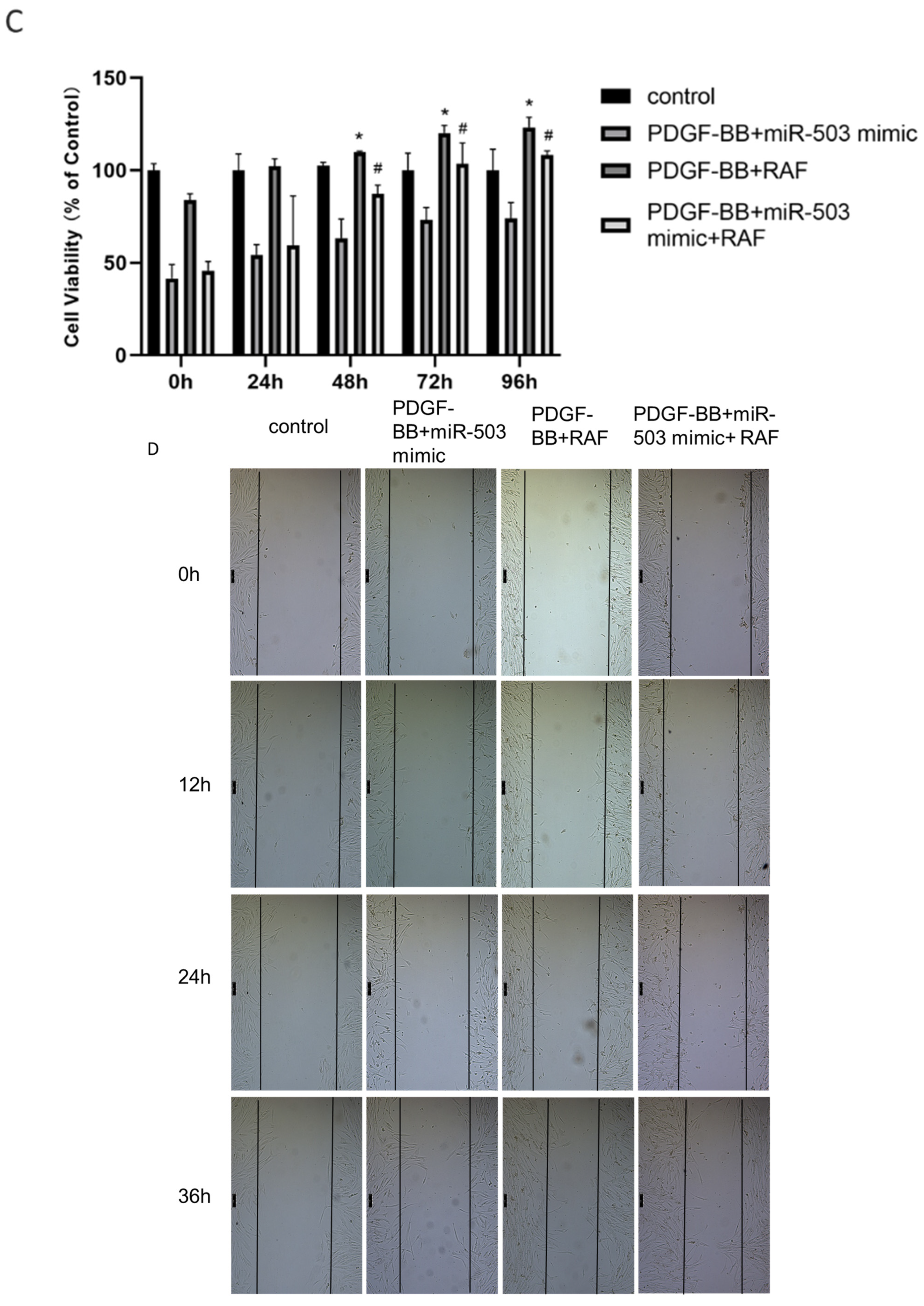
2.4. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
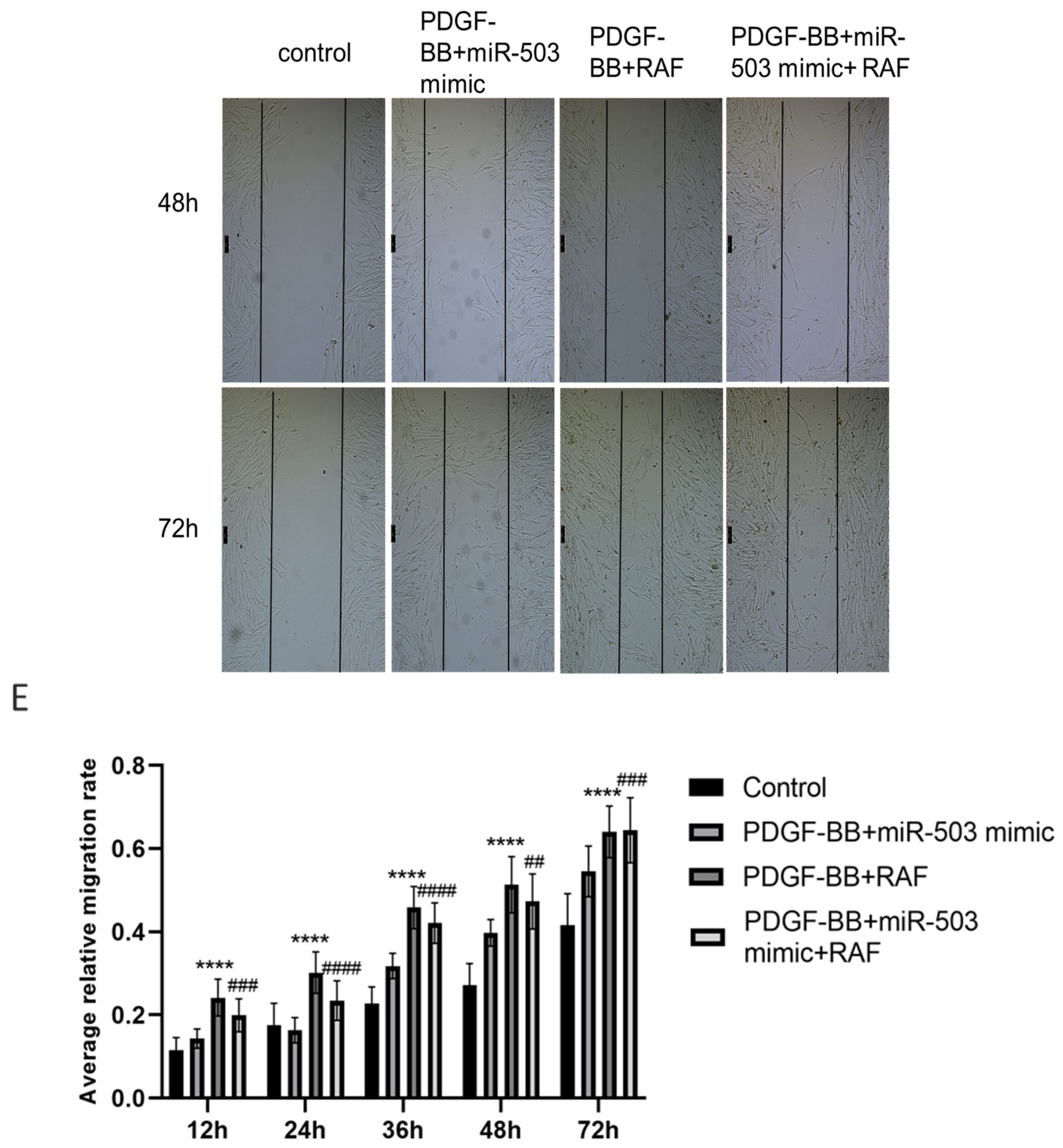
2.5. Cell Scratch Assay
2.6. Double Luciferase Reporter Gene Experiment
2.7. The Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA)
2.8. Other Databases
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PDGF-BB Decreased the Expression of miR-503 in Oral Mucosal Fibroblasts
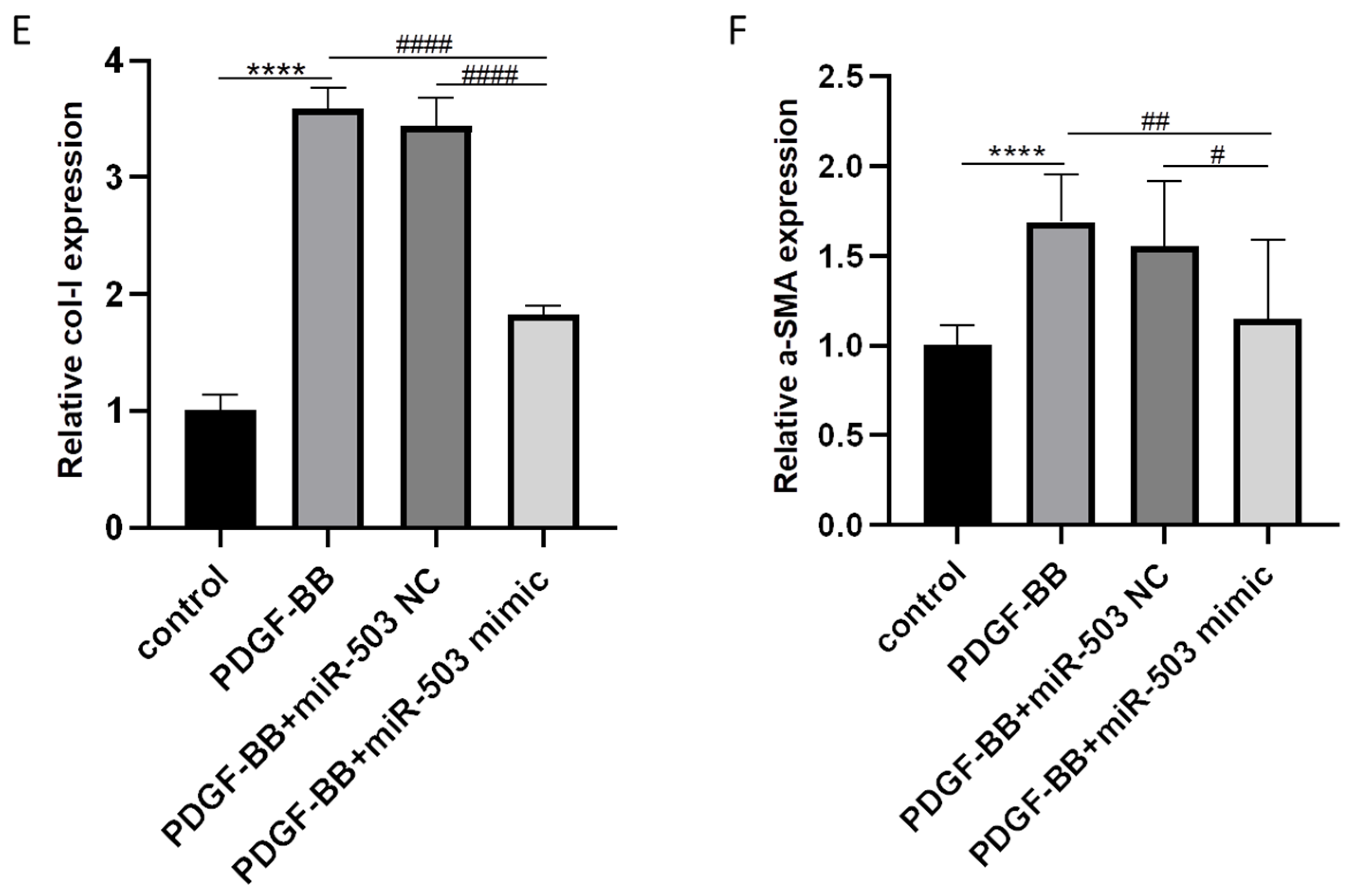
3.2. Overexpression of miR-503 Attenuates the Induction Effect of PDGF-BB on Oral Mucosal Fibroblast Differentiation
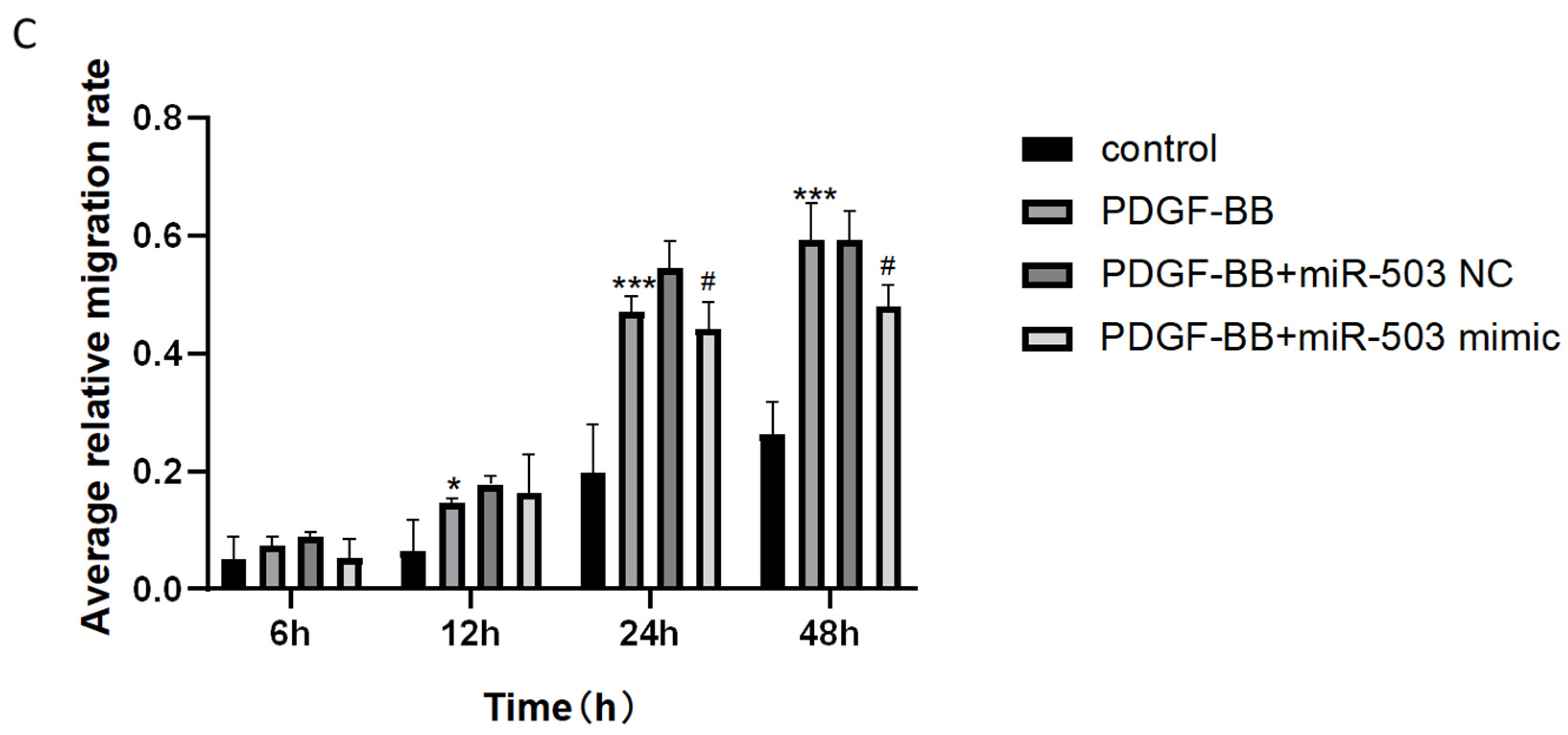
3.3. Overexpression of miR-503 Can Reduce the Proliferation and Migration of Oral Mucosa Fibroblasts Induced by PDGF-BB
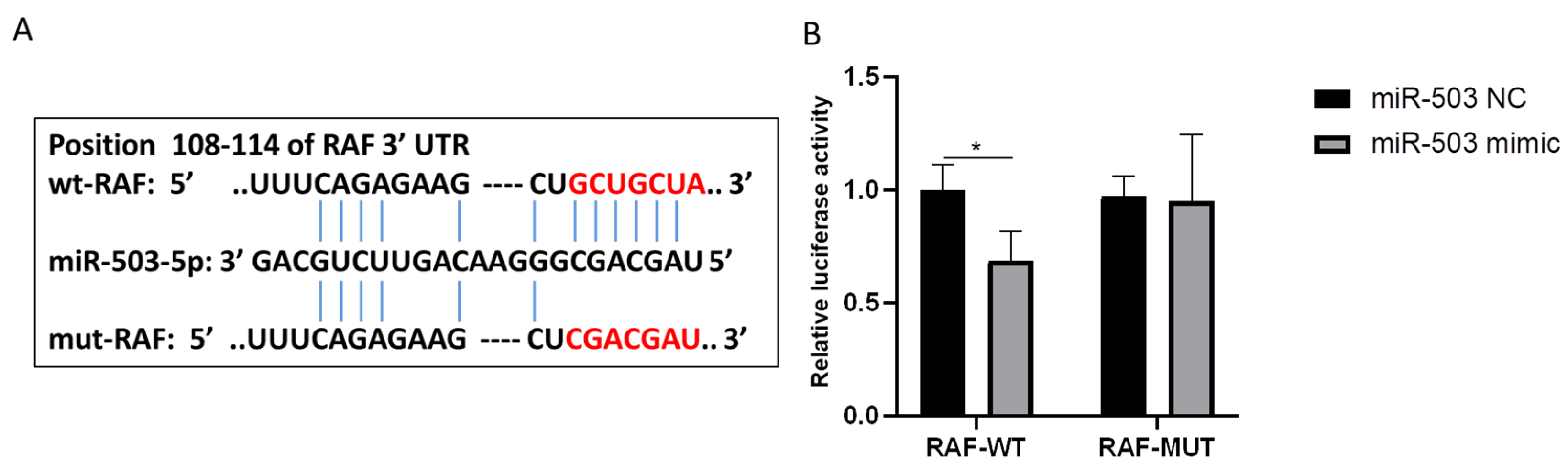
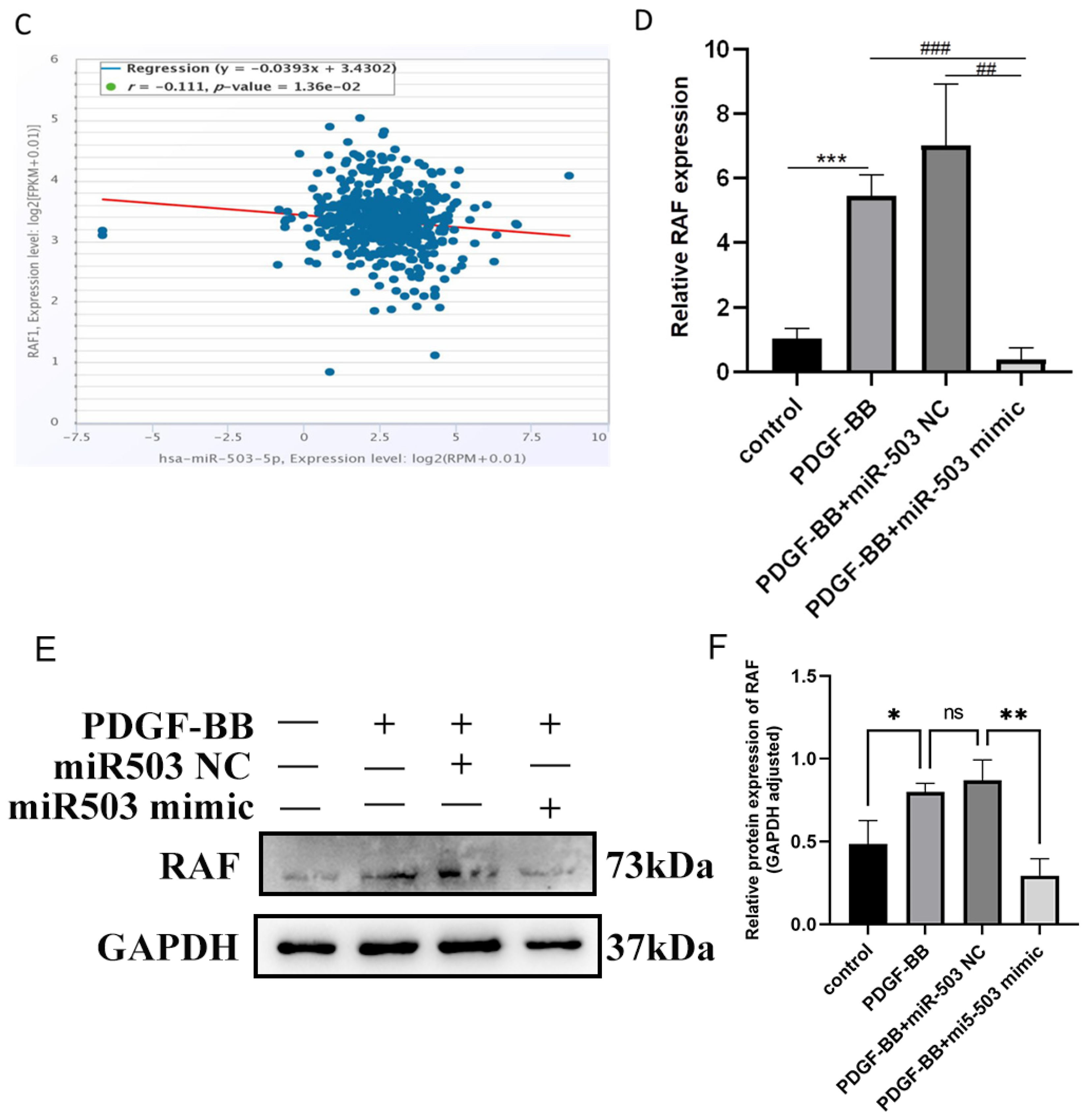
3.4. RAF Is the Direct Target of miR-503 and Can Be Negatively Regulated by IT
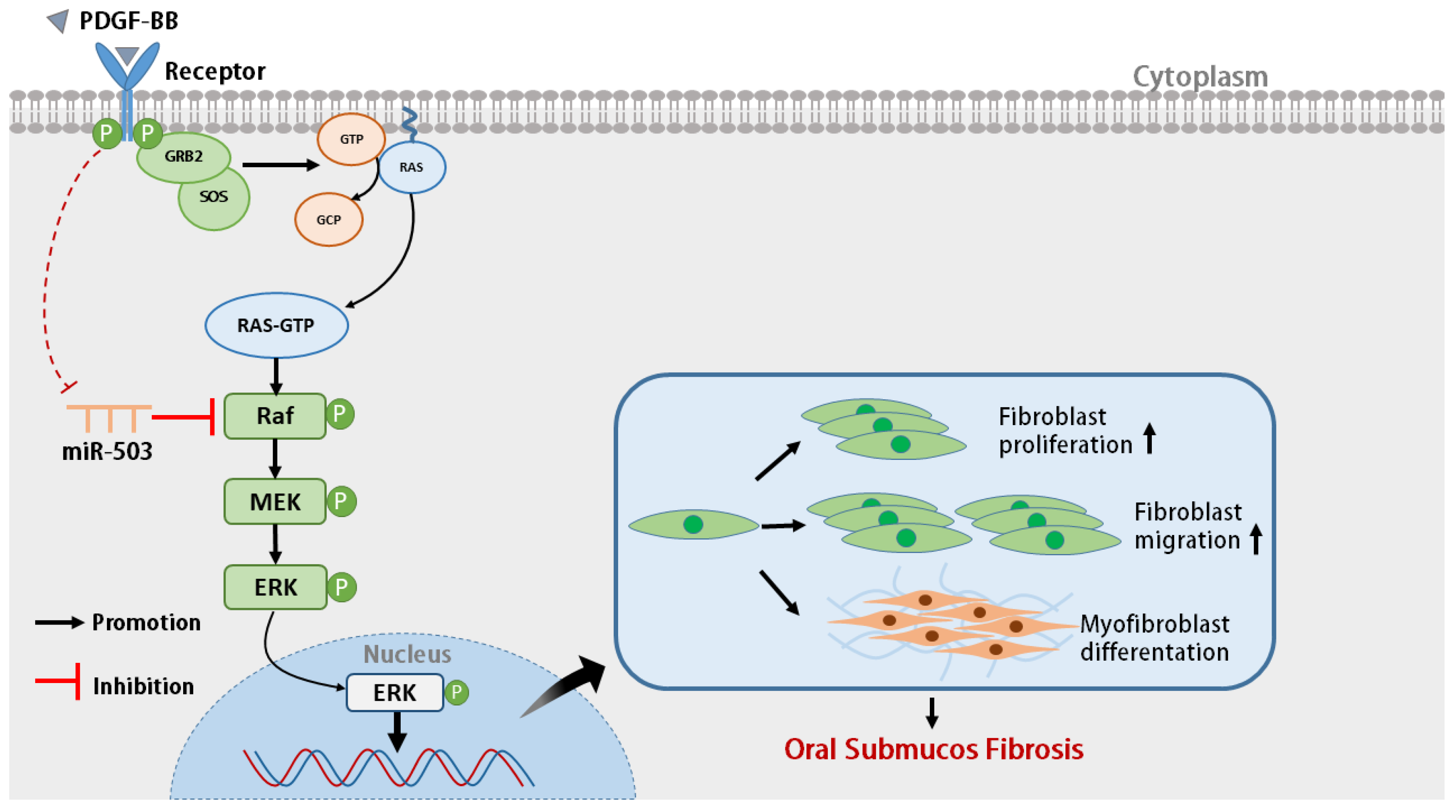
3.5. miR-503 Negatively Regulates the Induction Effect of PDGF-BB on Oral Mucosa FBs through the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pindborg, J.J.; Sirsat, S.M. Oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1966, 22, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Sarode, S.C.; Sarode, G.; Radhakrishnan, R. Areca nut-induced oral fibrosis—Reassessing the biology of oral submucous fibrosis. J. Oral Biosci. 2024, 66, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Tail, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kao, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Chen, C.-H. Malignant transformation in 5071 southern Taiwanese patients with potentially malignant oral mucosal disorders. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardena, B.S.M.S.; Jayawardena, K.L.T.D.; Senarath, N.H.; Tilakaratne, W.M. An Evaluation of Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of Patients with Oral Submucous Fibrosis in the Background of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4154165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Wang, T.-H.; Shieh, T.-M.; Tseng, Y.-H. Oral Submucous Fibrosis: A Review on Etiopathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, A. PDGFs and their receptors. Gene 2017, 614, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, L.; You, J.; Wen, D.; Yang, B.; Jiang, C. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Regulates the Biological Behavior of Oral Mucosal Fibroblasts by Inducing Cell Autophagy and Its Mechanism. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3405–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; You, J.; Gong, D.; Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Jiang, C. PDGF-BB induces conversion, proliferation, migration, and collagen synthesis of oral mucosal fibroblasts through PDGFR-β/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 30, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. Role of miRNAs in lung cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tsitsiou, E.; Herrick, S.E.; Lindsay, M.A. MicroRNAs and the regulation of fibrosis. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jian, X.; Guo, F.; Li, N.; Jiang, C.; Yin, P.; Min, A.-J.; Huang, L. miR-203 inhibits arecoline-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating secreted frizzled-related protein 4 and transmembrane-4 L six family member 1 in oral submucous fibrosis. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2753–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.-Y.; Yu, C.-C.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, P.-L.; Peng, C.-Y.; Liao, Y.-W.; Yu, C.-H.; Lin, K.-H. miR-200c inhibits the arecoline-associated myofibroblastic transdifferentiation in buccal mucosal fibroblasts. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.-Y.; Yu, C.-C.; Liao, Y.-W.; Hsieh, P.-L.; Ohiro, Y.; Chu, P.-M.; Huang, Y.-C.; Yu, C.-H.; Tsai, L.-L. miR-10b regulated by Twist maintains myofibroblasts activities in oral submucous fibrosis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-W.; Yu, C.-C.; Hsieh, P.-L.; Liao, Y.-W.; Chu, P.-M.; Yu, C.-H.; Fang, C.-Y. Arecoline enhances miR-21 to promote buccal mucosal fibroblasts activation. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 120, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, R.; Ding, F.; He, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Mei, J.; Liu, H. miR-503 inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced human aortic vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through targeting the insulin receptor. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wu, Q.; Yao, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Han, R.; Yang, J.; Ji, X.; Ni, C. MiR-503 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting PI3K p85 and is sponged by lncRNA MALAT1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Chellappan, D.K.; Pinto, T.d.J.A.; Hansbro, P.M.; Bebawy, M.; Dua, K. Tumor suppressor role of miR-503. Panminerva Medica 2018, 60, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Dou, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, H.-B. MicroRNA-503 Targets Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 7 Enhancing Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Hepatic Fibrosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 66, 1928–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhao, D.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Lv, L.; Leng, B.; Xu, W.; et al. MicroRNA-503 promotes angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting Apelin-13. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Han, L.; Gui, W.; Wang, F.; Yan, W.; Jiang, H. MiR-503 suppresses fibroblast activation and myofibroblast differentiation by targeting VEGFA and FGFR1 in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14339–14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.; Kaistha, B.P.; Kacik, M.; Stiewe, T.; Hoyer, J. Downregulation of miR-503 in Activated Kidney Fibroblasts Disinhibits KCNN4 in an in Vitro Model of Kidney Fibrosis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromann, P.A.; Korkaya, H.; Webb, C.P.; Miller, J.; Calvin, T.L.; Courtneidge, S.A. Platelet-derived Growth Factor Stimulates Src-dependent mRNA Stabilization of Specific Early Genes in Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10253–10263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, B.; Park, K.-K. Suppression of Hepatic Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Melittin via Blocking of TGFβ/Smad and MAPK-JNK Signaling Pathways. Toxins 2017, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; He, D.; Ling, F.; Chu, T.; Huang, D.; Wu, H.; Ge, J. CD4+ T cells and TGFβ1/MAPK signal pathway involved in the valvular hyperblastosis and fibrosis in patients with rheumatic heart disease. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 114, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019, 366, eaav1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Heikkinen, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Knott, K.E.; Wong, G. miRToolsGallery: A tag-based and rankable microRNA bioinformatics resources database portal. Database 2018, 2018, bay004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Heikkinen, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wong, G. Trends in the development of miRNA bioinformatics tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 20, 1836–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein–RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, H.; Tilakaratne, W.M.; Oshiro, K.; Maruyama, S.; Suzuki, M.; Ida-Yonemochi, H.; Cheng, J.; Saku, T. Extracellular matrix remodeling in oral submucous fibrosis: Its stage-specific modes revealed by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2005, 34, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Chen, J.; Bei, Y.; Han, B.; Wang, S. Influence of borneol on primary mice oral fibroblasts: A penetration enhancer may be used in oral submucous fibrosis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2009, 38, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutasim, K.A.; Jenei, V.; Sapienza, K.; Marsh, D.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Lewis, M.P.; Marshall, J.F.; Fortune, F.; Tilakaratne, W.M.; et al. Betel-derived alkaloid up-regulates keratinocyte alphavbeta6 integrin expression and promotes oral submucous fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2010, 223, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, L.A.; Boucher, S.; Ricupero, C.L.; Fenstermacher, S.; Swerdel, M.; Chase, L.G.; Adams, C.C.; Chesnut, J.; Lakshmipathy, U.; Hart, R.P. Differentiating human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells regulate microRNAs: Prediction of microRNA regulation by PDGF during osteogenesis. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1354–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.M.; Frost, R.J.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNAs Add a New Dimension to Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2010, 121, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-J.; Yang, J.; Lin, J.; Yao, N.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, J.Q.; Lin, J.-Y.; Ma, X. Identification of miRNAs associated with tumorigenesis of retinoblastoma by miRNA microarray analysis. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2008, 25, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, M. MiR-503 targets PI3K p85 and IKK-β and suppresses progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, H.; Xu, L.; Huo, Y.; Yin, L. MicroRNA-503 suppresses proliferation and cell-cycle progression of endometrioid endometrial cancer by negatively regulating cyclin D1. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3768–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Ma, R.; Si, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Tu, X.; Wang, Q. MicroRNA-503 targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, B.-J.; Chen, Z.-G.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Q. Effect of miR-503 Down-Regulation on Growth and Invasion of Esophagus Carcinoma and Related Immune Function. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3564–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Dey, B.K.; Dutta, A. MiR-322/424 and -503 are induced during muscle differentiation and promote cell cycle qui-escence and differentiation by down-regulation of Cdc25A. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-M.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Fan, K.-H.; Tsai, C.-N.; Huang, S.-F.; Kang, C.-J.; et al. Oncogenic Function and Early Detection Potential of miRNA-10b in Oral Cancer as Identified by microRNA Profiling. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, S.A.I.Z.; Paterson, I.C.; Hunt, S.; Lambert, D.W.; Higginbotham, S.; Pink, R.C. Myofibroblast transdifferentiation is associated with changes in cellular and extracellular vesicle miRNA abundance. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.-J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.L.; Shi, Y.; Le, G.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Q. 24-Week Exposure to Oxidized Tyrosine Induces Hepatic Fibrosis Involving Activation of the MAPK/TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Sprague-Dawley Rats Model. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2016, 3123294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Kim, J.M.; Nam, S.Y.; Yang, K.H.; Jeong, M.; Kim, H.S.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, C.S.; Jin, Y.W.; Kim, J. Low-dose of ionizing radiation enhances cell proliferation via transient ERK1/2 and p38 activation in normal human lung fibroblasts. J. Radiat. Res. 2007, 48, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.-Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Zhang, H.-H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Fang, J.; Yu, C.-H. PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7879–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Ma, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.M.; Chen, P.; Yan, J.B.; Li, Q.; Li, D.D.; Yang, F. AcSDKP attenuates PDGF-induced cardiac fibroblasts proliferation and collagen expression: Role of extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2 pathway. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2008, 36, 444–448. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| U6-F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6-R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| hsa-miR-503-F | TGCCCTAGCAGCGGGAAC |
| hsa-miR-503-R | ACCCTGGCAGCGGAAACAATA |
| GAPDH-F | CATGGGTGTGAACCATGAGAA |
| GAPDH-R | GGTCATGAGTCCTTCCACGAT |
| Col-I-F | GTGCGATGACGTGATCTGTGA |
| Col-I-R | CGGTGGTTTCTTGGTCGGT |
| α-SMA-F | TGCCAACAACGTCATGTCG |
| α-SMA-R | CAGCGCGGTGATCTCTTTCT |
| RAF1-F | AAAGTACGACTCCCTATCCGAC |
| RAF1-R | GGTTGGTGGTTTCGATGGACT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jian, N.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-503 Suppresses Oral Mucosal Fibroblast Differentiation by Regulating RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14101259
Wen D, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Jian N, Jiang C, Wang J. MicroRNA-503 Suppresses Oral Mucosal Fibroblast Differentiation by Regulating RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(10):1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14101259
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Dada, Huamin Zhang, Yutong Zhou, Ni Jian, Canhua Jiang, and Jie Wang. 2024. "MicroRNA-503 Suppresses Oral Mucosal Fibroblast Differentiation by Regulating RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway" Biomolecules 14, no. 10: 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14101259
APA StyleWen, D., Zhang, H., Zhou, Y., Jian, N., Jiang, C., & Wang, J. (2024). MicroRNA-503 Suppresses Oral Mucosal Fibroblast Differentiation by Regulating RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules, 14(10), 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14101259








