O-GlcNAcylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase Regulates Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Proliferation via the FAK/AKT Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Cell Lines
2.3. Expression Plasmids and Transfection
2.4. Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation
2.5. FAK Purification and MS Analysis of FAK O-GlcNAcylation Sites
2.6. Cell Adhesion Assay
2.7. Wound Healing Assay
2.8. Cell Proliferation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
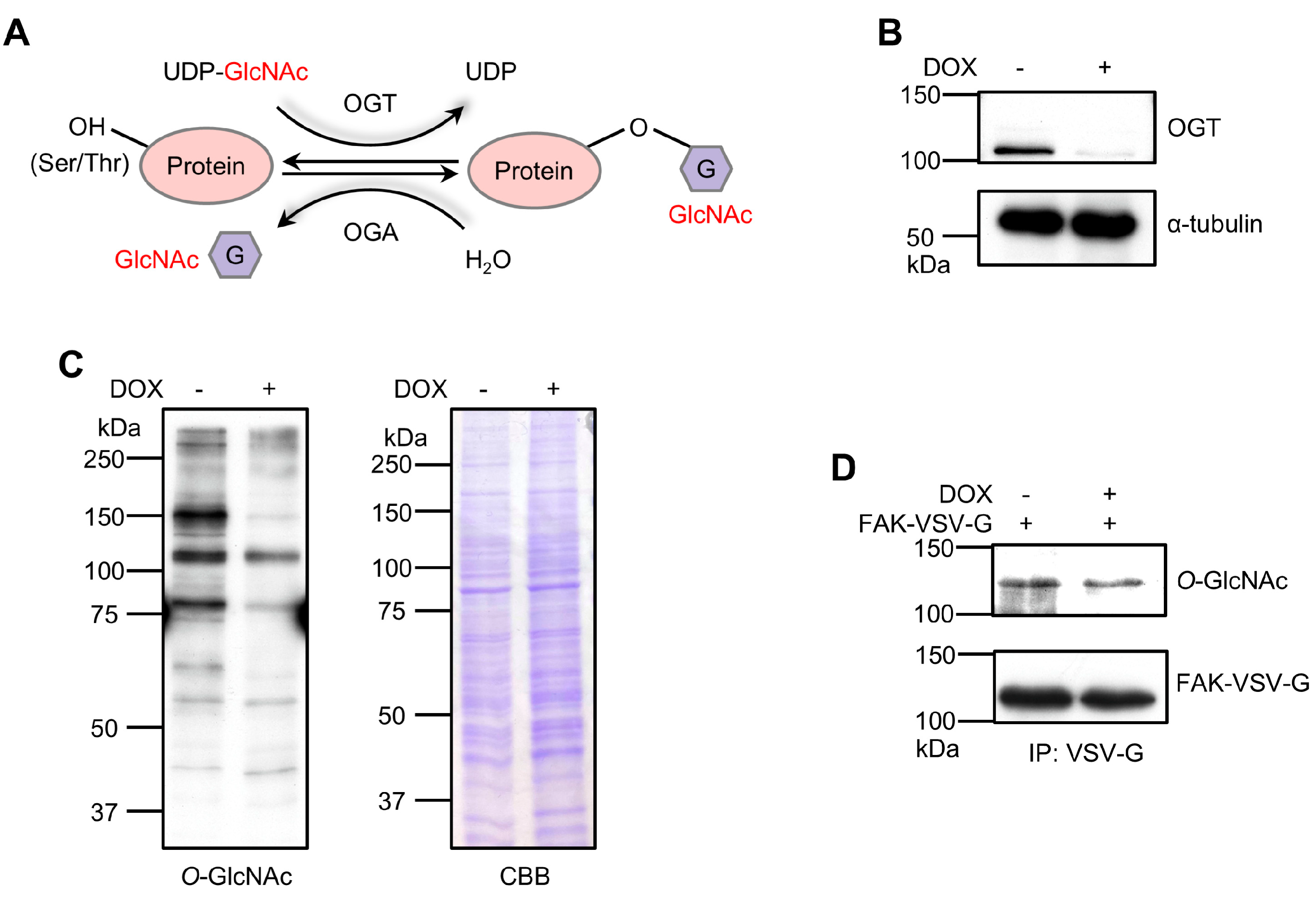
3.1. OGT KD Reduces FAK O-GlcNAcylation in 293T Cells
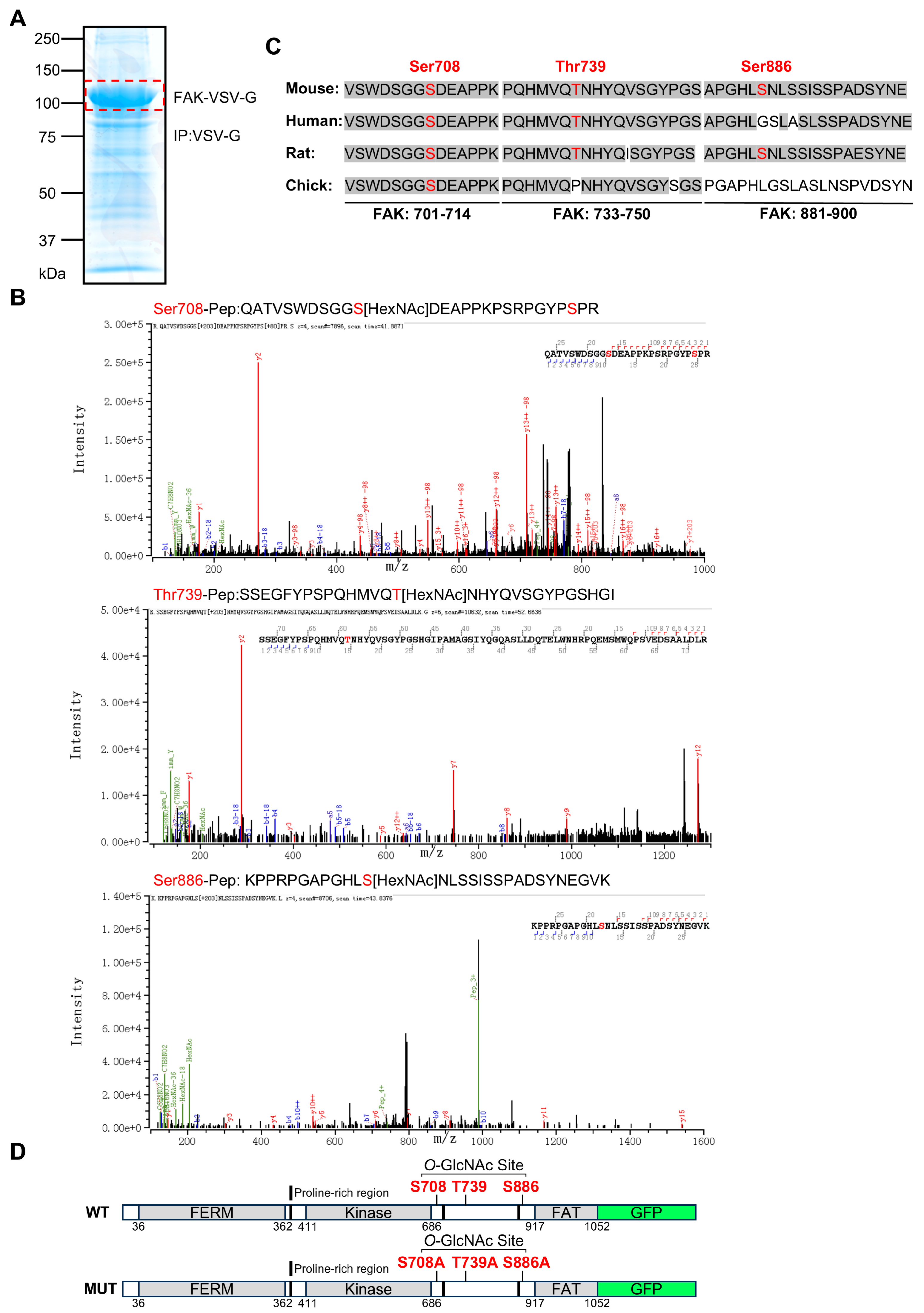
3.2. Identification of Specific O-GlcNAcylation Sites on FAK and Construction of Mutant
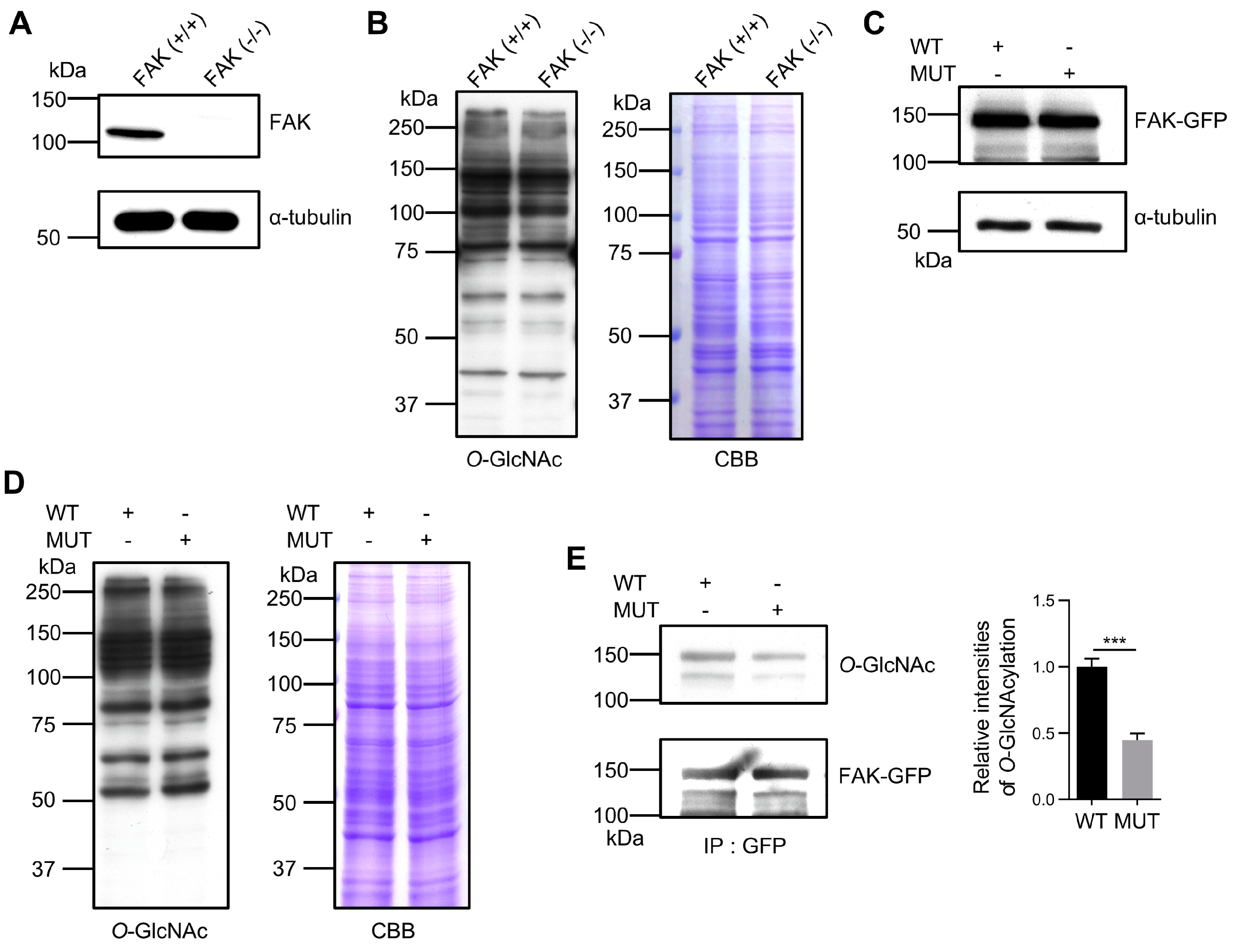
3.3. Confirming the Importance of O-GlcNAcylation Sites in FAK
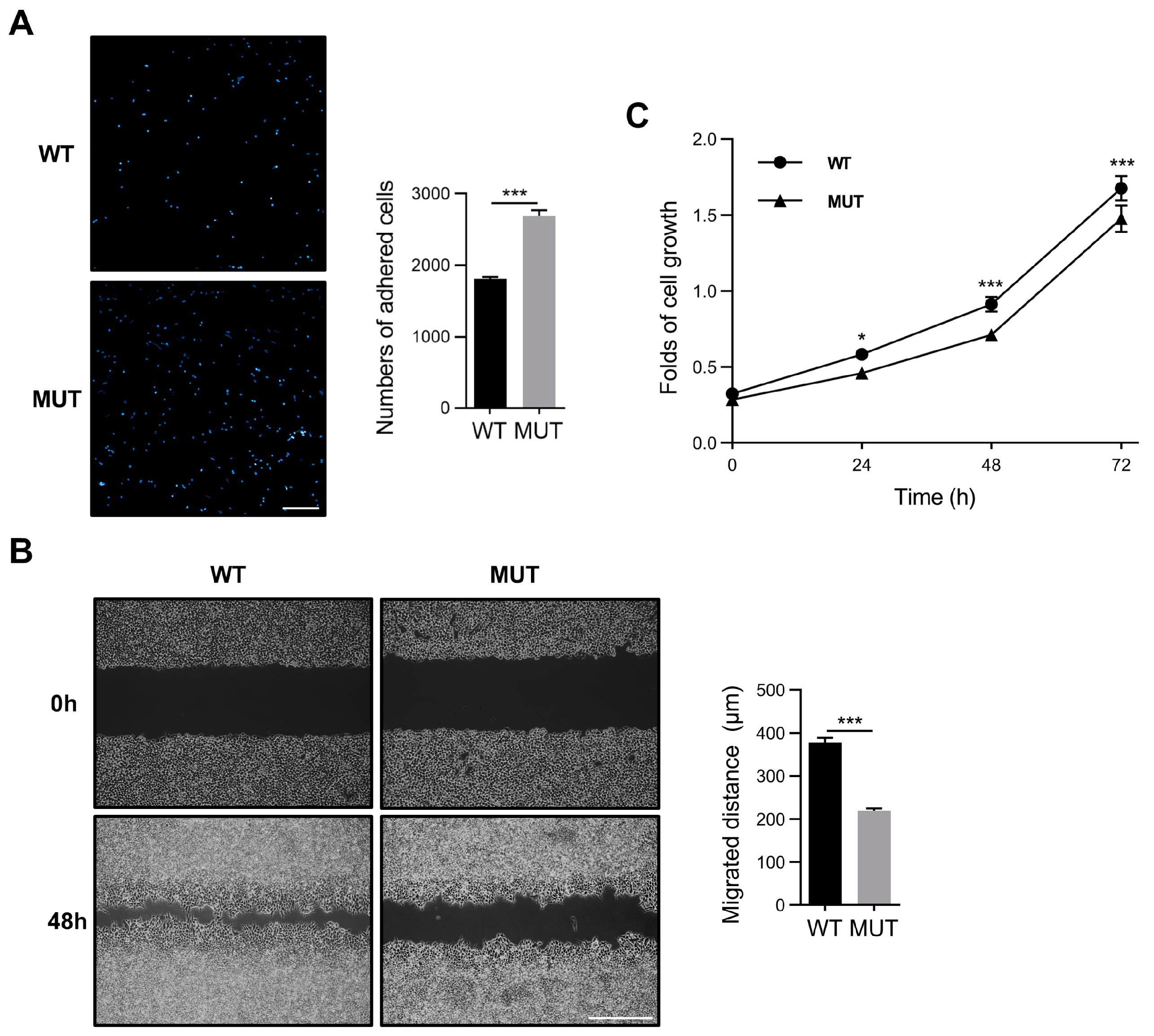
3.4. FAK O-GlcNAcylation Modulates Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Proliferation
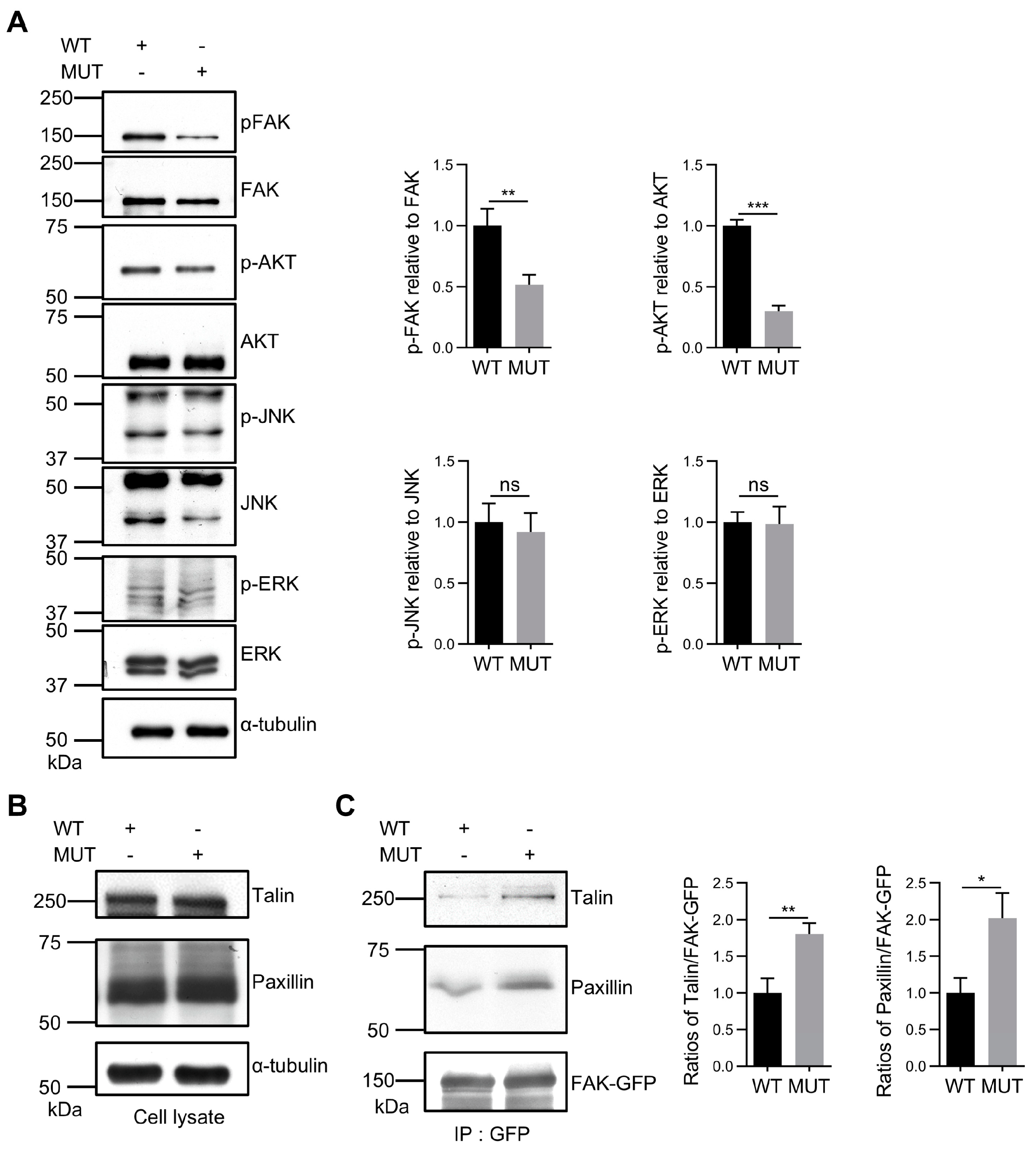
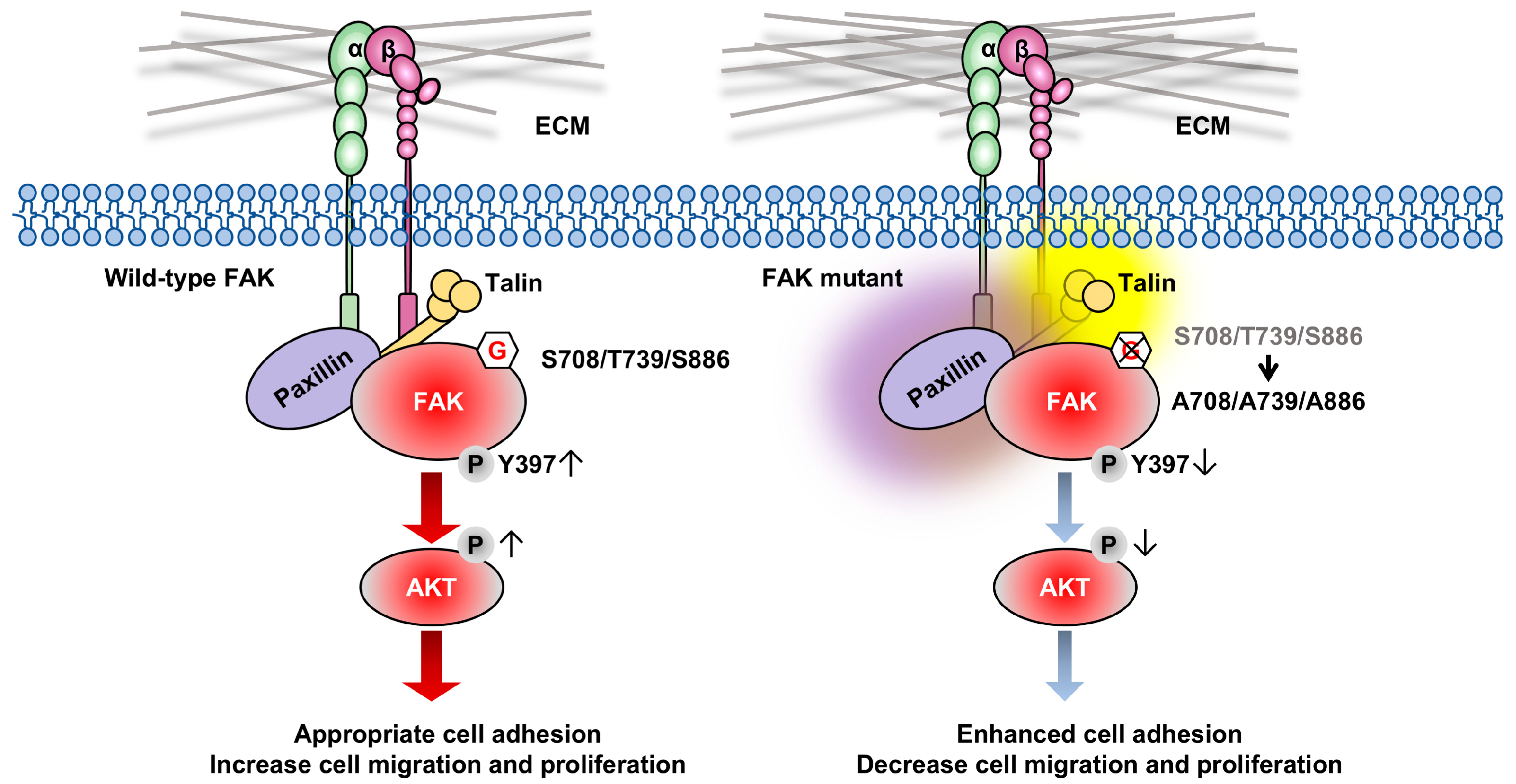
3.5. FAK O-GlcNAcylation Affects Tyr397 Phosphorylation and FA Complex Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanchanawong, P.; Calderwood, D.A. Organization, dynamics and mechanoregulation of integrin-mediated cell-ECM adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2023, 24, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: A family of cell surface receptors. Cell 1987, 48, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, L.; Desgrosellier, J.S.; Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins and cancer: Regulators of cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Salgado, E.G.; Lizano, S.; Sarkar, S.; Brugge, J.S.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Shattil, S.J. Src kinase activation by direct interaction with the integrin beta cytoplasmic domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13298–13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.K.; Hanson, D.A.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, D.J.; Hauck, C.R.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Required role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) for integrin-stimulated cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 2677–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, D.J.; Hauck, C.R.; Ilic, D.; Klingbeil, C.K.; Schaefer, E.; Damsky, C.H.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilghman, R.W.; Slack-Davis, J.K.; Sergina, N.; Martin, K.H.; Iwanicki, M.; Hershey, E.D.; Beggs, H.E.; Reichardt, L.F.; Parsons, J.T. Focal adhesion kinase is required for the spatial organization of the leading edge in migrating cells. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, D.A.; Mitra, S.K.; Hauck, C.R.; Streblow, D.N.; Nelson, J.A.; Ilic, D.; Huang, S.; Li, E.; Nemerow, G.R.; Leng, J.; et al. Differential regulation of cell motility and invasion by FAK. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, D.; Furuta, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Takeda, N.; Sobue, K.; Nakatsuji, N.; Nomura, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Okada, M.; Yamamoto, T. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 377, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiske, H.R.; Kao, S.C.; Cary, L.A.; Guan, J.L.; Lai, J.F.; Chen, H.C. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in focal adhesion kinase-promoted cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12361–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, M.; Stewart, J.E.; Golemis, E.A.; Pugacheva, E.N.; Alexandropoulos, K.; Cox, B.D.; Wang, W.; Grammer, J.R.; Gladson, C.L. HEF1 is a necessary and specific downstream effector of FAK that promotes the migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Tamura, M.; Pankov, R.; Danen, E.H.; Takino, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamada, K.M. Shc and FAK differentially regulate cell motility and directionality modulated by PTEN. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuyama, K.; Doi, R.; Mori, T.; Toyoda, E.; Ito, D.; Kami, K.; Koizumi, M.; Kida, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Fujimoto, K. Clinical significance of focal adhesion kinase in resectable pancreatic cancer. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lark, A.L.; Livasy, C.A.; Calvo, B.; Caskey, L.; Moore, D.T.; Yang, X.; Cance, W.G. Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in primary colorectal carcinomas and colorectal liver metastases: Immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR analyses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, L.; Hauck, W.; Aprikian, A.G.; Begin, L.R.; Chapdelaine, A.; Chevalier, S. Focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK) expression, activation and association with paxillin and p50CSK in human metastatic prostate carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 68, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lark, A.L.; Livasy, C.A.; Dressler, L.; Moore, D.T.; Millikan, R.C.; Geradts, J.; Iacocca, M.; Cowan, D.; Little, D.; Craven, R.J.; et al. High focal adhesion kinase expression in invasive breast carcinomas is associated with an aggressive phenotype. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, S.; Zadra, G.; Vaira, V.; Falleni, M.; Bottiglieri, L.; Nosotti, M.; Di Giulio, A.M.; Gorio, A.; Bosari, S. Up-regulation of focal adhesion kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 53, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, S.; Chen, H.; Callison, C.; Gonzalez, A.L.; Massion, P.P. Expression of focal adhesion kinase in small-cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2012, 118, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Koshikawa, K.; Nomoto, S.; Okochi, O.; Kaneko, T.; Inoue, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Takeda, S.; Nakao, A. Focal adhesion kinase is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and can be served as an independent prognostic factor. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.C.; Serrels, A.; Stupack, D.G.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Frame, M.C. Targeting FAK in anticancer combination therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, G.W.; Carragher, N.O.; Avizienyte, E.; Evans, J.; Brunton, V.G.; Frame, M.C. The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—A new therapeutic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, R.C.; Chang, J.M.; Chen, J.H.; Huang, W.R.; Tang, Y.A.; Kuo, I.Y.; Yan, J.J.; Lai, W.W.; Wang, Y.C. Deregulation of SLIT2-mediated Cdc42 activity is associated with esophageal cancer metastasis and poor prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.R.; Sieg, D.J.; Hsia, D.A.; Loftus, J.C.; Gaarde, W.A.; Monia, B.P.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase expression or activity disrupts epidermal growth factor-stimulated signaling promoting the migration of invasive human carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7079–7090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lechertier, T.; Hodivala-Dilke, K. Focal adhesion kinase and tumour angiogenesis. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarra-Niecko, V.; Schaller, M.D.; Dunty, J.M. FAK regulates biological processes important for the pathogenesis of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, J.R.; Camidge, D.R.; Mileshkin, L.R.; Chen, E.X.; Hicks, R.J.; Rischin, D.; Fingert, H.; Pierce, K.J.; Xu, H.; Roberts, W.G.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic phase I dose-escalation trial of PF-00562271, an inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.; Soria, J.C.; Blagden, S.P.; Plummer, R.; Fleming, R.A.; Nebot, N.; Zhang, J.; Mazumdar, J.; Rogan, D.; Gazzah, A.; et al. A phase Ib dose-finding, pharmacokinetic study of the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor GSK2256098 and trametinib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reily, C.; Stewart, T.J.; Renfrow, M.B.; Novak, J. Glycosylation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, C.; Song, W.; Li, M.; Shao, X.; Fukuda, T.; Gu, J.; Taniguchi, N.; Li, W. Core fucosylation regulates the ovarian response via FSH receptor during follicular development. J. Adv. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schjoldager, K.T.; Narimatsu, Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Clausen, H. Global view of human protein glycosylation pathways and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 21, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatham, J.C.; Zhang, J.; Wende, A.R. Role of O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Protein Modification in Cellular (Patho)Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 427–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, G.W.; Housley, M.P.; Slawson, C. Cycling of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins. Nature 2007, 446, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qian, K. Protein O-GlcNAcylation: Emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 18, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinidad, J.; Barkan, D.; Gulledge, B.; Thalhammer, A.; Sali, A.; Schoepfer, R.; Burlingame, A. Global identification and characterization of both O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation at the murine synapse. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gucek, M.; Hart, G.W. Cross-talk between GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: Site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in response to globally elevated O-GlcNAc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13793–13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Chalkley, R.; Vosseller, K. Hyper-O-GlcNAcylation activates nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kappaB) signaling through interplay with phosphorylation and acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 9150–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawson, C.; Hart, G.W. O-GlcNAc signalling: Implications for cancer cell biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Vosseller, K. Cancer metabolism and elevated O-GlcNAc in oncogenic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34457–34465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Mi, W.; Ge, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, Q.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Han, F.; Lu, X.; Yu, W. GlcNAcylation plays an essential role in breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6344–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, C.M.; Sodi, V.L.; Reginato, M.J. O-GlcNAcylation in Cancer Biology: Linking Metabolism and Signaling. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3282–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenackers, A.; Olivier-Van, S.S.; Baldini, S.; Dehennaut, V.; Toillon, R.; Le, B.X.; El, Y.-B.I.; Lefebvre, T. Silencing the Nucleocytoplasmic O-GlcNAc Transferase Reduces Proliferation, Adhesion, and Migration of Cancer and Fetal Human Colon Cell Lines. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Jin, X.; Jiang, B.; Chen, W.; Ji, Z.; Xu, X.; Tang, M.; Dai, K.; Han, L. Elevated O-GlcNAcylation Promotes Malignant Phenotypes of Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Stabilizing Nrf2 through Regulation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Isaji, T.; Fukuda, T.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J. O-GlcNAcylation regulates integrin-mediated cell adhesion and migration via formation of focal adhesion complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Isaji, T.; Oyama, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Hanamatsu, H.; Yokota, I.; Miura, N.; Furukawa, J.I.; Fukuda, T.; et al. Focal-adhesion kinase regulates the sialylation of N-glycans via the PI4KIIalpha-PI4P pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, M.; Vilardell, C.; Matsumoto, K.; Esparza, J.; Lozano, E.; Serra-Pages, C.; Urbano-Marquez, A.; Yamada, K.M.; Cid, M.C. Dual function of focal adhesion kinase in regulating integrin-induced MMP-2 and MMP-9 release by human T lymphoid cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1875–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, W.; Fang, P.; Cao, W.; Liu, C.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. pGlyco 2.0 enables precision N-glycoproteomics with comprehensive quality control and one-step mass spectrometry for intact glycopeptide identification. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Wirtz, D. Focal adhesion size uniquely predicts cell migration. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hunter, T. Focal adhesion kinase overexpression enhances ras-dependent integrin signaling to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase through interactions with and activation of c-Src. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13189–13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, A.P.; Romer, L.H. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling in focal adhesions decreases cell motility and proliferation. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1209–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.K.; Calalb, M.B.; Harper, M.C.; Patel, S.K. Focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase phosphorylated in response to cell attachment to fibronectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8487–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steentoft, C.; Vakhrushev, S.Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Vester-Christensen, M.B.; Schjoldager, K.T.; Lavrsen, K.; Dabelsteen, S.; Pedersen, N.B.; Marcos-Silva, L.; et al. Precision mapping of the human O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Shen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Chai, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; et al. Increased glucose metabolism in TAMs fuels O-GlcNAcylation of lysosomal Cathepsin B to promote cancer metastasis and chemoresistance. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1207–1222.E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wary, K.K.; Mainiero, F.; Isakoff, S.J.; Marcantonio, E.E.; Giancotti, F.G. The adaptor protein Shc couples a class of integrins to the control of cell cycle progression. Cell 1996, 87, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, B.L.; Turck, C.W.; Escobedo, J.A. Identification of Tyr-397 as the primary site of tyrosine phosphorylation and pp60src association in the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 2819–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legerstee, K.; Houtsmuller, A.B. A Layered View on Focal Adhesions. Biology 2021, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.S.; Baumann, F.; Daday, C.; Redondo, P.; Durner, E.; Jobst, M.A.; Milles, L.F.; Mercadante, D.; Pippig, D.A.; Gaub, H.E.; et al. Structural and mechanistic insights into mechanoactivation of focal adhesion kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6766–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapial Martinez, P.; Lopez Navajas, P.; Lietha, D. FAK Structure and Regulation by Membrane Interactions and Force in Focal Adhesions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Ye, K.; He, J.; Shen, Y.; Cui, S.; Huang, J.; Gu, Y.; Ding, J. Cell migration regulated by RGD nanospacing and enhanced under moderate cell adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 2020, 263, 120327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepat, X.; Chen, Z.; Jacobson, K. Cell migration. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 2369–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C. Focal adhesion: A focal point in current cell biology and molecular medicine. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2007, 1, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidel-Bar, R.; Milo, R.; Kam, Z.; Geiger, B. A paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation switch regulates the assembly and form of cell-matrix adhesions. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Colome, A.M.; Lee-Rivera, I.; Benavides-Hidalgo, R.; Lopez, E. Paxillin: A crossroad in pathological cell migration. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.E. Paxillin and focal adhesion signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, E231–E236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hunter, T. Integrin signalling and tyrosine phosphorylation: Just the FAKs? Trends Cell Biol. 1998, 8, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Schaller, M. Focal adhesion targeting: The critical determinant of FAK regulation and substrate phosphorylation. Mol. Biol. Cell 1999, 10, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quizi, J.; Baron, K.; Al-Zahrani, K.; O’Reilly, P.; Sriram, R.; Conway, J.; Laurin, A.; Sabourin, L. SLK-mediated phosphorylation of paxillin is required for focal adhesion turnover and cell migration. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, A.; Lawson, C.; Ghassemian, M.; Schlaepfer, D. Cortactin as a target for FAK in the regulation of focal adhesion dynamics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liao, K. Tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin by the FAK-Src complex at focal adhesions regulates cell motility. BMC Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, M.; Hildebrand, J.; Burnham, M.; Bouton, A.; Parsons, J. p130Cas, a substrate associated with v-Src and v-Crk, localizes to focal adhesions and binds to focal adhesion kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13649–13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polte, T.; Hanks, S. Complexes of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Crk-associated substrate (p130(Cas)) are elevated in cytoskeleton-associated fractions following adhesion and Src transformation. Requirements for Src kinase activity and FAK proline-rich motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 5501–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Panchenko, A.R. Phosphorylation in protein-protein binding: Effect on stability and function. Structure 2011, 19, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigera, P.; Jeffery, E.; Martin, K.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.; Parsons, J. FAK phosphorylation sites mapped by mass spectrometry. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4931–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brister, M.A.; Pandey, A.K.; Bielska, A.A.; Zondlo, N.J. OGlcNAcylation and phosphorylation have opposing structural effects in tau: Phosphothreonine induces particular conformational order. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3803–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.F.; Houle, F.; Sussman, M.; Huot, J. Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on Ser732 is induced by rho-dependent kinase and is essential for proline-rich tyrosine kinase-2-mediated phosphorylation of FAK on Tyr407 in response to vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 3508–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; De, L.S.; Marin, O.; Turner, D.; Hanks, S.; Villa-Moruzzi, E. Regulation of FAK Ser-722 phosphorylation and kinase activity by GSK3 and PP1 during cell spreading and migration. Biochem. J. 2005, 391, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.F.; Hu, X.; Wen, G.J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W.J. O-GlcNAcylation in cancer development and immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 566, 216258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itkonen, H.M.; Loda, M.; Mills, I.G. O-GlcNAc Transferase—An Auxiliary Factor or a Full-blown Oncogene? Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Isaji, T.; Oyama, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Lu, H.; Gu, J. O-GlcNAcylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase Regulates Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Proliferation via the FAK/AKT Pathway. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121577
Zhang Z, Isaji T, Oyama Y, Liu J, Xu Z, Sun Y, Fukuda T, Lu H, Gu J. O-GlcNAcylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase Regulates Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Proliferation via the FAK/AKT Pathway. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(12):1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121577
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiwei, Tomoya Isaji, Yoshiyuki Oyama, Jianwei Liu, Zhiwei Xu, Yuhan Sun, Tomohiko Fukuda, Haojie Lu, and Jianguo Gu. 2024. "O-GlcNAcylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase Regulates Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Proliferation via the FAK/AKT Pathway" Biomolecules 14, no. 12: 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121577
APA StyleZhang, Z., Isaji, T., Oyama, Y., Liu, J., Xu, Z., Sun, Y., Fukuda, T., Lu, H., & Gu, J. (2024). O-GlcNAcylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase Regulates Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Proliferation via the FAK/AKT Pathway. Biomolecules, 14(12), 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121577






