LSD2 Is an Epigenetic Player in Multiple Types of Cancer and Beyond
Abstract
1. Introduction
A Historical Overview of Research on LSD2
2. Roles and Structure of LSD2 Compared to LSD1
LSD2’s Enzymatic Activity
3. LSD2 in Human Cancers
3.1. Breast Cancer Cells
3.2. Pancreatic Cancer
3.3. Colorectal Cancer
3.4. Lung Cancer Cells
3.5. Liver Cancer Cells
4. Epigenetic Reprogramming of Cancer
5. DNA Methylation
6. DNA Damage Repair
7. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsukada, Y.; Fang, J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Warren, M.E.; Borchers, C.H.; Tempst, P.; Zhang, Y. Histone Demethylation by a Family of JmjC Domain-Containing Proteins. Nature 2006, 439, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klose, R.J.; Yamane, K.; Bae, Y.; Zhang, D.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Wong, J.; Zhang, Y. The Transcriptional Repressor JHDM3A Demethylates Trimethyl Histone H3 Lysine 9 and Lysine 36. Nature 2006, 442, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloos, P.A.C.; Christensen, J.; Agger, K.; Maiolica, A.; Rappsilber, J.; Antal, T.; Hansen, K.H.; Helin, K. The Putative Oncogene GASC1 Demethylates Tri- and Dimethylated Lysine 9 on Histone H3. Nature 2006, 442, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Tian, S.; Meng, Q.; Kim, H.-M. Histone Demethylase AMX-1 Regulates Fertility in a P53/CEP-1 Dependent Manner. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 929716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swahari, V.; West, A.E. Histone Demethylases in Neuronal Differentiation, Plasticity, and Disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 59, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Lan, F.; Matson, C.; Mulligan, P.; Whetstine, J.R.; Cole, P.A.; Casero, R.A.; Shi, Y. Histone Demethylation Mediated by the Nuclear Amine Oxidase Homolog LSD1. Cell 2004, 119, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wan, K.; Yamane, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, M. Crystal Structure of Human Histone Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13956–13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.M.; Link, J.E.; Morgan, B.S.; Heller, F.J.; Hargrove, A.E.; McCafferty, D.G. KDM1 Class Flavin-Dependent Protein Lysine Demethylases. Biopolymers 2015, 104, 213–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karytinos, A.; Forneris, F.; Profumo, A.; Ciossani, G.; Battaglioli, E.; Binda, C.; Mattevi, A. A Novel Mammalian Flavin-Dependent Histone Demethylase*. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17775–17782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosammaparast, N.; Shi, Y. Reversal of Histone Methylation: Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms of Histone Demethylases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, H.; Dong, Z.; Fang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhu, T.; Gong, W.; Fang, R.; Shi, Y.G.; Li, Z.; et al. Structural Insight into Substrate Recognition by Histone Demethylase LSD2/KDM1b. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Barbera, A.J.; Xu, Y.; Rutenberg, M.; Leonor, T.; Bi, Q.; Lan, F.; Mei, P.; Yuan, G.-C.; Lian, C.; et al. Human LSD2/KDM1b/AOF1 Regulates Gene Transcription by Modulating Intragenic H3K4me2 Methylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, S.; Xu, M.; Yu, L.; Tao, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Wong, J. Structure-Function Analysis Reveals a Novel Mechanism for Regulation of Histone Demethylase LSD2/AOF1/KDM1b. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Stewart, D.M.; Qi, S.; Yamane, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, J. AOF1 Is a Histone H3K4 Demethylase Possessing Demethylase Activity-Independent Repression Function. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, S.; Beese-Sims, S.E.; Chen, J.; Shin, N.; Colaiácovo, M.P.; Kim, H.-M. Histone Demethylase AMX-1 Is Necessary for Proper Sensitivity to Interstrand Crosslink DNA Damage. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabelli, C.; Marrocco, B.; Pilotto, S.; Chittori, S.; Picaud, S.; Marchese, S.; Ciossani, G.; Forneris, F.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Schoehn, G.; et al. A Tail-Based Mechanism Drives Nucleosome Demethylation by the LSD2/NPAC Multimeric Complex. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 387–399.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroli, J.; Mattevi, A. The NPAC-LSD2 Complex in Nucleosome Demethylation. In The Enzymes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 53, pp. 97–111. ISBN 978-0-443-16007-3. [Google Scholar]
- Marayati, B.F.; Tucker, J.F.; De La Cerda, D.A.; Hou, T.-C.; Chen, R.; Sugiyama, T.; Pease, J.B.; Zhang, K. The Catalytic-Dependent and -Independent Roles of Lsd1 and Lsd2 Lysine Demethylases in Heterochromatin Formation in Schizosaccharomyces Pombe. Cells 2020, 9, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, D.N.; Su, H.; Hevi, S.; Gay, F.; Lei, H.; Bajko, J.; Xu, G.; Li, E.; Chen, T. KDM1B Is a Histone H3K4 Demethylase Required to Establish Maternal Genomic Imprints. Nature 2009, 461, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Essen, D.; Zhu, Y.; Saccani, S. A Feed-Forward Circuit Controlling Inducible NF-κB Target Gene Activation by Promoter Histone Demethylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-L.; Chang, D.C.; Lin, C.-H.; Ying, S.-Y.; Leu, D.; Wu, D.T.S. Regulation of Somatic Cell Reprogramming through Inducible Mir-302 Expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, T.A.; Huang, Y.; Davidson, N.E.; Jankowitz, R.C. Epigenetic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer: From New Targets to New Therapies. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, T.A.; Vasilatos, S.N.; Harrington, E.; Oesterreich, S.; Davidson, N.E.; Huang, Y. Inhibition of Histone Demethylase, LSD2 (KDM1B), Attenuates DNA Methylation and Increases Sensitivity to DNMT Inhibitor-Induced Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Vasilatos, S.N.; Qin, Y.; Katz, T.A.; Cao, C.; Wu, H.; Tasdemir, N.; Levine, K.M.; Oesterreich, S.; Davidson, N.E.; et al. Functional Characterization of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 2 (LSD2/KDM1B) in Breast Cancer Progression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Luo, Y.; He, S. Knockdown of KDM1B Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, U.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G. Colorectal Cancer: Genetic Abnormalities, Tumor Progression, Tumor Heterogeneity, Clonal Evolution and Tumor-Initiating Cells. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Xia, Y.; Liao, G.-Q.; Pan, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.-S. LSD1-Mediated Epigenetic Modification Contributes to Proliferation and Metastasis of Colon Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Wang, J.; Zeng, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Li, W. Lysine-Specific Histone Demethylase 1B (LSD2/KDM1B) Represses P53 Expression to Promote Proliferation and Inhibit Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer through LSD2-Mediated H3K4me2 Demethylation. Aging 2020, 12, 14990–15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y. Histone Demethylase LSD2 Acts as an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase and Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth through Promoting Proteasomal Degradation of OGT. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; Fiore, E.J.; Dominguez, L.M.; Real, A.; Malvicini, M.; Rizzo, M.; Atorrasagasti, C.; García, M.G.; Argemi, J.; Martinez, E.D.; et al. A Comprehensive Study of Epigenetic Alterations in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Identifies Potential Therapeutic Targets. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagraba, G.; Yarmohammadi, M.; Javed, A.; Barceló, C.; Rubio-Tomás, T. The Role of LSD1 and LSD2 in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System: An Update. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.-F. HIF-miR-215-KDM1B Promotes Glioma-Initiating Cell Adaptation to Hypoxia. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1939–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musella, M.; Guarracino, A.; Manduca, N.; Galassi, C.; Ruggiero, E.; Potenza, A.; Maccafeo, E.; Manic, G.; Mattiello, L.; Soliman Abdel Rehim, S.; et al. Type I IFNs Promote Cancer Cell Stemness by Triggering the Epigenetic Regulator KDM1B. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Ye, Z.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. Lysine Demethylase 1B (Kdm1b) Enhances Somatic Reprogramming through Inducing Pluripotent Gene Expression and Promoting Cell Proliferation. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 420, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Wynder, C.; Schmidt, D.M.; McCafferty, D.G.; Shiekhattar, R. Histone H3 Lysine 4 Demethylation Is a Target of Nonselective Antidepressive Medications. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Valente, S.; Romanenghi, M.; Pilotto, S.; Cirilli, R.; Karytinos, A.; Ciossani, G.; Botrugno, O.A.; Forneris, F.; Tardugno, M.; et al. Biochemical, Structural, and Biological Evaluation of Tranylcypromine Derivatives as Inhibitors of Histone Demethylases LSD1 and LSD2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6827–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, P.; Botrugno, O.A.; Cappa, A.; Dal Zuffo, R.; Dessanti, P.; Mai, A.; Marrocco, B.; Mattevi, A.; Meroni, G.; Minucci, S.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Inhibitor of Histone Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1A (KDM1A/LSD1) as Orally Active Antitumor Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, L.; Boffo, F.L.; Ceccacci, E.; Conforti, F.; Pallavicini, I.; Bedin, F.; Ravasio, R.; Massignani, E.; Somervaille, T.C.P.; Minucci, S.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of LSD1 Triggers Myeloid Differentiation by Targeting GSE1 Oncogenic Functions in AML. Oncogene 2022, 41, 878–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.O.; Pishas, K.I.; Taslim, C.; Selich-Anderson, J.; Theisen, E.R.; Lessnick, S.L. Investigating the Role of LSD2 as an Epigenetic Regulator in Ewing Sarcoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3865–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ren, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, A.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, T.; Lv, P.; Song, D.; Hu, F.; Lan, J.; et al. PD-L1 Methylation Restricts PD-L1/PD-1 Interactions to Control Cancer Immune Surveillance. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Saüch, J.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET Cytoscape App: Exploring and Visualizing Disease Genomics Data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Bravo, À.; Deu-Pons, J.; Bauer-Mehren, A.; Baron, M.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. DisGeNET: A Discovery Platform for the Dynamical Exploration of Human Diseases and Their Genes. Database 2015, 2015, bav028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
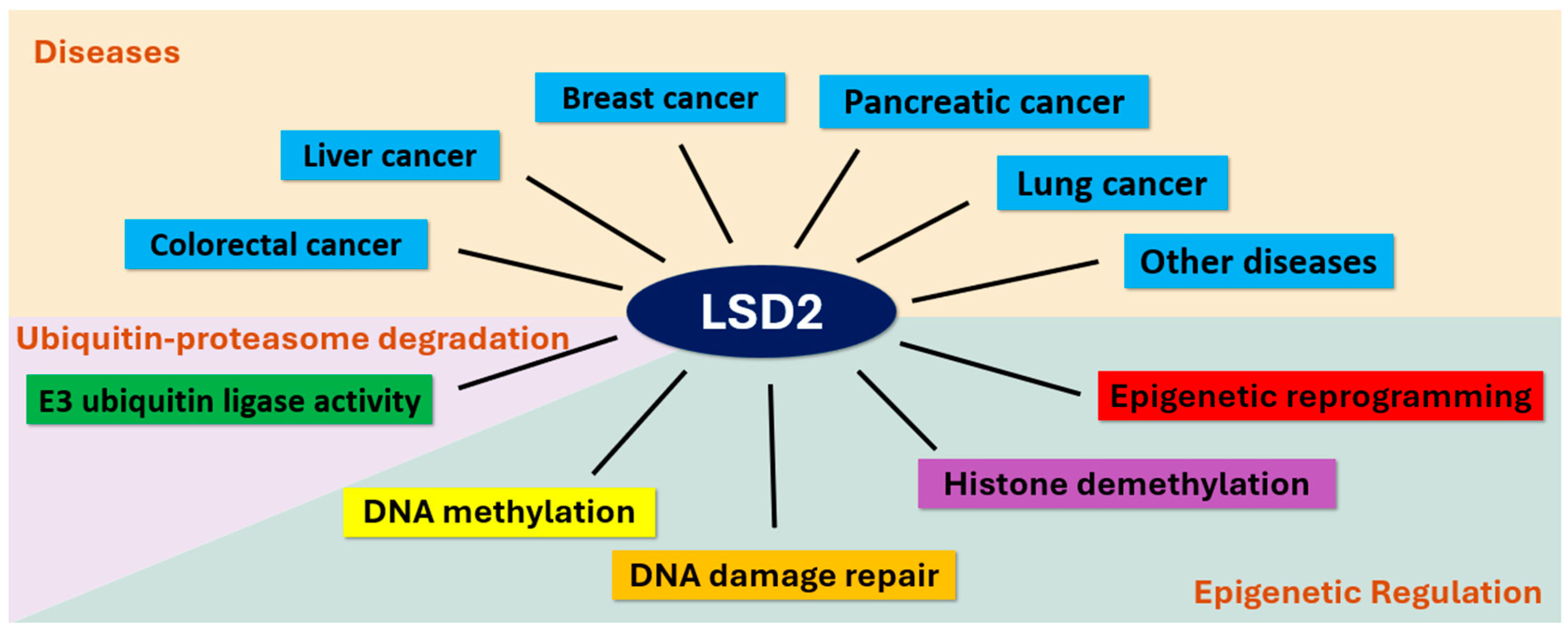


| Findings | Implication |
|---|---|
| Implicated in various cancers, with roles in promotion or suppression | Human cancer involvement: lung, breast, pancreatic, liver and colorectal cancer tissues or cell lines [23,24,25,28,29,30] |
| Involved in establishing DNA methylation imprints during oogenesis | Epigenetic regulation during oogenesis [19] |
| Implicated in non-transgenerational fertility defects in C. elegans | Role in fertility defects in model system [4] |
| Involved in ICL DNA damage repair in C. elegans | Role in DNA damage repair in model system [15] |
| Involved in E3 ubiquitin ligase activities, regulating specific genes | Role in ubiquitin-mediate proteasomal regulation [29] |
| Implicated in epigenetic reprogramming of cancers | HIF-miRNA-LSD2, IFN-I-induced CSCs and reprogramming through pluripotent gene expression [32,33,34] |
| Cancer Type | Experimental Results |
|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Knockdown of LSD2 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion [24]. |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Knock down of LSD2 correlates with cell proliferation decrease and leads to apoptosis increase [25]. |
| Colorectal Cancer | Overexpression of LSD2 leads cell proliferation and apoptosis decrease [28]. |
| Lung Cancer | LSD2 inhibits lung cancer cell growth by promoting OGT degradation [29]. |
| Liver Cancer | Expression levels of LSD2/KDM1B correlated with clinical prognosis of patients [30]. |
| No | Disease | Disease Class | Semantic Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atrial Fibrillation | Pathological conditions, signs and symptoms; cardiovascular diseases | Disease or Syndrome |
| 2 | Familial atrial fibrillation | Pathological conditions, signs and symptoms; cardiovascular diseases | Pathologic Function |
| 3 | Persistent atrial fibrillation | Pathological conditions, signs and symptoms; cardiovascular diseases | Pathologic Function |
| 4 | Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation | Pathological conditions, signs and symptoms; cardiovascular diseases | Disease or Syndrome |
| 5 | Alzheimer’s Disease | Nervous system diseases; mental disorders | Disease or Syndrome |
| 6 | Breast Carcinoma | Neoplasms; skin and connective tissue diseases | Neoplastic Process |
| 7 | Malignant Neoplasms | Neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 8 | Primary malignant neoplasm | Neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 9 | Neoplasms | Neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 10 | Malignant neoplasm of breast | Neoplasms; skin and connective tissue diseases | Neoplastic Process |
| 11 | Glioblastoma Multiforme | Neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 12 | Mammary Neoplasms | Neoplasms; skin and connective tissue diseases | Neoplastic Process |
| 13 | Tumor Cell Invasion | N/A | Neoplastic Process |
| 14 | Stomach Carcinoma | Digestive system diseases; neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 15 | Glioblastoma | Neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 16 | Carcinogenesis | Pathological conditions, signs and symptoms; neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 17 | Ewings sarcoma | Neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 18 | Conventional Renal Cell Carcinoma | Neoplasms; female urogenital diseases and pregnancy complications; male urogenital diseases | Neoplastic Process |
| 19 | Pancreatic carcinoma | Digestive system diseases; neoplasms; endocrine system diseases | Neoplastic Process |
| 20 | Renal Cell Carcinoma | Neoplasms; female urogenital diseases and pregnancy complications; male urogenital diseases | Neoplastic Process |
| 21 | Malignant neoplasm of stomach | Digestive system diseases; neoplasms | Neoplastic Process |
| 22 | Malignant neoplasm of pancreas | Digestive system diseases; neoplasms; endocrine system diseases | Neoplastic Process |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-M.; Liu, Z. LSD2 Is an Epigenetic Player in Multiple Types of Cancer and Beyond. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050553
Kim H-M, Liu Z. LSD2 Is an Epigenetic Player in Multiple Types of Cancer and Beyond. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(5):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050553
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun-Min, and Zifei Liu. 2024. "LSD2 Is an Epigenetic Player in Multiple Types of Cancer and Beyond" Biomolecules 14, no. 5: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050553
APA StyleKim, H.-M., & Liu, Z. (2024). LSD2 Is an Epigenetic Player in Multiple Types of Cancer and Beyond. Biomolecules, 14(5), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050553






