The Regulatory Network of hnRNPs Underlying Regulating PKM Alternative Splicing in Tumor Progression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SRs, hnRNPs, and RBM Contribute to the Oncogenesis and Tumor Progression via Alternative Splicing
3. The Different Functions Depending on hnRNP Intracellular Localization
4. The Regulatory Network of Different hnRNP Family Members
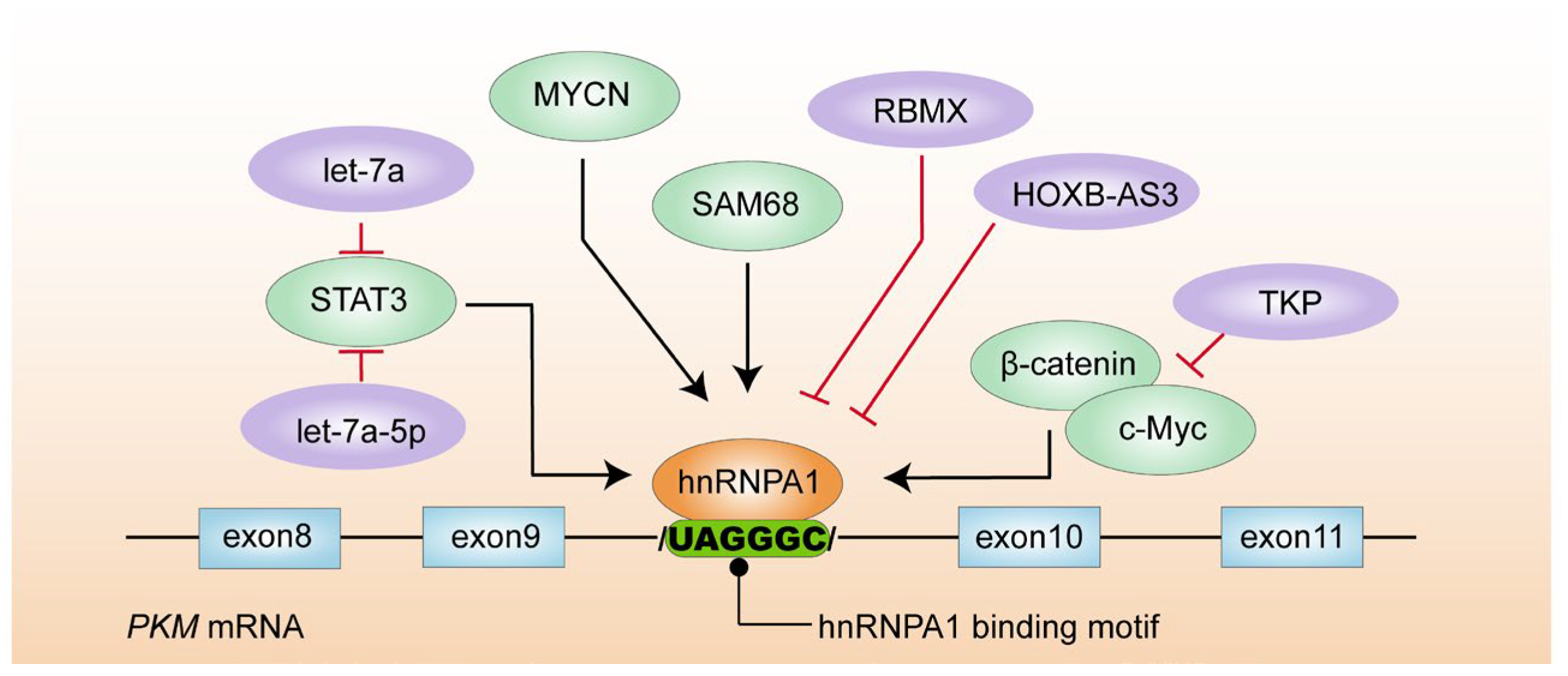
4.1. hnRNPA1
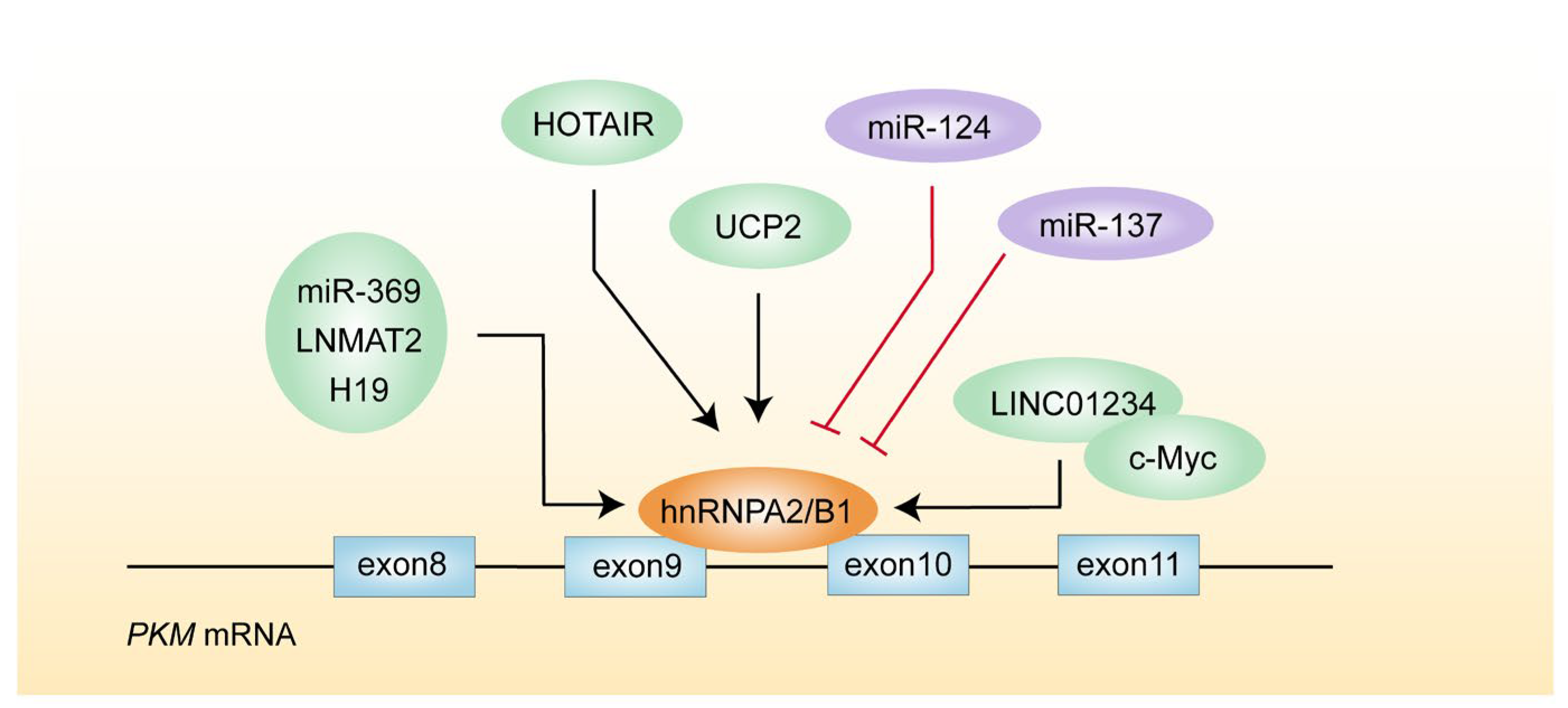
4.2. hnRNPA2/B1
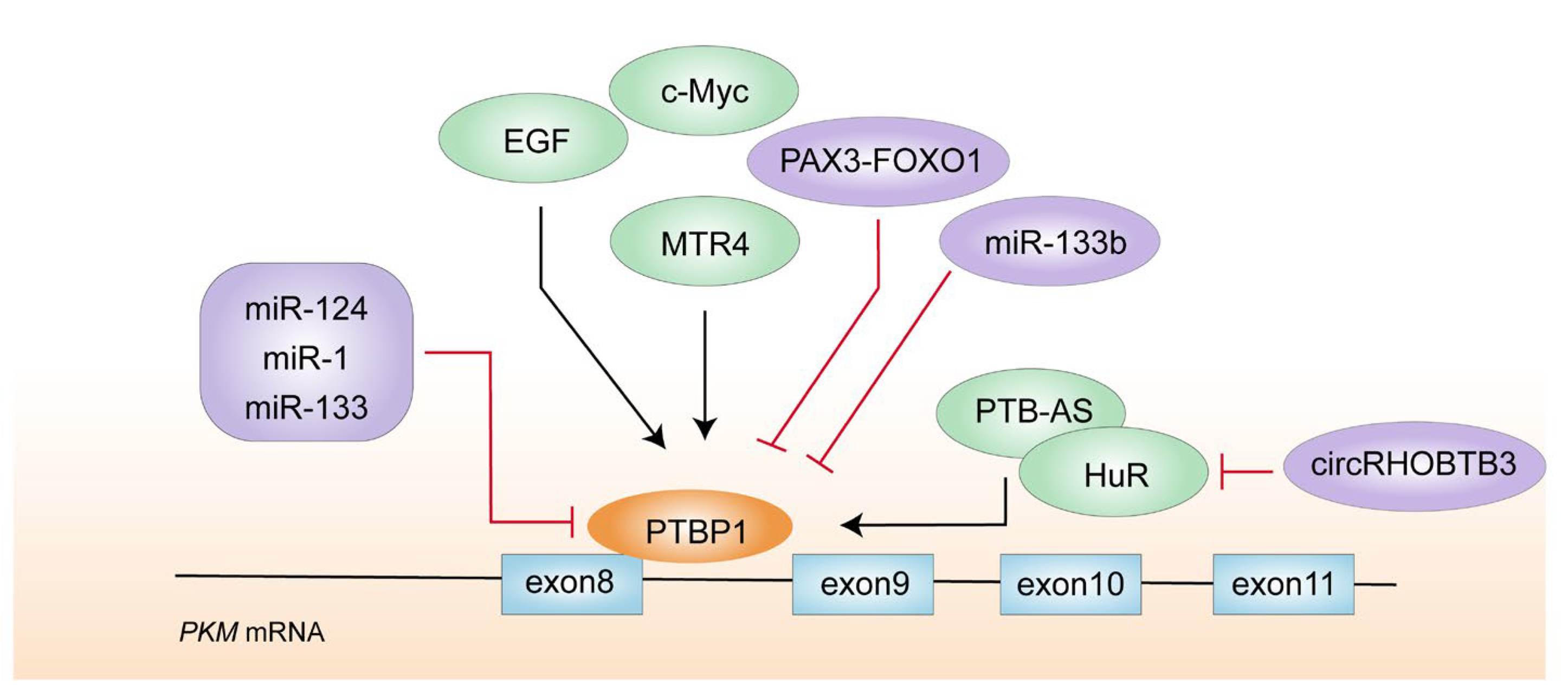
4.3. PTBP1
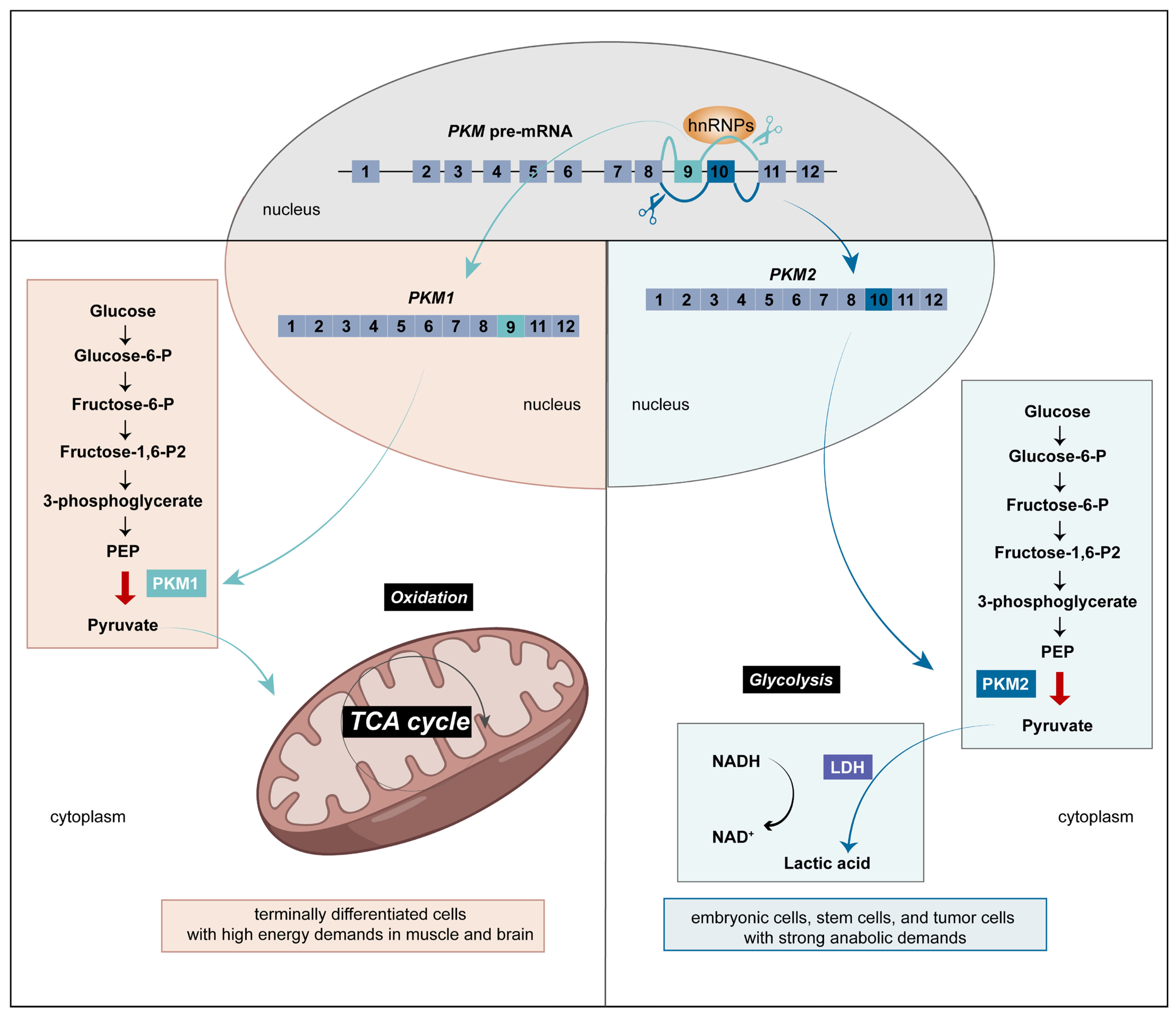
5. Epigenetic Modifications of hnRNPs Affect Glycolysis of Tumor Cells by Regulating PKM2
6. Potential Therapeutic Drugs or Inhibitors
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wang, G.S.; Cooper, T.A. Splicing in disease: Disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahles, A.; Lehmann, K.V.; Toussaint, N.C.; Huser, M.; Stark, S.G.; Sachsenberg, T.; Stegle, O.; Kohlbacher, O.; Sander, C.; Rätsch, G. Comprehensive analysis of alternative splicing across tumors from 8705 patients. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 211–224.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnal, S.C.; Lopez-Oreja, I.; Valcarcel, J. Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer—Implications for care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ule, J.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative splicing regulatory networks: Functions, mechanisms, and evolution. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppenol, W.H.; Bounds, P.L.; Dang, C.V. Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofk, H.R.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Harris, M.H.; Ramanathan, A.; Gerszten, R.E.; Wei, R.; Fleming, M.D.; Schreiber, S.L.; Cantley, L.C. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 2008, 452, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayton, T.L.; Jacks, T.; Vander Heiden, M.G. PKM2, cancer metabolism, and the road ahead. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.K.; Anczukow, O. RNA splicing dysregulation and the hallmarks of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clower, C.V.; Chatterjee, D.; Wang, Z.; Cantley, L.C.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Krainer, A.R. The alternative splicing repressors hnRNP A1/A2 and PTB influence pyruvate kinase isoform expression and cell metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, X.; Hu, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; et al. IGF2BP3 may contributes to lung tumorigenesis by regulating the alternative splicing of PKM. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 679. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z. Serine/arginine-rich splicing factors: The bridge linking alternative splicing and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, J.G. Small granules in the amphibian oocyte nucleus and their relationship to RNA. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1956, 2, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuens, T.; Bouhy, D.; Timmerman, V. The hnRNP family: Insights into their role in health and disease. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, S.; Dai, D.; Cheng, S.; Dong, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, X. Pan-cancer analysis of alternative splicing regulator heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) family and their prognostic potential. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11111–11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiselle, J.J.; Sutherland, L.C. RBM10: Harmful or helpful-many factors to consider. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 3809–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, L.C.; Wang, K.; Robinson, A.G. RBM5 as a putative tumor suppressor gene for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, K.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, Z.; Han, Z.W.; Lu, B.S.; Qi, J.-C.; Yin, Y.-W.; Teng, Z.-H.; Chang, X.-L.; et al. Down-regulated RBM5 inhibits bladder cancer cell apoptosis by initiating an miR-432-5p/beta-catenin feedback loop. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10973–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubise, B.; Jiang, Y.; Douet-Guilbert, N.; Troadec, M.B. RBM22, a key player of pre-mRNA splicing and gene expression regulation, is altered in cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, P.J.; Hertel, K.J. The SR protein family. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chatterjee, D.; Jeon, H.Y.; Akerman, M.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Krainer, A.R. Exon-centric regulation of pyruvate kinase M alternative splicing via mutually exclusive exons. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuranaga, Y.; Sugito, N.; Shinohara, H.; Tsujino, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Komura, K.; Ito, Y.; Soga, T.; Akao, Y. SRSF3, a splicer of the PKM gene, regulates cell growth and maintenance of cancer-specific energy metabolism in colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.; Yang, F.; Xu, P.; Gao, G.; Yang, C.; Cao, Y.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Fei, B.; et al. LINC01852 inhibits the tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by suppressing SRSF5-mediated alternative splicing of PKM. Mol Cancer. 2024, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury, A.; Chander, P.; Howe, P.H. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) in cellular processes: Focus on hnRNP E1’s multifunctional regulatory roles. RNA 2010, 16, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matunis, M.J.; Michael, W.M.; Dreyfuss, G. Characterization and primary structure of the poly(C)-binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex K protein. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992, 12, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dreyfuss, G.; Kim, V.N.; Kataoka, N. Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, H.; Piekielko-Witkowska, A. Splicing factors of SR and hnRNP families as regulators of apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.D.; Ares, M., Jr. Context-dependent control of alternative splicing by RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, Q.; Wang, J.; Sui, Y.; Wu, J.; Feng, J. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B: An emerging group of cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.P.; Friend, L.R.; Carson, J.H.; Korza, G.; Barbarese, E.; Maggipinto, M.; Hatfield, J.T.; Rothnagel, J.A.; Smith, R. Differential subcellular distributions and trafficking functions of hnRNP A2/B1 spliceoforms. Traffic 2010, 11, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Huang, Y.; Seckl, M.J.; Pardo, O.E. Emerging roles of hnRNPA1 in modulating malignant transformation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paronetto, M.P.; Achsel, T.; Massiello, A.; Chalfant, C.E.; Sette, C. The RNA-binding protein Sam68 modulates the alternative splicing of Bcl-x. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, C.-T.; Liu, Y.-C.; Cheng, F.-C.; Hsu, K.-C.; Chow, L.-P. Chemical proteomics identifies heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A1 as the molecular target of quercetin in its anti-cancer effects in PC-3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22078–22089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, J.; Jia, R.; Fan, M. Oral squamous cancer cell exploits hnRNP A1 to regulate cell cycle and proliferation. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, S.S.; Kovalev, L.I.; Pashintseva, N.V.; Kovaleva, M.A.; Lisitskaya, K. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in the functioning of telomeres in malignant cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.J.; Chen, M.; Assanah, M.; Canoll, P.; Manley, J.L. HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature 2010, 463, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, J.S.; Li, S.Q.; Badgett, T.C.; Song, Y.K.; Agarwal, S.; Coarfa, C.; Tolman, C.; Hurd, L.; Liao, H.; et al. MYCN controls an alternative RNA splicing program in high-risk metastatic neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Xiang, Y.; Si, Y.R.; Fan, L.J.; Li, J.P.; Li, H.; Guo, W.; He, H.-X.; Liang, X.-J.; Tan, Y.; et al. PKM2 promotes glucose metabolism through a let-7a-5p/Stat3/hnRNP-A1 regulatory feedback loop in breast cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 6542–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zeng, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, R.; Qiao, J.; Feng, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Chen, C. RBMX suppresses tumorigenicity and progression of bladder cancer by interacting with the hnRNP A1 protein to regulate PKM alternative splicing. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2635–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Qi, L.; Pan, H.; Feng, Z.; Tian, D. SAM68 promotes tumorigenesis in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating metabolic conversion via PKM alternative splicing. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3359–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Hassan, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z. Sam68 promotes aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer by regulating PKM2 alternative splicing. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Chen, M.; Chen Gao, X.C.; Zhu, S.; Huang, H.; Hu, M.; Zhu, H.; Yan, G.-R. A peptide encoded by a putative lncRNA HOXB-AS3 suppresses colon cancer growth. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 171–184.e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Song, L. TKP, a serine protease from trichosanthes kirilowii, inhibits cell proliferation by blocking aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 74, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, S.L. The roles of hnRNP A2/B1 in RNA biology and disease. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2021, 12, e1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeda, A.; Munroe, S.H.; Caceres, J.F.; Krainer, A.R. Function of conserved domains of hnRNP A1 and other hnRNP A/B proteins. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 5483–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, P.S.; Domsic, J.K.; Mayeda, A.; Krainer, A.R.; Stoltzfus, C.M. RNA splicing at human immunodeficiency virus type 1 3‘ splice site A2 is regulated by binding of hnRNP A/B proteins to an exonic splicing silencer element. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8487–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, H. Identification of anti-tumoral feedback loop between VHLalpha and hnRNPA2B1 in renal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yu, B.; Qian, D.; Zhao, R.; Wang, B.; Hu, M. Human cytomegalovirus ie2 affects the migration of glioblastoma by mediating the different splicing patterns of RON through hnRNP A2B1. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Yadav, S.; Pt, A.; Mishra, J.; Samaiya, A.; Panday, R.K.; Shukla, S. The HNRNPA2B1-MST1R-Akt axis contributes to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in head and neck cancer. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan-Gerstl, R.; Cohen, M.; Shilo, A.; Suh, S.S.; Bakacs, A.; Coppola, L.; Karni, R. Splicing factor hnRNP A2/B1 regulates tumor suppressor gene splicing and is an oncogenic driver in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4464–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, J.; Cecconi, D.; Cordani, M.; Torrens-Mas, M.; Pacchiana, R.; Pozza, E.D.; Butera, G.; Manfredi, M.; Marengo, E.; Oliver, J.; et al. The antioxidant uncoupling protein 2 stimulates hnRNPA2/B1, GLUT1 and PKM2 expression and sensitizes pancreas cancer cells to glycolysis inhibition. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 101, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, M.; Koseki, J.; Kawamoto, K.; Nishida, N.; Matsui, H.; Dewi, D.L.; Ozaki, M.; Noguchi, Y.; Mimori, K.; Gotoh, N.; et al. Embryonic microRNA-369 controls metabolic splicing factors and urges cellular reprograming. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y. miR-124, miR-137 and miR-340 regulate colorectal cancer growth via inhibition of the Warburg effect. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luo, Y.; He, W.; Zhao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhong, G.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA LNMAT2 promotes lymphatic metastasis in bladder cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 404–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Lei, T.; Gu, Y.; Gu, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, B.; Yuan, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z. Integrative analysis of NSCLC identifies LINC01234 as an oncogenic lncRNA that interacts with HNRNPA2B1 and regulates miR-106b biogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; He, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, C. Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via binding to hnRNPA2B1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, E.K.; Balas, M.M.; Sindy, K.; Haislop, K.; Johnson, A.M. An RNA matchmaker protein regulates the activity of the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR. RNA 2016, 22, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppetipola, N.; Sharma, S.; Li, Q.; Black, D.L. Neuronal regulation of pre-mRNA splicing by polypyrimidine tract binding proteins, PTBP1 and PTBP2. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.K.; Roh, S.A.; Lee, H.; Park, N.Y.; Choi, E.S.; Oh, J.-H.; Park, S.J.; Shin, J.H.; Suh, Y.-A.; Lee, E.K.; et al. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1-mediated down-regulation of ATG10 facilitates metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.C.; Hai, T.; Zhu, W.; Baggerly, K.A.; Tsavachidis, S.; Krahe, R.; Cote, G.J. Splicing factors PTBP1 and PTBP2 promote proliferation and migration of glioma cell lines. Brain 2009, 132, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Shao, J.; Xie, R.; Gu, P.; Duan, C. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating alternative splicing of PKM. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.R.; Murga-Zamalloa, C.; Brown, N.; Basappa, J.; McDonnell, S.R.; Mendoza-Reinoso, V.; Basrur, V.; Wilcox, R.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.; Lim, M.S.; et al. Pyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 mediates pyruvate kinase M2-dependent phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and oncogenesis in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Nishimura, J.; Kagawa, Y.; Kano, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Wu, X.; Hiraki, M.; Hamabe, A.; Konno, M.; Haraguchi, N.; et al. Significance of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 expression in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; Dong, W.; Gu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Dong, W.; Han, J.; et al. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 promotes lymphatic metastasis and proliferation of bladder cancer via alternative splicing of MEIS2 and PKM. Cancer Lett. 2019, 449, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Lei, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Czachor, A.; Breitzig, M.; Gao, Y.; Huang, M.; Mo, X.; et al. Skipping of exon 10 in Axl pre-mRNA regulated by PTBP1 mediates invasion and metastasis process of liver cancer cells. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5719–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgilis, A.; Klotz, S.; Hanley, C.J.; Herranz, N.; Weirich, B.; Morancho, B.; Leote, A.C.; D’Artista, L.; Gallage, S.; Seehawer, M.; et al. PTBP1-mediated alternative splicing regulates the inflammatory secretome and the pro-tumorigenic effects of senescent cells. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 85–102.e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, R.; Smith, C.W. Novel modes of splicing repression by PTB. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Xia, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Bu, W.; Zhang, L.; You, M.J.; Koh, M.Y.; Cote, G.; Aldape, K.; et al. EGFR-induced and PKCepsilon monoubiquitylation-dependent NF-kappaB activation upregulates PKM2 expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Kim, J.; Jiang, L.; Feng, B.; Ying, Y.; Ji, K.-Y.; Tang, Q.; Chen, W.; Mai, T.; Dou, W.; et al. MTR4 drives liver tumorigenesis by promoting cancer metabolic switch through alternative splicing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Sugito, N.; Shinohara, H.; Kuranaga, Y.; Inomata, Y.; Komura, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Akao, Y. Organ-Specific MicroRNAs (MIR122, 137, and 206) Contribute to tissue characteristics and carcinogenesis by regulating pyruvate kinase M1/2 (PKM) Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; McMillan-Ward, E.; Kong, J.; Israels, S.J.; Gibson, S.B. Oxidative stress induces autophagic cell death independent of apoptosis in transformed and cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Sugito, N.; Kumazaki, M.; Shinohara, H.; Yamada, N.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ito, Y.; Otsuki, Y.; Uno, B.; Uchiyama, K.; et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits cancer cell growth through PTB1/PKM1/PKM2 feedback cascade in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 363, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Li, M.; Plecita-Hlavata, L.; D‘Alessandro, A.; Tauber, J.; Riddle, S.; Kumar, S.; Flockton, A.; McKeon, B.A.; et al. Metabolic and proliferative state of vascular adventitial fibroblasts in pulmonary hypertension is regulated through a microRNA-124/PTBP1 (polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1)/pyruvate kinase muscle axis. Circulation 2017, 136, 2468–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugito, N.; Taniguchi, K.; Kuranaga, Y.; Ohishi, M.; Soga, T.; Ito, Y.; Miyachi, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Hosoi, H.; Akao, Y. Cancer-specific energy metabolism in rhabdomyosarcoma cells is regulated by microRNA. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2017, 27, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wei, Q.; Qi, Y.; Ruan, X.; Wu, F.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. PTB-AS, a novel natural antisense transcript, promotes glioma progression by improving PTBP1 mRNA stability with SND1. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y. A circGLIS3/miR-644a/PTBP1 positive feedback loop promotes the malignant biological progressions of non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Luo, X.; Jin, D.; Zhou, W.; Ju, Z.; Wang, D.; Meng, Q.; Wang, H.; Fu, X.; et al. Circular RNA circRHOBTB3 represses metastasis by regulating the HuR-mediated mRNA stability of PTBP1 in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7507–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okugawa, Y.; Grady, W.M.; Goel, A. Epigenetic alterations in colorectal cancer: Emerging biomarkers. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1204–1225.e1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.A.; Kouzarides, T. Cancer epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell. 2012, 150, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, F. PKM2, function and expression and regulation. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
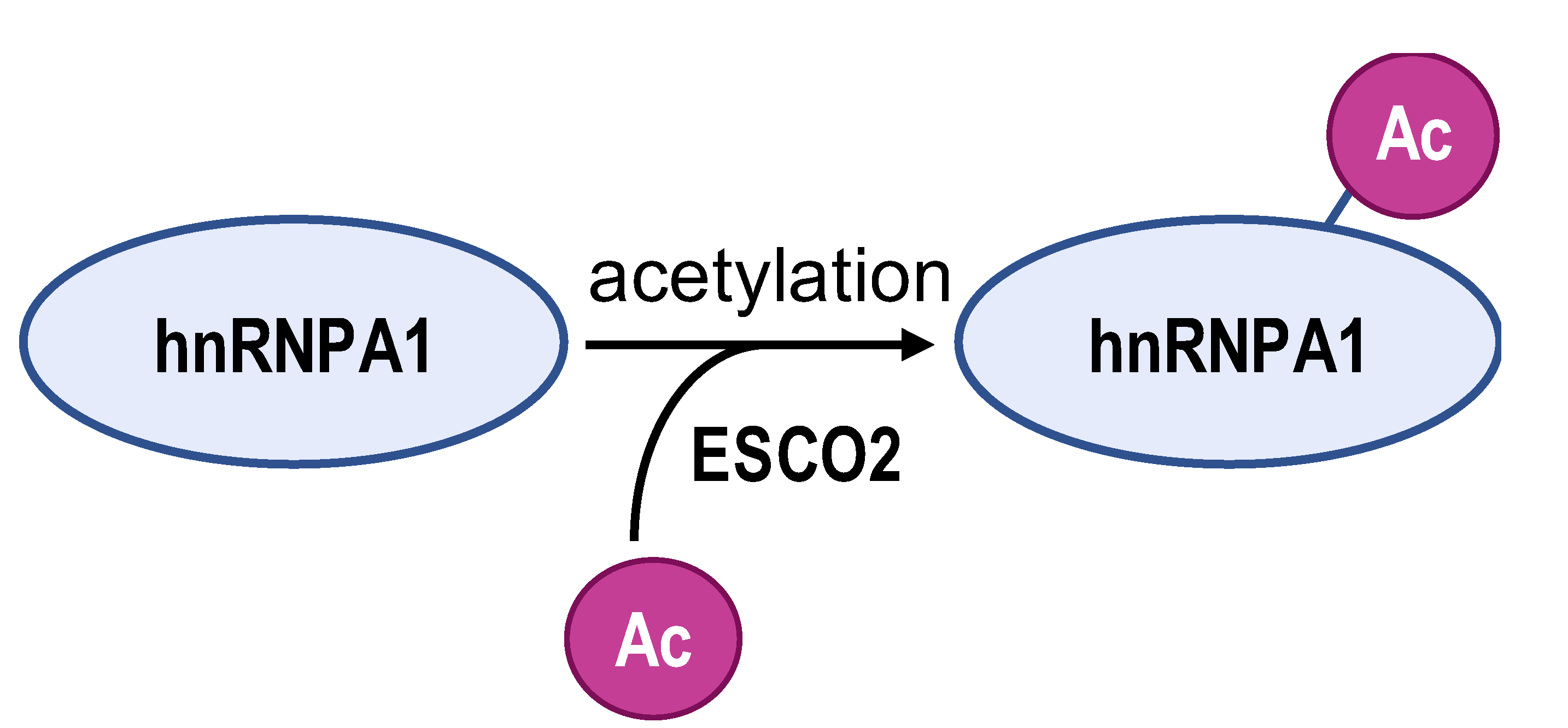
- Zhu, H.E.; Li, T.; Shi, S.; Chen, D.X.; Chen, W.; Chen, H. ESCO2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating hnRNPA1 acetylation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
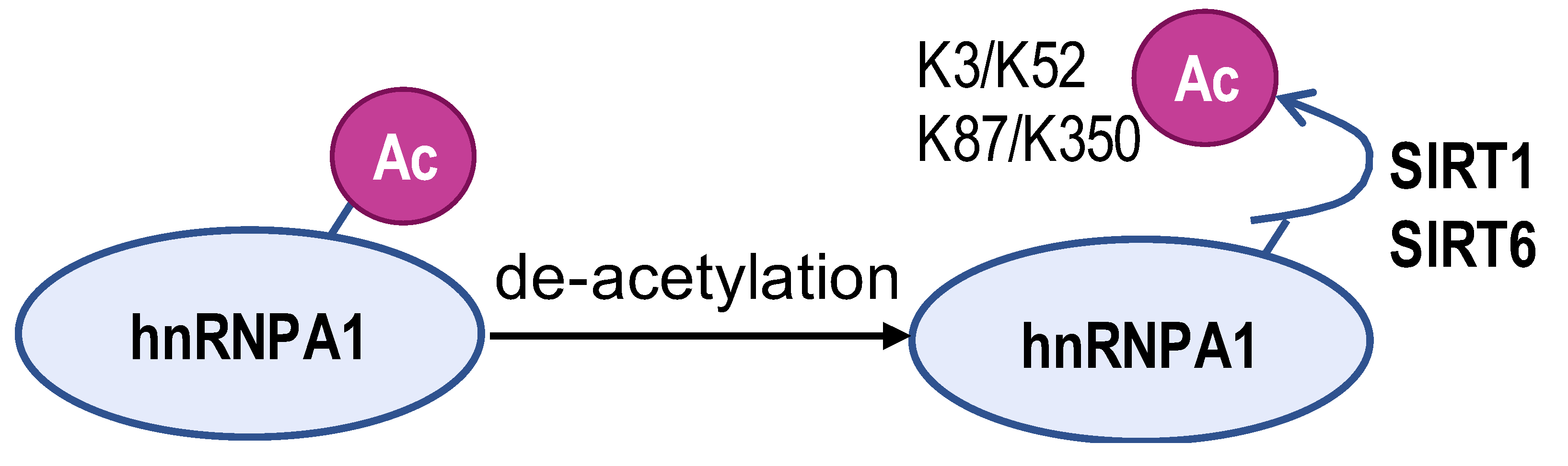
- Sun, Y.; Luo, M.; Chang, G.; Ren, W.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y. Phosphorylation of Ser6 in hnRNPA1 by S6K2 regulates glucose metabolism and cell growth in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7323–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liang, B.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Sirtuin-mediated deacetylation of hnRNP A1 suppresses glycolysis and growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4915–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
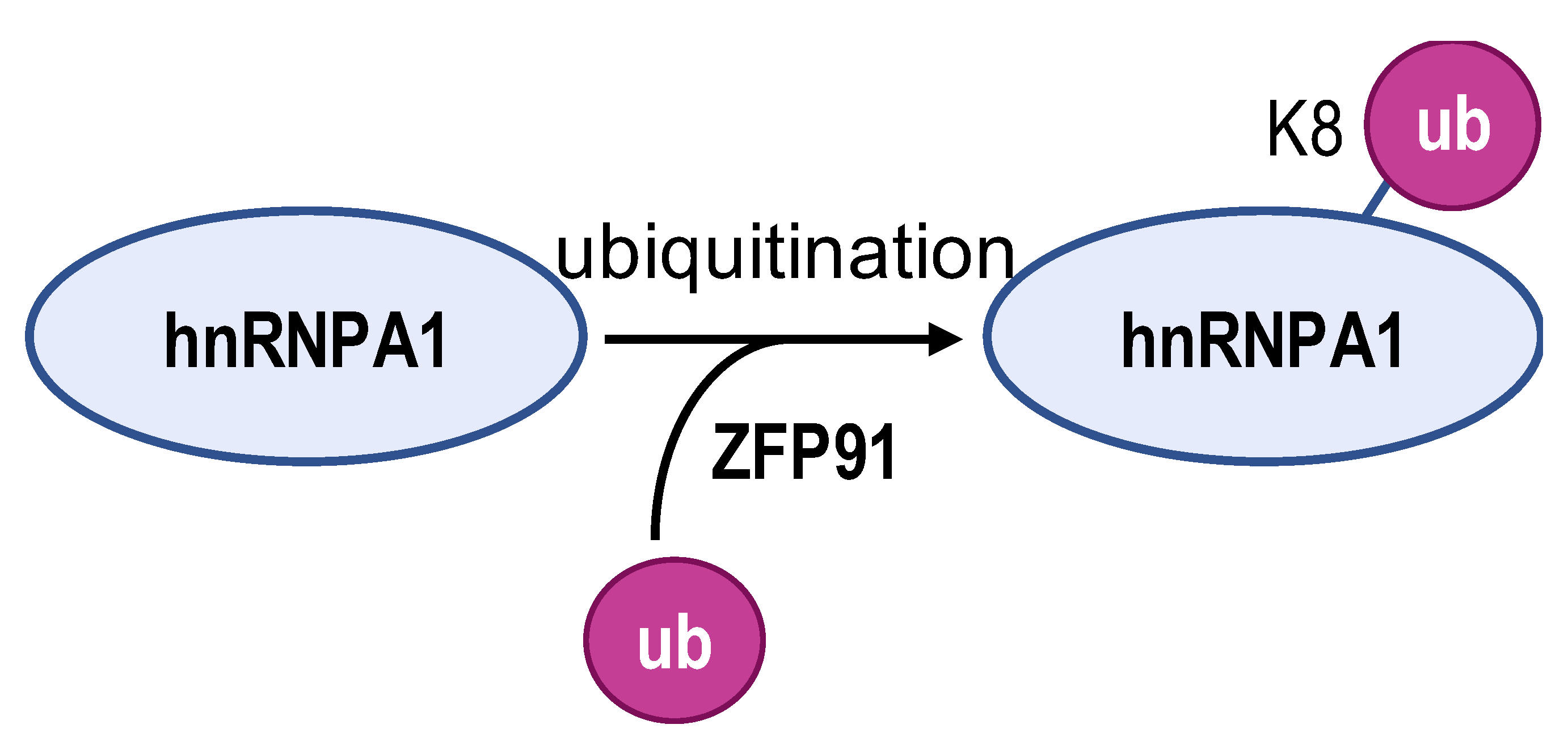
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, R.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Meng, N.; Chen, M.; Xie, S.; Yan, G.-R. E3 ligase ZFP91 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism reprogramming by regulating PKM splicing. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8558–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
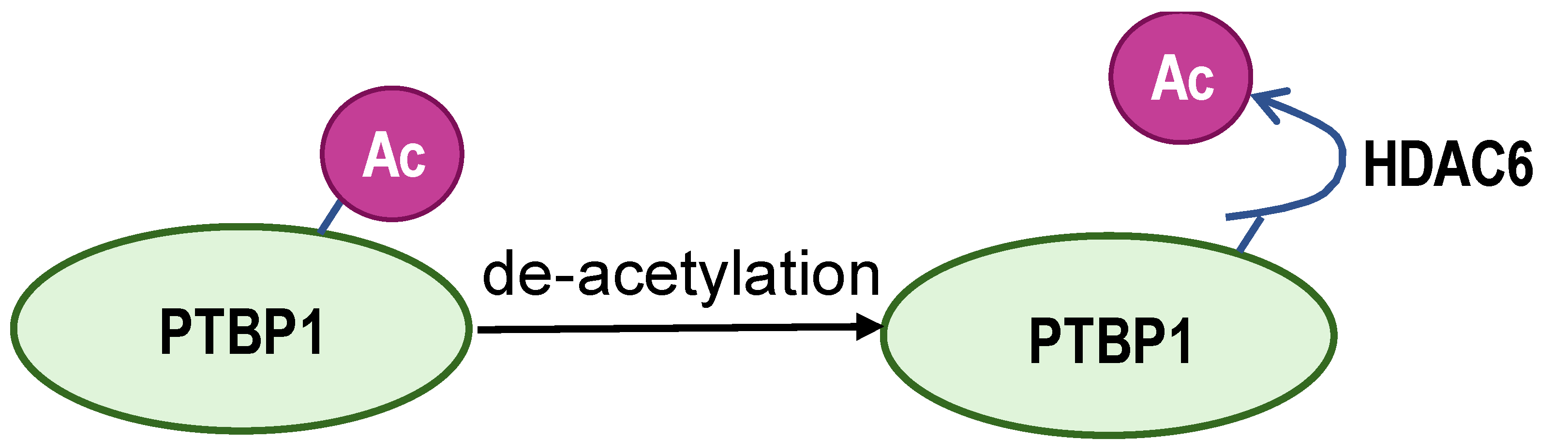
- Choksi, A.; Parulekar, A.; Pant, R.; Shah, V.K.; Nimma, R.; Firmal, P.; Singh, S.; Kundu, G.C.; Shukla, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Tumor suppressor SMAR1 regulates PKM alternative splicing by HDAC6-mediated deacetylation of PTBP1. Cancer Metab. 2021, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tong, H.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, S.; Si, Y.; Wang, S.; Tang, Z. CircRNA MBOAT2 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression and lipid metabolism reprogramming by stabilizing PTBP1 to facilitate FASN mRNA cytoplasmic export. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y. Cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 1 regulate reprogramming of lipid metabolism through SKP1-Cullin-1-F-boxFBXO11 -mediated heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 ubiquitination and promote hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habelhah, H.; Shah, K.; Huang, L.; Ostareck-Lederer, A.; Burlingame, A.L.; Shokat, K.M.; Hentze, M.W.; Ronai, Z. ERK phosphorylation drives cytoplasmic accumulation of hnRNP-K and inhibition of mRNA translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, F.; Nan, Y.; Qu, L.; Na, W.; Jia, C.; Chen, X. PKM2 Inhibitor shikonin overcomes the cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by inducing necroptosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetak, A.; Veress, R.; Ovadi, J.; Csermely, P.; Keri, G.; Ullrich, A. Nuclear translocation of the tumor marker pyruvate kinase M2 induces programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.P.; Fako, V.; Dang, H.; Dominguez, D.A.; Khatib, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, X.W. PKM2 inhibition may reverse therapeutic resistance to transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Yin, M.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) in cancer and cancer therapeutics. Cancer Lett. 2021, 503, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Qin, C.; Zhang, Y. PTBP1 knockdown overcomes the resistance to vincristine and oxaliplatin in drug-resistant colon cancer cells through regulation of glycolysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cui, M.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Dai, Y.; Cui, K.; Li, Z. Kaempferol reverses aerobic glycolysis via miR-339-5p-mediated PKM alternative splicing in colon cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, N.; Ma, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X. Oleanolic acid suppresses aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells by switching pyruvate kinase type M isoforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Dou, G.; He, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, N.; Qi, H.; et al. beta-asarone induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human glioma U251 Cells via suppression of HnRNP A2/B1-mediated pathway in vitro and in vivo. Molecules 2018, 23, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cho, S.B.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, M.J.; Bang, D. Cilostazol inhibits the expression of hnRNP A2/B1 and cytokines in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S108), 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, L.; Huang, A.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Dong, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Su, X.; et al. Nanoparticle-conjugated aptamer targeting hnRNP A2/B1 can recognize multiple tumor cells and inhibit their proliferation. Biomaterials 2015, 63, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.C.; Chen, M.X.; Zhang, K.L.; Reddy, A.S.N.; Cao, F.L.; Zhu, F.Y. QuantAS: A comprehensive pipeline to study alternative splicing by absolute quantification of splice isoforms. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Qi, L.; Yin, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wen, H.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, C.; Bello, S.F.; Zhang, X.; et al. Bulk and single-cell alternative splicing analyses reveal roles of TRA2B in myogenic differentiation. Cell Prolif. 2024, 57, e13545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Non-Coding RNA Partner | Mechanism | Function/Effect | Type of Cancer | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-124 | inhibits PTBP1 expression and reduces PKM2/PKM1 ratio | triggers a feedback cascade about PTBP1/PKM1/PKM2 and has anti-tumor effects | brain and colorectal cancers | [72,73,74] |
| miR-1 miR-133 | silences PTBP1 | leads to a high level of PKM1 mRNA | rhabdomyosarcoma | [75] |
| miR-133b | downregulates the pathogenic gene PAX3-FOXO1 | reduces PTBP1 expression | rhabdomyosarcoma | [75] |
| PTB-AS | binds to the 3′UTR region of PTBP1 | stabilizes and increases PTBP1 expression | glioma | [76] |
| circGLIS3 | sponge miR-644a and PTBP1 can bind to the flanking introns of cirGLIS3 | circGLIS3/miR-644a/PTBP1 positive feedback loop and promotes PTBP1 production | non-small cell lung cancer | [77] |
| HuR | binds to the 3’UTR region of PTBP1 | promotes PTBP1 stability | colorectal cancer | [78] |
| circRHOBTB3 | promotes HuR ubiquitination degradation | reduces the production of downstream PTBP1 | colorectal cancer | [78] |
 |  |  |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | ESCO2 | S6K2 | SIRT1 and SIRT6 | ZFP91 | HDAC6 |
| Modification sites | K277 | Ser6 | K3, K52, K87, and K350 | K8 | unreported |
| Mechanism | retains hnRNPA1 in the nucleus and increases hnRNPA1 binding to PKM EI9 | promotes hnRNPA1 binding to the splicing site of the PKM gene | weakens PKM metabolic activity and PKM2-β-catenin pathway | hnRNPA1 is degraded by the proteasome pathway | SMAR1, PTBP1, and HDAC6 can form a ternary complex |
| PKM2/PKM1 ratio | upregulated | upregulated | downregulated | downregulated | downregulated |
| Type of cancer | lung adenocarcinoma | colorectal cancer | hepatocellular carcinoma | hepatocellular carcinoma | breast cancer |
| Refs | [82] | [83] | [84] | [85] | [86] |
| Outcome | Pro-tumor | Anti-tumor | |||
| Drugs or Inhibitors | Therapeutic Target | Molecular Mechanisms | Cancer Characteristics | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kaempferol | miR-339-5p | promotes miR-339-5p expression which downregulates hnRNPA1 and PTBP1 | colon cancer | [95] |
| oleanolic acid | mTOR signaling | inhibits the c-Myc-dependent expression of hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2 | prostate carcinoma and breast cancer | [96] |
| quercetin | hnRNPA1 | impairs the ability of hnRNPA1 shuttling between the nucleus and cytoplasm and ultimately traps it in the cytoplasm | prostate cancer | [33] |
| β-caprylylone | hnRNPA2/B1 | inhibits the expression of hnRNPA2/B1 | glioma | [97] |
| cilostazol | hnRNPA2/B1 | reduces the overexpression of hnRNPA2/B1 | Bechet’s disease | [98] |
| nanoparticle-coupled aptamer aptamers | hnRNPA2/B1 | acts as a cancer-specific probe | hepatocellular carcinoma; breast cancer; non-small cell lung cancer; cervical cancer | [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Zang, W.; Pan, Y. The Regulatory Network of hnRNPs Underlying Regulating PKM Alternative Splicing in Tumor Progression. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050566
Li Y, Zhang S, Li Y, Liu J, Li Q, Zang W, Pan Y. The Regulatory Network of hnRNPs Underlying Regulating PKM Alternative Splicing in Tumor Progression. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(5):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050566
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuchao, Shuwei Zhang, Yuexian Li, Junchao Liu, Qian Li, Wenli Zang, and Yaping Pan. 2024. "The Regulatory Network of hnRNPs Underlying Regulating PKM Alternative Splicing in Tumor Progression" Biomolecules 14, no. 5: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050566
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, S., Li, Y., Liu, J., Li, Q., Zang, W., & Pan, Y. (2024). The Regulatory Network of hnRNPs Underlying Regulating PKM Alternative Splicing in Tumor Progression. Biomolecules, 14(5), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050566






