Early Life Adversity, Microbiome, and Inflammatory Responses
Abstract
:1. Early Life Adversity
2. Immune System
2.1. Innate Immune System
2.2. Adaptive Immune System
3. Effects of Early Life Adversity on the Immune System in Humans
3.1. Inflammation
3.1.1. Early Life Stress Is Associated with Inflammation
3.1.2. Comorbidities Render the Association between Early Life Stress and Inflammation More Complex
3.1.3. Stress Affects Inflammation
3.1.4. Other Factors Also Contribute to Early Life Stress Outcomes on Inflammation
3.2. Immune Cell Defect Is Associated with Early Life Stress
3.2.1. Innate Immunity Cell Defects
3.2.2. Adaptive Immunity Cell Defects
3.3. Early Life Adversity and Increased Susceptibility to Infection
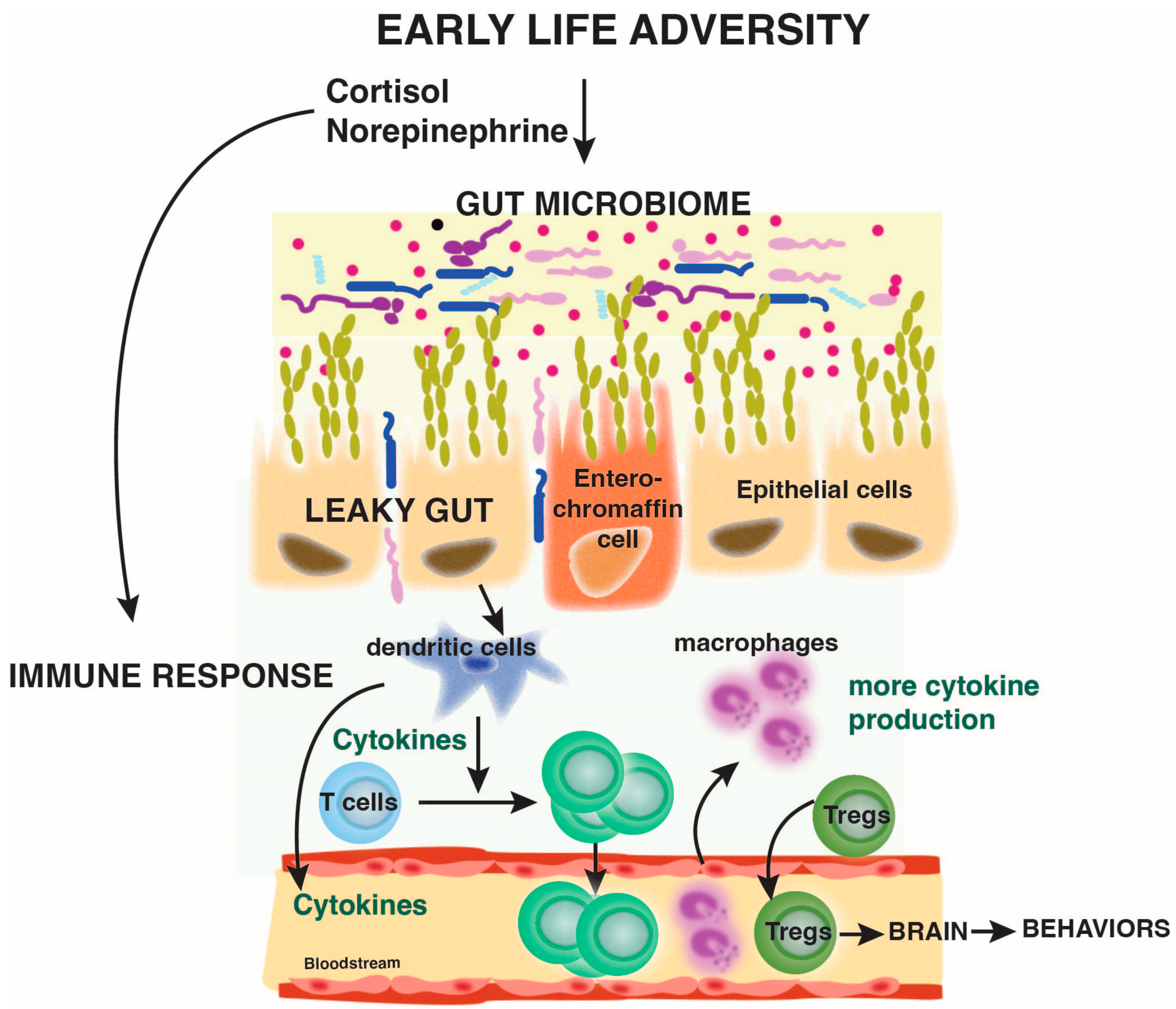
3.4. Early Life Adversity Affects the Microbiome
3.5. Effects of Early Life Adversity on Pregnancy Outcomes
4. Modeling Childhood Trauma in Animals and Effects of the Immune System
4.1. Proinflammatory Markers
4.2. Sex Differences
4.3. Microbiome
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felitti, V.J.; Anda, R.F.; Nordenberg, D.; Williamson, D.F.; Spitz, A.M.; Edwards, V.; Koss, M.P.; Marks, J.S. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1998, 14, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmakis, K.A.; Chandler, G.E. Health consequences of adverse childhood experiences: A systematic review. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2015, 27, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Green, J.G.; Gruber, M.J.; Sampson, N.A.; Zaslavsky, A.M.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Alhamzawi, A.O.; Alonso, J.; Angermeyer, M.; et al. Childhood adversities and adult psychopathology in the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 197, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkeila, J.; Vahtera, J.; Korkeila, K.; Kivimaki, M.; Sumanen, M.; Koskenvuo, K.; Koskenvuo, M. Childhood adversities as predictors of incident coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular disease. Heart 2010, 96, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Turiano, N.A.; Mroczek, D.K.; Miller, G.E. Association of Reports of Childhood Abuse and All-Cause Mortality Rates in Women. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Irving, M.; Lepage, B.; Dedieu, D.; Bartley, M.; Blane, D.; Grosclaude, P.; Lang, T.; Delpierre, C. Adverse childhood experiences and premature all-cause mortality. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 28, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D. Traumatic stress: Effects on the brain. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, D.; Akhtar, R.; Ciufolini, S.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Childhood trauma and adulthood inflammation: A meta-analysis of peripheral C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.; Viola, T.W.; Walss-Bass, C.; Brietzke, E.; Grassi-Oliveira, R. Childhood maltreatment and inflammatory markers: A systematic review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 129, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, W.T.; Levitt, P.; Martinez, F.D.; McEwen, B.S.; Shonkoff, J.P. Genes, Environments, and Time: The Biology of Adversity and Resilience. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e20201651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, L.L.; Gawuga, C.E.; Tyrka, A.R.; Lee, J.K.; Anderson, G.M.; Price, L.H. Association between plasma IL-6 response to acute stress and early-life adversity in healthy adults. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 2617–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Miller, G.E.; Yu, T.; Brody, G.H. Unsupportive parenting moderates the effects of family psychosocial intervention on metabolic syndrome in African American youth. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Tan, M. Childhood maltreatment and obesity: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, J.P.; Glaser, R.; Malarkey, W.B.; Beversdorf, D.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Childhood abuse and inflammatory responses to daily stressors. Ann. Behav. Med. 2012, 44, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.E.; Chen, E.; Parker, K.J. Psychological stress in childhood and susceptibility to the chronic diseases of aging: Moving toward a model of behavioral and biological mechanisms. Psychol. Bull. 2011, 137, 959–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.R.; Cole, S.W. Reciprocal regulation of the neural and innate immune systems. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapolsky, R.M.; Romero, L.M.; Munck, A.U. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, E.M. Neural regulation of innate immunity: A coordinated nonspecific host response to pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, A.K.; Hollander, G.A.; McMichael, A. Evolution of the immune system in humans from infancy to old age. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, A.C.; Fragaszy, E.B.; Bermingham, A.; Wang, L.; Copas, A.; Edmunds, W.J.; Ferguson, N.; Goonetilleke, N.; Harvey, G.; Kovar, J.; et al. Comparative community burden and severity of seasonal and pandemic influenza: Results of the Flu Watch cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Immunization Schedules. 2015. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules (accessed on 7 April 2024).
- Klein, U.; Dalla-Favera, R. Germinal centres: Role in B-cell physiology and malignancy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Counotte, J.; Drexhage, H.A.; Wijkhuijs, J.M.; Pot-Kolder, R.; Bergink, V.; Hoek, H.W.; Veling, W. Th17/T regulator cell balance and NK cell numbers in relation to psychosis liability and social stress reactivity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwenspoek, M.M.C.; Hengesch, X.; Leenen, F.A.D.; Schritz, A.; Sias, K.; Schaan, V.K.; Meriaux, S.B.; Schmitz, S.; Bonnemberger, F.; Schachinger, H.; et al. Proinflammatory T Cell Status Associated with Early Life Adversity. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 4046–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakir, J.; Shannon, J.; Molet, S.; Fukakusa, M.; Elias, J.; Laviolette, M.; Boulet, L.P.; Hamid, Q. Airway remodeling-associated mediators in moderate to severe asthma: Effect of steroids on TGF-beta, IL-11, IL-17, and type I and type III collagen expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molet, S.; Hamid, Q.; Davoine, F.; Nutku, E.; Taha, R.; Page, N.; Olivenstein, R.; Elias, J.; Chakir, J. IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Hanson, M.D.; Paterson, L.Q.; Griffin, M.J.; Walker, H.A.; Miller, G.E. Socioeconomic status and inflammatory processes in childhood asthma: The role of psychological stress. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, H.M.C.; Chen, E.; Miller, G.E. Child maltreatment and pediatric asthma: A review of the literature. Asthma Res. Pract. 2016, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Medina-Rodriguez, E.M.; Jope, R.S. Targeting the Adaptive Immune System in Depression: Focus on T Helper 17 Cells. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, D.; Toth, S.L. Child maltreatment. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 1, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W. The environment of childhood poverty. Am. Psychol. 2004, 59, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Lissitsyn, Y.; Miller, G.E.; Becker, A.B.; HayGlass, K.T.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Influence of socioeconomic status trajectories on innate immune responsiveness in children. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, R.J.; Visness, C.M.; Calatroni, A.; Grayson, M.H.; Gold, D.R.; Sandel, M.T.; Lee-Parritz, A.; Wood, R.A.; Kattan, M.; Bloomberg, G.R.; et al. Prenatal maternal stress and cord blood innate and adaptive cytokine responses in an inner-city cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreier, H.M.; Roy, L.B.; Frimer, L.T.; Chen, E. Family chaos and adolescent inflammatory profiles: The moderating role of socioeconomic status. Psychosom. Med. 2014, 76, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Miller, A.H. When not enough is too much: The role of insufficient glucocorticoid signaling in the pathophysiology of stress-related disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursich, M.; Neufeld, R.W.; Frewen, P.A.; Harricharan, S.; Kibler, J.L.; Rhind, S.G.; Lanius, R.A. Association of trauma exposure with proinflammatory activity: A transdiagnostic meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwenspoek, M.M.C.; Kuehn, A.; Muller, C.P.; Turner, J.D. The effects of early life adversity on the immune system. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 82, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlman, K.R.; Horn, S.R.; Chiang, J.J.; Bower, J.E. Early life adversity exposure and circulating markers of inflammation in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 86, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surtees, P.; Wainwright, N.; Day, N.; Luben, R.; Brayne, C.; Khaw, K.T. Association of depression with peripheral leukocyte counts in EPIC-Norfolk--role of sex and cigarette smoking. J. Psychosom. Res. 2003, 54, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulton, R.; Moffitt, T.E.; Silva, P.A. The Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study: Overview of the first 40 years, with an eye to the future. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2015, 50, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, A.; Pariante, C.M.; Caspi, A.; Taylor, A.; Poulton, R. Childhood maltreatment predicts adult inflammation in a life-course study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, K.; Upton, D.; Semple, S.; McKune, A. Systemic low-grade inflammation in post-traumatic stress disorder: A systematic review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirtcliff, E.A.; Coe, C.L.; Pollak, S.D. Early childhood stress is associated with elevated antibody levels to herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2963–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Moffitt, T.E.; Pariante, C.M.; Ambler, A.; Poulton, R.; Caspi, A. Elevated inflammation levels in depressed adults with a history of childhood maltreatment. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Gouin, J.P.; Weng, N.P.; Malarkey, W.B.; Beversdorf, D.Q.; Glaser, R. Childhood adversity heightens the impact of later-life caregiving stress on telomere length and inflammation. Psychosom. Med. 2011, 73, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, T.W.; Mletzko, T.C.; Alagbe, O.; Musselman, D.L.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Miller, A.H.; Heim, C.M. Increased stress-induced inflammatory responses in male patients with major depression and increased early life stress. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagaria, A.; Fiori, V.; Vacca, M.; Lombardo, C.; Pariante, C.M.; Ballesio, A. Inflammation as a mediator between adverse childhood experiences and adult depression: A meta-analytic structural equation model. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 357, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Caspi, A.; Williams, B.; Ambler, A.; Sugden, K.; Mika, J.; Werts, H.; Freeman, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Moffitt, T.E.; et al. Biological embedding of stress through inflammation processes in childhood. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slopen, N.; Kubzansky, L.D.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Koenen, K.C. Childhood adversity and inflammatory processes in youth: A prospective study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D.; Handley, E.D.; Rogosch, F.A. Child maltreatment, inflammation, and internalizing symptoms: Investigating the roles of C-reactive protein, gene variation, and neuroendocrine regulation. Dev. Psychopathol. 2015, 27, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Lv, J.; Fairhurst-Hunter, Z.; Millwood, I.Y.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; et al. Associations of Adiposity, Circulating Protein Biomarkers, and Risk of Major Vascular Diseases. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, K.R.; Repetti, R.L.; Reynolds, B.M.; Robles, T.F. Change in parent-child conflict and the HPA-axis: Where should we be looking and for how long? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 68, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, K.R.; Repetti, R.L.; Reynolds, B.M.; Robles, T.F. Interparental conflict and child HPA-axis responses to acute stress: Insights using intensive repeated measures. J. Fam. Psychol. 2018, 32, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: Molecular mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 1998, 94, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waage, A.; Slupphaug, G.; Shalaby, R. Glucocorticoids inhibit the production of IL6 from monocytes, endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Eur. J. Immunol. 1990, 20, 2439–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnar, M.R.; Donzella, B. Social regulation of the cortisol levels in early human development. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2002, 27, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnar, M.; Quevedo, K. The neurobiology of stress and development. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2007, 58, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarullo, A.R.; Gunnar, M.R. Child maltreatment and the developing HPA axis. Horm. Behav. 2006, 50, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.E.; Chen, E. Harsh family climate in early life presages the emergence of a proinflammatory phenotype in adolescence. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.L.; Nacewicz, B.M.; Sutterer, M.J.; Cayo, A.A.; Schaefer, S.M.; Rudolph, K.D.; Shirtcliff, E.A.; Pollak, S.D.; Davidson, R.J. Behavioral problems after early life stress: Contributions of the hippocampus and amygdala. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovallo, W.R. Early life adversity reduces stress reactivity and enhances impulsive behavior: Implications for health behaviors. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 90, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, K.D.; Hammen, C. Age and gender as determinants of stress exposure, generation, and reactions in youngsters: A transactional perspective. Child. Dev. 1999, 70, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, K.D.; Hammen, C.; Burge, D.; Lindberg, N.; Herzberg, D.; Daley, S.E. Toward an interpersonal life-stress model of depression: The developmental context of stress generation. Dev. Psychopathol. 2000, 12, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Haroon, E.; Raison, C.L.; Felger, J.C. Cytokine targets in the brain: Impact on neurotransmitters and neurocircuits. Depress. Anxiety 2013, 30, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavich, G.M.; Irwin, M.R. From stress to inflammation and major depressive disorder: A social signal transduction theory of depression. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 774–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, D.G.; Holmes, A.J.; Birk, J.L.; Brooks, N.; Lyons-Ruth, K.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Childhood adversity is associated with left basal ganglia dysfunction during reward anticipation in adulthood. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyer, A.E.; Kaufman, J.; Hodgdon, H.B.; Masten, C.L.; Jazbec, S.; Pine, D.S.; Ernst, M. Behavioral alterations in reward system function: The role of childhood maltreatment and psychopathology. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2006, 45, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Cytokines for psychologists: Implications of bidirectional immune-to-brain communication for understanding behavior, mood, and cognition. Psychol. Rev. 1998, 105, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Maletic, V.; Raison, C.L. Inflammation and its discontents: The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmiston, E.E.; Wang, F.; Mazure, C.M.; Guiney, J.; Sinha, R.; Mayes, L.C.; Blumberg, H.P. Corticostriatal-limbic gray matter morphology in adolescents with self-reported exposure to childhood maltreatment. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2011, 165, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianaros, P.J.; Marsland, A.L.; Sheu, L.K.; Erickson, K.I.; Verstynen, T.D. Inflammatory pathways link socioeconomic inequalities to white matter architecture. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.L.; Hair, N.; Shen, D.G.; Shi, F.; Gilmore, J.H.; Wolfe, B.L.; Pollak, S.D. Family poverty affects the rate of human infant brain growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, G.M.; Duda, J.T.; Avants, B.B.; Wu, J.; Farah, M.J. Associations between children’s socioeconomic status and prefrontal cortical thickness. Dev. Sci. 2013, 16, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luby, J.; Belden, A.; Botteron, K.; Marrus, N.; Harms, M.P.; Babb, C.; Nishino, T.; Barch, D. The effects of poverty on childhood brain development: The mediating effect of caregiving and stressful life events. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsland, A.L.; Gianaros, P.J.; Abramowitch, S.M.; Manuck, S.B.; Hariri, A.R. Interleukin-6 covaries inversely with hippocampal grey matter volume in middle-aged adults. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satizabal, C.L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Mazoyer, B.; Dufouil, C.; Tzourio, C. Circulating IL-6 and CRP are associated with MRI findings in the elderly: The 3C-Dijon Study. Neurology 2012, 78, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; McEwen, B.S. Adverse childhood experiences, allostasis, allostatic load, and age-related disease. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shonkoff, J.P.; Boyce, W.T.; McEwen, B.S. Neuroscience, molecular biology, and the childhood roots of health disparities: Building a new framework for health promotion and disease prevention. JAMA 2009, 301, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, M.H.; Samson, J.A. Childhood maltreatment and psychopathology: A case for ecophenotypic variants as clinically and neurobiologically distinct subtypes. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 1114–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusslock, R.; Miller, G.E. Early-Life Adversity and Physical and Emotional Health Across the Lifespan: A Neuroimmune Network Hypothesis. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.A.; Demetrikopoulos, M.K.; Schleifer, S.J.; Keller, S.E. Phagocytosis and killing of Staphylococcus aureus: Effects of stress and depression in children. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1997, 4, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birmaher, B.; Rabin, B.S.; Garcia, M.R.; Jain, U.; Whiteside, T.L.; Williamson, D.E.; al-Shabbout, M.; Nelson, B.C.; Dahl, R.E.; Ryan, N.D. Cellular immunity in depressed, conduct disorder, and normal adolescents: Role of adverse life events. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 1994, 33, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witek Janusek, L.; Tell, D.; Albuquerque, K.; Mathews, H.L. Childhood adversity increases vulnerability for behavioral symptoms and immune dysregulation in women with breast cancer. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 30, S149–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyman, P.A.; Moynihan, J.; Eberly, S.; Cox, C.; Cross, W.; Jin, X.; Caserta, M.T. Association of family stress with natural killer cell activity and the frequency of illnesses in children. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2007, 161, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaydin, H.; Abali, O.; Akdeniz, N.O.; Kok, B.E.; Gunes, A.; Yildirim, A.; Deniz, G. Immune system changes after sexual abuse in adolescents. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Chim, L.S.; Strunk, R.C.; Miller, G.E. The role of the social environment in children and adolescents with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.J.; Finn, P.; Contreras, J.P.; Cohen, S.; Wright, R.O.; Staudenmayer, J.; Wand, M.; Perkins, D.; Weiss, S.T.; Gold, D.R. Chronic caregiver stress and IgE expression, allergen-induced proliferation, and cytokine profiles in a birth cohort predisposed to atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, T.; Mizoi, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Yamada, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tatsuno, Y.; Nishi, K. Thymus of abused/neglected children. Forensic Sci. Int. 1992, 53, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.F.; Khandaker, G.M.; Dauvermann, M.R.; Morris, D.; Zammit, S.; Donohoe, G. Effects of early life adversity on immune function and cognitive performance: Results from the ALSPAC cohort. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2020, 55, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, B.M.; Coe, C.L.; Doyle, C.M.; Sheerar, D.; Slukvina, A.; Donzella, B.; Gunnar, M.R. Persistent skewing of the T-cell profile in adolescents adopted internationally from institutional care. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 77, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwenspoek, M.M.C.; Sias, K.; Hengesch, X.; Schaan, V.K.; Leenen, F.A.D.; Adams, P.; Meriaux, S.B.; Schmitz, S.; Bonnemberger, F.; Ewen, A.; et al. T Cell Immunosenescence after Early Life Adversity: Association with Cytomegalovirus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.A.; Jones, M.J.; Doom, J.R.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Gunnar, M.R.; Kobor, M.S. Differential DNA methylation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in adolescents exposed to significant early but not later childhood adversity. Dev. Psychopathol. 2016, 28, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, M.T.; O’Connor, T.G.; Wyman, P.A.; Wang, H.; Moynihan, J.; Cross, W.; Tu, X.; Jin, X. The associations between psychosocial stress and the frequency of illness, and innate and adaptive immune function in children. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clover, R.D.; Abell, T.; Becker, L.A.; Crawford, S.; Ramsey, C.N., Jr. Family functioning and stress as predictors of influenza B infection. J. Fam. Pract. 1989, 28, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyce, W.T.; Chesney, M.; Alkon, A.; Tschann, J.M.; Adams, S.; Chesterman, B.; Cohen, F.; Kaiser, P.; Folkman, S.; Wara, D. Psychobiologic reactivity to stress and childhood respiratory illnesses: Results of two prospective studies. Psychosom. Med. 1995, 57, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.J.; Haggerty, R.J. Streptococcal infections in families. Factors altering individual susceptibility. Pediatrics 1962, 29, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, R.J.; Cohen, S.; Carey, V.; Weiss, S.T.; Gold, D.R. Parental stress as a predictor of wheezing in infancy: A prospective birth-cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Doyle, W.J.; Turner, R.B.; Alper, C.M.; Skoner, D.P. Childhood socioeconomic status and host resistance to infectious illness in adulthood. Psychosom. Med. 2004, 66, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.E.; Chen, E.; Fok, A.K.; Walker, H.; Lim, A.; Nicholls, E.F.; Cole, S.; Kobor, M.S. Low early-life social class leaves a biological residue manifested by decreased glucocorticoid and increased proinflammatory signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14716–14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziol-Guest, K.M.; Duncan, G.J.; Kalil, A.; Boyce, W.T. Early childhood poverty, immune-mediated disease processes, and adult productivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109 (Suppl. 2), 17289–17293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Chiang, J.J.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Miller, G.E. Good Relationships with Parents During Childhood as Buffers of the Association between Childhood Disadvantage and Adult Susceptibility to the Common Cold. Psychosom. Med. 2020, 82, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, S.E.; Dowd, J.B.; Fletcher, H.; Nellums, L.B.; Wurie, F.; Boccia, D. A systematic review of the impact of psychosocial factors on immunity: Implications for enhancing BCG response against tuberculosis. SSM Popul. Health 2020, 10, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.G.; Wang, H.; Moynihan, J.A.; Wyman, P.A.; Carnahan, J.; Lofthus, G.; Quataert, S.A.; Bowman, M.; Burke, A.S.; Caserta, M.T. Observed parent-child relationship quality predicts antibody response to vaccination in children. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, A.A.; Shrout, M.R.; Renna, M.E.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Psychological and Behavioral Predictors of Vaccine Efficacy: Considerations for COVID-19. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2021, 16, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, R.P.; Peek, M.K.; Perez, N.A.; Yetman, D.L.; Cutchin, M.P.; Goodwin, J.S. Herpesvirus reactivation and socioeconomic position: A community-based study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2010, 64, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDade, T.W.; Stallings, J.F.; Angold, A.; Costello, E.J.; Burleson, M.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Glaser, R.; Worthman, C.M. Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in whole blood spots: A minimally invasive method for assessing an aspect of cell-mediated immunity. Psychosom. Med. 2000, 62, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeer, K.K.; Ford, J.L.; Browning, C.R. Early childhood family instability and immune system dysregulation in adolescence. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 102, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lendor, C.; Johnson, A.; Perzanowski, M.; Chew, G.L.; Goldstein, I.F.; Kelvin, E.; Perera, F.; Miller, R.L. Effects of winter birth season and prenatal cockroach and mouse allergen exposure on indoor allergen-specific cord blood mononuclear cell proliferation and cytokine production. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 101, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, J.; Kusel, M.; Holt, B.J.; Suriyaarachchi, D.; Serralha, M.; Hollams, E.; Yerkovich, S.T.; Subrata, L.S.; Ladyman, C.; Sadowska, A.; et al. Prenatal versus postnatal sensitization to environmental allergens in a high-risk birth cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F. Programming of host metabolism by the gut microbiota. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 58 (Suppl. 2), 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatsinki, A.K.; Keskitalo, A.; Laitinen, V.; Munukka, E.; Uusitupa, H.M.; Lahti, L.; Kortesluoma, S.; Mustonen, P.; Rodrigues, A.J.; Coimbra, B.; et al. Maternal prenatal psychological distress and hair cortisol levels associate with infant fecal microbiota composition at 2.5 months of age. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 119, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant-Beurmann, S.; Jumare, J.; Ndembi, N.; Matthew, O.; Shutt, A.; Omoigberale, A.; Martin, O.A.; Fraser, C.M.; Charurat, M. Dynamics of the infant gut microbiota in the first 18 months of life: The impact of maternal HIV infection and breastfeeding. Microbiome 2022, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnke, J.R.; Roach, J.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Thompson, A.L. Maternal precarity and HPA axis functioning shape infant gut microbiota and HPA axis development in humans. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlmans, M.A.; Korpela, K.; Riksen-Walraven, J.M.; de Vos, W.M.; de Weerth, C. Maternal prenatal stress is associated with the infant intestinal microbiota. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 53, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes, G.D.A.; Eckermann, H.A.; de Vos, W.M.; de Weerth, C. Does entry to center-based childcare affect gut microbial colonization in young infants? Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskitalo, A.; Aatsinki, A.K.; Kortesluoma, S.; Pelto, J.; Korhonen, L.; Lahti, L.; Lukkarinen, M.; Munukka, E.; Karlsson, H.; Karlsson, L. Gut microbiota diversity but not composition is related to saliva cortisol stress response at the age of 2.5 months. Stress 2021, 24, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasarevic, E.; Howerton, C.L.; Howard, C.D.; Bale, T.L. Alterations in the Vaginal Microbiome by Maternal Stress Are Associated with Metabolic Reprogramming of the Offspring Gut and Brain. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3265–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, B.M.; Horne, R.; Donzella, B.; Szamosi, J.C.; Coe, C.L.; Foster, J.A.; Gunnar, M.R. Microbiota-immune alterations in adolescents following early life adversity: A proof of concept study. Dev. Psychobiol. 2021, 63, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.L.; Fields, A.; Gee, D.G.; Gabard-Durnam, L.; Caldera, C.; Humphreys, K.L.; Goff, B.; Flannery, J.; Telzer, E.H.; Shapiro, M.; et al. Mind and gut: Associations between mood and gastrointestinal distress in children exposed to adversity. Dev. Psychopathol. 2020, 32, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Compher, C.; Chen, E.Z.; Smith, S.A.; Shah, R.D.; Bittinger, K.; Chehoud, C.; Albenberg, L.G.; Nessel, L.; Gilroy, E.; et al. Comparative metabolomics in vegans and omnivores reveal constraints on diet-dependent gut microbiota metabolite production. Gut 2016, 65, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, S.M.; Lee, E.J.; Kotter, C.V.; Austin, G.L.; Gianella, S.; Siewe, B.; Smith, D.M.; Landay, A.L.; McManus, M.C.; Robertson, C.E.; et al. Gut dendritic cell activation links an altered colonic microbiome to mucosal and systemic T-cell activation in untreated HIV-1 infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalambous, E.G.; Meriaux, S.B.; Guebels, P.; Muller, C.P.; Leenen, F.A.D.; Elwenspoek, M.M.C.; Thiele, I.; Hertel, J.; Turner, J.D. Early-Life Adversity Leaves Its Imprint on the Oral Microbiome for More Than 20 Years and Is Associated with Long-Term Immune Changes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajid, A.; van Zanten, S.V.; Mughal, M.K.; Biringer, A.; Austin, M.P.; Vermeyden, L.; Kingston, D. Adversity in childhood and depression in pregnancy. Arch. Women’s Ment. Health 2020, 23, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel Schetter, C.; Tanner, L. Anxiety, depression and stress in pregnancy: Implications for mothers, children, research, and practice. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2012, 25, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.M. Integrative Review of Pregnancy Health Risks and Outcomes Associated with Adverse Childhood Experiences. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2018, 47, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dachew, B.A.; Mamun, A.; Maravilla, J.C.; Alati, R. Association between hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the development of offspring mental and behavioural problems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 260, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.V.; Gotman, N.; Yonkers, K.A. Early Childhood Adversity and Pregnancy Outcomes. Matern. Child. Health J. 2016, 20, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, S.L.; Christian, L.M.; Alston, A.D.; Salsberry, P.J. Childhood stress and birth timing among African American women: Cortisol as biological mediator. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 84, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.E.; Culhane, J.; Grobman, W.; Simhan, H.; Williamson, D.E.; Adam, E.K.; Buss, C.; Entringer, S.; Kim, K.Y.; Felipe Garcia-Espana, J.; et al. Mothers’ childhood hardship forecasts adverse pregnancy outcomes: Role of inflammatory, lifestyle, and psychosocial pathways. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angerud, K.; Annerback, E.M.; Tyden, T.; Boddeti, S.; Kristiansson, P. Adverse childhood experiences and depressive symptomatology among pregnant women. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2018, 97, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.; Biswas, T.; Scott, J.; Sly, P.D.; McIntyre, H.D.; Thorpe, K.; Boyle, F.M.; Dekker, M.N.; Doi, S.; Mitchell, M.; et al. Adverse childhood experiences, the risk of pregnancy complications and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e063826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, A.M.; Szilagyi, M.A.; Jee, S.H.; Manly, J.T.; Briggs, R.; Szilagyi, P.G. Parental perspectives of screening for adverse childhood experiences in pediatric primary care. Fam. Syst. Health 2018, 36, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, A.M.; Goodman, S.H. The association between psychopathology in fathers versus mothers and children’s internalizing and externalizing behavior problems: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 746–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, B.R.; Sanchez, M.M. Understanding behavioral effects of early life stress using the reactive scope and allostatic load models. Dev. Psychopathol. 2011, 23, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widom, C.S.; Czaja, S.J.; DuMont, K.A. Intergenerational transmission of child abuse and neglect: Real or detection bias? Science 2015, 347, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, M.E.; Yehuda, R. Intergenerational Transmission of Stress in Humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, P.A.; Beauchamp, K.G.; Roos, L.E.; Noll, L.K.; Flannery, J.; Delker, B.C. The Neurobiology of Intervention and Prevention in Early Adversity. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2016, 12, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querdasi, F.R.; Enders, C.; Karnani, N.; Broekman, B.; Yap Seng, C.; Gluckman, P.D.; Mary Daniel, L.; Yap, F.; Eriksson, J.G.; Cai, S.; et al. Multigenerational adversity impacts on human gut microbiome composition and socioemotional functioning in early childhood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2213768120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, A.J.; de Aguero, M.G.; Ganal-Vonarburg, S.C. How nutrition and the maternal microbiota shape the neonatal immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moog, N.K.; Entringer, S.; Rasmussen, J.M.; Styner, M.; Gilmore, J.H.; Kathmann, N.; Heim, C.M.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Buss, C. Intergenerational Effect of Maternal Exposure to Childhood Maltreatment on Newborn Brain Anatomy. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ader, R.; Friedman, S.B. Differential Early Experiences and Susceptibility to Transplanted Tumor in the Rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1965, 59, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, G.F.; Levine, S.; Kraft, J.K. Early experience and immunity. Nature 1968, 220, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, C.A.; Pierre, P.J.; Haddad, T.; Bice, C.; Suomi, S.J.; Grant, K.A.; Friedman, D.P.; Bennett, A.J. Long-term effects of differential early rearing in rhesus macaques: Behavioral reactivity in adulthood. Dev. Psychobiol. 2012, 54, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, B.R.; Grand, A.P.; McCormack, K.M.; Shi, Y.; LaPrarie, J.L.; Maestripieri, D.; Styner, M.A.; Sanchez, M.M. Early adverse experience increases emotional reactivity in juvenile rhesus macaques: Relation to amygdala volume. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schino, G.; Speranza, L.; Troisi, A. Early maternal rejection and later social anxiety in juvenile and adult Japanese macaques. Dev. Psychobiol. 2001, 38, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, P.; Brenhouse, H.C. Broken or maladaptive? Altered trajectories in neuroinflammation and behavior after early life adversity. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2015, 11, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, M.B.; Deak, T.; Schiml-Webb, P.A. Early attachment-figure separation and increased risk for later depression: Potential mediation by proinflammatory processes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, N.; Lightman, S.L. The maternal-neonatal neuro-immune interface: Are there long-term implications for inflammatory or stress-related disease? J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, C.L.; Rosenberg, L.T.; Levine, S. Effect of maternal separation on the complement system and antibody responses in infant primates. Int. J. Neurosci. 1988, 40, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.W.; Conti, G.; Arevalo, J.M.; Ruggiero, A.M.; Heckman, J.J.; Suomi, S.J. Transcriptional modulation of the developing immune system by early life social adversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20578–20583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieck, A.; Andersen, S.L.; Brenhouse, H.C. Evidence for a neuroinflammatory mechanism in delayed effects of early life adversity in rats: Relationship to cortical NMDA receptor expression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 28, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, M.B.; Deak, T.; Schiml-Webb, P.A.; Carlisle, C.W.; O’Brien, E. Maternal separation produces, and a second separation enhances, core temperature and passive behavioral responses in guinea pig pups. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 100, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumertz, F.S.; Kestering-Ferreira, E.; Orso, R.; Creutzberg, K.C.; Tractenberg, S.G.; Stocchero, B.A.; Viola, T.W.; Grassi-Oliveira, R. Effects of early life stress on brain cytokines: A systematic review and meta-analysis of rodent studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 139, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekhbat, M.; Neigh, G.N. Sex differences in the neuro-immune consequences of stress: Focus on depression and anxiety. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, H.; Benson, S.; Wegner, A.; Spreitzer, I.; Schedlowski, M.; Elsenbruch, S. Men and women differ in inflammatory and neuroendocrine responses to endotoxin but not in the severity of sickness symptoms. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 52, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Simen, A.; Mane, S.; Kaffman, A. Early life stress inhibits expression of a novel innate immune pathway in the developing hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocyk, A.; Dudys, D.; Przyborowska, A.; Majcher, I.; Mackowiak, M.; Wedzony, K. Maternal separation affects the number, proliferation and apoptosis of glia cells in the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area of juvenile rats. Neuroscience 2011, 173, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviani, B.; Boraso, M.; Valero, M.; Gardoni, F.; Marco, E.M.; Llorente, R.; Corsini, E.; Galli, C.L.; Di Luca, M.; Marinovich, M.; et al. Early maternal deprivation immunologically primes hippocampal synapses by redistributing interleukin-1 receptor type I in a sex dependent manner. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 35, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuru, Y.; Nabekura, J.; Ishikawa, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Koibuchi, N. Early-life stress increases the motility of microglia in adulthood. J. Physiol. Sci. 2015, 65, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachiller, S.; Paulus, A.; Vazquez-Reyes, S.; Garcia-Dominguez, I.; Deierborg, T. Maternal separation leads to regional hippocampal microglial activation and alters the behavior in the adolescence in a sex-specific manner. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 9, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitsur, R.; Hunzeker, J.; Sheridan, J.F. Role of early stress in the individual differences in host response to viral infection. Brain Behav. Immun. 2006, 20, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.R.; Holland, F.H.; Shansky, R.M.; Brenhouse, H.C. Sex-specific effects of early life stress on social interaction and prefrontal cortex dendritic morphology in young rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 310, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, K.A.; Ossenkopp, K.P.; Kavaliers, M.; Macfabe, D.F. Pre- and neonatal exposure to lipopolysaccharide or the enteric metabolite, propionic acid, alters development and behavior in adolescent rats in a sexually dimorphic manner. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, A.S.; Mello, B.S.F.; Borella, V.C.M.; da Silva Araujo, T.; da Silva, F.E.R.; Sousa, F.C.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Gama, C.S.; Seeman, M.V.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; et al. Two-hit model of schizophrenia induced by neonatal immune activation and peripubertal stress in rats: Study of sex differences and brain oxidative alterations. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 331, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourlon, V.; Baudin, A.; Blanc, O.; Lauber, A.; Giros, B.; Naudon, L.; Dauge, V. Maternal deprivation induces depressive-like behaviours only in female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 213, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotten, H.A.; Kalinichev, M.; Hagan, J.J.; Marsden, C.A.; Fone, K.C. Long-lasting changes in behavioural and neuroendocrine indices in the rat following neonatal maternal separation: Gender-dependent effects. Brain Res. 2006, 1097, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez de Cossio, L.; Guzman, A.; van der Veldt, S.; Luheshi, G.N. Prenatal infection leads to ASD-like behavior and altered synaptic pruning in the mouse offspring. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 63, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Yim, Y.S.; Ha, S.; Atarashi, K.; Tan, T.G.; Longman, R.S.; Honda, K.; Littman, D.R.; Choi, G.B.; et al. Maternal gut bacteria promote neurodevelopmental abnormalities in mouse offspring. Nature 2017, 549, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincel, M.; Lepinay, A.L.; Delage, P.; Fioramonti, J.; Theodorou, V.S.; Laye, S.; Darnaudery, M. Maternal high-fat diet prevents developmental programming by early-life stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.Y.; Han, S.H.; Woo, R.S.; Jang, S.H.; Min, S.S. Adolescent mice show anxiety- and aggressive-like behavior and the reduction of long-term potentiation in mossy fiber-CA3 synapses after neonatal maternal separation. Neuroscience 2016, 316, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin Yim, Y.; Park, A.; Berrios, J.; Lafourcade, M.; Pascual, L.M.; Soares, N.; Yeon Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Waisman, A.; et al. Reversing behavioural abnormalities in mice exposed to maternal inflammation. Nature 2017, 549, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M.C.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ogawa, S. Early life stress disrupts peripubertal development of aggression in male mice. Neuroreport 2011, 22, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincel, M.; Aubert, P.; Chevalier, J.; Grohard, P.A.; Basso, L.; Monchaux de Oliveira, C.; Helbling, J.C.; Levy, E.; Chevalier, G.; Leboyer, M.; et al. Multi-hit early life adversity affects gut microbiota, brain and behavior in a sex-dependent manner. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; McVey Neufeld, K.A. Gut-brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Rodriguez, E.M.; Cruz, A.A.; De Abreu, J.C.; Beurel, E. Stress, inflammation, microbiome and depression. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2023, 227–228, 173561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1420, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.T.; Dowd, S.E.; Galley, J.D.; Hufnagle, A.R.; Allen, R.G.; Lyte, M. Exposure to a social stressor alters the structure of the intestinal microbiota: Implications for stressor-induced immunomodulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharwani, A.; Mian, M.F.; Foster, J.A.; Surette, M.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Forsythe, P. Structural & functional consequences of chronic psychosocial stress on the microbiome & host. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 63, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, G.; Blennerhassett, P.; Lu, J.; Deng, Y.; Park, A.J.; Green, W.; Denou, E.; Silva, M.A.; Santacruz, A.; Sanz, Y.; et al. Microbiota and host determinants of behavioural phenotype in maternally separated mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubeva, A.V.; Crampton, S.; Desbonnet, L.; Edge, D.; O’Sullivan, O.; Lomasney, K.W.; Zhdanov, A.V.; Crispie, F.; Moloney, R.D.; Borre, Y.E.; et al. Prenatal stress-induced alterations in major physiological systems correlate with gut microbiota composition in adulthood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 60, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Marchesi, J.R.; Scully, P.; Codling, C.; Ceolho, A.M.; Quigley, E.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: Implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasarevic, E.; Howard, C.D.; Misic, A.M.; Beiting, D.P.; Bale, T.L. Stress during pregnancy alters temporal and spatial dynamics of the maternal and offspring microbiome in a sex-specific manner. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Chen, R.; Lee, T.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Nie, Y.; Sun, T. Prenatal stress leads to deficits in brain development, mood related behaviors and gut microbiota in offspring. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 15, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusceddu, M.M.; El Aidy, S.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.; Stanton, C.; Kelly, P.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs) Reverse the Impact of Early-Life Stress on the Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodenas, C.L.; Bergonzelli, G.E.; Nutten, S.; Schumann, A.; Cherbut, C.; Turini, M.; Ornstein, K.; Rochat, F.; Corthesy-Theulaz, I. Nutritional approach to restore impaired intestinal barrier function and growth after neonatal stress in rats. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Kamada, K.; Mizushima, K.; Higashimura, Y.; Katada, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Handa, O.; Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Itoh, Y. Changes in Intestinal Motility and Gut Microbiota Composition in a Rat Stress Model. Digestion 2017, 95, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Long, X.; Zuo, X.L.; Hou, X.H.; Cong, Y.Z.; Li, Y.Q. Visceral hypersensitive rats share common dysbiosis features with irritable bowel syndrome patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5211–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini-Khoei, H.; Haghani-Samani, E.; Beigi, M.; Soltani, A.; Mobini, G.R.; Balali-Dehkordi, S.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Alizadeh, A.; Hojjati, M.R.; et al. On the role of corticosterone in behavioral disorders, microbiota composition alteration and neuroimmune response in adult male mice subjected to maternal separation stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 66, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.T.; Coe, C.L. Maternal separation disrupts the integrity of the intestinal microflora in infant rhesus monkeys. Dev. Psychobiol. 1999, 35, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Perez, A.; Perez-Villalba, A.; Benitez-Paez, A.; Campillo, I.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium CECT 7765 modulates early stress-induced immune, neuroendocrine and behavioral alterations in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Early-life adversity and brain development: Is the microbiome a missing piece of the puzzle? Neuroscience 2017, 342, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnsten, A.F. Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Herman, J.P. Neural regulation of endocrine and autonomic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoban, A.E.; Stilling, R.M.; Gerard, M.M.; Moloney, R.D.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Clarke, G. Microbial regulation of microRNA expression in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Microbiome 2017, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, A.E.; Stilling, R.M.; Ryan, F.J.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Claesson, M.J.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. Regulation of prefrontal cortex myelination by the microbiota. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beurel, E.; Nemeroff, C.B. Early Life Adversity, Microbiome, and Inflammatory Responses. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070802
Beurel E, Nemeroff CB. Early Life Adversity, Microbiome, and Inflammatory Responses. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(7):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070802
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeurel, Eléonore, and Charles B. Nemeroff. 2024. "Early Life Adversity, Microbiome, and Inflammatory Responses" Biomolecules 14, no. 7: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070802
APA StyleBeurel, E., & Nemeroff, C. B. (2024). Early Life Adversity, Microbiome, and Inflammatory Responses. Biomolecules, 14(7), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070802






