Abstract
Red blood cell (RBC) storage solutions have evolved significantly over the past decades to optimize the preservation of cell viability and functionality during hypothermic storage. This comprehensive review provides an in-depth analysis of the effects of various storage solutions and conditions on critical RBC parameters during refrigerated preservation. A wide range of solutions, from basic formulations such as phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), to advanced additive solutions (ASs), like AS-7 and phosphate, adenine, glucose, guanosine, saline, and mannitol (PAGGSM), are systematically compared in terms of their ability to maintain key indicators of RBC integrity, including adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels, morphology, and hemolysis. Optimal RBC storage requires a delicate balance of pH buffering, metabolic support, oxidative damage prevention, and osmotic regulation. While the latest alkaline solutions enable up to 8 weeks of storage, some degree of metabolic and morphological deterioration remains inevitable. The impacts of critical storage conditions, such as the holding temperature, oxygenation, anticoagulants, irradiation, and processing methods, on the accumulation of storage lesions are also thoroughly investigated. Personalized RBC storage solutions, tailored to individual donor characteristics, represent a promising avenue for minimizing storage lesions and enhancing transfusion outcomes. Further research integrating omics profiling with customized preservation media is necessary to maximize post-transfusion RBC survival and functions. The continued optimization of RBC storage practices will not only enhance transfusion efficacy but also enable blood banking to better meet evolving clinical needs.
1. Introduction
Of the ~5 billion cells per milliliter of blood, red blood cells (RBCs) make up >99% of all cellular components, playing a central role in oxygen delivery throughout the body [1]. Most of the oxygen transport is carried out by the RBC protein hemoglobin (Hb), which comprises four subunits, each having one polypeptide chain and one heme group; each single Hb has four binding sites for oxygen in the iron (Fe) atoms present in the heme groups [2,3]. For many medical conditions, including certain types of anemia, RBC transfusions are required to supply the body with healthy RBCs and maintain a sufficient level of Hb [4] since vital organs, such as the heart, brain, and kidneys, have a limited ability to increase oxygen uptake during anemia, necessitating RBC transfusions to increase oxygen supply to the tissues [5].
Approximately 36,000 units of RBCs are used daily in the U.S., and hospitals have a great challenge to maintain a reliable supply, given the 6-week expiration period from the blood donation date [6]. Many hospitals have already amended their transfusion protocols since the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and due to blood donor shortage by diluting RBC units (as well as tightening transfusion criteria) [6]. To maintain an appropriate supply of RBC units, RBCs obtained from healthy donors must be appropriately stored at blood banks because no widely available artificial oxygen-carrying substitutes exist to replace human blood [7]. Blood banks face several challenges in collecting and preserving donated RBCs to meet transfusion needs. Donations are limited due to the low number of eligible donors and restrictions on donation frequency to avoid adverse effects like donor anemia [8]. Therefore, research is directed toward improving storage techniques that can prolong the RBC unit’s shelf life to optimize donated blood utilization. Currently, the allowed storage duration is 42 days from donation. Enhancing RBC preservation efficacy and durability could expand blood reserves and reduce donor reliance. Refining RBC storage strategies is critical due to the lack of synthetic substitutes and persistent blood shortage and may result in the more effective use of the finite available supply of RBC units. Given the RBCs’ critical function, the effects of blood storage solutions and conditions on RBC viability and activity are substantial.
Different storage solutions have been developed over the last decades, like phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), different additive solutions (ASs), like AS-1, AS-3, AS-5, AS-7, and others, like SAGM, and PAGGSM, named after their constituents saline, adenine, glucose, and mannitol, and phosphate, adenine, glucose, guanosine, saline, and mannitol, respectively [9]. These contain preservatives to prolong the RBC shelf life, but an ideal storage solution has not been developed. For instance, PBS helps protect the RBC membrane integrity, but declined cell activity has been observed during prolonged storage [10]. SAGM preserves Hb levels but can increase free Hb accumulation [11]. Precisely, storage lesions, like declining adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and membrane integrity, compromise RBC functions and viability over time [12]. Moreover, RBC functions and viability are also affected by a multitude of storage factors, like pH, temperature, and changes in the solution composition [10,11]. For instance, changes in the pH can significantly affect RBC viability and stability [13]. On the other hand, other factors, like temperature, can influence the Hb levels and the protein activity [14,15]. Despite recent advancements in the development of improved storage solutions, limitations still remain. This review aims to address current challenges and to provide an overview of the progress in the field by presenting recently developed storage methods to minimize RBC storage-related lesions and maximize the RBC unit shelf life.
This review comprehensively analyzes various solutions and conditions employed for RBC unit storage, assessing their efficacy in maintaining viability and functions during hypothermic (1–6 °C) preservation. Key outcomes examined based on stored RBCs include ATP levels, the redox balance, membrane integrity, morphology, and Hb levels and stability, among others. By presenting and summarizing current evidence on different solutions and storage conditions, this review sheds light on the best practices for RBC storage that uphold cell integrity and function, minimizing potential side effects on transfusion recipients. Specifically, we aim to provide an exhaustive examination of the effects of storage solutions by assimilating pertinent research and evaluating both conventional and novel techniques to find optimal evidence-based approaches that minimize RBC storage lesions and maximize shelf life. The insights gathered from this work can inform blood-banking protocols, guide research directions for improving donated blood product preservation, and optimize real-world banking practices in this critical area.
2. Methodology
2.1. Search Strategy
A comprehensive systematic literature search following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines was conducted to identify as many as possible studies on RBC storage solutions, additives, and conditions. PRISMA provides an evidence-based protocol for conducting systematic reviews, including guidance on the optimal search strategies, study selection, data extraction, and reporting methodology. Using PRISMA enhances the thoroughness, consistency, and transparency of the review process. Comprehensive searches were conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus. These databases were chosen because they cover novel research in biomedical and life sciences, ensuring a thorough search foundation for identifying relevant studies on RBC storage approaches. Search strategies combined controlled vocabulary terms (MeSH, Emtree), as well as free text keywords, such as “blood storage”, “red blood cell”, “erythrocyte”, “additive solution”, “hemolysis”, “metabolism”, “ATP”, “oxidative stress”, “cytokine”, “storage lesion”, and names of specific storage solutions. Reference lists of eligible studies were hand-searched. This rigorous, systematic search of multiple databases using both controlled and free-text terminology related to RBC storage maximized the identification of potentially relevant studies for inclusion in the review; thus, the comprehensive PRISMA-guided search methodology enhanced the scientific quality of this work.
2.2. Study Selection
The selection of studies was executed meticulously, with a strong emphasis on the quality and scientific rigor of the published data [16]. In this context, we favored peer-reviewed original articles while excluding other publication formats, like short communications, technical reports, letters, notes, abstracts, and surveys. Unpublished works were also excluded to maintain the standard of trustworthiness. To incorporate only the most recent research in the field, only studies published between an inclusive timeline of 2000 and 2023 were finally incorporated in our analysis. The selection process involved deduplication, screening, and filtering stepwise. An initial search using the defined terms returned a substantial number of articles, the majority of which were unrelated to the focus of this work. The selection criteria focused on including only peer-reviewed journal publications, using the English language, and studies emphasizing how RBC storage solutions and conditions influence the properties and biological functions of the cells. A total of 84 studies were finally included in this work. This meticulous selection process was crucial in maintaining the quality and relevance of the studies included in our analysis. The study selection process is shown in Figure 1.
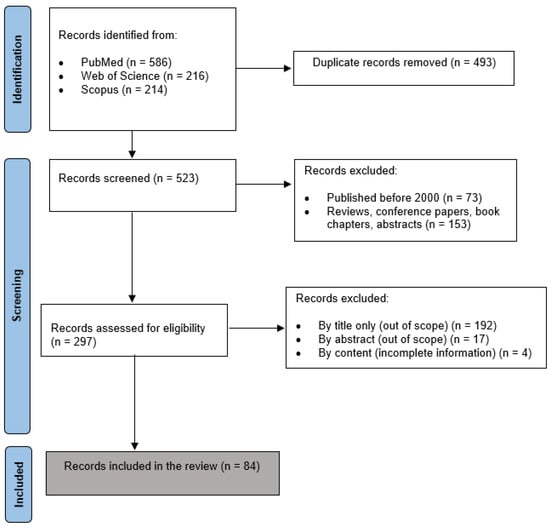
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of the study selection process.
2.3. Data Extraction
A comprehensive, standardized data extraction form was created in Microsoft Excel 2021 (version 18.0) to systematically collect all relevant data from the included studies. Separate columns were designated in the spreadsheet to record study identification data, including the authors and publication year; sample size or number of blood units examined; storage solutions and additives (including the concentrations and composition of the solutions); duration of storage (usually ranging from 10 days to over 50 days); storage temperature (typically standard blood bank refrigeration of 1–6 °C); viability and functionality measures assessed via hemolysis, ATP, and 2,3 diphosphoglyceric acid (2,3-DPG) levels indicating metabolic status, cytokine levels, oxidative stress markers (protein carbonyls, oxysterols, isoprostanes, polyamines, and many more) [17,18], microvesicle formation, band 3 protein profiles (the most abundant protein in the RBC membrane responsible partly for membrane stability and functional regulation [18]), morphology, osmotic fragility, and others; time points at which the viability measures were assessed during storage; relevant statistical analyses performed and results; and author interpretations, conclusions, and discussions regarding the efficacy and performance of the different storage solutions and additives tested under the storage conditions examined. The standardized spreadsheet was populated to comprehensively extract and compile the relevant data from each of the 84 included studies in a consistent, unbiased manner. Careful data cleaning and quality control measures were implemented to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the final dataset. This methodology facilitated organizing the collected evidence on various RBC storage solutions, parameters, and storage durations for a comparative analysis to determine optimal approaches to maintain viability during prolonged, refrigerated RBC storage.
3. Storage Solutions and Their Measured Effect on RBC Storage
Over the years, various solutions have been developed with the goal of improving RBC storage and preservation. These formulations contain different relative concentrations of salts, sugars, buffers, and other constituents meticulously designed to address the challenges of extended RBC storage. The different components of the storage solutions can significantly impact the quality, safety, and efficacy of transfusions performed with the stored RBCs. Solutions are carefully designed to maintain RBC viability, prevent hemolysis, and ensure the effective oxygen delivery of stored RBCs when transfused. Currently, a wide variety of RBC storage solutions are available, each with unique compositions and attributes, as presented in Table 1. Having an array of options allows for customization to optimize RBC preservation and transfusion efficacy. Both inexpensive, straightforward solutions and more advanced additive media have been studied and utilized.

Table 1.
Composition of most common RBC storage solutions [19,20,21,22,23]. The table presents the composition of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), various additive solutions (ASs), like AS-1, AS-3, AS-5, AS-7, Erythro-Sol 5 (E-Sol 5), saline, adenine, glucose, and mannitol (SAGM), phosphate, adenine, glucose, guanosine, saline, and mannitol (PAGGSM), phosphate, adenine, gluconate, guanosine, glucose, mannitol (PAG3M), and mannitol, adenine, phosphate (MAP).
Extensive research has been conducted comparing these solutions to determine the optimal formulation for RBC storage. Table 2 presents a selection of key studies from 2000–2023 that analyzed and compared different RBC storage solutions and their resulting effects. By evaluating variables, such as the shelf life, biochemical changes, and post-transfusion recovery, these investigations provide insight into the relative merits of the available options. The continued comparative analysis serves to elucidate the ideal storage composition needed to balance prolonged preservation with the maintenance of cell quality and efficacy. Selecting the optimal solution remains imperative for ensuring positive outcomes for the transfusion recipients.

Table 2.
Effects of different storage solutions on RBC preservation. These studies analyzed and compared different storage solutions (first column) and their effect on RBC storage (fourth column).
PBS is one of the earliest and most basic RBC storage solutions, first introduced in the 1950s. Comprised of a simple salt solution of sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and phosphate buffer, PBS provides some essential electrolytes to stored cells while maintaining osmotic balance [44]. The phosphate buffers help regulate pH by providing limited buffering capacity. However, the lack of glucose or other energy sources in PBS offers no nutrition to fuel RBC metabolism. While the balanced salts and osmotic environment help preserve the cells short-term, the limited composition of PBS cannot prevent metabolic derangements and acidosis during prolonged storage. Indeed, research has proven that PBS is restricted to a maximum RBC storage time of less than 1 week before substantial viability and functional loss occurs [27]. After this point, the inadequate buffering capacity and limited nutritional components of PBS fail to counteract accumulating biochemical and biomechanical storage lesions. Thus, while PBS continues to be widely used due to its low cost and ease of preparation, it has largely been replaced by more advanced ASs with additional compounds, as seen in Table 1, that enable extended storage while optimizing the preservation of RBCs. However, PBS may still provide a straightforward, inexpensive option for short-term storage needs of 1 week in duration.
While PBS provides a basic and inexpensive storage solution, its composition limits its use for extended preservation. This led to the development of the first AS in the 1960s, known as AS-1 (adenine-saline, commercially known as Adsol), which sought to build upon the simple PBS formulation by incorporating the key metabolite adenine [20]. Adenine helps maintain ATP levels to support basic metabolic functions during storage. AS-1 also contains glucose and mannitol, and the presence of mannitol in the AS-1 solution reduces hemolysis even in the presence of leukocyte proteases [42]. Even though the limited electrolytes and saline provide some osmotic balance, they cannot prevent metabolic derangements, oxidative damage, and cell swelling during prolonged hypothermic storage [45]. Research indicates that AS-1 leads to decreased ATP and 2,3-DPG levels, reduced oxygen offloading capacity, and increased oxidative lesions over time, as presented in some of the studies reported in Table 2 [46]. Specifically, the study of Meyer et al. demonstrated a 20% decrease in ATP levels of RBC units stored in AS-1 for 42 days [40]. With no additional nutritional or pH-modulating compounds, AS-1 allows for a maximum RBC storage time of up to 6 weeks before substantial viability and functional decline occurs [46]. After this, irreversible oxidative stress, vesiculation, and biomechanical changes accumulate without means to counteract them [46]. While offering a slight improvement over PBS, the minimalist composition of AS-1 prompted the development of more advanced solutions, such as AS-3.
The AS-3 solution (Nutricel) was developed in the 1980s as the next generation of ASs. As shown in Table 1, AS-3 builds upon the formulation of AS-1 by incorporating citrate and phosphate along with adenine and balanced salts, while omitting mannitol, which is present in AS-1. Additionally, AS-3 has been formulated to buffer intracellular pH by exploiting the chloride shift phenomenon through a low-chloride loading (70 mmol/L of NaCl in AS-3 vs. 154 mmol/L in AS-1) [20,38]. A high phosphate loading in AS-3 also provides a key substrate for salvage reactions for ATP biosynthesis [38]. However, storage in AS-3 is still associated with metabolic and structural changes over time that can impact RBC functions. For example, Rolfsson et al. found distinct metabolic profiles in AS-3-stored RBCs, characterized by decreased intracellular citrate and increased levels of metabolites [41]. The presence of glucose in this solution may also enhance oxidative damage through increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation during prolonged storage periods [30]. Additionally, the pH of AS-3 (around 5.8), while preventing severe acidosis, may accelerate the oxidative degradation of Hb and membrane proteins over extended storage compared to alkaline solutions [30]. Thus, AS-3 lacks some components to fully optimize long-term storage beyond 6 weeks without negative impacts on RBC function.
Although AS-3 can extend storage time compared to more rudimentary solutions, it is still limited in preventing RBC storage lesions beyond 6 weeks, as shown in the study of D’Amici et al. [30]. This spurred the development of the AS-5 solution (Optisol) in the 1970s as a further iteration on previous additive approaches [47]. AS-5 contains adenine, glucose, mannitol, and saline, as presented in Table 1. This composition is designed to maintain pH, control RBC swelling, and support cellular metabolism during its 42-day storage period [48]. The inclusion of mannitol, present in AS-5 and AS-1 but not in AS-3, serves as a free radical scavenger and provides membrane stabilization [30]. Additionally, the adenine in AS-5 helps mitigate the impact of adenine deaminase. While AS-5 improves cell preservation in comparison to earlier solutions, enabling RBC storage for up to 42 days, it still faces challenges in fully preventing storage lesions over this extended period. Like other ASs, AS-5 generates some level of oxidative damage during storage [48]. Despite its advancements, AS-5 lacks certain critical components for optimal prolonged storage without negatively impacting RBC functions. Therefore, and despite some incremental improvements over other storage solutions, AS-5 remains restricted to 6 weeks of storage before substantial lesions occur.
Capitalizing on AS-5’s progress, scientists developed the more advanced AS-7 solution (commercial name SOLX) in the 1990s seeking to further augment the RBC shelf life [49]. AS-7 is an advanced storage solution containing optimized adenine, mannitol, glucose, and electrolytes to prolong preservation to 6–7 weeks. The pH-balancing properties of mannitol prevent acidosis, while other components maintain the osmotic balance, metabolism, and ATP levels. This suggests that AS-7 can effectively protect against oxidative damage during storage. Nevertheless, AS-7 only slows but does not prevent the gradual depletion of metabolites, like ATP and 2,3-DPG, over time, indicating ongoing metabolic disturbances during storage. Structural changes, including membrane vesiculation, still occur with this solution, revealing that storage-related lesions continue to accumulate in AS-7 after 6–7 weeks of storage. Thus, while AS-7 constitutes an advance, it lacks the ability to prevent biochemical, biomechanical, and functional alterations.
AS-7 allows for RBC storage for up to 7 weeks through specialized nutrient additives. Seeking to build upon advancements, like AS-7, and further extend shelf life, next-generation solutions have been developed leveraging intracellular alkalinization, such as Erythro-Sol 5 (E-Sol 5) and phosphate-adenine-gluconate-guanosine-glucose-mannitol (PAG3M). Both induce sustained alkalinization by excluding chloride and incorporating cell-impermeant organic anions, like citrate (E-Sol 5) or gluconate (PAG3M), initiating the chloride shift mechanism that raises the intracellular pH [9]. Additionally, phosphate provides the substrate for ATP and 2,3 DPG generation. Compared to prior additives, RBCs stored in E-Sol 5 or PAG3M exhibit higher glycolysis rates, PPP activity, and ATP and 2,3 DPG preservation. Specifically, the study of Radwanski et al. [36] presented in Table 2 showed evidence of the chloride shift through elevated intracellular pH and concomitant decreased extracellular pH, increased RBC metabolism, and prolonged 2,3-DPG maintenance of RBCs when stored in E-Sol 5. Additionally, the gluconate-containing storage solution PAG3M has proven to be the only solution showing significant positive correlations between the levels of ATP and 2,3-DPG, highlighting a metabolic peculiarity of RBCs stored in the presence of the PAG3M formula [9]. Thus, through specialized formulations and induced intracellular alkalinization, these next-generation solutions aim to build on prior advancements to further prolong the RBC shelf life while maintaining metabolic functions and integrity.
While SAGM (saline-adenine-glucose-mannitol) has been extensively used to extend RBC storage for 6 weeks, recent research suggests that it may not be the most effective solution for maintaining key molecules, like ATP and 2,3-DPG [20,23]. Developed in the 1990s, SAGM aimed to optimize storage with its blend of salts, sugars, and other components, as outlined in Table 1. These ingredients aim to maintain osmotic pressure, provide metabolic fuel, support ATP production, and regulate pH. Additionally, chloride salts and antioxidants were included for protection from oxidative damage. Although SAGM can extend the RBC shelf life to at least 6 weeks, some works have reported that it may not maintain higher levels of ATP and 2,3-DPG compared to newer solutions, like PAGGGM or AS-7 [23,25,35]. Additionally, metabolic and oxidative changes continue to accumulate during storage with SAGM. One potential drawback of SAGM is its acidic pH, which can contribute to protein and membrane damage over long storage periods. Thus, while SAGM offers some improvements in RBC preservation, storage lesions still occur highlighting opportunities to further optimize the additives and buffering capacity for storage beyond 6 weeks.
A novel RBC storage solution called MAP (mannitol-adenine-phosphate) has been developed to better maintain cell functions and morphology during hypothermic storage. MAP provides energizing substrates, like glucose, adenine, and phosphate, to fuel RBC metabolism via glycolysis and the hexose monophosphate shunt [43]. By preserving ATP, MAP also maintains RBC deformability, which relies on the ATP-dependent calcium pumping and membrane PL asymmetry [43]. Compared to saline, MAP better retains the discoid morphology and deformability throughout storage and washing-associated RBC damage and destruction. While the precise mechanisms are still being elucidated, it is hypothesized that the impermeant sugar mannitol in MAP may also protect against oxidative damage during processing [43]. Overall, through tailored nutrient additives that boost metabolism and help maintain membrane integrity, MAP prevents functional and morphological lesions induced by standard cell washing protocols—improving RBC quality during storage.
As research continues to advance RBC storage solutions, a promising novel option is PAGGSM. This solution builds on prior formulations but incorporates additional key compounds to further optimize RBC preservation, such as guanosine. The phosphate buffers of this solution help regulate the pH to prevent acidosis, while mannitol provides osmotic balance and prevents excessive cell swelling. Glucose supplies the necessary energy substrate to fuel metabolic processes, and adenine supports ATP generation. Uniquely, PAGGSM also contains guanosine, which aids in the synthesis of protective guanosine triphosphate. This component has antioxidant properties that can help counteract oxidative damage during storage. Together, these ingredients create an optimized storage environment that counteracts damaging acidosis, oxidative stress, and harmful biomechanical changes. Published works showed that PAGGSM can extend the RBC shelf life to over 42 days, while maintaining higher ATP levels and limited hemolysis compared to other solutions [23,25,35]. Moreover, PAGGSM enables improved oxygen-delivery capacity after prolonged storage compared to other ASs [9].
As presented in Table 2, an important parameter to follow during storage to determine appropriate storage conditions is adequate gas diffusion, which is an essential function of RBCs. However, balancing permeability with osmosis remains challenging [50]. Maintenance of the optimal pH and electrolyte gradients also impacts gas transport and exchange. Although solutions like PAGGSM better maintain oxygenation in comparison to other options, like AS-1, deficiencies still alter metabolism [50].
Sufficient nutrient availability is also critical to support RBC viability during prolonged storage. Providing key nutrients, like glucose, adenine, and guanosine, fuels RBC metabolism to maintain functions during storage. However, the buildup of toxic metabolic intermediates must also be prevented over time. Available data presented in Table 2 indicate that PAGGSM and AS-7 optimally sustain nutrient availability to maintain the metabolism, energy status, oxygen delivery, and biosynthesis in the RBC units [23]. Additionally, the research by De Bruin et al. [25] revealed that PAGGSM had lower glucose utilization than SAGM and AS-3 over 6 weeks. These data suggest that PAGGSM and AS-7 better retain nutrients, while AS-1, AS-3, SAGM, and PBS demonstrate depletion during storage time.
Moreover, PAGGSM and AS-7 can also optimize oxidative stress control and membrane preservation during storage. Managing oxidative damage and preserving membrane structural stability are both essential during prolonged hypothermic RBC storage. Oxidative stress directly damages membrane components, like lipids and proteins. Even minor oxidation over time can lead to protein denaturation, lipid peroxidation, and cytoskeletal disruption [9]. Recent investigations indicate that PAGGSM and AS-7 best limit oxidative stress while maintaining membrane integrity in stored RBCs [23,37,49].
Complementing membrane integrity, Hb stability is also a key factor during prolonged hypothermic storage due to the function of this protein in O2 transport throughout the body. Limiting Hb oxidation and denaturation during storage preserves the oxygen delivery capacity after transfusion. However, prolonged hypothermic conditions can enhance instability over time. Assessing methemoglobin (metHb) levels, heme loss, and denatured Hb could identify solutions that better stabilize Hb [9]. Accumulated evidence suggests that AS-3, AS-5, AS-7, and PAGGSM most effectively maintain Hb stability during prolonged storage, as presented in Table 2 [19,24,29,37]. These data indicate that solutions like AS-3, AS-5, AS-7, and PAGGSM can be used to optimize Hb preservation in RBC units.
Finally, knowledge about how long RBC units may be safely stored is a crucial consideration for the reliability of the RBC unit supply. Several groups have explored storage time using several storage solutions, especially AS-3. According to published research, RBCs can be retained in AS-3 for up to 42 days if the solution is kept at 4 °C [48]. However, other solutions, like PAGGSM and AS-7, have shown promising results in maintaining nutrient availability, controlling oxidative stress, and preserving membrane integrity during longer storage periods of up to 56 days [23]. These findings highlight that while current solutions offer extended storage times, there is still room for improvement. Additionally, storage can be enhanced and extended by modifying the solution parameters, which is the focus of the next section.
4. Other Preservation Strategies for Enhancing RBC Storage
Beyond storage solutions, other RBC preservation parameters, like the pH, temperature, oxygenation, anticoagulants, and presence of other molecules and contaminants, can impact RBC viability during refrigerated storage. The pH affects protein structure and enzyme functions, and the storage temperature regulates metabolic processes [51,52]. The oxygen content requires careful control to balance supply and oxidative damage. Anticoagulants differ in maintaining RBC membrane integrity. The level of contaminants may accumulate reactive byproducts, impairing cells. The optimization of these secondary factors represents a complementary approach to enhance RBC quality and minimize storage lesions [53]. In this section, we introduce the effects of these conditions, as well as some of the most relevant recent studies that have been published in the literature (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Effect of solution parameters on RBC preservation. These studies analyzed the effect of several storage parameters (first column) on RBC storage (sixth column).
Table 3 summarizes critical studies investigating the roles of modifying the pH, temperature, oxygenation, and anticoagulants (among others) in RBC preservation outcomes. This provides an evidence-based guide to multifaceted blood storage strategies maximizing viability and function. Indeed, the maintenance of an alkaline pH throughout prolonged storage limits metabolic abnormalities and improves morphology. However, optimal recovery and functionality post-transfusion require balancing multiple factors beyond just pH optimization. The current, conventional RBC storage solutions are adjusted to a pH of 5.5–5.8, which is well below the physiological pH of 7.4 [83]. Within this pH range, RBCs utilize their natural buffering capacity to counteract the buildup of lactic acid and other metabolites. However, below a pH of 6.5, viability and function decline more rapidly. Recent studies have explored the impact of maintaining a higher pH throughout storage to extend the shelf life of RBC units [20]. They found that units stored in alkaline PAGGGM had higher ATP and 2,3-DPG levels, a normal morphology, and lower hemolysis compared to conventional storage [25,84]. However, the PTR of these alkaline-stored RBCs was no different than the conventional units. This approach could extend the tolerable storage duration while utilizing existing standard-of-care solutions. Collectively, the maintenance of a more alkaline pH during prolonged RBC storage has physiological benefits in terms of metabolism, morphology, and hemolysis markers [9].
While preserving an alkaline pH during extended storage mitigates metabolic derangements and morphological anomalies, attaining favorable clinical outcomes after transfusion necessitates optimizing multiple elements, not just pH. Another pivotal factor is storage temperature. The standard practice of 1–6 °C refrigeration enables practical blood banking, even though storing at room temperature could offer logistical benefits [50]. However, decreasing the temperature below 0 °C might not offer additional advantages. A recent study by William et al. [50] explored the utility of extracellular additives to mitigate damage during experimental hypothermic storage at −4 °C. Storing RBCs at this reduced temperature alone exacerbated the typical storage-induced decline in deformability and increase in hemolysis compared to 4 °C, despite beneficially retaining more ATP. Additionally, Eckstein et al. [71] investigated the impact of a 24 h room temperature hold (RTH) prior to rejuvenation and subsequent refrigerated storage on the RBC integrity. Compared to rapidly cooled (RC) units, RBCs subjected to RTH initially showed reduced potassium and 2,3-DPG levels but conventional assessment markers like hemolysis and morphology were unaffected. Therefore, while refrigeration remains essential for current blood banking viability, both hypothermic enhancement and transient ambient-damage ramifications demand additional meticulous exploration as storage science continues advancing.
The choice of anticoagulants impacts the preservation quality of stored RBCs intended for transfusion. Burger et al. [79] compared RBC units collected and stored in different anticoagulant/AS combinations over 5 weeks. Units collected in standard CPD anticoagulant and stored in conventional SAGM showed substantially worsened ATP maintenance by 35 days in comparison to units collected in TNC and stored in experimental PAGGGM solutions. The acidic CPD conditions (pH 5.6) likely contributed to a different metabolism and storage lesion accumulation versus the more physiologic TNC pH of 7.4. Moreover, the TNC and PAGGGM formulations specifically aimed to optimize the pH buffering capacity. Burger et al. [79] also prepared PAGGGM solutions at both physiologic (7.4) and alkaline (8.2) pH from TNC-collected blood, finding no significant differences. Thus, starting with a physiologic anticoagulant pH enabled reducing the storage solution pH without sacrificing beneficial metabolic preservation. On another hand, Meledeo et al. [77] recently assessed the coagulation function in whole blood units collected with CPD, CP2D, and CPDA-1 anticoagulants over 5 weeks of refrigerated storage. Surprisingly, most parameters showed minimal deterioration beyond 21 days across all groups. Specifically, the RBC count, HCT, and Hb level did not significantly decline over time in any anticoagulant. Additionally, the RBC count was significantly different between CPD and CP2D on day 3 but not at any other time point. In all three anticoagulants, the pH declined significantly over the storage duration, likely due to an observed 10-fold increase in lactate (and complementary reduction in bicarbonate). CP2D units displayed greater derangements for the lactate, bicarbonate, and base deficit by 2 weeks. No exclusive detriments appeared in the CPD/CP2D units by 3 weeks versus CPDA-1 units at 5 weeks. They also found that a fresher blood sample provided greater hemostatic functionality, particularly over the first 2 weeks, but these studies show no reason for CPD/CP2D to be restricted to a shorter shelf-life than CPDA-1. Therefore, anticoagulant selections significantly, and often undeservedly, dictate acceptable storage durations. Clarifying the evidence-based limits for deterioration could expand the usage of extended-preserved products, potentially improving the availability and quality of blood products for transfusion.
The oxygenation state of the storage environment can significantly influence metabolic processes and oxidative damage accrual affecting RBC quality over time. While original preservative solutions utilize atmospheric oxygen tensions, anaerobic storage below 20 mmHg is now becoming more common to mitigate oxidative threats. However, optimal targets balancing benefits and feasibility remain debated. Meng et al. [85] recently explored replacing air with helium to create hypoxic erythrocyte storage. This effectively reduced dissolved oxygen by 75% and pO2 five-fold versus air-equilibrated controls throughout storage. Despite consuming more glucose and ATP, hypoxic cells better maintained 2,3-DPG levels. Hemolysis remained under 0.8% at 9 weeks, meeting quality thresholds, while controls exceeded specifications. Though deformability and osmotic fragility changes were comparable, hypoxic cells had reduced PS exposure indicating less membrane oxidative damage. Critically, over half of the hypoxic RBCs retained reversible discocyte morphology by week 9, whereas controls showed predominantly irreversible spherocytosis. D’Alessandro et al. [86] meanwhile found that anaerobic storage uniquely enabled the intact maintenance of metabolic and redox homeostasis. Anaerobic cells displayed sustained glycolytic fluxes and 2,3-DPG, decreased lipid oxidation, preserved glutathione and protein thiol, and retained the ATP and antioxidant capacity. Oxygenated storage severely depleted glutathione and ATP by 6 weeks as oxidant lesions accumulated. In summary, ambient aerobic storage permits escalating oxidative damage over time. Anaerobic and hypoxic conditions prevent ROS accumulation, conferring functional preservation advantages. However, anaerobic storage poses logistical tradeoffs, while hypoxic storage largely averted storage-associated derangements. Nevertheless, limiting oxidant exposure through reduced oxygenation emerges as a pivotal strategy for attenuating storage-related injury.
While oxygen minimization helps mitigate oxidative damage, the progressive accumulation of metabolic dysfunction also intrinsically correlates with the length of hypothermic RBC storage itself. Current 42-day limits attempt to balance availability, economics, and safety [10]. However, several countries mandate shorter 35-day thresholds given accumulating indications [87]. Product integrity measurably deteriorates over prolonged hypothermic maintenance. Even though defining optimal storage durations remains an open question, the specific milieu within which prolonged hypothermic preservation unfolds profoundly influences the pace of accrued metabolic anomalies and functional decays. The compositional properties of supplementary storage media emerge as pivotal tools for incrementally mitigating the multifaced storage lesion progression [57].
In addition to the listed effects, several other factors can significantly impact RBC quality during hypothermic preservation. One such consideration is irradiation. Gamma or x-ray irradiation helps prevent transfusion-associated graft versus host disease by inactivating residual lymphocytes in cellular blood products before transfusion [88]. However, multiple studies have indicated that irradiation exacerbates free radicals and ROS can damage RBC membranes and worsen metabolic dysfunction. Sparrow et al. [20] found that irradiating RBCs dramatically increased hemolysis, potassium leakage, PS exposure, and vesiculation after 2 weeks of storage compared to unirradiated controls. Meanwhile, irradiation after just 3 days of storage minimally impacted in vitro measures, though in vitro 24 h recoveries declined 10% regardless of timing. Thus, pre-storage leukoreduction helps avoid irradiation-related quality decays in stored RBCs [89]. When irradiation is necessary, treating the units as early as possible, preferably before storage, mitigates deleterious effects on overlaying storage lesion accumulation [89].
Washing and rejuvenating old blood units have also been explored as a means to partially reverse storage-related changes before transfusion. Rejuvenation refers to incubation with metabolic substrates and cofactors to regenerate ATP and 2,3-DPG, reverse membrane changes, and restore NO scavenging capacity and deformability [30,81]. Tchir et al. [61] found that a cold rejuvenation of RBCs during hypothermic storage increased intracellular ATP, but this change did not ameliorate, or exacerbate, the metabolic or biochemical symptoms of the storage lesion. Meanwhile, washing younger units can reduce pro-inflammatory bioactive metabolites, like lipids, iron, and cytokines, that accumulate by later storage phases [67]. Still, the clinical benefits of these approaches remain uncertain.
Maintaining the sterility of stored blood is also essential. Pathogen reduction methods, like the INTERCEPT Blood System, help prevent bacterial or viral transmission risks. A study by Dimberg et al. [82] examined the impacts of the Mirasol pathogen reduction technique on stored RBCs. While ATP levels and other in vitro parameter levels remained unaffected compared to non-treated controls, Mirasol treatment did significantly increase potassium levels, which worsened further over the storage time. Interestingly, metHb in Mirasol-treated samples returned to normal levels within 24 h of treatment, even though it was high on day 0. The study suggested that RBCs derived from Mirasol-treated samples are suitable for transfusion throughout 21 days of storage. Thus, while ensuring sterility, Mirasol intensified the biochemical and morphological expressions of the storage lesion.
Finally, and although not fully considered in the literature and in this work, it should be noted that intrinsic genetic and environmental donor variables also influence baseline RBC properties in ways that may affect storage lesion progression. Parameters like the donor age, gender, diet, and lifestyle can affect the RBC status at collection and during subsequent refrigeration. For example, a study by Mykhailova et al. [63] reported that RBCs from females contribute less to the storage lesion and age slower than males’ RBCs. Nevertheless, a different study reported that females tend to donate blood units with lower Hb levels, an effect also seen in older donors and individuals with lower body weight [90].
Overall, while incremental advancements continue, storage solutions remain inadequate to fully arrest storage progressive derangements. Further efforts to integrate multi-omics profiling illuminating patient-attributable fragilities with customized, stabilized media are imperative to shift from generalized population standards toward personalized optimization maximizing post-transfusion circulatory fitness and survival.
5. Conclusions and Further Research
RBC storage solutions have advanced considerably over the last decades, evolving from early basic formulations, like PBS and AS-1, to more optimized options, like SAGM and PAGGSM, that better maintain cell integrity and functions during prolonged hypothermic preservation [10,44]. Key storage parameters include the pH-buffering capacity to prevent acidosis, the osmotic balance, metabolic substrates to support RBC metabolism and ATP generation, antioxidants like AA and uric acid to counter oxidative threats, and electrolyte blends sustaining transport and volume regulation [44,45,52,91,92,93]. First-generation solutions lacked comprehensive components, like PBS, restricting storage to 1 week before substantial lesions occur. Second-generation options added key ingredients enabling 4–6-week stability, while third-generation solutions further optimized constituents to prolong storage to 8 weeks without significant adverse impacts [38,46]. These latest generation solutions leverage intracellular alkalinization or tailored supplementation to enable reliable 8-week storage with preserved structural morphology, gas diffusion, and transfusion capacity [9,19,23,36,38,44]. Recent comparative studies of these various storage solutions provide valuable insights into their relative efficacies in preserving RBC quality during storage [23,94].
However, despite incremental advancements, current solutions can only partially prevent time-dependent biochemical, biomechanical, and functional decay [44]. Metabolic anomalies, oxidative damage, and morphological changes still accumulate by later storage phases across present formulations [45]. Therefore, continued efforts to clarify multi-scale mechanisms underlying progressive storage fragility combined with solutions tailored to match discrete deficiency profiles offer paths toward personalized optimization, maximizing post-transfusion circulatory fitness and survival [44]. Hence, while incremental advancements have extended achievable storage limits, truly optimized solutions require personalized profiling coupled with targeted stabilization countermeasures.
While this review has primarily focused on refrigerated storage methods for RBCs in a liquid form, it is important to acknowledge the significance of frozen RBC storage. Recent global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic, have highlighted the potential benefits of more long-term preservation techniques using alternative, frozen storage methods [95,96]. Future research efforts should aim to comprehensively compare liquid refrigeration and frozen storage methods, evaluating their respective advantages, limitations, and impacts on RBC quality and functionality over extended periods. Such comparative studies could provide crucial insights for optimizing blood banking practices, potentially extending the RBC shelf life while maintaining cellular integrity and function. This approach aligns with the broader goal of developing more personalized and efficient storage strategies.
Further research should focus on elucidating donor-specific differences in baseline RBC properties and storage lesion progression rates utilizing multi-omics profiling correlated to clinical outcomes. These data can inform the development of tailored storage solutions catering to inherent weaknesses based on identifiable molecular patterns linked to factors like donor age, sex, genetics, lifestyle, and disease status [97,98]. Research should also continue to investigate the complex interplay between storage duration, temperature, oxygenation, anticoagulants, irradiation, handling methods, and intrinsic storage media properties in driving storage-related decay [45]. Incrementally mitigating identified deleterious changes through multi-factor optimization could better maintain homeostasis. Finally, another critical need is developing rapid and cost-effective analysis and tests gauging RBC structural integrity, metabolic fitness, oxidative resilience, and gas diffusion capacity to enable standardization of acceptable quality benchmarks for stored units before release. Ultimately, these multifaceted research efforts will revolutionize blood banking practices, ensuring the highest quality and longest shelf life of stored RBCs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.G.-P.; methodology, J.G.-P.; validation, J.G.-P. and C.G.-F.; formal analysis, L.N.T.T., J.G.-P. and C.G.-F.; investigation, L.N.T.T. and J.G.-P.; resources, J.G.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.N.T.T. and J.G.-P.; writing—review and editing, J.G.-P. and C.G.-F.; supervision, J.G.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Texas Tech University (HEF New Faculty Startup, NRUF Startup, and Core Research Support Fund). Cristina González-Fernández thanks the Spanish Ministry of Universities for the Margarita Salas postdoctoral fellowship (grants for the requalification of the Spanish university system for 2021–2023, University of Cantabria), funded by the European Union-NextGenerationEU.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hou, H.W.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Lee, W.C.; Huang, S.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Microfluidic Devices for Blood Fractionation. Micromachines 2011, 2, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Ciannella, S.; Tijani, L.; Gomez-Pastora, J. Iron in blood cells: Function, relation to disease, and potential for magnetic separation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2023, 120, 1707–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Romeiro, F.G.; Li, Y. Red Blood Cell Transfusion Strategy for Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. In Transfusion Medicine and Scientific Developments; Koopman-van Gemertt, A.W.M.M., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; p. 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pastora, J.; Weigand, M.; Kim, J.; Palmer, A.; Yazer, M.; Payal, C.; Zborowski, M.; Chalmers, J. Potential of cell tracking velocimetry as an economical and portable hematology analyzer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberson, R.S.; Bennett-Guerrero, E. Impact of red blood cell transfusion on global and regional measures of oxygenation. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2012, 79, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, M.; Gomez-Pastora, J.; Palmer, A.; Zborowski, M.; Desai, P.; Chalmers, J. Continuous-Flow Magnetic Fractionation of Red Blood Cells Based on Hemoglobin Content and Oxygen Saturation—Clinical Blood Supply Implications and Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment. Processes 2022, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresie, L. Artificial blood: An update on current red cell and platelet substitutes. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2001, 14, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantadakis, E.; Panagopoulou, P.; Kontekaki, E.; Bezirgiannidou, Z.; Martinis, G. Iron Deficiency and Blood Donation: Links, Risks and Management. J. Blood Med. 2022, 13, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Reisz, J.A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Korsten, H.; van Bruggen, R.; de Korte, D. Metabolic effect of alkaline additives and guanosine/gluconate in storage solutions for red blood cells. Transfusion 2018, 58, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Gray, A.D.; Szczepiorkowski, Z.M.; Hansen, K.; Herschel, L.H.; Dumont, L.J. Red blood cell metabolic responses to refrigerated storage, rejuvenation, and frozen storage. Transfusion 2017, 57, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelou, M.H.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Stamoulis, K.E.; Economou-Petersen, E.; Margaritis, L.H.; Papassideri, I.S. Red blood cell aging markers during storage in citrate-phosphate-dextrose-saline-adenine-glucose-mannitol. Transfusion 2009, 50, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Lee, J.; Gladwin, M.T. Storage lesion: Role of red blood cell breakdown. Transfusion 2011, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzman, D.; Znidarcic, T.; Gros, M.; Vrhovec, S.; Svetina, S.; Zeks, B. Effect of pH on red blood cell deformability. Pflug. Arch. 2000, 440 (Suppl. 5), R193–R194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, K.; Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Yan, K. Study on Oxidation Stability and Oxygen Affinity of Hemoglobin During Storage. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, K.P.; Cortés-Puch, I.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Solomon, S.B.; Feng, J.; Gladwin, M.T.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Basu, S.; Perlegas, A.; et al. Impact of different standard red blood cell storage temperatures on human and canine RBC hemolysis and chromium survival. Transfusion 2018, 59, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prager, E.M.; Chambers, K.E.; Plotkin, J.L.; McArthur, D.L.; Bandrowski, A.E.; Bansal, N.; Martone, M.E.; Bergstrom, H.C.; Bespalov, A.; Graf, C. Improving transparency and scientific rigor in academic publishing. Brain Behav. 2018, 9, e01141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzaid, F.; Patel, V.B.; Preedy, V.R. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Blood. In General Methods in Biomarker Research and Their Applications; Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 567–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchwell, T.J.; Toye, A.M. Band 3, an essential red blood cell hub of activity. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2792–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancelas, J.A.; Dumont, L.J.; Maes, L.A.; Rugg, N.; Herschel, L.; Whitley, P.H.; Szczepiokowski, Z.M.; Siegel, A.H.; Hess, J.R.; Zia, M. Additive solution-7 reduces the red blood cell cold storage lesion. Transfusion 2015, 55, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, R.L. Time to revisit red blood cell additive solutions and storage conditions: A role for “omics” analyses. Blood Transfus. 2012, 10 (Suppl. 2), S7–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, M.J.; Park, Y.; Bae, H.-R.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, M.-G.; Yang, S. Effects of osmolality and solutes on the morphology of red blood cells according to three-dimensional refractive index tomography. PLoS ONE 2022, 16, e0262106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfsson, O.; Johannsson, F.; Magnusdottir, M.; Paglia, G.; Sigurjonsson, O.E.; Bordbar, A.; Palsson, S.; Brynjólfsson, S.; Gudmundsson, S.; Palsson, B. Mannose and fructose metabolism in red blood cells during cold storage in SAGM. Transfusion 2017, 57, 2665–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerberg, J.W.; Korsten, H.; Van Der Meer, P.F.; De Korte, D. Prevention of red cell storage lesion: A comparison of five different additive solutions. Blood Transfus. 2017, 15, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehnder, L.; Schulzki, T.; Goede, J.S.; Hayes, J.; Reinhart, W.H. Erythrocyte storage in hypertonic (SAGM) or isotonic (PAGGSM) conservation medium: Influence on cell properties. Vox Sang. 2008, 95, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruin, S.; Peters, A.-L.; Wijnberge, M.; van Baarle, F.E.H.P.; AbdelRahman, A.H.A.; Vermeulen, C.; Beuger, B.M.; Reisz, J.A.; D’Alessandro, A.; Vlaar, A.P.J.; et al. Storage of red blood cells in alkaline PAGGGM improves metabolism but has no effect on recovery after transfusion. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3899–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanyam, P.; Basavarajegowda, A.; Hanumanthappa, N.; Ram, A.; Negi, V. Storage lesions after irradiation: Comparison between blood stored in citrate phosphate dextrose adenine and saline adenine glucose mannitol. Glob. J. Transfus. Med. 2022, 7, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebesi, T.; Kitka, D.; Gaál, A.; Szigyártó, I.C.; Deák, R.; Beke-Somfai, T.; Koprivanacz, K.; Juhász, T.; Bóta, A.; Varga, Z.; et al. Storage conditions determine the characteristics of red blood cell derived extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, R.L.; Sran, A.; Healey, G.; Veale, M.F.; Norris, P.J. In vitro measures of membrane changes reveal differences between red blood cells stored in saline-adenine-glucose-mannitol and AS-1 additive solutions: A paired study. Transfusion 2014, 54, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandarenko, N.; Hay, S.N.; Holmberg, J.; Whitley, P.; Taylor, H.L.; Moroff, G.; Rose, L.; Kowalsky, R.; Brumit, M.; Rose, M.; et al. Extended storage of AS-1 and AS-3 leukoreduced red blood cells for 15 days after deglycerolization and resuspension in AS-3 using an automated closed system. Transfusion 2004, 44, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amici, G.M.; Mirasole, C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Yoshida, T.; Dumont, L.J.; Zolla, L. Red blood cell storage in SAGM and AS3: A comparison through the membrane two-dimensional electrophoresis proteome. Blood Transfus. = Trasfus. Sangue 2012, 10 (Suppl. 2), S46–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkelman, S.; Dijkstra-Tiekstra, M.J.; De Wildt-Eggen, J.; Graaff, R.; Rakhorst, G.; Van Oeveren, W. Is red blood cell rheology preserved during routine blood bank storage? Transfusion 2010, 50, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, B.A.; Ansari, A.K.; Srinivasan, A.J.; Kamyszek, R.W.; Stoner, K.C.; Fuller, M.; Poisson, J.L.; Welsby, I.J. Rejuvenation solution as an adjunct cold storage solution maintains physiological haemoglobin oxygen affinity during early-storage period of red blood cells. Vox Sang. 2020, 115, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurén, E.; Tigistu-Sahle, F.; Valkonen, S.; Westberg, M.; Valkeajärvi, A.; Eronen, J.; Siljander, P.; Pettilä, V.; Käkelä, R.; Laitinen, S.; et al. Phospholipid composition of packed red blood cells and that of extracellular vesicles show a high resemblance and stability during storage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevi, F.; D’Alessandro, A.; Rinalducci, S.; Zolla, L. Alterations of red blood cell metabolome during cold liquid storage of erythrocyte concentrates in CPD–SAGM. J. Proteom. 2012, 76, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.; Korsten, H.; De Korte, D.; Rombout, E.; Van Bruggen, R.; Verhoeven, A.J. An improved red blood cell additive solution maintains 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and adenosine triphosphate levels by an enhancing effect on phosphofructokinase activity during cold storage. Transfusion 2010, 50, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwanski, K.; Thill, M.; Min, K. Red cell storage in E-Sol 5 and Adsol additive solutions: Paired comparison using mixed and non-mixed study designs. Vox Sang. 2014, 106, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veale, M.F.; Healey, G.; Sparrow, R.L. Effect of additive solutions on red blood cell (RBC) membrane properties of stored RBCs prepared from whole blood held for 24 hours at room temperature. Transfusion 2011, 51 (Suppl. 1), 25S–33S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Hansen, K.C.; Szczepiorkowski, Z.M.; Dumont, L.J. Red blood cell storage in additive solution-7 preserves energy and redox metabolism: A metabolomics approach. Transfusion 2015, 55, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittag, D.; Sran, A.; Chan, K.S.; Boland, M.P.; Bandala-Sanchez, E.; Huet, O.; Xu, W.; Sparrow, R.L. Stored red blood cell susceptibility to in vitro transfusion-associated stress conditions is higher after longer storage and increased by storage in saline-adenine-glucose-mannitol compared to AS-1. Transfusion 2015, 55, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.K.; Dumont, D.F.; Baker, S.; Dumont, L.J. Rejuvenation capacity of red blood cells in additive solutions over long-term storage. Transfusion 2011, 51, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfsson, Ó.; Sigurjonsson, Ó.E.; Magnusdottir, M.; Johannsson, F.; Paglia, G.; Guðmundsson, S.; Bordbar, A.; Palsson, S.; Brynjólfsson, S.; Palsson, B. Metabolomics comparison of red cells stored in four additive solutions reveals differences in citrate anticoagulant permeability and metabolism. Vox Sang. 2017, 112, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makroo, R.N.; Raina, V.; Bhatia, A.; Gupta, R.; Majid, A.; Thakur, U.K.; Rosamma, N.L. Evaluation of the red cell hemolysis in packed red cells during processing and storage. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2011, 5, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, J.; Kang, Y.; Gong, L.N.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Yin, X.R.; Zhang, C.W.; Liu, G.Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Mannitol-adenine-phosphate: A novel solution for intraoperative blood salvage. Transfusion 2014, 54, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Prudent, M.; D’Alessandro, A. Red blood cell storage lesion: Causes and potential clinical consequences. Blood Transfus. = Trasfus. Sangue 2019, 17, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.R. Red cell changes during storage. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2010, 43, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roback, J.D.; Josephson, C.D.; Waller, E.K.; Newman, J.L.; Karatela, S.; Uppal, K.; Jones, D.P.; Zimring, J.C.; Dumont, L.J. Metabolomics of ADSOL (AS-1) Red Blood Cell Storage. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2014, 28, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFaul, S.J.; Corley, J.B.; Mester, C.W.; Nath, J. Packed blood cells stored in AS-5 become proinflammatory during storage. Transfusion 2009, 49, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Kelher, M.; West, F.B.; Schwindt, R.K.; Banerjee, A.; Moore, E.E.; Silliman, C.C.; Hansen, K.C. Routine storage of red blood cell (RBC) units in additive solution-3: A comprehensive investigation of the RBC metabolome. Transfusion 2015, 55, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veale, M.F.; Healey, G.; Sran, A.; Payne, K.A.; Zia, M.; Sparrow, R.L. AS-7 improved in vitro quality of red blood cells prepared from whole blood held overnight at room temperature. Transfusion 2015, 55, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, N.; Isiksacan, Z.; Mykhailova, O.; Olafson, C.; Yarmush, M.L.; Usta, O.B.; Acker, J.P. Comparing two extracellular additives to facilitate extended storage of red blood cells in a supercooled state. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1165330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, R.; Aboul Enein, A.; El-Desoukey, N.; Abo Elfetouh, R.; Abdel Hafez, A.A. Impact of storage, leukofiltration, and ascorbic acid fortification on red cell-derived microparticles in stored packed red blood cells: A flow cytometric and procoagulant study. J. Appl. Hematol. 2020, 11, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Nguyen T Tran, L.; Weigand, M.; Ciannella, S.; Wu, X.; Strayer, J.; Choe, H.; J Chalmers, J.; Gomez-Pastora, J. Effect of pH Modulation and Anaerobic Conditions on Prolonged Storage of Red Blood Cells. J. Blood Disord. 2024, 11, 1086. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, L.; Ohlsson, S.; Derving, J.; Diedrich, B.; Sandgren, P.; Larsson, S.; Uhlin, M. DEHT is a suitable plasticizer option for phthalate-free storage of irradiated red blood cells. Vox Sang. 2022, 117, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, H.; Yang, L.; Song, F.; Liu, H.; Wei, C.; Ding, H.; Ma, Q.; Su, Y. Effect of low concentration of melatonin on the quality of stored red blood cells in vitro. Russ. J. Hematol. Transfusiol. 2022, 67, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Spence, D.M. A quantitative, in vitro appraisal of experimental low-glucose storage solutions used for blood banking. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6856–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzounakas, V.L.; Anastasiadi, A.T.; Lekka, M.E.; Papageorgiou, E.G.; Stamoulis, K.; Papassideri, I.S.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Antonelou, M.H. Deciphering the Relationship Between Free and Vesicular Hemoglobin in Stored Red Blood Cell Units. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 840995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relevy, H.; Koshkaryev, A.; Manny, N.; Yedgar, S.; Barshtein, G. Blood banking–induced alteration of red blood cell flow properties. Transfusion 2008, 48, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graminske, S.; Puca, K.; Schmidt, A.; Brooks, S.; Boerner, A.; Heldke, S.; de Arruda Indig, M.; Brucks, M.; Kossor, D. In vitro evaluation of di(2-ethylhexyl)terephthalate–plasticized polyvinyl chloride blood bags for red blood cell storage in AS-1 and PAGGSM additive solutions. Transfusion 2018, 58, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.M.; Roback, J.D.; Uppal, K.; Yu, T.; Jones, D.P.; Josephson, C.D. Metabolomics profile comparisons of irradiated and nonirradiated stored donor red blood cells. Transfusion 2015, 55, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, F.; Machin, A.; Touriño, C.; Rodríguez, I.; Denicola, A.; Thomson, L. N -acetylcysteine improves the quality of red blood cells stored for transfusion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 621, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchir, J.D.R.; Acker, J.P.; Holovati, J.L. Rejuvenation of ATP during storage does not reverse effects of the hypothermic storage lesion. Transfusion 2013, 53, 3184–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, S.; Shivhare, A.; Murugesan, M.; Baliga, P.B. Red cell storage lesion and the effect of buffy-coat reduction on the biochemical parameters. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailova, O.; Olafson, C.; Turner, T.R.; D’Alessandro, A.; Acker, J.P. Donor-dependent aging of young and old red blood cell subpopulations: Metabolic and functional heterogeneity. Transfusion 2020, 60, 2633–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, J.S.; Fontes, J.; Banerjee, U.; Yazer, M.H.; Mank, E.; Palmer, A.F. Ascorbic acid improves membrane fragility and decreases haemolysis during red blood cell storage. Transfus. Med. 2013, 23, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, S.M.; Chen, D.; Schubert, P.; Perruzza, D.L.; Bhakta, V.; Devine, D.V.; Sheffield, W.P. Pathogen inactivation by riboflavin and ultraviolet light illumination accelerates the red blood cell storage lesion and promotes eryptosis. Transfusion 2017, 57, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezelbash, B.; Azarkeivan, A.; Pourfathollah, A.A.; Deyhim, M.; Hajati, E.; Goodarzi, A. Comparative Evaluation of Biochemical and Hematological Parameters of Pre-Storage Leukoreduction during RBC Storage. Int. J. Hematol.-Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 12, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrke, S.; Srinivasan, A.I.; Culp-Hill, R.; Reisz, J.A.; Ansari, A.; Gray, A.; Landrigan, M.; Welsby, I.; D’Alessandro, A. Metabolomics evaluation of early-storage red blood cell rejuvenation at 4 °C and 37 °C. Transfusion 2018, 58, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamzada, E.; Matthews, K.; Lamoureux, E.; Duffy, S.P.; Scott, M.D.; Ma, H. Blood unit segments accurately represent the biophysical properties of red blood cells in blood bags but not hemolysis. Transfusion 2022, 62, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, S.M.; Chen, D.; Schubert, P.; Devine, D.V.; Sheffield, W.P. Early γ-irradiation and subsequent storage of red cells in SAGM additive solution potentiate energy imbalance, microvesiculation, and susceptibility to stress-induced apoptotic cell death. Vox Sang. 2017, 112, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Hao, P.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ye, X.; Li, Z. Effect of irradiation and/or leucocyte filtration on RBC storage lesions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, M.; Zimmermann, R.; Roth, T.; Hauck-Dlimi, B.; Strasser, E.F.; Xiang, W. The effects of an overnight holding of whole blood at room temperature on haemoglobin modification and in vitro markers of red blood cell aging. Vox Sang. 2015, 108, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira Cavalcante, L.; Acker, J.P.; Holovati, J.L. Effect of Liposome Treatment on Hemorheology and Metabolic Profile of Human Red Blood Cells During Hypothermic Storage. Biopreserv. Biobanking 2018, 16, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Blair, A.; D’Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Dioguardi, M.; Silliman, C.C.; Dunham, A. Enhancing uniformity and overall quality of red cell concentrate with anaerobic storage. Blood Transfus. = Trasfus. Sangue 2017, 15, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Janes, J.; Stapley, R.; Patel, R.P.; Gladwin, M.T.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B. Mechanism of faster NO scavenging by older stored red blood cells. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinalducci, S.; Ferru, E.; Blasi, B.; Turrini, F.; Zolla, L. Oxidative stress and caspase-mediated fragmentation of cytoplasmic domain of erythrocyte band 3 during blood storage. Blood Transfus. = Trasfus. Sangue, 2012; 10, (Suppl. 2), S55–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Grandmont, M.J.; Ducas, É.; Girard, M.; Méthot, M.; Brien, M.; Thibault, L. Quality and safety of red blood cells stored in two additive solutions subjected to multiple room temperature exposures. Vox Sang. 2014, 107, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meledeo, M.A.; Peltier, G.C.; McIntosh, C.S.; Bynum, J.A.; Cap, A.P. Optimizing whole blood storage: Hemostatic function of 35-day stored product in CPD, CP2D, and CPDA-1 anticoagulants. Transfusion 2019, 59, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Gevi, F.; Zolla, L. Red blood cell metabolism under prolonged anaerobic storage. Mol. BioSyst. 2013, 9, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, P.; Korsten, H.; Verhoeven, A.J.; de Korte, D.; van Bruggen, R. Collection and storage of red blood cells with anticoagulant and additive solution with a physiologic pH. Transfusion 2012, 52, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, M.M.; Kelher, M.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Hansen, K.C.; Banerjee, A.; West, F.B.; Stanley, C.; Briel, M.; Silliman, C.C. A comparison of different methods of red blood cell leukoreduction and additive solutions on the accumulation of neutrophil-priming activity during storage. Transfusion 2018, 58, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; AuBuchon, J.P.; Dumont, L.J.; Gorham, J.D.; Gifford, S.C.; Foster, K.Y.; Bitensky, M.W. The effects of additive solution pH and metabolic rejuvenation on anaerobic storage of red cells. Transfusion 2008, 48, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimberg, L.Y.; Doane, S.K.; Yonemura, S.; Reddy, H.L.; Hovenga, N.; Gosney, E.J.; Tran, M.; Wilkinson, S.; Goodrich, R.P.; Marschner, S. Red Blood Cells Derived from Whole Blood Treated with Riboflavin and UV Light Maintain Adequate Cell Quality through 21 Days of Storage. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2019, 46, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.R.; Brown, M.R.; Vance, D.E. From Donor to Recipient: Considerations for Blood Transfusion Outcomes Research. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2017, 19, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelkens, C.C.M.; Lagerberg, J.W.M.; de Korte, D. The effect of prefreeze rejuvenation on postthaw storage of red blood cells in AS-3 and SAGM. Transfusion 2017, 57, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Cai, R.; Fan, Y. Hypoxic storage of erythrocytes slows down storage lesions and prolongs shelf-life. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22833–22844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Yoshida, T.; Nestheide, S.; Nemkov, T.; Stocker, S.; Stefanoni, D.; Mohmoud, F.; Rugg, N.; Dunham, A.; Cancelas, J.A. Hypoxic storage of red blood cells improves metabolism and post-transfusion recovery. Transfusion 2020, 60, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegel, W.A.; Natanson, C.; Klein, H.G. Does prolonged storage of red blood cells cause harm? Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 165, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Irsch, J.; Corash, L.; Benjamin, R.J. Is pathogen reduction an acceptable alternative to irradiation for risk mitigation of transfusion-associated graft versus host disease? Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 61, 103404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshghifar, N.; Maghsudlu, M.; Amini Kafi-abad, S. The Effect of Pre-Storage Irradiation Blood on Quality of Red Blood Cells. Int. J. Hematol.-Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2021, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, N.; Pal, L.; Thakur, M.; Kumar, P. The need to label red blood cell units with their haemoglobin content: A single centre study on haemoglobin variations due to donor-related factors. Blood Transfus. 2014, 12, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardyn, M.; Chen, J.; Dussiot, M.; Crettaz, D.; Schmid, L.; Längst, E.; Amireault, P.; Tissot, J.-D.; Jolicoeur, M.; Prudent, M. Restoration of Physiological Levels of Uric Acid and Ascorbic Acid Reroutes the Metabolism of Stored Red Blood Cells. Metabolites 2020, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzounakas, V.L.; Anastasiadi, A.T.; Arvaniti, V.-Z.; Lelli, V.; Fanelli, G.; Paronis, E.C.; Apostolidou, A.C.; Balafas, E.G.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.G.; Papageorgiou, E.G.; et al. Supplementation with uric and ascorbic acid protects stored red blood cells through enhancement of non-enzymatic antioxidant activity and metabolic rewiring. Redox Biol. 2022, 57, 102477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadi, A.T.; Stamoulis, K.; Papageorgiou, E.G.; Lelli, V.; Rinalducci, S.; Papassideri, I.S.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Antonelou, M.H.; Tzounakas, V.L. The time-course linkage between hemolysis, redox, and metabolic parameters during red blood cell storage with or without uric acid and ascorbic acid supplementation. Front. Aging 2023, 4, 1161565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen T Tran, L.; González-Fernández, C.; Weigand, M.; Chalmers, J.; Gomez-Pastora, J. Analysis of Storage Lesions in Refrigerated Red Blood Cells in Different Storage Solutions. J. Blood Disord. 2024, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, C.N. Frozen Red Blood Cells in Transfusion. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2011, 65, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeri, C.R.; Runck, A.H. Long Term Frozen Storage of Human Red Blood Cells: Studies in Vivo and in Vitro of Autologous Red Blood Cells Preserved up to Six Years with High Concentrations of Glycerol. Transfusion 1969, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubinian, N.H.; Plimier, C.; Woo, J.P.; Lee, C.; Bruhn, R.; Liu, V.X.; Escobar, G.J.; Kleinman, S.H.; Triulzi, D.J.; Murphy, E.L.; et al. Effect of donor, component, and recipient characteristics on hemoglobin increments following red blood cell transfusion. Blood 2019, 134, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubinian, N.H.; Reese, S.E.; Qiao, H.; Plimier, C.; Fang, F.; Page, G.P.; Cable, R.G.; Custer, B.; Gladwin, M.T.; Goel, R.; et al. Donor genetic and nongenetic factors affecting red blood cell transfusion effectiveness. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e152598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).