Complex Interplay between DNA Damage and Autophagy in Disease and Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
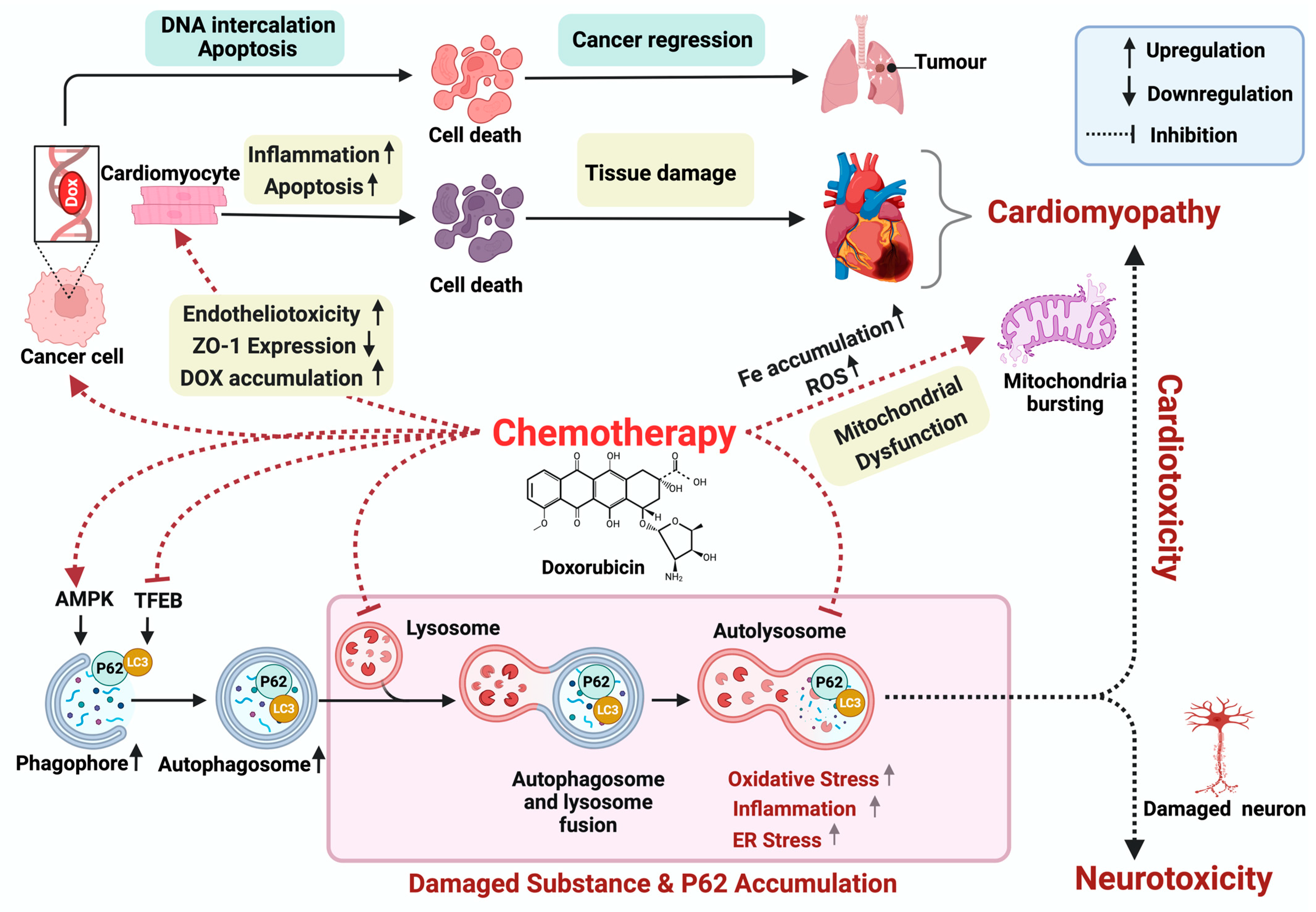
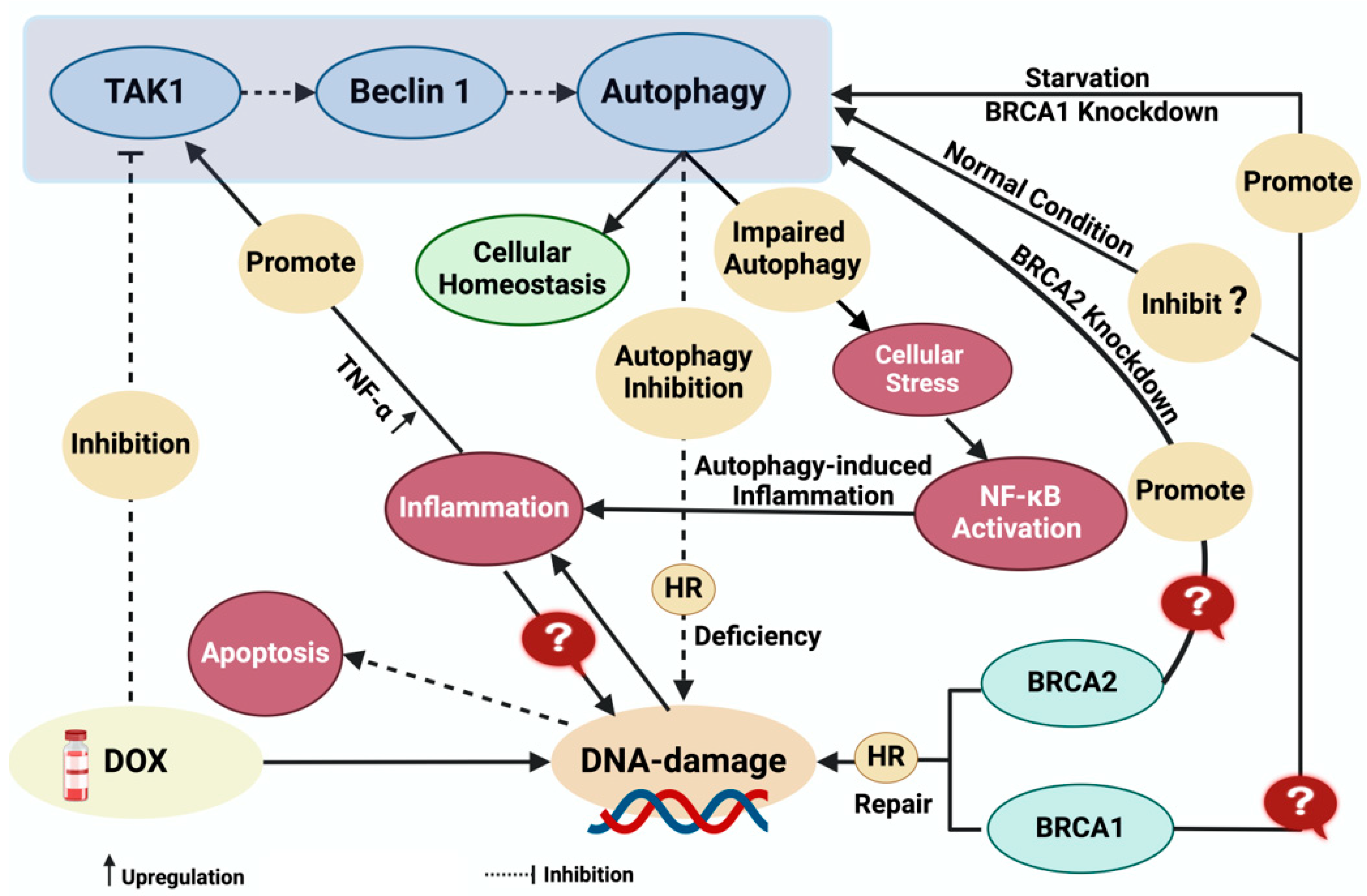
2. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
3. Doxorubicin-Induced Neurotoxicity
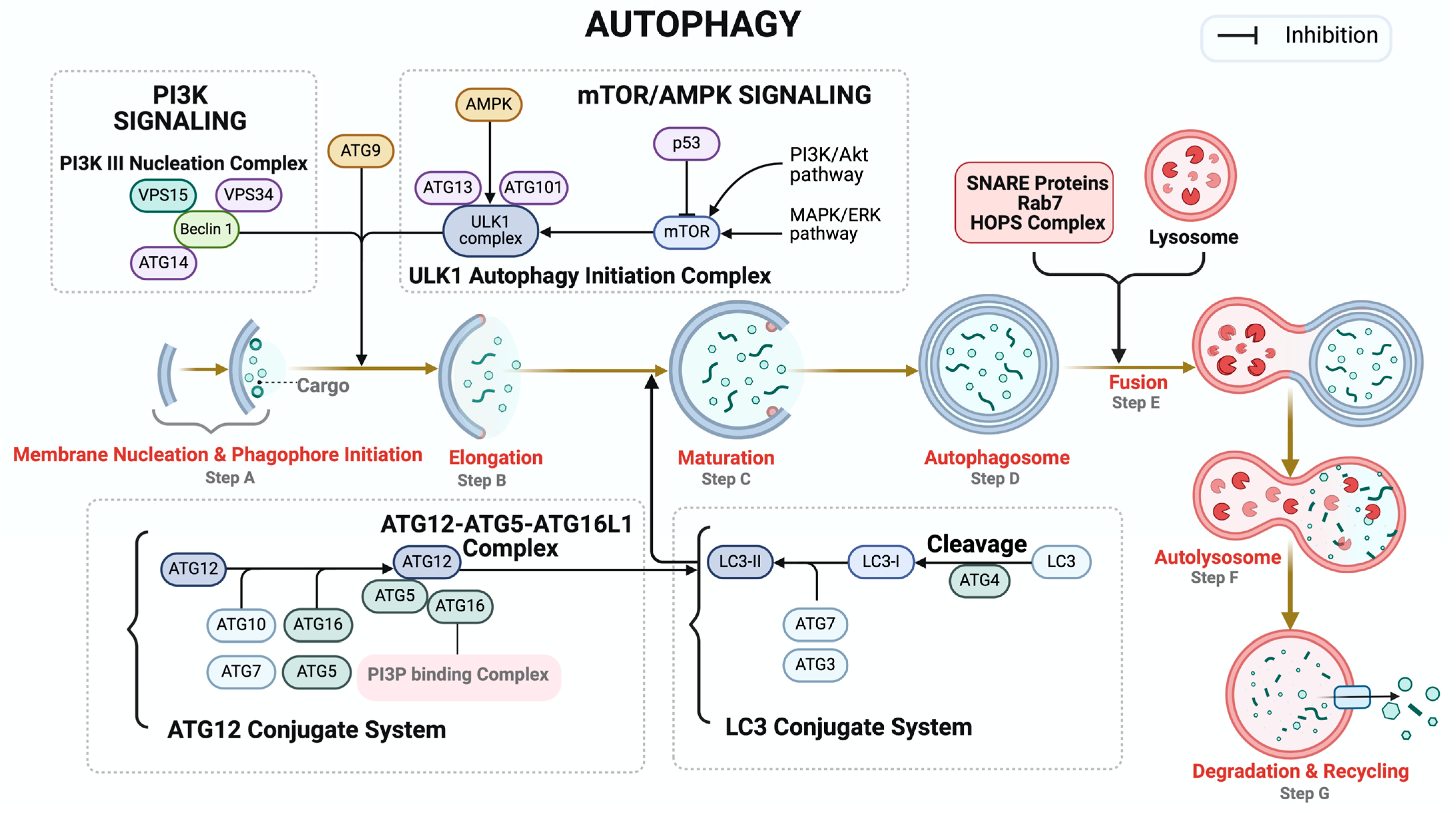
4. Autophagy
5. Doxorubicin and Mitophagy
6. Autophagy Modulation for Therapeutic Intervention
7. Challenges and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, J.S.; Amend, S.R.; Austin, R.H.; Gatenby, R.A.; Hammarlund, E.U.; Pienta, K.J. Updating the Definition of Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2023, 21, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L.M.E.; Ramsay, E.E.; Logsdon, C.D.; Overwijk, W.W. The immune system in cancer metastasis: Friend or foe? J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, B. Teaching the basics of cancer metabolism: Developing antitumor strategies by exploiting the differences between normal and cancer cell metabolism. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakara, A.B.; Sundaram, C.; Harikumar, K.B.; Tharakan, S.T.; Lai, O.S.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Cancer is a Preventable Disease that Requires Major Lifestyle Changes. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2097–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgovnick, A.; Schumacher, B. DNA repair mechanisms in cancer development and therapy. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rocha, H.; Garcia-Garcia, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Franco, R. DNA damage and autophagy. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.C.; Singh, K.K.; Quan, A.; Al-Omran, M.; Teoh, H.; Lovren, F.; Cao, L.; Rovira, I.I.; Pan, Y.; Brezden-Masley, C.; et al. BRCA1 is an essential regulator of heart function and survival following myocardial infarction. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Shukla, P.C.; Quan, A.; Desjardins, J.F.; Lovren, F.; Pan, Y.; Garg, V.; Gosal, S.; Garg, A.; Szmitko, P.E.; et al. BRCA2 protein deficiency exaggerates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac failure. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6604–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nguyen, H.; Michels, D.; Bazinet, H.; Matkar, P.N.; Liu, Z.; Esene, L.; Adam, M.; Bugyei-Twum, A.; Mebrahtu, E.; et al. BReast CAncer susceptibility gene 2 deficiency exacerbates oxidized LDL-induced DNA damage and endothelial apoptosis. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.; Stratton, M.R. The genetics of breast cancer susceptibility. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1998, 32, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, F.; Bertwistle, D.; Mee, P.J.; Ross, G.M.; Swift, S.; Grigorieva, E.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Ashworth, A. Tumorigenesis and a DNA repair defect in mice with a truncating Brca2 mutation. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikfarjam, S.; Singh, K.K. DNA damage response signaling: A common link between cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 4380–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Frisbee, J.C.; Singh, K.K. Different Mechanisms in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Impact of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations. Hearts 2024, 5, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Staffurth, J. Hormonal therapy for cancer. Medicine 2016, 44, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.P.; Ming, L.C.; Dhaliwal, J.S.; Gupta, M.; Ardianto, C.; Goh, K.W.; Hussain, Z.; Shafqat, N. Role of Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Kamiya, K. Molecular nature of radiation injury and DNA repair disorders associated with radiosensitivity. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.; Loeffler, J.S. Charged particles in radiation oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, R.; Dai, J.; Wenlong, N.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.W. Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2014, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, G.; Jacob, S.; Featherstone, C.; Barton, M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: Estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer 2005, 104, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis, K.S.; Lai Yau, T.H.; Sideris, M. Chemoradiotherapy in Cancer Treatment: Rationale and Clinical Applications. Anticancer. Res. 2021, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, C.P.; Bundy, B.N.; Homesley, H.D.; Creasman, W.T.; Hornback, N.B.; Kurman, R.; Thigpen, J.T. Doxorubicin as an adjuvant following surgery and radiation therapy in patients with high-risk endometrial carcinoma, stage I and occult stage II: A Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 1990, 36, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, M.Z. Chemoirradiation: A new initiative in cancer treatment. 1991 RSNA annual oration in radiation oncology. Radiology 1992, 184, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick, J.; Stewart, H.; Rutqvist, L.; Houghton, J.; Edwards, R.; Redmond, C.; Peto, R.; Baum, M.; Fisher, B.; Host, H. Cause-specific mortality in long-term survivors of breast cancer who participated in trials of radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Favourable and unfavourable effects on long-term survival of radiotherapy for early breast cancer: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2000, 355, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dracham, C.B.; Shankar, A.; Madan, R. Radiation induced secondary malignancies: A review article. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2018, 36, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Sahin, A.A.; Huo, L.; Ward, K.C.; O’Regan, R.; Torres, M.A.; Meisel, J.L. Triple-negative breast cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 161, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, Y. Exploring DNA-Binding Proteins with In Vivo Chemical Cross-Linking and Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakkala, P.A.; Penumallu, N.R.; Shafi, S.; Kamal, A. Prospects of Topoisomerase Inhibitors as Promising Anti-Cancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger-Pabst, U.; Bucur, P.; Roger, S.; Falkenstein, T.A.; Tabchouri, N.; Le Pape, A.; Lerondel, S.; Demtröder, C.; Salamé, E.; Ouaissi, M. Comparison of Tissue and Blood Concentrations of Oxaliplatin Administrated by Different Modalities of Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4445–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Rong, D.; Li, Z.; Sun, G.; Wu, F.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, W.; Sun, Y. Role of Small Molecule Targeted Compounds in Cancer: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 694363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetoh, L.; Ladoire, S.; Coukos, G.; Ghiringhelli, F. Combining immunotherapy and anticancer agents: The right path to achieve cancer cure? Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivek, R.; Thangam, R.; NipunBabu, V.; Rejeeth, C.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Gunasekaran, P.; Muthuchelian, K.; Kannan, S. Multifunctional HER2-antibody conjugated polymeric nanocarrier-based drug delivery system for multi-drug-resistant breast cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6469–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piktel, E.; Niemirowicz, K.; Watek, M.; Wollny, T.; Deptula, P.; Bucki, R. Recent insights in nanotechnology-based drugs and formulations designed for effective anti-cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.M.; Marina, N.; Hudson, M.M.; Hodgson, D.C.; Adams, M.J.; Landier, W.; Bhatia, S.; Meeske, K.; Chen, M.H.; Kinahan, K.E.; et al. Monitoring for cardiovascular disease in survivors of childhood cancer: Report from the Cardiovascular Disease Task Force of the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e387–e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Probin, V.; Zhou, D. Cancer therapy-induced residual bone marrow injury-Mechanisms of induction and implication for therapy. Curr. Cancer Ther. Rev. 2006, 2, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuter, D.J. Managing thrombocytopenia associated with cancer chemotherapy. Oncology 2015, 29, 282–294. [Google Scholar]
- Horie, S.; Oya, M.; Nangaku, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Komatsu, Y.; Yanagita, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kuwano, H.; Nishiyama, H.; Ishioka, C.; et al. Guidelines for treatment of renal injury during cancer chemotherapy 2016. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 210–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, Y.; Malnick, S. Liver injury induced by anticancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Int. J. Hepatol. 2013, 2013, 815105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Zhang, J.; Honbo, N.; Karliner, J.S. Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Cardiology 2010, 115, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A. A Review on the Neurotoxic Effects of Doxorubicin. Neurotox. Res. 2023, 41, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson-Arbor, K.; Dubey, R. Doxorubicin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sritharan, S.; Sivalingam, N. A comprehensive review on time-tested anticancer drug doxorubicin. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, S.; Feng, Z.P. Doxorubicin chemotherapy-induced “chemo-brain”: Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 881, 173078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zang, T.; Chen, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Shen, L.; Qian, J.; Ge, J. Deubiquitinase OTUB1 regulates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via deubiquitinating c-MYC. Cell Signal 2024, 113, 110937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demby, T.; Gross, P.S.; Mandelblatt, J.; Huang, J.K.; Rebeck, G.W. The chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin induces brain senescence, with modulation by APOE genotype. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 371, 114609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Layard, M.W.; Basa, P.; Davis, H.L., Jr.; Von Hoff, A.L.; Rozencweig, M.; Muggia, F.M. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 91, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M.; Whaley, F.S.; Ewer, M.S. Congestive heart failure in patients treated with doxorubicin: A retrospective analysis of three trials. Cancer 2003, 97, 2869–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshow, J.H. Doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, M.R.; Mason, J.W.; Billingham, M.E.; Daniels, J.R. Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy: Evaluation by phonocardiography, endomyocardial biopsy, and cardiac catheterization. Ann. Intern. Med. 1978, 88, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beer, E.L.; Bottone, A.E.; Voest, E.E. Doxorubicin and mechanical performance of cardiac trabeculae after acute and chronic treatment: A review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 415, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Ghanefar, M.; Bayeva, M.; Wu, R.; Khechaduri, A.; Naga Prasad, S.V.; Mutharasan, R.K.; Naik, T.J.; Ardehali, H. Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin is mediated through mitochondrial iron accumulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, V.B.; Kanwal, A.; Fang, Y.H.; Sharp, W.W.; Samant, S.; Arbiser, J.; Gupta, M.P. Honokiol, an activator of Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3) preserves mitochondria and protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34082–34098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, J.H.; Castellino, S.M.; Melendez, G.C.; Klepin, H.D.; Ellis, L.R.; Lamar, Z.; Vasu, S.; Kitzman, D.W.; Ntim, W.O.; Brubaker, P.H.; et al. Left Ventricular Mass Change After Anthracycline Chemotherapy. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Ma, P.; Wang, R.; Lou, X.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Xue, R.; Blasig, I.; Erben, U.; Qin, Z. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity involves IFNgamma-mediated metabolic reprogramming in cardiomyocytes. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, H.G.; Pinedo, H.M.; Schuurhuis, G.J.; Joenje, H. Doxorubicin (adriamycin): A critical review of free radical-dependent mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 47, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ma, Z.; Di, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Reiter, R.J.; Qiao, S.; Yuan, J. AMPK/PGC1alpha activation by melatonin attenuates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity via alleviating mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, G.R.; Cai, H.; Davis, M.E.; Ramasamy, S.; Harrison, D.G. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression by hydrogen peroxide. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Nguyen, H.C.; Nikfarjam, S.; Michels, D.C.R.; Rasheed, B.; Maheshkumar, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, K.K. Endothelial cell-specific loss of eNOS differentially affects endothelial function. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, E.L.; Sidaway, J.E.; Cross, M.J. Cardiotoxic drugs Herceptin and doxorubicin inhibit cardiac microvascular endothelial cell barrier formation resulting in increased drug permeability. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, A.Z.; Chowdhury, B.; Al-Omran, M.; Teoh, H.; Hess, D.A.; Verma, S. Role of Endothelium in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, T.; Buczek, E.; Majzner, K.; Kolodziejczyk, A.; Miszczyk, J.; Kaczara, P.; Kwiatek, W.; Baranska, M.; Szymonski, M.; Chlopicki, S. Comparative endothelial profiling of doxorubicin and daunorubicin in cultured endothelial cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, N.; Zordoky, B.N.; Robertson, I.M.; Hamza, S.M.; Parajuli, N.; Soltys, C.M.; Beker, D.L.; Grant, M.K.; Razzoli, M.; Bartolomucci, A.; et al. Co-administration of resveratrol with doxorubicin in young mice attenuates detrimental late-occurring cardiovascular changes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Luo, F.; Wang, Y.; Zou, B.S.; Man, Y.; Liu, J.S.; Li, H.; Arshad, B.; Li, H.; Li, S.; et al. Cognitive impairments in breast cancer survivors treated with chemotherapy: A study based on event-related potentials. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchon, J.F.; Dabaghian, Y.; Uzor, N.E.; Kesler, S.R.; Wefel, J.S.; Tsvetkov, A.S. Levetiracetam mitigates doxorubicin-induced DNA and synaptic damage in neurons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokoohinia, Y.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Moieni-Arya, M.; Mostafaie, A.; Mohammadi-Motlagh, H.R. Osthole attenuates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 156848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Sarkar, S.; Scott, L.; Danelisen, I.; Trush, M.A.; Jia, Z.; Li, Y.R. Doxorubicin Redox Biology: Redox Cycling, Topoisomerase Inhibition, and Oxidative Stress. React. Oxyg. Species 2016, 1, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, Glutamate, and Glia: A Trio of Trouble in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Tseng, C.H.; Tu, Y.F.; Liao, N.S.; Huang, C.C.; Ho, C.J. TNFR1-JNK signaling is the shared pathway of neuroinflammation and neurovascular damage after LPS-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic injury in the immature brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, I.; Joung, H.Y.; Yu, A.R.; Shim, I.; Kim, J.S. PET Evidence of the Effect of Donepezil on Cognitive Performance in an Animal Model of Chemobrain. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6945415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Keeney, J.T.R.; Miriyala, S.; Noel, T.; Powell, D.K.; Chaiswing, L.; Bondada, S.; St Clair, D.K.; Butterfield, D.A. The triangle of death of neurons: Oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and loss of choline-containing biomolecules in brains of mice treated with doxorubicin. Advanced insights into mechanisms of chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment (“chemobrain”) involving TNF-alpha. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 134, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, L.A.; Acharya, M.M.; Parihar, V.K.; Nguyen, A.; Martirosian, V.; Limoli, C.L. Impaired cognitive function and hippocampal neurogenesis following cancer chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1954–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigotte, L.; Arvidson, B.; Olsson, Y. Cytofluorescence localization of adriamycin in the nervous system. I. Distribution of the drug in the central nervous system of normal adult mice after intravenous injection. Acta Neuropathol. 1982, 57, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangpong, J.; Sompol, P.; Vore, M.; St Clair, W.; Butterfield, D.A.; St Clair, D.K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated nitric oxide production enhances manganese superoxide dismutase nitration and mitochondrial dysfunction in primary neurons: An insight into the role of glial cells. Neuroscience 2008, 151, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangpong, J.; Cole, M.P.; Sultana, R.; Estus, S.; Vore, M.; St. Clair, W.; Ratanachaiyavong, S.; St. Clair, D.K.; Butterfield, D.A. Adriamycin-mediated nitration of manganese superoxide dismutase in the central nervous system: Insight into the mechanism of chemobrain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.R.; Broshek, D.K. Assessing cognitive dysfunction in breast cancer: What are the tools? Clin. Breast Cancer 2002, 3 (Suppl. 3), S91–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.B.; Sadighi, Z.S.; Zabrowski, J.; Gajjar, A.; Jeha, S. Imaging Patterns and Outcome of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome During Childhood Cancer Treatment. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya-Matsuoka, C.; Paker, A.M.; Chi, L.; Youssef, A.; Tummala, S.; Loghin, M.E. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in cancer patients: A single institution retrospective study. J. Neurooncol 2016, 128, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Carreras, M.T.; Chaftari, P.; Shamsnia, A.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; Gonzalez, C. Methotrexate-induced leukoencephalopathy presenting as stroke in the emergency department. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, M.m.A.A.; El Kiki, H.A.; Madney, Y.; Youssef, A.A. Chemotherapy-related neurotoxicity in pediatric cancer patients: Magnetic resonance imaging and clinical correlation. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.L.; Yang, C.M. Role of redox signaling in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 484613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, U.; Tudu, C.K.; Nandy, S.; Sunita, K.; Tripathi, V.; Loake, G.J.; Dey, A.; Prockow, J. Ethnodermatological use of medicinal plants in India: From ayurvedic formulations to clinical perspectives—A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Anand, U.; Dey, S.; Nandy, S.; Ghorai, M.; Saha, S.C.; Patil, M.T.; Kandimalla, R.; Prockow, J.; et al. Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Ashwagandha): A comprehensive review on ethnopharmacology, pharmacotherapeutics, biomedicinal and toxicological aspects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.R.; Chang, C.H.; Hsu, C.F.; Tsai, M.J.; Cheng, H.; Leong, M.K.; Sung, P.J.; Chen, J.C.; Weng, C.F. Natural compounds as potential adjuvants to cancer therapy: Preclinical evidence. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1409–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, G.R.; De Keulenaer, G.W.; Martinet, W. Role of autophagy in heart failure associated with aging. Heart Fail. Rev. 2010, 15, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, A.T.L.; Singh, S.R.; Schlossarek, S.; Carrier, L. Autophagy in cardiomyopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, S.; Singh, K.K. Epigenetic Regulation of Autophagy in Cardiovascular Pathobiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein, D.C. The roles of intracellular protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature 2006, 443, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.H.; Jackson, S.; Seaman, M.; Brown, K.; Kempkes, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; Levine, B. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 1999, 402, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, P.; Fu, S.; Calay, E.S.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Dysregulated autophagy contributes to the pathogenesis of enterovirus A71 infection. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.; Kim, J. Autophagy: An Essential Degradation Program for Cellular Homeostasis and Life. Cells 2018, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampada, A.; O’Prey, J.; Szabadkai, G.; Ryan, K.M.; Hochhauser, D.; Salomoni, P. mTORC1-independent autophagy regulates receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in colorectal cancer cells via an mTORC2-mediated mechanism. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwinn, D.M.; Shackelford, D.B.; Egan, D.F.; Mihaylova, M.M.; Mery, A.; Vasquez, D.S.; Turk, B.E.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.H. Redefining the role of AMPK in autophagy and the energy stress response. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Fan, H.; Cai, Z. Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1015500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriondo, M.N.; Etxaniz, A.; Varela, Y.R.; Ballesteros, U.; Lazaro, M.; Valle, M.; Fracchiolla, D.; Martens, S.; Montes, L.R.; Goni, F.M.; et al. Effect of ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 autophagy E3-like complex on the ability of LC3/GABARAP proteins to induce vesicle tethering and fusion. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lystad, A.H.; Carlsson, S.R.; Simonsen, A. Toward the function of mammalian ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex in autophagy and related processes. Autophagy 2019, 15, 1485–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Yu, S.; Jin, J.; Mugo, B.; Nguyen, N.; O’Brien, A.; Nag, S.; Lystad, A.H.; Melia, T.J. Delipidation of mammalian Atg8-family proteins by each of the four ATG4 proteases. Autophagy 2018, 14, 992–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.C.; Devenish, R.J. LC3-Associated Phagocytosis (LAP): Connections with Host Autophagy. Cells 2012, 1, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, C.; Borges, M.; Melo, S.; da Silva, E.T.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Teixeira, N. Apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells following exemestane treatment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xue, H.; He, L.H.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. The Role and Mechanism of Autophagy in Pancreatic Cancer: An Update Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 8231–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patergnani, S.; Missiroli, S.; Morciano, G.; Perrone, M.; Mantovani, C.M.; Anania, G.; Fiorica, F.; Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C. Understanding the Role of Autophagy in Cancer Formation and Progression Is a Real Opportunity to Treat and Cure Human Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.; DiPaola, R.S. The double-edged sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5308–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofani, R.; Montagnani Marelli, M.; Cicardi, M.E.; Fontana, F.; Marzagalli, M.; Limonta, P.; Poletti, A.; Moretti, R.M. Dual role of autophagy on docetaxel-sensitivity in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.P.; Patil, P.B.; Thakkannavar, S.S.; Pujari, V.B. Inflammation and cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Drie, J.H. Protein folding, protein homeostasis, and cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fei, W.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q.; Kuang, Y.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Hu, X. CHAC2, downregulated in gastric and colorectal cancers, acted as a tumor suppressor inducing apoptosis and autophagy through unfolded protein response. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, J.P.; Lazarou, M.; Dewson, G. Parkin and mitophagy in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Wang, H.G. The association of AMPK with ULK1 regulates autophagy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiassen, S.G.; De Zio, D.; Cecconi, F. Autophagy and the Cell Cycle: A Complex Landscape. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gan, Y.; Li, H.; Yin, J.; He, X.; Lin, L.; Xu, S.; Fang, Z.; Kim, B.W.; Gao, L.; et al. Inhibition of the CDK2 and Cyclin A complex leads to autophagic degradation of CDK2 in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Hong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Shen, R.; Dong, Q. The role of interaction between autophagy and apoptosis in tumorigenesis (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2022, 48, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Vetrivel, P.; Ha, S.E.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, G.S. Apigetrin induces extrinsic apoptosis, autophagy and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in AGS human gastric cancer cell. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.W.; Lee, S.H. The Roles of Autophagy in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Kong, N.; Zhang, M.; Han, W.; Lou, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agalakova, N.I. Chloroquine and Chemotherapeutic Compounds in Experimental Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear, D.; Bhagirath, E.; Balachandar, A.; Vegh, C.; Pandey, S. Autophagy Inhibition via Hydroxychloroquine or 3-Methyladenine Enhances Chemotherapy-Induced Apoptosis in Neuro-Blastoma and Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Zou, C.; Zhang, J. Chloroquine against malaria, cancers and viral diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.L.; Warri, A.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Clarke, P.A.; Cruz, M.I.; Zwart, A.; Clarke, R. Hydroxychloroquine inhibits autophagy to potentiate antiestrogen responsiveness in ER+ breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3222–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Takabatake, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Isaka, Y. Chloroquine in cancer therapy: A double-edged sword of autophagy. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, A.K.; Saadeldin, M.K.; Salem, A.H.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Shouman, S.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Orecchia, R. A Critical Review of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine as Potential Adjuvant Agents for Treating People with Cancer. Future Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.X.; Huang, Y.J.; Yao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Min, D.L. Incidence and risk of treatment-related mortality with mTOR inhibitors everolimus and temsirolimus in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, L.M.; Lin, R.Z. Rapamycin and mTOR kinase inhibitors. J. Chem. Biol. 2008, 1, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Jing, J.; Huang, R.; Zhou, T.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Doxorubicin downregulates autophagy to promote apoptosis-induced dilated cardiomyopathy via regulating the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleini, N.; Kardami, E. Autophagy and mitophagy in the context of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46663–46680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, M.; Guo, Z.; Valenzuela Ripoll, C.; Diab, A.; Picataggi, A.; Rawnsley, D.; Lotfinaghsh, A.; Bergom, C.; Szymanski, J.; Hwang, D.; et al. Sustained alternate-day fasting potentiates doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 928–942.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, E.; Tang, Y.; Mao, J.; Shen, J.; Zheng, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. miR-223 overexpression inhibits doxorubicin-induced autophagy by targeting FOXO3a and reverses chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiensch, A.E.; Bolam, K.A.; Mijwel, S.; Jeneson, J.A.L.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Kranenburg, O.; van der Wall, E.; Rundqvist, H.; Wengstrom, Y.; May, A.M. Doxorubicin-induced skeletal muscle atrophy: Elucidating the underlying molecular pathways. Acta Physiol. 2020, 229, e13400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Singh, A.; Nguyen, H.C.; Peddi, B.; Bhatt, K.; Ravendranathan, N.; Frisbee, J.C.; Singh, K.K. Protein Disulfide Isomerase 4 Is an Essential Regulator of Endothelial Function and Survival. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Xiaojun, X.; Peilong, C. Magnoflorine improves sensitivity to doxorubicin (DOX) of breast cancer cells via inducing apoptosis and autophagy through AKT/mTOR and p38 signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Mao, Q.; Gao, D.; Xiong, L.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X. HMGB1 Promotes Resistance to Doxorubicin in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inducing Autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 739145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, H.; Oka, T.; Zou, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Mizukami, M.; Sano, M.; Yamamoto, R.; Sugaya, T.; Komuro, I. Angiotensin II type 1a receptor mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Hypertens. Res. 2002, 25, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Sia, E.A. Mitochondrial DNA repair and damage tolerance. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.A.; Ryan, K.M. Autophagy is critically required for DNA repair by homologous recombination. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2016, 3, e1030538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; Patel, S.; Kravchuk, O.; Chen, G.; Mathew, R.; Jin, S.; White, E. Autophagy mitigates metabolic stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis. Genes. Dev. 2007, 21, 1621–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.Y.; Xu, N.; O’Prey, J.; Lao, L.Y.; Joshi, S.; Long, J.S.; O’Prey, M.; Croft, D.R.; Beaumatin, F.; Baudot, A.D.; et al. Loss of autophagy causes a synthetic lethal deficiency in DNA repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, Z.S.; Brunt, V.E.; Hutton, D.A.; Casso, A.G.; Ziemba, B.P.; Melov, S.; Campisi, J.; Seals, D.R. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-Mediated Inflammation and Remodeling of the Extracellular Matrix Underlies Aortic Stiffening Induced by the Common Chemotherapeutic Agent Doxorubicin. Hypertension 2021, 77, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Yan, P.; Xiao, G. Hsp90 inhibition results in autophagy-mediated proteasome-independent degradation of IkappaB kinase (IKK). Cell Res. 2006, 16, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Hyttinen, J.M.; Kauppinen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Context-Dependent Regulation of Autophagy by IKK-NF-kappaB Signaling: Impact on the Aging Process. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 849541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niso-Santano, M.; Criollo, A.; Malik, S.A.; Michaud, M.; Morselli, E.; Marino, G.; Lachkar, S.; Galluzzi, L.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Direct molecular interactions between Beclin 1 and the canonical NFkappaB activation pathway. Autophagy 2012, 8, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Shin, D.M.; Yuk, J.M.; Shi, G.; Choi, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Huang, S.M.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Autophagy negatively regulates keratinocyte inflammatory responses via scaffolding protein p62/SQSTM1. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.F.; Yan, H.; Hu, Y.; Springer, L.E.; Yang, X.; Wickline, S.A.; Pan, D.; Lanza, G.M.; Pham, C.T. Fumagillin prodrug nanotherapy suppresses macrophage inflammatory response via endothelial nitric oxide. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7305–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, C.S.; Alam, S.; Aishwarya, R.; Miriyala, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.N.; Panchatcharam, M.; Pattillo, C.B.; Orr, A.W.; Sadoshima, J.; Hill, J.A.; et al. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy associated with inhibition of autophagic degradation process and defects in mitochondrial respiration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, J. Potential Doxorubicin-Mediated Dual-Targeting Chemotherapy in FANC/BRCA-Deficient Tumors via Modulation of Cellular Formaldehyde Concentration. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmorstein, L.Y.; Ouchi, T.; Aaronson, S.A. The BRCA2 gene product functionally interacts with p53 and RAD51. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13869–13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Miller, J.; Kinnucan, E.; Sun, Y.; Thoma, N.H.; Zheng, N.; Chen, P.L.; Lee, W.H.; Pavletich, N.P. BRCA2 function in DNA binding and recombination from a BRCA2-DSS1-ssDNA structure. Science 2002, 297, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, L.Y.; Yu, X. The role of BRCA1 in DNA damage response. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Huang, J. The Fanconi anemia pathway and DNA interstrand cross-link repair. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z. Fanconi anemia pathway defects in inherited and sporadic cancers. Transl. Pediatr. 2014, 3, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svojgr, K.; Sumerauer, D.; Puchmajerova, A.; Vicha, A.; Hrusak, O.; Michalova, K.; Malis, J.; Smisek, P.; Kyncl, M.; Novotna, D.; et al. Fanconi anemia with biallelic FANCD1/BRCA2 mutations—Case report of a family with three affected children. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.C.; Marks, J.H.; Mandell, J.B.; New York Breast Cancer Study, G. Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science 2003, 302, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.; Seal, S.; Thompson, D.; Kelly, P.; Renwick, A.; Elliott, A.; Reid, S.; Spanova, K.; Barfoot, R.; Chagtai, T.; et al. PALB2, which encodes a BRCA2-interacting protein, is a breast cancer susceptibility gene. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.K.; Kwong, A.; Tam, K.F.; Cheung, A.N.; Ngan, H.Y.; Xia, W.; Wong, A.S. BRCA1 deficiency induces protective autophagy to mitigate stress and provides a mechanism for BRCA1 haploinsufficiency in tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2014, 346, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve, J.M.; Armengod, M.E.; Knecht, E. BRCA1 negatively regulates formation of autophagic vacuoles in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, B.; Akar, U.; Gutierrez-Barrera, A.M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Ozpolat, B. The PARP inhibitor AZD2281 (Olaparib) induces autophagy/mitophagy in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutant breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Shukla, P.C.; Yanagawa, B.; Quan, A.; Lovren, F.; Pan, Y.; Wagg, C.S.; Teoh, H.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Regulating cardiac energy metabolism and bioenergetics by targeting the DNA damage repair protein BRCA1. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 146, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S.; Stanbery, L.; Walter, A.; Rocconi, R.P.; Nemunaitis, J. BRCA1/2 Mutation Status Impact on Autophagy and Immune Response: Unheralded Target. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 4, pkaa077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osellame, L.D.; Blacker, T.S.; Duchen, M.R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial function. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 26, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.C. A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: A dawn for evolutionary medicine. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 359–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza-Lombo, C.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Franco, R. Redox homeostasis, oxidative stress and mitophagy. Mitochondrion 2020, 51, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamori, T.; Yasui, H.; Yamazumi, M.; Wada, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Inanami, O. Ionizing radiation induces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production accompanied by upregulation of mitochondrial electron transport chain function and mitochondrial content under control of the cell cycle checkpoint. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyton, R.O.; McEwen, J.E. Crosstalk between nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 563–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarou, M.; Sliter, D.A.; Kane, L.A.; Sarraf, S.A.; Wang, C.; Burman, J.L.; Sideris, D.P.; Fogel, A.I.; Youle, R.J. The ubiquitin kinase PINK1 recruits autophagy receptors to induce mitophagy. Nature 2015, 524, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Volden, P.; Timm, D.; Mao, K.; Xu, X.; Liang, Q. Transcription factor GATA4 inhibits doxorubicin-induced autophagy and cardiomyocyte death. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, E.F.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Chua, K.F.; Mattson, M.P.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Nuclear DNA damage signalling to mitochondria in ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Middleton, A.; Carmichael, P.L.; et al. Doxorubicin-induced mitophagy and mitochondrial damage is associated with dysregulation of the PINK1/parkin pathway. Toxicol In Vitro 2018, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpter, R., Jr.; Sirasanagandla, S.; Fernandez, A.F.; Wei, Y.; Dong, X.; Franco, L.; Zou, Z.; Marchal, C.; Lee, M.Y.; Clapp, D.W.; et al. Fanconi Anemia Proteins Function in Mitophagy and Immunity. Cell 2016, 165, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohjoismaki, J.L.; Goffart, S.; Tyynismaa, H.; Willcox, S.; Ide, T.; Kang, D.; Suomalainen, A.; Karhunen, P.J.; Griffith, J.D.; Holt, I.J.; et al. Human heart mitochondrial DNA is organized in complex catenated networks containing abundant four-way junctions and replication forks. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21446–21457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Saxena, S.; Kaushal, A.; Nagaraju, G. RAD51C/XRCC3 Facilitates Mitochondrial DNA Replication and Maintains Integrity of the Mitochondrial Genome. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 38, e00489-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coene, E.D.; Hollinshead, M.S.; Waeytens, A.A.; Schelfhout, V.R.; Eechaute, W.P.; Shaw, M.K.; Van Oostveldt, P.M.; Vaux, D.J. Phosphorylated BRCA1 is predominantly located in the nucleus and mitochondria. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, C.K.; Kim, H.B.; Wu, T.T.; Park, S.; Cho, S.I.; Lee, J.-H. 53BP1 contributes to regulation of autophagic clearance of mitochondria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.; Karp, C.; Strohecker, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Mathew, R. Role of autophagy in suppression of inflammation and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Wu, X.; Yin, D.; Jia, X.H.; Chen, X.; Gu, Z.Y.; Zhu, X.M. Autophagy inhibitors for cancer therapy: Small molecules and nanomedicines. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 249, 108485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Debnath, J. Targeting Autophagy in Cancer: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Rick, J.; Yagnik, G.; Aghi, M.K. Autophagy as a mechanism for anti-angiogenic therapy resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 66, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Abdulmomen Ali Mohammed, S.; Li, H.; Cai, W.; Guan, W.; Liu, D.; Wei, Y.; Rong, D.; Fang, Y.; et al. Adaptor SH3BGRL drives autophagy-mediated chemoresistance through promoting PIK3C3 translation and ATG12 stability in breast cancers. Autophagy 2022, 18, 1822–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Q.; Wang, S.B.; Shao, Y.F.; Shi, J.N.; Wang, W.; Chen, W.Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Jiang, J.Y.; Fang, Q.X.; Zhang, G.B.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine potentiates the anti-cancer effect of bevacizumab on glioblastoma via the inhibition of autophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Yu, D.; Lum, J.J.; Bui, T.; Christophorou, M.A.; Evan, G.I.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Thompson, C.B. Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Z.; Wang, W.W.; Hu, T.T.; Zhu, G.Y.; Li, L.N.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, H.B.; Wu, H.F.; Zhu, J.G. FOXM1 contributes to docetaxel resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer by inducing AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torisu, K.; Singh, K.K.; Torisu, T.; Lovren, F.; Liu, J.; Pan, Y.; Quan, A.; Ramadan, A.; Al-Omran, M.; Pankova, N.; et al. Intact endothelial autophagy is required to maintain vascular lipid homeostasis. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Lovren, F.; Pan, Y.; Quan, A.; Ramadan, A.; Matkar, P.N.; Ehsan, M.; Sandhu, P.; Mantella, L.E.; Gupta, N.; et al. The essential autophagy gene ATG7 modulates organ fibrosis via regulation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, H.; Kuchnio, A.; Peric, A.; Moens, S.; Nys, K.; De Bock, K.; Quaegebeur, A.; Schoors, S.; Georgiadou, M.; Wouters, J.; et al. Tumor vessel normalization by chloroquine independent of autophagy. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, N.; Ansari, M.I.; Kainat, K.M.; Singh, V.K.; Sharma, P.K. Chloroquine synergizes doxorubicin efficacy in cervical cancer cells through flux impairment and down regulation of proteins involved in the fusion of autophagosomes to lysosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 656, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimori, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Moriyama, Y.; Futai, M.; Tashiro, Y. Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase, inhibits acidification and protein degradation in lysosomes of cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17707–17712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jing, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.; Diao, A. Lysosome Inhibitors Enhance the Chemotherapeutic Activity of Doxorubicin in HepG2 Cells. Chemotherapy 2017, 62, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, R.N.; Doerr, V.; Kwon, O.S.; Talbert, E.E.; Yoo, J.-K.; Hwang, M.-H.; Nguyen, B.L.; Christou, D.D.; Kavazis, A.N.; Smuder, A.J. Protection against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction Is Not Maintained Following Prolonged Autophagy Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ye, H.L.; Zhang, G.; Yao, W.M.; Chen, X.Z.; Zhang, F.C.; Liang, G. Autophagy inhibition contributes to the synergistic interaction between EGCG and doxorubicin to kill the hepatoma Hep3B cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, R.J.; Zakikhani, M.; Fantus, I.G.; Pollak, M.; Sonenberg, N. Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10804–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Hong, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nada, S.; Mannan, A.M.; Wang, J.; Okada, M.; Guan, K.L.; Inoki, K. Redox regulates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity by modulating the TSC1/TSC2-Rheb GTPase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32651–32660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasznicki, J.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Metformin in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sishi, B.J.; Loos, B.; van Rooyen, J.; Engelbrecht, A.M. Autophagy upregulation promotes survival and attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, V.; Singh, A.; Bhatt, M.; Tonk, R.K.; Azizov, S.; Raza, A.S.; Sengupta, S.; Kumar, D.; Garg, M. Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, L. Thymoquinone-induced autophagy mitigates doxorubicin-induced H9c2 cell apoptosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, L. Spinacetin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by initiating protective autophagy through SIRT3/AMPK/mTOR pathways. Phytomedicine 2022, 101, 154098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.D.; Pang, Y.X.; Zhao, X.R.; Li, R.; Jin, C.J.; Xue, J.; Dong, R.Y.; Liu, P.S. Curcumin induces apoptotic cell death and protective autophagy by inhibiting AKT/mTOR/p70S6K pathway in human ovarian cancer cells. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2019, 299, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, D.; Wei, Z.; Xu, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, R.; Cai, Q. Curcumin regulates proliferation, autophagy, and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by affecting PI3K and P53 signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 4634–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Luo, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, D.; Yao, J.; You, J.; He, M. Curcumin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via suppressing oxidative stress and preventing mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by 14-3-3gamma. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4404–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, P.; Wang, L.; Zha, W.; Ren, J. Curcumin suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via a PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent manner. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 752–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T.; Levine, B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 2010, 140, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Lamark, T.; Sjottem, E.; Larsen, K.B.; Awuh, J.A.; Overvatn, A.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Johansen, T. p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22576–22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Kim, C.; Wang, X.D.; Scherer, P.E.; Gao, J.; Levine, B.; Yu, Y. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analyses identify STK11IP as a lysosome-specific substrate of mTORC1 that regulates lysosomal acidification. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacal, M.; Zhang, B.; Hao, Y.; Norberg, E.; Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H. Quantitative proteomic analysis of temporal lysosomal proteome and the impact of the KFERQ-like motif and LAMP2A in lysosomal targeting. Autophagy 2021, 17, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Lin, Y.; Wu, C. Resolving mutational signatures in cancer development. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.R.; Krug, K.; Zhang, B.; Satpathy, S.; Clauser, K.R.; Ding, L.; Ellis, M.; Gillette, M.A.; Carr, S.A. Cancer proteogenomics: Current impact and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 2008, 132, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, S.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Diao, L.; Zeng, Y. Multi-omics reveals a relationship between endometrial amino acid metabolism and autophagy in women with recurrent miscarriagedagger. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 105, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirin, A.; Klickstein, I.S.; Feng, S.; Lin, Y.T.; Hlavacek, W.S.; Sorrentino, F. Prediction of Optimal Drug Schedules for Controlling Autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuy, O.; Papp, D.; Vellai, T.; Banhegyi, G.; Korcsmaros, T. Systems-Level Feedbacks of NRF2 Controlling Autophagy upon Oxidative Stress Response. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, T.E.; Barnett, K.J.; Wallis, L.; Hanneman, W.H. A multimethod computational simulation approach for investigating mitochondrial dynamics and dysfunction in degenerative aging. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, M. Computational modeling of the effects of autophagy on amyloid-beta peptide levels. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2020, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.T.; Weis, J.A.; Barnes, S.L.; Tyson, D.R.; Miga, M.I.; Quaranta, V.; Yankeelov, T.E. A Predictive Mathematical Modeling Approach for the Study of Doxorubicin Treatment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Elazar, Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Codogno, P.; Levine, B. Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.; Kimmelman, A.C.; White, E. Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes. Dev. 2016, 30, 1913–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewirtz, D.A. The four faces of autophagy: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.; Ravendranathan, N.; Frisbee, J.C.; Singh, K.K. Complex Interplay between DNA Damage and Autophagy in Disease and Therapy. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080922
Singh A, Ravendranathan N, Frisbee JC, Singh KK. Complex Interplay between DNA Damage and Autophagy in Disease and Therapy. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(8):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080922
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Aman, Naresh Ravendranathan, Jefferson C. Frisbee, and Krishna K. Singh. 2024. "Complex Interplay between DNA Damage and Autophagy in Disease and Therapy" Biomolecules 14, no. 8: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080922
APA StyleSingh, A., Ravendranathan, N., Frisbee, J. C., & Singh, K. K. (2024). Complex Interplay between DNA Damage and Autophagy in Disease and Therapy. Biomolecules, 14(8), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080922





