Abstract
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) is broadly used as a traditional remedy and food ingredient, and numerous preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated health benefits in a range of age-related disorders. Moreover, longevity-promoting effects have been demonstrated in several (preclinical) research models. With this work, we aimed to comprehensively review the reported effects of ginger and its bioactive constituents on the twelve established hallmarks of aging, with the ultimate goal of gaining a deeper understanding of the potential for future interventions in the area of longevity-extension and counteracting of aging-related diseases. The reviewed literature supports the favorable effects of ginger and some of its constituents on all twelve hallmarks of aging, with a particularly high number of animal research studies indicating counteraction of nutrient-sensing dysregulations, mitochondrial dysfunction, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis. On this background, validation in human clinical trials is still insufficient or is entirely missing, with the exception of some studies indicating positive effects on deregulated nutrient-sensing, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis. Thus, the existing body of literature clearly supports the potential of ginger to be further studied in clinical trials as a supplement for the promotion of both lifespan and health span.
Keywords:
ginger; hallmarks of aging; longevity; life-extension; lifespan; health span; metabolism; inflammation 1. Introduction
Aging is a complex multi-component process that is defined by the gradual decline of physiological functions and homeostasis maintenance, ultimately resulting in the death of the organism. The compromised physiological functions and homeostasis result in increased susceptibility to diverse age-related neoplastic and degenerative diseases. Twelve prominent hallmarks of the aging process have been outlined, which include genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, disabled macroautophagy, deregulated nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, altered intercellular communication, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis [1,2] (Figure 1). Counteracting aging by targeting mechanisms associated with its hallmarks is of great interest, and modulation of diet and specific dietary ingredients have emerged as a powerful approach to improving health and expanding the lifespan [3,4,5].
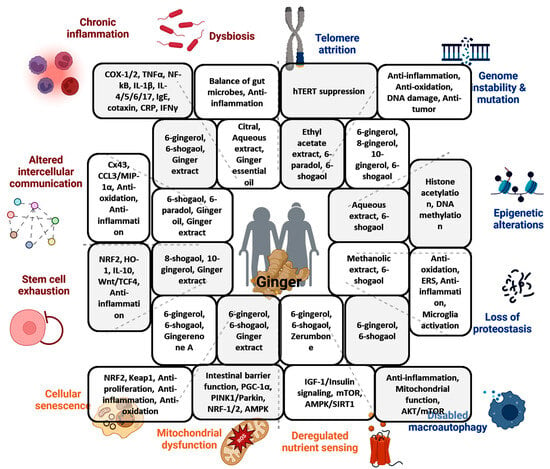
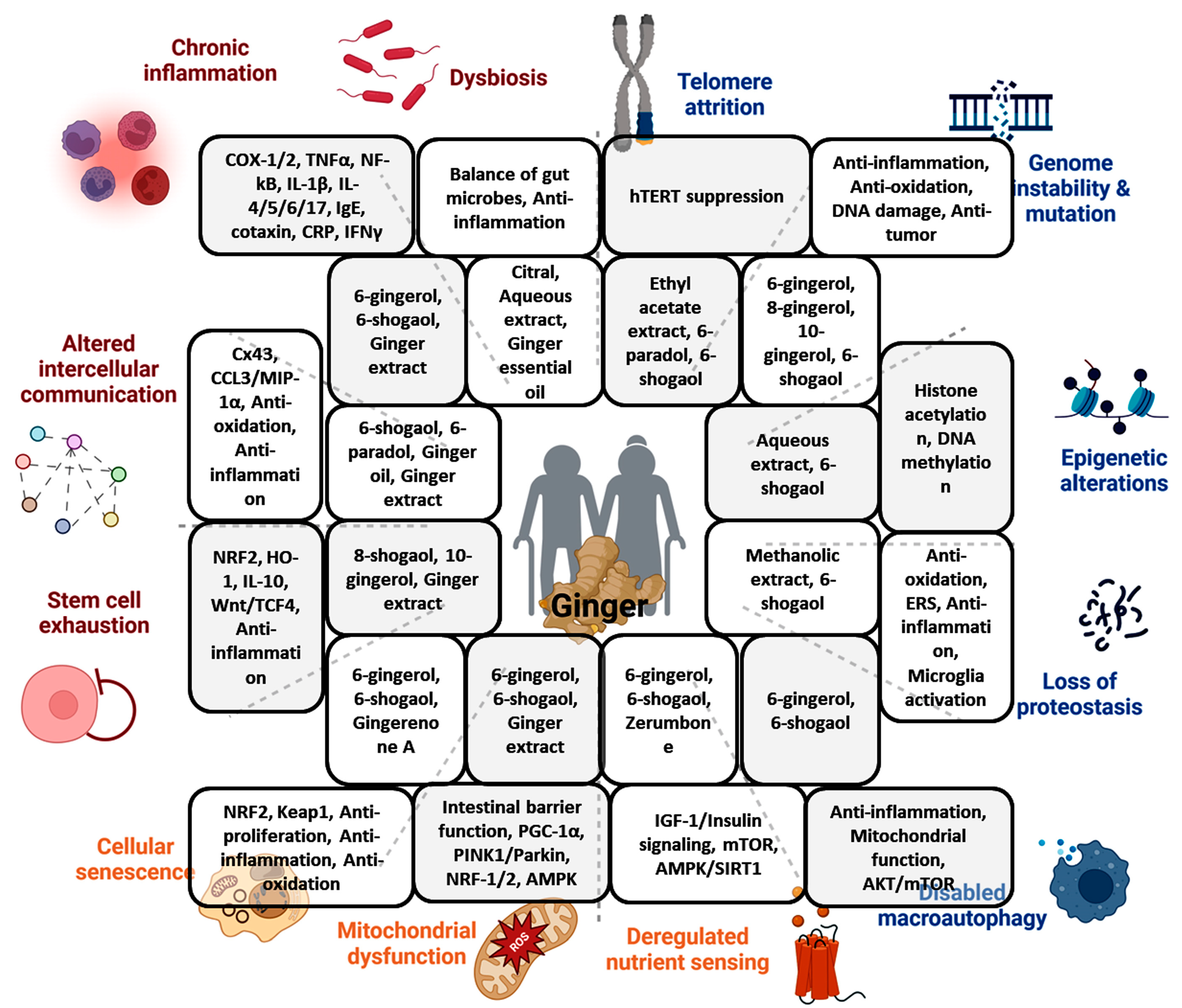
Figure 1.
Summary of the effects of ginger and its constituents on the hallmarks of aging and the respective involved mechanisms (created with BioRender.com (accessed on 18 July 2024)).
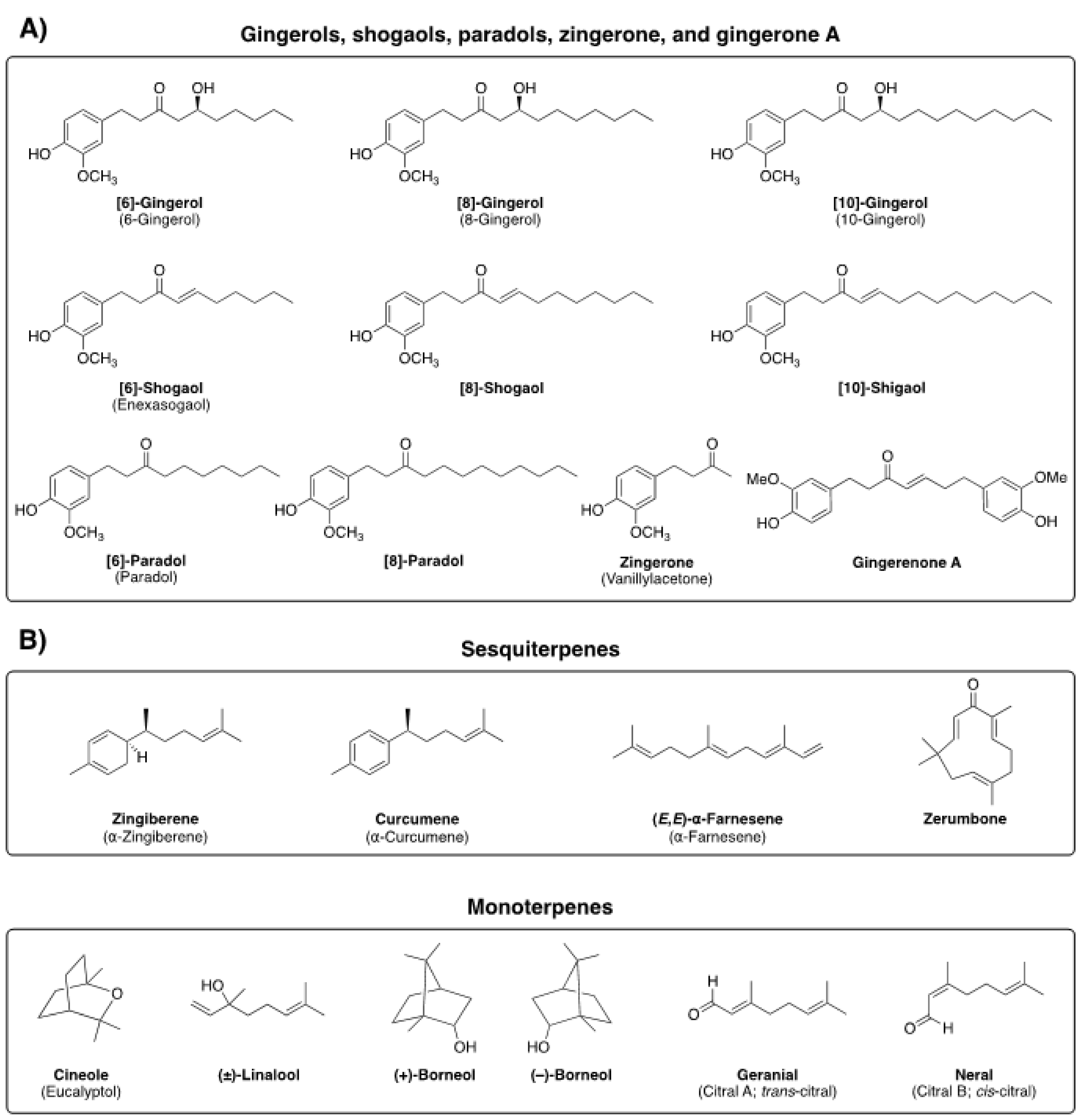
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) is broadly used in culinary as well as utilized as a versatile remedy in the traditional folk medicine of many countries [6,7]. The major bioactive constituents of ginger are nonvolatile and include gingerols, shogaols, paradols, and zingerone, while ginger volatile oil constituents that have been identified include sesquiterpenes (zingiberene, curcumene, and farnesene) and monoterpenes (cineole, linalool, borneol, geranial, and neral) (Figure 2) [8,9]. 6-gingerol specifically is considered to be a major pungent phytochemical found in fresh ginger, whereas, in dried rhizomes, 6-gingerol is dehydrated to 6-shogaol.
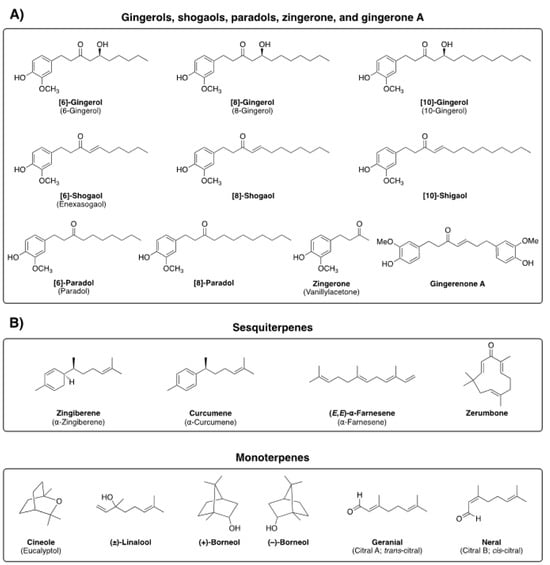
Figure 2.
Chemical structures and common names of the major bioactive constituents of ginger, including nonvolatile (panel (A)) and volatile compounds (sesqui- and monoterpenes, panel (B)).
There has been a broad clinical interest in verifying in patients ginger bioactivities indicated by preclinical research and traditional folk medicine, and a recent systematic study of conducted randomized controlled trials indicated robust evidence for efficacy in counteracting metabolic syndrome, for improvement of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy, for anti-inflammatory activity, for digestive function support, and for positive impact on colorectal cancer’s markers [10]. According to the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA’s) Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC), the most established pharmacological properties of ginger rhizomes are its use in adults to prevent nausea and vomiting in motion sickness, to counteract mild symptoms of affecting the stomach or gut (e.g., bloating and flatulence), and its application in children aged six and above to combat the symptoms of motion sickness (EMA website accessed on 11 of February 2024; https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/herbal/zingiberis-rhizoma). The efficacy of ginger and its ingredients for counteracting dementia and other age-related neurological disorders has also been broadly studied [11,12]. Moreover, longevity-promoting effectiveness has been demonstrated upon the application of both ginger extract [13] and 6-shogaol [14] in a Caenorhabditis elegans model. Similarly, the lifespan-promoting effect of ginger was also demonstrated in Drosophila melanogaster models [15,16,17].
Taking into consideration that ginger is a broadly consumed medicinal plant that has shown promising potential in modulating age-related disorders and promoting healthy aging, the aim of this work is to comprehensively review the impact of ginger on the hallmarks of aging, as inspired by the two influential reviews on the latter topic by López-Otín C et al. [1,2]. Evaluation of effects by single key constituents of ginger, such as 6-gingerol, 6-shogaol, and 6-paradol, on the recently recognized hallmarks of aging is also aimed. Special attention will be given to molecular mechanisms and affected cell signaling pathways underlying ginger’s anti-aging effects, with the ultimate goal to gain a deeper understanding of the therapeutic potential of ginger and its constituents and inspire future research avenues in the area of longevity-extension interventions.
2. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Genomic Instability
Genomic instability represents an important contributor to aging, and it is characterized by diverse genetic lesions such as point mutations, single- and double-strand breaks, deletions, or translocations of DNA fragments, telomere shortening, and changes in chromosomal and nuclear architecture. These lesions are the result of exogenous agents (chemical, physical, or biological), as well as endogenous processes such as oxidative metabolic processes or DNA replication errors, among others. Genomic instability is counteracted by diverse mechanisms of repair and maintenance of both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA [18], and aging is associated with decreased efficiency of these protective repair mechanisms.
Several works examined in vitro or in vivo the effects of ginger or its constituents on genomic stability or parameters related to it. Ginger and some of its bioactive constituents have been shown to possess significant antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities [19], which can counteract DNA damage induced by oxidative stress. Direct comparison of the antioxidant potential of several of the major bioactive constituents of ginger, 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 10-gingerol, and 6-shogaol, revealed the activity of all of the studied compounds, with 6-gingerol being the least potent and 6-shogaol being most potent in the scavenging of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picyrlhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals (IC50 of 8.05 µM), as well as superoxide (IC50 of 0.85 µM) and hydroxyl radicals (IC50 of 0.72 µM) [20]. In the same work, applied at 6 micromolar concentration, all four compounds also inhibited the oxidative burst induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (f-MLP) in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. In rats, ethanolic ginger extract applied orally (at 100, 200, 300 mg/kg body weight, applied daily for 21 days) exhibited marked protective effects against bromobenzene-induced oxidative stress by boosting antioxidant defense mechanisms (increasing hepatic glutathione levels, as well as the activities of glutathione reductase, glutathione S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase) [21]. Similarly, co-administration of dietary ginger (1%, w/w, in parallel with oral lindane administration of 30 mg/kg bw for 4 weeks) counteracted lindane-induced lipid peroxidation, along with changes of oxygen free radical scavenging enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, reduced glutathione, and the enzymes glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione-S-transferase [22]. Moreover, clinical studies in humans also supported the antioxidant effects of ginger. Thus, it was shown that newly diagnosed patients with solid tumors receiving moderate-to-high emetogenic potential chemotherapy, when compared to placebo, had a significant increase in antioxidant enzyme blood levels (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase) and the levels of the nonenzymatic antioxidant glutathione, and also exhibited reduced oxidative marker levels (malondialdehyde and NO2−/NO3−) upon oral administration of standardized 6-gingerol (standardized 6-gingerol 20 mg/day) capsules of 5 mg twice daily, starting 3 days prior to the first cycle of chemotherapy until the fourth [23].
Anti-inflammatory properties have also been well-established for ginger, and some of its constituents, and this may also contribute to potential protective effects against genomic instability since chronic inflammation can induce DNA damage that can ultimately result in carcinogenesis [24]. In this context, aside from the mitigation of oxidative stress (that is known to be associated with chronic inflammation), the ability of ginger to counteract pro-inflammatory pathways could be of significance. In particular, research studies have indicated the inhibitory effects of ginger on pro-inflammatory enzymes such as lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), as well as the NF-κB pathway, among other inflammatory mediators [25].
In line with the postulated above potential of ginger to counteract DNA damage through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, a study in rats demonstrated that the pretreatment with the ginger constituent zingerone (150 mg/kg (p.o.) administrated 2 h before lipopolysaccharide challenge) abolished the increase of 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG, DNA damage marker) levels that was associated with lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation [26]. Similarly, the levels of the DNA damage marker 8-OHdG were suppressed upon oral aqueous ginger extract (500 mg/kg body weight, orally, for two months) application in a rat model of monosodium glutamate-induced neurotoxicity [27], upon co-application of hydro-alcoholic extract of ginger (50 mg/kg body weight, intragastrically by gavage, for six weeks) in a rat ethanol-induced kidney damage model [28], and upon hydro-alcoholic extract of ginger pretreatment (50 mg/kg body weight, intragastrically by gavage, for 10 days) in a rat model of radiation-induced kidney damage [29].
A summary of the effects of ginger and its constituents on genomic instability and the other hallmarks of aging with an outline of key supporting in vitro and animal research studies is presented in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
In vitro studies linked to the potential of ginger to modulate hallmarks of aging.
3. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Telomere Attrition
Telomeres are nucleoprotein structures composed of repeated sequences of DNA that cap the end of chromosomes to maintain the function of genomic stability by protecting from degradation of each cell cycle. An enzyme called telomerase, responsible for the maintenance of telomere length, functions in the cell by adding TTAGGG repeats to the 3′ end of the sequence by retrotranscription. Each time the cell divides, telomeres become shorter by losing a small amount of DNA. Over time, as a result of the progressive shortening of telomeres, chromosomes become damaged, and the cells can no longer divide, resulting in cell apoptosis. However, the telomeres can be rebuilt by telomerase to restore cell division. The largest activities of telomerase are notably observed to function in stem cells, gametes, and tumor cells. During cellular replication in somatic cells, telomere length shortens gradually, giving rise to chromosomal instability and mutagenesis, resulting in tumorigenesis [47]. Short telomere length has been linked to many age-related diseases and noncommunicable diseases, which may reflect the effects of numerous behavioral, psychosocial, and environmental factors on health status [47]. Many factors linked to certain lifestyles, such as smoking, high consumption of unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, and obesity, can increase the chance of telomere shortening, leading to premature death [48]. Risk for various cancers, such as bladder, colorectal, breast, and gastric cancer, has been associated with accelerated telomere shortening [48].
Telomeres can also be highly sensitive to damage by oxidative stress due to plenty of guanines in the telomeric repeats. This oxidative stress can be the result of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or free radicals that are produced from ATP production of mitochondria and as a by-product of aerobic metabolism [49]. Due to oxidative stress, most telomere attrition occurs during the replication of DNA, resulting in single-stranded DNA damage [50]. Along this line, a study indicated that a diet containing antioxidant omega-3 fatty acids reduced the rate of telomere shortening, whereas a lack of these antioxidants increased the rate of telomere attrition [51]. Moreover, it was demonstrated that women who consumed a diet lacking antioxidants had shorter telomeres and had moderate chances of developing breast cancer, whereas consumption of a diet rich in antioxidants had longer telomeres and a lower risk of breast cancer [52]. Cytometry studies have also shown that patients with rheumatoid arthritis (chronic inflammatory disease associated with increased oxidative stress) have accelerated shortening of telomere lengths with the increase in age, resulting in premature cellular aging [53].
Diverse dietary phytochemicals have gained interest because of their potential for the prevention of cancer because of their therapeutic efficacy, bioavailability, and safety [54]. Telomerase enzymes are one of the attractive targets for cancer prevention because telomerase-specific inhibition causes cancer cells and cancer-initiating cells to undergo apoptosis and cell senescence without any effect on somatic cells. Several phytochemicals were found to inhibit telomerase in cancer cells, including curcumin, resveratrol, silibinin, pristimerin, EGCG, and sulforaphane, among others [55]. In recent years, scientists have revealed various chemical compounds found in ginger rhizomes, which exhibited anticancer properties in many experimental models [56]. In relation to telomerase in particular, a research study revealed that the crude ethyl acetate fraction of ginger extract exhibited inhibition of the expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) and c-Myc in A549 lung cancer cells in a time-(up to 72 h) and concentration-dependent (up to 64 µg/mL) manner [57]. Moreover, the result showed that from the major bioactive compounds in ginger, only 6-paradol and 6-shogaol could suppress hTERT expression and telomerase activity in A549 lung cancer cells, whereas 6-gingerol could not [58].

Table 2.
In vivo animal research studies linked to the potential of ginger to modulate hallmarks of aging.
Table 2.
In vivo animal research studies linked to the potential of ginger to modulate hallmarks of aging.
| Hallmark of Aging | In Vivo Model and Reference | Ginger Ingredient | Dose, Mode of Administration, and Time of Treatment | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomic instability | Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in rats [26] | Zingerone | 150 mg/kg (p.o.) administrated 2 h before lipopolysaccharide challenge | Counteracted DNA damage, quantified by measuring the DNA damage marker 8-OHdG |
| Monosodium glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rats [27] | Aqueous extract of ginger | 500 mg/kg body weight, orally, for two months | Counteracted DNA damage, quantified by measuring the DNA damage marker 8-OHdG | |
| Chronic ethanol administration in rats [28] | Hydro-alcoholic extract of ginger | 50 mg/kg body weight, intragastrically by gavage, for six weeks | Counteracted DNA damage, quantified by measuring the DNA damage marker 8-OHdG | |
| Radiation exposed rats [29] | Hydro-alcoholic extract of ginger | 50 mg/kg body weight, intragastrically by gavage, for 10 days | Counteracted DNA damage, quantified by measuring the DNA damage marker 8-OHdG | |
| Epigenetic alterations | C57BL/6j male mice subjected to transverse aortic coarctation surgery (to create pressure overload) [30] | 6-Shogaol | Daily oral administration of 0.2 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg of 6-shogaol for eight weeks | Increases in histone H3K9 acetylation due to the transverse aortic coarctation surgery were significantly suppressed by 6-shogaol |
| Loss of proteostasis | Alzheimer’s disease induced in rats by using AlCl3 [59] | Aqueous infusion of ginger | 108 and 216 mg/kg b.wt/day applied orally for 12 weeks | Reduction in amyloid plaques and improvement in cognition, psychological state as well as in the locomotor activity, as determined by rewarded alternation T-Maze test, grid floor activity cage, and accelerating speed rotarod |
| MPTP-induced model of Parkinson’s disease in C57/BL mice [60] | 6-Shogaol | 10 mg·kg−1·d−1, orally, for 3 days | Reversal of the MPTP-induced changes in motor coordination and bradykinesia and reversal of dopaminergic neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta and in stratum | |
| MPTP-induced model of Parkinson’s disease in C57BL/6J mice [61] | 6-shogaol and ginger extract | Ginger extract was applied at 30, 100, 300 mg/kg and 6-shogaol at 10 mg/kg, by gavage, for 15 days (including the period of the MPTP exposure) | Ginger and 6-shogaol protected intestinal tight junction proteins disrupted by MPTP in the mouse colon, inhibited the increase of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, TNF-α, and IL-1β produced by macrophages, and suppressed the MPTP-induced enteric dopaminergic neuronal damage | |
| Disabled macroautophagy | High-fat-diet + streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats [62] | Gingerol-enriched ginger (18.7% 6-gingerol, 1.81% 8-gingerol, 2.86% 10-gingerol, 3.09% 6-shogoal, 0.39% 8-shogaol, and 0.41% 10-shogaol) | The gingerol-enriched ginger was applied as 0.75% wt/wt in the diet for 8 weeks | The ginger extract improved gastrointestinal health in part by improving mitochondrial function, including increased mitophagy (stimulating the removal of damaged mitochondria) |
| Rats subjected to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by middle cerebral artery occlusion (for 1 h, ischemia induction) followed by reperfusion for 24 h [63] | 6-Gingerol | 6-Gingerol was intraperitoneally injected (3 mg/kg or 6 mg/kg) 30 min before middle cerebral artery occlusion | 6-Gingerol treatment induced autophagy, which counteracted the pathophysiological manifestations of the ischemia/reperfusion injury | |
| Deregulated nutrient-sensing | Caenorhabditis elegans [13] | Ginger extract | Applied life-long at 60 μg/mL | Prolonged lifespan by 23.16% through the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway |
| Mice with impaired insulin signaling as a result of sodium arsenite exposure [64] | 6-Gingerol | 50 mg/kg or 75 mg/kg body weight, daily supplied orally by gavage for 3 weeks | 6-Gingerol treatment reduced elevated blood glucose levels, increased diminished plasma insulin levels, and counteracted the sodium arsenite-induced downregulation of GLUT4, IRS-1, IRS-2, PI3K, AKT, PPARγ at protein and mRNA levels | |
| Liquid fructose-induced adipose tissue insulin resistance in rats [65] | Alcoholic extract of ginger | 50 mg/kg/day, by oral gavage, for five weeks | Attenuated hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) induced by liquid fructose, also reversed the increases in the Adipo-insulin resistance index and upregulated insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 | |
| High-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model [66] | Steamed ginger extract (20,437.13 ± 228.75 mg/kg of 6-gingerol and 7356.67 ± 80.83 mg/kg of 6-shogaol) | 40 mg/kg or 80 mg/kg daily, orally by gavage, for 8 weeks | Reduced body weight gain and fat mass accumulation, reduced liver steatosis, reversed the effect of the high-fat diet on the level of hepatic p-AMPK and SIRT1 | |
| Obesity model induced by high-fat diet in C57BL/6N mice [34] | Zerumbone | Applied as 0.01% or 0.025% of the diet for 8 weeks | Decreased adiposity induced from the high-fat diet, increased the phosphorylation of AMPK in the white adipose tissues, and reversed the dysregulation of miR-146b as well as attenuated decrease in SIRT1 expression | |
| High-fat diet-fed rats [67] | 6-Gingerol | 200 mg/kg body weight, via oral gavage, for 2 weeks | Induced hypoglycemic effect, enhanced phosphorylated AMPK-a1, and suppressed P65 via upregulation of Sirt-6 and downregulation of resistin | |
| Mitochondrial dysfunction | High-fat-diet + streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats [62] | Gingerol-enriched ginger (18.7% 6-gingerol, 1.81% 8-gingerol, 2.86% 10-gingerol, 3.09% 6-shogoal, 0.39% 8-shogaol, and 0.41% 10-shogaol) | The gingerol-enriched ginger was applied as 0.75% wt/wt in the diet for 8 weeks | The ginger extract improved gastrointestinal health in part by improving mitochondrial function, including increased mitophagy and influencing the balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission |
| High-fat diet-fed rats [68] | Ginger water extract | Supplemented at 0.25% or 0.5% of the diet for 14 weeks | Reduced weight gain and increased mitochondrial size and mtDNA content in rat skeletal muscle, upregulating PGC1ɑ, NRF1, and Tfam mRNA expression | |
| High-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model [66] | Steamed ginger extract (20,437.13 ± 228.75 mg/kg of 6-gingerol and 7356.67 ± 80.83 mg/kg of 6-shogaol) | 40 mg/kg or 80 mg/kg daily, orally by gavage, for 8 weeks | Reduced body weight gain and fat mass accumulation, reduced liver steatosis, inhibited whitening of brown adipose tissue, prevented mitochondrial dysfunction, reversed the effect of the high-fat diet on the level of hepatic p-AMPK and SIRT1 | |
| Balb/c mice [38] | Ginger water extract | 2 g/kg administrated for 7 days in drinking water | Increased oxygen consumption, intrascapular temperature, and mitochondrial DNA copy number in muscle and liver, as well as increased the expression of proteins related to oxidative phosphorylation and proteins associated with the AMPK/PGC1ɑ signaling pathway in muscle, liver, and brown adipose tissue | |
| Aging (22-month-old) rats [69] | 6-Gingerol | At 0.05 or 0.2 mg/kg, once daily via oral gavage, for 7 weeks | Counteracted age-related hepatic steatosis, increased fat oxidation, decreased fat synthesis, and improved mitochondrial function in the liver, upregulating mitochondrial marker enzymes NOX, SDH, and SIRT3 | |
| Stem cell exhaustion | plcg1−/− mutant zebrafish embryos with hematopoiesis deficiency [70] | Ginger extract or 10-gingerol | Applied at 5 µg/mL and 2 µg/mL, respectively, from the from the late gastrulation (9–10 hpf) stage onward | Rescues the formation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in hemogenic endothelium and caudal hematopoietic tissue |
| Chronic inflammation | Mouse model of ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma [71] | Ginger ethanol extract and aqueous extract | The ginger ethanol extract was applied at 500 mg/kg and the aqueous extract at 720 mg/kg, both for 7 days | Both extracts significantly inhibited Th2-mediated immune response, with reduction in goblet cell hyperplasia, infiltration of inflammatory cells in airways, edema with vascular congestion, and total and differential count of eosinophils and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| Male A/J mice challenged with methacholine (a model to study airway resistance in the context of asthma) [43] | 8-Gingerol | The compound (at 100 μM) was aerosolized and sprayed to the mice 15 min before challenge by methacholine | Attenuated changes in central airway resistance | |
| High-fat diet-fed rats [72] | Ginger standardized ethanoic extract | Applied daily at 400 mg/kg by oral gavage for 6 weeks | Suppressed hepatic NFκB activation and reduced the hepatic levels of several key pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and TNFα | |
| Collagen-induced arthritis in mice [73] | Ginger water extract | Orally administered at 100 and 200 mg/kg body weight, once daily from day 22 to day 35 after the induction of arthritis | Exerted an anti-arthritic effect by inhibiting the production in the serum of the IL-17, IL-4, and IFN –γ, and the paw tissue expression of MMP-1, MMP-13, and MMP-3 | |
| DSS-induced colitis mouse model [74] | 6-Gingerol | Applied once a day by gavage at 250 mg/kg for 14 days | Ameliorated bowel damage and reduced incidence of weight loss, as well as suppressed the increased serum and bowel levels of cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-17 (indicating inhibition of inflammatory responses both systematically as well as locally), and affected the cell balance of Th17/Treg | |
| Dysbiosis | High-fat diet-fed mice [75] | Dried ginger powder | Applied at 500 mg/kg body weight, once daily via gavage for 16 weeks | Induced a decrease in low-grade inflammation, liver steatosis, and body weight, improved insulin resistance, and produced modulation in the composition of gut microbiota with an increase in the species that belong to the genus Bifidobacterium and bacteria that produce SCFA. Importantly, through fecal microbiota transplantation, it was demonstrated that the anti-obesity and health-promoting effects of ginger were transferrable |
| DSS-induced colitis in mice [76] | Ginger powder | Orally administered at 500 mg/kg daily for 7 days | Mice with colitis had lower species diversity and richness, a higher abundance of pathogenic bacteria, Proteobacteria and firmicutes, an increase in Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, and an increase in the abundance of Lactobacillus_murinus, Lachnospiraceae_bacterium_615, and Ruminiclostridium_sp._KB18. These increased pathogenic bacteria were decreased by ginger intake. Similarly, the DSS-treated mice showed a lower abundance of Muribaculaceae, and ginger application reversed this trend | |
| Apo E mice made atherosclerotic through the administration of Gubra Amylin NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) diet with L-carnitine [77] | Ginger essential oil or citral | Ginger essential oil was applied at 50 mg/kg bw/day or 100 mg/kg bw/day via oral gavage for 16 weeks, and citral was applied at 20 mg/kg bw/day via oral gavage for 16 weeks | Citral and ginger essential oil produced improvement in resistance to insulin and plasma lipid profile; decreased levels of sugar in blood and trimethylamine-N-oxide levels; inhibited plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-1β, and most importantly, inhibited the formation of aortic atherosclerotic lesions in the animals used in the study, while also leading to an increase in the abundance of microbes that are beneficial and decreased the abundance of microbes that are involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases |
4. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Epigenetic Alterations
Epigenetics is concerned with functional and heritable changes in the regulation of gene activity and expression caused by non-genetic mechanisms without altering the primary DNA sequence, which is susceptible to environmental exposures [78]. A variety of epigenetic alterations can be cell- or tissue-specific and can persist throughout life and be passed on to multiple generations [79]. Epigenetic modification is attained by specific mechanisms, involving DNA methylation, miRNAs expression, and histone modifications, and the action of non-coding RNAs, which play an important role in maintaining the stability of the genome [80]. DNA methylation is an epigenetic process involved in many cellular functions that silences expression by the addition of a small chemical modification, in particular methyl group addition, to cytosine in DNA sequence. Histone modifications regulate the physical properties of chromatin and its corresponding transcriptional state, and non-coding RNA attaches the complementary sequence, resulting in silencing of the respective gene. To regulate the gene expression, these epigenetic modifications work in coordination with each other [81].
The potential of ginger or ginger-derived compounds to impact chromatin in a cell’s nucleus and regulate epigenetic mechanisms is under investigation, whereby there are indications for effects on histone acetylation. Along this line, one research study showed that both phenylephrine and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) induced histone H3K9 acetylation pathways were blocked in primary cultured cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts in rats when treated with 6-shogaol (0.3 or 1 μM pretreatment for 2 h), followed by stimulation with 30 μM phenylephrine for 48 h or TGF-β 10 ng/mL for 6 h, respectively [30]. Furthermore, upon oral administration in mice, 6-shogaol (daily oral administration of 0.2 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg for eight weeks) inhibited transverse aortic constriction-induced left ventricular hypertrophy and progression to left ventricular systolic dysfunction. All these results demonstrated the potential of 6-shogaol as a therapy for heart failure. Another in vitro histone acetyltransferase (HAT) assay was also carried out next to investigate whether 6-shogaol directly diminishes p300-HAT activity, and the results revealed that p300 HAT activity was suppressed by 6-shogaol in a dose-dependent manner (upon 30 min incubation with 6-shogaol at 0.01–100 μM) [30]. In another work, an aqueous extract of ginger (applied at a dose of 10, 30, 50, 80, and 100 μg for 24, 48, and 72 h) was demonstrated to regulate breast cancer stem cells associated-miRNAs in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231, restoring of the expression of tumor suppressive miRNAs, miR-200c, miR-30a, and miR-128, as well as significantly decreasing miR-200C promoter methylation, whereby the methylation of LINE1 sequences, which correlates with global genomic DNA methylation, was increased upon ginger extract treatment, predicting an increase in genomic stability [31].
5. Potential of Ginger to Modulate the Loss of Proteostasis
Aging itself, as well as some age-related pathologies, such as Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and cataracts, are linked to impaired protein homeostasis (proteostasis), resulting in the accumulation of oxidized, glycated, misfolded, or ubiquitinylated proteins that readily aggregate as extracellular plaques or intracellular inclusion bodies [1]. Along this line, aging represents a major risk factor for the development of a broader range of impactful diseases, such as cancer, inflammation-associated disorders, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, or Huntington’s disease, which are associated with diverse dysfunctions in protein homeostasis (proteostasis) leading to the accumulation of intracellular damage [82]. Proteostasis is a process that regulates the protein metabolism within the cell for maintaining the cellular proteome and the organism itself, through a vast network of biochemical pathways. This requires regulated control of protein folding, post-translational modification, and protein degradation [83]. In healthy cells, a complex proteostasis network consisting of molecular chaperones and proteolytic machinery helps to maintain the proteostasis [82]. Highly complex interactions and intersections of proteostasis pathways might result in stress on the level of the cells and organelles, leading to the disruption of the entire network [83]. Alzheimer’s disease is an example of a complex multifactorial disease associated with protein degradation and aggregation, the pathogenesis of which involves the intersection of many biochemical pathways, and the exact mechanisms triggering the disease are still being debated [84]. In the context of this disorder, one study investigated the possible prophylactic and curative effects of an aqueous infusion of ginger (108 and 216 mg/kg b.wt/day, applied orally for 12 weeks) to assess behavioral effects on rats with induced Alzheimer’s disease [59]. The result showed that both doses exhibited a significant improvement (cognition, psychological state as well as in locomotor activity, as determined by rewarded alternation T-Maze test, grid floor activity cage, and accelerating speed rotarod, respectively) on Alzheimer’s disease features by increasing acetylcholine and decreasing acetylcholinesterase in the brain. However, it also showed the high dose of ginger (216 mg/kg) exhibited a better effect than the low dose (108 mg/kg). Histopathological findings in brain cells showed closer to the control group phenotype, and the amyloid plaques disappeared [59]. The second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease is Parkinson’s disease. Its pathogenesis is mainly characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain and the abnormal accumulation and aggregation of the protein alpha-synuclein in the form of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. Thereby, the protein misfolds to give rise to beta-sheet-rich amyloid fibrils. This phenomenon leads to a deficiency of dopamine with associated symptoms such as posture rigidity, bradykinesia or slow movement, instability, and resting tremors [85]. Current treatment of this disease includes levodopa and dopamine agonists which provide systematic relief accompanied with severe side effects. In contrast, natural phytochemicals have obtained promising attention as potential candidates for the therapeutic and preventative effect of Parkinson’s disease, given their multitarget pharmaceutical mechanism of actions and good safety profile; ginger and its bioactive compounds, in particular, have shown a beneficial effect in multiple Parkinson’s disease models [86,87,88]. One study, for example, demonstrated that the pungent compound of ginger, 6-shogaol (10 mg·kg−1·d−1, orally, for 3 days), protected against MPTP- (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) or MPP+- (metabolite of MPTP) induced movement impairment and neuronal damage (reversal of dopaminergic neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta and in stratum) by regulating microglial activation and downstream pro-inflammatory factors in a mouse (C57/BL) model of Parkinson’s disorder [60]. Another similar work showed that ginger and 6-shogaol (ginger extract was applied at 30, 100, 300 mg/kg and 6-shogaol at 10 mg/kg, by gavage, for 15 days, including the period of the MPTP exposure) restored the disruption of intestinal barrier and enteric dopaminergic neurons in an MPTP-injected mouse Parkinson’s disease model by impeding the processes of inflammation and apoptosis, suggesting that they may have potential application to attenuate the gastrointestinal dysfunction in patients with Parkinson’s disorder [61].
In general, different lines of evidence have pointed out the correlation between aging and the accumulation of oxidatively damaged proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Oxidatively modified proteins increase along with age, as well as the manifestation of age-related diseases associated with oxidatively modified proteins also increases [89,90]. The accumulation of these oxidized proteins during aging randomly damages the DNA responsible for protein synthesis, which also controls the generation of reactive oxygen species, proteolytic activities to degrade oxidized proteins, and antioxidant defense mechanisms [91]. Protein oxidation serves as a useful marker for assessing oxidative stress in vivo. Proteins are oxidized when there is an imbalance of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defenses. One research study investigated the effect of ginger on the occurrence of oxidative stress in the small intestine of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The results revealed that consumption of ginger (applied as a ginger powder as 5% of the daily food for 6 weeks), l, a potent oxidant, improved diabetes-induced oxidative stress in diabetic rats with attenuation of lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation and increased catalase activity [92]. Patients suffering from diabetic conditions produce oxidative stress, and various tissues are damaged [93,94]. Ginger showed hypoglycemic effects and helped to delay the development of diabetes mellitus in several studies, highlighting its antidiabetic potential [95]. One of the relevant studies was undertaken to see the dose-response effect of ginger in the inhibition of oxidative stress and clastogenicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The results of this study in vivo showed that feeding the rats with ginger at different concentrations, such as 0.5%, 1%, and 5% of the total diet, significantly lowered the glucose, cholesterol, and triglycerides in streptozotocin (30 mg/kg)-induced diabetic rats in a dose-dependent manner. It was noted that serum glucose levels did not reach up to normal levels when ginger was fed to diabetic rats, but a reduction was observed in a dose-dependent manner [96]. Similar results were also reported in other studies in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, with ginger administration leading to a significant decrease in fasting glucose levels [97] and delay of diabetic cataracts [98]. In another in vitro study, the therapeutic potential of methanolic extract from ginger was investigated against glycation and oxidative stress, along with several other methods of anti-glycating and anti-aggregation test of glucose-exposed bovine serum albumin in the presence and absence of the ginger extract [32]. Taking into consideration the known pro-inflammatory action of advanced glycation end-products [99], the results of the latter study indicated that the ability of the ginger extract to inhibit glycation and heat-induced protein denaturation could be a possible contributing factor to its anti-inflammatory activity. In more detail, in the discussed work, the ginger extract (prepared by soaking of hundred grams of ginger powder in 1 L of 97% methanol) was effective in vitro against heat-induced albumin denaturation, and the percent of inhibition increased along with the increased concentration of the ginger extract that was applied in the concentration range 100–600 µg/mL [32]. A similar result was reported in another study, which showed that ginger extracts (at 125–500 µg/mL) possessed high anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting the heat-induced albumin denaturation [100]. The highest percentage of inhibition (66%) was exerted by 50% of ethanolic extract, followed by 70% and 90% of ethanol extracts (65% and 63%, respectively), and moderate inhibition activity was observed with 80% ethanol extract (58%) [100].
While the research described above indicates that ginger counteracts protein modification and denaturation in the context of conditions such as diabetes and inflammation, another work indicated that activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, associated with accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the ER lumen and unfolded protein response, underlies the mode of the killing of cancer cells exposed to ginger extract [101]. ER is, in general, responsible for the biosynthesis, folding, maturation, and stabilization of proteins and represents an organelle of major importance for proteostasis maintenance. A variety of pathophysiological conditions disrupt the protein folding capacity, resulting in the accumulation of unfolded, misfolded or toxic proteins in this organelle, with the process being termed “ER stress” [102]. Previous research has demonstrated that ER dilation is a characteristic response to ER stress, which develops as a result of the buildup of misfolded proteins in the ER lumen. To overcome the imbalance of ER protein folding capacity, cells have a signal transduction pathway called unfolded protein response (UPR) that becomes triggered and integrates ER stress signals to relieve the ER stress resulting in the re-establishment of the proteostasis balance. The UPR is controlled by three ER-transmembrane receptors, namely inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) [103]. When these ER transmembrane receptors detect the onset of ER stress, it initiates the unfolded protein response, whereby the prolongation of the stress causes apoptotic death of the cell [102]. In the above-mentioned study with ginger extract-exposed cancer cells [101], expressions of important ER stress markers such as polyubiquitinated proteins, Bip and CHOP were probed, and it was found that the ER stress proteins were increased when treated with increasing ginger extract concentrations. Moreover, this work indicated that ginger extract induced the paraptosis mode of death in cancer cells [101].
6. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Disabled Macroautophagy
Macroautophagy represents a process in which cytoplasmic content is incorporated in double-membrane vesicles, autophagosomes, which fuse with lysosomes and mediate degradative processes that are of essential importance for cellular homeostasis and adaptation to stress conditions such as energy- or nutrient-starvation. Autophagy declines with age advancement, and impaired autophagy is involved in the pathogenesis of a number of age-related diseases, while interventions stimulating autophagy have been shown to promote longevity [104].
In the context of autophagy modulation, one research work examined the effect of gingerol-enriched ginger extract in diabetic rats [62]. In this study, dietary application of gingerol-enriched ginger (at 0.75% of the total diet for 8 weeks) induced improved glucose tolerance and increased pancreatic insulin content in the diabetic animals, which was in part explained by improved intestinal integrity and mitochondrial dysfunction [62]. Along this line, the gingerol-enriched ginger supplementation was associated with an increase in the intestinal tissue expression of tight junction (Claudin-3) and antioxidant capacity (SOD1) genes in the intestine, and diminished expression of genes associated with mitochondrial fusion (MFN1), fission (FIS1), biogenesis (PGC-1α, TFAM), mitophagy (the removal of dysfunctional mitochondria through autophagy; LC3B, P62, PINK1), and inflammation (NF-κB) [62]. In another work, 6-gingerol (upon pretreatment with 10–40 μM 6-gingerol for 24 h) was also shown to induce autophagy in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, resulting in their improved survival from apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide exposure, with the findings suggesting that the compound may be beneficial in the prevention of atherosclerosis (a pathological process promoted by endothelial apoptosis) [33]. Moreover, 6-gingerol also displayed potential for the treatment of ischemia-reperfusion injury by a mechanism involving inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and apoptosis through TRPV1/FAF1 complex dissociation-mediated autophagy [63].
Several compounds from ginger also displayed anticancer cell-specific effects mediated through autophagy induction. Thus, 6-shogaol was shown to induce autophagy associated with inhibiting the AKT/mTOR pathway in the human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells and in cervical carcinoma HeLa and SiHa cells [105,106]. 6-shogaol was also shown to enhance the anticancer effects of several chemotherapeutics via increase of apoptosis and autophagy in colon cancer cells under hypoxic/aglycemic conditions [107], and to suppress breast cancer cells and stem cell-like spheroids by modulation of the Notch pathway and autophagic cell death [108]. Similarly, anticancer cell-specific effects mediated through autophagy induction were reported for other ginger constituents. Thus, 6-gingerol induced caspase-3 dependent apoptosis and autophagy in cancer HeLa cells [109], zingiberene suppressed in vivo (xenografted tumors, zingiberene applied at 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) and in vitro (growth inhibition IC50 of 20 µM) human colon cancer HT-29 cell growth via autophagy induction with inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and caspase-2 [110], and zerumbone activated apoptosis and autophagy in human hormone-refractory prostate cancers [111].
7. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Deregulated Nutrient-Sensing
Nutrients are simple organic chemical compounds in food that are involved in biochemical reactions producing energy for the maintenance of health and the ability to grow, move, and reproduce [112]. Nutrition has scientifically been proved by various studies as one of the key factors for healthy aging. Imbalance in diet can cause deficiency- or excess-related diseases such as blindness, anemia, scurvy, rickets, and goiter, as well as common chronic systemic diseases associated with aging such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis [113]. It has been demonstrated that caloric restriction can be a successful dietary approach to increase the lifespan in a healthy manner [114]. Alterations in nutrient sensing pathways have gained increased attention in the field of aging as they can be regulated both pharmacologically and with dietary interventions [115]. Nutrient sensing pathways become deregulated (a hallmark of cellular aging) and lose their effectiveness along with age. Metabolic processes are causing stress to cells. Vigorous metabolic activity and changes in nutrient composition can cause cells to age faster. Metabolism and its by-products over time damage the cells through oxidative stress, ER stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and calcium signaling [116]. Some of the key protein mediators/pathway hubs that regulate some of the nutrient-sensing pathways in the context of aging are the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and sirtuins [115,117]. Nutrient-sensing pathways play an important role in the regulation of protein synthesis, cell cycle, DNA replication, autophagy, stress response, and glucose homeostasis [115,118].
One of the most discussed topics in gerontology is the role of IGF-1/insulin signaling in the regulation of longevity. Accumulating evidence suggests that downregulated IGF-1 significantly prolonged the lifespan in vertebrate and invertebrate models [119]. Several in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated favorable modulation of IGF-1/insulin signaling by ginger or some of its bioactive ingredients. Thus, a longevity-promoting effect of ginger (lifespan extension of 23.16% upon application of 60 µg/mL ginger extract) via the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway was demonstrated in a Caenorhabditis elegans model [13]. Suppression of IGF-1 was also observed in humans, in particular in obese women diagnosed with breast cancer, who received orally four capsules containing 750 mg of ginger flour for 6 weeks [120]. Multiple studies also demonstrated the beneficial effects of ginger on insulin signaling in the context of diabetes. Thus, ginger extract enhanced the differentiation of mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes (in vitro model for anti-diabetic action), and the isolated active constituent 6-gingerol upregulated insulin-sensitive glucose uptake [121]. Moreover, 6-gingerol (50 mg/kg or 75 mg/kg body weight, daily supplied orally by gavage for 3 weeks) was also shown to display anti-hyperglycemic activity and to attenuate sodium arsenite-induced impairment of insulin signaling in mice [64]. Along the same line, orally applied ginger extract (50 mg/kg/day, for five weeks) attenuated hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance induced by liquid fructose supplementation in rats [65], and human trials (Table 3) have consistently demonstrated improvement of blood glucose levels (key target of insulin action) in type 2 diabetes patients supplemented with ginger [122]. As one example, Arablou et al. performed a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with 70 type 2 diabetes patients who were allocated randomly to receive a placebo or 1600 mg ginger (equaling two capsules) for 12 weeks, and the ginger-receiving group displayed both improved metabolic parameters (reduction of fasting glucose, HbA1C, insulin, HOMA, triglycerides, and total cholesterol) as well as reduction in the level of the inflammatory markers CRP and PGE2 [123]. Similarly, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with 103 individuals demonstrated that daily intake of 1.2 g of ginger (two capsules, 600 mg ginger powder in each) for 90 days resulted in a greater reduction in the blood glucose and total cholesterol in comparison to the placebo group [124].

Table 3.
Human research studies linked to the potential of ginger to modulate hallmarks of aging.
mTOR is a key coordinator of eukaryotic cell growth and metabolism with input from environmental signals, including growth factors and nutrients (notably, being activated by high amino acid concentrations) [127]. Suppression of mTOR activity is one of the most established interventions resulting in extended lifespan in a wide range of different species [128]. Several research works reported the modulation of mTOR by ginger and some of its bioactive constituents. Thus, supplementation with steamed ginger extract (40 mg/kg or 80 mg/kg daily, orally by oral gavage, for 8 weeks) was demonstrated to inhibit mTOR activation and fat accumulation induced by high-fat diet in mice [66]. Several studies also reported that 6-shogaol inhibited mTOR and induced cell death in non-small cell lung cancer and cervical carcinoma cells [105,106]. Similarly, zingerone (applied at 15 and 20 µM for 24 h) and zerumbone induced apoptosis and inhibition of the mTOR signaling in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells [129] and oral squamous cell carcinoma cells [130], respectively. 6-Gingerol was also reported to act as an mTOR inhibitor, and the compound was shown to counteract neuroinflammation and ischemic brain injuries through suppression of Akt/mTOR/STAT3 signaling in microglia cells [131].
AMPK senses low energy status in cells by detecting high levels of adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which is a product of the energy production happening through ATP hydrolysis. The activation of AMPK by high AMP levels activates catabolic processes aiming to restore energy homeostasis (to generate more ATP) and, among other effects, increases cellular NAD+ levels, which in turn leads to the activation of sirtuins, NAD+-dependent family of deacetylases, the activation of which is also viewed as a key anti-aging mechanism [132,133], along with the suppression of mTOR and IGF-1/insulin signaling [117]. Similarly to modulating mTOR and the IGF-1/insulin signaling (as discussed above), many research works have also studied the effects of ginger and some of its compounds on AMPK and sirtuins. Thus, it was demonstrated that steamed ginger extract supplementation reduces liver steatosis and adipocyte metabolic dysfunction through AMPK-SIRT-1 activation in a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity mouse model [66]. Similarly, zerumbone, a ginger sesquiterpene (applied as 0.01% or 0.025% of the diet for 8 weeks), counteracted the obesity induced by high-fat diet in C57BL/6N mice through activation of AMPK and sirtuins (SIRT1) [34] and 6-gingerol (20 μM, for 8–9 days) promoted browning (favorable metabolic phenotype) in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes with the upregulation of SIRT1 and p-AMPK/AMPK together with several other biomarkers [35], as well as it exhibited hypoglycemic effect in high-fat diet-fed rats that was associated with increased phosphorylated (activated) AMPK-α1 and sirtuin-6 [67].
8. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondria exhibit the capability to produce ROS alongside their electron transport process. While ROS at low concentrations function as physiological signals, their excessive generation in response to stress exerts a toxic influence, leading to detrimental effects on mitochondrial components and gradual impairment of mitochondrial function. To counterbalance this potential harm, a range of endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms come into play. These encompass antioxidant proteins like glutathione peroxidase 1, superoxide dismutase 2, and peroxiredoxin 3/5, which are regulated by transcription factors such as Nuclear factor (erythroid 2-like)-2 (Nrf2) [134]. Additionally, small molecules including coenzyme Q and glutathione contribute to mitigating the oxidative stress within mitochondria [135]. As individuals age, there is a decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential, resulting in diminished ATP generation. This decline is further associated with the activation of molecules associated with inflammation and ROS, ultimately culminating in cellular demise [136]. A notable hallmark of aging mitochondria is the surge in somatic point mutations and large deletions in mtDNA, leading to dysfunction. These mtDNA mutations, often arising due to oxidative damage in proximity to ROS sources, play a central role in mitochondrial dysfunction. The Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory of Aging (MFRTA) posits a cycle where oxidative damage to mtDNA initiates respiratory chain protein dysfunction, elevating ROS production, thereby perpetuating mitochondrial dysfunction [137]. Mitochondrial dynamics, involving fusion, fission, and mitophagy, are crucial for cellular functions. One recent study indicated that Gingerol Enriched Ginger (GEG, 18.7% 6-gingerol, 1.81% 8-gingerol, 2.86% 10-gingerol, 3.09% 6-shogoal, 0.39% 8-shogaol, and 0.41% 10-shogaol) applied as 0.75% wt/wt in the diet for 8 weeks could enhance insulin production, improve intestinal integrity, and counteract mitochondrial dysfunction in high-fat-diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats [62]. GEG supplementation boosted intestinal barrier function by increasing Claudin-3 expression and curbing mitochondrial oxidative stress and inflammation. Along this line, GEG influenced the balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission, triggering mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway, and regulating PGC-1α and TFAM expression [62]. The findings suggest that GEG has the potential to alleviate type 2 diabetes-induced intestinal dysfunction, enhance insulin production, and boost beta cell number (as evidenced by the observed increase in insulin-producing beta cells detected through insulin-immunohistochemistry staining) [62].
Mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle is linked to various transcription regulators involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1-a (PGC-1α) increases nuclear respiratory factor (NRF)-1 and NRF-2, leading to mitochondrial DNA transcription [138]. A study showed that ginger ethanol extract (applied at 100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg daily by oral gavage for 10 weeks) improves insulin resistance by enhancing AMPK-α1 expression in skeletal muscle in high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet-fed rats [36]. Additionally, 6-gingerol (50–150 µM, applied up to 24 h) promotes AMPK-α1 activity, PGC-1α mRNA expression, and mitochondrial biogenesis in L6 myotubes [36]. One study also sheds light on the putative anti-tumor effects of 6-gingerol, focusing on the promotion of mitochondrial biogenesis in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and their cytotoxic effect [37]. The latter study indicates that 6-gingerol (applied at 25–50 mg/kg, i.p., for 16 days) inhibits tumor growth by 33–37% in a Lewis lung carcinoma xenograft mouse model. The ginger extract increased mitochondrial mass in CD8+ T cells in vivo as well as in vitro in the CTLL-2 cells model (upon application at 5 and 10 mg/mL for 24 h), enhancing their cytotoxicity against cancer cells [37]. Further analysis with the active ingredient 6-gingerol showed that it promotes mitochondrial function and biogenesis, potentially contributing to the CD8+ T cells’ anti-tumor effects. These findings offer a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind ginger’s anti-tumor properties and its potential application in cancer management [37].
Muscle mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with obesity-related metabolic disorders [139]. Ginger water extract supplementation (at 0.25% or 0.5% of the diet for 14 weeks) in high-fat diet-fed rats reduced weight gain and increased mitochondrial size and mtDNA content in rat skeletal muscle, upregulating PGC1α, NRF1, and Tfam mRNA expression [68]. The ginger extract supplementation also raises serum HDL-C levels and contains compounds like 6-gingerol, known for antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-obesity effects [140]. Another research study shows that the addition of Steamed Ginger Extract (SGE) (applied at 40 mg/kg or 80 mg/kg daily, via gavage, for 8 weeks) inhibited the whitening of brown adipose tissue in supplemented mice groups by preventing increased lipid deposition and mitochondrial dysfunction [66]. This resulted in the restoration of reduced mitochondrial DNA, enzyme activities, and thermogenesis genes like UCP1. In liver and adipose tissues, SGE controlled ROS amplification and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by hyper-nutrient conditions through the mTOR-SREBP1-ER stress pathway. AMPK-SIRT1 activation by SGE was found to regulate cellular pathological signaling for liver and adipocyte dysmetabolism, mitigating liver steatosis and adipocyte metabolic issues while addressing ER and mitochondrial redox-linked disorders [66].
Another relevant study showed that ginger water extract, particularly at a dose of 2 g/kg administrated for 7 days, increased oxygen consumption, intrascapular temperature, and mitochondrial DNA copy number in muscle and liver in Balb/c mice [38]. This outcome was accompanied by an increase in the expression of proteins related to oxidative phosphorylation and proteins associated with the AMPK/PGC1α signaling pathway in muscle, liver, and brown adipose tissue. In HepG2 cells, the ginger extract (applied at 2.5 and 5 mg/mL for 3 days) enhanced mitochondrial mass, mtDNA copy number, ATP production, and activities of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes. The study suggests that the extract promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and function through the AMPK-PGC1α signaling pathway, with 6-gingerol being the likely active component, while 6-shogaol showed inhibitory effects on cell viability [38]. It is also demonstrated that 6-gingerol (applied at 2 µM) acts as a PPARδ ligand, enhancing PGC-1α expression and muscle mitochondrial biogenesis [141].
Hepatic fat accumulation is controlled by factors like lipid processing and oxidative stress. 6-gingerol showed promise in reducing liver fat in models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Along this line, one study showed that in aging (22-month-old) rats, 6-gingerol treatment (0.05 or 0.2 mg/kg, once daily oral gavage for 7 weeks) counteracted age-related hepatic steatosis, increased fat oxidation, decreased fat synthesis, and improved mitochondrial function in the liver, upregulating mitochondrial marker enzymes such as NOX, SDH, and SIRT3 [69]. These effects were achieved by affecting specific proteins and microRNAs related to fat metabolism. The results suggested that 6-gingerol application could be a valuable approach to combat age-related hepatic steatosis, potentially aiding in treating metabolic disorders [69].
9. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Cellular Senescence
Cellular senescence is characterized by a permanent cell cycle arrest state where cells are unable to divide and no longer proliferate. Senescent cells exhibit distinct features such as alterations in appearance and metabolism, modifications in chromatin structure, and shifts in gene expression patterns [142,143]. Senescence plays a crucial role in the age-related decline of tissue regenerative potential. This notion is supported, for example, by evidence from BubR1 progeroid mice, where progenitor cell populations in skeletal muscle and fat tissues show a high susceptibility to cellular senescence [144]. Apart from inducing a persistent growth arrest in stem cells, senescence can also disrupt the local stem-cell niche through the secretion of a group of pro-inflammatory and pro-growth factors known as the Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) [145] or Senescence Messaging Secretome [146]. Moreover, additional SASP-related mechanisms may contribute to tissue dysfunction. As an example, senescent cells release proteases that can continuously affect the structure and organization of tissues by breaking down membrane-bound receptors, proteins, or surrounding components within the tissue environment [147]. In Blagosklonny’s theory of ‘hyperfunction,’ aging is conceptualized as a quasi-program resulting from the intricate processes that take place during early life’s development and growth [148]. For instance, when growth arrest happens, certain nutrient-sensing pathways, such as mTOR, continue to operate. However, instead of promoting cell proliferation and growth as they did before, these pathways now trigger cellular senescence [148]. As human lifespans increase, age-related diseases become more prevalent in the aging population. Some of these diseases, such as sarcopenia [149], osteoarthritis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease exhibit features related to the activation of senescence [150].
Ginger might hold promise as a potential dietary additive to counteract muscle aging due to its antioxidant properties. Such effects of ginger can be attributed to 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol, which both were shown to exert antioxidant properties through the Nrf2 signaling pathway [151]. Nrf2 dissociates from its inhibitory protein partner, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), leading to Nrf2 translocation into the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, Nrf2 binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE) and induces the transcription of antioxidant genes [152]. One research study investigated the effects of 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol, present in two different standardized ginger extracts (GE1 and GE2), on myoblast cells in culture. The composition of these extracts differed significantly in their content of 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol, likely attributed to variations in the extraction conditions (GE1 contained 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol at concentrations of 289.531 μg/mL and 15.466 μg/mL, while GE2 contained 181.257 μg/mL and 63.425 μg/mL, respectively). The findings revealed that treatment with 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol enriched extracts (at 100 or 300 μg/mL, for 24 h) led to morphological changes in senescent (population doubling = 21) primary human myoblasts, resembling the morphology of young myoblasts [39]. These extracts exhibited an aging-reversal effect on myoblast cells by reducing the expression of senescence-associated β-galactosidase, a marker of replicative senescence. The study further demonstrated that both 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol, despite their distinct chemical structures, produced similar effects on myoblasts when used in combination with the standardized ginger extracts. Moreover, treatment with 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol enriched extracts influenced the progression of the cell cycle in myoblast cells, with cell cycle arrest observed during the G0/G1 phase. The study suggested that the expression of the Ki67 protein, crucial for cell proliferation, was lower during the G0/G1 phase, indicating a reduction in proliferative capacity in the myoblast cells. Taken together, these findings demonstrate the potential of 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol, present in ginger extracts, to protect against cellular senescence and promote myoblast differentiation.
Replicative senescence, caused by telomere shortening, is a tumor-suppressor mechanism. However, cancer cells can evade this process by reactivating telomerase. As already mentioned in the chapter “Potential of ginger to modulate telomere attrition”, a study by Kaewtunjai et al. demonstrated that ginger extract suppressed hTERT expression, inhibited telomerase, and induced cellular senescence in A549 lung cancer cells [58]. Further investigations confirmed that prolonged treatment of A549 cancer cells with sub-cytotoxic ginger extract doses (5 and 10 μg/mL) resulted in decreased telomere length, induced cellular senescence, and reduced clonogenicity. Additionally, the active compounds within the ginger extract, 6-paradol, and 6-shogaol, showed a favorable safety profile in rats and exhibited an ancillary chemoprotective effect against the formation of liver micronuclei induced by diethylnitrosamine (DEN) [58]. The latter finding is of relevance in the context of aging since micronuclei (generally linked to chromosome instability, mutagenesis, and genome rearrangements) are frequently observed during cellular senescence [153].
Senescence is a complex phenomenon with both beneficial and harmful effects depending on the physiological context and the age of the organism. In young organisms, senescence plays a positive role in processes like wound healing, tissue remodeling, embryonic development, and tumor suppression [154]. However, in aging tissues, the accumulation of senescent cells can lead to premature aging and age-related disorders, including chronic inflammation, tumorigenesis, liver fibrosis, atherosclerosis, insulin resistance, and neurodegenerative disorders [150]. To address this issue, senotherapies, such as senolytics and senomorphics, have emerged, aiming to selectively target and eliminate senescent cells to mitigate their adverse impact. In this context, a ginger ingredient, gingerenone A (applied for 48 h at 10 or 20 μM), is identified as a senolytic compound as it effectively and selectively reduced the viability of senescent cells (WI-38 human fibroblasts rendered senescent by exposure to ionizing radiation), enhanced the expression of cleaved caspase-3 (a marker of apoptosis), and decreased levels of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-XL [40]. Additionally, gingerenone A treatment led to a reduction in secreted levels of pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, CCL2 (MCP-1), and interferon γ-induced protein 10 (IP-10) while increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-13. Interestingly, treatment with 72.4 nM of 6-shogaol resulted in a notable increase in the number of proliferating cells, indicating its ability to promote cell proliferation at that application dose [40].
According to global cancer statistics from 2020, breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths [155]. It accounts for 11.7% of all cancer cases. Various markers, including estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and Ki67, are used for its diagnosis [156]. One study demonstrated that gingerenone A had a higher cytotoxic impact (IC50 values ranging from 50 to 76 μM) on breast cancer cells compared to normal breast cells [157]. Gingerenone A also demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition of cell viability in various breast cancer cell lines (SKBR3, MCF7, and MDA-MB-231). The study also revealed that gingerenone A upregulated senescence-associated gene expressions and oxidative stress were identified to play a crucial role in the antiproliferative effects of the compound on breast cancer cells [157].
10. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Stem Cell Exhaustion
Stem cell exhaustion represents a qualitative and quantitative decline of stem cells, that is characteristic to senescent tissues and organs and is regarded as one of the driving forces of aging in general [1]. Several works explored the effects of ginger and some of its bioactive compounds on stem cells. One study investigated exosome-like nanoparticles from four edible plants, including ginger, demonstrating that upon oral delivery (1 mg per mouse via gavage for 6 h), these nanoparticles are taken up by intestinal macrophages and stem cells [158]. Importantly, the ginger nanoparticles activated Nrf2, enhanced the expression of the antioxidant gene heme oxygenase-1 and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, as well as enhanced the activity of the Wnt/TCF4 pathway, which is known to be of critical importance for stem cell maintenance [159].
Another study investigated the effect of 8-shogaol on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (sometimes referred to in the literature as “synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells” [160]), a cell type with a crucial role in rheumatoid arthritis development [161]. In this work, 8-shogaol application resulted in significant inhibition of TNF-α-, IL-1β-, and IL-17-mediated inflammation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritis patients (applied at 5 µM and 10 µM) as well as in 3D synovial culture system. Further study of the associated mechanism of action revealed that the compound suppressed IKK, Akt, and MAPK signaling pathways [161] via direct inhibition of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), signaling protein of key importance for both inflammatory responses and mesenchymal stem cell proliferation [162,163]. Reflecting these molecular events, 8-shogaol treatment reduced paw thickness and improved walking performance in the adjuvant-induced arthritic rat model.
It was also demonstrated that ginger extract or 10-gingerol treatment (applied at 5 µg/mL and 2 µg/mL, respectively, from the late gastrulation (9–10 hpf) stage onward) could rescue the formation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in hemogenic endothelium and caudal hematopoietic tissue in plcg1−/− mutant zebrafish embryos with hematopoiesis deficiency [70]. The latter research suggests that ginger may act towards the promotion of hematopoiesis.
11. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Altered Intercellular Communication
Effective intercellular communication is a fundamental requirement for maintaining the balanced functioning of cells, tissues, and organs within a healthy organism. When this communication breaks down, it has been linked to the aging process and the emergence of various age-related disorders. This disrupted communication is considered a key aspect of aging, along with other factors like cellular senescence, mitochondrial dysfunction, and genomic instability [2]. A notable example of communication disruption during aging is “inflammaging”, a persistent low-grade inflammatory state observed in older individuals. This state arises due to continuous stimulation of the immune system by various signals, including misdirected molecules and the presence of senescent cells. Intercellular communication mediated by various mechanisms, including gap junctions, tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), and extracellular vesicles, plays a critical role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and coordinating cellular functions. Gap junctions are channels connecting adjacent cells, allowing the exchange of ions, small molecules, and regulatory RNAs. They are essential for processes like electrical signaling in the heart and metabolic coupling. However, during aging, there is a decline in gap junction function due to changes in protein levels and distribution, contributing to age-related disorders in various organs [164]. A decline in the levels of Connexin 43 (Cx43), a protein involved in gap junction formation, leads to impaired intercellular communication in various organs. For example, in the heart, reduced Cx43 levels and disrupted gap junctions result in slower electrical impulse propagation and cardiac dysfunction [165]. One study using obese rats fed with a high-fat diet showed that ginger (applied orally at 500 mg/kg body weight/day for 40 days) markedly reduced triacylglycerol, total cholesterol, LDL-C, MDA, collagen I, and MMP-2, potentially mitigating tissue damage and the progression of cardiovascular complications [166]. In bone tissue, reduced Cx43 levels contribute to increased susceptibility to oxidative stress-induced cell death and decreased bone strength. Notably, manipulating Cx43 expression can mitigate these age-related changes, indicating its significance in protecting against age-induced alterations [167]. Notably, TNF-α expression-inhibitory effects were also demonstrated in other works, for example, upon application of ginger extract in human synoviocyte cultures [168], and upon ginger extract (100 mg/Kg b.wt) oral application before gamma radiation exposure in Swiss albino mice [169].
Tunneling nanotubes are thin, dynamic membrane structures that facilitate the transfer of cellular components between distant cells. While they can promote beneficial signals and rescue cells from damage, they can also propagate harmful molecules and cellular stress. These nanotubes are increasingly recognized for their role in various physiological processes and diseases, including cancer, development, and immune responses [170]. During aging, the formation of TNTs may increase due to elevated oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to age-related changes and disease progression. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), such as exosomes and microvesicles, are small membrane-bound particles that carry various biomolecules and can influence neighboring cells. EVs derived from senescent cells are known to be part of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) and contribute to age-related changes. They can trigger cellular responses and spread senescence-related signals, impacting inflammation, immune responses, and tissue regeneration. The composition of EVs changes with aging, affecting their functional effects on recipient cells [164]. One research finding specifically indicates that ginger-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (EPDENs) exert notable effects on cellular behavior. When ginger EPDENs (applied at 1.0 µg/mL for 24 h) were introduced to RAW 264.7 macrophages, they distinctly induced the expression of two significant elements: antioxidation gene heme oxygenase-1 and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. This differential impact of ginger EPDENs showcases their potential to modulate key genetic factors associated with antioxidation and anti-inflammatory responses within macrophages. This insight into ginger EPDENs’ ability to influence specific gene expression highlights their unique properties and underscores their potential therapeutic value for enhancing antioxidative and anti-inflammatory cellular pathways [158].
The process of aging is characterized by deficiencies in various neural, neuroendocrine, and hormonal signaling pathways [171]. One study focused on assessing the anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of 6-shogaol, a key active compound in ginger, across molecular, cellular, and in vivo contexts. The investigation centered on its potential to regulate neuroinflammation by inhibiting microglial activation in the brain. The study found that 6-shogaol exhibited anti-inflammatory properties, downregulated microglial activation, and demonstrated significant neuroprotective effects in a model of ischemia (applied at 1, 3, and 6 mg/kg). The results highlighted the potential of 6-shogaol in combating neurodegenerative diseases associated with inflammation and its possible utility as a therapeutic agent [172]. Another study showcased Fermented Ginger’s potential anti-amnesic effects against Aβ1–42 plaque toxicity by safeguarding against neuronal cell loss and synaptic disturbance. The presence of 6-paradol, stemming from the fermentation process, was identified as a potential mediator of memory improvement. The research suggests that fermented ginger prepared using Schizosaccharomyces pombe fermentation could offer relief from memory dysfunction and neuronal degradation associated with conditions like Alzheimer’s disease [173]. Through heterochronic parabiosis experiments and detailed single-cell transcriptomic analysis, it has been confirmed that young blood can rejuvenate various tissues [174]. On the level of molecular mediators, for example, the chemokine CCL3/MIP-1a rejuvenates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, the metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP2 is implicated in hippocampal rejuvenation, and the anti-inflammatory interleukin IL-37 enhances endurance exercise and metabolic function in aged mice [175]. On this background, numerous studies demonstrated brain-specific benefits in numerous works [11]. Thus, one study showed that 6-shogaol showed improved brain function and reduced brain damage caused by ischemia, partly by impacting oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cell signaling pathways. The compound also protects against hippocampal cell damage [11]. 6-Paradol had a similar effect, reducing brain damage and neurological deficits. Zingerone alleviated behavioral and histological issues linked to brain ischemia by countering oxidative stress and apoptotic markers [11]. The compounds’ potential benefits were proposed to be related to their structural similarity to curcumin, which has shown protective effects in endothelial function decline and vascular atherosclerosis [176]. Taken together, while ginger and some of its bioactive compounds have demonstrated numerous presumably beneficial effects specific to the nervous system (being an important part of the body’s intercellular communication), the underlying molecular modes of action merit further research.
12. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Chronic Inflammation
The anti-inflammatory actions of ginger have been proven by several studies [25,177]. Inflammation has been implicated in several impactful diseases like arthritis, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. For many centuries people have used ginger against conditions suggesting potential anti-inflammatory effects [178]. It was confirmed decades ago by researchers that ginger has an inhibitory effect on prostaglandin synthesis, and its anti-inflammatory properties resemble that of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Along this line, ginger has an inhibitory effect on cyclooxygenase 1 and 2, and thereby, it produces an inhibitory effect on prostaglandin synthesis [41,42]. Along this line, among several ginger-derived compounds tested for COX-1 inhibition 8-paradol exhibited the strongest inhibitory activity, with an IC50 value of 4 µM [41], and among several ginger-derived compounds tested for COX-2 inhibition, the most potent was 10-shogaol, with an IC50 value of 7.5 μM [42]. Besides the above inhibitory action, ginger also suppresses 5-lipoxygenase and inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes [177,179,180]. Thus, gingerdione, in particular, was shown to inhibit in human leukocytes 5-HETE produced by 5-lipoxygenase with an IC50 of 15 µM [179]. Chronic inflammation is an important cause of various diseases like cancer, atherosclerosis, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis [177,178,180,181]. Ginger and its various phytoconstituents can play a potential role in reducing inflammation. In Asian traditional medicinal preparations, ginger rhizomes have been used for the treatment of mild forms of rheumatoid arthritis and fever, and in line with such effect, ginger phenylpropanoids (gingerols, shogaols) were found to target phospholipases A2, inhibiting IL-1beta and prostanoid secretion and disrupting arachidonate-phospholipid remodeling [181].
In a study carried out on ginger extract in rats, it was found that ginger extract possessed both anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties [182]. This effect was observed by inducing hepatoma in the rats by ethionine. It was found in the study that ginger extract (100 mg/kg body weight) suppressed the increased levels of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) in rats that had liver cancer thus expressing both anticancer and anti-inflammatory potential [182]. Ginger also exhibited good potential in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) [183]. Ginger and its constituents have also been shown to be effective in the context of airway inflammation, ameliorating ovalbumin-induced Th2 responses and enhancing Th1 response resulting in decreased airway inflammation in mice [71,184,185]. In the work of Khan et al. specifically, both ethanol extract (500 mg/kg) and aqueous extract (720 mg/kg) of ginger were tested (applied for 7 days) in a mouse model of ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma, and both extracts significantly inhibited Th2-mediated immune response, with reduction in goblet cell hyperplasia, infiltration of inflammatory cells in airways, edema with vascular congestion, and total and differential count of eosinophils and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid [71]. Also, levels of interleukin (IL)4, IL5, immunoglobulin E (IgE), and eotaxin have been found to be decreased by ginger, mediating the reduction of airway inflammation [184,186]. Ginger also regulates the functions of calcium ion channels, and by virtue of this effect, it is able to relax smooth muscles present in the airways to provide relief in symptoms of asthmatic patients [43]. In more detail, when food-grade ginger powder (0.5 mg, 1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg, suspended in 1 mL water) was applied for 30 min to human tracheas with epithelia removed and contracted with acetylcholine, a dose-dependent relaxation of the airway smooth muscle was observed [43]. Further study of the bioactive compounds of ginger identified 8-gingerol as one of the key ingredients, and when the compound (at 100 μM) was aerosolized and sprayed to naively hyperresponsive male A/J mice 15 min before challenge by methacholine it attenuated changes in central airway resistance [43]. With respect to its actions on the liver, ginger has been shown to decrease levels of interferon-gamma (INFγ) and IL6 and inhibit inflammation while also inducing improvements in pathological changes in the liver. In this context, through inhibition of NFκB activation ginger (standardized ethanoic extract, applied daily at 400 mg/kg by oral gavage, for 6 weeks) reduced the hepatic levels of several key pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, TNFα, and blunted liver pro-inflammatory responses in rats fed a high-fat diet [72]. The anti-inflammatory action of ginger is also beneficial in the case of patients suffering from diabetes. It has been found that ginger consumption shows improvements in diabetes patients by decreasing inflammatory factors like C-reactive protein (CRP), TNFα, and IL6 [123,125,184]. Along this line, Mahluji et al. conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 64 type 2 diabetes patients randomly assigned to receive ginger (2 g per day) or placebo tablets for 2 months, and the ginger supplemented group displayed significantly lower serum TNF-α and hs-CRP levels [125]. Similarly, Arablou et al. performed a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with 70 type 2 diabetes patients who were allocated to receive placebo or 1600 mg ginger (equaling 2 capsules) for 12 weeks, and the ginger-receiving group displayed not just significantly improved metabolic parameters (reduction of fasting glucose, HbA1C, insulin, HOMA, triglycerides, and total cholesterol) but also reduction in the level of the inflammatory markers CRP and PGE2 [123]. Through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects ginger might also provide protection against arthritis, musculoskeletal disorders, and joint inflammation [180,187]. In the latter context, a study examining the effects of ginger water extract on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice and IL-1β-induced inflammation in human synovial fibroblasts [73]. The results of the study showed that ginger water extract (orally administered at 100 and 200 mg/kg body weight, once daily from day 22 to day 35 after the induction of arthritis) exerted an anti-arthritic effect by inhibiting the production in the serum of the IL-17, IL-4, and IFN –γ (interferon gamma) and the paw tissue expression of MMP (matrix metalloproteinase)-1, MMP-13, and MMP-3 in CIA mice and IL-1β-activated synovial cells were decreased [73]. Another study investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of steamed ginger extract on Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric (AGS) cells, that was mediated by inhibition of NF-κB [44]. The results of the study showed that the ginger extract used in the study (applied at 1–200 μg/mL for 24 h) not only inhibited the growth of Helicobacter pylori but also reduced in the gastric cells Helicobacter pylori induced inflammation markers including IL-8, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, iNOS, and myeloperoxidase [44].
Several specific phytochemicals present in ginger were demonstrated to play a role in its anti-inflammatory actions. The inhibitory effects of 6-shogaol on cell functions related to angiogenesis and inflammation were evaluated in primary endothelial cells of human origin (HUVEC) [45]. The results of the study showed that 6-shogaol (applied 30 min before LPS challenge at 1–30 µM) showed inhibitory effects on angiogenesis and inflammation in LPS-activated HUVECs, inhibiting the activation of NF-κB, the expression of pro-inflammatory adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, E-selectin), and the attachment of leukocytes [45]. Another study also concluded that 6-shogaol (applied daily via gavage at 6.2 mg/kg for 28 days) was effective in decreasing chronic inflammatory response, and provided protection against damage to femoral cartilage (reflected in reduced swelling, preservation of the morphological integrity of the cartilage lining the femur, reduced leukocyte infiltration and lower concentration of soluble 1 VCAM-1) in rats who were subjected to monoarthritis in the right knee (by Freund’s Adjuvant injection) [46]. Agents that can inhibit microglial activation have the potential to counteract neurodegenerative diseases, and in this context, one study examined the effects of 6-shogaol (applied at 10 µM for up to 24 h) on microglia activation in BV-2 and primary microglial cell cultures [172]. The results of the study demonstrated that 6-shogaol proved to be an effective candidate for treating neurodegenerative diseases since it inhibited microglial activation and showed neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory actions [172]. Another study showed that 6-shogaol (10 mg·kg−1·d−1, orally, for 3 days) in a mouse (C57/BL) model of Parkinson’s disease provided anti-neuroinflammatory action and neuroprotective effects to dopaminergic neurons (including reversal of the MPTP-induced changes in motor coordination and bradykinesia, and reversal of dopaminergic neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta and in stratum) [60]. Anti-inflammatory activities have been also demonstrated for 6-gingerol. Thus, one study found that 6-gingerol (given once a day by gavage at 250 mg/kg for 14 days) showed beneficial effects on ulcerative colitis mice model (dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis) by ameliorating bowel damage and reducing incidence of weight loss, as well as suppressing the increased serum and bowel levels of cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-17 (indicating inhibition of inflammatory responses both systematically as well as locally), and affecting the cell balance of Th17/Treg [74].
13. Potential of Ginger to Modulate Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis can be regarded as an alteration in the composition or balance of gut microbes that has an impact on the health of a person, and new research is indicating an increasing number of diverse diseases associated with gut dysbiosis [188,189]. In this context, newer medicines that can produce a positive effect to restore the proper balance of intestinal microbes and cure dysbiosis are urgently required, and natural products can be good candidates with potential effectiveness and proven safety [190,191]. Several studies have assessed the impact of ginger on dysbiosis. In one study, the effect of a combined aqueous extract of olive leaves and ginger rhizome was assessed on gut microbiota in healthy rats as well as rats that were made diabetic with alloxan [192]. The results of the study showed that as a result of the application of the extracts (given separately or in a combination at a dose of 500 mg/kg per day, with or without insulin, for 7 days) there was a general enhancement in the bacterial diversity and an increase in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio observed in both healthy and diabetic rats upon the administration of the combined aqueous extract. In insulin treated diabetic rats, the combined extract decreased the levels of the unfavorable Clostridium. The results in healthy rats showed that the administration of the combined extract caused an increase in the relative abundance of the considered as favorable Lactobacillus and Prevotella whereas there was a decrease in the relative abundance of the considered as unfavorable Clostridium and Bacteroides [192].
Research was also carried out to evaluate the effect of dried ginger rhizome powder (DGRP) to reduce obesity by modulation of gastrointestinal microbiota in mice [75]. In this study, two groups of mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), and two groups of mice were fed a normal chow diet (NCD). Among the HFD groups, one group received HFD only and one group received HFD along with DGRP. On the other hand, in the NCD groups, one group received only NCD, and the other group received NCD along with DGRP. Also, mice that had depleted microbiota were transplanted with the fecal microbiota of mice administered a HFD or mice administered a HFD and ginger supplementation [75]. Different parameters were studied in this work, and it was found that in mice who received HFD along with DGRP treatment (applied at 500 mg/kg body weight ginger once daily via gavage for 16 weeks), there was a decrease in low-grade inflammation, liver steatosis, and body weight. Also, improvements with respect to insulin resistance were observed in these mice. It was found that ginger supplementation produced modulation in the composition of gut microbiota with an increase in the species which belong to the genus Bifidobacterium and bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Fecal concentration of SCFAs was also found to increase [75]. Bifidobacterium bacteria play an important role in improving metabolic health. This group of microorganisms is considered to provide protection to the body against obesity, insulin resistance, and low-grade inflammation [193,194]. SCFA-producing bacteria are also considered beneficial for health in general, with a negative correlation existing between these bacteria and obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance [195,196,197]. Importantly, through fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), it was demonstrated that the anti-obesity and health-promoting effects of ginger were transferrable [75].
Another study was conducted on healthy humans (crossover intervention study with 123 healthy subjects, of which 63 men and 60 women) to study the effect of a short-term intake of fresh ginger juice (20 mL freshly squeezed ginger juice per day for 7 days) on the variation of gut microbiota and its relevance to human health [126]. The results of the study demonstrated that the species number of the microbial flora of intestines was increased. An increase in the ratio of Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes, levels of anti-inflammatory Faecalibacterium, and levels of Proteobacteria was also observed [126]. Also, a decrease in relative abundance in the ratio of Prevotella-to-Bacteroides and levels of pro-inflammatory Ruminococcus_1 and Ruminococcus_2 was observed in the same study. Overall, this work provides evidence that ginger juice had a strong effect on the function and composition of gut microbiota in people who were healthy [126].
In the context of dysbiosis, a study was also carried out in mice (BALB/c mice) administered dextran sulfate sodium to induce ulcerative colitis [76]. In this study, the effect of ginger powder on reducing the severity of ulcerative colitis by improving the function and diversity of gut microbiota was assessed. The results of the study highlighted the fact that ginger powder (orally administered at 500 mg/kg daily for 7 days) produced a beneficial effect on ulcerative colitis by positively influencing the microbial population of the intestine [76]. Mice with colitis had lower species diversity and richness, a higher abundance of pathogenic bacteria, Proteobacteria and firmicutes, an increase in Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, and an increase in the abundance of Lactobacillus_murinus, Lachnospiraceae_bacterium_615, and Ruminiclostridium_sp._KB18. These increased pathogenic bacteria were decreased by ginger intake. Similarly, the DSS-treated mice showed a lower abundance of Muribaculaceae, and ginger application reversed this trend [76].
The role of gut microbiota with respect to cardiovascular diseases is gaining increasing interest in modern medical science [188]. The effect of ginger essential oil (50 mg/kg bw/day or 100 mg/kg bw/day, via oral gavage, for 16 weeks) and one of its bioactive compounds, citral (20 mg/kg bw/day, via oral gavage, for 16 weeks), on atherosclerosis was evaluated in Apo E mice made atherosclerotic through administration of Gubra Amylin NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) diet with L-carnitine [77]. During the metabolism of L-carnitine, trimethylamine-N-oxide is formed which is involved in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques leading to thrombosis. The conducted study showed that citral and ginger essential oil produced improvement in resistance to insulin and plasma lipid profile; decreased levels of sugar in blood and trimethylamine-N-oxide levels; inhibited plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-1β, and most importantly, inhibited the formation of aortic atherosclerotic lesions in the animals used in the study [77]. Treatment with citral and the essential oils of ginger also produced a modulating effect on the function and diversity of gut microbiota. Both treatments lead to an increase in the abundance of microbes that are beneficial and a decrease in the abundance of microbes that are involved in the production of cardiovascular diseases. Thus, by positively influencing the gut microbiota, citral and ginger essential oils demonstrated a good potential recommending them as beneficial supplements to counteract cardiovascular diseases [77].
Since dysbiosis has been suggested to be implicated in a variety of diseases and ginger supplementation displayed benefits in restoring a healthy microbiota composition, the study of the potential of ginger-based supplements to combat such diseases can prove to be a highly interesting topic for researchers in the coming years.
14. Conclusions
Preclinical research has shown that ginger extracts and bioactive compounds are able to exhibit some favorable effects on all twelve hallmarks of aging. Particularly, numerous preclinical animal research studies have indicated positive impacts on deregulated nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis. The reviewed research suggests that ginger might have the potential to act as a multi-targeting nutraceutical, simultaneously affecting multiple hallmarks of aging through several of its bioactive constituents and a range of diverse mechanisms. However, the present work also reveals that validation in human clinical trials is still insufficient or entirely missing, with the exception of some studies indicating benefits on deregulated nutrient-sensing, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis. Thus, the accumulated compelling body of research evidence warrants further clinical validation studies of ginger and some of its constituents as interventions for lifespan extension and healthy aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and A.G.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M., T.J., D.W., N.T.T. and F.B.M.; writing—review and editing, A.W., A.J., J.O.H. and A.G.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell 2023, 186, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, L.F.; Gutierrez-Casado, E.; Varela-Lopez, A.; Villalba, J.M. Olive Oil and the Hallmarks of Aging. Molecules 2016, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catana, C.S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Natural products with anti-aging potential: Affected targets and molecular mechanisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.; Carrascosa, J.M. Current nutritional and pharmacological anti-aging interventions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaie, L.; Sadeghpoor, O. Ginger from ancient times to the new outlook. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2015, 10, e18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Corke, H.; Beta, T.; Li, H.B. Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Foods 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, V.S. Ginger—Chemistry, technology, and quality evaluation: Part 1. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1982, 17, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyama, R. Nutritional implications of ginger: Chemistry, biological activities and signaling pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 86, 108486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.H.; Kim, S.J.; Long, N.P.; Min, J.E.; Yoon, Y.C.; Lee, E.G.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Son, E.Y.; et al. Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, M.; Oh, M.S. Pharmacotherapeutic potential of ginger and its compounds in age-related neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 182, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepici, G.; Contestabile, V.; Valeri, A.; Mazzon, E. Ginger, a Possible Candidate for the Treatment of Dementias? Molecules 2021, 26, 5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Tao, M.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Wu, T. Longevity-promoting properties of ginger extract in Caenorhabditis elegans via the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9893–9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Noh, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, I.H.; Kim, D.K. Lifespan-extending property of 6-shogaol from Zingiber officinale Roscoe in Caenorhabditis elegans. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naorem, A.S.; Thongatabam, B.; Aggarwal, P.; Gupta, G.; Raza, A.; Yadav, A. Efficacy of Manjistha and Ginger Powder in Extending the Lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2021, 20, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-Z.; Xue, L.-Y.; Gao, L.; Qin, X.-M.; Du, G.-H. Ginger extract extends the lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster through antioxidation and ameliorating metabolic dysfunction. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 49, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalko, V.; Dzyuba, V.; Kozlova, O.; Sheremet, H.; Protsenko, O. Zingiber officinale extends Drosophila melanogaster life span in xenobiotic-induced oxidative stress conditions. Front. Biol. 2018, 13, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhou, P.K. DNA damage repair: Historical perspectives, mechanistic pathways and clinical translation for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, N.S.; Ghiasvand, R.; Askari, G.; Hariri, M.; Darvishi, L.; Mofid, M.R. Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of ginger in health and physical activity: Review of current evidence. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, S36–S42. [Google Scholar]
- Dugasani, S.; Pichika, M.R.; Nadarajah, V.D.; Balijepalli, M.K.; Tandra, S.; Korlakunta, J.N. Comparative antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-gingerol, [8]-gingerol, [10]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharaky, A.S.; Newairy, A.A.; Kamel, M.A.; Eweda, S.M. Protective effect of ginger extract against bromobenzene-induced hepatotoxicity in male rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.S.; Suke, S.G.; Seth, V.; Chakraborti, A.; Tripathi, A.K.; Banerjee, B.D. Protective effects of dietary ginger (Zingiber officinales Rosc.) on lindane-induced oxidative stress in rats. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danwilai, K.; Konmun, J.; Sripanidkulchai, B.; Subongkot, S. Antioxidant activity of ginger extract as a daily supplement in cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: A pilot study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.; Thadhani, E.; Samson, L.; Engelward, B. Inflammation-induced DNA damage, mutations and cancer. DNA Repair 2022, 83, 102673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, P.; Cerda, B.; Arcusa, R.; Marhuenda, J.; Yamedjeu, K.; Zafrilla, P. Effect of Ginger on Inflammatory Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, A.F.; Rehman, M.U.; Raish, M.; Kazi, M.; Rao, P.G.M.; Alnemer, O.; Ahmad, P.; Ahmad, A. Zingerone [4-(3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-butan-2] Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Protects Rats from Sepsis Associated Multi Organ Damage. Molecules 2020, 25, 5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, U.K.; Hassan, N.E.Y.; Elhalwagy, M.E.A.; Zaki, A.R.; Abubakr, H.O.; Nagulapalli Venkata, K.C.; Jang, K.Y.; Bishayee, A. Ginger and Propolis Exert Neuroprotective Effects against Monosodium Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirpoor, A.; Rezaei, F.; Fard, A.A.; Afshari, A.T.; Gharalari, F.H.; Rasmi, Y. Ginger extract protects rat’s kidneys against oxidative damage after chronic ethanol administration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, H.; Keshavarzi, B.; Shirpoor, A.; Gharalari, F.H.; Rasmi, Y. Rescue effects of ginger extract on dose dependent radiation-induced histological and biochemical changes in the kidneys of male Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, Y.; Sunagawa, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Funamoto, M.; Hamabe-Horiike, T.; Katanasaka, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Hawke, P.; Mori, K.; Komiyama, M.; et al. 6-Shogaol, an Active Component of Ginger, Inhibits p300 Histone Acetyltransferase Activity and Attenuates the Development of Pressure-Overload-Induced Heart Failure. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazbak, A.E.-R.A.; Salem, S.M.; Rady, H.H.; Bashandy, M.A. Regulation of Breast Cancer Stem Cells Associated-miRNAs by Ginger and Persimmon Extracts. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. C Physiol. Mol. Biol. 2023, 15, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Almatroudi, A.; Allemailem, K.S.; Jacob Joseph, R.; Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Protective Effects of Ginger Extract against Glycation and Oxidative Stress-Induced Health Complications: An In Vitro Study. Processes 2020, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Yao, X.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G. 6-Gingerol induces autophagy to protect HUVECs survival from apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 256, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Lee, H.; Jung, C.H.; Choi, W.H.; Ha, T.Y. Zerumbone ameliorates high-fat diet-induced adiposity by restoring AMPK-regulated lipogenesis and microRNA-146b/SIRT1-mediated adipogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36984–36995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, L.; Hu, X.; Feng, F.; Chen, F. 6-Gingerol, a Functional Polyphenol of Ginger, Promotes Browning through an AMPK-Dependent Pathway in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 14056–14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tran, V.H.; Kota, B.P.; Nammi, S.; Duke, C.C.; Roufogalis, B.D. Preventative effect of Zingiber officinale on insulin resistance in a high-fat high-carbohydrate diet-fed rat model and its mechanism of action. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 115, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, D.; Sun, X.; Dong, J.; Huang, J. Effects of ginger extract and its major component 6-gingerol on anti-tumor property through mitochondrial biogenesis in CD8(+) T cells. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 3307–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, Z.; Dong, J.; Huang, J. Promotion of Mitochondrial Biogenesis via Activation of AMPK-PGC1a Signaling Pathway by Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) Extract, and Its Major Active Component 6-Gingerol. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sahardi, N.F.N.; Jaafar, F.; Mad Nordin, M.F.; Makpol, S. Zingiber Officinale Roscoe Prevents Cellular Senescence of Myoblasts in Culture and Promotes Muscle Regeneration. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1787342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaddel, R.; Rossi, M.; Rodriguez, S.; Munk, R.; Khadeer, M.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M.; Ferrucci, L. Identification of gingerenone A as a novel senolytic compound. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurtjahja-Tjendraputra, E.; Ammit, A.J.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Tran, V.H.; Duke, C.C. Effective anti-platelet and COX-1 enzyme inhibitors from pungent constituents of ginger. Thromb. Res. 2003, 111, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, R.B.; Tao, Y.; Li, W. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in ginger (Zingiber officinale). Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, E.A.; Siviski, M.E.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Hoonjan, B.; Emala, C.W. Effects of ginger and its constituents on airway smooth muscle relaxation and calcium regulation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Seo, S.A.; Hwang, J.S.; Heo, S.H.; Kim, E.H. Steamed Ginger Extract Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells through Inhibition of NF-kappaB. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 26, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Kont, I.; Primke, T.; Niebergall, L.S.; Zech, T.; Furst, R. Ginger Constituent 6-Shogaol Inhibits Inflammation- and Angiogenesis-Related Cell Functions in Primary Human Endothelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 844767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.S.; Simon, O.; Shelly, J.; Gardener, M. 6-Shogaol reduced chronic inflammatory response in the knees of rats treated with complete Freund’s adjuvant. BMC Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Ibarra, M.J.; Hernandez, J.; Caire-Juvera, G. Diet, physical activity and telomere length in adults. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M.A. Telomeres, lifestyle, cancer, and aging. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, S.; Stier, A. Does oxidative stress shorten telomeres in vivo? A review. Biol. Lett. 2017, 13, 20170463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Zglinicki, T. Oxidative stress shortens telomeres. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh-Far, R.; Lin, J.; Epel, E.S.; Harris, W.S.; Blackburn, E.H.; Whooley, M.A. Association of marine omega-3 fatty acid levels with telomeric aging in patients with coronary heart disease. JAMA 2010, 303, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Gammon, M.D.; Terry, M.B.; Wang, Q.; Bradshaw, P.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Neugut, A.I.; Santella, R.M. Telomere length, oxidative damage, antioxidants and breast cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen-Lane, J.H.; Zurier, R.B.; Lawrence, D.A. Analysis of the thiol status of peripheral blood leukocytes in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Takami, A.; Espinoza, J.L. Dietary phytochemicals and cancer chemoprevention: A review of the clinical evidence. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52517–52529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Telomerase Inhibitors from Natural Products and Their Anticancer Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, J.K.; Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Ginger-derived phenolic substances with cancer preventive and therapeutic potential. Forum Nutr. 2009, 61, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntiwechapikul, W.; Taka, T.; Songsomboon, C.; Kaewtunjai, N.; Imsumran, A.; Makonkawkeyoon, L.; Pompimon, W.; Lee, T.R. Ginger extract inhibits human telomerase reverse transcriptase and c-Myc expression in A549 lung cancer cells. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewtunjai, N.; Wongpoomchai, R.; Imsumran, A.; Pompimon, W.; Athipornchai, A.; Suksamrarn, A.; Lee, T.R.; Tuntiwechapikul, W. Ginger Extract Promotes Telomere Shortening and Cellular Senescence in A549 Lung Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 18572–18581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, K.A.; Gouda, N.A.M.; Marrie, A.E.F.H.; Yassin, N.A.Z.; El-Shenawy, S.M.A.; Farrag, A.R.H.; Ibrahim, B.M.M. Protective Effect of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) on Alzheimer’s disease Induced in Rats. J. Neuroinfect. Dis. 2014, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kim, H.G.; Ju, M.S.; Ha, S.K.; Park, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, protects dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease models via anti-neuroinflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, E.; Choi, J.G.; Noh, D.; Yoo, H.S.; Ryu, J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, H.; Oh, M.S. Ginger and 6-shogaol protect intestinal tight junction and enteric dopaminergic neurons against 1-methyl-4-phenyl 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Santos, J.M.; Dufour, J.M.; Stephens, E.R.; Miranda, J.M.; Washburn, R.L.; Hibler, T.; Kaur, G.; Lin, D.; Shen, C.L. Ginger Root Extract Improves GI Health in Diabetic Rats by Improving Intestinal Integrity and Mitochondrial Function. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Tan, J.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, Y. 6-Gingerol protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and apoptosis via TRPV1/FAF1 complex dissociation-mediated autophagy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Mukherjee, A.; Sikdar, S.; Paul, A.; Ghosh, S.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. [6]-Gingerol isolated from ginger attenuates sodium arsenite induced oxidative stress and plays a corrective role in improving insulin signaling in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 210, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Ke, D.; Zuo, G.; Yang, Y.; Yamahara, J.; Li, Y. Improvement of liquid fructose-induced adipose tissue insulin resistance by ginger treatment in rats is associated with suppression of adipose macrophage-related proinflammatory cytokines. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 590376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-H.; Peng, C.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Park, S.-A.; Lee, H.-Y.; Hoang, T.-H.; Kim, J.; Chae, H.-J. Ginger extract controls mTOR-SREBP1-ER stress-mitochondria dysfunction through AMPK activation in obesity model. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, R.M.; Rashed, L.A.; Hassanin, K.M.A.; Hetta, M.H.; Ahmed, A.O. Effect of 6-gingerol on AMPK- NF-kappaB axis in high fat diet fed rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lee, M.-S.; Jung, S.; Kim, S.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, C.-T.; Jo, Y.-H.; Kim, I.-H.; et al. Ginger extract increases muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and serum HDL-cholesterol level in high-fat diet-fed rats. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yao, L.; Ma, P.; Chen, Z.; Han, T.L.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, L.; et al. 6-gingerol ameliorates age-related hepatic steatosis: Association with regulating lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 362, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri-Lagneau, K.F.; Haider, J.; Sang, S.; Leung, T. Rescue of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells formation in plcg1 zebrafish mutant. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.M.; Shahzad, M.; Raza Asim, M.B.; Imran, M.; Shabbir, A. Zingiber officinale ameliorates allergic asthma via suppression of Th2-mediated immune response. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; McGrath, K.C.; Nammi, S.; Heather, A.K.; Roufogalis, B.D. Attenuation of liver pro-inflammatory responses by Zingiber officinale via inhibition of NF-kappa B activation in high-fat diet-fed rats. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 110, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Jung, H.W.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, J.-S.; Kim, J.-P.; Park, Y.-K. Effects of Zingiber officinale extract on collagen-induced arthritis in mice and IL-1β-induced inflammation in human synovial fibroblasts. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2017, 15, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Ji, K.; Zhong, Y.; Xue, Y. The effect of 6-gingerol on inflammatory response and Th17/Treg balance in DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Beneficial effects of ginger on prevention of obesity through modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Geng, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Rong, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Xiong, L.; Huang, J.; Pang, X.; et al. Ginger Alleviates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Severity by Improving the Diversity and Function of Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 632569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyod, S.; Wu, W.K.; Peng, S.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chen, R.A.; Huang, H.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Chuang, H.L.; Hsu, C.C.; et al. Ginger essential oil and citral ameliorates atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice by modulating trimethylamine-N-oxide and gut microbiota. NPJ Sci. Food 2023, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Ronn, T. Epigenetics in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talens, R.P.; Christensen, K.; Putter, H.; Willemsen, G.; Christiansen, L.; Kremer, D.; Suchiman, H.E.; Slagboom, P.E.; Boomsma, D.I.; Heijmans, B.T. Epigenetic variation during the adult lifespan: Cross-sectional and longitudinal data on monozygotic twin pairs. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.X.; Riddle, N.C. Epigenetics and genome stability. Mamm. Genome 2020, 31, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiman, T.M.; Robertson, K.D. Chromatin remodeling, histone modifications, and DNA methylation-how does it all fit together? J. Cell Biochem. 2002, 87, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipp, M.S.; Kasturi, P.; Hartl, F.U. The proteostasis network and its decline in ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtishi, A.; Rosen, B.; Patil, K.S.; Alves, G.W.; Moller, S.G. Cellular Proteostasis in Neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3676–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcusa, R.; Villano, D.; Marhuenda, J.; Cano, M.; Cerda, B.; Zafrilla, P. Potential Role of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 809621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Piperi, C. Elucidating the Beneficial Effects of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Sahardi, N.F.N.; Makpol, S. Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the Prevention of Ageing and Degenerative Diseases: Review of Current Evidence. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 5054395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Nakamura, A. Age-associated, oxidatively modified proteins: A critical evaluation. Age 1997, 20, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.N.; Ahn, B.W.; Moerman, E.J.; Goldstein, S.; Stadtman, E.R. Age-related changes in oxidized proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5488–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R. Protein oxidation in aging and age-related diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 928, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadem Ansari, M.; Karimipour, M.; Salami, S.; Shirpoor, A. The Effect of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) on Oxidative Stress Status in the Small Intestine of Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 6, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Xu, B.-T.; Wan, S.-R.; Ma, X.-M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.-Z. The role of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohi, T.F.; Faizan, S.; Parray, Z.A.; Baig, M.; Mehdi, S.; Kinattingal, N.; Krishna, K.L. Beyond Glucose: The Dual Assault of Oxidative and ER Stress in Diabetic Disorders. High. Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2023, 30, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Tariq, M.; Chen, S. Zingiber officinale and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evidence from Experimental Studies. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2015, 25, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, N.; Panpatil, V.V.; Kaleb, R.; Varanasi, B.; Polasa, K. Dose-dependent effect in the inhibition of oxidative stress and anticlastogenic potential of ginger in STZ induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2954–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhani, S.P.; Vishwakarma, S.L.; Goyal, R.K. Anti-diabetic activity of Zingiber officinale in streptozotocin-induced type I diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswat, M.; Suryanarayana, P.; Reddy, P.Y.; Patil, M.A.; Balakrishna, N.; Reddy, G.B. Antiglycating potential of Zingiber officinalis and delay of diabetic cataract in rats. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, K.; Yoo, Y.; Son, M.; Lee, J.; Jeong, G.B.; Park, Y.M.; Salekdeh, G.H.; Lee, B. Advanced glycation end-products produced systemically and by macrophages: A common contributor to inflammation and degenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 177, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M.; Ezzat, M.I.; Okba, M.M.; Menze, E.T.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. The hidden mechanism beyond ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) potent in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedungadi, D.; Binoy, A.; Vinod, V.; Vanuopadath, M.; Nair, S.S.; Nair, B.G.; Mishra, N. Ginger extract activates caspase independent paraptosis in cancer cells via ER stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, AIF translocation and DNA damage. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.M.; Jeon, Y.J. Proteostasis in The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Road to Cure. Cancers 2019, 11, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazzari, M.; Gagliardi, M.; Fimia, G.M.; Piacentini, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Unfolded Protein Response, and Cancer Cell Fate. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidal, A.M.; Levine, B.; Debnath, J. Autophagy and the cell biology of age-related disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, J.Y.; Hsu, Y.L.; Li, C.T.; Ko, Y.C.; Ni, W.C.; Huang, M.S.; Kuo, P.L. 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of dietary ginger, induces autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9809–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.D.; He, Z.L.; Yao, H.L.; Xiao, J.S.; Li, L.; Gu, J.Z.; Shi, P.Z.; Wang, J.H.; Jiang, L.H. 6-Shogaol from ginger shows anti-tumor effect in cervical carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2781–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, M.; Makuch, S.; Winograd, K.; Wisniewski, J.; Ziolkowski, P.; Agrawal, S. 6-Shogaol enhances the anticancer effect of 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan via increase of apoptosis and autophagy in colon cancer cells in hypoxic/aglycemic conditions. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Vasudevan, S.; Sengupta, S. 6-Shogaol Inhibits Breast Cancer Cells and Stem Cell-Like Spheroids by Modulation of Notch Signaling Pathway and Induction of Autophagic Cell Death. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Bishayee, K.; Ghosh, S.; Biswas, R.; Mandal, S.K.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. [6]-Gingerol induces caspase 3 dependent apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells: Drug-DNA interaction and expression of certain signal genes in HeLa cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 694, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Liu, T.; Jing, L.; Wu, J. Zingiberene inhibits in vitro and in vivo human colon cancer cell growth via autophagy induction, suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and caspase 2 deactivation. J. BUON 2019, 24, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, M.L.; Liang, J.W.; Hsu, L.C.; Chang, W.L.; Lee, S.S.; Guh, J.H. Zerumbone, a ginger sesquiterpene, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hormone-refractory prostate cancers through tubulin binding and crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial insult. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efeyan, A.; Comb, W.C.; Sabatini, D.M. Nutrient-sensing mechanisms and pathways. Nature 2015, 517, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittikpina, N.K.; Issa, A.-R.; Yerima, M.; Dermane, A.; Dossim, S.; Salou, M.; Bakoma, B.; Diallo, A.; Potchoo, Y.; Diop, Y.M. Aging and Nutrition: Theories, Consequences, and Impact of Nutrients. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 5, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, F.; Aujard, F. Caloric restriction, longevity and aging: Recent contributions from human and non-human primate studies. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 95, 109702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.D.; Antebi, A.; Bartke, A.; Barzilai, N.; Brown-Borg, H.M.; Caruso, C.; Curiel, T.J.; de Cabo, R.; Franceschi, C.; Gems, D.; et al. Interventions to Slow Aging in Humans: Are We Ready? Aging Cell 2015, 14, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Finkel, T. Key proteins and pathways that regulate lifespan. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 6452–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mico, V.; Berninches, L.; Tapia, J.; Daimiel, L. NutrimiRAging: Micromanaging Nutrient Sensing Pathways through Nutrition to Promote Healthy Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.; Pellegrino, G.; Vollery, M.; Hofland, L.J. ROLE of IGF-1 System in the Modulation of Longevity: Controversies and New Insights From a Centenarians’ Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani Shorkaii, Z.; Dabidi Roshan, V. Changes in growth factors and estrogens in course of breast cancer: Role of the individual and combined of water-based exercise and ginger supplementation. QHMS 2014, 19, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya, K.; Ohtani, A.; Kusano, S. Enhancement of insulin sensitivity in adipocytes by ginger. Biofactors 2004, 22, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, J.W.; Yang, M.; Kim, D.S.; Park, S. Efficacy of ginger for treating Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Ethn. Foods 2015, 2, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arablou, T.; Aryaeian, N.; Valizadeh, M.; Sharifi, F.; Hosseini, A.; Djalali, M. The effect of ginger consumption on glycemic status, lipid profile and some inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.C.N.; Lira-Neto, J.C.G.; Araujo, M.F.M.; Freitas, R.; Zanetti, M.L.; Damasceno, M.M.C. Effectiveness of ginger in reducing metabolic levels in people with diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2020, 28, e3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahluji, S.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Mobasseri, M.; Ebrahimzade Attari, V.; Payahoo, L. Anti-inflammatory effects of zingiber officinale in type 2 diabetic patients. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S.; Pang, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Variation with Short-Term Intake of Ginger Juice on Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 576061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannick, J.B.; Lamming, D.W. Targeting the biology of aging with mTOR inhibitors. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Fang, H.; Zheng, L.; Liu, M. Zingerone suppresses cell proliferation via inducing cellular apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.S.; Gan, C.P.; Lau, B.F.; Yee, P.S.; Tiong, K.H.; Abdul Rahman, Z.A.; Patel, V.; Cheong, S.C. Zerumbone targets the CXCR4-RhoA and PI3K-mTOR signaling axis to reduce motility and proliferation of oral cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 39, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xia, S.; Bao, X.; Cao, X.; Xu, Y. 6-Gingerol attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and ischemic brain injuries through Akt-mTOR-STAT3 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Feige, J.N.; Lagouge, M.; Noriega, L.; Milne, J.C.; Elliott, P.J.; Puigserver, P.; Auwerx, J. AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 2009, 458, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, W.; Sikora, E.; Bielak-Zmijewska, A. Sirtuins, a promising target in slowing down the ageing process. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 447–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; An, C.; Gao, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 100, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, M.; Sideris, D.P.; Biddle, M. Modulation of mitochondrial dysfunction for treatment of disease. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivapathasuntharam, C.; Sivaprasad, S.; Hogg, C.; Jeffery, G. Improving mitochondrial function significantly reduces the rate of age related photoreceptor loss. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 185, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurey, P.; Pizzo, P. The Aging Mitochondria. Genes 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleyzer, N.; Vercauteren, K.; Scarpulla, R.C. Control of mitochondrial transcription specificity factors (TFB1M and TFB2M) by nuclear respiratory factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 family coactivators. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.B. Exercise and obesity-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Integr. Med. Res. 2013, 2, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma Naidu, P.; Uddandrao, V.V.S.; Ravindar Naik, R.; Suresh, P.; Meriga, B.; Begum, M.S.; Pandiyan, R.; Saravanan, G. Ameliorative potential of gingerol: Promising modulation of inflammatory factors and lipid marker enzymes expressions in HFD induced obesity in rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 419, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, K.; Hashizume, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Minegishi, Y.; Hase, T.; Shimotoyodome, A. Ginger extract prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice via activation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Jat, P. Mechanisms of Cellular Senescence: Cell Cycle Arrest and Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, K.; Lu, J.; Bao, X.; Wang, R.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, H. Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.J.; Weaver, R.L.; van Deursen, J.M. p21 both attenuates and drives senescence and aging in BubR1 progeroid mice. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppe, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Munoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 2853–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilman, T.; Peeper, D.S. Senescence-messaging secretome: SMS-ing cellular stress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Deursen, J.M. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 2014, 509, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagosklonny, M.V. Aging is not programmed: Genetic pseudo-program is a shadow of developmental growth. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3736–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walston, J.D. Sarcopenia in older adults. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, D.; Gil, J. Senescence and aging: Causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 217, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, D.; Zhang, X.; Fang, J. Activation of Nrf2 target enzymes conferring protection against oxidative stress in PC12 cells by ginger principal constituent 6-shogaol. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Li, J.; Johnson, D.A.; Stein, T.D.; Kraft, A.D.; Calkins, M.J.; Jakel, R.J.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2, a multi-organ protector? FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupina, K.; Goginashvili, A.; Cleveland, D.W. Causes and consequences of micronuclei. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 70, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, K. The emerging role of senescent cells in tissue homeostasis and pathophysiology. Pathobiol. Aging Age Relat. Dis. 2015, 5, 27743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.J.; Tang, J.Y.; Shiau, J.P.; Hou, M.F.; Yen, C.H.; Ou-Yang, F.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, H.W. Gingerenone A Induces Antiproliferation and Senescence of Breast Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Deng, Z.B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Kakar, S.; Jun, Y.; Miller, D.; et al. Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 58, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Es, J.H.; Haegebarth, A.; Kujala, P.; Itzkovitz, S.; Koo, B.K.; Boj, S.F.; Korving, J.; van den Born, M.; van Oudenaarden, A.; Robine, S.; et al. A critical role for the Wnt effector Tcf4 in adult intestinal homeostatic self-renewal. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Song, B.; Yu, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Hou, J.; Yang, R. Nomenclature clarification: Synovial fibroblasts and synovial mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Samarpita, S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Son, J.E.; Jeong, M.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, W.U.; et al. 8-Shogaol inhibits rheumatoid arthritis through targeting TAK1. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.R.; Lei, C.Q. TAK1-TABs Complex: A Central Signalosome in Inflammatory Responses. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 608976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, Y.; Teramura, T.; Takehara, T.; Fukuda, K. Transforming Growth Factor beta-Activated Kinase 1 Regulates Mesenchymal Stem Cell Proliferation Through Stabilization of Yap1/Taz Proteins. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Rodrigues, T.M.; Kelly, G.; Korolchuk, V.I.; Girao, H.; Oliveira, P.J.; Malva, J.O.O. Chapter 9—Intercellular communication and aging. In Aging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 257–274. [Google Scholar]
- Michela, P.; Velia, V.; Aldo, P.; Ada, P. Role of connexin 43 in cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 768, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; El-Baky, A.E.A.; Hassanean, H.A.; Othman, M.S.; Hafez, M.M. The Role of Natural Products in Coronary Artery Diseases Caused By Hyperlipidemia. Onl. Int. Res. J. 2014, IV, 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, H.M.; Aref, M.W.; Aguilar-Perez, A.; Pacheco-Costa, R.; Allen, K.; Valdez, S.; Herrera, C.; Atkinson, E.G.; Mohammad, A.; Lopez, D.; et al. Cx43 overexpression in osteocytes prevents osteocyte apoptosis and preserves cortical bone quality in aging mice. JBMR Plus 2018, 2, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frondoza, C.G.; Sohrabi, A.; Polotsky, A.; Phan, P.V.; Hungerford, D.S.; Lindmark, L. An in vitro screening assay for inhibitors of proinflammatory mediators in herbal extracts using human synoviocyte cultures. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.—Anim. 2004, 40, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Salam, H.S.; Hassan, A.A. Phytochemicals Boost Anti-inflammatory Effect Against Gamma Radiation: Activities of Ginger and Coriander Extracts. Arab. J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2017, 50, 278–291. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y. Tunneling-nanotube development in astrocytes depends on p53 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 18, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, H.A.; Dean, E.S.; Pletcher, S.D.; Leiser, S.F. Cell non-autonomous regulation of health and longevity. eLife 2020, 9, e62659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.K.; Moon, E.; Ju, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.Y. 6-Shogaol, a ginger product, modulates neuroinflammation: A new approach to neuroprotection. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, E.; Lim, S.; Kim, H.G.; Ha, S.K.; Park, H.Y.; Huh, Y.; Oh, M.S. Ginger fermented with Schizosaccharomyces pombe alleviates memory impairment via protecting hippocampal neuronal cells in amyloid beta(1-42) plaque injected mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Wang, S.; Ye, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, R.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, G.; et al. Heterochronic parabiosis induces stem cell revitalization and systemic rejuvenation across aged tissues. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 990–1005.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Mosher, K.I.; Abbey, R.J.; McBride, A.A.; James, M.L.; Berdnik, D.; Shen, J.C.; Zou, B.; Xie, X.S.; Tingle, M.; et al. Human umbilical cord plasma proteins revitalize hippocampal function in aged mice. Nature 2017, 544, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Profumo, E.; Buttari, B.; D’Arcangelo, D.; Tinaburri, L.; Dettori, M.A.; Fabbri, D.; Delogu, G.; Rigano, R. The Nutraceutical Dehydrozingerone and Its Dimer Counteract Inflammation- and Oxidative Stress-Induced Dysfunction of In Vitro Cultured Human Endothelial Cells: A Novel Perspective for the Prevention and Therapy of Atherosclerosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 1246485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Saxena, K.; Singh, U.N.; Saxena, R. Anti-inflammatory action of ginger: A critical review in anemia of inflammation and its future aspects. Int. J. Herbal. Med. 2013, 1, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkur, M.; Benlier, N.; Takan, I.; Vasileiou, C.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Cetin, Z.; Saygili, E.I. Ginger for Healthy Ageing: A Systematic Review on Current Evidence of Its Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anticancer Properties. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 4748447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, D.L.; Rafferty, M.F.; Boctor, A.M. Inhibition of human neutrophil 5-lipoxygenase activity by gingerdione, shogaol, capsaicin and related pungent compounds. Prostaglandins Leukot. Med. 1986, 24, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K.C.; Mustafa, T. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) in rheumatism and musculoskeletal disorders. Med. Hypotheses 1992, 39, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievergelt, A.; Marazzi, J.; Schoop, R.; Altmann, K.H.; Gertsch, J. Ginger phenylpropanoids inhibit IL-1beta and prostanoid secretion and disrupt arachidonate-phospholipid remodeling by targeting phospholipases A2. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4140–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.H.; Makpol, S.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.; Das, S.; Ngah, W.Z.; Yusof, Y.A. Ginger extract (Zingiber officinale) has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects on ethionine-induced hepatoma rats. Clinics 2008, 63, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi Poor Ranjbar, F.; Mohammadyari, F.; Omidvar, A.; Nikzad, F.; Doozandeh Nargesi, N.; Varmazyar, M.; Dehghankar, S.; Vosoughian, F.; Olangian-Tehrani, S.; Nanbakhsh, S.; et al. Zingiber officinale (Ginger) as a treatment for inflammatory bowel disease: A review of current literature. Front. Drug Discov. 2022, 2, 1043617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryaeian, N.; Tavakkoli, H. Ginger and its Effects on Inflammatory Diseases. Adv. Food Technol. Nutr. Sci. 2015, 1, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, Y.H.; Huang, H.M.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, C.C.; Fan, C.K.; Lee, Y.L. Zerumbone enhances the Th1 response and ameliorates ovalbumin-induced Th2 responses and airway inflammation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 24, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahui, M.L.; Champy, P.; Ramadan, A.; Pham Van, L.; Araujo, L.; Brou Andre, K.; Diem, S.; Damotte, D.; Kati-Coulibaly, S.; Offoumou, M.A.; et al. Ginger prevents Th2-mediated immune responses in a mouse model of airway inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, K.C.; Mustafa, T. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) and rheumatic disorders. Med. Hypotheses 1989, 29, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieczynska, M.D.; Yang, Y.; Petrykowski, S.; Horbanczuk, O.K.; Atanasov, A.G.; Horbanczuk, J.O. Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Atherosclerosis Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, L.J.; Monga, M.; Miller, A.W. Defining Dysbiosis for a Cluster of Chronic Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, H.M.; Wright, M.L.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Qawasmeh, A.; Hassan, S.T.S.; Mocan, A.; Nabavi, S.M.; Rastrelli, L.; Atanasov, A.G.; Haddad, P.S. Significance of Microbiota in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases and the Modulatory Potential by Medicinal Plant and Food Ingredients. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, A.; Ji, G.; Xu, H. New insights into natural products that target the gut microbiota: Effects on the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 964793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaer, S.; El-Hajji, F.D.; Abu-Tayeh, R.; Basheti, I.; Al-Najjar, M.A.A. Changes in gut microbiota of alloxan-induced diabetic rats in response to orally administered combined aqueous extracts of olive leaves and ginger. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Henning, S.M.; Lee, R.; Hsu, M.; Grojean, E.; Pisegna, R.; Ly, A.; Heber, D.; Li, Z. Dietary pomegranate extract and inulin affect gut microbiome differentially in mice fed an obesogenic diet. Anaerobe 2017, 48, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Knauf, C.; Burcelin, R.G.; Tuohy, K.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Delzenne, N.M. Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Lazarevic, V.; Gaïa, N.; Johansson, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Bäckhed, F.; Delzenne, N.M.; Schrenzel, J.; Francois, P.; Cani, P.D. Microbiome of prebiotic-treated mice reveals novel targets involved in host response during obesity. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).