A Modular Customizable Ligand-Conjugate (LC) System Targeting Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Peptide Ligand Concentration Determination
2.3. Bifunctional Adapter Synthesis
2.4. hGOAT Channel Computational Analysis
2.5. Copper-Catalyzed Cycloaddition for Cargo Attachment
2.5.1. Cu(I)I Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition
2.5.2. Cu(II)SO4 Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition
2.6. Thiol–Maleimide Conjugation for Cargo Attachment
2.7. Purification of LCs via Semipreparative HPLC
2.8. MALDI Characterization of LCs
2.9. IC50 Protocol
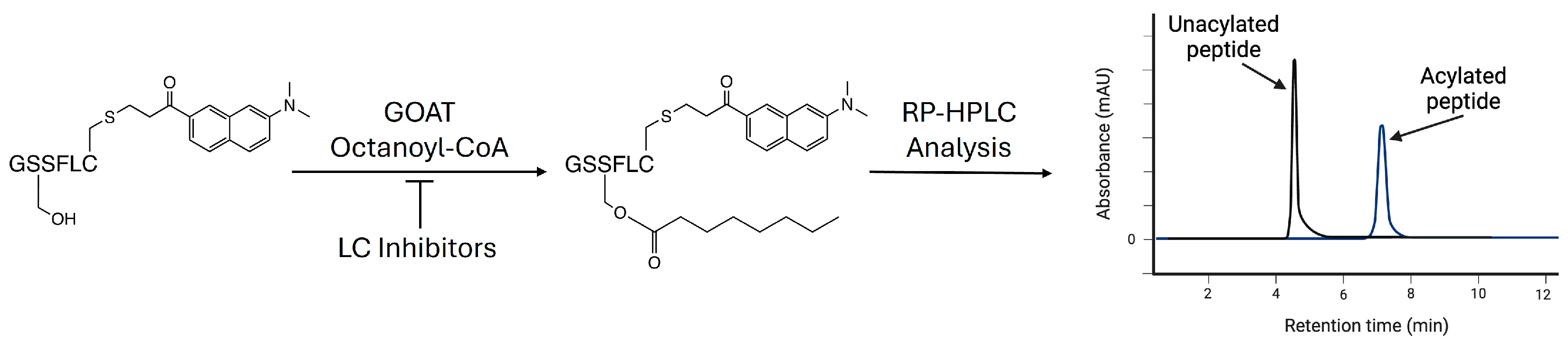
2.10. Analysis of GOAT Inhibition Assays via Analytical HPLC
2.11. Determination of IC50 Values
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of Modular Ligand-Conjugate System
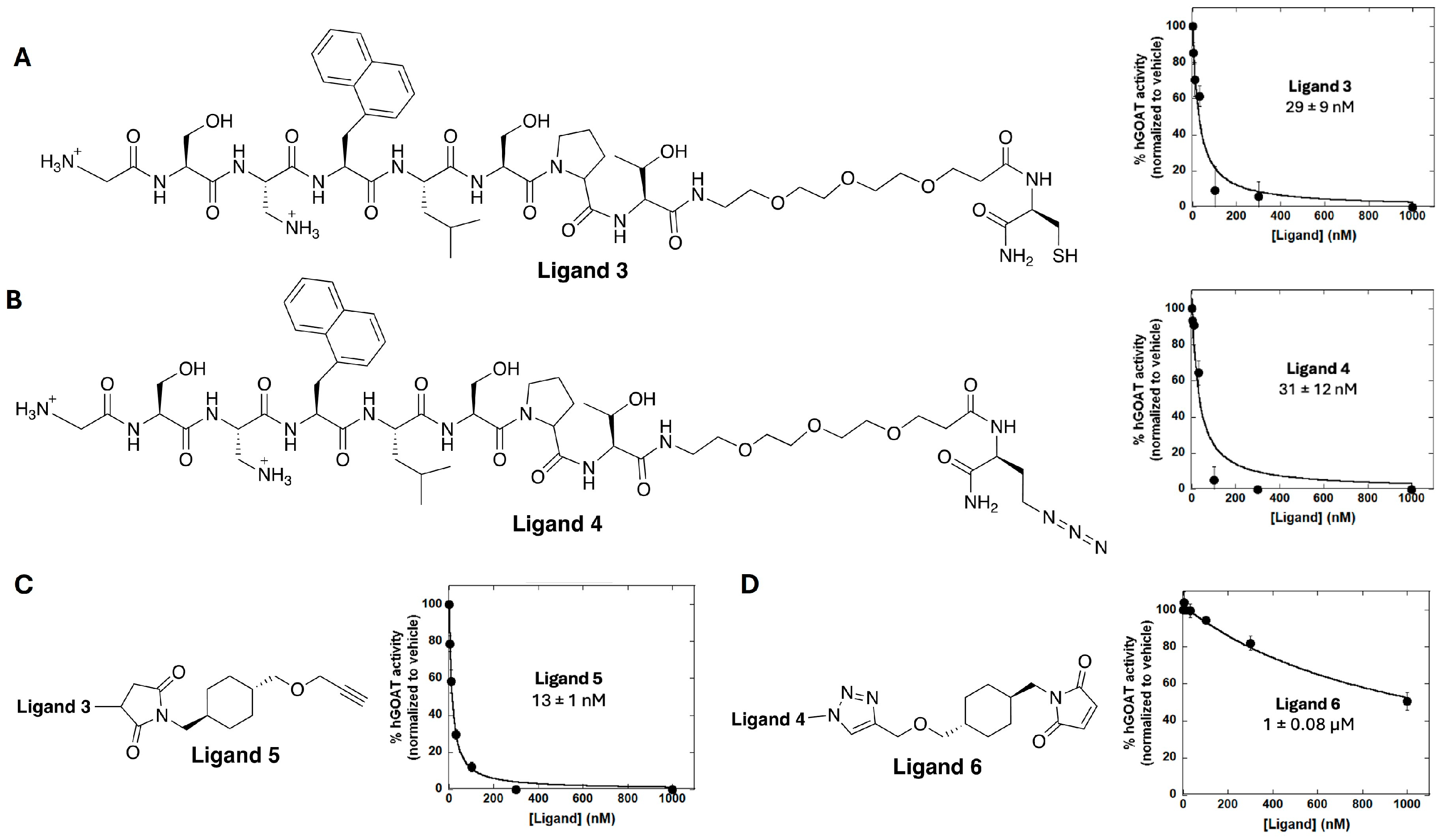
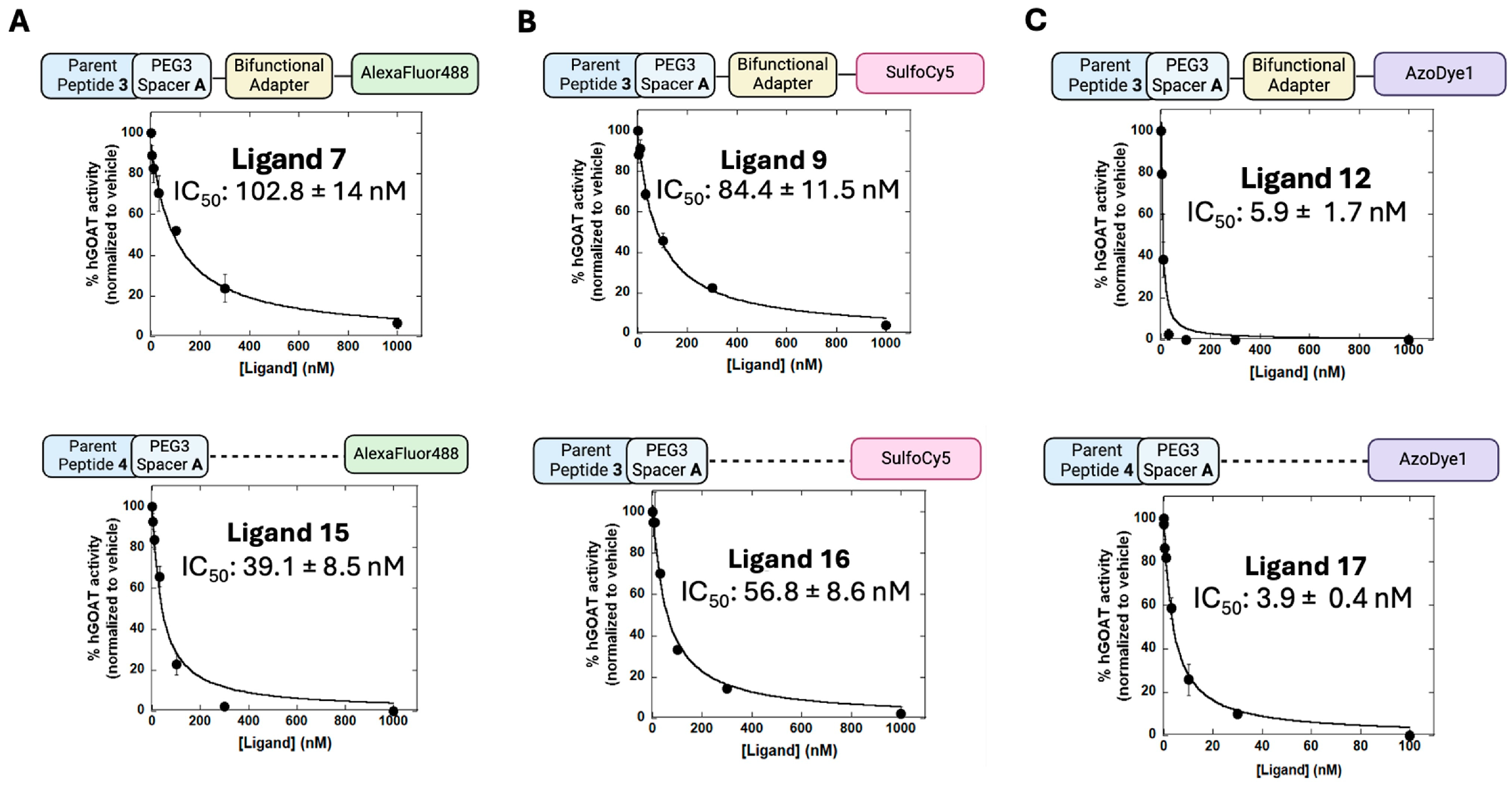
3.2. Ligand Synthesis and Characterization of GOAT-Binding Potency
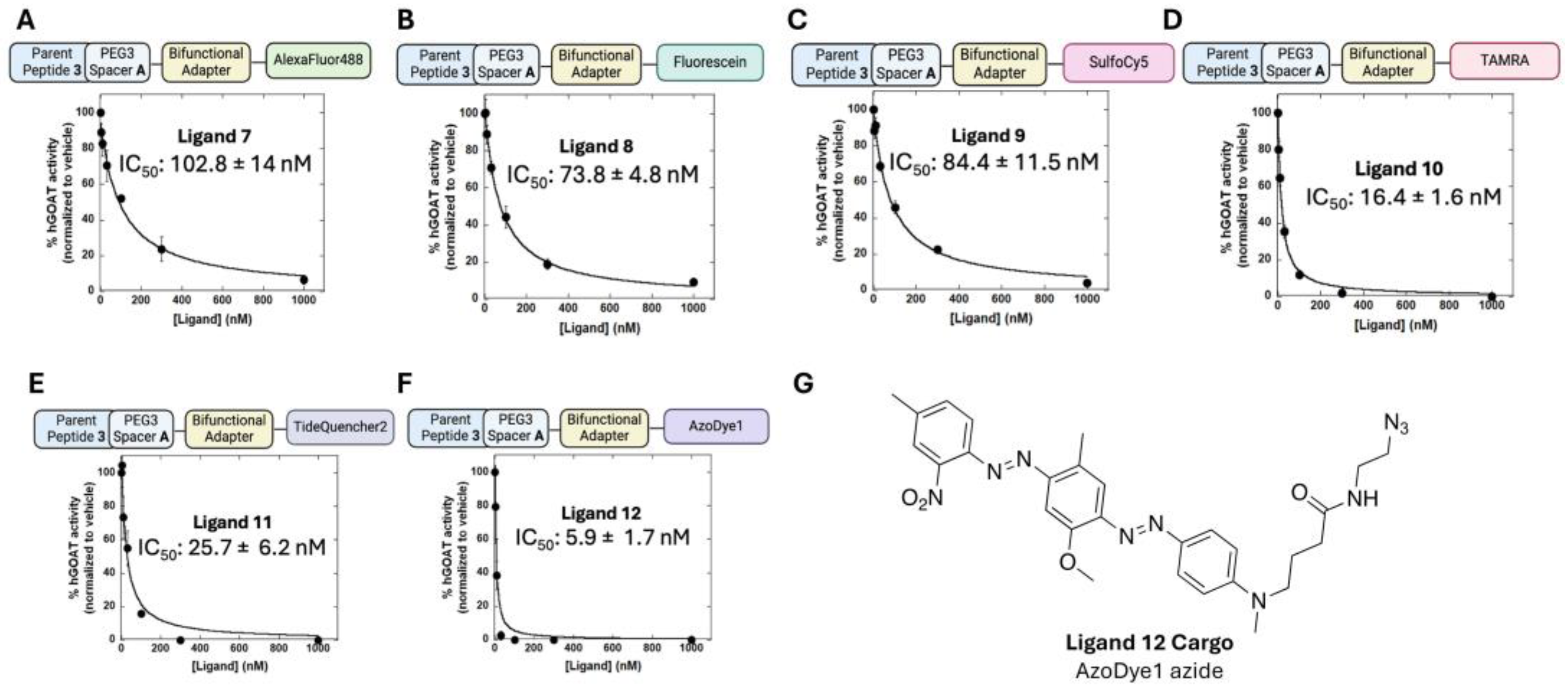
3.3. Exploring the Scope of Potential Cargo Molecules for GOAT Ligand-Conjugates
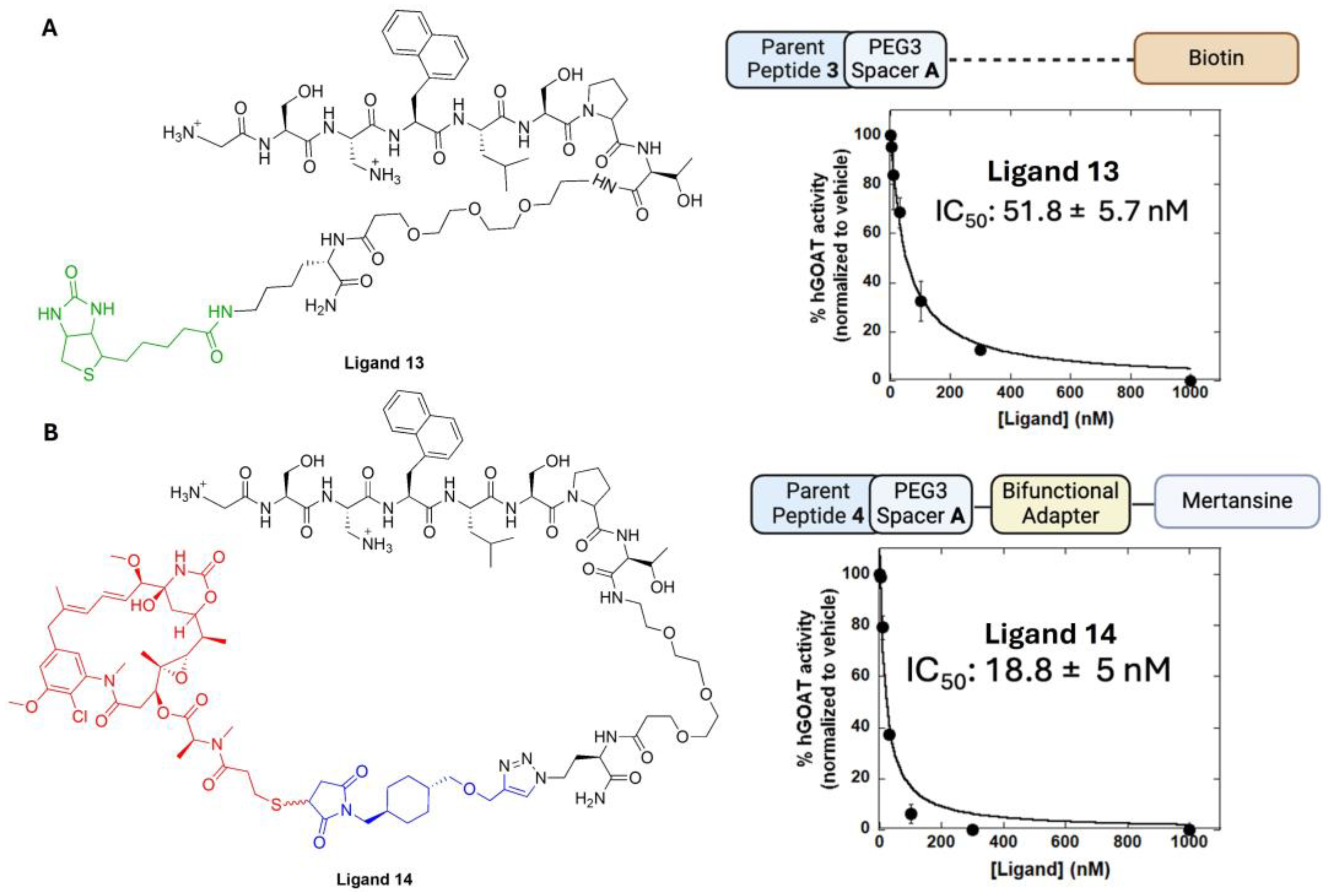
3.4. Determining the Impact of Linker Groups on GOAT Ligand Conjugate Binding
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Is a Growth-Hormone-Releasing Acylated Peptide from Stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smith, R.G.; Diano, S.; Tschöp, M.; Pronchuk, N.; Grove, K.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Esterman, M.; Heiman, M.L.; et al. The Distribution and Mechanism of Action of Ghrelin in the CNS Demonstrates a Novel Hypothalamic Circuit Regulating Energy Homeostasis. Neuron 2003, 37, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.E.; Frayo, R.S.; Marmonier, C.; Aubert, R.; Chapelot, D. Plasma ghrelin levels and hunger scores in humans initiating meals voluntarily without time- and food-related cues. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2004, 287, E297–E304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Purnell, J.Q.; Frayo, R.S.; Schmidova, K.; Wisse, B.E.; Weigle, D.S. A Preprandial Rise in Plasma Ghrelin Levels Suggests a Role in Meal Initiation in Humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, N. Ghrelin: Ghrelin as a Regulatory Peptide in Growth Hormone Secretion. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, MC13–MC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. The Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor: Its Intracellular Signaling and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4837–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutter, M.; Sakata, I.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; A Rovinsky, S.; Anderson, J.G.; Jung, S.; Birnbaum, S.; Yanagisawa, M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Nestler, E.J.; et al. The orexigenic hormone ghrelin defends against depressive symptoms of chronic stress. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, Z.B.; Erion, D.; Beiler, R.; Liu, Z.-W.; Abizaid, A.; Zigman, J.; Elsworth, J.D.; Savitt, J.M.; DiMarchi, R.; Tschöp, M.; et al. Ghrelin Promotes and Protects Nigrostriatal Dopamine Function via a UCP2-Dependent Mitochondrial Mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14057–14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.M.; Burgos-Robles, A.; Liu, E.; Correia, S.S.; A Goosens, K. A ghrelin–growth hormone axis drives stress-induced vulnerability to enhanced fear. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 19, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmatz, E.S.; Stone, L.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, G.; McGrath, A.; Gisabella, B.; Peng, X.; Kosoy, E.; Yao, J.; Liu, E.; et al. Central Ghrelin Resistance Permits the Overconsolidation of Fear Memory. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 81, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousufzai, M.I.U.A.; Harmatz, E.S.; Shah, M.; Malik, M.O.; Goosens, K.A. Ghrelin is a persistent biomarker for chronic stress exposure in adolescent rats and humans. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Guillén, L.; Barrios, V.; Campos-Barros, Á.; Argente, J. Ghrelin levels in obesity and anorexia nervosa: Effect of weight reduction or recuperation. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, L.A.; Brown, T.A.; Lavender, J.M.; Lopez, E.; Wierenga, C.E.; Kaye, W.H. Neuroendocrinology of reward in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: Beyond leptin and ghrelin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 497, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, A.M.; Castellini, G.; Volpe, U.; Ricca, V.; Lelli, L.; Monteleone, P.; Maj, M. Neuroendocrinology and brain imaging of reward in eating disorders: A possible key to the treatment of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 80, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, M.; Ohwada, R.; Akamizu, T.; Shibasaki, T.; Takano, K.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Increases Hunger and Food Intake in Patients with Restricting-type Anorexia Nervosa: A Pilot Study. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, P.K.; Lawson, E.A.; Faje, A.T.; Eddy, K.T.; Lee, H.; Fiedorek, F.T.; Breggia, A.; Gaal, I.M.; DeSanti, R.; Klibanski, A. Treatment With a Ghrelin Agonist in Outpatient Women With Anorexia Nervosa. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2018, 79, 17m11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zallar, L.J.; Farokhnia, M.; Tunstall, B.J.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Leggio, L. Chapter Four—The Role of the Ghrelin System in Drug Addiction. In International Review of Neurobiology; Thiele, T.E., Ed.; The Role of Neuropeptides in Addiction and Disorders of Excessive Consumption; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, L.; Ferrulli, A.; Cardone, S.; Nesci, A.; Miceli, A.; Malandrino, N.; Capristo, E.; Canestrelli, B.; Monteleone, P.; Kenna, G.A.; et al. Ghrelin system in alcohol-dependent subjects: Role of plasma ghrelin levels in alcohol drinking and craving. Addict. Biol. 2011, 17, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmann, A.; Bach, P.; Schuster, R.; Bumb, J.M.; Vollstädt-Klein, S.; Reinhard, I.; Rietschel, M.; Witt, S.H.; Wiedemann, K.; Kiefer, F. Ghrelin modulates mesolimbic reactivity to alcohol cues in alcohol-addicted subjects: A functional imaging study. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhnia, M.; Faulkner, M.L.; Piacentino, D.; Lee, M.R.; Leggio, L. Ghrelin: From a gut hormone to a potential therapeutic target for alcohol use disorder. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 204, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhnia, M.; Portelli, J.; Lee, M.R.; McDiarmid, G.R.; Munjal, V.; Abshire, K.M.; Battista, J.T.; Browning, B.D.; Deschaine, S.L.; Akhlaghi, F.; et al. Effects of exogenous ghrelin administration and ghrelin receptor blockade, in combination with alcohol, on peripheral inflammatory markers in heavy-drinking individuals: Results from two human laboratory studies. Brain Res. 2020, 1740, 146851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhnia, M.; Abshire, K.M.; Hammer, A.; Deschaine, S.L.; Saravanakumar, A.; Cobbina, E.; You, Z.-B.; Haass-Koffler, C.L.; Lee, M.R.; Akhlaghi, F.; et al. Neuroendocrine Response to Exogenous Ghrelin Administration, Combined With Alcohol, in Heavy-Drinking Individuals: Findings From a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Human Laboratory Study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, M.A.; Feighner, S.D.; Pong, S.-S.; McKee, K.K.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Silva, M.V.; Warren, V.A.; Howard, A.D.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.Y.; Heck, J.V. Structure−Function Studies on the New Growth Hormone-Releasing Peptide, Ghrelin: Minimal Sequence of Ghrelin Necessary for Activation of Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor 1a. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4370–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, D.; Myasnikov, A.; Damian, M.; Baneres, J.-L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, C. Structural basis of human ghrelin receptor signaling by ghrelin and the synthetic agonist ibutamoren. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.D.; Feighner, S.D.; Cully, D.F.; Arena, J.P.; Liberator, P.A.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Hamelin, M.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Palyha, O.C.; Anderson, J.; et al. A Receptor in Pituitary and Hypothalamus That Functions in Growth Hormone Release. Science 1996, 273, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Saeki, A.; Teraoka, H.; Hiraga, T.; Kaiya, H. Molecular identification of ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1a) and its functional role in the gastrointestinal tract of the guinea-pig. Peptides 2011, 32, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiimura, Y.; Horita, S.; Hamamoto, A.; Asada, H.; Hirata, K.; Tanaka, M.; Mori, K.; Uemura, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwata, S.; et al. Structure of an antagonist-bound ghrelin receptor reveals possible ghrelin recognition mode. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizaid, A.; Hougland, J.L. Ghrelin Signaling: GOAT and GHS-R1a Take a LEAP in Complexity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 31, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G.; Grishin, N.V.; Goldstein, J.L. Identification of the Acyltransferase that Octanoylates Ghrelin, an Appetite-Stimulating Peptide Hormone. Cell 2008, 132, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Solenberg, P.J.; Perkins, D.R.; Willency, J.A.; Knierman, M.D.; Jin, Z.; Witcher, D.R.; Luo, S.; Onyia, J.E.; Hale, J.E. Ghrelin octanoylation mediated by an orphan lipid transferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6320–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.E.; Zhao, F.; Loftus, R.J.; Patton, L.M.; Gibbs, R.A.; Hougland, J.L. Structure–Activity Analysis of Human Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase Reveals Chemical Determinants of Ghrelin Selectivity and Acyl Group Recognition. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.T.; Kola, B.; Grossman, A.; Korbonits, M. The expression of ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) in human tissues. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; Ibáñez-Costa, A.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Rivero-Cortés, E.; L-López, F.; Pedraza-Arevalo, S.; Valero-Rosa, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Ortega-Salas, R.; et al. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) enzyme is overexpressed in prostate cancer, and its levels are associated with patient’s metabolic status: Potential value as a non-invasive biomarker. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; L-López, F.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Guler, I.; Blanca, A.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; Carrasco, J.; et al. Clinical Utility of Ghrelin-O-Acyltransferase (GOAT) Enzyme as a Diagnostic Tool and Potential Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Gómez, E.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Blanca-Pedregosa, A.M.; León-González, A.J.; Valero-Rosa, J.; Fernández-Rueda, J.L.; González-Serrano, T.; López-Miranda, J.; et al. Plasma ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) enzyme levels: A novel non-invasive diagnosis tool for patients with significant prostate cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5688–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahete, M.D.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Martínez-Fuentes, A.J.; Kineman, R.D.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Luque, R.M.; Castaño, J.P. A Novel Human Ghrelin Variant (In1-Ghrelin) and Ghrelin-O-Acyltransferase Are Overexpressed in Breast Cancer: Potential Pathophysiological Relevance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, I.; Jeffery, P.L.; de Amorim, L.; Walpole, C.M.; Fung, J.; Whiteside, E.J.; Lourie, R.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) is expressed in prostate cancer tissues and cell lines and expression is differentially regulated in vitroby ghrelin. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, P.L.; E Murray, R.; Yeh, A.H.; McNamara, J.F.; Duncan, R.P.; Francis, G.D.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Expression and function of the ghrelin axis, including a novel preproghrelin isoform, in human breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Endocr. -Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.H.; Jeffery, P.L.; Duncan, R.P.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Ghrelin and a Novel Preproghrelin Isoform Are Highly Expressed in Prostate Cancer and Ghrelin Activates Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8295–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassoni, P.; Ghe, C.; Marrocco, T.; Tarabra, E.; Allia, E.; Catapano, F.; Deghenghi, R.; Ghigo, E.; Papotti, M.; Muccioli, G. Expression of ghrelin and biological activity of specific receptors for ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin in human prostate neoplasms and related cell lines. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 150, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, P.; Herington, A.; Chopin, L. Expression and action of the growth hormone releasing peptide ghrelin and its receptor in prostate cancer cell lines. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 172, R7–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; Gahete, M.D.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; Ibáñez-Costa, A.; L-López, F.; Rivero-Cortés, E.; Sarmento-Cabral, A.; Valero-Rosa, J.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; et al. The oncogenic role of the In1-ghrelin splicing variant in prostate cancer aggressiveness. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campaña, M.B.; Davis, T.R.; Novak, S.X.; Cleverdon, E.R.; Bates, M.; Krishnan, N.; Curtis, E.R.; Childs, M.D.; Pierce, M.R.; Morales-Rodriguez, Y.; et al. Cellular Uptake of a Fluorescent Ligand Reveals Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase Interacts with Extracellular Peptides and Exhibits Unexpected Localization for a Secretory Pathway Enzyme. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, J.T.; Lin, D.W. Improving the Specificity of PSA Screening with Serum and Urine Markers. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaña, M.B.; Irudayanathan, F.J.; Davis, T.R.; McGovern-Gooch, K.R.; Loftus, R.; Ashkar, M.; Escoffery, N.; Navarro, M.; Sieburg, M.A.; Nangia, S.; et al. The ghrelin O-acyltransferase structure reveals a catalytic channel for transmembrane hormone acylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 14166–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Zijlstra, A.; A Rubin, M.; Di Vizio, D. Extracellular vesicles for liquid biopsy in prostate cancer: Where are we and where are we headed? Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Zieren, R.C.; Wang, Y.; de Reijke, T.M.; Xue, W.; Pienta, K.J. Recent advances in extracellular vesicle research for urological cancers: From technology to application. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleverdon, E.R.; Davis, T.R.; Hougland, J.L. Functional group and stereochemical requirements for substrate binding by ghrelin O-acyltransferase revealed by unnatural amino acid incorporation. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 79, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. A Phase 1/2 Dose Escalation Trial of Multiple Doses of MLN2704 (DM1 Conjugated Monoclonal Antibody MLN591) in Subjects with Metastatic Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer; Clinical Trial Registration NCT00070837; clinicaltrials.gov. 2007. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00070837 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Ambrx, Inc. A Phase 1, Multicenter, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation, and Dose-Expansion Study to Evaluate the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Anti-Tumor Activity of ARX517 in Subjects With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Who Are Resistant or Refractory to Prior Standard Therapies; Clinical Trial Registration NCT04662580; clinicaltrials.gov. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04662580 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Flavell, R. A First-in-Human, Pilot PET Imaging Study of 89Zr-DFO-YS5, an immunoPET Agent for Detecting CD46 Positive Malignancy in Men with Prostate Cancer; Clinical Trial Registration NCT05245006; clinicaltrials.gov. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05245006 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Aggarwal, R. A Phase 1b/2 Study of FOR46 in Combination with Enzalutamide in Patients with Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer; Clinical Trial Registration NCT05011188; clinicaltrials.gov. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05011188 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Fu, Z.; Li, S.; Han, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y. Antibody drug conjugate: The “biological missile” for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, S.T.; Beltran, H.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Goldsmith, S.J.; Osborne, J.; Matulich, D.; Petrillo, K.; Parmar, S.; Nanus, D.M.; Bander, N.H. Anti–prostate-Specific membrane antigen-based radioimmunotherapy for prostate cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsässer-Beile, U.; Reischl, G.; Wiehr, S.; Bühler, P.; Wolf, P.; Alt, K.; Shively, J.; Judenhofer, M.S.; Machulla, H.-J.; Pichler, B.J. PET Imaging of Prostate Cancer Xenografts with a Highly Specific Antibody against the Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mjaess, G.; Aoun, F.; Rassy, E.; Diamand, R.; Albisinni, S.; Roumeguère, T. Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Prostate Cancer: Where Are we? Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 21, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, A.F.P.; Barreira, J.V.; Pacey, S.; Luz, R.; Sardinha, M.S.; Reis, A.P.; Sousa, M.F. Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e34490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.M.; Ito, A.S.; Schiöth, H.B.; Lamy, M. Structural study of melanocortin peptides by fluorescence spectroscopy: Identification of β-(2-naphthyl)-D-alanine as a fluorescent probe. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2003, 1623, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, T.; Wendeln, C.; Gokmen, M.T.; Rinnen, S.; Becker, M.M.; Arlinghaus, H.F.; Du Prez, F.; Ravoo, B.J. Chemically orthogonal trifunctional Janus beads by photochemical “sandwich” microcontact printing. Chem. Commun. 2012, 49, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, I.C.; Borner, T.; Swanson, M.L.; Chepurny, O.G.; Doebley, S.A.; Kamat, V.; Sweet, I.R.; Holz, G.G.; Hayes, M.R.; De Jonghe, B.C.; et al. Synthesis, Optimization, and Biological Evaluation of Corrinated Conjugates of the GLP-1R Agonist Exendin-4. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3479–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, V.; Presolski, S.I.; Ma, C.; Finn, M.G. Analysis and Optimization of Copper-Catalyzed Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition for Bioconjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 9879–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieburg, M.A.; Cleverdon, E.R.; Hougland, J.L. Biochemical Assays for Ghrelin Acylation and Inhibition of Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase. In Protein Lipidation: Methods and Protocols; Linder, M.E., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.R.; Hougland, J.L. A rising tide lifts all MBOATs: Recent progress in structural and functional understanding of membrane bound O-acyltransferases. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1167873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Donnelly, L.; Elghobashi-Meinhardt, N.; Long, T.; Zhou, R.W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, X. Mechanisms and inhibition of Porcupine-mediated Wnt acylation. Nature 2022, 607, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupland, C.E.; Andrei, S.A.; Ansell, T.B.; Carrique, L.; Kumar, P.; Sefer, L.; Schwab, R.A.; Byrne, E.F.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; et al. Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of Hedgehog acyltransferase. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 5025–5038.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Benz, T.L.; Long, S.B. Substrate and product complexes reveal mechanisms of Hedgehog acylation by HHAT. Science 2021, 372, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainavarapu, S.R.K.; Brujić, J.; Huang, H.H.; Wiita, A.P.; Lu, H.; Li, L.; Walther, K.A.; Carrion-Vazquez, M.; Li, H.; Fernandez, J.M. Contour Length and Refolding Rate of a Small Protein Controlled by Engineered Disulfide Bonds. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Venkatramani, R.; Rao, B.J.; Asgeirsson, B.; Dandekar, A.M. Protein structure quality assessment based on the distance profiles of consecutive backbone Cα atoms. F1000Research 2013, 2, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassy, E.; Rached, L.; Pistilli, B. Antibody drug conjugates targeting HER2: Clinical development in metastatic breast cancer. Breast 2022, 66, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.E.; Prybolsky, E.P.; Sieburg, M.; Hougland, J.L. A fluorescent peptide substrate facilitates investigation of ghrelin recognition and acylation by ghrelin O-acyltransferase. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 437, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis Phillips, G.D.; Li, G.; Dugger, D.L.; Crocker, L.M.; Parsons, K.L.; Mai, E.; Blättler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Chari, R.V.J.; Lutz, R.J.; et al. Targeting HER2-Positive Breast Cancer with Trastuzumab-DM1, an Antibody–Cytotoxic Drug Conjugate. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9280–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ford, A.L.; Taft, C.W.; Sprague-Getsy, A.M.; Carlson, G.C.; Mate, N.A.; Sieburg, M.A.; Chisholm, J.D.; Hougland, J.L. A Modular Customizable Ligand-Conjugate (LC) System Targeting Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020204
Ford AL, Taft CW, Sprague-Getsy AM, Carlson GC, Mate NA, Sieburg MA, Chisholm JD, Hougland JL. A Modular Customizable Ligand-Conjugate (LC) System Targeting Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020204
Chicago/Turabian StyleFord, Amber L., Caine W. Taft, Andrea M. Sprague-Getsy, Gracie C. Carlson, Nilamber A. Mate, Michelle A. Sieburg, John D. Chisholm, and James L. Hougland. 2025. "A Modular Customizable Ligand-Conjugate (LC) System Targeting Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase" Biomolecules 15, no. 2: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020204
APA StyleFord, A. L., Taft, C. W., Sprague-Getsy, A. M., Carlson, G. C., Mate, N. A., Sieburg, M. A., Chisholm, J. D., & Hougland, J. L. (2025). A Modular Customizable Ligand-Conjugate (LC) System Targeting Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase. Biomolecules, 15(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020204







