Immunohistochemical Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Human Carotid Sinus and Carotid Body
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunohistochemistry
2.2. Double Immunofluorescence
2.3. Quantitative Analysis
3. Results
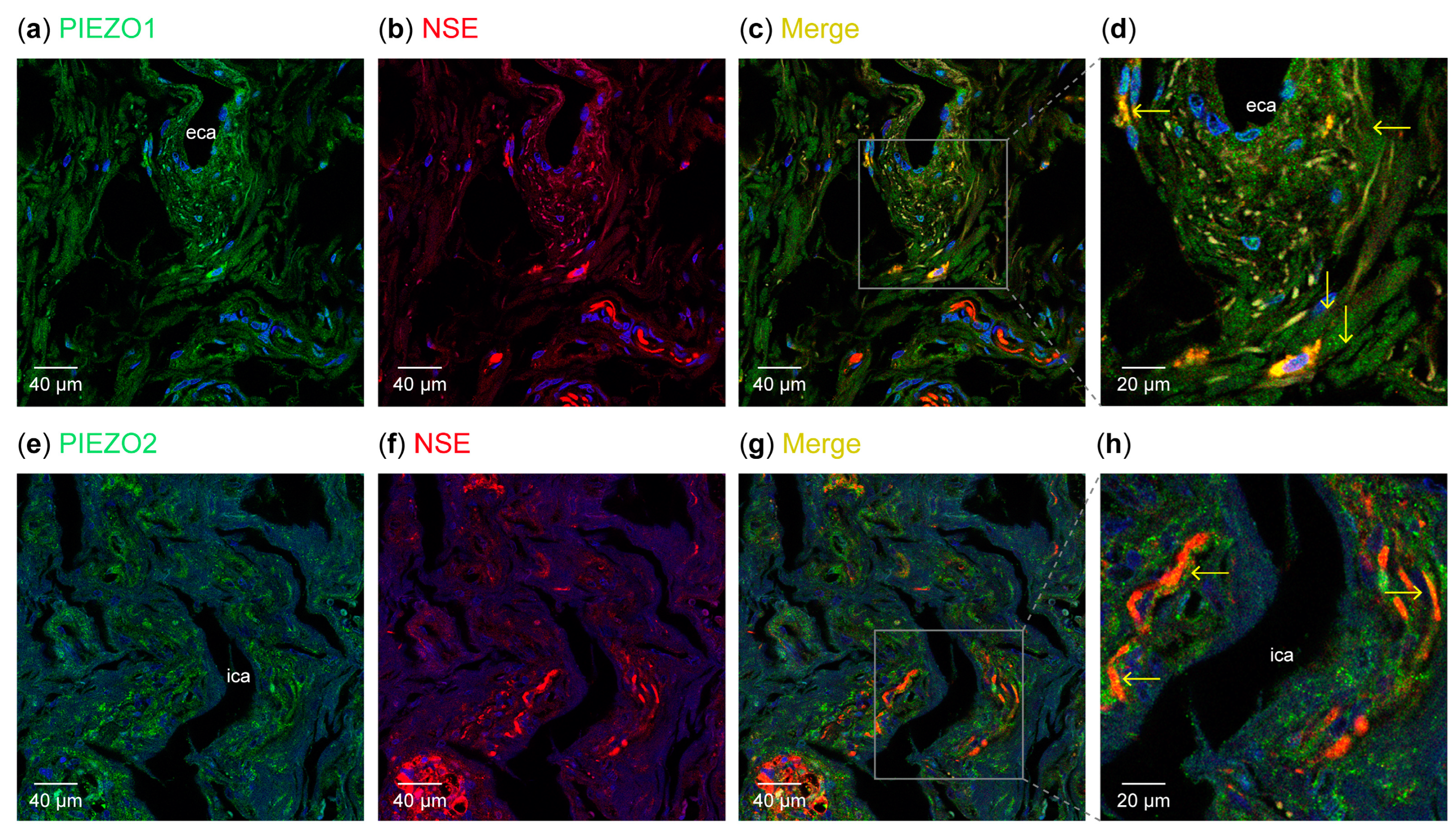
3.1. Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Carotid Sinus
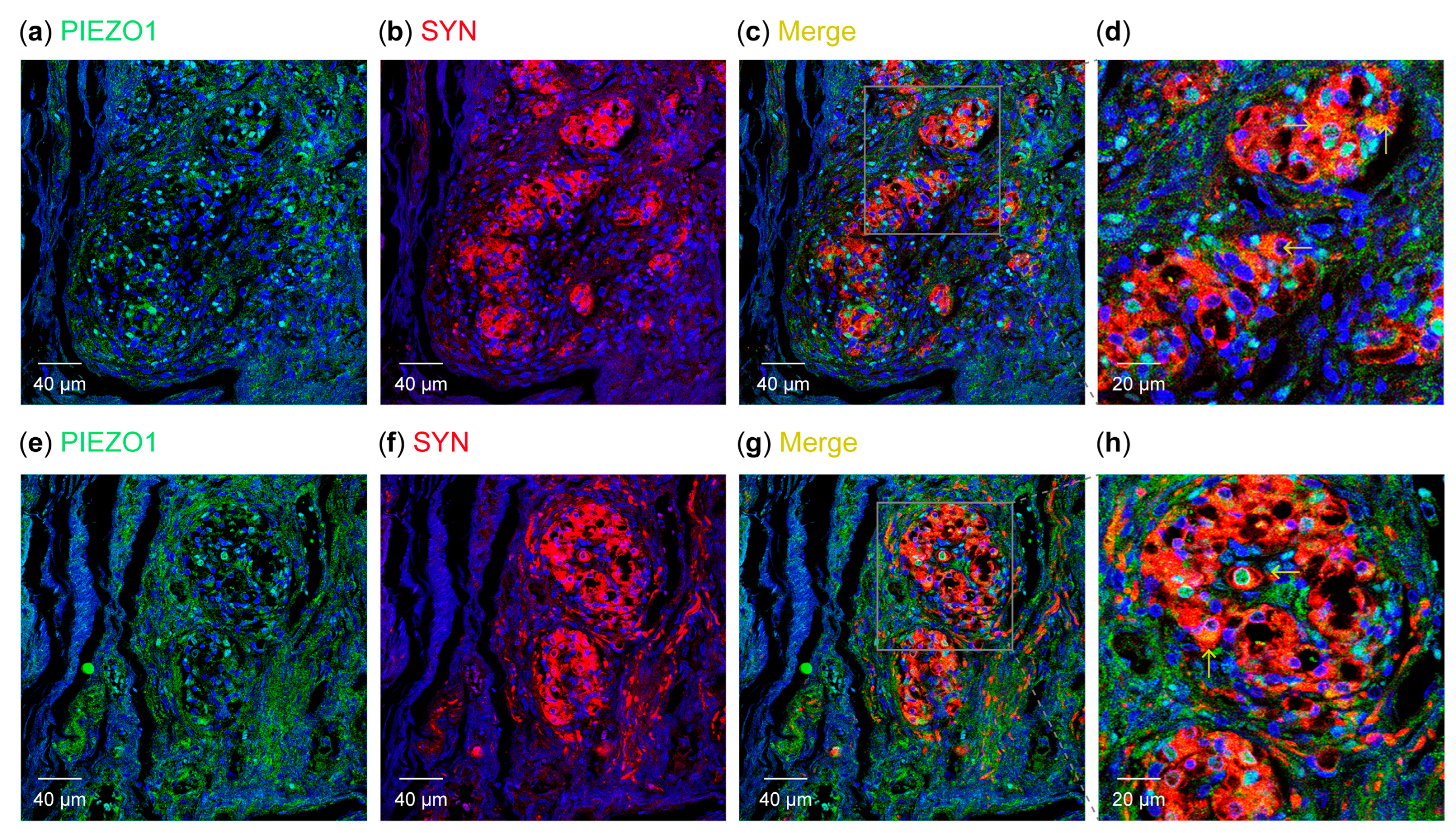
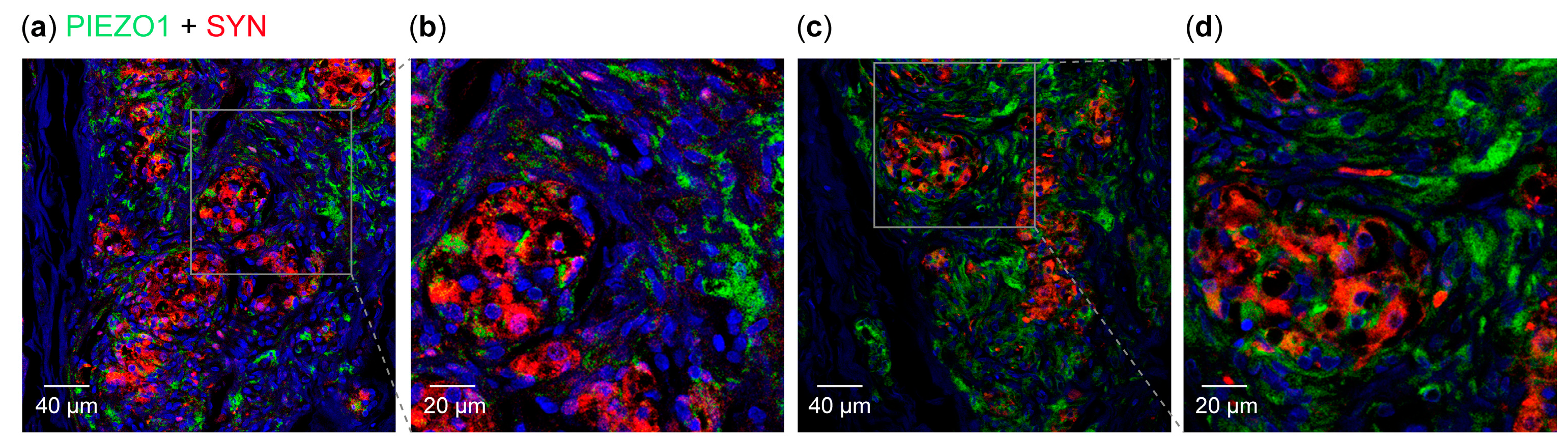
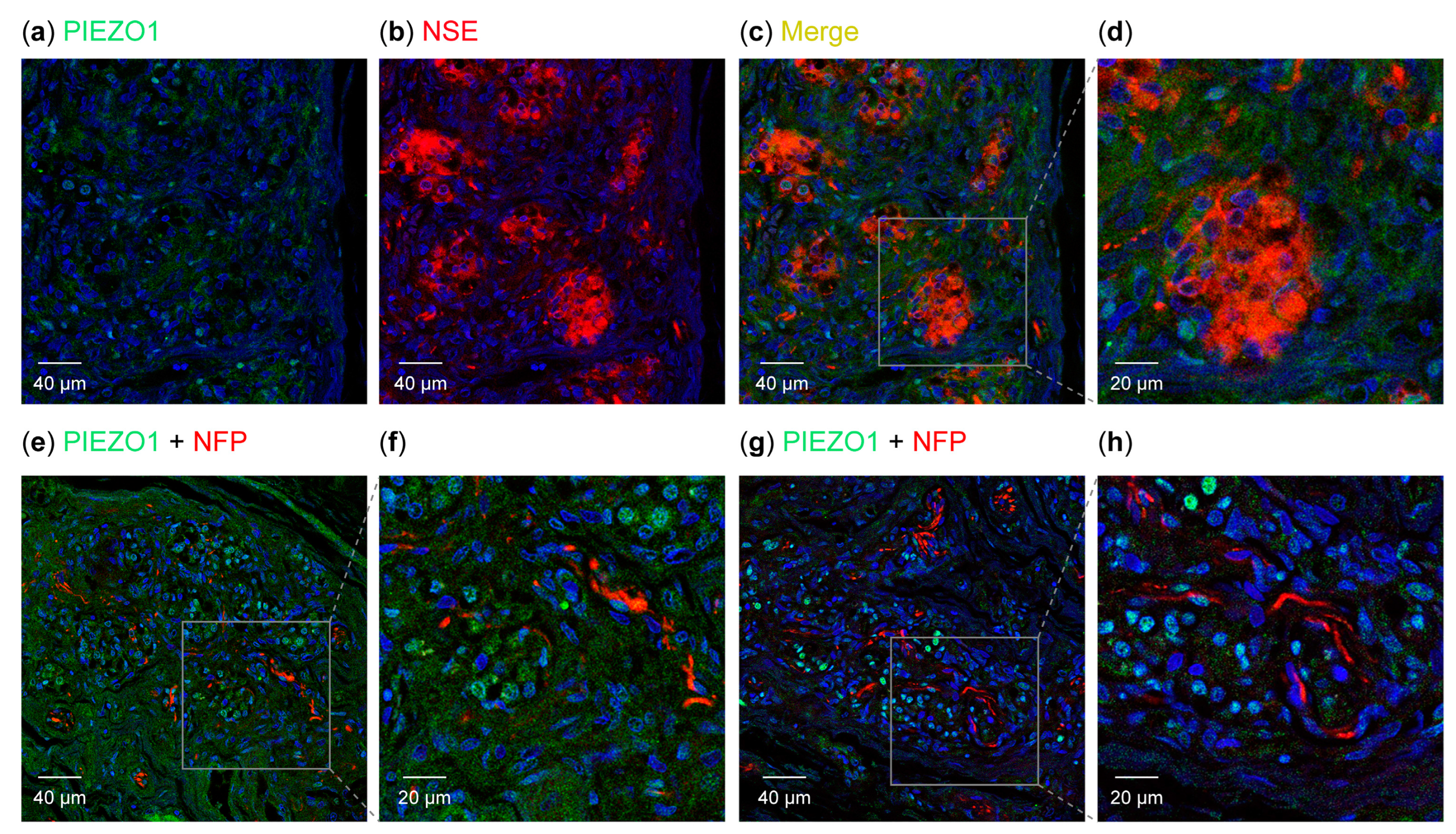
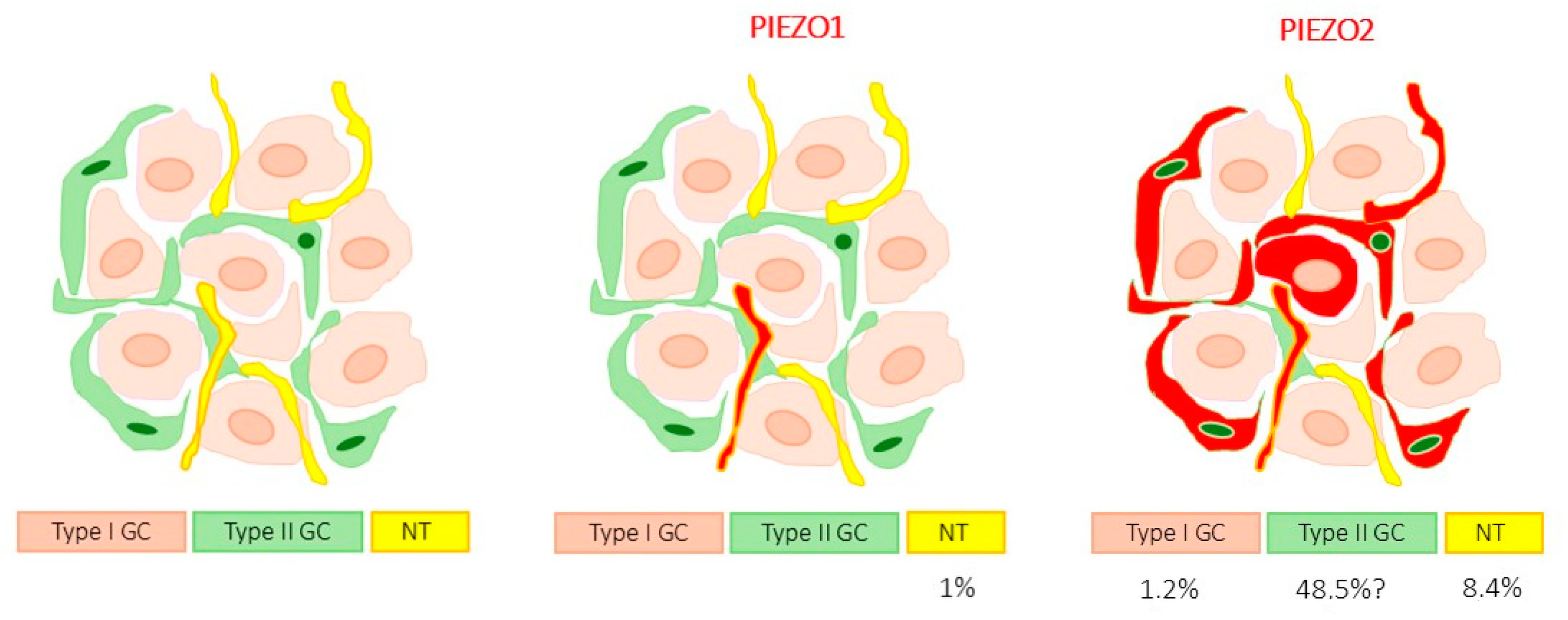
3.2. Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Carotid Body
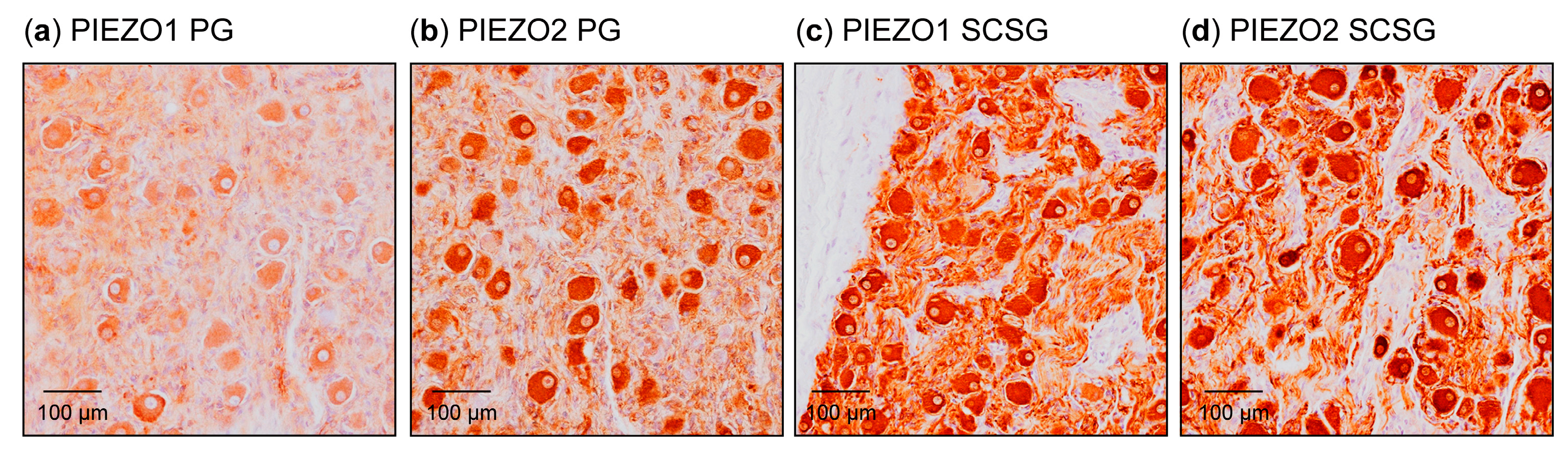
3.3. Detection of PIEZO Channels in the Petrosal Ganglion and Superior Cervical Sympathetic Ganglion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, P.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Mechanosensitive Ion Channels: Structural Features Relevant to Mechanotransduction Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Mizuno, K. Roles of the cytoskeleton, cell adhesion and rho signalling in mechanosensing and mechanotransduction. J. Biochem. 2017, 161, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, B.; Mathur, J.; Schmidt, M.; Earley, T.J.; Ranade, S.; Petrus, M.J.; Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science 2010, 330, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, P.; Parpaite, T.; Coste, B. PIEZO channels and newcomers in the mammalian mechanosensitive ion channel family. Neuron 2022, 110, 2713–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B. Mechanisms of mechanotransduction and physiological roles of PIEZO channels. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, K.; Monaghan-Benson, E.; Graham, D.M. Mechanotransduction: From the cell surface to the nucleus via RhoA. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, S. Mechanobiology in Cells and Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, E.P.; Strowitzki, M.J.; Taylor, C.T. Mechanisms and Consequences of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Sensing in Mammals. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Sáenz, P.; López-Barneo, J. Physiology of the Carotid Body: From Molecules to Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturriaga, R.; Alcayaga, J. Neurotransmission in the carotid body: Transmitters and modulators between glomus cells and petrosal ganglion nerve terminals. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 47, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Barbero, G.; García-Mesa, Y.; Cobo, R.; Cuendias, P.; Martín-Biedma, B.; García-Suarez, O.; Feito, J.; Cobo, T.; Vega, J.A. Acid-sensing ion channels immunoreactivity in nerve profiles and glomus cells of the human carotid body. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyzaguirre, C.; Fidone, S.J. Transduction mechanisms in carotid body: Glomus cells, putative neurotransmitters, and nerve endings. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1980, 239, C135–C152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, V.; Pavri, B.B. Carotid sinus syndrome. Cardiol. Rev. 2015, 23, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskander, A.J.; Naftalovich, R.; Yang, X. The carotid sinus acts as a mechanotransducer of shear oscillation rather than a baroreceptor. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 134, 109441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, H.A.; Price, M.P.; Welsh, M.J.; Abboud, F.M. A molecular component of the arterial baroreceptor mechanotransducer. Neuron 1998, 21, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, X.; Sabharwal, R.; Snitsarev, V.; Morgan, D.; Rahmouni, K.; Drummond, H.A.; Whiteis, C.A.; Costa, V.; Price, M.; et al. The ion channel ASIC2 is required for baroreceptor and autonomic control of circulation. Neuron 2009, 64, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, O.C.; Shen, B.; Wong, C.O.; Tjong, Y.W.; Lo, C.Y.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, Y.; Yung, W.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Fung, M.L.; et al. TRPC5 channels participate in pressure-sensing in aortic baroreceptors. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakore, P.; Brain, S.D.; Beech, D.J. Correspondence: Challenging a proposed role for TRPC5 in aortic baroreceptor pressure-sensing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hong, G.S.; Pak, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Shen, Y.; Ryu, P.D.; et al. Tentonin 3/TMEM150C senses blood pressure changes in the aortic arch. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3671–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.Z.; Marshall, K.L.; Min, S.; Daou, I.; Chapleau, M.W.; Abboud, F.M.; Liberles, S.D.; Patapoutian, A. PIEZOs mediate neuronal sensing of blood pressure and the baroreceptor reflex. Science 2018, 362, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.; Chang, R.B.; Prescott, S.L.; Beeler, B.; Joshi, N.R.; Strochlic, D.E.; Liberles, S.D. Arterial Baroreceptors Sense Blood Pressure through Decorated Aortic Claws. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2192–2201.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, T.; Nagase, M. Piezo ion channels: Long-sought-after mechanosensors mediating hypertension and hypertensive nephropathy. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2786–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, S.D.; Sved, A.F.; Andresen, M.C. Missing pieces of the Piezo1/Piezo2 baroreceptor hypothesis: An autonomic perspective. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 122, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, P.L.; Castania, J.A.; Dias, D.P.; Patel, K.P.; Fazan, R., Jr.; Salgado, H.C. Role of chemoreceptor activation in hemodynamic responses to electrical stimulation of the carotid sinus in conscious rats. Hypertension 2015, 66, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, S.V.; Sacramento, J.F.; Melo, B.F.; Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Romero-Ortega, M.I.; Guarino, M.P. Blood Pressure Regulation by the Carotid Sinus Nerve: Clinical Implications for Carotid Body Neuromodulation. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 725751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porzionato, A.; Macchi, V.; Stecco, C.; De Caro, R. The Carotid Sinus Nerve-Structure, Function, and Clinical Implications. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otlyga, D.; Tsvetkova, E.; Junemann, O.; Saveliev, S. Immunohistochemical Characteristics of the Human Carotid Body in the Antenatal and Postnatal Periods of Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Nakajima, T. Immunocytochemical study on the localization of neuron-specific enolase and S-100 protein in the carotid body of rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1982, 227, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Clark, C.D.; Chancellor, T.J.; Papavassiliou, D.V. Carotid geometry effects on blood flow and on risk for vascular disease. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, A.B.; Thapar, A.; Davies, A.H. History of carotid stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, e66–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andani, R.; Khan, Y.S. Anatomy, Head and Neck: Carotid Sinus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Tenorio Lopes, L.; Barioni, N.O.; Roeske, J.; Incognito, A.V.; Baker, J.; Raj, S.R.; Wilson, R.J.A. The molecular makeup of peripheral and central baroreceptors: Stretching a role for Transient Receptor Potential (TRP), Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC), Acid Sensing Ion Channel (ASIC), and Piezo channels. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3052–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturriaga, R. Translating carotid body function into clinical medicine. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 3067–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturriaga, R.; Alcayaga, J.; Chapleau, M.W.; Somers, V.K. Carotid body chemoreceptors: Physiology, pathology, and implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1177–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coste, B.; Xiao, B.; Santos, J.S.; Syeda, R.; Grandl, J.; Spencer, K.S.; Kim, S.E.; Schmidt, M.; Mathur, J.; Dubin, A.E.; et al. Piezo proteins are pore-forming subunits of mechanically activated channels. Nature 2012, 483, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefauver, J.M.; Ward, A.B.; Patapoutian, A. Discoveries in structure and physiology of mechanically activated ion channels. Nature 2020, 587, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Ru, K.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liang, S.; Khan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Qian, A.; et al. Piezo Channels: Awesome Mechanosensitive Structures in Cellular Mechanotransduction and Their Role in Bone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciriello, J.; Hochstenbach, S.; Roder, S. Central Projections of Baroreceptor and Chemoreceptor Afferent Fibers in the Rat. In Nucleus of the Solitary Tract; Robin, I., Barraco, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, D.; McCormack, E.; Cardona, J.J.; Chaiyamoon, A.; Shekhawat, D.; Reina, F.; Carrera, A.; Iwanaga, J.; Dumont, A.S.; Tubbs, R.S. Histology and immunohistochemistry of the human carotid sinus nerve. Anat. Cell Biol. 2023, 56, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schild, J.H.; Kunze, D.L. Differential distribution of voltage-gated channels in myelinated and unmyelinated baroreceptor afferents. Auton. Neurosci. 2012, 172, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.F.; Paton, J.F.; Schwaber, J.S. NTS neuronal responses to arterial pressure and pressure changes in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, R1355–R1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seagard, J.L.; Hopp, F.A.; Drummond, H.A.; Van Wynsberghe, D.M. Selective contribution of two types of carotid sinus baroreceptors to the control of blood pressure. Circ. Res. 1993, 72, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehmke, H. The mechanotransduction of blood pressure. Science 2018, 362, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.J. PIEZOs in baroreceptor reflex. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, S.D.; Jordan, J.; Harrison, D.G.; Karumanchi, S.A. Solving baroreceptor mystery: Role of PIEZO ion channels. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglis, M.G.; Muppidi, S. Ion channels PIEZOs identified as the long-sought baroreceptor mechanosensors for blood pressure control, and other updates on autonomic research. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaafien, K.; Harden, S.W.; Johnson, D.N.; Kimball, A.K.; Sheng, W.; Smith, J.A.; Scott, K.A.; Frazier, C.J.; de Kloet, A.D.; Krause, E.G. A Novel Organ-Specific Approach to Selectively Target Sensory Afferents Innervating the Aortic Arch. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 841078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. The arterial baroreflex: Functional organization and involvement in neurologic disease. Neurology 2008, 71, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrwein, E.A.; Joyner, M.J. Regulation of blood pressure by the arterial baroreflex and autonomic nervous system. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 117, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.M.; Itson-Zoske, B.; Fan, F.; Gani, U.; Rahman, M.; Hogan, Q.H.; Yu, H. Peripheral sensory neurons and non-neuronal cells express functional Piezo1 channels. Mol. Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231174315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Moehring, F.; Itson-Zoske, B.; Fan, F.; Stucky, C.L.; Hogan, Q.H.; Yu, H. Piezo2 mechanosensitive ion channel is located to sensory neurons and nonneuronal cells in rat peripheral sensory pathway: Implications in pain. Pain 2021, 162, 2750–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuendias, P.; Vega, J.A.; García-Suárez, O.; Suazo, I.; Cobo, R.; García-Piqueras, J.; García-Mesa, Y. Axonal and Glial PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 Immunoreactivity in Human Clitoral Krause’s Corpuscles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mesa, Y.; Cuendias, P.; Alonso-Guervós, M.; García-Piqueras, J.; Martín-Biedma, B.; Cobo, T.; García-Suárez, O.; Vega, J.A. Immunohistochemical detection of PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 in human digital Meissner’s corpuscles. Ann. Anat. 2024, 252, 152200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdala, A.P.; McBryde, F.D.; Marina, N.; Hendy, E.B.; Engelman, Z.J.; Fudim, M.; Sobotka, P.A.; Gourine, A.V.; Paton, J.F. Hypertension is critically dependent on the carotid body input in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 4269–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, R.; Andrade, D.C.; Lucero, C.; Arias, P.; Iturriaga, R. Carotid Body Ablation Abrogates Hypertension and Autonomic Alterations Induced by Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats. Hypertension 2016, 68, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijacka, W.; McBryde, F.D.; Marvar, P.J.; Lincevicius, G.S.; Abdala, A.P.; Woodward, L.; Li, D.; Paterson, D.J.; Paton, J.F. Carotid sinus denervation ameliorates renovascular hypertension in adult Wistar rats. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 6255–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBryde, F.D.; Abdala, A.P.; Hendy, E.B.; Pijacka, W.; Marvar, P.; Moraes, D.J.; Sobotka, P.A.; Paton, J.F. The carotid body as a putative therapeutic target for the treatment of neurogenic hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, K. Surgical removal of the carotid body for bronchial asthma. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1962, 31, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, J.F.; Sobotka, P.A.; Fudim, M.; Engelman, Z.J.; Hart, E.C.; McBryde, F.D.; Abdala, A.P.; Marina, N.; Gourine, A.V.; Lobo, M.; et al. The carotid body as a therapeutic target for the treatment of sympathetically mediated diseases. Hypertension 2013, 61, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Antigen | Origin | Dilution | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIEZO1 | Rabbit | 1:200 | Invitrogen 1 |
| PIEZO2 | Rabbit | 1:200 | Sigma 2 |
| NSE (clone BBS/NC/VI-H14) | Mouse | 1:500 | Dako 3 |
| NFP (clone 2F11) | Mouse | 1:200 | Roche 4 |
| Synaptophysin (clone 27G12) | Mouse | Prediluted | Leica Biosystems 5 |
| S100P | Mouse | 1:500 | Dako 3 |
| PIEZO1 | Total: 1.1 ± 0.9% (Type I glomus cells + nerves) |
| Type I glomus cells: 0.0 | |
| Nerves: 1.0 ± 0.9% | |
| PIEZO2 | Total: 58.1 ± 5.7% (Type I glomus cells + nerves) |
| Type I glomus cells: 1.2 ± 3.9% | |
| Nerves: 8.4 ± 2.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alba, E.; García-Mesa, Y.; Cobo, R.; Cuendias, P.; Martín-Cruces, J.; Suazo, I.; Martínez-Barbero, G.; Vega, J.A.; García-Suárez, O.; Cobo, T. Immunohistochemical Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Human Carotid Sinus and Carotid Body. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030386
Alba E, García-Mesa Y, Cobo R, Cuendias P, Martín-Cruces J, Suazo I, Martínez-Barbero G, Vega JA, García-Suárez O, Cobo T. Immunohistochemical Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Human Carotid Sinus and Carotid Body. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030386
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlba, Elda, Yolanda García-Mesa, Ramón Cobo, Patricia Cuendias, José Martín-Cruces, Iván Suazo, Graciela Martínez-Barbero, José A. Vega, Olivia García-Suárez, and Teresa Cobo. 2025. "Immunohistochemical Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Human Carotid Sinus and Carotid Body" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030386
APA StyleAlba, E., García-Mesa, Y., Cobo, R., Cuendias, P., Martín-Cruces, J., Suazo, I., Martínez-Barbero, G., Vega, J. A., García-Suárez, O., & Cobo, T. (2025). Immunohistochemical Detection of PIEZO Ion Channels in the Human Carotid Sinus and Carotid Body. Biomolecules, 15(3), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030386







