Role of Transcription Factor Fli-1 in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Role of Fli-1 in Regulating Inflammation
2.1. Inflammatory Mediators Regulated by Fli-1
2.2. Fli-1 Affects Cellular Processes
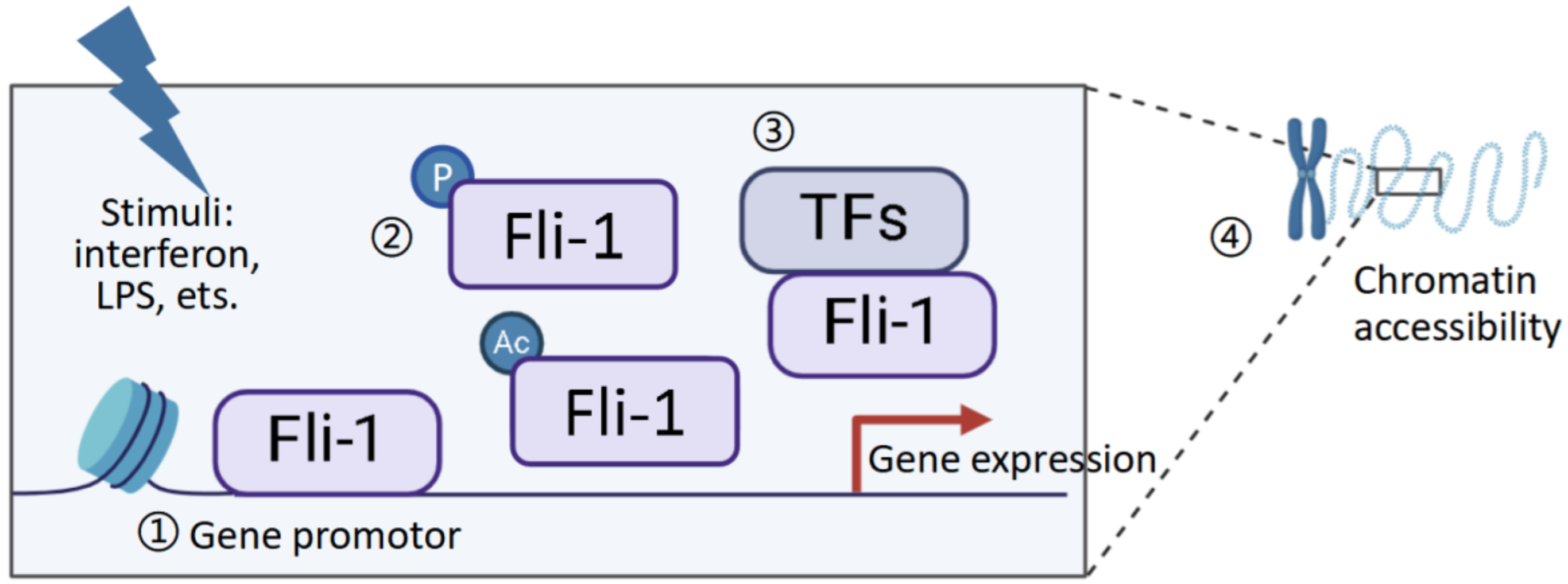
2.3. Mechanisms Underlying Fli-1 Regulation in Inflammatory Mediators
3. Implications of Fli-1 in Autoimmune/Inflammatory Diseases
3.1. The Role of Fli-1 in Lupus
3.2. Fli-1 in SSc
3.3. Fli-1 in Cancer
3.4. Fli-1 in Sepsis
4. Fli-1 in Pharmaceutical Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heidland, A.; Klassen, A.; Rutkowski, P.; Bahner, U. The contribution of Rudolf Virchow to the concept of inflammation: What is still of importance? J. Nephrol. 2006, 19 (Suppl. S10), S102–S109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orozco, L.D.; Bennett, B.J.; Farber, C.R.; Ghazalpour, A.; Pan, C.; Che, N.; Wen, P.; Qi, H.X.; Mutukulu, A.; Siemers, N.; et al. Unraveling Inflammatory Responses using Systems Genetics and Gene-Environment Interactions in Macrophages. Cell 2012, 151, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, Y.; Giddens, E.B.; Bernstein, A. Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, H.; Liu, T.; Zacksenhaus, E.; Ben-David, Y. The ets transcription factor Fli-1 in development, cancer and disease. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, A.H.; Ben-David, Y. The role of Fli-1 in normal cell function and malignant transformation. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6482–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.K.; E Smyth, F.; Thompson, D.M.; Cheng, J.Q.; Testa, J.R.; Papas, T.S.; Seth, A. The ERGB/Fli-1 gene: Isolation and characterization of a new member of the family of human ETS transcription factors. Cell Growth Differ. 1992, 3, 705–713. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, E.; Williams, S.; Sato, S.; Gilkeson, G.; Watson, D.K.; Zhang, X.K. The transcription factor Fli-1 regulates monocyte, macrophage and dendritic cell development in mice. Immunology 2013, 139, 318–327. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, M.L.L.; Nowling, T.K.; Brandon, D.; Watson, D.K.; Zhang, X.K. Fli-1 controls transcription from the MCP-1 gene promoter, which may provide a novel mechanism for chemokine and cytokine activation. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Karam, E.; Williams, S.; Watson, D.K.; Gilkeson, G.; Zhang, X.K. Fli-1 transcription factor affects glomerulonephritis development by regulating expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in endothelial cells in the kidney. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 145, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard, R.M.; Sato, S.; Suzuki, E.; Williams, S.; Nowling, T.K.; Zhang, X.K. The Fli-1 transcription factor regulates the expression of CCL5/RANTES. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2661–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Richard, M.L.; Brandon, D.; Buie, J.N.J.; Oates, J.C.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Zhang, X.K. A Critical Role of the Transcription Factor Fli-1 in Murine Lupus Development by Regulation of Interleukin-6 Expression. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3436–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennard Richard, M.L.; Brandon, D.; Lou, N.; Sato, S.; Caldwell, T.; Nowling, T.K.; Gilkeson, G.; Zhang, X.K. Acetylation impacts Fli-1-driven regulation of granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lou, N.; Richard, M.L.L.; Yu, J.; Kindy, M.; Zhang, X.K. The Fli-1 transcription factor is a critical regulator for controlling the expression of chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 2 (CXCL2). Mol. Immunol. 2017, 81, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Zhang, X.K.; Temmoku, J.; Fujita, Y.; Matsuoka, N.; Yashiro-Furuya, M.; Asano, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Migita, K. Ets Family Transcription Factor Fli-1 Promotes Leukocyte Recruitment and Production of IL-17A in the MRL/Lpr Mouse Model of Lupus Nephritis. Cells 2020, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.-W.; Vecchiarelli-Federico, L.M.; Li, Y.-J.; Wang, G.-J.; Ben-David, Y. Continuous Fli-1 expression plays an essential role in the proliferation and survival of F-MuLV-induced erythroleukemia and human erythroleukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, H. Blocking the road, stopping the engine or killing the driver? Advances in targeting EWS/FLI-1 fusion in Ewing sarcoma as novel therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, Y.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Toyama, T.; Tada, Y.; Sugaya, M.; Sato, S.; et al. Progranulin Overproduction Due to Fli-1 Deficiency Contributes to the Resistance of Dermal Fibroblasts to Tumor Necrosis Factor in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 3245–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Asano, Y.; Nishimura, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Fujiu, K.; Manabe, I.; Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Akamata, K.; et al. Simultaneous downregulation of KLF5 and Fli1 is a key feature underlying systemic sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Goodwin, A.J.; A Cook, J.; Halushka, P.V.; Zhang, X.K.; Wilson, C.L.; Schnapp, L.M.; Zingarelli, B.; Fan, H. Fli-1 Governs Pericyte Dysfunction in a Murine Model of Sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Goodwin, A.J.; Cook, J.A.; Halushka, P.V.; Zhang, X.K.; Fan, H. Fli-1 transcription factor regulates the expression of caspase-1 in lung pericytes. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 108, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.M.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Bunni, M.A.; Basher, F.; Roddy, P.O.; Siskind, L.J.; Nietert, P.J.; Nowling, T.K. Reducing FLI1 Levels in the MRL/lpr Lupus Mouse Model Impacts T Cell Function by Modulating Glycosphingolipid Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, S.; Zheng, W.J.; Tsoi, L.C.; Gilkeson, G.; Zhang, X.K. A role for Fli-1 in B cell proliferation: Implications for SLE pathogenesis. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Noda, S.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Trojanowska, M.; Sato, S. Fibrosis, vascular activation, and immune abnormalities resembling systemic sclerosis in bleomycin-treated Fli-1-haploinsufficient mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigusa, R.; Asano, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Hirabayashi, M.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, S.; Yamashita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; et al. Fli1-haploinsufficient dermal fibroblasts promote skin-localized transdifferentiation of Th2-like regulatory T cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.H.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Downregulation of Friend Leukemia Virus Integration 1 as a Feedback Mechanism That Restrains Lipopolysaccharide Induction of Matrix Metalloproteases and Interleukin-10 in Human Macrophages. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yuan, M.; Ma, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, L.; Wen, M.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; An, H. Transcription factor Fli-1 positively regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-27 production in macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 71, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Khurana, N.; Ahmed, R.S.; Umar, S.; Sarwar, A.H.M.G.; Alam, Q.; Kamal, M.A.; Ashraf, G.M. Chemokines: A Potential Therapeutic Target to Suppress Autoimmune Arthritis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, A.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and Their Receptors: Drug Targets in Immunity and Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Bao, Z.; Tang, P.; Gong, W.; Yoshimura, T.; Wang, J.M. Chemokines in homeostasis and diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Zhang, X.K. The Friend leukaemia virus integration 1 (Fli-1) transcription factor affects lupus nephritis development by regulating inflammatory cell infiltration into the kidney. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaj, K.P.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Molano, I.; Basher, F.; Powers, T.W.; Drake, R.R.; Nowling, T.K. FLI1 Levels Impact CXCR3 Expression and Renal Infiltration of T Cells and Renal Glycosphingolipid Metabolism in the MRL/lpr Lupus Mouse Strain. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 5551–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, Y.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Takahashi, T.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Toyama, T.; Aozasa, N.; Sumida, H.; Kuwano, Y.; et al. Fli1 deficiency contributes to the suppression of endothelial CXCL5 expression in systemic sclerosis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Asano, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Toyama, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Sato, S. Fli1 Deficiency Induces CXCL6 Expression in Dermal Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells, Contributing to the Development of Fibrosis and Vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Richard, M.L.; Caldwell, T.S.; Sundararaj, K.; Sato, S.; Nowling, T.K.; Zhang, X.K. Role of the transcription factor Fli-1 on the CXCL10/CXCR3 Axis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1219279. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, T.; Miyagawa, T.; Toyama, S.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamura, K.; Saigusa, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Toyama, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; et al. CXCL13 produced by macrophages due to Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the development of tissue fibrosis, vasculopathy and immune activation in systemic sclerosis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Richard, M.L.; Li, P.; Henry, B.; Schutt, S.; Yu, X.-Z.; Fan, H.; Zhang, W.; Gilkeson, G.; Zhang, X.K. Expression of GM-CSF Is Regulated by Fli-1 Transcription Factor, a Potential Drug Target. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakerakanti, S.S.; Kapanadze, B.; Yamasaki, M.; Markiewicz, M.; Trojanowska, M. Fli1 and Ets1 Have Distinct Roles in Connective Tissue Growth Factor/CCN2 Gene Regulation and Induction of the Profibrotic Gene Program. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25259–25269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Nobori, H.; Shimizu, M.; Watanabe, M.; Yonekura, M.; Nakai, T.; Kamikawa, Y.; Wakimura, A.; Funahashi, N.; Naruse, H.; et al. Multiple ETS Family Proteins Regulate PF4 Gene Expression by Binding to the Same ETS Binding Site. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamata, K.; Asano, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Nakamura, K.; Noda, S.; Aozasa, N.; Toyama, T.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Increased expression of chemerin in endothelial cells due to Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the development of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, K.-B.; Cho, K.; Lee, C.; Im, Y.-H.; Chang, J.; Choi, S.-G.; Sorensen, P.H.; Thiele, C.J.; Kim, S.-J. Repression of the gene encoding the TGF-beta type II receptor is a major target of the EWS-FLI1 oncoprotein. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutt, S.D.; Wu, Y.; Kharel, A.; Bastian, D.; Choi, H.-J.; Sofi, M.H.; Mealer, C.; Mims, B.M.; Nguyen, H.; Liu, C.; et al. The druggable transcription factor Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e143950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathenia, J.; Reyes-Cortes, E.; Williams, S.; Molano, I.; Ruiz, P.; Watson, D.K.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Zhang, X.K. Impact of Fli-1 transcription factor on autoantibody and lupus nephritis in NZM2410 mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 162, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; Song, W.; He, H.; Dong, J.; Liu, X.; Cui, J. Friend leukemia virus integration 1 is a predictor of poor prognosis of breast cancer and promotes metastasis and cancer stem cell properties of breast cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 3548–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenhorst, P.C.; Jones, D.A.; Graves, B.J. Expression profiles frame the promoter specificity dilemma of the ETS family of transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 5693–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, R.; Brosamle, D.; Yuan, X.; Beyer, M.; Neher, J.J. Epigenetic control of microglial immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 323, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackers, P.; Szalai, G.; Moussa, O.; Watson, D.K. Ets-dependent Regulation of Target Gene Expression during Megakaryopoiesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52183–52190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Trojanowska, M. Phosphorylation of Fli1 at threonine 312 by protein kinase C delta promotes its interaction with p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor and subsequent acetylation in response to transforming growth factor beta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Arai, E.; Khan, O.; Zhang, Z.; Ngiow, S.F.; He, Y.; Huang, H.; Manne, S.; Cao, Z.; Baxter, A.E.; et al. In vivo CD8(+) T cell CRISPR screening reveals control by Fli1 in infection and cancer. Cell 2021, 184, 1262–1280.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, P.; Maroulakou, I.; Green, J.; Dantis, P.; Romano-Spica, V.; Kottaridis, S.; Lautenberger, J.; Watson, D.; Papas, T.; Fischinger, P.; et al. Expression of ets family of genes in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome. Int. J. Oncol. 1996, 9, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.K.; Gallant, S.; Molano, I.; Moussa, O.M.; Ruiz, P.; Spyropoulos, D.D.; Watson, D.K.; Gilkeson, G. Decreased Expression of the Ets Family Transcription Factor Fli-1 Markedly Prolongs Survival and Significantly Reduces Renal Disease in MRL/lpr Mice. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6481–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Czuwara-Ladykowska, J.; Moussa, O.; Markiewicz, M.; Smith, E.; Silver, R.M.; Jablonska, S.; Blaszczyk, M.; Watson, D.K.; Trojanowska, M. Persistent Down-Regulation of Fli1, a Suppressor of Collagen Transcription, in Fibrotic Scleroderma Skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, P.; Kahaleh, B. Association between enhanced type I collagen expression and epigenetic repression of the FLI1 gene in scleroderma fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Bujor, A.M.; Trojanowska, M. The impact of Fli1 deficiency on the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 59, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.P.; Patil, P.B.; Thakkannavar, S.S.; Pujari, V.B. Inflammation and cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David, Y.; Gajendran, B.; Sample, K.M.; Zacksenhaus, E. Current insights into the role of Fli-1 in hematopoiesis and malignant transformation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Hu, A.; Yu, K.; Kuang, Y.; Gajendran, B.; Zacksenhaus, E.; Sample, K.M.; Xiao, X.; Liu, W.; et al. FLI1 induces erythroleukemia through opposing effects on UBASH3A and UBASH3B ex-pression. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 326. [Google Scholar]
- Maiorino, L.; Egeblad, M. Tumours pick the path to cancer inflammation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakos, C.I.; Charles, K.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e493–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, G.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A. Cytokines as a key component of cancer-related inflammation. Cytokine 2008, 43, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, G.; Libert, C.; Aquilina, M.; Cappelletti, M.; Ciliberto, G.; Musiani, P.; Poli, V. Defective development of pristane-oil-induced plasmacytomas in interleukin-6-deficient BALB/c mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Garlanda, C.; Riva, F.; Veliz, T.; Polentarutti, N.; Pasqualini, F.; Radaelli, E.; Sironi, M.; Nebuloni, M.; Zorini, E.O.; Scanziani, E.; et al. Increased susceptibility to colitis-associated cancer of mice lacking TIR8, an inhibitory member of the interleukin-1 receptor family. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6017–6021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Goodwin, A.J.; A Cook, J.; Halushka, P.V.; Zingarelli, B.; Fan, H. miR-145a Regulates of Pericyte Dysfunction in a Murine Model of Sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Zhao, X.; Vecchiarelli-Federico, L.M.; Datti, A.; Cheng, Y.; Ben-David, Y. Drug-mediated inhibition of Fli-1 for the treatment of leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ge, T.; Cui, J. FLI-1-driven regulation of endothelial cells in human diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Hamlett, E.D.; Goodwin, A.J.; Halushka, P.V.; Carroll, S.L.; Liu, M.; Fan, H. Suppression of Fli-1 protects against pericyte loss and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Oates, J.C.; Helke, K.L.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Zhang, X.K. Camptothecin and Topotecan, Inhibitors of Transcription Factor Fli-1 and Topoisomerase, Markedly Ameliorate Lupus Nephritis in (NZB × NZW)F1 Mice and Re-duce the Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Human Renal Cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Xia, L.; Yao, Y.; Yan, C.; Fan, Y.; Gajendran, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.-J.; Chen, J.; Filmus, J.; et al. Identification of diterpenoid compounds that interfere with Fli-1 DNA binding to suppress leukemogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yuan, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Yao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Gajendran, B.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Novel flavagline-like compounds with potent Fli-1 inhibitory activity suppress diverse types of leukemia. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 4631–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, C.M.; Gurley, J.M.; Kurylowicz, K.; Lin, P.K.; Chen, W.; Elliott, M.H.; Davis, G.E.; Bhatti, F.; Griffin, C.T. An inhibitor of endothelial ETS transcription factors promotes physiologic and therapeutic vessel regression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26494–26502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhu, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, D.; Li, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, Z.; et al. FLI1 promotes IFN-gamma-induced kynurenine production to impair anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, Y.; Biswas, A.; Kumar, U.; Banerjee, I.; Das, S.; Maji, S.; Das, S.K.; Emdad, L.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mandal, M.; et al. Lumefantrine, an antimalarial drug, reverses radiation and temozolomide resistance in gli-oblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12324–12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamata, K.; Asano, Y.; Aozasa, N.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Sato, S. Bosentan reverses the pro-fibrotic phenotype of systemic sclerosis dermal fibroblasts via increasing DNA binding ability of transcription factor Fli1. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Asano, Y.; Saigusa, R.; Taniguchi, T.; Hirabayashi, M.; Miyagawa, T.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, S.; Yoshizaki, A.; Trojanowska, M.; et al. Cyclophosphamide Pulse Therapy Normalizes Vascular Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of Systemic Sclerosis Vasculopathy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujor, A.M.; Haines, P.; Padilla, C.; Christmann, R.B.; Junie, M.; Sampaio-Barros, P.D.; Lafyatis, R.; Trojanowska, M. Ciprofloxacin has antifibrotic effects in scleroderma fibroblasts via downregulation of Dnmt1 and upregulation of Fli1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Deng, B.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Han, F.; Xiao, X.; Yang, J.; et al. A screen for Fli-1 transcriptional modulators identifies PKC agonists that induce erythroid to megakaryocytic differentiation and suppress leukemogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16728–16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Interleukin | Stimuli | Cell Types In Vitro | Regulation In Vitro * | Regulation Through Binding to Its Promoter | Other Mechanism | Animal Model | Tissue/Cells In Vivo | Regulation In Vivo * | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [23] |
| MRL/lpr mice | Kidney | Positive | [14] | ||||||
| CLP-induced sepsis * | Lung pericytes | Positive | [19] | ||||||
| IL-4 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc * | Skin | Negative | [23] |
| MRL/lpr mice | Splenic T cells | Positive | [21] | ||||||
| IL-6 | LPS | Lung pericytes | Positive | Fli-1 binding to the IL-6 promoter | Fli-1 drives transcription from the IL-6 promoter | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [19,23,24] |
| LPS | Mouse endothelial cells MS1 | Positive | MRL/lpr mice | Serum, kidney and splenic T cells | Positive | [11,14] | |||
| IL-10 | LPS with or without IFNγ | Primary human monocytes | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [23,25] |
| IL-12a | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Positive | [23] |
| MRL/lpr mice | Splenic B cells | Negative | [22] | ||||||
| IL-17A | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [23] |
| MRL/lpr mice | Kidney | Positive | [14] | ||||||
| IL-18 | Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (contain LPS) | Mouse lung pericytes | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | MRL/lpr mice | Kidney | Positive | [14,20] |
| CLP-induced sepsis | Lung pericytes | Positive | [19] | ||||||
| IL-27 | LPS | Mouse peritoneal macrophages, mouse fibroblast L929 | Positive | Directly binds to the IL-27 promoter in mouse peritoneal macrophages | Fli-1 increases IL-27 p28 promoter-controlled gene transcription and cooperates with IRF1 to regulate IL-27 p28 gene expression | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [26] |
| IL-33 | Unknown | Dermal fibroblasts | Negative | Unknown | Both of IL-1β and TNFα induced the dissociation of Fli1 from the IL-33 promoter | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [24] |
| Chemokine | Stimuli | Cell Types In Vitro | Regulation In Vitro a | Regulation Through Binding to Its Promoter | Other Mechanism | Animal Model | Tissue/Cells In Vivo | Regulation In Vivo a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCL2 (MCP-1) | LPS | Lung pericytes, primary endothelial cells from Fli-1 +/− NZM2410 mice and MS1 endothelial cells | Positive | Fli-1 binding to the MCP-1 promoter. Fli-1 drives transcription from the MCP-1 promoter. | Mutation of the Fli-1 DNA binding domain partially inhibits transcriptional activation from the MCP-1 promoter. Fli-1 interacts with the Ets-1 transcription factor to drive transcription from the MCP-1 promoter. Fli-1 and NFκB p65 enhance transcription from the MCP-1 promoter, while NFκB p50 and Sp1 suppress it. Ets-1 binding sites located in the distal and proximal promoter region are important for Fli-1 transcriptional activation. | Bleomycin-induced SSc a | Skin | Negative | [8,23] |
| MRL/lpr mice | kidneys | Positive | [19,30] | ||||||
| NZM2410 mice | Kidney, serum | Positive | [9] | ||||||
| CCL3 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | MRL/lpr mice | kidneys | Positive | [30] |
| CCL4 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | MRL/lpr mice | kidneys | Positive | [30] |
| CCL5 (RANTES) | LPS | Mouse endothelial cells MS1 | Positive | Fli-1 binds to the CCL5 promoter | Fli-1 drives transcription from the CCL5 promoter in a dose-dependent fashion. Ets1 acts as a dominant negative transcription factor to Fli-1 in the context of the CCL5 promoter. Activation of the CCL5 promoter by Fli-1 occurs between −746 bp and −520 bp. Fli-1 drives transcription from the CCL5 promoter more strongly than Ets1. Fli-1 regulates CCL5 through direct binding of the promoter. | MRL/lpr mice | kidneys | Positive | [30] |
| NZM2410 mice | kidneys | Positive | [10] | ||||||
| CXCL2 | LPS or TNFα | Mouse endothelial cells MS1 and HUVECs | Positive | Fli-1 binding to the CXCL2 promoter | Drives transcription from the CXCL2 promoter, Fli-1 regulates CXCL2 expression by directly binding to the promoter. NFκB acts in an additive manner. | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [13] |
| CXCL5 | None | HDMECs | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Fli-1 ECKO mice a | Skin (dermal small vessels) | Positive | [32] |
| CXCL6 | LPS | Human dermal fibroblasts and HDMEC, | Negative | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [33] |
| peritoneal macrophages from Fli1+/− mice | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [33] | ||
| CXCL9 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | MRL/lpr | Kidney | Positive | [31] |
| CXCL10 | Unknown | HUVECs, human renal glomerular endothelial cells (HRGECs), and mouse endothelial MS1 cells | Positive | FLI-1 binds to the Cxcl10 promoter but failed to directly drive transcription from the human CXCL10 promoter | The DNA-binding domain of FLI-1 is necessary for its regulation of CXCR3 promoter activity in T cells | MRL/lpr | Kidney | Positive | [31,34] |
| CXCL13 | LPS | Peritoneal macrophages from Fli1+/− mice | Negative | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [35] |
| Inflammatory Mediators | Stimuli | Cell Types In Vitro | Regulation In Vitro a | Regulation Through Binding to Its Promoter | Other Mechanism | Animal Model | Tissue/Cells In Vivo | Regulation In Vivo a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-CSF | LPS | Lung pericytes, MS1 mouse endothelial cells, and HUVECs | Positive | Fli-1 binds to the proximal region of the G-CSF promoter. Fli-1 drives transcription from the G-CSF promoter. | Fli-1 regulates G-CSF expression by directly binding to the promoter. The role of acetylation in Fli-1 driven activation of the G-CSF promoter. | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [12,19] |
| GM-CSF | LPS, TNFα, IFNγ | T cells and HUVECs | Positive | Fli-1 binds directly to the GM-CSF promoter | Mutation of a known phosphorylation site within the Fli-1 protein led to a significant increase in GM-CSF promoter activation. | Unknown | T cells | Positive | [36] |
| MMP (MMP1, MMP3, MMP10) | LPS with or without IFNγ | Primary human monocytes | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [25] |
| MMP1 | / | Normal dermal fibroblasts | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [37] |
| Caspase-1 | OMV (contain LPS) | Mouse lung pericytes | Positive | Binding to its promoter | Fli-1 drives transcription from the caspase-1 promoter. | CLP-induced sepsis mice | Lung pericytes | Positive | [19,20] |
| Platelet factor 4 (PF4) | FLI-1 vector | HepG2 cells | Positive | FLI-1, ELF-1, and GABP bind to the −51 ETS site. FLI-1, ELF-1, and GABP activate the PF4 promoter through the −51 ETS site. | FLI-1 and GATA-1 synergistically activate the PF4 promoter. FLI-1 activates the PF4 promoter through the −51 ETS site. | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [38] |
| Chemerin | NA | HDMEC | Negative | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc a | Skin | Negative | [39] |
| TNFα | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [23] |
| Caspase-11 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | CLP-induced sepsis mice a | Lung pericytes | Positive | [19] |
| IFNγ | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bleomycin-induced SSc | Skin | Negative | [23] |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) | LPS | Lung pericytes | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [19] |
| Keratinocyte chemoattractant | LPS | Lung pericytes | Positive | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [19] |
| Flt3L (Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand) | Flt3L, stem cell factor, IL-6, IL-6R, long-range insulin-like growth factor-1. | Multipotent progenitors (MPPs) from Fli-1∆CTA/∆CTA B6 mice | Positive | Fli-1 binding to the Flt3L promoter. | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [7] |
| Single immunoglobulin IL-1 related receptor (SIGIRR) | Ewing tumor cells | EWSR1-FLI1 fusion reduction | Unknown | Unknown | Interacting with the TGFBR2 promoter to suppress transcriptional activity. | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | [40] |
| Drug | Disease |
|---|---|
| Suppression of Fli-1 | |
| Antisense oligonucleotide Fli-1 Gapmer | Alzheimer’s disease [66] |
| Calcimycin | Leukemia [64] |
| Camptothecin, topotecan, and etoposide | Graft-versus-host disease [41], lupus nephritis [67], and hematologic tumors [64] |
| A665, A661, A1544, and A1545 | Hematologic tumors [68,69] |
| YK-4-279 | Vascular proliferative disorders and tumors [70,71] |
| Lumefantrine | Glioblastomae [72] |
| Activation of Fli-1 | |
| Bosentan, ciprofloxacin, and cyclophosphamide | Scleroderma [73,74,75] |
| Phorbol ester-like compounds | Hematologic tumors [76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, X.K. Role of Transcription Factor Fli-1 in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040480
Wang X, Zhang XK. Role of Transcription Factor Fli-1 in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040480
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuan, and Xian K. Zhang. 2025. "Role of Transcription Factor Fli-1 in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040480
APA StyleWang, X., & Zhang, X. K. (2025). Role of Transcription Factor Fli-1 in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases. Biomolecules, 15(4), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040480








