Similar Structures to the E-to-H Helix Unit in the Globin-Like Fold are Found in Other Helical Folds
Abstract
:1. Introduction



2. Results
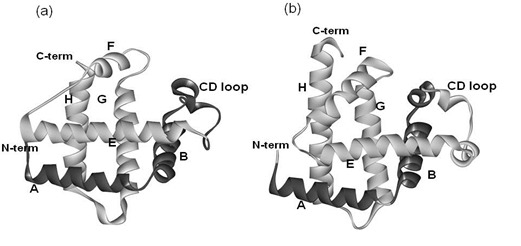
2.1. Dali Search and ADM Analyses

| Protein(Source, PDB ID) | Family | Fold | Region Hit by DALI Search with the Following Query(Z Score, rmsd(a)) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leghemoglobin E-to-H (Soy Bean, 1fsl) | Myoglobin E-to-H (Sperm Whale, 1mbn) | |||
| circadian clock protein Kai A (Synechococcus, 1R8J) | Circadian clock protein KaiA, C-terminal domain | KaiA/RbsU domain | E-to-H helices (4.4, 3.8) | E-to-H helices (7.0, 3.3) |
| secretion control protein A chain(Yersinia, 1XL3) | LcrE-like | Type III secretion system domain | EGH helices (2.0, 4.5) | FGH helices (4.1, 3.9) |
| cell invasion protein SipA (Salmonella, 2FM9) | SipA N-terminal domain-like | SipA N-terminal domain-like | E-to-H helices (2.9, 9.3) | H helix (3.0, 8.0) |
| transcriptional regulator RHA1_ro04179 (Rodococcus, 2NP5) | Tetracyclin repressor-like, C-terminal domain | Tetracyclin repressor-like, C-terminal domain | GH helices (4.4, 9.7) | GH helices (2.1, 4.7) |
| hypothetical protein AF0060 (E. coli, 2P06) | AF0060-like | all-alpha NTP pyrophosphatases | GH helices with a part of the E helix (3.2, 4.8) | GH helices (3.5, 3.5) |

2.2. Detailed Comparisons of the Folding Units Predicted by ADMs with a Region Hit by the Dali Search
| Protein (PDB ID) | Predicted Folding Unit | η Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1FSL | 9–34 | 0.228 |
| 65–140 | 0.324 | |
| 1MBN | 7–33 | 0.273 |
| 99–151 | 0.276 | |
| 1R8J | 5–34 | 0.218 |
| 51–82 | 0.203 | |
| 223–270 | 0.254 | |
| 1XL3 | 3–44 | 0.195 |
| 77–99 | 0.202 | |
| 124–201 | 0.297 | |
| 2FM9 | 1–51 | 0.292 |
| 79–115 | 0.157 | |
| 166–199 | 0.297 | |
| 2NP5 | 5–38 | 0.253 |
| 76–103 | 0.175 | |
| 128–186 | 0.372 | |
| 2P06 | 3–83 | 0.370 |
2.2.1. Circadian Clock Protein KaiA (1R8J)

2.2.2. Secretion Control Protein (1XL3)
2.2.3. Cell Invasion Protein SipA (2FM9)
2.2.4. Transcriptional Regulator RHA1_ro04179 (2NP5)
2.2.5. Hypothetical Protein AF0060 (2P06)

2.3. Conserved Residues in the E-to-H Unit
| Protein(Source, PDB) | Number of Homologs | Number of Conserved Residue | Number of Residues Containing E-to-H Helices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leghemoglobin (soybean 1FSl) | 45 | 34 | 88 |
| Myoglobin (sperm whale 1MBN) | 82 | 38 | 96 |
| Circadian clock protein KaiA (Synechococcus, 1R8J) | 49 | 50 | 98 |
| Secretion control protein) A chain (Yersinia, 1XL3) | 29 | 25 | 76 |
| Cell invasion protein SipA (Salmonella, 2FM9) | 6 | 0 | 79 |
| Transcriptional regulator RHA1_ro04179 (Rodococcus, 2NP5) | 3 | 0 | 74 |
| Hypothetical protein AF0060 (E. coli, 2P06) | 0 | 0 | 81 |

2.4. Residues Involved in Hydrophobic Packing Assigned Based on Buried Surface
2.5. Common Residue Patterns Specific to the E-to-H Helix Unit Defined from the Packing Patterns of Conserved Hydrophobic Residues
| Protein | E Helix | G Helix | H Helix |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1FSL | φx(2)φx(4)φ | φx(3)φ(2)x(2)φ | φx(2)φ(2)x(2)φ |
| 1MBN | φx(3)φx(3)φ | φx(3)φ(2)x(2)φ | φx(2)φ(2)x(2)φ |
| 1R8J | φx(3)φx(3)φ | φx(3)φ(2)x(2)φ | φx(2)φx(3)φ |
| 1XL3 | φx(3)φx(3)φ | φx(2)φ(2)x(3)φ | φx(2)φ(2)x(3)φ |
| 2FM9 | — | φx(6)φ | φx(10)φ |
| 2NP5 | φx(2)φx(3)φ | φx(3)φ(2)x | φx(3)φ(2)x(2)φ |
| 2P06 | — | φx(3)φ | φx(3)φ(2)x(1)φ |
3. Discussion

4. Method
4.1. Search Protein 3D Structures Similar to that of the E-to-H Helix Unit in Leghemoglobin
4.2. Prediction of Compact Regions Based on the Average Distance Map Method
 , where N is the total number of residues of a protein and C is an adjustable constant, approximately predicts the average values of the contact density of the entire region of an RDM [5]. C = 36.12, which corresponds to the 15Å threshold for the construction of an RDM, is used in the present work [5]. The cutoff distances for the construction of an ADM from the amino acid sequence of a protein are determined to reproduce a value of
, where N is the total number of residues of a protein and C is an adjustable constant, approximately predicts the average values of the contact density of the entire region of an RDM [5]. C = 36.12, which corresponds to the 15Å threshold for the construction of an RDM, is used in the present work [5]. The cutoff distances for the construction of an ADM from the amino acid sequence of a protein are determined to reproduce a value of  . A different cutoff distance is found for a different range to construct an ADM, whereas in the case of an RDM construction just one cutoff distance is required. In the construction of an ADM, it is assumed that the number of residue pairs that make contacts (and should therefore be plots on a map) obeys the following Equation in a range M [5]:
. A different cutoff distance is found for a different range to construct an ADM, whereas in the case of an RDM construction just one cutoff distance is required. In the construction of an ADM, it is assumed that the number of residue pairs that make contacts (and should therefore be plots on a map) obeys the following Equation in a range M [5]:

 represent the contact density of the triangular and trapezoidal parts, respectively, when the whole area of a map is divided into two parts by a line parallel to the abscissa at the i-th residue or by a line parallel to the ordinate at the i-th residue as illustrated in Figure 10a and 10b. The contact density difference value is defined as
represent the contact density of the triangular and trapezoidal parts, respectively, when the whole area of a map is divided into two parts by a line parallel to the abscissa at the i-th residue or by a line parallel to the ordinate at the i-th residue as illustrated in Figure 10a and 10b. The contact density difference value is defined as  .
. and ρi, respectively.
and ρi, respectively.
 and ρi, respectively.
and ρi, respectively.
 or
or  .
.
 or
or  .
.
 (Figure 11b) [5].
(Figure 11b) [5].4.3. Identification of Residues Forming Hydrophobic Packing
4.4. Identification of Conserved Residues in the E-to-H Helix Unit in Each Protein
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orengo, C.A.; Jones, D.T.; Thornton, J.M. Protein superfamilies and domain superfolds. Nature 1994, 372, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Álvarez-Salgado, E.; Kikuchi, T.; Arredondo-Peter, R. Prediction of folding pathway and kinetics among plant hemoglobins by using an average distance map method. Proteins 2005, 61, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, C.; Prytulla, S.; Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Conservation of folding pathways in evolutionarily distant globin sequences. Nature Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L.; Park, J. DaliLite workbench for protein structure comparison. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Némethy, G.; Scheraga, H.A. Prediction of the location of structural domains in globular proteins. J. Protein Chem. 1988, 7, 427–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T. Decoding s of proteins using inter-residue average distance statistics to extract information on protein folding mechanisms. In Protein Folding; Walters, E.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 465–487, ISBN 978-1-61728-990-32011. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, C.H.; Sam, V.; Gibrat, J.F.; Garnier, J.; Munson, P.J.; Lee, B. Protein domain assignment from the recurrence of locally similar structures. Proteins 2011, 79, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szustakowski, J.D.; Kasif, S.; Weng, Z. Less is more: Towards an optimal universal description of protein folds. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, ii66–ii71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlacci, L.; Chou, K.C. Energetic approach to the folding of four a-helices connected sequentially. Protein Eng. 1990, 3, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Maggiora, G.M.; Némethy, G.; Scheraga, H.A. Energetics of the structure of the four-alpha-helix bundle in proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 8, 4295–4299. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, K.C.; Maggiora, G.M.; Scheraga, H.A. The role of loop-helix interactions in stabilizing four-helix bundle proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7315–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Némethy, G.; Pottle, M.; Scheraga, H.A. Energy of stabilization of the right-handed beta-alpha-beta crossover in proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 205, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Némethy, G.; Scheraga, H.A. Energetic approach to packing of a-helices: 2. General treatment of nonequivalent and nonregular helices. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C. Review: Applications of graph theory to enzyme kinetics and protein folding kinetics. Steady and non-steady state systems. Biophys. Chem. 1990, 35, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C. Does the folding type of a protein depend on its amino acid composition? FEBS Lett. 1995, 363, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Carlacci, L. Energetic approach to the folding of alpha/beta barrels. Proteins 1991, 9, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Zhang, C.T. Predicting protein folding types by distance functions that make allowances for amino acid interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22014–22020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.T.; Chou, K.C. An eigenvalue-eigenvector approach to predicting protein folding types. J. Protein Chem. 1995, 14, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, M.; Chou, K.C.; Némethy, G.; Scheraga, H.A. Energetics of multi-helix interactions in protein folding: Application to myoglobin. Biopolymers 1985, 24, 1271–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Lin, W.Z.; Xiao, X. Wenxiang: A web-server for drawing wenxiang diagrams. Natur. Sci. 2011, 3, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Zhang, C.T.; Maggiora, G.M. Disposition of amphiphilic helices in heteropolar environments. Proteins 1997, 28, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.P. The disposition of the LZCC protein residues in wenxiang diagram provides new insights into the protein-protein interaction mechanism. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 284, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.P. The Structural Determinations of the leucine zipper coiled-coil domains of the cgmp-dependent protein kinase i alpha and its interaction with the myosin binding subunit of the myosin light chains phosphase. Protein Peptide Lett. 2011, 18, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.P.; Huang, R.B. The pH-triggered conversion of the PrP(c) to PrP(sc.). Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Matsuoka, M.; Kikuchi, T. Analyses of Protein Sequences Using Inter-Residue Average Distance Statistics to Study Folding Processes and the Significance of Their Partial Sequences. Protein Peptide Lett. 2011, 18, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimaru, T.; Kikuchi, T. Analysis of the differences in the folding kinetics of structurally homologous proteins based on predictions of the gross features of residue contacts. Proteins 2003, 51, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, Y.; Kikuchi, T. Analysis of the Local Sequences of Folding Sites in β Sandwich Proteins with Inter-Residue Average Distance Statistics. Open Bioinforma. J. 2011, 5, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Kikuchi, T. Analysis of the differences in the folding mechanisms of c-type lysozymes based on contact maps constructed with interresidue average distances. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrake, A.; Rupley, J.A. Environment and exposure to solvent of protein atoms. Lysozyme and insulin. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 79, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuoka, M.; Fujita, A.; Kawai, Y.; Kikuchi, T. Similar Structures to the E-to-H Helix Unit in the Globin-Like Fold are Found in Other Helical Folds. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 268-288. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010268
Matsuoka M, Fujita A, Kawai Y, Kikuchi T. Similar Structures to the E-to-H Helix Unit in the Globin-Like Fold are Found in Other Helical Folds. Biomolecules. 2014; 4(1):268-288. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010268
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuoka, Masanari, Aoi Fujita, Yosuke Kawai, and Takeshi Kikuchi. 2014. "Similar Structures to the E-to-H Helix Unit in the Globin-Like Fold are Found in Other Helical Folds" Biomolecules 4, no. 1: 268-288. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010268
APA StyleMatsuoka, M., Fujita, A., Kawai, Y., & Kikuchi, T. (2014). Similar Structures to the E-to-H Helix Unit in the Globin-Like Fold are Found in Other Helical Folds. Biomolecules, 4(1), 268-288. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010268