Two-Dimensional N-Glycan Distribution Mapping of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues by MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. FFPE Tissues
2.3. Washes for Deparaffinization and Rehydration
2.4. N-Glycan MALDI-IMS
2.5. Ethyl Esterification
2.6. Lectin Histochemistry
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Histopathology on MALDI-IMS of N-Glycans
| MALDI-IMS | Ethyl Esterification | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Glycan | Database m/z | Observed | m/z | Observed | m/z |
| Hex5HexNAc2 | 1257.422 | Yes | 1257.497 | Yes | 1257.422 |
| Hex4HexNAc3 | 1298.449 | Yes | 1298.522 | Yes | 1298.450 |
| Hex6HexNAc2 | 1419.476 | Yes | 1419.530 | Yes | 1419.473 |
| Hex4dHex1HexNAc3 | 1444.507 | Yes | 1444.546 | Yes | 1444.507 |
| Hex3dHexHexNAc4 | 1485.534 | Yes | 1485.587 | Yes | 1485.540 |
| Hex4HexNAc4 | 1501.529 | Yes | 1501.592 | Yes | 1501.536 |
| Hex7HexNAc2 | 1581.528 | Yes | 1581.562 | Yes | 1581.532 |
| Hex4dHex1HexNAc4 | 1647.587 | Yes | 1647.617 | Yes | 1647.589 |
| Hex5HexNAc4 | 1663.581 | Yes | 1663.582 | Yes | 1663.591 |
| Hex8HexNAc2 | 1743.581 | Yes | 1743.562 | Yes | 1743.592 |
| Hex5dHex1HexNAc4 | 1809.639 | Yes | 1809.661 | Yes | 1809.644 |
| Hex4dHex1HexNAc5 | 1850.666 | Yes | 1850.686 | Yes | 1850.683 |
| Hex5HexNAc5 | 1866.661 | Yes | 1866.663 | Yes | 1866.686 |
| Hex9HexNAc2 | 1905.634 | Yes | 1905.612 | Yes | 1905.647 |
| Hex5HexNAc4NeuAc1 | 1954.677 | Yes | 1954.589 | Yes | 1936.692 a |
| 1976.707 e | 1982.733 b | ||||
| Hex5dHex2HexNAc4 | 1955.697 | Yes | 1955.692 | Yes | 1955.719 |
| Hex5dHex1HexNAc5 | 2012.719 | Yes | 2012.711 | Yes | 2012.745 |
| Hex6HexNAc5 | 2028.714 | Yes | 2028.737 | Yes | 2028.737 |
| Hex5dHex1HexNAc4NeuAc1 | 2100.735 | Yes | 2100.759 | Yes | 2082.733 a |
| 2122.720 e | 2128.798 b | ||||
| Hex5dHex2HexNAc5 | 2158.777 | Yes | 2158.806 | No | N/A |
| Hex6dHex1HexNAc5 | 2174.772 | Yes | 2174.768 | Yes | 2174.807 |
| Hex5dHex1HexNAc6 | 2215.798 | Yes | 2215.847 | Yes | 2215.837 |
| Hex6HexNAc6 | 2231.973 | No | N/A | Yes | 2231.828 |
| Hex6HexNAc5NeuAc1 | 2319.809 | Yes | 2319.804 | Yes | 2301.869 a |
| 2341.804 e | 2347.878 b | ||||
| Hex6dHex2HexNAc5 | 2320.829 | Yes | 2320.746 | Yes | 2320.902 |
| Hex6dHex1HexNAc6 | 2377.851 | Yes | 2377.859 | Yes | 2377.897 |
| Hex7HexNAc6 | 2393.846 | Yes | 2393.796 | Yes | 2393.888 |
| Hex6dHex1HexNAc5NeuAc1 | 2465.867 | Yes | 2465.803 | Yes | 2447.904 a |
| 2487.886 e | 2493.916 b | ||||
| Hex6dHex3HexNAc5 | 2466.887 | Yes | 2466.716 | No | N/A |
| Hex7dHex1HexNAc6 | 2539.904 | Yes | 2539.856 | Yes | 2539.886 |
| Hex7dHex2HexNAc6 | 2685.962 | Yes | 2686.010 | Yes | 2686.028 |
| Hex6dHex1HexNAc5NeuAc2 | 2756.962 | Yes | 2756.976 | Yes | 2767.056 c |
| 2778.961 e | 2813.066 d | ||||
| Hex8HexNAc7 | 2758.978 | Yes | 2758.976 | No | N/A |


3.2. Similarities of Glycan Distribution across Tissue Types

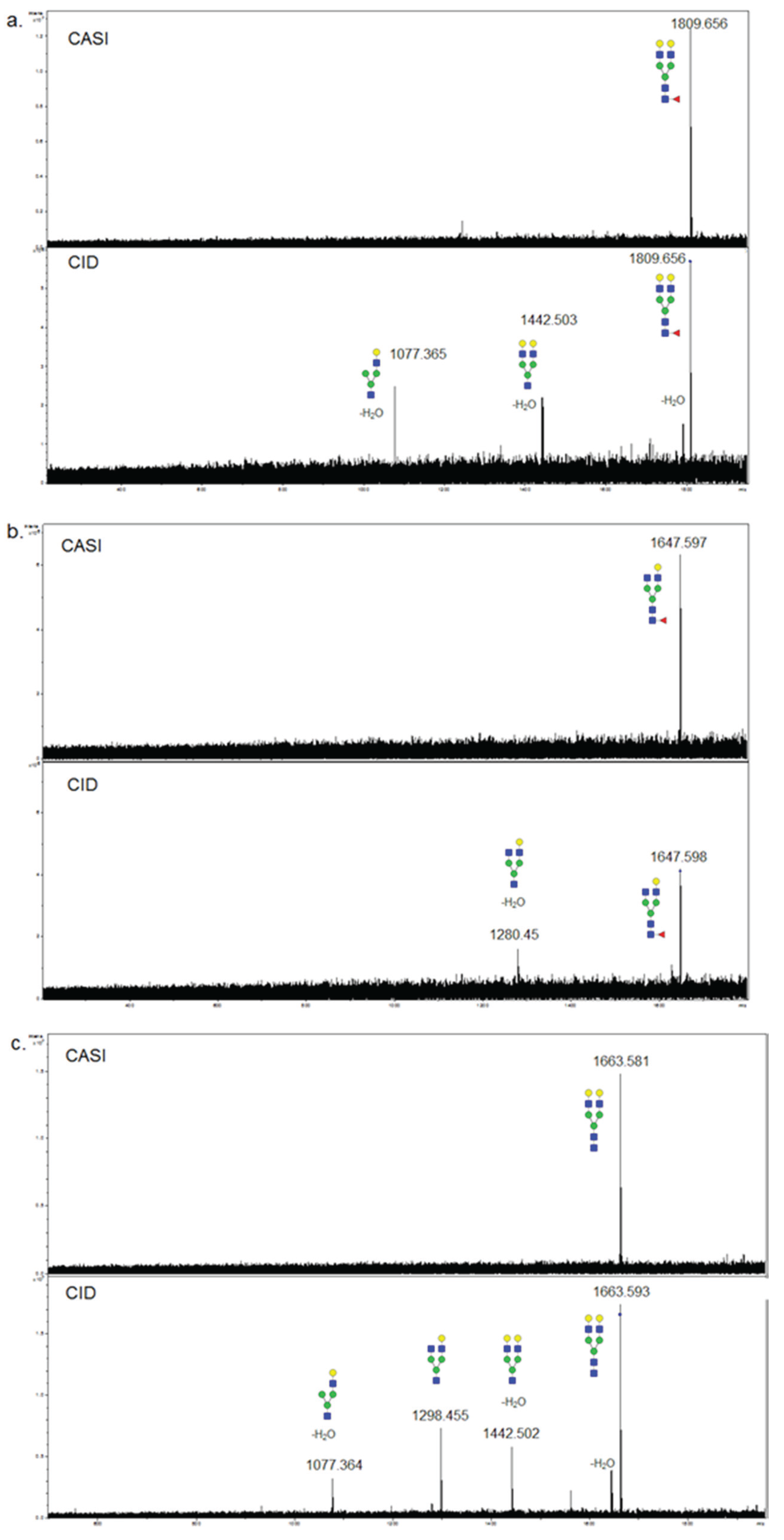
3.3. Validation of N-Glycans Structures by off-Slide Glycomic Analysis

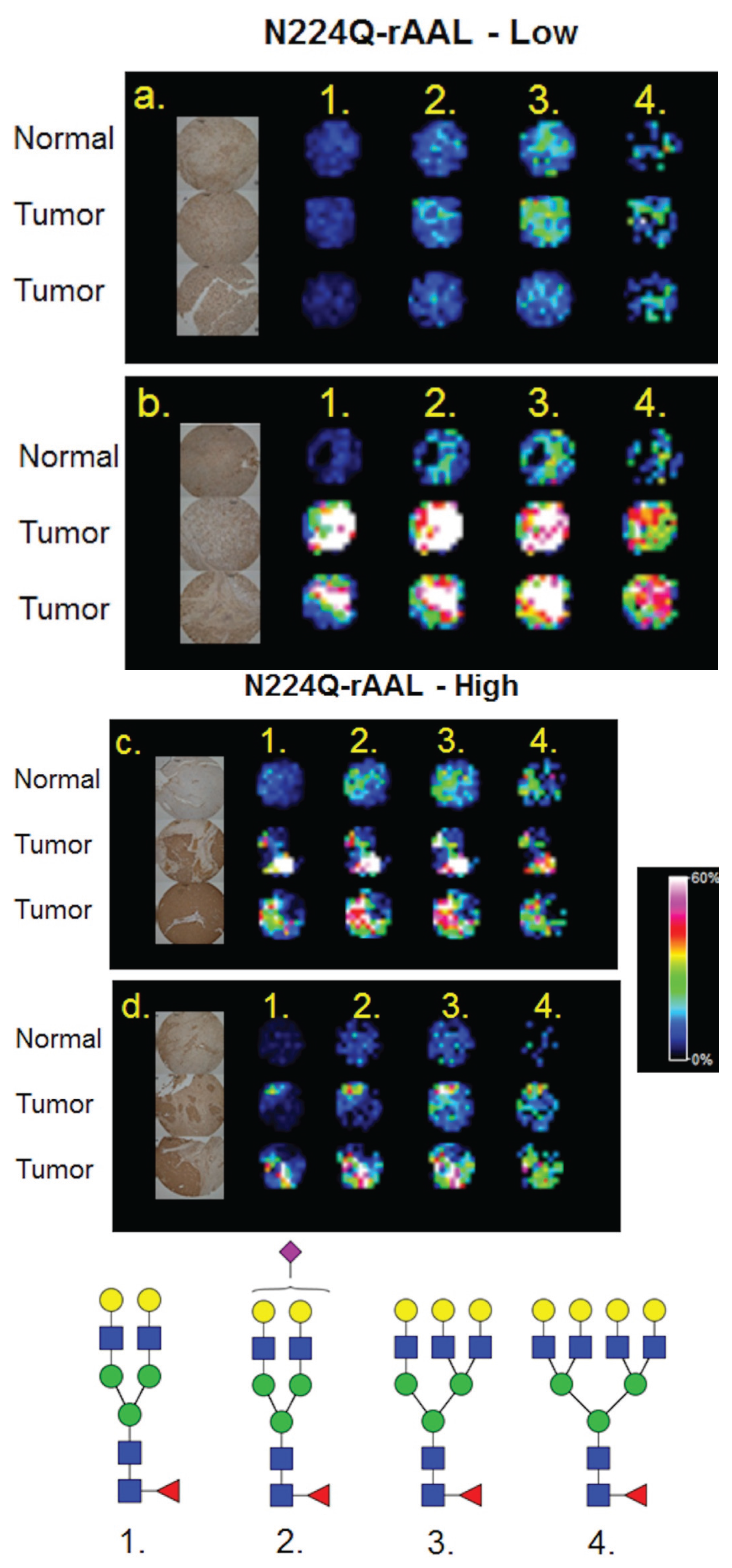
3.4. Detection of Core Fucosylation in HCC Tissue Microarrays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Block, T.M.; Mehta, A.S.; Fimmel, C.J.; Jordan, R. Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5093–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Herrera, H.; Block, T. Glycosylation and liver cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 126, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiao, B.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Niu, Y.; Ye, S.; Wan, Q.; Ye, Q. Detection and identification of peroxiredoxin 3 as a biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma by a proteomic approach. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ai, J.; Tan, Y.; Ying, W.; Hong, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, M.; Qian, X.; Wang, H. Proteome analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma by laser capture microdissection. Proteomics 2006, 6, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ki, S.S.; Lee, S.D.; Han, C.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, S.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Hong, H.J.; Park, M.; Lee, H.Y.; et al. Elevated plasma osteopontin levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.X.; Xia, Y.H.; Cui, J.F.; Xue, T.C.; Ye, S.L. Osteopontin, a single marker for predicting the prognosis of patients with tumor-node-metastasis stage I hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Plymoth, A.; Ge, S.; Feng, Z.; Rosen, H.R.; Sangrajrang, S.; Hainaut, P.; Marrero, J.A.; Beretta, L. Identification of osteopontin as a novel marker for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 55, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buamah, P.K.; Cornell, C.; Cassells-Smith, A.J.; Harris, A.L. Fucosylation of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinomas. Lancet 1986, 1, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, Y. Molecular discrimination between alpha-fetoprotein from patients with hepatocellular-carcinoma and nonneoplastic liver-diseases by their carbohydrate structures (review). Int. J. Oncol. 1994, 4, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, Y.; Isokawa, O.; Suda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Asakura, H. The fucosylation index of alpha-fetoprotein as a possible prognostic indicator for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 1998, 83, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naitoh, A.; Aoyagi, Y.; Asakura, H. Highly enhanced fucosylation of serum glycoproteins in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1999, 14, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comunale, M.A.; Lowman, M.; Long, R.E.; Krakover, J.; Philip, R.; Seeholzer, S.; Evans, A.A.; Hann, H.W.; Block, T.M.; Mehta, A.S. Proteomic analysis of serum associated fucosylated glycoproteins in the development of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comunale, M.A.; Rodemich-Betesh, L.; Hafner, J.; Wang, M.; Norton, P.; di Bisceglie, A.M.; Block, T.; Mehta, A. Linkage specific fucosylation of alpha-1-antitrypsin in liver cirrhosis and cancer patients: Implications for a biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comunale, M.A.; Wang, M.; Hafner, J.; Krakover, J.; Rodemich, L.; Kopenhaver, B.; Long, R.E.; Junaidi, O.; Bisceglie, A.M.; Block, T.M.; et al. Identification and development of fucosylated glycoproteins as biomarkers of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Romano, P.R.; Nikolaeva, O.; Steel, L.; Mehta, A.; Fimmel, C.J.; Comunale, M.A.; D’Amelio, A.; Lok, A.S.; Block, T.M. GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is a novel serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelle, W.; Flahaut, C.; Michalski, J.C.; Louvet, A.; Mathurin, P.; Klein, A. Mass spectrometric approach for screening modifications of total serum N-glycome in human diseases: Application to cirrhosis. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.E.; Desmyter, L.; Gao, C.F.; Laroy, W.; Dewaele, S.; Vanhooren, V.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H.; Callewaert, N.; Libert, C.; et al. N-glycomic changes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with liver cirrhosis induced by hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldman, R.; Ressom, H.W.; Varghese, R.S.; Goldman, L.; Bascug, G.; Loffredo, C.A.; Abdel-Hamid, M.; Gouda, I.; Ezzat, S.; Kyselova, Z.; et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma using glycomic analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1808–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Norton, P.; Liang, H.; Comunale, M.A.; Wang, M.; Rodemich-Betesh, L.; Koszycki, A.; Noda, K.; Miyoshi, E.; Block, T. Increased levels of tetraantennary N-linked glycan but not core fucosylation are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma tissue. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, T.W.; Jones, E.E.; Betesh, L.R.; Romano, P.R.; Gao, P.; Copland, J.A.; Mehta, A.S.; Drake, R.R. Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization imaging mass spectrometry workflow for spatial profiling analysis of N-linked glycan expression in tissues. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9799–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, T.W.; Neely, B.A.; Shao, Y.; Tang, H.; Troyer, D.A.; Mehta, A.S.; Haab, B.B.; Drake, R.R. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry profiling of N-glycans in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded clinical tissue blocks and tissue microarrays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiding, K.R.; Blank, D.; Kuijper, D.M.; Deelder, A.M.; Wuhrer, M. High-throughput profiling of protein N-glycosylation by MALDI-TOF-MS employing linkage-specific sialic acid esterification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5784–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Weinstein, J.N. Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.J.; Kronewitter, S.R.; de Leoz, M.L.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycomics and disease markers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceroni, A.; Maass, K.; Geyer, H.; Geyer, R.; Dell, A.; Haslam, S.M. GlycoWorkbench: A Tool for the computer-assisted annotation of mass spectra of glycans. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.H.; Hemayatkar, M.; Deelder, A.M.; Wuhrer, M. Cotton HILIC SPE microtips for microscale purification and enrichment of glycans and glycopeptides. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, P.R.; Mackay, A.; Vong, M.; DeSa, J.; Lamontagne, A.; Comunale, M.A.; Hafner, J.; Block, T.; Lec, R.; Mehta, A. Development of recombinant Aleuria aurantia lectins with altered binding specificities to fucosylated glycans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, R.R.; Jones, E.E.; Powers, T.W.; Nyalwidhe, J.O. Altered glycosylation in prostate cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 126, 345–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawano, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Miyama, T.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. Prediction of glycan structures from gene expression data based on glycosyltransferase reactions. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3976–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, A.; Yamanishi, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. An improved scoring scheme for predicting glycan structures from gene expression data. Genome Inform. 2007, 18, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F.; Kanehisa, M. Glycomic analysis using KEGG GLYCAN. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1273, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saba, J.; Dutta, S.; Hemenway, E.; Viner, R. Increasing the productivity of glycopeptides analysis by using higher-energy collision dissociation-accurate mass-product-dependent electron transfer dissociation. Int. J. Proteomics 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, B.L.; Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Solis, N.; Scott, N.E.; Larsen, M.R.; Graham, M.E.; Packer, N.H.; Cordwell, S.J. Site-specific glycan-peptide analysis for determination of N-glycoproteome heterogeneity. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5791–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaia, J. Mass spectrometry and glycomics. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2010, 14, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechref, Y.; Kang, P.; Novotny, M.V. Differentiating structural isomers of sialylated glycans by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelle, W.; Michalski, J.C. Analysis of protein glycosylation by mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, D.J. Structural determination of N-linked glycans by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, P.B.; Costello, C.E. A high pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization fourier transform mass spectrometry ion source for thermal stabilization of labile biomolecules. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 15, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, P.B.; Mirgorordskaya, E.; Costello, C.E. High pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization Fourier transform mass spectrometry for minimization of ganglioside fragmentation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 13, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Terasawa, K.; Kaneshiro, K.; Uchimura, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Fukuyama, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Sato, T.A.; Tanaka, K. Improvement of mass spectrometry analysis of glycoproteins by MALDI-MS using 3-aminoquinoline/α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4289–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, D.J. Derivatization of carbohydrates for analysis by chromatography; electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 1196–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Yang, S.; Sun, S.; Aiyetan, P.; Yarema, K.J.; Zhang, H. Mass spectrometric analysis of sialylated glycans with use of solid-phase labeling of sialic acids. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deininger, S.O.; Cornett, D.S.; Paape, R.; Becker, M.; Pineau, C.; Rauser, S.; Walch, A.; Wolski, E. Normalization in MALDI-TOF imaging datasets of proteins: Practical considerations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadonte, R.; Caprioli, R.M. Proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, S.; Wuhrer, M.; Rombouts, Y. Glycosylation characteristics of colorectal cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 126, 203–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Hsueh, P.; Kletter, D.; Bern, M.; Haab, B. The detection and discovery of glycan motifs in biological samples using lectins and antibodies: New methods and opportunities. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 126, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, O.J.; Briggs, M.T.; Condina, M.R.; Winderbaum, L.J.; Pelzing, M.; McColl, S.R.; Everest-Dass, A.V.; Packer, N.H.; Hoffmann, P. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry of N-linked glycans on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded murine kidney. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Powers, T.W.; Holst, S.; Wuhrer, M.; Mehta, A.S.; Drake, R.R. Two-Dimensional N-Glycan Distribution Mapping of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues by MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2554-2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042554
Powers TW, Holst S, Wuhrer M, Mehta AS, Drake RR. Two-Dimensional N-Glycan Distribution Mapping of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues by MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules. 2015; 5(4):2554-2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042554
Chicago/Turabian StylePowers, Thomas W., Stephanie Holst, Manfred Wuhrer, Anand S. Mehta, and Richard R. Drake. 2015. "Two-Dimensional N-Glycan Distribution Mapping of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues by MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry" Biomolecules 5, no. 4: 2554-2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042554
APA StylePowers, T. W., Holst, S., Wuhrer, M., Mehta, A. S., & Drake, R. R. (2015). Two-Dimensional N-Glycan Distribution Mapping of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues by MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules, 5(4), 2554-2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042554






