Combination of Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Application: A Review
Abstract
:1. Cell-Penetrating Peptides
1.1. Mechanism of Penetration
1.2. Cell-Penetrating Peptide Therapeutics Potential: Delivery Molecules
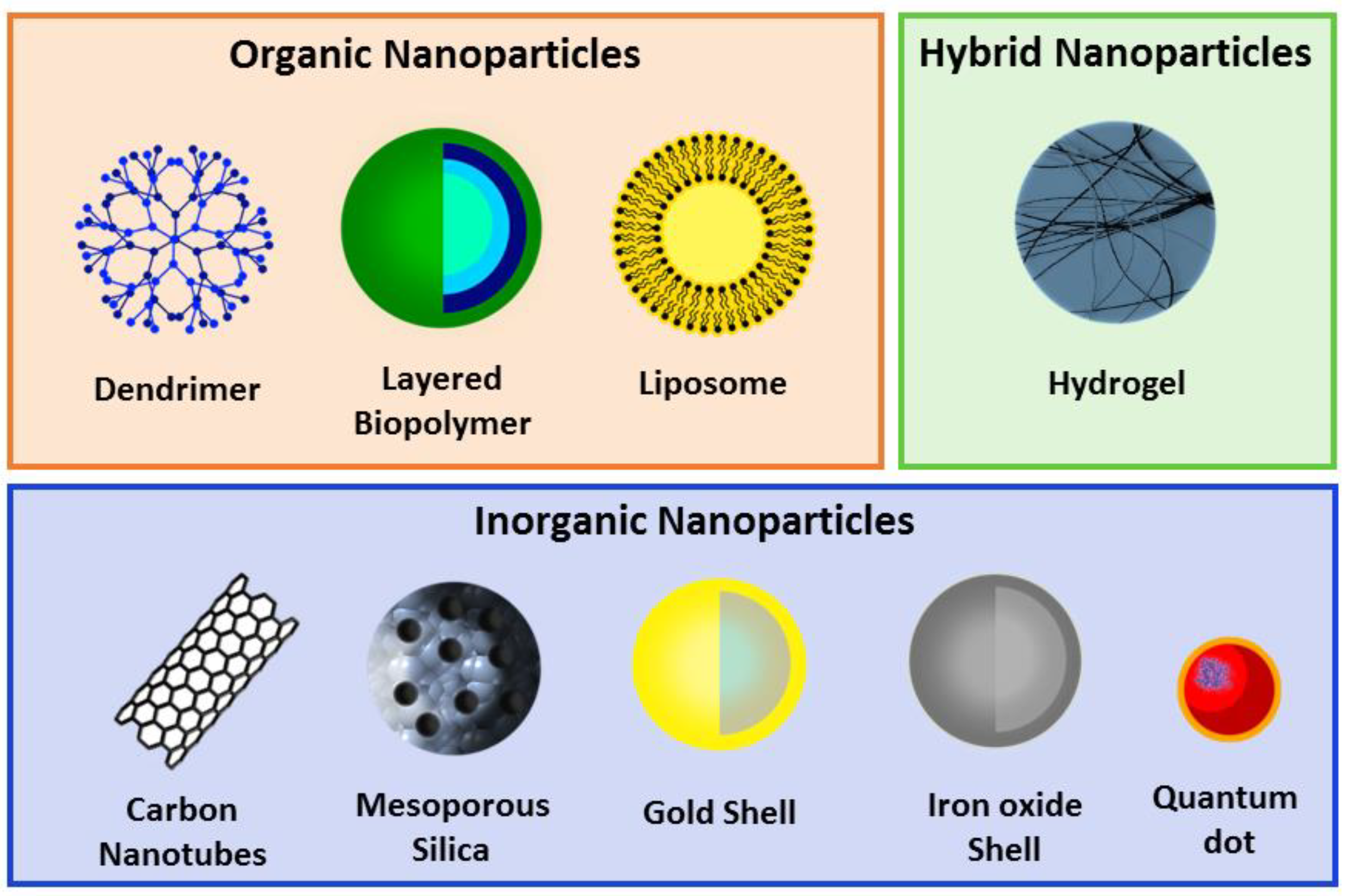
2. Nanoparticles
3. Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugation with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Applications
3.1. Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Nanoparticles in Cancer
3.2. Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Nanoparticles as Imaging Agents
3.3. Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Nanoparticles in Inflammation
3.4. Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Nanoparticles in Central Nervous System Disorders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zorko, M.; Langel, Ü. Cell-penetrating peptides: Mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, P.; Langel, U. A brief introduction to cell-penetrating peptides. J. Mol. Recognit. 2003, 16, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Temsamani, J.; Vidal, P. The use of cell-penetrating peptides for drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, A.D.; Pabo, C.O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell 1988, 55, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivès, E.; Brodin, P.; Lebleu, B. A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16010–16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joliot, A.; Pernelle, C.; Deagostini-Bazin, H.; Prochiantz, A. Antennapedia homeobox peptide regulates neural morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Joliot, A.H.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10444–10450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Calvet, S.; Trembleau, A.; Brunissen, A.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. Cell internalization of the third helix of the antennapedia homeodomain is receptor-independent. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18188–18193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Singh, H.; Tyagi, A.; Chaudhary, K.; Kumar, R.; Kapoor, P.; Raghava, G.P.S. CPPsite: A curated database of cell penetrating peptides. Database 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.S.; Jiang, T.; Aguilera, T.A.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Ellies, L.G.; Scadeng, M.; Tsien, R.Y. Activatable cell penetrating peptides linked to nanoparticles as dual probes for in vivo fluorescence and MR imaging of proteases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4311–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Sato, Y.; Akita, H.; Takayama, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Futaki, S.; Harashima, H. Endosomal escape and the knockdown efficiency of liposomal-siRNA by the fusogenic peptide shGALA. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5733–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, T.A.; Olson, E.S.; Timmers, M.M.; Jiang, T.; Tsien, R.Y. Systemic in vivo distribution of activatable cell penetrating peptides is superior to that of cell penetrating peptides. Integr. Biol. 2009, 1, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, T.; Morisaki, K.; Suzuki, S.; Takashima, Y. Prolongation of life in rats with malignant glioma by intranasal siRNA/drug codelivery to the brain with cell-penetrating peptide-modified micelles. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Modgil, A.; Layek, B.; Arora, K.; Sun, C.; Law, B.; Singh, J. Cell penetrating peptide tethered bi-ligand liposomes for delivery to brain in vivo: Biodistribution and transfection. J. Control. Release 2013, 167, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wender, P.A.; Mitchell, D.J.; Pattabiraman, K.; Pelkey, E.T.; Steinman, L.; Rothbard, J.B. The design, synthesis, and evaluation of molecules that enable or enhance cellular uptake: Peptoid molecular transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13003–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Feng, L.; Fan, L.; Zha, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Pang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Targeting the brain with PEG-PLGA nanoparticles modified with phage-displayed peptides. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4943–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yokota, T.; Gama, V.; Yoshida, T.; Gomez, J.A.; Ishikawa, K.; Sasaguri, H.; Cohen, H.Y.; Sinclair, D.A.; Mizusawa, H.; et al. Bax-inhibiting peptide protects cells from polyglutamine toxicity caused by Ku70 acetylation. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mussa Farkhani, S.; Asoudeh Fard, A.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Shahbazi Mojarrad, J.; Valizadeh, H. Enhancing antitumor activity of silver nanoparticles by modification with cell-penetrating peptides. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Tsuzuku, T.; Takahashi, S.; Okamoto, A.; Dewa, T.; Nango, M.; Hyodo, K.; Ishihara, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Oku, N. Cell-penetrating peptide-conjugated lipid nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthuvanich, C.; Veiga, A.S.; Gupta, K.; Gaspar, D.; Blumenthal, R.; Schneider, J.P. Anticancer β-hairpin peptides: Membrane-induced folding triggers activityc. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6210–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, Y.-M.; Yang, J.-L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Shen, N.; Wang, S.-C.; Guo, X.-J.; Wu, Q.-F. Application of cell penetrating peptide in magnetic resonance imaging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai). 2006, 38, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, E.; Saito, K.; Tashiro, Y.; Kamide, K.; Uno, S.; Furuya, T.; Mashita, M.; Nakajima, K.; Tsumuraya, T.; Kobayashi, N.; et al. Tumour lineage-homing cell-penetrating peptides as anticancer molecular delivery systems. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 913–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, G.; Curran, G.L.; Mahlum, E.; Decklever, T.; Wengenack, T.M.; Blahnik, A.; Hoesley, B.; Lowe, V.J.; Poduslo, J.F.; Jenkins, R.B. A carrier for non-covalent delivery of functional beta-galactosidase and antibodies against amyloid plaques and IgM to the brain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeule, M.; Regina, A.; Che, C.; Poirier, J.; Nguyen, T.; Gabathuler, R.; Castaigne, J.-P.; Beliveau, R. Identification and Design of Peptides as a New Drug Delivery System for the Brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 324, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brugnano, J.L.; Chan, B.K.; Seal, B.L.; Panitch, A. Cell-penetrating peptides can confer biological function: Regulation of inflammatory cytokines in human monocytes by MK2 inhibitor peptides. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Rist, B.; Beck-Sickinger, A.; Wunderli-Allenspach, H.; Rubas, W.; Sadée, W.; Merkle, H.P. Translocation of human calcitonin in respiratory nasal epithelium is associated with self-assembly in lipid membrane. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 16582–16590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, G.; O’Hare, P. Intercellular trafficking and protein delivery by a herpesvirus structural protein. Cell 1997, 88, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlke, J.; Scheller, A.; Wiesner, B.; Krause, E.; Beyermann, M.; Klauschenz, E.; Melzig, M.; Bienert, M. Cellular uptake of an α-helical amphipathic model peptide with the potential to deliver polar compounds into the cell interior non-endocytically. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1998, 1414, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fotin-mleczek, M.; Welte, S.; Mader, O.; Duchardt, F.; Fischer, R.; Hufnagel, H.; Scheurich, P.; Brock, R. Cationic cell-penetrating peptides interfere with TNF signalling by induction of TNF receptor internalization. J. Cell. Sci. 2005, 118, 3339–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, R.; Köhler, K.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Brock, R. A Stepwise Dissection of the Intracellular Fate of Cationic Cell-penetrating Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12625–12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reissmann, S. Cell penetration: Scope and limitations by the application of cell-penetrating peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2014, 20, 760–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melikov, K.; Chernomordik, L. V Arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides: From endosomal uptake to nuclear delivery. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.P.; Melikov, K.; Vives, E.; Ramos, C.; Verbeure, B.; Gait, M.J.; Chernomordik, L.V.; Lebleu, B. Cell-penetrating peptides: A reevaluation of the mechanism of cellular uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.; Fotin-mleczek, M.; Hufnagel, H.; Brock, R. Break on through to the Other Side—Biophysics and Cell Biology Shed Light on Cell-Penetrating Peptides. Chembiochem 2005, 6, 2126–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, W.B.; Fuselier, T.; He, J.; Wimley, W.C. Mechanism Matters: A Taxonomy of Cell Penetrating Peptides. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Andaloussi, S.; Holm, T.; Langel, U. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Mechanisms and Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 3597–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouny, Y.; Rapaport, D.; Mor, A.; Nicolas, P.; Shai, Y. Interaction of antimicrobial dermaseptin and its fluorescently labeled analogues with phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 12416–12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.W.; Christison, R.; Bundell, K.; Voyce, C.J.; Brockbank, S.M.V.; Newham, P.; Lindsay, M.A. Characterisation of cell-penetrating peptide-mediated peptide delivery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazit, E.; Shai, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Brey, P.T. Mode of Action of the Antibacterial Cecropin B2: A Spectrofluorometric Study. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 10681–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, G.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: From Basic Research to Clinics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, I.M.; Wadia, J.S.; Dowdy, S.F. Cationic TAT peptide transduction domain enters cells by macropinocytosis. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, M.E.; Hallbrink, M.M.; Elmquist, A.M.; Langel, U. Passage of cell-penetrating peptides across a human epithelial cell layer in vitro. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäger, I.; Eiríksdóttir, E.; Langel, K.; EL Andaloussi, S.; Langel, Ü. Assessing the uptake kinetics and internalization mechanisms of cell-penetrating peptides using a quenched fluorescence assay. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, H.; Kato, T.; Oba, M.; Misawa, T.; Hattori, T.; Ohoka, N.; Tanaka, M.; Naito, M.; Kurihara, M.; Demizu, Y. Development of a Cell-penetrating Peptide that Exhibits Responsive Changes in its Secondary Structure in the Cellular Environment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitz, T.; Iten, R.; Gardiner, J.; Namoto, K.; Walde, P.; Seebach, D. Interaction of α- and β-oligoarginine-acids and amides with anionic lipid vesicles: A mechanistic and thermodynamic study. Biochemistry 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Kato, T.; Furukawa, K.; Tanaka, M. OPEN A Cell-Penetrating Peptide with a Guanidinylethyl Amine Structure Directed to Gene Delivery. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.L.; Dowdy, S.F. Cell penetrating peptides in drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadia, J.S.; Stan, R.V.; Dowdy, S.F. Transducible TAT-HA fusogenic peptide enhances escape of TAT-fusion proteins after lipid raft macropinocytosis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.; Muir, L.; Mousdell, S.; Sexton, D.; Jones, S.; Howl, J.; Ross, K. Modulation of mitochondrial activity in HaCaT keratinocytes by the cell penetrating peptide Z-Gly-RGD(DPhe)-mitoparan. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Figueiredo, I.R.; Freire, J.M.; Flores, L.; Veiga, A.S.; Castanho, M.A.R.B. Cell-penetrating peptides: A tool for effective delivery in gene-targeted therapies. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, L.; Pärn, K.; Langel, Ü. Therapeutic potential of cell-penetrating peptides. Ther. Deliv. 2013, 4, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkhani, S.M.; Valizadeh, A.; Karami, H.; Mohammadi, S.; Sohrabi, N.; Badrzadeh, F. Cell penetrating peptides: Efficient vectors for delivery of nanoparticles, nanocarriers, therapeutic and diagnostic molecules. Peptides 2014, 57, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 53. Dubuc, C.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Lessard, A.; Fortier, A.; Côté, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Rizzolio, F.; Geha, S.; Giordano, A.; et al. Targeting intracellular B2 receptors using novel cell-penetrating antagonists to arrest growth and induce apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9885–9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.; Zhang, M.; Gao, F.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z. A Novel Peptide Delivers Plasmids across Blood-Brain Barrier into Neuronal Cells as a Single-Component Transfer Vector. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, M.; Nielsen, H.M. Cell-penetrating peptides as tools to enhance non-injectable delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järver, P.; Langel, Ü. The use of cell-penetrating peptides as a tool for gene regulation. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oller-Salvia, B.; Sánchez-Navarro, M.; Ciudad, S.; Guiu, M.; Arranz-Gibert, P.; Garcia, C.; Gomis, R.R.; Cecchelli, R.; García, J.; Giralt, E.; et al. MiniAp-4: A Venom-Inspired Peptidomimetic for Brain Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regberg, J.; Srimanee, A.; Erlandsson, M.; Sillard, R.; Dobchev, D.A.; Karelson, M.; Langel, Ü. Rational design of a series of novel amphipathic cell-penetrating peptides. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 464, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakoutikhah, M.; Pradesh, R.; Teixidó, M.; Giralt, E. N-Methyl Phenylalanine-Rich peptides as highly versatile blood-brain barrier shuttles. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lättig-Tünnemann, G.; Prinz, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Behlke, J.; Palm-Apergi, C.; Morano, I.; Herce, H.D.; Cardoso, M.C. Backbone rigidity and static presentation of guanidinium groups increases cellular uptake of arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronewold, A.; Horn, M.; Ranđelović, I.; Tóvári, J.; Muñoz Vázquez, S.; Schomäcker, K.; Neundorf, I. Characterization of a Cell-Penetrating Peptide with Potential Anticancer Activity. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Wu, H.; McBride, J.L.; Jung, K.E.; Kim, M.H.; Davidson, B.L.; Lee, S.K.; Shankar, P.; Manjunath, N. Transvascular delivery of small interfering RNA to the central nervous system. Nature 2007, 448, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasaki-Hamada, S.; Funane, T.; Nakao, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Nagai, M.; Ueta, Y.; Yoshizawa, K.; Horiguchi, M.; Yamashita, C.; Oka, J.I. Intranasal administration of neuromedin U derivatives containing cell-penetrating peptides and a penetration-accelerating sequence induced memory improvements in mice. Peptides 2018, 99, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Q. Dual-functional liposomes based on pH-responsive cell-penetrating peptide and hyaluronic acid for tumor-targeted anticancer drug delivery. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9246–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, F.F. The origin of pegnology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.J.; Couvreur, P. Chapter 1 Historical View of the Design and Development of Nanocarriers for Overcoming Biological Barriers. In Nanostructured Biomaterials for Overcoming Biological Barriers; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 3–36. ISBN 978-1-84973-363-2. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, R.; Folkman, J. Polymers for the sustained release of proteins and other macromolecules. Nature 1976, 263, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvreur, P.; Barratt, G.; Fattal, E.; Vauthier, C. Nanocapsule Technology: A Review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2002, 19, 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaspar, D.P.; Faria, V.; Quintas, J.P.; Almeida, A.J. Targeted Delivery of Lipid Nanoparticles by Means of Surface Chemical Modification. Curr. Org. Chem. 2017, 21, 2360–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in drug delivery: Past, present and future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, H.K.; Hong, W.J.; Kim, J.; Seo, H.; Choi, I.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Min, S.; et al. Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Patchy Deformable Polymeric Nanovehicles with Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Transdermal Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Hou, H.; Zhou, S. Peptide-Based Nanocarriers for Cancer Therapy. Small Methods 2018, 1700358, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.L.; Sharma, S.; Panitch, A. Cell-penetrating peptides released from thermosensitive nanoparticles suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine response by specifically targeting inflamed cartilage explants. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tata, A.; Zheng, J.; Ginsberg, H.J.; Jaffray, D.A.; Ifa, D.R.; Zarrine-Afsar, A. Contrast Agent Mass Spectrometry Imaging Reveals Tumor Heterogeneity. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7683–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Kumari, P.; Lakhani, P.M.; Ghosh, B. Recent advances in polymeric micelles for anti-cancer drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Qian, J.; Cao, S.; Yang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Pan, S.; Fan, L.; Xi, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Q. Precise glioma targeting of and penetration by aptamer and peptide dual-functioned nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M. Glioblastoma: Overview of Disease and Treatment. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2016, 20, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Jiang, X.; Gu, J.; Sha, X.; Chen, L.; Law, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, X. Angiopep-conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles as dual-targeting drug delivery system for brain glioma. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4293–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; He, Q.; Gao, H. Angiopep-2 and activatable cell penetrating peptide dual modified nanoparticles for enhanced tumor targeting and penetrating. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Cao, S.; Yang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Jiang, X. Angiopep-2 and activatable cell-penetrating peptide dual-functionalized nanoparticles for systemic glioma-targeting delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. Highly efficacious and specific anti-glioma chemotherapy by tandem nanomicelles co-functionalized with brain tumor-targeting and cell-penetrating peptides. J. Control. Release 2018, 278, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadari, A.; Pooja, D.; Gora, R.H.; Gudem, S.; Kolapalli, V.R.M.; Kulhari, H.; Sistla, R. Design of multifunctional peptide collaborated and docetaxel loaded lipid nanoparticles for antiglioma therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 132, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, T.; Akiyama, F.; Kakizaki, S.; Takashima, Y.; Seta, Y. Delivery of siRNA to the brain using a combination of nose-to-brain delivery and cell-penetrating peptide-modified nano-micelles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9220–9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redig, A.J.; Mcallister, S.S. Breast cancer as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedolini, C.; Bertozzi, S.; Londero, A.P.; Bernardi, S.; Seriau, L.; Concina, S.; Cattin, F.; Risaliti, A. Type of breast cancer diagnosis, screening, and survival. Clin. Breast Cancer 2014, 14, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Cho, H.Y.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, J.W. In situ monitoring of doxorubicin release from biohybrid nanoparticles modified with antibody and cell-penetrating peptides in breast cancer cells using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, R.A.; Muroski, M.E.; Dai, Q.; Wegscheid, M.L.; Auffinger, B.; Yu, D.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Modified Gold Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Doxorubicin to Brain Metastatic Breast Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, R.R.; Desai, P.R.; Belay, K.; Singh, M.S. Translocation of cell penetrating peptide engrafted nanoparticles across skin layers. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5598–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y. Twin-Arginine Translocation Peptide Conjugated Epirubicin-Loaded Nanoparticles for Enhanced Tumor Penetrating and Targeting. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 4185–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Bai, L.; Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Yin, X. Paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles decorated with bivalent fragment HAb18 F(ab’)2 and cell penetrating peptide for improved therapeutic effect on hepatocellular carcinoma. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, A.; Medina, S.H.; Wang, W.; Palui, G.; Schneider, J.P.; Mattoussi, H. Intracellular Delivery of Gold Nanocolloids Promoted by a Chemically Conjugated Anticancer Peptide. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12754–12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, X.; He, Q. Tumor homing cell penetrating peptide decorated nanoparticles used for enhancing tumor targeting delivery and therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Perche, F.; Taigind, A.; Torchilin, V.P. Enhanced anticancer activity of nanopreparation containing an MMP2-sensitive PEG-drug conjugate and cell-penetrating moiety. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17047–17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carnevale, K.J.F.; Muroski, M.E.; Vakil, P.N.; Foley, M.E.; Laufersky, G.; Kenworthy, R.; Zorio, D.A.R.; Morgan, T.J.; Levenson, C.W.; Strouse, G.F. Selective Uptake Into Drug Resistant Mammalian Cancer By Cell Penetrating Peptide-Mediated Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, F.; Zhou, Q.L.; Liao, Y.Y. Advance of molecular imaging technology and targeted imaging agent in imaging and therapy. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, J.-F.; Lu, S.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Huang, Y.-W.; Shannon, K.; Aronstam, R. Cellular Internalization of Quantum Dots Noncovalently Conjugated with Arginine-Rich Cell-Penetrating Peptides. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, F.; Shao, Q.; Min, Y.; Costa, M.; Yeow, E.K.L.; Xing, B. Enzyme-responsive cell-penetrating peptide conjugated mesoporous silica quantum dot nanocarriers for controlled release of nucleus-targeted drug molecules and real-time intracellular fluorescence imaging of tumor cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Wu, K.; Wang, W.; Guan, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Fan, J. Synthesis of a cell penetrating peptide modified superparamagnetic iron oxide and MRI detection of bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4718–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, F.; Wang, Z.; Yue, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, W. Tumor-microenvironment controlled nanomicelles with AIE property for boosting cancer therapy and apoptosis monitoring. Biomaterials 2019, 188, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.; Yang, X.; Emory, S.R.; Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Mei, L.; Xie, J.; Ruan, G. A potent, minimally invasive and simple strategy of enhancing intracellular targeted delivery of Tat peptide-conjugated quantum dots: Organic solvent-based permeation enhancer. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Schön, M.P.; Wallbrecht, K.; Gruber-Wackernagel, A.; Wang, X.J.; Wolf, P. Involvement of IL-9 in Th17-Associated Inflammation and Angiogenesis of Psoriasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, H.; Von Hegedus, J.; Toes, R.; Kloppenburg, M.; Ioan-Facsinay, A. Lipid mediators of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 29, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, M.; Jeon, H.; Choe, K.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, P.; Jon, S. Nanoparticle-Assisted Transcutaneous Delivery of a Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3-Inhibiting Peptide Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6904–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majithia, V.; Geraci, S.A. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M.; Yu, C.; Lee, R.J.; Sun, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Teng, L. Dual-functional lipid polymeric hybrid pH-responsive nanoparticles decorated with cell penetrating peptide and folate for therapy against rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesselheim, A.S.; Hwang, T.J.; Franklin, J.M. Two decades of new drug development for central nervous system disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L. Modern methods for delivery of drugs across the blood–brain barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 640–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, Y. Cell-penetrating peptide-modified PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced nose-to-brain macromolecular delivery. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Ma, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Kuang, Y.; Shao, K.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Angiopep-conjugated nanoparticles for targeted long-term gene therapy of parkinson’s disease. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlschwede, K.M.; Curran, G.L.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Grant, S.C.; Sarkar, G.; Jenkins, R.B.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Poduslo, J.F.; Kandimalla, K.K. Cationic carrier peptide enhances cerebrovascular targeting of nanoparticles in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Nanomedicine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| CPPs | Structure/Sequence | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| TAT |  GRKKRRQRRRP | [4] |
| R8 |  RRRRRRRR | [15] |
| TGN |  TGNYKALHPHNG | [16] |
| Derived Ku-70 |  VPMLK | [17] |
| RW(n) |  RW(n) | [18] |
| CPP (RRRRRRGGRRRRG) |  RRRRRRGGRRRRG | [19] |
| SVS-1 |  KVKVKVKVDPPTKVKVKVK-NH2 | [20] |
| L-CPP |  LAGRRRRRRRRRK | [21] |
| RLW |  RLWMRWYSPRTRAYG | [22] |
| K16ApoE |  KKKKKKKKKKKKKKKKLRVRLASHLRKLRKRLLRDA | [23] |
| Angiopep-2 |  TFFYGGSRGKRNNFKTEEY | [24] |
| ACPP |  EEEEEEEEPLGLAGRRRRRRRRN | [12] |
| KAFAK |  KAFAKLAARLYRKALARQLGVAA | [25] |
| hCT (9–32) |  LGTYTQDFNKFHTFPQTAIGVGAP | [26] |
| VP22 |  DAATATRGRSAASRPTQRPRAPARSASRPRRPVE | [27] |
| CPP Conjugation with NP | |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Selective targeting Intracellular delivery Delivery of therapeutic compounds Low toxicity Bioaction High Stability | Resistance to drug Drug release Aggregation Endosomal entrapment |
| Construct | CPP | NP | Delivery Cargo | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPEG-PCL-TAT+siRNA micelles | TAT | Methoxypoly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ε-caprolactone) | siRNA | Brain cancer | [84] |
| TGN-NP | TGN | PEG-PLGA | Coumarin-6 | BBB targeting | [16] |
| MPEG-PCL-TAT micelles | TAT | MPEG-PCL | Anti RafsiRNA/CPT drug | Glioblastoma | [13] |
| ANG/TAT/DTX | Angiopep-2 and TAT | Tandem micelles | DTX | Glioblastoma | [82] |
| AsTNP | TGN | PEG-PCL | DTX | Glioblastoma | [77] |
| ANG-NP-PTX | Angiopep-2 | PEG-PCL | PTX | Glioblastoma | [79] |
| A-SLN | Angiopep-2 | Solid lipid nanoparticle | DTX/DiR/coumarin-6 | Glioblastoma | [83] |
| AnACNPs | ACPP and Angiopep-2 | PEG-PCL | Coumarin-6/DiR | Glioblastoma | [80] |
| AnACNps | ACPP and Angiopep-2 | PEG-PCL NP | DTX | Glioblastoma | [81] |
| CPP-QD@mSiO2 | ACPP | Mesoporous silica-coated QD | DOX | Cancer | [98] |
| TAT-Au-DOX | TAT | PEG and dodecylamine coated Au NP | DOX | Breast metastatic cancer | [88] |
| AuNP/DOX/TAT/PEG/antibody | TAT-C | Au NP | DOX | Breast cancer | [87] |
| AgNP-RWn | [RW]3,4,5,6 | Silver NP (AgNP) | ---- | Breast cancer | [18] |
| PLGA-TAT-ADM | TAT | Poly(lactic-glycolic acid) | Epirubicin | Hepatic cancer | [90] |
| H+C-NPs | R9 | PLGA-PEG | PTX | Hepatic cancer | [91] |
| TNPs | RLW | PEG-PCL | DTX/coumarin-6/DiR | Lung cancer | [93] |
| PEG2000-peptide-PTX and TATp-PEG1000-PE | TAT | PEG1000-PE | PTX | Lung cancer | [94] |
| CPP-LNP-siRNA | Arginine rich and siRNA carrier | Protamine-decorated lipid NP | SiRNA GFP/luciferase | Melanoma cancer | [19] |
| AuNP-SVS-1/TXR | SVS-1 | AuNP | Texas red dye (TXR) | Cancer | [92] |
| QD-CPP | Ku-70; TAT; hCT; HSV1-VP22; | Quantum dot (CdTE@CdSe@CdS@ZnS) | ---- | Multidrug resistant cancer | [95] |
| STD-NMdrug | TAT | Nanomicelles | DOX | Cancer and Imaging agent | [100] |
| QD-TAT | TAT | Quantum dots coated PEG | ---- | Imaging agent | [101] |
| SPIO-R11 | Arginine rich peptide (R11) | Supermagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) | ---- | Imaging agent MRI (Bladder cancer) | [99] |
| Gd-DTPA-CPP | L-CPP | DTPA | Gadolinium | Imaging agent | [21] |
| SR9-QD | R9 | Quantum dots (CdSe/Z S) core shell | ---- | Imaging agent | [97] |
| ACPP-GD | ACPP | PAMAM dendrimer | Gadolinium | Imaging agent | [10] |
| Poli(NIPAM)-KAFAK | KAFAK | Thermosensitive polymer poly(N-isopropylacrylamine) | KAFAK | Inflammation | [74] |
| Sta-R8+FA- PPLPNs/MTX | R8 | Lipid polymeric hybrid NP | MTX | Rheumatoid arthritis | [107] |
| APTstat3-9R | R9 | Discoid shaped lipid NP | STAT | Inflammation | [105] |
| K16APoE-TargetedNP-DutchAβ40 | K16ApoE | PGLA | Curcumin | Alzheimer model | [112] |
| Insulin-loaded-TAT-NP | TAT | PLGA | Insulin | Alzheimer disease | [110] |
| DPA-hGDNF | Angiopep-2 | Dendigraft poly-l-lysine (DGL-PEG) and PAMAM dendrimer | Gene therapy (hGDNF) | Parkinson disease | [111] |
| MPEG-PCL-TAT+siRNA micelles | TAT | Poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ε-caprolactone) | siRNA | Brain cancer | [84] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, S.; Almeida, A.J.; Vale, N. Combination of Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Application: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010022
Silva S, Almeida AJ, Vale N. Combination of Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Application: A Review. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Sara, António J. Almeida, and Nuno Vale. 2019. "Combination of Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Application: A Review" Biomolecules 9, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010022
APA StyleSilva, S., Almeida, A. J., & Vale, N. (2019). Combination of Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Application: A Review. Biomolecules, 9(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010022






