Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a known chronic autoimmune disease can cause joint deformity and even loss of joint function. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), one of the main cell types in synovial tissues of RA patients, are key effector cells in the development of RA and are considered as promising therapeutic targets for treating RA. Herbal medicines are precious resources for finding novel agents for treating various diseases including RA. It is reported that induction of apoptosis in FLS is an important mechanism for the herbal medicines to treat RA. Consequently, this paper reviewed the current available references on pro-apoptotic effects of herbal medicines on FLS and summarized the related possible signal pathways. Taken together, the main related signal pathways are concluded as death receptors mediated apoptotic pathway, mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathway, NF-κB mediated apoptotic pathways, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) mediated apoptotic pathway, endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) mediated apoptotic pathway, PI3K-Akt mediated apoptotic pathway, and other reported pathways such as janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) signal pathway. Understanding the apoptosis induction pathways in FLS of these herbal medicines will not only help clear molecular mechanisms of herbal medicines for treating RA but also be beneficial for finding novel candidate therapeutic drugs from natural herbal medicines. Thus, we expect the present review will highlight the importance of herbal medicines and its components for treating RA via induction of apoptosis in FLS, and provide some directions for the future development of these mentioned herbal medicines as anti-RA drugs in clinical.
1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, invasive autoimmune disease that can cause joint deformity, even complete loss of joint function, so it is often referred to as “Deathless cancer” [1]. Pathological characteristic of RA is excessive synovial tissue hyperplasia, pannus formation, and erosion of cartilage, and the typical clinical features is the symmetry of joint swelling, pain, morning stiffness, and deformity, often accompanied by joint organ involvement [2,3]. RA can occur at any age, with the highest incidence occurring between the ages of 40 and 60 years, and it is more common in women, and the incidence is about four times that of men [4,5]. In China, the prevalence rate of RA is 0.2–0.4%, while in European and American countries, the prevalence rate of RA can be as high as 1% [6,7,8]. At present, the clear pathogenesis of RA is still uncovered, this immune disease has a high disability rate, poor prognosis, and is prone to repeated attacks. Meanwhile, the treatment cycle is very long, so it will bring heavy economic burden to patients’ families and society. Currently, the treatment strategies for RA in clinical practice are mainly chemical drugs, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), glucocorticoids, and biological agents [1,8]. However, these treatments are costly and often associated with adverse reactions, such as cardiovascular and gastrointestinal bleeding risk, liver and kidney toxicity, growth inhibition, infection, and tumor risk [9,10,11,12].
With the number of RA patients increasing year by year, medicinal researchers are actively looking for cheap and effective alternative drugs with fewer side effects to treat RA. Recently, herbal medicines have been given more and more attention for their remarkable curative effects and fewer side effects [13,14]. Herbal medicines have been used for the clinical management of RA for thousands of years, and its efficacy and safety have been proved by its long-term clinical application [15,16]. It is interesting and known that herbal medicines can through multiple components act in multiple pathways to give play to the role of prevention and treatment of RA. The main components in herbal medicines for treating RA are complex including alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, phenylpropanins, etc., and the main pharmacological effects are related to pain relief, improvement of inflammation, regulation of immune function, protection of cartilage, reduction of pannus formation, inhibition of synovial hyperplasia, etc. [16,17]. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), one of the main cell types in the synovial tissues of RA patients, are key effector cells in the development of RA, and are considered as promising therapeutic targets for treating RA [1,18]. It is worth noting that a large number of herbal medicines and their monomers seem to have a good effect for inhibiting synovial hyperplasia of arthritis, and the detailed molecular mechanisms are mainly related to inhibiting proliferation of FLS via induction of apoptosis. However, there is no systematic analysis or summary regarding the apoptotic effects of herbal medicines on FLS for treating RA. Thus, our study aims to review the important researches on herbal medicines and its monomer components inducing FLS apoptosis, and summarize the related possible molecular signal pathways for apoptosis, so as to provide references for the follow-up studies of herbal medicines on treating RA.
2. Cell Apoptosis
Currently, the cell death modes discovered by humans mainly include apoptosis, necrosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis, which have great differences in morphological characteristics and biochemical signal transduction [19]. Apoptosis is the cell independent orderly death in order to resist the external stimulation and maintain the homeostasis of the internal environment, which is often referred to as programmed death. Different from other ways of cell death, apoptosis is not a self-injury phenomenon, but a self-protection mechanism, which is activated, expressed and regulated by a series of specific genes [19,20]. In 1972, Kerr et al. first proposed the term apoptosis to describe a morphological feature of cell death that had never occurred before [21]. Programmed cell death during the development of Caenorhabditis elegans has led to the recognition and understanding of the mechanisms involved in mammalian apoptosis [22]. Apoptosis is a basic physiological phenomenon, which plays an important role in organism growth, development, and evolution [23]. On the one hand, apoptosis can maintain the homeostasis and the dynamic balance of cell number in the body, and on the other hand, it can be used as a defense mechanism to eliminate unnecessary or abnormal cells [24]. Appearing in cell apoptosis, cell shrinkage, smaller volume, nuclear enrichment, nuclear membrane nucleoli, DNA fragmentation, then the cell cleaves into apoptotic corpuscles, which are formed by the cell membrane enclosed cytoplasm, organelles and broken nucleus, and eventually the apoptotic body are recognized around the macrophage, which in turn being swallowed, degradation. During the whole process of cell apoptosis, the cell membrane structure is complete, no contents are spilled, no cytokines are released, and the duration is short, so the surrounding inflammatory reaction is basically not caused. However, when abnormal regulation of this cellular program occurs in the body, it can induce many serious diseases, such as tumors, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, etc. [25].
3. Apoptosis of FLS in RA Patients and RA Pathology
RA is a complex disease due to heterogeneous reasons, and the precise etiology of this disease remains unclear until now. Increasing scientific evidence has suggested that FLS, also named synovial lining fibroblasts, play a key role in the development of RA [18,26,27]. For the pathogenesis of RA, characteristic of RA is excessive synovial tissue hyperplasia, pannus formation, and erosion of cartilage, and the excessive proliferation and inadequate apoptosis of FLS is generally recognized as the pathological basis of RA.
Normal synovial fibroblasts are mainly distributed in synovial lining layer, secreting appropriate synovial fluid to reduce bone friction and reduce joint injury, and secreting various cytokines to nourish joints and ensure the normal progress of joint activities. When synovial fibroblasts have stable activation, the defects in apoptosis, began with abnormal proliferation and transformation in tumor samples, showed similar characteristics of aggression and adhesion [7,28]. It is reported that FLS in RA patients are resistant to apoptosis due to the unbalance of the anti- and pro-apoptotic molecules, and the increasing evidences have revealed that anti-apoptotic mediators, such as Bcl-2, Mcl-2, and FLICE-inhibitory protein (FLIP), are up-regulated in the FLS of RA patients whereas the pro-apoptotic proteins, such as tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), p53 up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) and Bid, are down-regulated in the FLS of RA patients [29,30,31,32]. In addition, it is also reported that increased p53 mutants are found in the FLS of RA patients (RA-FLS) whereas the p53 expressions were relatively decreased, which is considered one of the important reasons for the excessive proliferation and inadequate apoptosis of FLS [31]. In addition, RA-FLS increase the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM), blocking of articular cartilage nutrition supply, infiltration and organization of the joint destruction [18]. On the other hand, FLS secretes a variety of chemokines, such as RANTES, IP-10, ENA-78, MCP-1, SDF-1, CXCL16, etc., which can recruit macrophages, T cells, and B cells to migrate to joints, enhance inflammatory response, and indirectly destroy bones and joints. In addition, FLS can also inhibit the apoptosis of T and B cells, so that the inflammatory response persists, reinforcing the damage to bones and joints [33]. In summary, the apoptotic defect of FLS can lead to abnormal synovial hyperplasia, pannus formation, and inflammatory cell infiltration, resulting in cartilage and bone erosion, joint destruction, joint deformity, and eventually joint function loss. Therefore, how to effectively promote the apoptosis of FLS and inhibit synovial hyperplasia has important clinical significance for the treatment of RA, providing a feasible direction for the development of anti-RA drugs.
4. Effects and Mechanisms for Herbal Medicine and its Components on FLS Apoptosis in RA
4.1. Death Receptors Mediated Apoptotic Pathway
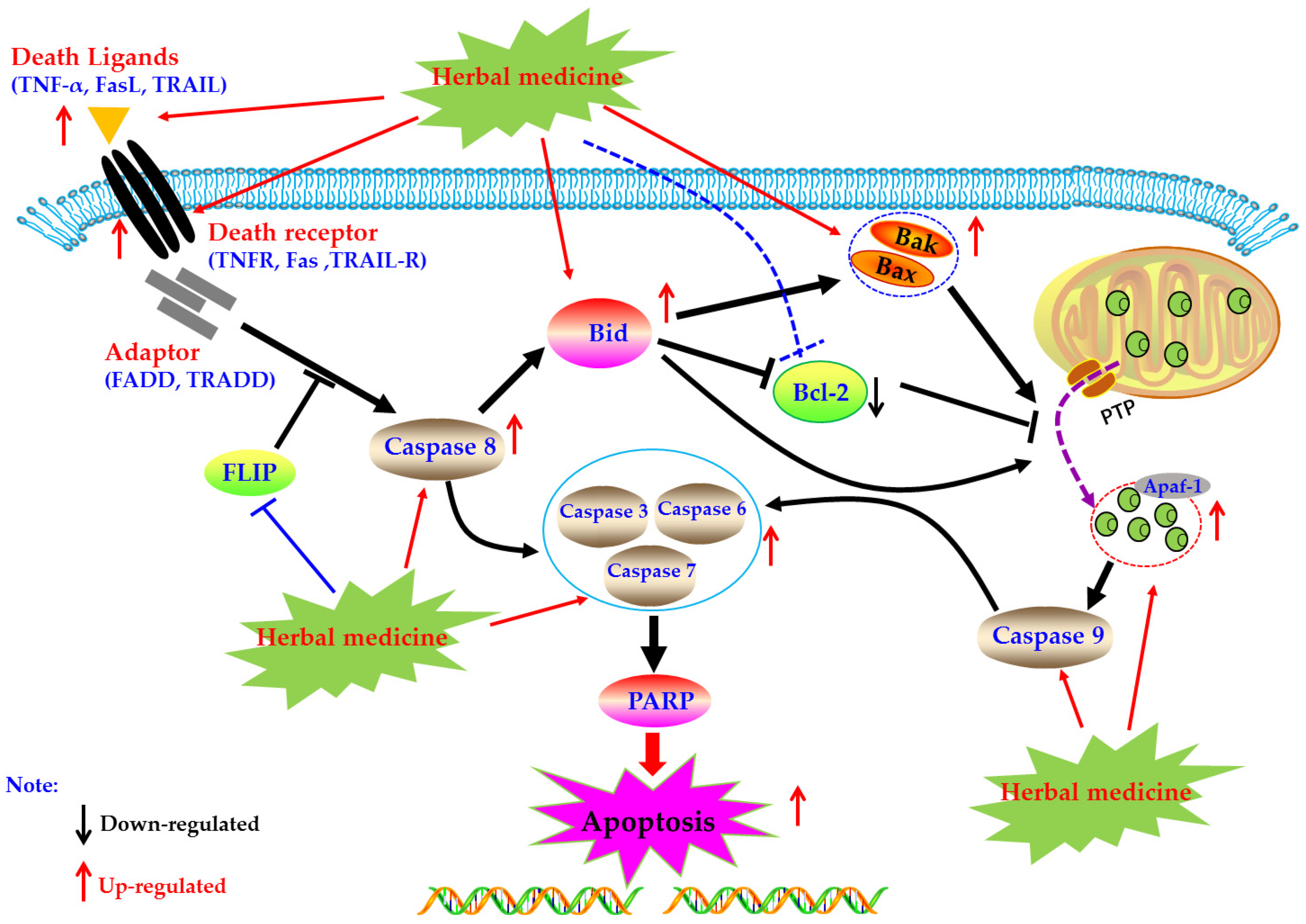
Death receptors mediated apoptosis, known as the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, is one of the main well-characterized apoptotic routes [34]. The death receptor mediated apoptotic pathway is mainly triggered by extracellular stimuli which are commonly recognized by the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family of proteins (also called death receptors), such as the TNFR, Fas, and TRAIL-R [20,35,36]. Activated death receptors by their ligands, such as TNF-α, FasL, and TRAIL, would further form the death inducing signaling complex (DISC), and subsequently bind to the Caspase-8, resulting in the activation of Caspase-8 by dimerization. Then, the activated Caspase-8 could further activate the Caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway via two routes [20]. Firstly, the activated Caspase-8 catalyze and active the executioner Caspases (including Caspase-3, -6, and -7), lead to the apoptosis. Secondly, the activated Caspase-8 could trigger the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway via the Bid cleavage, following a series of apoptotic events, such as cytchrome c (Cyt-C) release from the mitochondria, apoptosome formation, Caspase cascade reaction, and PARP cleavage, and eventually lead to apoptosis [20,37,38,39]. Currently, increasing evidences have suggested that induction of apoptosis in FLS via death receptors mediated apoptotic pathway is an important molecular mechanism for herbal medicine extracts and its active components to treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
4.1.1. Herbal Medicine Extracts
In 2002, a study reported by Liu et al. revealed that a clinical RA drug of Xinfeng capsule (XFC, 1.8 g/kg, p.o.) possessed significant anti-RA effects in rats via reduction of arthritis index, and the potential mechanisms are correlated to up-regulation of Fas and FasL, whereas down-regulation of Bcl-2 in synovia tissues of joints [40]. Furthermore, Liu et al. (2010) investigated the effects of extracts from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (ERSM) on FLS of clinical RA patients (RA-FLS). From the results of this investigation, Liu et al. suggested that ERSM (0.4 mg/mL) has obvious apoptosis inducing activities in RA-FLS via up-regulation of mRNA expressions of Fas [41]. In addition, another research article by Liang et al., in 2017, investigated the anti-RA effects of an interesting traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) clinical prescription, named Fengshi Bitong Prescription (FSBT), and reported that FSBT (9.5, 19, and 38 g/kg, p.o.) could decrease the paw swelling of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats. Similar to tripterygium glycosides, the potential molecular mechanisms of FSBT are closely correlated to the regulation of Caspase-8, Fas and FasL in synovial tissues of CIA rats [42].
4.1.2. Monomers from Herbal Medicine
In 2008, Zhao et al. reported that Resveratrol (1), which is a natural active compound existed in Polygounm cuspidatum [43], has promising curative effects on RA symptoms of CIA rats and could induce the primary cultured FLS (rFLS) from CIA rats via up-regulation of Caspase-8, whereas down-regulation of FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP) [44] which is an important anti-apoptotic protein that can suppresses the death receptors ligands (such as TNF-α, FasL, and TRAIL) induced apoptosis in FLS of RA patients (RA-FLS) (Figure 1), and is also an important reason for the resistance of RA-FLS to apoptosis [45,46,47]. Later, in 2013, it is reported that Propyl gallate (2) (64 μg/mL) which is an active component in Radix paeoniae rubra could induce the apoptosis of RA-FLS via up-regulating the mRNA expressions of Fas [48,49]. Furthermore, a study reported that Daphnetin (3) (40 μg/mL) significantly induced apoptosis in rFLS from CIA rats, and the related molecular mechanisms were closely related to up-regulation of Caspase -3, -8, and -9 and FasL [50,51]. The potential mechanisms of herbal medicine for inducing apoptosis in this part are summarized in Figure 1 and Table 1.
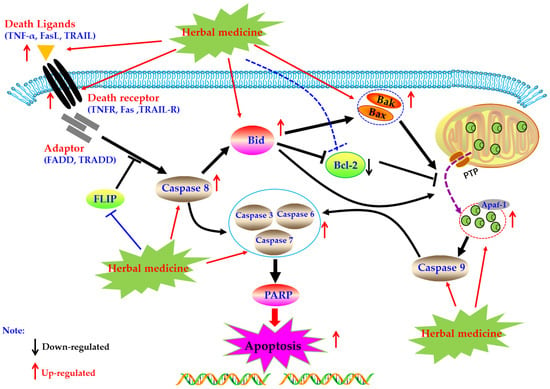
Figure 1.
Death receptors mediated apoptotic pathway in FLS induced by herbal medicines.

Table 1.
Apoptosis inducting activities of herbal medicine and its active components in fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
4.2. Mitochondrial Dependent Apoptotic Pathway
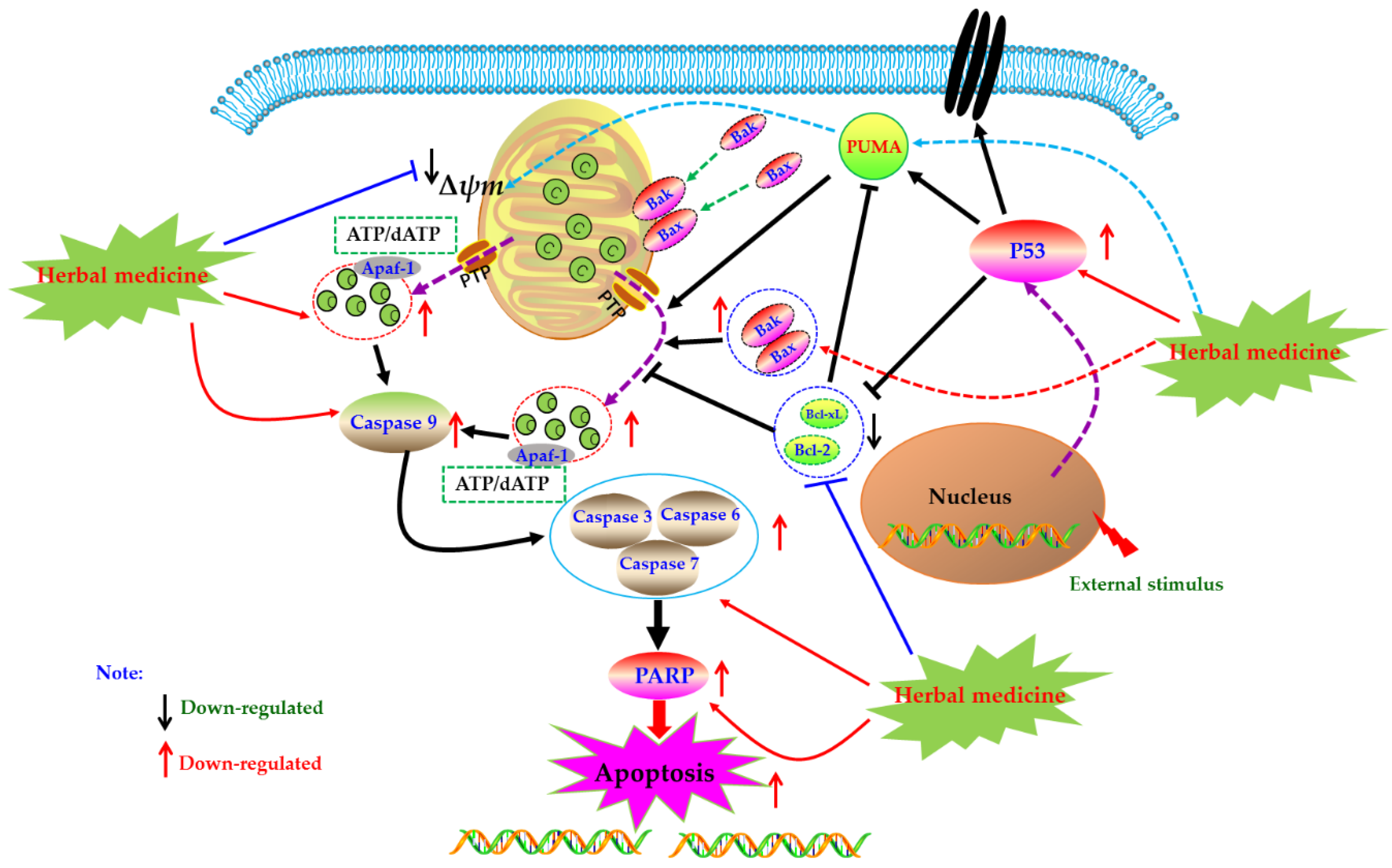
Mitochondrion, as an important organelle of cell, is the energy factory of cell activities. The integrity of its structure and function is an important premise to ensure the normal life activities of cells. Mitochondria mediated cell apoptosis is also known as the endogenous pathway of cell apoptosis, which is one of the important ways of cell apoptosis. In 1994, Newmeyer et al. reported that mitochondria in the extract of Xenopus afroensis egg could coagulate the nucleus chromatin, and the nucleus showed contractile and fragmented, suggesting that mitochondria were closely correlated to programmed cell death [52]. Since then, increasing studies have also proved that mitochondria play an important role in the process of cell apoptosis, which is the key element of apoptosis. Briefly, when cells receive apoptosis signals from p53-PUMA signal or death receptor signal pathways (Figure 2), the pro-apoptotic proteins of Bcl-2 family were up-regulated and activated, whereas expressions of anti-apoptotic proteins were down-regulated. The pro-apoptotic proteins, such as Bax and Bak, were transferred from the cytoplasm to the mitochondrial membrane, forming transmembrane pores and decreasing the mitochondrial membrane potential (MCMP). Meanwhile, due to breaking of the balance of pro-/anti-apoptotic proteins, the permeability transition pore (PT) was induced to open, which further reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential (MCMP), increased the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane, resulting in the releases of cytochrome C (Cyto C). With the participation of ATP or dATP, Cyto C enters the cytoplasm and subsequently binds to Apaf-1 and other apoptotic protease activators to form apoptotic complexes. Apoptosis complexes recruit and activate the initiator cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase (Caspase), such as Caspase 9, etc. Then, the activated initiators activate executioner Caspases (such as Caspase-3, -6, -7), and start the Caspase cascade, cutting poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), actin and other substrates, eventually leading to the cell death and cell lysis [20,26,27]. As natural products, herbal medicines and its active ingredients are considered as effective strategies for RA treatment due to their good efficacy and low toxicity. Meanwhile, increasing studies have proved that these drugs can play anti-RA effects by mediating mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in FLS.
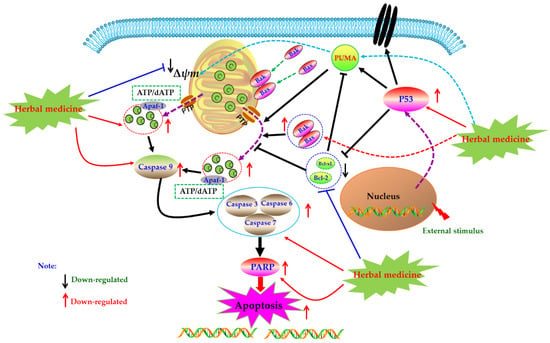
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) induced by herbal medicines.
4.2.1. Herbal Medicine Extracts
An investigation in 2011 by Dai et al. studied the anti-RA effects of seaweed polysaccharide (SWPD) in vitro on RA-FLS, and the results revealed SWPD (15, 20, 25 mg/mL) has significantly anti-proliferative activity on RA-FLS via inducing mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in RA-FLS through up-regulating Bax and Caspase-3 whereas down-regulating Bcl-2 [53]. Later in 2013, it is also reported that an Chinese patent drug called Feng-shi-ning capsule has significant anti-rheumatic activities and the related mechanisms were related to induction of mitochondrial dependent apoptosis in via increasing the releases of Cyt-C, up-regulating Caspase-3, as well as down-regulating Bcl-2 [54]. In 2018, Gao and Lu studied effect of medicated serum of Duhuo Jisheng decoction (DHJS medicated serum, 0.75, 1.5 and 3 g/kg) on rFLS from Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) rats, the results showed that 20% DHJS medicated serum can induce apoptosis in rFLS (AIA), and the mechanisms are related to regulating Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 [55]. Furthermore, a research by Ci et al. isolated an interesting polysaccharide from the Saposhnikovia divaricate (SDP), and the SDP (5–15 mg/mL) dose-dependently induced apoptosis in the rFLS from AIA rats. The possible mechanisms are closely related to up-regulating p53, Bax and Caspase-3, whereas down-regulating Bcl-2 [56]. Later in 2019, Wu et al. investigated the apoptosis inducing effects of Pterocarya Hupehensis Skan extracts (PHSE) on MH7A cells, and the results showed that PHSE (25, 50, 100 μg/mL) resulted in obvious anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects in MH7A cells. The further mechanisms research revealed that PHSE can up-regulate p53, Bak, Cyt-C, Caspase-3, -9 and Bax, whereas down-regulate Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and activate the Caspase-3 in MH7A cells [57]. Recently, Zhang et al. investigated the curative effects of Guizhishaoyaozhimu Decoction (GZSD), which is a known classical prescription of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), on type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in rats. It is found that GZSD has a significant anti-arthritic effect on CIA rats, and the further in vitro study in MH7A cells revealed GZSD (0.4, 0.8, 1.6 mg/mL) could induce apoptosis in MH7A cells and up-regulate pro-apoptotic proteins such as Caspase-3, -9, Bax and down-regulate Bcl-2 [16].
4.2.2. Monomers from Herbal Medicine
In the year of 2009, Li et al. reported that after 24 h treatment with Scopoletin (4) (250, 500, 1000 μM), the MCMP (Δψm) of FLS in AIA rat was depolarized, resulting in mitochondrial dependent apoptosis; and the further studies found that Scopoletin can activate caspase-3 and down-regulate Bcl-2 whereas up-regulate Bax [58]. Later in 2010, Li et al. found that the 7, 3′-Dimethoxy hesperetin (5) (DMHP, 10, 50, 250 μM), a derivative of hesperidin, can significantly decrease the proliferation of the rFLS from AIA rats via induction of apoptosis, which is closely related to regulation of Bax, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, and activation of Caspase-3 in rFLS (AIA) [59]. Another work in 2011 by Wang reported that Berberine (6) (5–75 μM) can induce apoptosis in RA-FLS by increasing Caspase-3, -9, Bax and PARP, whereas decreasing MCMP (Δψm), Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL [60]. Later in 2012, after prepared the primary cultured rFLS from AIA rats, Ren et al. investigated effect of the 5,7,3′-Triacetyl hesperetin (TAHP, 7) on rFLS (AIA), and they found that TAHP (50 and 250 μM) can notable inhibit the proliferation of rFLS (AIA) in vitro, and the molecular mechanisms might be related to induction of apoptosis via up-regulating Bax, Caspase-3 whereas down-regulating Bcl-2 in rFLS (AIA) [61]. In another study by Yan et al. in 2012, Andrographolide (8) (10, 20 and 30 μM) showed a highly anti-rheumatic activity on RA-FLS from RA patients cultured in vitro via inducing apoptosis, which was associated with decrease of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio, promotion of Cyt-C release, and activation of Caspase-3 [62]. Moreover, a natural polyphenolic acid named Gallic acid (9) was investigated by Yoon et al. in 2013, and Yoon et al. found that this Gallic acid (0.1, 1 μM) could induce apoptosis in RA-FLS via regulation of Bcl-2, Bax, p53 and Caspase-3 [63]. Another work in 2013 by Xu suggested that Celastrol (10) (1, 2, 5 μM) also induced apoptosis in RA-FLS via increasing Caspase-3, -9, PARP, Fas and Bax, whereas decreasing Bcl-2 and MCMP (Δψm) [64]. Besides, in 2013, another important natural monomer named Quercetin (11) (100–300 μM) also reported to be an effective agent can promote apoptosis in RA-FLS through regulation of Caspase-3, -9, Cyto C and Bcl-2 [65]. In 2014, Chang et al. reported that Bufalin (12) (10, 20, 40 nM), the major active digoxin-like component of Chansu isolated from the skin and parotid venom glands of toad, possessed significant anti-proliferative and apoptosis inducing activities on RA-FLS; the investigators found that Bufalin can up-regulate Bax, down-regulate Bcl-2, activate Caspase -3 and PARP, increase Cyt-C release, and decrease MCMP (Δψm), and consequently the authors thought mitochondrial mediated apoptosis might be one of the possible molecular mechanisms [66]. Additionally, another report by Jie et al. studied the effect of Tanshinone IIA (13), and found that this compound (2.5–20 μM) could induce apoptosis in RA-FLS by mitochondrial pathway via up-regulating Bax, cytosolic Cyto C, Apaf-1, Caspase-3, -9 whereas down-regulating Bcl-2 [67]. Afterwards, Liu et al. in 2016 recorded another natural coumarin constituent named Daphnetin (3) (40 μg/mL) extracted from Daphne odora could induce apoptosis in RA-FLS of CIA rats, and after Daphnetin treatment, the Caspase-3, -8, -9, Bax, Bid, Cyt-C were significantly up-regulated whereas the Bcl-2 were down-regulated [51]. In the study of Shang et al. (2016), it was found that Oridonin (14) (5, 10, 25, 40 μM) can induce the apoptosis in RA-FLS, regulate the mRNA expressions of Bax and Bcl-2, reduce cells’ MCMP, promote the outflow of Cyt-C, and activate Caspase-3 [68]. Besides, an in vitro study has found that Resveratrol (1) (50, 100, 200, 400 μM) can decrease the MCMP (Δψm), destroy the mitochondrial structure and function, trigger mitochondria mediated apoptosis in rFLS (AIA) [69]. Another report by Gu and Jin reported that Resveratrol (100, 200 μM) (1) inhibited the proliferation of RA-FLS via increasing the Bax expression while decreasing the Bcl-2 expression [70]. PUMA is a key protein that mediates p53-dependent and p53-independent apoptosis, and current investigations also found that natural monomers, such as Resveratrol and Gallic acid, can increase the expressions of p53 and PUMA to promote apoptosis of various cancer cells or fibroblasts [51,71,72]; thus we speculated that up-regulation of PUMA is also a possible target for herbal medicines and its constituents for treating RA. In 2016, Gao reported that Pristimerin (15) (0.4, 0.8 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly improved the RA symptoms of AIA rats, and further investigations revealed that Pristimerin (0.75–3 μM) can induce apoptosis of rFLS (AIA) via regulation of expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 [73]. Liquiritin (16) is a known active constituent isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and recently, Zhai et al. reported that Liquirtin (0.345–34.5 μM) induced apoptosis in RA-FLS via down-regulating the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax [74]. Besides, it is reported that Cryptotanshinone (17) (5 μM), a fat soluble anthraquinone derivative isolated from the Salvia miltiorrhiza, could induce the apoptosis in MH7A cells and RA-LFS cells via reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced apoptosis by regulation of Bcl-2, Bad, cleaved-Caspase-3 and PARP [75]. The potential mechanisms of herbal medicine for inducing apoptosis in this part are summarized in Figure 2 and Table 1.
4.3. NF-κB Mediated Apoptotic Pathways
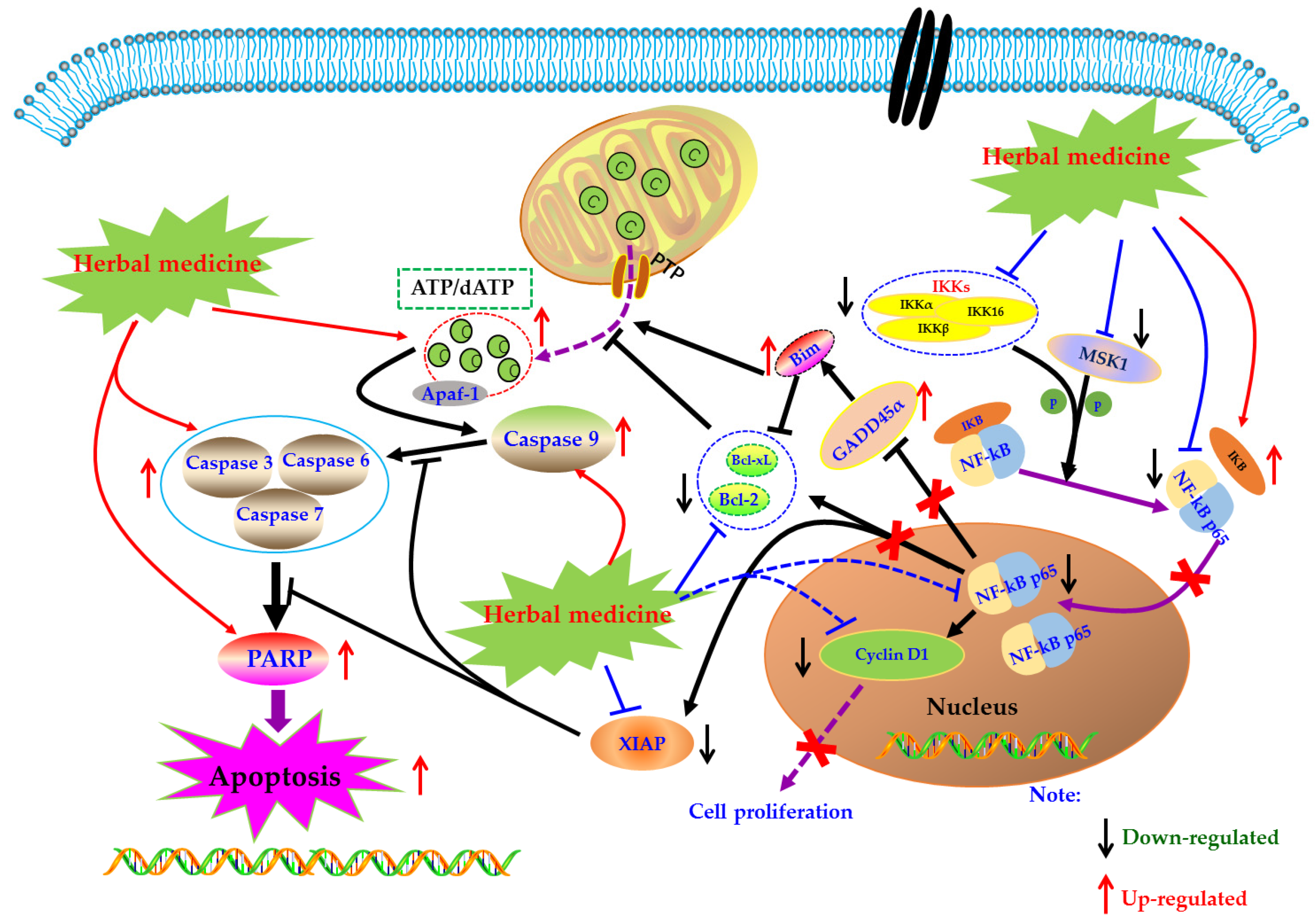
Under normal physiological conditions, cells receive extracellular signal stimulation, and receptor proteins on the membrane polyaggregate and transmit the signal to IKK (IκB kinase). IKK, a kinase, phosphorylates IκB, which is subsequently dissociated from the trimer complex formed with Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) [76]. The released NF-κB regenerates its activity, quickly enters the nucleus from the cytoplasm, and combines with specific sequences on DNA in the nucleus to control protein transcription, and participate in physiological processes such as cell proliferation and apoptosis, stress response, and release of cytokines. However, when NF-κB is abnormally activated, the body can develop a series of serious diseases, such as cancer, atherosclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Beg et al. showed that fetal mice with defects in the Re1A subunit of NF-κB would show programmed cell death or apoptosis in the second trimester, leading to large-scale degradation of the liver and ultimately the death of the embryo. It was the first time that NF-κB was involved in the process of cell apoptosis. Subsequently, more and more studies have found that NF-κB is closely related to apoptosis [77].
Currently, NF-κB has attracted more and more attention as a potential therapeutic target in the management of RA [78,79,80]. Modern pharmacological studies have proved that natural products can induce FLS apoptosis to prevent synovial hyperplasia via regulation of NF-κB pathway. As early as 2007, Zhang et al. found that Sinomenine (SIN, 18) (3.2 mM), an active alkaloid from the Caulis Sinomenii, can induce apoptosis in RA-FLS using flow cytometry analysis [81]. Later, in 2008, Fang et al. revealed the SIN (2.8–3.2 mM) resulted in significant cell cycle arrest and down-regulation of Bcl-2 in RA-FLS [82]. Another investigation in 2015 by Zhang et al. studied the effect of SIN on proliferation of RA-FLS, and found that SIN has significant anti-proliferative activity on RA-FLS via inhibition of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal pathway through down-regulating MyD88 and TRAF-6 proteins in RA-FLS [83]. In 2009, it is reported by Li et al. that besides mitochondrial dependent apoptosis, the anti-proliferative effects of Scopoletin (4) on RA-FLS also closely related to NF-κB pathway via regulation of Bax, IκBα, p-IKK and p-IκBα [57]. Later, in 2010, Shang et al. reported that Curcumin (19) (80 μM) could inhibit the proliferation and arrest the cell-cycle of RA-FLS [84]. Furthermore, Klosech et al. systemically investigated the apoptotic effects of Curcumin on MH7A cells and its related molecular mechanisms, and the results showed that Curcumin has notable pro-apoptotic effects on MH7A via modulation of the NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways [85]. In 2017, Fang et al. studied the effects of Celastrol (9) on activated FLS from RA patients. The results showed that Celastrol attenuated the proliferation of RA-FLS, and inhibited phosphorylation of IKK and IκBα as well as down-regulated NF-κB p65 [86]. The monomer of 1,7-Dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone (XAN, 20) is isolated from Securidaca inappendiculata Hassk, and can induce apoptosis in RA-FLS by inhibiting the activities of NF-κB and p38. It is worth noting that XAN can also regulate the transcription of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), mediate the occurrence of Caspase cascade reaction, and induce cell apoptosis [87,88]. Furthermore, previous research in 2017 also found that Jinwu-Jiangu decoction (JJD) could reduce inflammatory symptoms of CIA rats and inhibit tumor like hyperplasia of FLS, and the in-depth study found that JJD medicated serum could promote FLS apoptosis by interfering with the expressions of NF-κB p65, IKK-α, and IKK-β [89,90]. Another paper by Wang et al., in 2017, reported that Baicalin (21) (10, 20, and 30 μM) could inhibit the proliferation of RA-FLS by decrease of NF-κB p65, phospho-NF-κB p65 and acetyl-NF-κB p65, as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines [91]. Piperlongumine (PLM, 22) is the main component of Piperlongum Linn. Studies have found that low-dose PLM (1 μM) can inhibit the proliferation of RA-FLS, and high-dose PLM (15 μM) can induce apoptosis in RA-FLS. Further studies have found that PLM intervention can reduce the phosphorylation of NF-κB P65, suggesting that NF-κB pathway is involved in regulating the activity and function of FLS [92]. Recently, Wang and Zhao investigated the effect of Kaempferitrin (23), a natural flavonoid glycoside comprehensively existed in plants, on MH7A cells. The related results suggested that Kaempferitrin (5, 10, and 20 μM) can trigger apoptosis in MH7A cells by blocking activation of NF-κB and protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways (Akt/mTOR) [93]. In 2018, Zhang et al. reported that by photodynamic therapy, Hypericin (24) (0.25–4 μM) could induce NF-κB mediated apoptosis in MH7A cells via increasing ROS, cleaved Caspase-9, Cleaved PARP, whereas decreasing NF-κB p65 [94]. The α-Mangostin (25) is an active monomer isolated from the Garcinia mangostana Linn, and an interesting study by Zuo et al. reported that α-Mangostin (15 μg/mL) decreased XIAP and increased cleaved Caspase-3, as well as inhibited phosphorylation of NF-κB p65, IκB, and IKK in FLS, suggesting the pro-apoptotic potential of α-mangostin in FLS which is closely related to inhibition of NF-κB [95]. The potential mechanisms of herbal medicine for inducing apoptosis in this part are summarized in Figure 3 and Table 1.
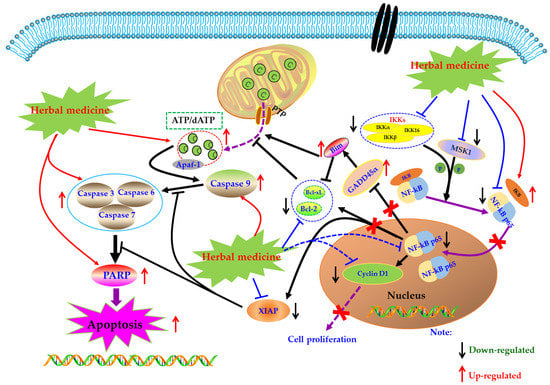
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathway in FLS induced by herbal medicines.
4.4. MAPK Mediated Apoptotic Pathway
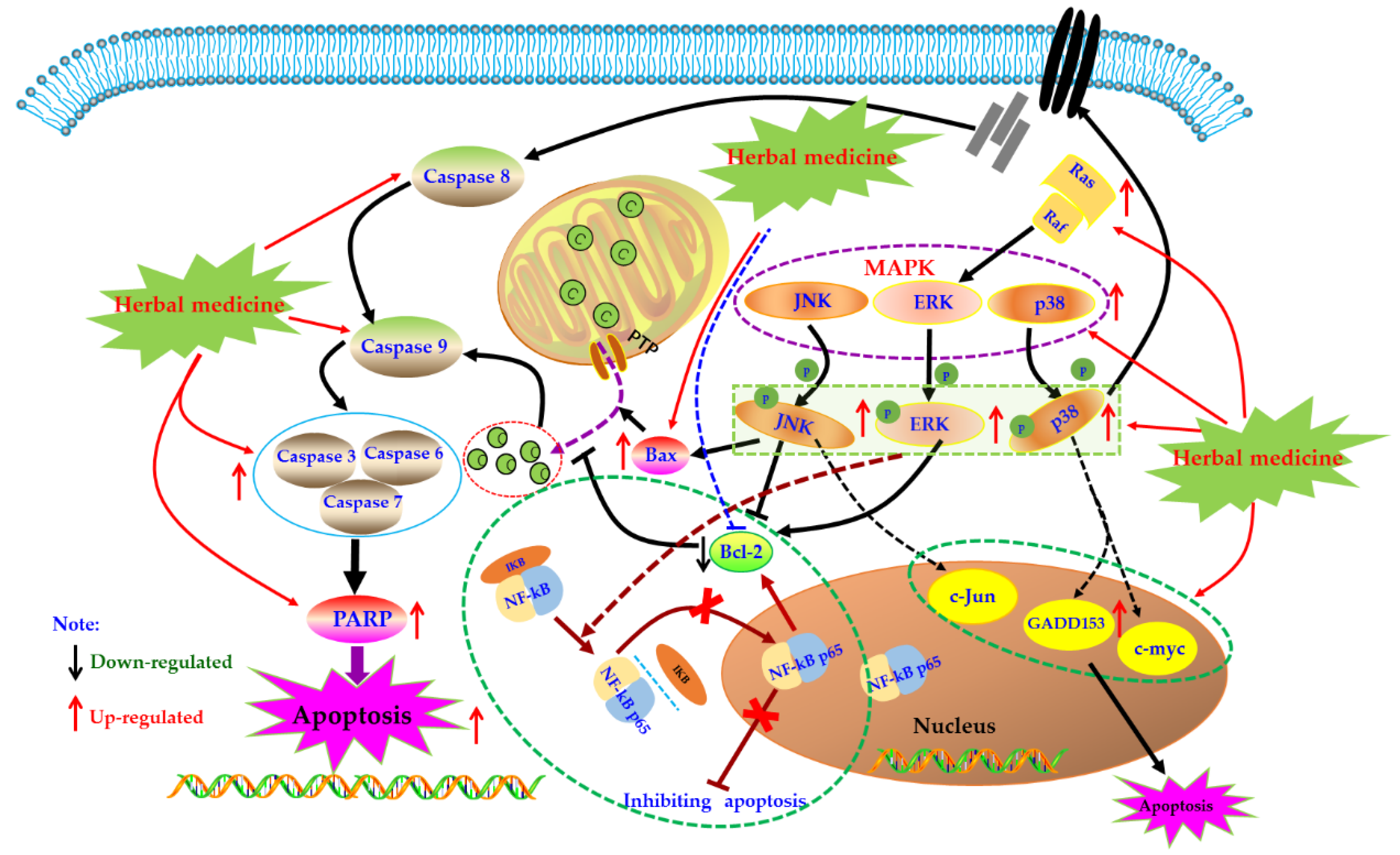
MAPK pathway is an important signal transduction pathway in eucaryotic cells, which exists in most cells and is regulated step by step by MAP kinases kinases kinases (MAPKKK) and mapkinases kinases (MAPKKK). In brief, extracellular signal stimulation phosphorylates receptors on cell membrane, such as Ras, binds and activates intracellular MAPKKK, such as Raf. Activated MAPKKK then activates MAPKK, and MAPKK reactivates MAPKs to transmit signals to cells and their nuclei, and this pathway playing a crucial role in the physiological process of cell proliferation, differentiation, as well as apoptosis [96,97,98]. MAPKs mainly include extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK), P38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Generally speaking, ERK regulates Bcl-2 expression and is mainly involved in cell proliferation and differentiation. JNK and p38 are mainly involved in the stress response and apoptosis of cells by regulating the expression of downstream proteins, such as Bax, GADD153, and c-Jun [99,100]. It has been reported that MAPKs also play crucial roles in activation of Caspase cascades [101,102]. Currently, effects of the MAPK pathway in immune diseases such as RA have been comprehensively investigated. An increasing number of studies have found that MAPKs expressions in synovial tissues of RA patients are abnormally increased, which promotes synovial proliferation. Consequently, MAPKs are considered as promising potential treatment targets for treating RA [103,104,105,106].
In recent years, the effects of herbal medicine and its active monomers on MAPK pathway in articular synovium have been comprehensively reported in vivo and in vitro. In 2007, Liagreh et al. found that Diosgenin (26) can induce apoptosis in RA-FLS cells, and Diosgenin (40 μM) can activate p38 and JNK, but inhibit phosphorylation of ERK. In addition, DNA fragmentation induced by Diosgenin could be reduced by SB203580 and SP600125 (p38 and JNK inhibitors) [107]. Another similar study also reported that Hecogenin (27) and Tigogenin (28), which are similar to Diosgenin (26) in structure, have anti-proliferation and pro-apoptotic potential in FLS of arthritis patients cultured in vitro, but these two saponins only seem to activate p38, and have no significant effect on the phosphorylation of JNK and ERK [108]. Later, in 2009, Shin et al. studied the effects of Apigenin (29) which is a dietary plant-flavonoid and known natural compound with various bioactivities on MH7A cells. Form a systemic research in vitro, the authors found that Apigenin (25, 50, and 100 μM) intervention can significantly induce the apoptosis of RA-FLS by activating ERK1/2 and activating Caspases-3 and -7 [109]. In addition, Zuo et al. reported that XAN (20) (10, 30 μg/mL) can induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in MH7A cells which can be blocked by MAPKs inhibitors, and XAN intervention can increase the proportion of Bax/Bcl-2 in MH7A cell, as well as up-regulate the phosphorylation of ERK, JNK, and p38 [110]. β-Elemene (30) is a known natural sesquiterpene compound, treatment with β-Elemene (10–200 μg/mL) can improve the phosphorylation level of p38 and promote cell apoptosis in RA-FLS, and p38 inhibitors can significantly reverse the pro-apoptotic effect of β-Elemene, consequently these results suggested that the MAPK pathway is closely involved in the pro-apoptotic effects of β-Elemene on RA-FLS [111].
However, there are also some investigations that showed that suppression of the MAPK signal pathway might be beneficial for induction of apoptosis in FLS. Triptolide (31) is a known natural monomer isolated from the Tripterygium wilfordii with immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities. It is reported that Triptolide (0.28–140 nM) possessed notable anti-proliferative effects on RA-FLS, as well as induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in RA-FLS. Furthermore, the possible mechanism is related to suppression of Ras-MAPK signaling [100,112]. Brucine (32) is an important alkaloid of Strychni Semen, and is reported by Tang that Brucine (0.125–2 mg/mL) has potential inhibitory effect on proliferation of TNF-αstimulated RA-FLS cells via down-regulating JNK MAPK and p-JNK MAPK [113]. Previous literatures have showed that the MAPK signal could activate the NF-κB signal which is also a known anti-apoptosis signal pathway in FLS cells [114], consequently we speculated that in a certain condition, blocking MAPK signal might also induce cell proliferation suppression or apoptosis in FLS. The potential mechanisms of herbal medicine for inducing apoptosis in this part are summarized in Figure 4 and Table 1.
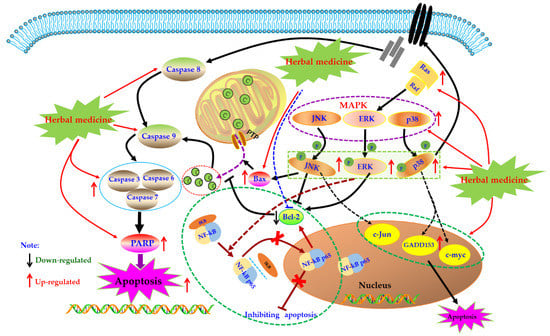
Figure 4.
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) mediated apoptotic pathway in FLS induced by herbal medicines.
4.5. ERS Mediated Apoptotic Pathway
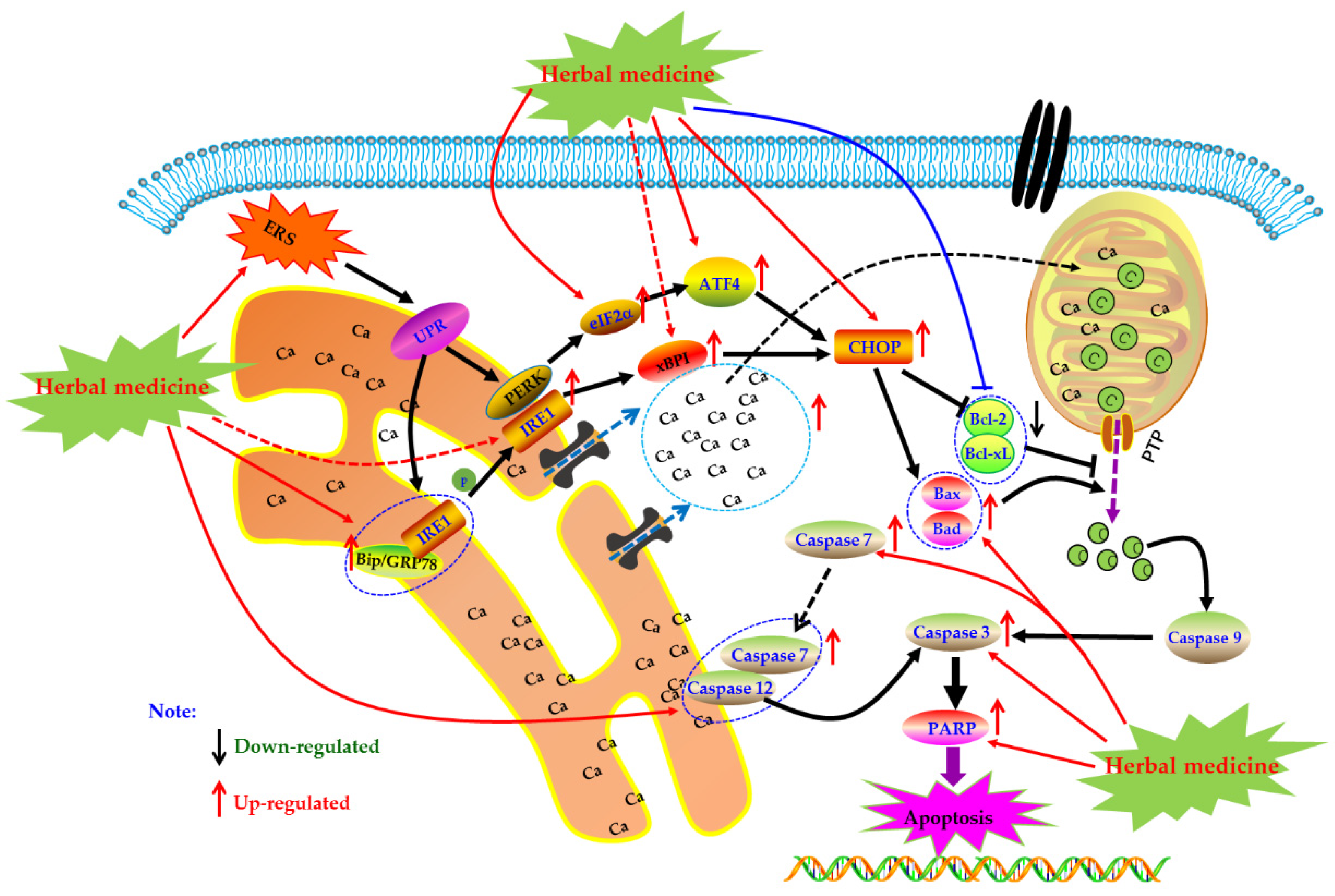
As an important organelle of the cell, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) can guide the synthesis, folding, and secretion of proteins in eukaryotic cells. The endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) of cells caused by endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction can enhance protein folding ability, retards translation of most proteins, as well as accelerate protein degradation, etc., which is the self-protective mechanism of cells [115]. When ERS function is abnormal, Caspase-12 can be activated to directly induce apoptosis. It can also activate the unfolded protein response (UPR), induce the expression of molecular chaperones such as glucose-2 regulated protein 78kD (GRP78), GRP94, Bip, etc., regulate the Irel/xBPT pathway, p-ERK/eIF2 α pathway, and up-regulate the expression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein epsilon (CHOP), indirectly promoting apoptosis. In addition, ESR can induce the opening of calcium channels, promote Ca2+ outflow, and break the Bax/bcl-2 balance. These responses are collectively called endoplasmic reticulum associated with death (ERAD) [116,117,118].
Currently, it is abundantly reported that herbal medicines and its monomers can induce apoptosis of FLS through ERS pathway to exert anti-RA activity. In 2014, Jeong et al. found that Hempseed oil (0–2.5%) can reduce the survival rate of MH7A cells via promoting apoptosis in MH7A with a time-, dose-dependent manner. Further mechanism studies of the pro-apoptotic activities of Hempseed oil suggested that Hempseed oil can increase CHOP expression in MH7A cell, which is an important transcription factor closely related to apoptotic effect of Hempseed oil in MH7A cells [119]. Later, in 2015, Kim et al. investigated the effects of a novel chalcone derivative named (E)-3-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)-prop-2-en-1-one (DK-59, 33) on MH7A cells. The results showed that DK-59 reduced cell viability and induced ROS production and apoptosis in MH7A cells via up-regulating ATF4 and CHOP, activating Caspase-7 and PARP, as well as increasing phosphorylation of eIF2α [120]. Similarly, the extracts of Eupatorium japonicum Thunb (EJTE, 37.5 μg/mL) also showed apoptosis inducing activities in RA-FLS via ERS-mediated apoptotic pathway, such as up-regulation of ATF4 and CHOP [121]. Another in vitro experiment by Lu et al. showed that in the presence of H2O2, resveratrol (1) (50–400 μM) could induce the apoptosis in FLS with a dose-dependent manner. Meanwhile, resveratrol treatment increased the expression of Caspase-12 and CHOP, suggesting that ERS was involved in the occurrence of FLS apoptosis. Additionally and interestingly, resveratrol did not seem to cause intracellular calcium overload [122]. The potential mechanisms of herbal medicine for inducing apoptosis in this part are summarized in Figure 5 and Table 1.
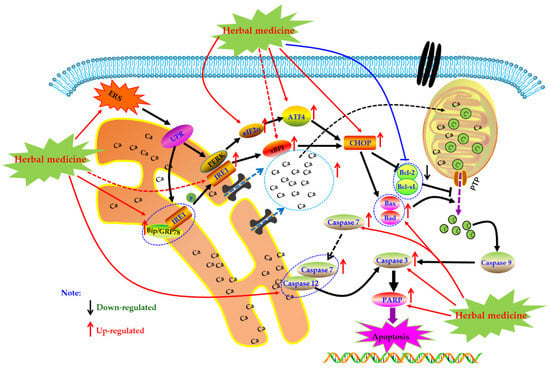
Figure 5.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) mediated apoptotic pathway in FLS induced by herbal medicines.
4.6. PI3K-Akt Mediated Apoptotic Pathway
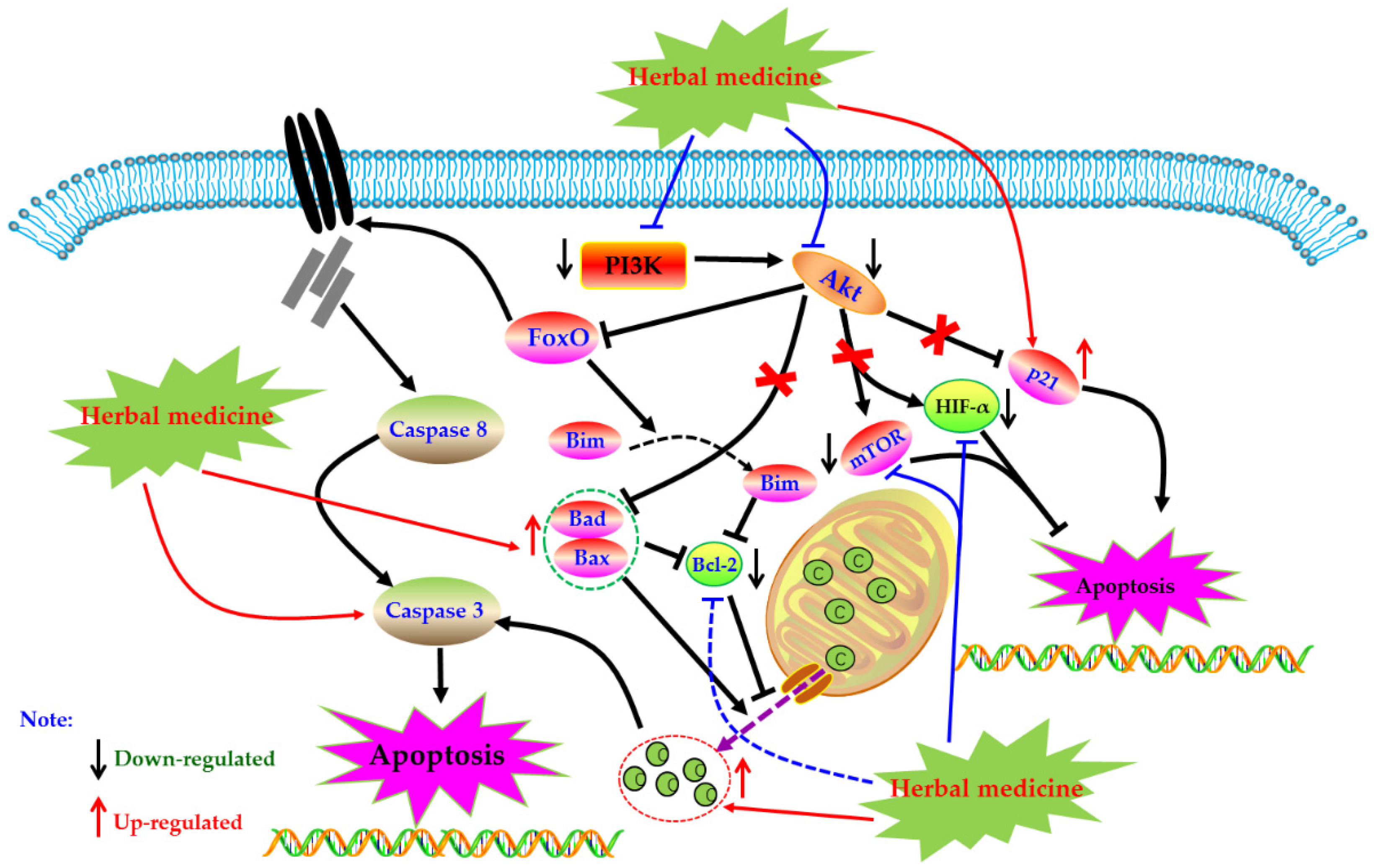
Phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) is an important kinase, when phosphorylated, activates inositol and phosphatidylinositol, catalyzing Akt migration to the membrane and complete activation. Activated Akt is involved in physiological activities such as cell survival, growth, proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis by activating a series of downstream intracellular proteins. However, the abnormal regulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway may lead to the increase of these activities and induce serious diseases in the body. Studies have found that the PI3K-Akt pathway is abnormally activated in synovial cells of RA patients, which can also lead to increased expression of anti-apoptotic genes in cells [123,124]. More and more studies have proved that inhibiting the abnormally activated PI3K-Akt pathway can induce RA-HFLS apoptosis, and improve synovial hyperplasia, cartilage destruction, and other pathological phenomena of RA patients [125,126]. Currently, increasing evidence has revealed that regulation of PI3K-Akt pathway is also an important way for herbal medicines to treating RA.
4.6.1. Herbal Medicine Extracts
In 2012, an in vivo experiment showed that the apoptosis rate of rat synovial fibroblasts induced by IL-1β increased by intervention of total saponin of Dioscoreae Nipponicae Rhizoma (TSDN, 100 μg/L), and at the same time, the phosphorylation levels of PI3K and Akt protein in FLS cells were down-regulated, suggesting that PI3K-AKT pathway was involved in the apoptotic activity of TSDN [127]. Recently, Pan et al. reported that the intervention of Duan tengyimu decoction (DTYD, 100 and 200 μg/mL) significantly inhibited the activation of PI3K and Akt, further enhanced the expression of Bax, and reduced the expression of Bcl-2 in RA-FLS [128]. In addition, it is reported that medicated serum of Shuangwuxuan bi granule also showed similar pro-apoptotic effect on RA-FLS, and the mechanism was related to the exception of PI3K/Akt signal pathway [129]. Heiguteng-Zuifenghuoluo Capsule (HGTZFC) is a Chinese patent medicine used for treating RA, Liu et al. reported that HGTZFC (0.315 g/kg) could down-regulate the HIF-α, p-PI3K, p-Akt, and Bcl-2, whereas up-regulate Bax in synovial tissue of CIA rats [130].
4.6.2. Monomers from Herbal Medicine
In 2011, Zhang et al. found that Genistein (34) (50, 100, and 200 μM) can induce apoptosis in vitro cultured FLS of CIA rats, and the mechanism regulates the expression of apoptosis-related proteins Bax and Bcl-2 by inhibiting Akt expression [131]. Another study by Li et al. reported that Tanshinone IIA (12, 40 µM) can promote apoptosis in RA-FLS via up-regulating lncRNA GAS5, cleaved Caspase-3 and -9 and inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling [132]. In addition, Yang studied the effect of Anacardic acid (35) on RA, and found that anacardic acid has good therapeutic effect on symptoms of CIA rats, and the Anacardic acid (5, 30, and 60 µM) can induce apoptosis of the RA-FLS, and the possible mechanism is closely related to the PI3K/Akt signal pathway [133]. Another study in 2019 by Zuo and Wang reported that Juglone (30 µM) can promote the apoptosis in RA-FLS via inhibiting the phosphorylation of Akt and increasing expression of p21 [134]. Besides, from the results of Feng et al., Diosgenin (26) (10, 20, and 40 μg/mL) could also result in apoptosis in RA-FLS via regulation of the proteins related to PI3K-Akt signal [135]. In a recent study, Wang et al. investigated the effect of Pectolinarin (36) (20 µM) on RA-FLS, and found that besides mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathway, regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling might be also an important molecular mechanism responding to the apoptosis inducing effects of Pectolinarin [136]. The potential mechanisms of herbal medicine for inducing apoptosis in this part are summarized in Figure 6 and Table 1.
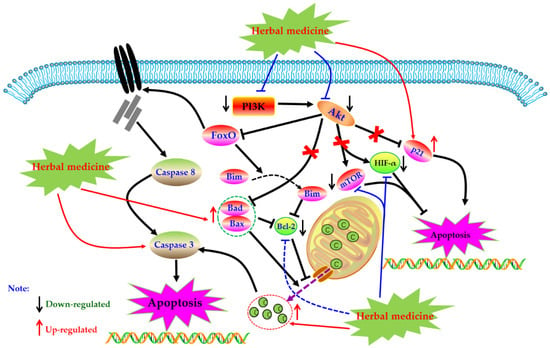
Figure 6.
PI3K-Akt mediated apoptotic pathway in FLS induced by herbal medicines.
4.7. Other Reported Pathways
Additionally to the apoptotic pathways mentioned above, other mechanisms also reported to be closely related to the apoptosis inducing activities of herbal medicines on FLS. Previous research has also revealed that janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) signal is closely correlated to the apoptosis induced by herbal medicines. Ren et al. reported that TAHP (6) (50 and 250 μM) treatment induced apoptosis in FLS, and can down-regulate Jak2 and STAT3, resulting in inhibition of the Jak2/STAT3 signal pathway [60]. Another report by Yang et al. also revealed that the pro-apoptotic effect of Matrine (37) (0.75 mg/mL) which is a known natural monomer from Sophora flavescens on rFLS in CIA rats was achieved by inhibiting the JAK/STAT pathway [137]. Recently, Zhang et al. suggested that suppression of JAK-STAT signaling is also an important molecular mechanism for the pro-apoptotic effects of GZSD in MH7A cells [16]. In 2013, Celastrol (9) (1–5 µM) was reported to be an active neutral compound that could dose-dependently induce apoptosis of RA-FLS, the possible mechanism is the induction of DNA damage, the G2/M phase of the cell cycle arrest and apoptosis related proteins (Bax/Bcl-2, Caspase-3 and -9) [138]. In 2016, Ren studied the inhibitory effect of 10-Hydroxycamptothecine (10-HCPT) (38) on proliferation of RA-FLS, and the results showed that 10-HCPT (1 and 10 μg/mL) induced obvious apoptosis in RA-FLS. In addition, the further investigation revealed that the pro-apoptotic effects of this compound might be related to down-regulation of VEGF and MMP-3 [139]. In 2017, Yao et al. reported that three natural compounds including Tamaractam (39), Cis-N-feruloyl-3-O-methylaids (40), and Trans-N-feruloyl-3-O-methylaids (41) isolated from Tamarix ramosissima showed in vitro pro-apoptotic effects on RA-FLS and up-regulated caspase-3 and-7. Flow cytometry results showed these compounds can increase the sub-G1 fraction in the cell cycle, suggesting that activation of the Caspase family and induction of cycle arrest are involved in pro-apoptotic effects [140]. Later, in 2018, it was also reported that Huangqichongteng Drink (HQCD) can induce the synovial cells in G0/G1 stage of cell growth, promoting apoptosis in RA-FLS [141]. Besides, it is also found resveratrol (9) (40–320 µM) down-regulated the autophagy related proteins (LC3A/B and ATG-5) in H2O2 induced FLS cells, and increase the ROS production and Ca2+ release, resulting in apoptosis of FLS [142]. Besides, it is reported that Wogonin (42), total glucosides of paeonia (TGP), Cinnamic aldehyde (CINA, 43), and Paclitaxel (44) also have pro-apoptosis effects on the RA-FLS [143,144,145,146].
The related monomers in the section (Effect of FLS apoptosis in RA) for inducing apoptosis in FLS and its possible molecular mechanism are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2 and Figure 7 and Figure 8.

Table 2.
Monomers for inducing apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
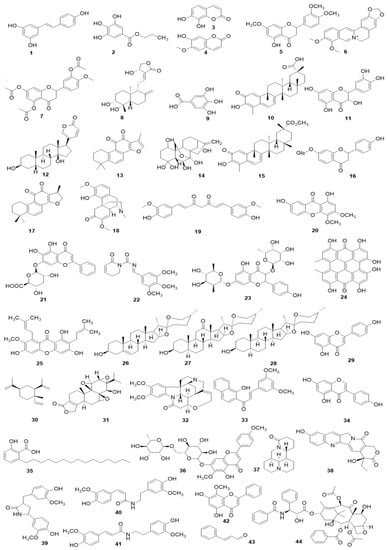
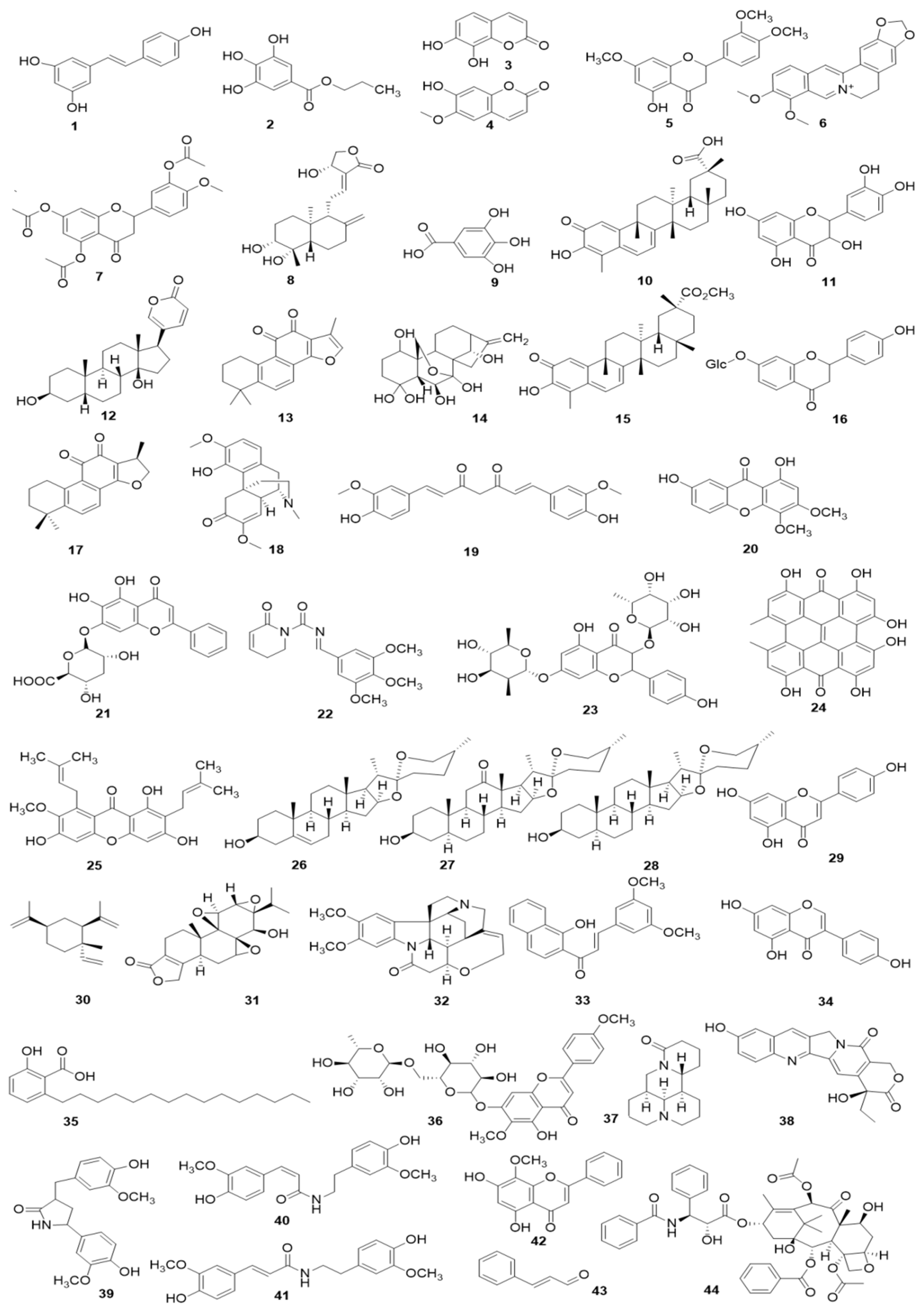
Figure 7.
The related monomers for inducing apoptosis in FLS. Resveratrol (1), Propyl gallate (2), Daphnetin (3), Scopoletin (4), 7, 3′-dimethoxy hesperetin (5), Berberine (6), 5,7,3′-triacetyl hesperetin (TAHP, 7), Andrographolide (8), Gallic acid (9), Celastrol (10), Quercetin (11), Bufalin (12), Tanshinone IIA (13), Oridonin (14), Pristimerin (15), Liquiritin (16), Cryptotanshinone (17), Sinomenine (18), Curcumin (19), 1,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone (XAN, 20), Baicalin (21), Piperlongumine (22), Kaempferitrin (23), Hypericin (24), α-mangostin (25), Diosgenin (26), Hecogenin (27), Tigogenin (28), Apigenin (29), β-Elemene (30), Triptolide (31), Brucine (32), (E)-3-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)-prop-2-en-1-one (DK-59, 33), Genistein (34), Anacardic acid (35), Pectolinarin (36), Matrine (37), 10-Hydroxycamptothecine (10-HCPT, 38), Tamaractam (39), Cis-N-feruloyl-3-O-methylaids (40), Trans-N-feruloyl-3-O-methylaids (41), Wogonin (42), Cinnamic aldehyde (CINA, 43), and Paclitaxel (44).
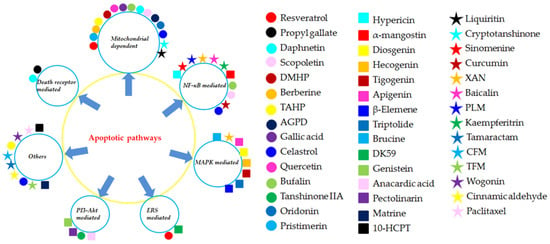
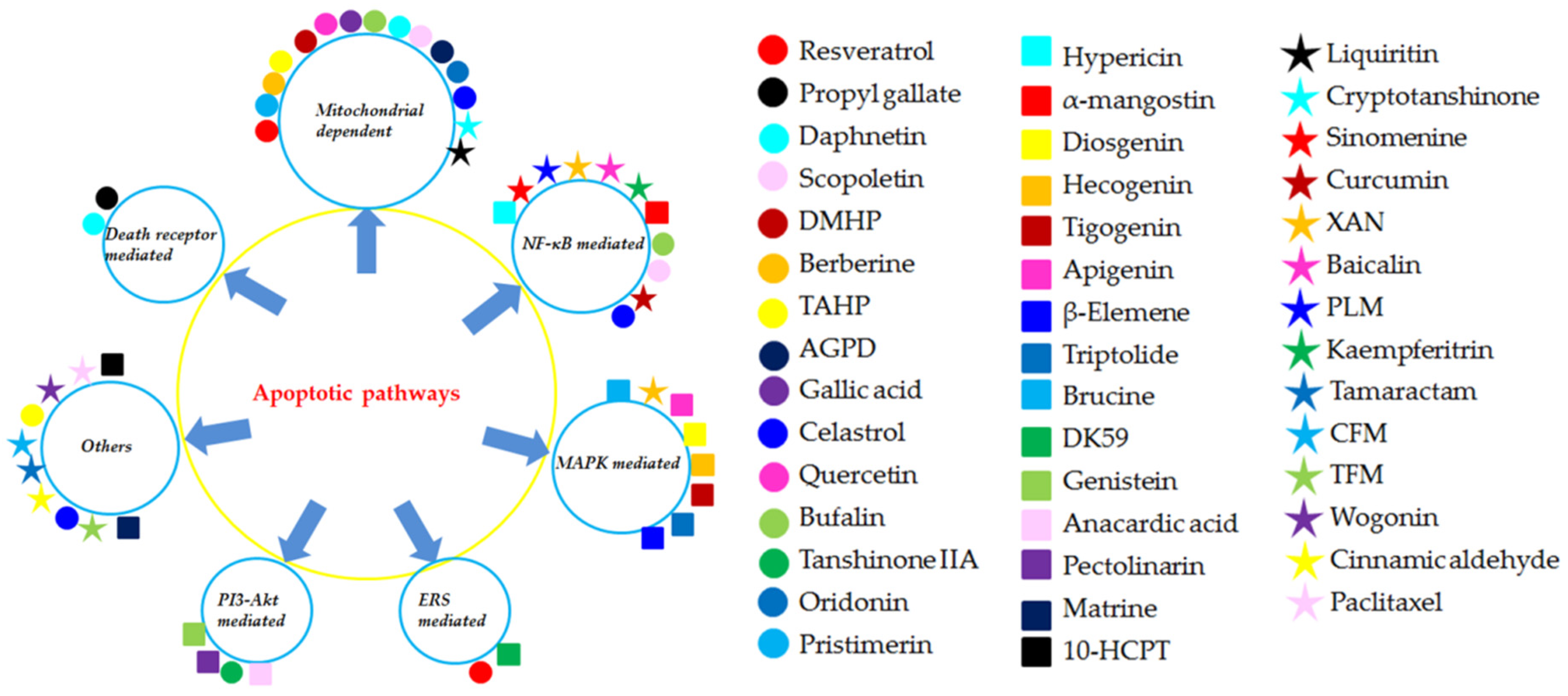
Figure 8.
The different apoptotic pathways of the natural monomers isolated from herbal medicines. 10-HCPT, 10-Hydroxycamptothecine; AGPD, Andrographolide; CFM, cis-n-feruloyl-3-o-methylaids; CINA, Cinnamic aldehyde; DK-59, (E)-3-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one; DMHP, 7,3′-Dimethoxy Hesperetin; PLM, Piperlongumine; TAHP, 5,7,3′-triacetyl-hesperetin; TFM, trans-n-feruloyl-3-O-methyla; XAN, 1,7-dihydroxy-,4-dimethoxyxanthone.
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
It is reported that after simulation by the pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, the fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) would grow rapidly like tumor cells, and development of RA is closely related to an imbalance between cell proliferation, survival, and death of FLS [16,147]. Thus, promoting death of FLS in RA patients might be a feasible way for treating RA, and compared with other therapeutic approaches, targeting FLS might ameliorate clinical symptoms of RA without suppressing systemic immunity. Apoptosis is the main typical programmed cell death ways (PCD) and physiological cell suicide processes. Recently, apoptosis is considered as an ideal way for treatment of cancers, and increasing studies have also indicated that inducing apoptosis in FLS of RA patients would be beneficial for controlling the symptoms and development of RA [16,18].
It is generally recognized that herbal medicines have played important roles in human health maintenance and disease therapy for thousands of years before the appearance of synthetic drugs [148]. Currently, natural products including extracts and monomers derived from herbal medicines are receiving increasing attention in the world, and are commonly considered as precious resource for screening and finding novel candidate drugs with less toxicity [14,149]. In addition, a large number of herbal medicines and its components have the pro-apoptotic activities on FLS, and we have summarized these herbal medicines in this present review. Taken together, apoptosis induction of FLS is an important molecular mechanism for herbal medicine and its active components in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, and the main related signal pathways are concluded as death receptors mediated apoptotic pathway, mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathway, NF-κB mediated apoptotic pathways, MAPK mediated apoptotic pathway, ERS mediated apoptotic pathway, PI3K-Akt mediated apoptotic pathway, and other reported pathways such as JAK-STAT signal pathway. Understanding the apoptosis induction pathways in FLS of these natural medicines will not only help clear molecular mechanisms of herbal medicines for treating RA but also be beneficial for finding novel candidate therapeutic drugs from natural herbal medicines. Consequently, we expect the present review will highlight the importance of herbal medicines and its components for treating RA via induction of apoptosis in FLS, and provide some directions for the future development of these mentioned herbal medicines as anti-RA drugs in clinical.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.P. and C.W.; methodology, Q.Z.; software, J.L.; validation, Q.Z., J.L., and M.Z.; formal analysis, Y.G.; investigation, Q.Z.; resources, R.L.; data curation, R.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z. and W.P.; writing—review and editing, C.W.; visualization, Q.Z. and W.P.; supervision, C.W.; project administration, C.W.; funding acquisition, W.P.
Funding
This work was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number 2018M631071), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (grant number 2019JDRC0074), and National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant number 2018ZX09721004-009-002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: A review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Han, F.; Cui, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J. Matrine suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma cells through suppression of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G. The use of biologic therapies in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2014, 15, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutolo, M.; Sulli, A.; Capellino, S.; Villaggio, B.; Montagna, P.; Seriolo, B.; Straub, R.H. Sex hormones influence on the immune system: Basic and clinical aspects in autoimmunity. Lupus 2004, 13, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.F.; Zhu, S.L.; Tian, A.C.; Xie, X.P. Systematic review of research on disease burden and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis in China. Chin. J. Evid. Based Med. 2013, 13, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Rheumatology Association. 2018 Chinese guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. J. Int. Med. 2018, 57, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Nissen, S.E.; Yeomans, N.D.; Solomon, D.H.; Luscher, T.F.; Libby, P.; Husni, M.E.; Graham, D.Y.; Borer, J.S.; Wisniewski, L.M.; Wolski, K.E.; et al. Cardiovascular safety of Celecoxib, Naproxen, or Ibuprofen for arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 375, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Hsieh, F.I.; Chang, C.Cl.; Chi, N.F.; Wu, H.C.; Chiou, H.Y. Effect on risk of stroke and acute myocardial infarction of nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 10, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushibara, M.; Takayanagi, H.; Koga, T.; Kim, S.; Isobe, M.; Morishita, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Löeffler, M.; Kodama, T.; Kurosawa, H.; et al. The antirheumatic drug leflunomide inhibits osteoclastogenesis by interfering with receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand-stimulated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, A.K.; Li, C.; Brennan, F.M. Recent developments in the immunobiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.H.; Xu, X.R.; Wei, X.C.; Feng, W.W.; Huang, H.Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Xu, R.C.; Lin, J.Z.; Han, L.; Zhang, D.K. Natural medicines for the treatment of fatigue: Bioactive components, pharmacology, and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Gragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Fang, F.F.; Li, X.Q.; Shu, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.P.; Han, T.; Peng, W.; Zheng, C.J. Matrine Exerts a Strong Anti-Arthritic Effect on Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats by Inhibiting Inflammatory Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Peng, W.; Wei, S.J.; Wei, D.N.; Li, R.L.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.Y.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction possesses anti-arthritic effects on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats via suppression of inflammatory reactions, inhibition of invasion and migration and induction of apoptosis in synovial fibroblasts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeken, K.L.; Miller, S.A.; Ernst, E. Herbal medicines for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartox, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblat-like synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczanowski, S. Apoptosis: Its origin, history, maintenance and the medical implications for cancer and aging. Phys. Biol. 2016, 13, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntuli, T.M. Apoptosis and Medicine; InTech Prepress: Novi Sad, Croatia, 2012; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, H.R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1701s–1706s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, Y.; Steller, H. Live to die another way: Modes of programmed cell death and the signals emanating from dying cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norbury, C.J.; Hickson, I.D. Cellular responses to DNA damage. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 367–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, B.; Allocati, N.; Graziano, V.; Di Ilio, C.; De Laurenzi, V. Role of apoptosis in disease. Aging 2012, 4, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pap, T.; Gay, S. Fibroblasts and fibroblast-like synoviocytes. In Kelly’s Textbook of Rheumatology, 8th ed.; Firestein, G.S., Budd, R.C., Harris, T., McInnes, I.B., Ruddy, S., Sergent, J.S., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jia, X.Z.; Sui, C.J. Effects of thapsigargin on the proliferation and survival of human rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 605416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, A.; Abramson, S.B.; Pillinger, M.H. The fibroblast-like synovial cell in rheumatoid arthritis: A key player in inflammation and joint destruction. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Gay, R.E.; Nishioka, K.; Gay, S. Ultrastructural demonstration of apoptosis, Fas and Bcl-2 expression of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Perlman, H.; Georganas, C.; Pagliari, L.J.; Koch, A.E.; Haines, K., 3rd; Pope, R.M. Bcl-2 expression in synovial fibroblasts is essential for maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis and cell viability. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5227–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.S.; Rosengren, S.; Doyle, D.L.; Firestein, S. PUMA regulation and proapoptotic effects in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhamedi-Cherradi, S.E.; Zheng, S.J.; Maguschak, K.A.; Peschon, J.; Chen, Y.H. Defective thymocyte apoptosis and accelerated autoimmune diseases in TRAIL-/- mice. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, A.; Pavenstädt, H.; Pap, T. Cell death in rheumatoid arthritis. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.W.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, Y.H.; Seo, J.; Ko, A.; Jeong, M.; Kim, S.J.; Ro, J.Y.; Park, K.M.; Lee, H.W.; et al. Ubiquitination and degradation of the FADD adaptor protein regulate death receptor-mediated apoptosis and necroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, M.E.; Budd, R.C.; Desbarats, J.; Hedrick, S.M.; Hueber, A.O.; Newell, M.K. The CD95 receptor: Apoptosis revisited. Cell 2007, 129, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audo, R.; Combe, B.; Coulet, B.; Morel, J.; Hahne, M. The pleiotropic effect of TRAIL on tumor-like synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients is mediated by caspases. Cell Death Dis. 2009, 16, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, C.J.; Yuan, J. Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 1998, 94, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatizzi, J.C.; Hutcheson, J.; Bickel, E.; Haines, G.K., III; Perlman, H. Pro-apoptotic Bid is required for the resolution of the effector phase of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Conde, C. The role of poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Med. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 837250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.D.; Chen, G.L.; Hu, W.; Han, M.X. Therapeutic effect of Xinfeng Capsule in treating adjuvant arthritis in rats and its effect on fas, fasL and bcl-2 expression in synovial membrane. Chin. J. Integr. Trad. West. Med. 2002, 22, 599–602. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Tang, Z.; Yuang, G. Salvia miltiorrhiza induces expressions of Fas/FasL in fibroblat-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Acad. Med. Milt. Tert. 2010, 32, 2452–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Liang, T.; Zhang, L.L.; Shen, J.M.; Sun, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Y.Z. Study on Fengshi Bitong Prescription in the treatment of rats with collagen-induced arthritis. J. Emerg. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 26, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Qin, R.X.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, H. Botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential application of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb.et Zucc.: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.J. Effects of Resveratrol on the Expression of Caspase-8 and FLIP of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rats Induced by Type II Collagen. Master’s Thesis, North China Coal Medical College, Tangshan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Palao, G.; Santiago, B.; Galindo, M.; Paya, M.; Ramirez, J.C.; Pablos, J.L. Down-regulation of FLIP sensitizes rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedel, J.; Gay, R.E.; Kuenzler, P.; Seemaye, C.; Simmen, B.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, S. FLICE-inhibitory protein expression in synovial fibroblasts and at sites of cartilage and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palao, G.; Stantiago, B.; Galindo, M.; Rullas, J.; Alcami, J.; Ramirez, J.C.; Pablos, J.L. Fas activation of a proinflammatory program in rheumatoid synoviocytes and its regulation by FLIP and Caspase 8 signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Peng, A. The changes of expression of fas/fasl mRNA in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes induced by Radix paeoniae rubra 801. J. Hunan Normal Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2013, 10, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, A.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H. Apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast- like synoviocytes induced by Radix Paeoniae rubra 801. Prac. Prev. Med. 2013, 20, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.J.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, L.; Xue, B. Research progress on effects of Chinese materia medica and active components on proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. Trad. Herb. Drugs. 2016, 47, 844–850. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M. Daphnetin Induces Apoptosis in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes from Collagen-Induced Arthritic Rat and its Mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer, D.D.; Farschon, D.M.; Reed, J.C. Cell-free apoptosis in Xenopus egg extracts: Inhibition by Bcl-2 and requirement for an organelle fraction enriched in mitochondria. Cell 1994, 79, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.J. Effect and related mechanism of seaweed polysaccharide on apoptosis of fibroblast like synovlocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. J. Integr. Trad. West. Med. 2011, 31, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, R. Effects of Fengshining Capsule on synoviocyte apoptosis of CIA rats in mitochondria pathway. Chin. J. Trad. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2013, 28, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.P.; Lu, G.S. Medicated serum of Duhuo Jisheng Tang has effect on proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rats with adjuvant-incluced arthritis. J. New Chin. Med. 2018, 50, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ci, B.; Wang, W.; Ni, Y. Inhibitory effect of Saposhnikovia divaricate polysaccharide on fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis rat in vitro. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 2791–2798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.L.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, Q.S.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, Y. Effects and mechanism of Pterocarya Hupehensis Skan extracts on proliferation and apoptosis of MH7A cells. Chin. Immunol. J. 2019, 35, 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Liu, M. Scopoletin induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from adjuvant arthritis rats by a mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2009, 70, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cai, L.; Xie, X.F.; Peng, L.; Li, J. 7,3′-dimethoxy hesperetin induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rats with adjuvant arthritis through Caspase 3 activation. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H. Effect of Berberine on Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Its Underlying Molecular Mechanim. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.Y.; Xu, T.; Huang, C.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.L.; Yu, M.Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, J. The influence of 5,7,3′-triacetyl hesperetin on Jak2/Stat3 signalling pathway and related apoptosis proteins of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2012, 28, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; He, C. Andrographolide induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2012, 28, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.H.; Chung, S.J.; Lee, S.W.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, S.K.; Park, M.C. Gallic acid, a natural polyphenolic acid, induces apoptosis and inhibits proinflammatory gene expressions in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Joint Bone Spine 2013, 80, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.T. Celastrol-Introduced Apoptosis, Cell Cycle Arrest and DNA Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synovial. Ph.D. Thesis, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X. The Effects of Quercetin on the Apoptosis of Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Associated Molecular Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.W.; Zhao, Y.F.; Cao, Y.L. Bufalin exerts inhibitory effects on IL-1β-mediated proliferation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation 2014, 37, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.; Du, H.; Huang, Q.; Wei, S.; Huang, R.; Sun, W. Tanshinone IIA Induces Apoptosis in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Blockade of the Cell Cycle in the G2/M Phase and a Mitochondrial Pathway. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, C.H.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhou, J.H. Oridonin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation 2016, 39, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Song, X.B.; Cao, W. Autophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction in adjuvant-arthritis rats treatment with resveratrol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Jin, X. Effect of Resveratrol on proliferation and apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Jiangsu Med. J. 2015, 41, 2182–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Athar, M.; Back, J.H.; Kopelovich, L.; Bickers, D.R.; Kim, A.L. Multiple molecular targets of resveratrol: Anti-carcinogenic mechanisms. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 486, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Wu, L.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, J.T.; Hsu, S.L. Gallic acid induces apoptosis of lung fibroblasts via a reactive oxygen species-dependent ataxia telangiectasia mutated-p53 activation pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.J. Pristimerin Inhibits Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Proliferation and Underlying Mechanisms. Master’s Thesis, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, K.F.; Duan, H.; Cui, C.Y.; Cao, Y.Y.; Si, J.L.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Cao, W.G.; Gao, G.Z.; Wei, Z.J. Liquiritin from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Attenuating Rheumatoid Arthritis via Reducing Inflammation, Suppressing Angiogenesis, and Inhibiting MAPK Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.N.; Luo, Y.H.; Meng, L.Q.; Piao, X.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.Q.; Xu, W.T.; et al. Cryptotanshinone induces reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast like synoviocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Yang, S.; Xin, F.; Wang, M. Anti-inflammatory activity of phlomisoside F isolated from Phlomis younghusbandii Mukerjee. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, A.A.; Sha, W.C.; Bronson, R.T. Embryonic lehality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the ReLa component of NF-κB. Nature 1995, 376, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierkot, J.; Nowak, B.; Czarny, A.; Zaczynska, E.; Sokolik, R.; Madej, M.; Korman, L. The activity of JAK/STAT and NF-kappaB in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Wang, Y.; Cen, X.M. Lipid peroxidation-mediated inflammation promotes cell apoptosis through activation of NF-kappaB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells. Med. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 460310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xai, Z.B.; Meng, F.R.; Fang, Y.X. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and angiogenesis of human fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine 2018, 97, e10920. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Huang, X.L. Effects of sinomenine on in vitro proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast like synoviocyte from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Acad. Med. Milt. Tert. 2007, 29, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of sinomenine on synovioctye apoptosis, cell cycle and change of bcl-2 protein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. Remed. Clin. 2008, 8, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.C.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, E.P.; Lin, Z.; Lv, G.F.; Chen, X. Effect of sinomenine on the expression of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes MyD88 and TRAF6. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 18928–18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, J.; Cai, H. Effect of curcumin on rats with adjuvant arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cell proliferation. Guid. J. Trad. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2010, 16, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kloesch, B.; Becker, T.; Dietersdorfer, E. Anti-inflammatory and apoptotic effects of the polyphenol curcumin on human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.Y.; He, D.Y.; Yu, B.; Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Zuo, J.P.; Li, Y.X.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, X.D.; Wang, Q.W. High-throughput study of the effects of Celastrol on activated fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Genes 2017, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.L.; Jiang, H.; Tao, M.Q.; Wu, W.T.; Jiang, J.; Zuo, J. Selective regulation of IKKb/NF-kB pathway involved in proliferation inhibition of HFLS-RA cells induced by 1,7-dihydroxyl-3,4-dimethoxylxanthone. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Dou, D.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Zhu, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Luan, J.J. Reactive oxygen species mediated NF-κB/p38 feedback loop implicated in proliferation inhibition of HFLS-RA cells induced by 1,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.K.; Ning, Q.Y.; Li, D.X.; Yao, X.M.; Zhou, J.; Hou, L.; Tang, F.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y. Effects of medicated serum frozen powder of Jinwu Jiangu Formula on synovial cell proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. J. Trad. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2017, 32, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, D.X.; Yao, X.M.; Ma, W.K.; Hou, L. Effect of Miao Medicine Jinwu Jiangu decoction on expression of NF-κB p65, IKK-α and IKK-β in FLS of RA. Chin. J. Exp. Trad. Med. Formul. 2017, 23, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, S.; Guo, J.Y.; Ni, G.H.; Chen, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, X.L.; Wen, Y.B.; Guo, Y.X. Hypericin-photodynamic therapy inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes cell line MH7A. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zou, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhan, Z.; Liang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H. Piperlongumine inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Q. Kaempferitrin inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and ameliorates inflammation in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Z.; Ge, C.X.; Wang, G.Z.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, N. Effects of Baicalin on human fibroblast like synoviocytes (rheumatoid arthritis). J. Qiqihar Univ. Med. 2017, 38, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.; Yin, Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Xiao, Z.G.; Wang, G.D.; Luan, J.J. Inhibition of NF-κB pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes by α-mangostin implicated in protective effects on joints in rats suffering from adjuvant-induced arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 56, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, B.; Dai, Y.; Gu, Y. PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in IGF-1-induced VEGF-C upregulation in breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Du, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W. Human chorionic gonadotropin beta induces migration and invasion via activating ERK1/2 and MMP-2 in human prostate cancer DU145 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54592. [Google Scholar]
- Stanciu, Y.; Wang, R.; Kentor, N.; Burke, S.; Watkins, G.; Kress, I.; Reynolds, E.; Klann, M.R.; Angiolieri, J.W.; Johnson, D.B. Persistent activation of ERK contributes to glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and primary cortical neuron cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12200–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Z.; Lian, J.R.; Kong, X.Y.; Lin, N. Effects of triptolide on cell proliferation and regulation of RAS MAPKs pathway in synoviocytes induces by tumor necrosis factor. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2010, 35, 888–891. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, D. Furanodienone induces G0/G1 arrest and causes apoptosis via the ROS/MAPKs-mediated caspase-dependent pathway in human colorectal cancer cells: A study in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 25, e2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Iyer, A.K. Tumor-targeted induction of oxystress for cancer therapy. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C. Drug evaluation: VX-702, a MAP kinase inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis and acute coronary syndrome. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2006, 7, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ralph, J.A.; Morand, E.F. MAPK phosphatases as novel targets for rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A. MAP kinases in the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalhamer, T.; McGrath, M.A.; Harnett, M.M. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liagre, B.; Leger, D.; Vergne-Salle, P.; Beneytout, J.L. MAP kinase subtypes and Akt regulate diosgenin-induced apoptosis of rheumatoid synovial cells in association with COX-2 expression and prostanoid production. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liagre, B.; Vergne-Salle, P.; Leger, D.; Beneytout, J.L. Inhibition of human rheumatoid arthritis synovial cell survival by hecogenin and tigogenin is associated with increased apoptosis, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity and upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shin, G.C.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, W.S.; Lee, S.G.; Jeong, M.; Cho, J.; Lee, K. Apigenin-induced apoptosis is mediated by reactive oxygen species and activation of ERK1/2 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 182, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, X.; Ou-yang, Z.; Chen, J.W. Selective modulation of MAPKs contribute to the anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities of 1,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone in rheumatoid arthritis-derived fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Wang, C.; Cui, Z.; Guo, P.; Meng, Q.; Shi, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, G.; Han, Z. β-Elemene induces apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via reactive oxygen species-dependent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 68, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Jia, S.; Pan, W.P. Study on inhibitory effects of Triptolide on the proliferation of fibroblast-like synovial cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis in vitro. Chin. Pharm. 2015, 26, 4357–4359. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M. Study on Brucine’s Effect on Proliferation and JNK Regulation in MAPK Signal Transduction Pathway on RA HFLS Induced by TNF-α. Master Thesis, Luzhou Medical College, Luzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.B.; Man, Z.T.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.Q.; Sun, S. Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 87, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faitova, J.; Krekac, D.; Hrstka, R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2006, 11, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Emi, M.; Tanabe, K.; Murakami, S. Role of the unfolded protein response in cell death. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailidou, C.; Papazian, I.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Kiaris, H. CHOP-dependent regulation of p21/waf1 during ER stress. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 25, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccullough, K.D.; Martindale, J.L.; Klotz, L.O. Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Cho, J.; Shin, J.I.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, E.S.; Lee, K. Hempseed oil induces reactive oxygen species-and C/EBP homologous protein-mediated apoptosis in MH7A human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Cho, J.; Shin, J.I.I.; Baek, C.Y.; Lim, Y.; Koh, D.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, K. A novel synthetic chalcone derivative promotes caspase-dependent apoptosis through ROS generation and activation of the UPR in MH7A cells. Genes Genom. 2015, 37, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.I.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, S. Apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of Eupatorium japonicum Thunb. in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J. Resveratrol alleviates inflammatory injury and enhances the apoptosis of fibroblast like synoviocytes via mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.J.; Foster, J.G.; Ward, S.G. PI3K isoforms as drug targets in inflammatory diseases: Lessons from pharmacological and genetic strategies. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2009, 10, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.D.; Weedon, H.; Papangelis, V.; Walker, J.; Roberts-Thomson, P.J.; Ahern, M.J. Apoptosis in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane: Modulation by disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug treatment. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.D. Apoptosis a relevant therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatology 2004, 43, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hongtao, L.; Pope, R.M. The role of apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.H.; Liu, L.; Lu, F.; Yang, C.; Xue, H.H.; Liu, S.M. Effect of total saponin of dioscoreae nipponicae rhizoma on PI3K/Akt signal pathway by in rIL-1β induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chin. J. Exp. Trad. Med. Formaul. 2012, 18, 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.M.; Wang, Q.; Cai, X.D.; Guo, T.F.; Wei, Z.Q.; Han, L.Y.; Jiang, Y.B.; Liu, M.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Guo, W.J.; et al. Duanteng Yimu Decoction induces apoptosis through inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chin. J. Trad. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2018, 33, 2051–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.H.; Hou, C.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Hua, Z.; Wei, S. Effects of Shuangwuxuanbi granule on the apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Med. J. Chin. PLA 2018, 43, 721–726. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.S.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, X.; Yan, F.L.; Cao, F.; Yang, C.F.; Liang, J. Effect of Hei Gu Teng Zhui Feng Huo Luo Capsule on PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α protein signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Chin. J. Immun. 2019, 35, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Shen, W.G.; Xu, J.X.; Ma, Y.Y. Effect of Genistein on the proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rats with collagen II induced arthritis. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2011, 27, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Meng, F.; Xia, Z.; Wu, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D. Tanshinone IIA promotes the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by up-regulating lncRNA GAS5. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H. Therapeutic Effects of Anacardic Acid on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Associated Molecular Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, R.T.; Wang, X.B. Effects of juglone on cell proliferation and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chin. Trad. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.J.; Wang, Z.X.; Yang, J. Effects of diosgenin on cell apoptosis and cell cycle of fibroblast like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Immunol. J. 2019, 35, 752–758. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ding, Y. Pectolinarin inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and suppresses inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by inactivating the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 15202–15210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, R. Matrine induces the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rats with collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing the activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, G.; Wei, X. Celastrol induced DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synovial cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.L. Effect of 10-Hydroxycamptothecine on Inhibiting Fibroblast-Like Synocytes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Master Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Cheng-Shuai, J.; Na, S.; Li, W.Q.; Niu, Y.; Han, H.Q.; Miao, Z.H.; Zhao, X.X.; Zhao, J.; Li, J. Tamaractam, a new bioactive lactam from Tamarix ramosissima, induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Molecules 2017, 22, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Effects of Huangqi Chongteng drink on the growth and proliferation of synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis rats. J. Hunan Univ. Chin. Med. 2018, 38, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Lu, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, X. Reducing-autophagy derived mitochondrial dysfunction during resveratrol promotes FLS cell apoptosis. Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. A Preliminary Research on the Effect of Wogonin for Synovial Fibroblasts on Rheumatoid Arthritis. Master Thesis, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.P.; Tang, X.Z.; Ding, H.T.; Zhang, M.L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.R.; Liu, S.T.; Fan, X.Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Experimental research on the influence of total glucosides of paeonia on the proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle of fibroblast-like synovial cells. Tianjing J. Trad. Chin. Med. 2017, 34, 841–844. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.F.; Yang, L.L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.L.; Ding, H.B.; Guo, Y.R.; Du, W.Y.; Xu, M.K.; Gan, W. Experimental research on the influence of cinnamic aldehyde on the proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle of fibroblast-like synovial cells. Tianjing J. Trad. Chin. Med. 2017, 34, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.L.; Quan, F.; Nie, Y.K. Effect of water-soluble paclitaxel on inhibition of synovial fibroblasts cells. J. Harbin Med. Univ. 2018, 52, 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.N.; Guo, L.H. Role of synovial fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 31, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Yang, H.; Long, F.; Hao, H.P.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.W.; Zhang, D.D.; Zheng, H.C.; Wen, Q.Y.; et al. Bioactive equivalence of combinatorial components identified in screening of an herbal medicine. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Shen, H.; Lin, B.; Han, P.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Ye, B.Z.; Rahman, K.; Xin, H.L.; Qin, L.P.; et al. Docking study and antiosteoporosis effects of a dibenzylbutane lignan isolated from Litsea cubeba targeting Cathepsin K and MEK1. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).