Evaluation of Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Malate Dehydrogenase 1 as a Marker in Genetic Prion Disease Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Determination of Human Malate Dehydrogenase 1
2.3. Determination of 14-3-3 Via Immunoblotting
2.4. Determination of Tau in CSF Via ELISA
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
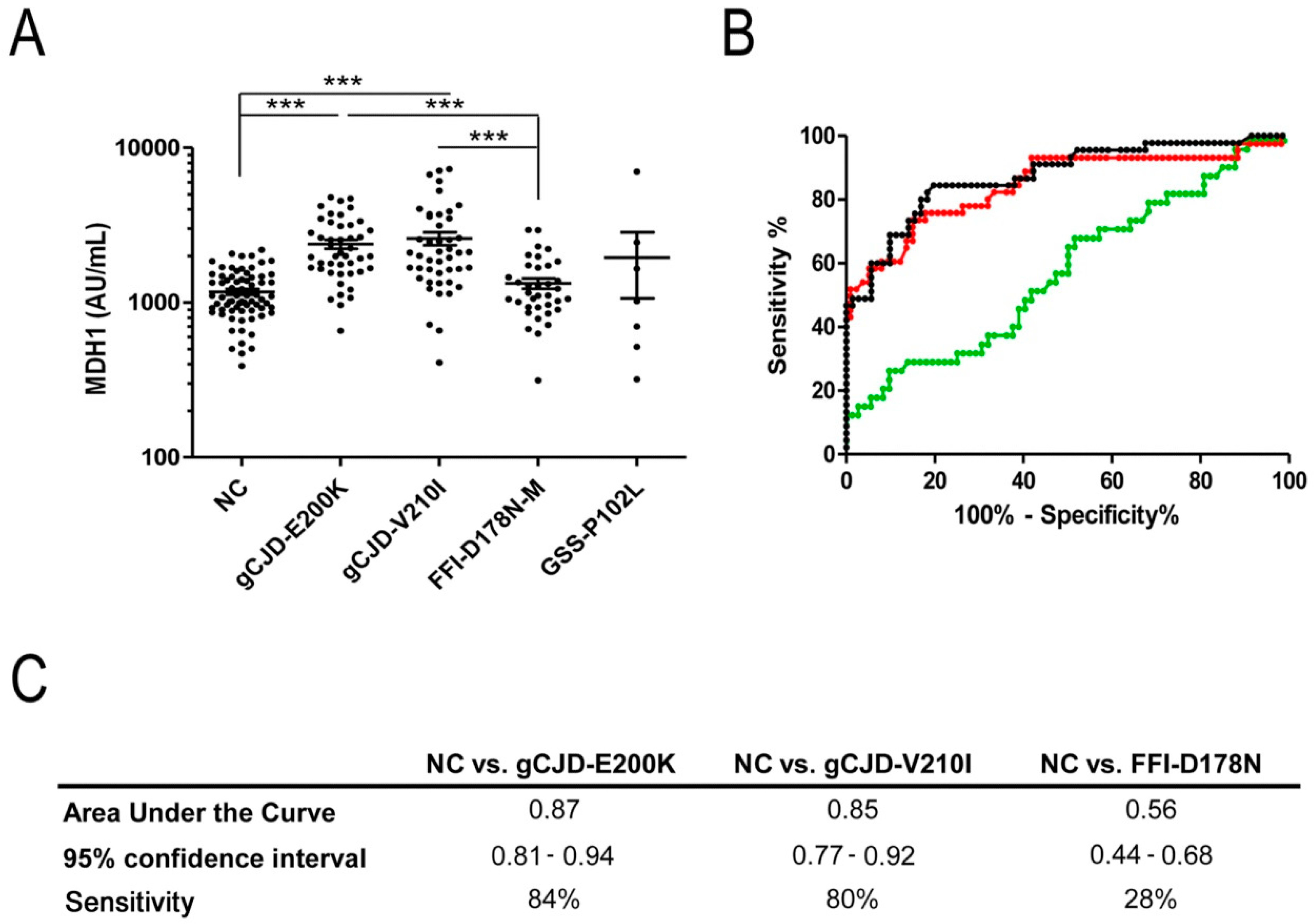
3.1. Analysis of CSF-MDH1 Levels in gCJD Patients
3.2. Correlation between MDH1 and Other Neurodegenerative Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beck, J.A.; Poulter, M.; Campbell, T.A.; Adamson, G.; Uphill, J.B.; Guerreiro, R.; Jackson, G.S.; Stevens, J.C.; Manji, H.; Collinge, J.; et al. PRNP allelic series from 19 years of prion protein gene sequencing at the MRC prion unit. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, E1551–E1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, M.; Dittmar, K.; Llorens, F.; Gelpi, E.; Ferrer, I.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Zerr, I. Hereditary human prion diseases: An update. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4138–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.; Yin, S.; Yu, S.; Wong, P.; Kang, S.C.; Li, C.; Sy, M.S. Normal cellular prion protein with a methionine at position 129 has a more exposed helix 1 and is more prone to aggregate. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 368, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.J.; Sanchez-Juan, P.; Masters, C.L.; Klug, G.M.; van Duijn, C.; Poleggi, A.; Pocchiari, M.; Almonti, S.; Cuadrado-Corrales, N.; de Pedro-Cuesta, J.; et al. Determinants of diagnostic investigation sensitivities across the clinical spectrum of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain 2006, 129, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnianski, A.; Meissner, B.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Kallenberg, K.; Bartl, M.; Heinemann, U.; Varges, D.; Kretzschmar, H.; Zerr, I. Clinical features and diagnosis of the MM2 cortical subtype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, B.; Westner, I.; Kallenberg, K.; Krasnianski, A.; Bartl, M.; Varges, D.; Boesenberg, C.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Knauth, M.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; et al. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Clinical and diagnostic characteristics of the rare VV1 type. Neurology 2005, 65, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerr, I.; Pocchiari, M.; Collins, S.; Brandel, J.P.; de Pedro Cuesta, J.; Knight, R.S.G.; Bernheimer, H.; Cardone, F.; Delasnerie-Lauprêtre, N.; Cuadrado Corrales, N.; et al. Analysis of EEG and CSF 14-3-3 proteins as aids to the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 2000, 55, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerr, I.; Bodemer, M.; Racker, S.; Grosche, S.; Poser, S.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Weber, T. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of neuron-specific enolase in diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1995, 345, 1609–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, P.; Cohen, P.; Brandel, J.P.; Delasnerie-Laupretre, N.; Richard, S.; Launay, J.M.; Laplanche, J.L. 14-3-3 protein, neuron-specific enolase, and s-100 protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 1999, 10, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M.; Wiltfang, J.; Cepek, L.; Neumann, M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Steinacker, P.; Ciesielczyk, B.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Poser, S. Tau protein and 14-3-3 protein in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 2002, 58, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Ebert, E.; Stoeck, K.; Karch, A.; Collins, S.; Calero, M.; Sklaviadis, T.; Laplanche, J.L.; Golanska, E.; Baldeiras, I.; et al. Validation of 14-3-3 protein as a marker in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease diagnostic. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, R.; Satoh, K.; Sano, K.; Fuse, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ishibashi, D.; Matsubara, T.; Nakagaki, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Shirabe, S.; et al. Ultrasensitive human prion detection in cerebrospinal fluid by real-time quaking-induced conversion. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens, F.; Kruse, N.; Schmitz, M.; Shafiq, M.; da Cunha, J.E.; Gotzman, N.; Zafar, S.; Thune, K.; de Oliveira, J.R.; Mollenhauer, B.; et al. Quantification of CSF biomarkers using an electrochemiluminescence-based detection system in the differential diagnosis of ad and sCJD. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2305–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramm, M.; Schmitz, M.; Karch, A.; Mitrova, E.; Kuhn, F.; Schroeder, B.; Raeber, A.; Varges, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Satoh, K.; et al. Stability and reproducibility underscore utility of RT-QuIC for diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Pique, A.; Schmitz, M.; Lachmann, I.; Karch, A.; Calero, O.; Stehmann, C.; Sarros, S.; Ladogana, A.; Poleggi, A.; Santana, I.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid total prion protein in the spectrum of prion diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, F.; Kruse, N.; Schmitz, M.; Gotzmann, N.; Golanska, E.; Thune, K.; Zejneli, O.; Kanata, E.; Knipper, T.; Cramm, M.; et al. Evaluation of alpha-synuclein as a novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarker in different forms of prion diseases. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, F.; Kruse, N.; Karch, A.; Schmitz, M.; Zafar, S.; Gotzmann, N.; Sun, T.; Kochy, S.; Knipper, T.; Cramm, M.; et al. Validation of alpha-synuclein as a CSF biomarker for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Cramm, M.; Llorens, F.; Muller-Cramm, D.; Collins, S.; Atarashi, R.; Satoh, K.; Orru, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Zafar, S.; et al. The real-time quaking-induced conversion assay for detection of human prion disease and study of other protein misfolding diseases. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minárik, P.; Tomásková, N.; Kollárová, M.; Antalík, M. Malate dehydrogenases-structure and function. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2002, 21, 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Gawinecka, J.; Cardone, F.; Asif, A.R.; De Pascalis, A.; Wemheuer, W.M.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Pocchiari, M.; Zerr, I. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease subtype-specific alterations of the brain proteome: Impact on Rab3A recycling. Proteomics 2012, 12, 3610–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawinecka, J.; Dieks, J.; Asif, A.R.; Carimalo, J.; Heinemann, U.; Streich, J.H.; Dihazi, H.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Zerr, I. Codon 129 polymorphism specific cerebrospinal fluid proteome pattern in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and the implication of glycolytic enzymes in prion-induced pathology. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 5646–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, M.; Llorens, F.; Pracht, A.; Thom, T.; Correia, A.; Zafar, S.; Ferrer, I.; Zerr, I. Regulation of human cerebrospinal fluid malate dehydrogenase 1 in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients. Aging 2016, 8, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Wkly Epidemiol. Rec. 1998, 73, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Windl, O.; Giese, A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Zerr, I.; Skworc, K.; Arendt, S.; Oberdieck, C.; Bodemer, M.; Poser, S.; Kretzschmar, H.A. Molecular genetics of human prion diseases in Germany. Hum. Genet. 1999, 105, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Schlomm, M.; Hasan, B.; Beekes, M.; Mitrova, E.; Korth, C.; Breil, A.; Carimalo, J.; Gawinecka, J.; Varges, D.; et al. Codon 129 polymorphism and the E200k mutation do not affect the cellular prion protein isoform composition in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Lullmann, K.; Zafar, S.; Ebert, E.; Wohlhage, M.; Oikonomou, P.; Schlomm, M.; Mitrova, E.; Beekes, M.; Zerr, I. Association of prion protein genotype and scrapie prion protein type with cellular prion protein charge isoform profiles in cerebrospinal fluid of humans with sporadic or familial prion diseases. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrianni, J.A. The genetics of prion diseases. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladogana, A.; Kovacs, G.G. Genetic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 219–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zanusso, G.; Monaco, S.; Pocchiari, M.; Caughey, B. Advanced tests for early and accurate diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramm, M.; Schmitz, M.; Karch, A.; Zafar, S.; Varges, D.; Mitrova, E.; Schroeder, B.; Raeber, A.J.; Kuhn, F.; Zerr, I. Characteristic CSF prion-seeding efficiency in humans with prion diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnianski, A.; Bartl, M.; Sanchez-Juan, P.J.; Heinemann, U.; Meissner, B.; Varges, D.; Schulze-Sturm, U.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Zerr, I. Fatal familial insomnia: Clinical features and early identification. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladogana, A.; Sanchez-Juan, P.; Mitrova, E.; Green, A.; Cuadrado-Corrales, N.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Koscova, S.; Aguzzi, A.; Sklaviadis, T.; Kulczycki, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in human genetic transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koscova, S.; Zakova Slivarichova, D.; Tomeckova, I.; Melicherova, K.; Stelzer, M.; Janakova, A.; Kosorinova, D.; Belay, G.; Mitrova, E. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Slovak patients: Over 10-year period review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 5919–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiner, Z.; Kahana, E.; Baitcher, F.; Korczyn, A.D.; Chapman, J.; Cohen, O.S.; Milo, R.; Aharon-Perez, J.; Abramsky, O.; Gabizon, R.; et al. Tau and 14-3-3 of genetic and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients in Israel. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, F.; Schmitz, M.; Karch, A.; Cramm, M.; Lange, P.; Gherib, K.; Varges, D.; Schmidt, C.; Zerr, I.; Stoeck, K. Comparative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmitterova, K.; Heinemann, U.; Bodemer, M.; Krasnianski, A.; Meissner, B.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Zerr, I. 14-3-3 CSF levels in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease differ across molecular subtypes. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karch, A.; Hermann, P.; Ponto, C.; Schmitz, M.; Arora, A.; Zafar, S.; Llorens, F.; Muller-Heine, A.; Zerr, I. Cerebrospinal fluid tau levels are a marker for molecular subtype in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Age (years) | MDH1 (AU/mL) | Tau (pg/mL) | 14-3-3 | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Sex (f/m) | Mean +/− SD | Mean +/− SD | 95% CI | Mean +/− SD | Pos/Neg | MDH1 vs. Sex | MDH1 vs. Age | |
| NC | 71 | 35/36 | 61± 9 | 1172 ± 413 | 1075–1270 | 304 ± 212 * | NA | 0.37 | 0.12 |
| gCJD—E200K | 45 | 28/17 | 59 ± 11 | 2385 ± 1066 | 2065–2705 | 6263 ± 6310 | 40/5 | 0.84 | 0.19 |
| gCJD—V210I | 46 | 24/22 | 63 ± 9 | 2595 ± 1669 | 2100–3091 | 12710 ± 10815 | 37/9 | 0.45 | 0.31 |
| FFI—D178N-M | 36 | 12/24 | 51 ± 10 | 1330 ± 606 | 1125–1535 | 1122 ± 1741 | 5/31 | 0.79 | 0.24 |
| GSS—P102L | 7 | 3/4 | 52 ± 10 | 1954 ± 2348 | 0–4125 | 1337 ± 1264 | 0/7 | 0.85 | 0.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zerr, I.; Villar-Piqué, A.; Schmitz, V.E.; Poleggi, A.; Pocchiari, M.; Sánchez-Valle, R.; Calero, M.; Calero, O.; Baldeiras, I.; Santana, I.; et al. Evaluation of Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Malate Dehydrogenase 1 as a Marker in Genetic Prion Disease Patients. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120800
Zerr I, Villar-Piqué A, Schmitz VE, Poleggi A, Pocchiari M, Sánchez-Valle R, Calero M, Calero O, Baldeiras I, Santana I, et al. Evaluation of Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Malate Dehydrogenase 1 as a Marker in Genetic Prion Disease Patients. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(12):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120800
Chicago/Turabian StyleZerr, Inga, Anna Villar-Piqué, Vanda Edit Schmitz, Anna Poleggi, Maurizio Pocchiari, Raquel Sánchez-Valle, Miguel Calero, Olga Calero, Inês Baldeiras, Isabel Santana, and et al. 2019. "Evaluation of Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Malate Dehydrogenase 1 as a Marker in Genetic Prion Disease Patients" Biomolecules 9, no. 12: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120800
APA StyleZerr, I., Villar-Piqué, A., Schmitz, V. E., Poleggi, A., Pocchiari, M., Sánchez-Valle, R., Calero, M., Calero, O., Baldeiras, I., Santana, I., Kovacs, G. G., Llorens, F., & Schmitz, M. (2019). Evaluation of Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Malate Dehydrogenase 1 as a Marker in Genetic Prion Disease Patients. Biomolecules, 9(12), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120800








