Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and SAR Studies of Novel 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1H- Benzimidazole Analogues
Abstract
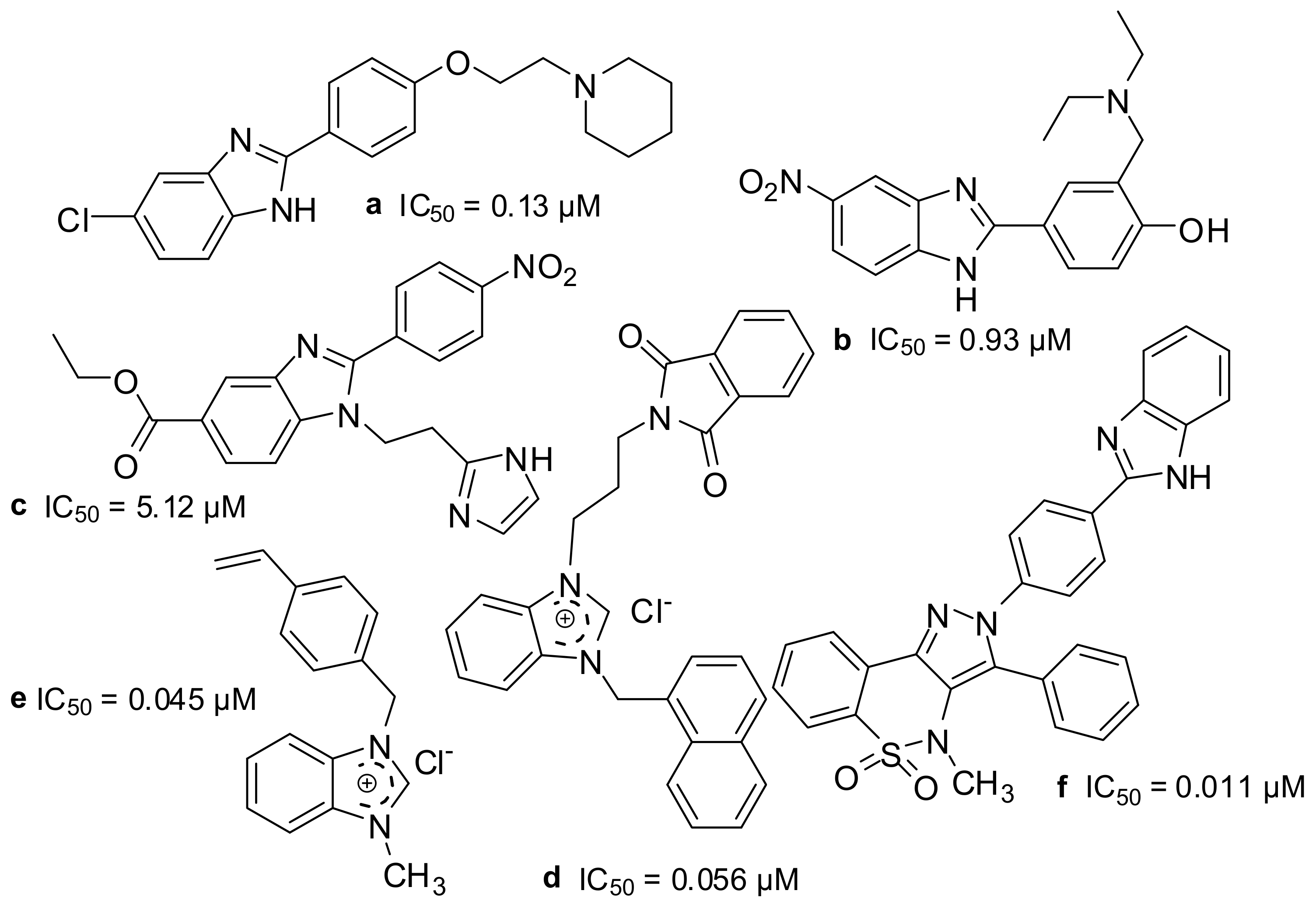
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical Studies
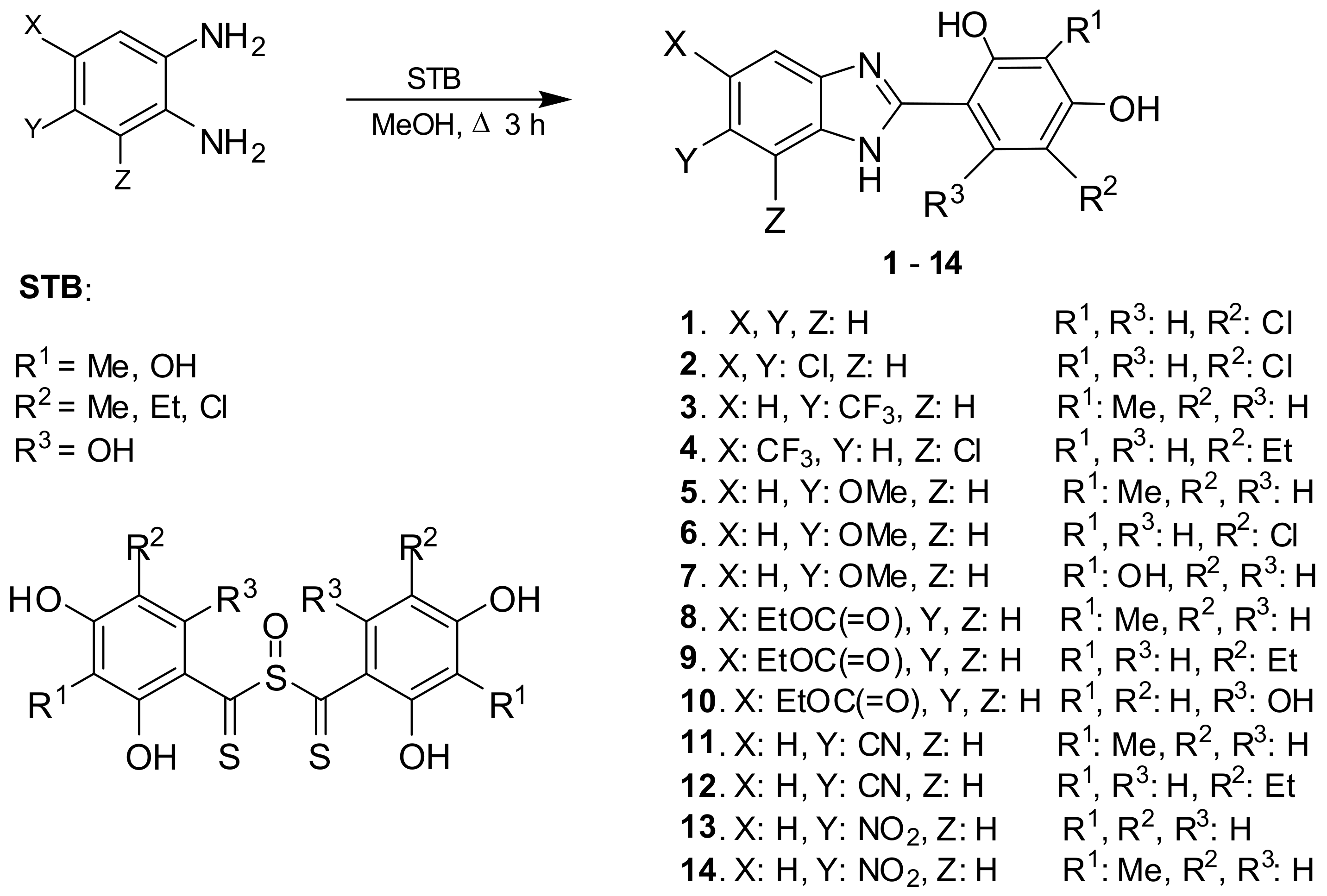
2.2. Synthesis of the Compounds
2.3. RP-18 HPLC Chromatography
2.4. In Vitro AChE and BuChE Inhibition Assay
2.5. Kinetic Characterization of AChE and BuChE Inhibition
2.6. Determination of the Inhibitory Effect on the Self-Mediated Aβ(1–42) Aggregation
2.7. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Assay
2.8. Computational Methods
2.9. Molecular Modeling Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Inhibitory Potency Against AChE and BuChE
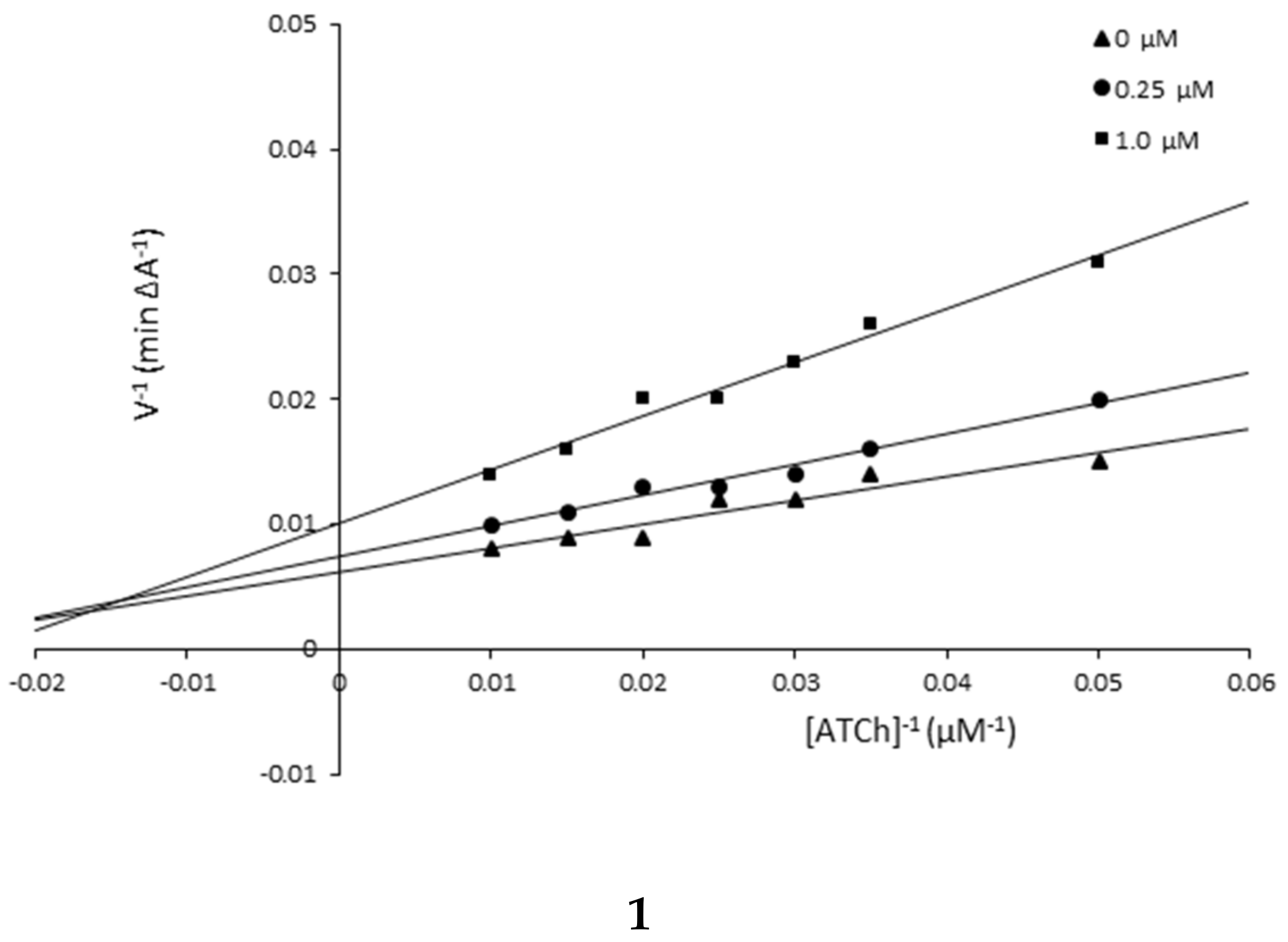
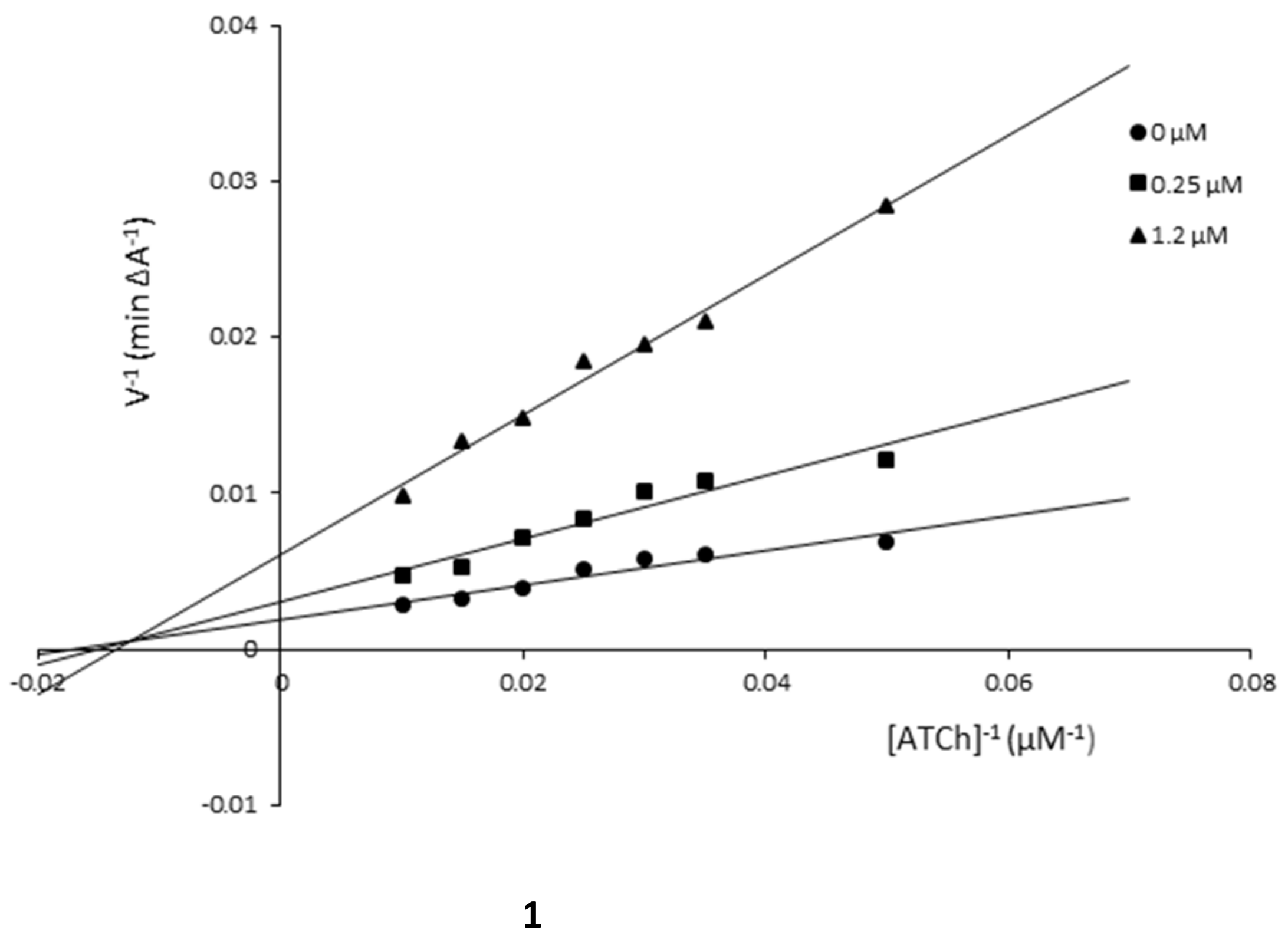
3.3. Kinetic Studies
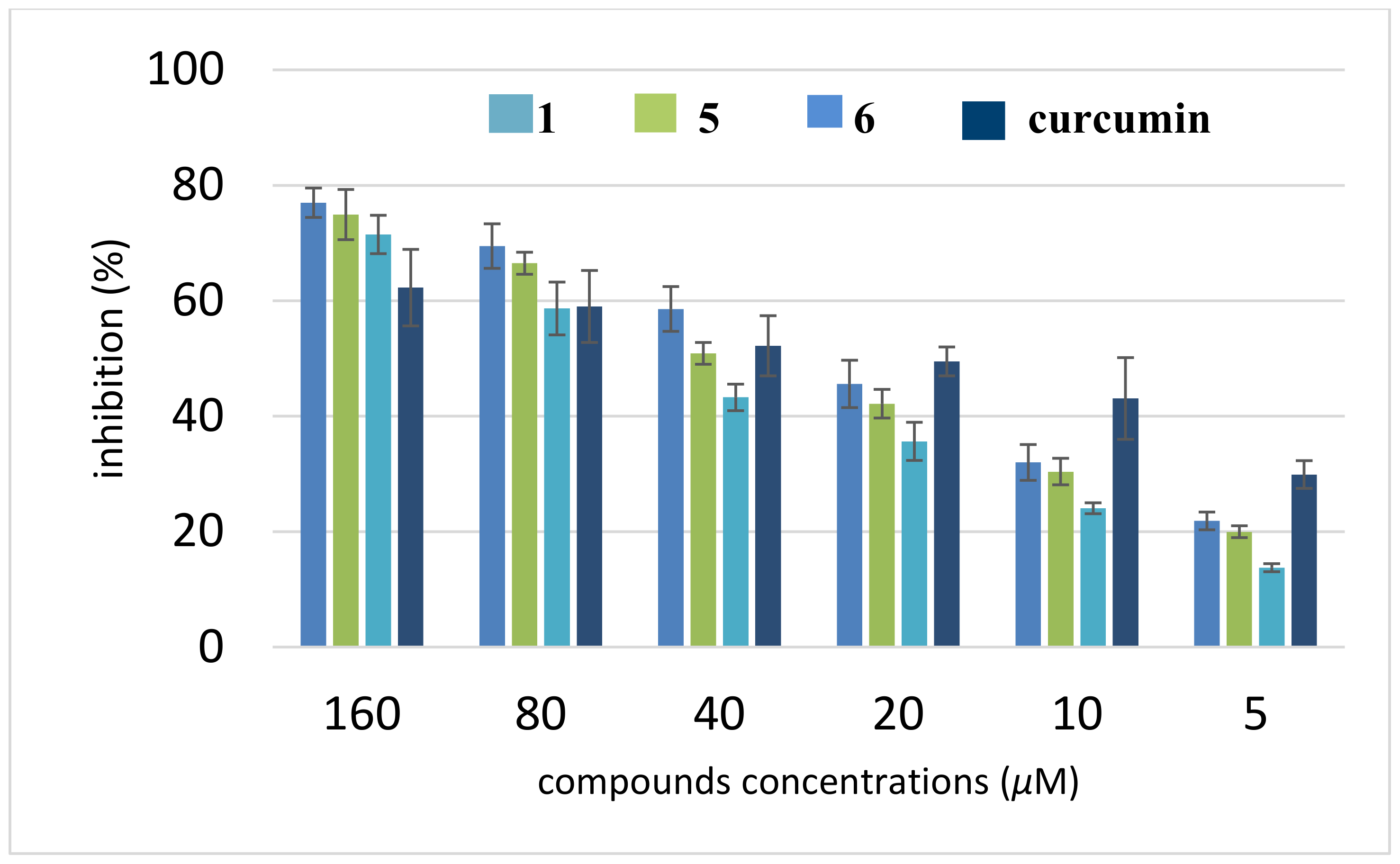
3.4. Inhibition of Self-induced Aβ Aggregation
3.5. Antioxidant Potential
3.6. Molecular Modeling Studies
3.7. SAR Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brookmeyer, R.; Johnson, E.; Ziegler-Graham, K.; Arrighi, H.M. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers. Dement. 2007, 3, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiecki, J.; Wasag, B. Butyrylcholinesterase protein ends in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease - could BCHE genotyping be helpful in Alzheimer’s therapy? Biomolecules 2019, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar Cevik, U.; Saglik, B.N.; Levent, S.; Osmaniye, D.; Kaya Cavusoglu, B.; Ozkay, Y.; Kaplancikli, Z.A. Synthesis and AChE-Inhibitory activity of new benzimidazole derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refolo, L.M.; Fillit, H.M. Drug discovery for Alzheimer’s Disease: The end of the beginning. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, C.F.; Li, X.; Wu, G.S.; Xie, S.; Hu, Q.N.; Deng, Z.; Zhu, M.X.; Luo, H.R.; Hong, X. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of substituted 2-aminobenzimidazoles as novel inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4218–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpan, A.S.; Parlar, S.; Carlino, L.; Tarikogullari, A.H.; Alptuzun, V.; Gunes, H.S. Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling studies on 1H-benzimidazole derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4928–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpan, A.S.; Sarikaya, G.; Coban, G.; Parlar, S.; Armagan, G.; Alptuzun, V. Mannich-benzimidazole derivatives as antioxidant and anticholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluations, and molecular docking study. Arch. Pharm. 2017, 350, e1600351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozadali-Sari, K.; Tuylu Kucukkilinc, T.; Ayazgok, B.; Balkan, A.; Unsal-Tan, O. Novel multi-targeted agents for Alzheimer’s disease: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling of novel 2-[4-(4-substitutedpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]benzimidazoles. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 72, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczak-Swiatkiewicz, K.; Sikora, J.; Szymanski, J.; Danilewicz, M.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E. Biological evaluation of the toxicity and the cell cycle interruption by some benzimidazole derivatives. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 11135–11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.K.; Ali, M.A.; Wei, A.C.; Choon, T.S.; Khaw, K.Y.; Murugaiyah, V.; Osman, H.; Masand, V.H. Synthesis, characterization, and molecular docking analysis of novel benzimidazole derivatives as cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2013, 49, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.; Aktas, A.; Taslimi, P.; Gok, Y.; Gulcin, I. Novel N-propylphthalimide- and 4-vinylbenzyl-substituted benzimidazole salts: Synthesis, characterization, and determination of their metal chelating effects and inhibition profiles against acetylcholinesterase and carbonic anhydrase enzymes. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katalinic, M.; Macek Hrvat, N.; Baumann, K.; Morasi Pipercic, S.; Makaric, S.; Tomic, S.; Jovic, O.; Hrenar, T.; Milicevic, A.; Jelic, D.; et al. A comprehensive evaluation of novel oximes in creation of butyrylcholinesterase-based nerve agent bioscavengers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2016, 310, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, S.; Zaib, S.; Ahmad, M.; Gardiner, J.M.; Ahmad, A.; Hameed, A.; Furtmann, N.; Gutschow, M.; Bajorath, J.; Iqbal, J. Novel structural hybrids of pyrazolobenzothiazines with benzimidazoles as cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungordu, A.; Sireci, N.; Kucukbay, H.; Birhanli, A.; Ozmen, M. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo toxic effects of newly synthesized benzimidazole-based organophosphorus compounds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Yang, L. Novel benzothiazole, benzimidazole and benzoxazole derivatives as potential antitumor agents: Synthesis and preliminary in vitro biological evaluation. Molecules 2012, 17, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.K.; Taha, M.; Ahmat, N.; Wadood, A.; Ismail, N.H.; Rahim, F.; Ali, M.; Abdullah, N.; Khan, K.M. Novel 2,5-disubtituted-1,3,4-oxadiazoles with benzimidazole backbone: A new class of beta-glucuronidase inhibitors and in silico studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, A.; Akhtar, S.; Noureen, S.; Saify, Z.S.; Jahan, S.; Khan, K.M.; Rahim, F.; Mushtaq, N.; Arif, M.; Perveen, S.; et al. 2-(2-Pyridyl)benzimidazole analogs and their beta-glucuronidase inhibitory activity. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2015, 37, 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Zawawi, N.K.; Taha, M.; Ahmat, N.; Wadood, A.; Ismail, N.H.; Rahim, F.; Azam, S.S.; Abdullah, N. Benzimidazole derivatives as new alpha-glucosidase inhibitors and in silico studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 64, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, T.; Khan, K.M.; Rasool, N.; Salar, U.; Hussain, S.; Tahir, T.; Ashraf, M.; Wadood, A.; Riaz, M.; Perveen, S.; et al. Syntheses, in vitro evaluation and molecular docking studies of 5-bromo-2-aryl benzimidazoles as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, T.; Khan, K.M.; Rasool, N.; Salar, U.; Hussain, S.; Asghar, H.; Ashraf, M.; Wadood, A.; Riaz, M.; Perveen, S.; et al. 5-Bromo-2-aryl benzimidazole derivatives as non-cytotoxic potential dual inhibitors of alpha-glucosidase and urease enzymes. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 72, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegboye, A.A.; Khan, K.M.; Salar, U.; Aboaba, S.A.; Chigurupati, S.; Fatima, I.; Taha, M.; Wadood, A.; Mohammad, J.I.; Khan, H.; et al. 2-Aryl benzimidazoles: Synthesis, in vitro alpha-amylase inhibitory activity, and molecular docking study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypek, A.; Matysiak, J.; Niewiadomy, A.; Bajda, M.; Szymanski, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,3,4-thiadiazole analogues as novel AChE and BuChE inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypek, A.; Matysiak, J.; Karpinska, M.M.; Niewiadomy, A. Synthesis and anticholinesterase activities of novel 1,3,4-thiadiazole based compounds. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2013, 28, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzeski, W.; Matysiak, J.; Kandefer-Szerszen, M. Anticancer, neuroprotective activities and computational studies of 2-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole based compound. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3201–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinska, M.M.; Matysiak, J.; Niewiadomy, A.; Wietrzyk, J.; Klopotowska, D. Synthesis and biological activity of novel 4-and 6-(1-alkyl/aryl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-diols. Mon. Fur. Chem. 2012, 143, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinka, M.M.; Matysiak, J.; Niewiadomy, A. Synthesis of novel 4-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-diols and their cytotoxic activity against human cancer cell lines. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavman, A.; Birteksoz, A.S. Spectral characterization and antimicrobial activity of 4-(5-H/Me/Cl/NO2-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-benzene-1,3-diols and some metal complexes. Revi. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 29, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavman, A.; Cinarli, A.; Gurbuz, D.; Birteksoz, A.S. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of 2-(5-H/Me/F/Cl/NO2-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-benzene-1,4-diols and some transition metal complexes. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2012, 9, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.K.; Tomlinson, B.E.; Blessed, G.; Bergmann, K.; Gibson, P.H.; Perry, R.H. Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia. Br. Med. J. 1978, 2, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Perry, G.; Lee, H.G.; Zhu, X. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1842, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://scifinder.cas.org (accessed on 4 September 2019).
- Soczewinski, E.; Axelwach, C. Relation between composition of certain ternary 2-phase solvent systems and Rm values. J. Chromatogr. 1962, 7, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozylo, J.K.; Zabinska, A.; Matysiak, J.; Niewiadomy, A. Reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography with different stationary phases in studies of quantitative structure-biological activity relationship of new antimycotic compounds. J. Aoac. Int. 1999, 82, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharm. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Design, Synthesis, and evaluation of orally available Clioquinol-Moracin M hybrids as multitarget-directed ligands for cognitive improvement in a rat model of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8616–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecka, K.; Girek, M.; Krecisz, P.; Skibinski, R.; Latka, K.; Jonczyk, J.; Bajda, M.; Kabzinski, J.; Majsterek, I.; Szymczyk, P.; et al. Discovery of new cyclopentaquinoline analogues as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.A.; Anwar, M.M.; Abu-Zied, K.M.; Awad, H.M. Synthesis, tumor inhibitory and antioxidant activity of new polyfunctionally 2-substituted 5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene derivatives containing pyridine, thioxopyridine and pyrazolopyridine moieties. Acta. Pol. Pharm. 2013, 70, 987–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, H.N.; Awad, H.M.; El-Sayed, N.H.; Pare, P.W. Chemical and antioxidant investigations: Norfolk pine needles (Araucaria excelsa). Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Crippen, G.M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for three-dimensional-structure-directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 2. Modeling dispersive and hydrophobic interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1987, 27, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysiak, J.; Niewiadomy, A. Application of sulfinyl bis(2,4-dihydroxythiobenzoyl) in the synthesis of N-substituted 2-amino-5-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazoles. Synth. Commun. 2006, 36, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysiak, J.; Niewiadomy, A. Synthesis and antimycotic activity of N-azolyl-2,4-dihydroxythiobenzamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 2285–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepp, K.P. Ten challenges of the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2017, 55, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, N.J.; Davies, N.O.; Lovett, J.E.; Miller, M.R.; Cook, G.; Becker, T.; Becker, C.G.; McPhail, D.B.; Kunath, T. A synthetic cell permeable antioxidant protects neurons against acute oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajda, M.; Wieckowska, A.; Hebda, M.; Guzior, N.; Sotriffer, C.A.; Malawska, B. Structure-based search for new inhibitors of cholinesterases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5608–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, R.E.; Martinez, A.M.; Aragones, M.D.; Miguel, B.G.; Hernandez, F.; Cruz, E. Tetrahydroaminoacridine affects the cholinergic function of blood-brain barrier. Life. Sci. 1993, 53, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godyn, J.; Hebda, M.; Wieckowska, A.; Wieckowski, K.; Malawska, B.; Bajda, M. Lipophilic properties of anti-Alzheimer’s agents determined by micellar electrokinetic chromatography and reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicka, M.; Kwietniewski, L.; Matysiak, J. A new method for estimating log k(w) values and solute biological activity. Jpc-J. Planar. Chromat. 2000, 13, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Niewiadomy, A.; Zabinska, A.; Matysiak, J.; Rozylo, J.K. Influence of modifier and molecular structure of some dihydroxythiobenzanilides on retention in reversed-phase high-performance thin-layer chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 791, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | AChE 1 IC50 [μM] | BuChE 2 IC50 [μM] | Selectivity for AChE 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.076 ± 0.002 | 4.24 ± 0.205 | 55.8 |
| 2 | 0.541 ± 0.036 | 22.69 ± 0.078 | 41.9 |
| 3 | 0.098 ± 0.005 | 14.022 ± 0.111 | 143.1 |
| 4 | 0.118 ± 0.009 | 46.025 ± 0.104 | 390.0 |
| 5 | 0.086 ± 0.021 | 0.117 ± 0.041 | 1.4 |
| 6 | 0.092 ± 0.002 | 18.711 ± 0.173 | 203.4 |
| 7 | >500 | >500 | - |
| 8 | 0.184 ± 0.022 | 25.352 ± 0.232 | 137.8 |
| 9 | 0.962 ± 0.023 | 43.855 ± 0.381 | 45.6 |
| 10 | >500 | >500 | - |
| 11 | >500 | >500 | - |
| 12 | >500 | >500 | - |
| 13 | 1.487 ± 0.118 | 106.557 ± 0.201 | 71.7 |
| 14 | 1.003 ± 0.196 | 88.363 ± 0.155 | 88.1 |
| bib-1,3-diol 4 | 0.284 ± 0.014 | 31.024 ± 0.133 | 109.2 |
| neostigmine | 0.052 ± 0.003 | 0.068 ± 0.005 | 1.3 |
| donepezil | 0.020 ± 0.008 | 7.520 ± 0.200 | 376 |
| Compound/Concentration [μM] | KM [μM] | υmax [A min−1] |
|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | ||
| 1.0 | 46.41 | 105.26 |
| 0.25 | 33.16 | 135.14 |
| 0 | 28.45 | 153.85 |
| Compound 5 | ||
| 1.0 | 487.09 | 120.48 |
| 0.15 | 147.05 | 175.44 |
| 0 | 70.33 | 454.55 |
| Compound/Concentration [µM] | KM [μM] | υmax [A min−1] |
|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | ||
| 1.2 | 73.53 | 163.93 |
| 0.25 | 64.92 | 322.58 |
| 0 | 58.14 | 526.32 |
| Compound 5 | ||
| 0.55 | 209.21 | 178.57 |
| 0.25 | 154.08 | 196.08 |
| 0 | 110.74 | 222.22 |
| Compound | IC50(Aβ(1–42)) [μM] 1 | IC50(DPPH) [μM] 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48.00 ± 3.43 | 0.641 ± 0.03 |
| 2 | - 2 | 0.213 ± 0.08 |
| 5 | 33.07 ± 2.07 | 0.627 ± 0.11 |
| 6 | 27.04 ± 2.29 | 0.362 ± 0.01 |
| 8 | - 2 | 0.125 ± 0.06 |
| 12 | - 2 | 0.209 ± 0.02 |
| rutin | - 2 | 0.087 ± 0.04 |
| No. | log kw | −S | n | r2 | log P | tPSA [Å2] | MR [cm3·mol−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.602 | 3.896 | 6 | 0.992 | 2.64 | 64.85 | 67.86 |
| 2 | 5.460 | 5.770 | 5 | 0.985 | 3.76 | 64.85 | 77.07 |
| 3 | 5.720 | 6.299 | 6 | 0.992 | 3.49 | 64.85 | 75.66 |
| 4 | 4.237 | 4.635 | 6 | 0.992 | 4.47 | 64.85 | 84.87 |
| 5 | 4.591 | 5.179 | 6 | 0.994 | 2.45 | 74.08 | 76.40 |
| 6 | 4.808 | 5.390 | 6 | 0.993 | 2.54 | 74.08 | 75.11 |
| 7 | 3.589 | 3.870 | 6 | 0.996 | 1.57 | 94,31 | 72.32 |
| 8 | 2.566 | 4.097 | 5 | 0.875 | 2.73 | 91.15 | 86.20 |
| 9 | 3.067 | 4.160 | 6 | 0.999 | 3.15 | 91.15 | 90.80 |
| 10 | 2.088 | 3.237 | 6 | 0.979 | 1.85 | 111.38 | 82.12 |
| 11 | 3.590 | 3.867 | 6 | 0.996 | 2.61 | 88.64 | 75.25 |
| 12 | 3.360 | 4.854 | 5 | 0.975 | 3.02 | 88.64 | 79.85 |
| 13 | 2.475 | 4.655 | 4 | 0.999 | 2.52 | 116.66 | - 1 |
| 14 | 2.674 | 4.596 | 5 | 0.981 | 2.94 | 116.66 | - 1 |
| bib-1,3-diol | 1.732 | 2.979 | 5 | 0.968 | 2.09 | 64.85 | 63.26 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matysiak, J.; Skrzypek, A.; Karpińska, M.; Czarnecka, K.; Szymański, P.; Bajda, M.; Niewiadomy, A. Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and SAR Studies of Novel 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1H- Benzimidazole Analogues. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120870
Matysiak J, Skrzypek A, Karpińska M, Czarnecka K, Szymański P, Bajda M, Niewiadomy A. Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and SAR Studies of Novel 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1H- Benzimidazole Analogues. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(12):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120870
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatysiak, Joanna, Alicja Skrzypek, Monika Karpińska, Kamila Czarnecka, Paweł Szymański, Marek Bajda, and Andrzej Niewiadomy. 2019. "Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and SAR Studies of Novel 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1H- Benzimidazole Analogues" Biomolecules 9, no. 12: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120870
APA StyleMatysiak, J., Skrzypek, A., Karpińska, M., Czarnecka, K., Szymański, P., Bajda, M., & Niewiadomy, A. (2019). Biological Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and SAR Studies of Novel 2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1H- Benzimidazole Analogues. Biomolecules, 9(12), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120870





