The Effect of Cytochalasans on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Eukaryotic Cells and Preliminary Structure–Activity Relationships
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Material
2.2. Purification of the Compounds
2.3. Spectral Data
2.3.1. Fragiformin C
2.3.2. Fragiformin D
2.4. Cytochalasans
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cytochalasan Treatment
2.7. Immunofluorescence
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure Elucidation of the New Compounds
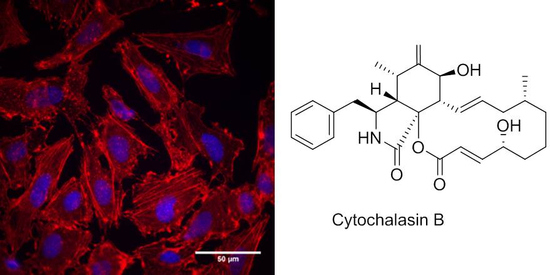
3.2. Effects of Cytochalasans on Cell Cultures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skellam, E. The biosynthesis of cytochalasans. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helaly, S.E.; Thongbai, B.; Stadler, M. Diversity of biologically active secondary metabolites from endophytic and saprotrophic fungi of the ascomycete order Xylariales. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrigde, D.C.; Armstrong, J.J.; Speake, R.N.; Turner, W.B. The cytochalasins, a new class of biologically active mould metabolites. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1967, 3, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, M.D.; Lin, S. Cytochalasins block actin filament elongation by binding to high affinity sites associated with F-actin. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.S.; Spudich, J.A. Mechanism of action of cytochalasin: Evidence that it binds to actin filament ends. J. Cell Biol. 1981, 88, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahara, I.; Harada, F.; Sekita, S.; Yoshihira, K.; Natori, S. Correlation between effects of 24 different cytochalasins on cellular structures and cellular events and those on actin in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 92, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trendowski, M. Using cytochalasins to improve current chemotherapeutic approaches. anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuyama, K.T.; Wendt, L.; Surup, F.; Kretz, R.; Chepkirui, C.; Wittstein, K.; Boonlarppradab, C.; Wongkanoun, S.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Stadler, M.; et al. Cytochalasans act as inhibitors of biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus. Biomolecules 2015, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lim, A.; Lee, J.; Chen, S.; An, S.; Dong, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.-H. Diffusible signal factor (DSF) quorum sensing signal and structurally related molecules enhance the antimicrobial efficacy of antibiotics against some bacterial pathogens. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, N.; Zheng, Y.; Opoku-Temeng, C.; Du, Y.; Bonsu, E.; Sintim, H.O. Biofilm formation mechanisms and targets for developing antibiofilm agents. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noumeur, S.R.; Helaly, S.E.; Jansen, R.; Gereke, M.; Stradal, T.E.B.; Harzallah, D.; Stadler, M. Preussilides A-F, bicyclic polyketides from the endophytic fungus Preussia similis with antiproliferative activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narmani, A.; Pichai, S.; Palani, P.; Arzanlou, M.; Surup, F.; Stadler, M. Saccalasins A and B, two new cytochalasins from Daldinia sacchari (Ascomycota, Hypoxylaceae) and its phylogenetic position, based on a specimen from India. Mycol. Prog. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.; Helaly, S.E.; Schroers, H.J.; Stadler, M.; Richert-Poeggeler, K.R.; Dababat, A.A.; Maier, W. Ijuhya vitellina sp. nov., a novel source for chaetoglobosin A, is a destructive parasite of the cereal cyst nematode Heterodera filipjevi. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongkanoun, S.; Wendt, L.; Stadler, M.; Luangsa-ard, J.; Srikitikulchai, P. A novel species and a new combination of Daldinia from Ban Hua Thung community forest in the northern part of Thailand. Mycol. Prog. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, M.; Quang, D.N.; Tomita, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Asakawa, Y. Changes in secondary metabolism during stromatal ontogeny of Hypoxylon fragiforme. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, M.; Tamm, C.; Turner, W.B.; Minato, H. Nomenclature of a class of biologically active mould metabolites: The cytochalasins, phomins, and zygosporins. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1973, 11, 1146–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, M.S.; Hashimoto, T.; Asakawa, Y. Five 10-phenyl-[11]-cytochalasans from a Daldinia fungal species. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, M.S.; Hashimoto, T.; Asakawa, Y. Cytochalasins from a Daldinia sp. of fungus. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, M.; Læssøe, T.; Fournier, J.; Decock, C.; Schmieschek, B.; Tichy, H.-V.; Peršoh, D. A polyphasic taxonomy of Daldinia (Xylariaceae). Stud. Mycol. 2014, 77, 1–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surup, F.; Narmani, A.; Wendt, L.; Pfütze, S.; Kretz, R.; Becker, K.; Menbrivès, C.; Giosa, A.; Elliott, M.; Petit, C.; et al. Identification of fungal fossils and novel azaphilone pigments in ancient carbonized specimens of Hypoxylon fragiforme from forest soils of Châtillon-sur-Seine (Burgundy). Fungal Divers. 2018, 92, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, L.; Sir, E.B.; Kuhnert, E.; Heitkämper, S.; Lambert, C.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Srikitikulchai, P.; Peršoh, D.; et al. Resurrection and emendation of the Hypoxylaceae, recognized from a multi-gene genealogy of the Xylariales. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D.C.; Armstrong, J.J.; Speake, R.N.; Turner, W.B. The structures of cytochalasins A and B. J. Chem. Sci. (C) 1967, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothweiler, W.; Tamm, C. Isolierung und Struktur der Antibiotica Phomin und 5-Dehydrophomin. Helv. Chim. Acta 1970, 53, 696–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechi, G.; Kitaura, Y.; Yuan, S.-S.; Wright, H.E.; Clardy, J.; Demain, A.L.; Glinsukon, T.; Hunt, N.; Wogan, G.N. Structure of cytochalasin E, a toxic metabolite of Aspergillus clavatus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 5423–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D.C.; Greatbanks, D.; Turner, W.B. Revised structures for cytochalasins E and F. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1973, 551–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evidente, A.; Andolfi, A.; Vurro, M.; Zonno, M.C.; Motta, A. Cytochalasins Z1, Z2 and Z3, three 24-oxa[1 4]cytochalasans produced by Pyrenophora semeniperda. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, R.; Lidman, K.; Fagraeus, A. Effects of cytochalasin B on fibroblasts, lymphoid cells, and platelets revealed by human anti-actin antibodies. Cell 1975, 6, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Rathke, P.C.; Osborn, M.; Franke, W.W. Distribution of actin and tubulin in cells and in glycerinated cell models after treatment with cytochalasin B (CB). Exp. Cell Res. 1976, 102, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ujihara, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Wada, S. Morphological study of fibroblasts treated with cytochalasin D and colchicine using a confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Physiol. Sci. 2008, 68, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goietsenoven, G.; Mathieu, V.; Andolfi, A.; Cimmino, A.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R.; Evidente, A. In Vitro growth inhibitory effects of cytochalasins and derivatives in cancer cells. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottalico, A.; Capasso, R.; Evidente, A.; Randazzo, G.; Vurro, M. Cytochalasins: Structure-activity relationships. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 1 a | 2 b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, mult. | δH, mult. | δC, mult. | δH, mult. | |
| 1 | 174.2, C | 173.2, C | ||
| 2 | 5.56, br s | 8.35, br s | ||
| 3 | 59.1, CH | 3.41, m | 52.5, CH | 3.59, m |
| 4 | 47.0, CH | 3.64, br s | 43.9, CH | 3.01, br d (6.3) |
| 5 | 126.2, C | 35.3, CH | 1.45, m | |
| 6 | 131.6, C | 57.5, C | ||
| 7 | 69.5, CH | 4.08, d (9.5) | 61.7, CH | 2.78, d (5.8) |
| OH: 1.26, br s | ||||
| 8 | 53.5, CH | 2.09, m | 49, CH | 1.94, m |
| 9 | 62.6, C | 65.5, C | ||
| 10 | 42.8, CH2 | 2.69, dd (13.4, 7.5)2.63, dd (13.4, 7.5) | 43.3, CH2 | 2.71, dd (13.0, 4.1) |
| 2.19, dd (13.0, 9.2) | ||||
| 11 | 17.1, CH3 | 1.44, s | 12.1, CH3 | 0.56, d (7.2) |
| 12 | 14.1, CH3 | 1.70, s | 19.1, CH3 | 1.12, s |
| 13 | 127.2, CH | 6.04, ddd (15.7, 10.1, 1.0) | 127.3, CH | 5.85, ddd (15.5, 9.6, 1.0) |
| 14 | 138.6, CH | 5.20, ddd (15.7, 10.9, 4.8) | 135.4, CH | 4.94, ddd (15.5, 10.8, 4.5) |
| 15 | 42.6, CH2 | 2.01, m | 42.5, CH2 | 1.93, m |
| 1.84, ddd (12.0, 11.0, 10.9) | 1.69, m | |||
| 16 | 32.7, CH | 1.33, m | 28.3, CH | 1.61, m |
| 17 | 49.2, CH2 | 1.70, m | 53.9, CH2 | 1.69, m |
| 1.50, dt (13.8, 3.8) | 1.52, m | |||
| 18 | 34.8, CH | 2.44, m | 73, C | OH: 4.83, s |
| 19 | 155.4, CH | 7.14, dd (16.4, 7.2) | 155.4, CH | 6.58, d (16.5) |
| 20 | 130.6, CH | 7.01, br d (16.4) | 129.2, CH | 6.73, d (16.5) |
| 21 | 196.7, C | 195.5, C | ||
| 22 | 25.0, CH3 | 1.03, d (7.0) | 26.2, CH3 | 0.98, d (6.8) |
| 23 | 20.8, CH3 | 1.10, d (6.9) | 30, CH3 | 1.21, s |
| 1′ | 137.4, C | 136.8, C | ||
| 2′/6′ | 129.2, CH | 7.21, br d (7.8) | 129.7, CH | 7.18, br d (7.7) |
| 3′/5′ | 128.7, CH | 7.33, br t (7.8) | 128.2, CH | 7.29, br t (7.7) |
| 4′ | 126. 9, CH | 7.25, br t (7.8) | 126.5, CH | 7.21, br t (7.7) |
| Trivial Name | Actin Disruption | Reversible | Anti-Biofilm [8] | Biological source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fragiformin C | + | +/- | nd | Hypoxylon fragiforme (this study) |
| 2 | Fragiformin D | +++ | - | nd | H. fragiforme (this study) |
| 3 | Saccalasin A | - | nt | + | Daldinia sacchari [12] |
| 4 | Cytochalasin B | ++ | + | - | Preussia similis (this study) |
| 5 | Deoxaphomin | +++ | - | + | P. similis (this study) |
| 6 | Cytochalasin D | +++ | +/- | - | Zygosporium mansorii (Sigma) |
| 7 | Cytochalasin F | + | + | nd | P. similis (this study) |
| 8 | Cytochalasin H | +++ | + | - | H. fragiforme [8] |
| 9 | L-696,474 | +++ | + | ++ | H. fragiforme [8] |
| 10 | 21-O-Deacyl-L-696,474 | +++ | + | + | H. fragiforme [8] |
| 11 | Cytochalasin Z2 | + | + | nd | P. similis (this study) |
| 12 | “Cytochalasin 6” [16] | +++ | - | +++ | D. eschscholtzii [8] |
| 13 | “Cytochalasin 9” [16] | ++ | - | - | D. eschscholtzii [8] |
| 14 | “Cytochalasin 10” [17] | + | +/- | +++ | D. eschscholtzii [8] |
| 15 | “Cytochalasin 11” [17]} | + | +/- | +++ | D. eschscholtzii [8] |
| 16 | “Cytochalasin 12” [18] | - | nt | + | D. eschscholtzii [8] |
| 17 | New Cytochalasin | + | +/- | nd | D. eschscholtzii [8] |
| 18 | 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin C | +++ | + | ++ | Rosellinia rickii [8] |
| 19 | 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin D | +++ | +/- | - | R. rickii [8] |
| 20 | 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin N | + | + | - | R. rickii [8] |
| 21 | 18-Deoxy-19,20-Epoxy-cytochalasin Q | ++ | + | - | R. rickii [8] |
| 22 | Phenochalasin C | ++ | - | + | H./D. kretzschmarioides [8] |
| 23 | Phenochalasin D | - | nt | ++ | H./D. kretzschmarioides [8] |
| 24 | Chaetoglobosin A | + | + | +++ | Ijuhya vitellina [13] |
| 25 | Chaetoglobosin D | ++ | - | nd | Il. vitellina [13] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kretz, R.; Wendt, L.; Wongkanoun, S.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Surup, F.; Helaly, S.E.; Noumeur, S.R.; Stadler, M.; Stradal, T.E.B. The Effect of Cytochalasans on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Eukaryotic Cells and Preliminary Structure–Activity Relationships. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020073
Kretz R, Wendt L, Wongkanoun S, Luangsa-ard JJ, Surup F, Helaly SE, Noumeur SR, Stadler M, Stradal TEB. The Effect of Cytochalasans on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Eukaryotic Cells and Preliminary Structure–Activity Relationships. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020073
Chicago/Turabian StyleKretz, Robin, Lucile Wendt, Sarunyou Wongkanoun, J. Jennifer Luangsa-ard, Frank Surup, Soleiman E. Helaly, Sara R. Noumeur, Marc Stadler, and Theresia E.B. Stradal. 2019. "The Effect of Cytochalasans on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Eukaryotic Cells and Preliminary Structure–Activity Relationships" Biomolecules 9, no. 2: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020073
APA StyleKretz, R., Wendt, L., Wongkanoun, S., Luangsa-ard, J. J., Surup, F., Helaly, S. E., Noumeur, S. R., Stadler, M., & Stradal, T. E. B. (2019). The Effect of Cytochalasans on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Eukaryotic Cells and Preliminary Structure–Activity Relationships. Biomolecules, 9(2), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020073