Tubulin Acetylation Mediates Bisphenol A Effects on the Microtubule Arrays of Allium cepa and Triticum turgidum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Exposure Conditions
2.2. Combined Treatments with BPA and Anti-Microtubule Drugs
2.3. Treatment with Trichostatin A
2.4. Imaging of Microtubules and Chromatin
2.5. Acetylated α-Tubulin Determination
3. Results
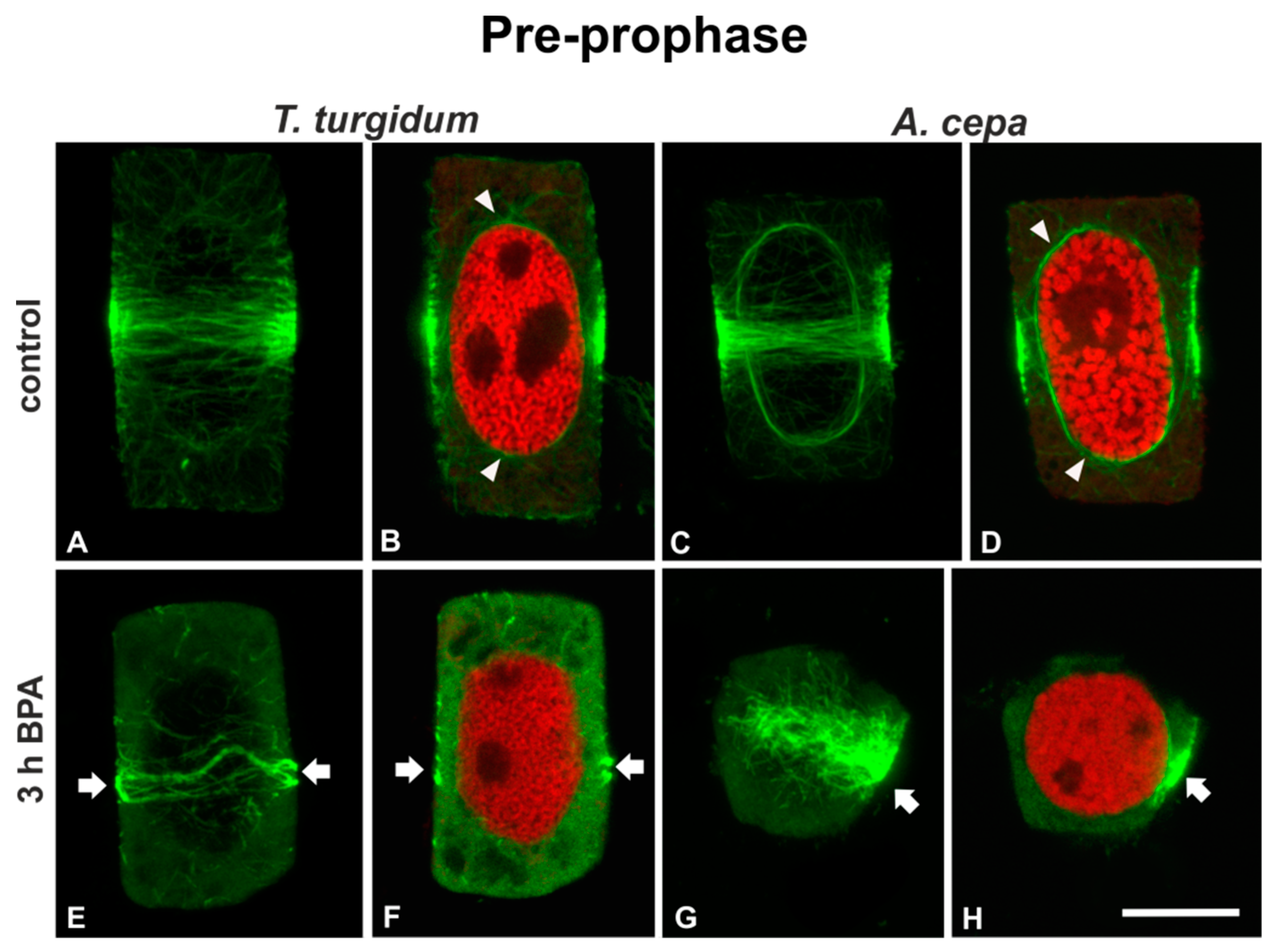
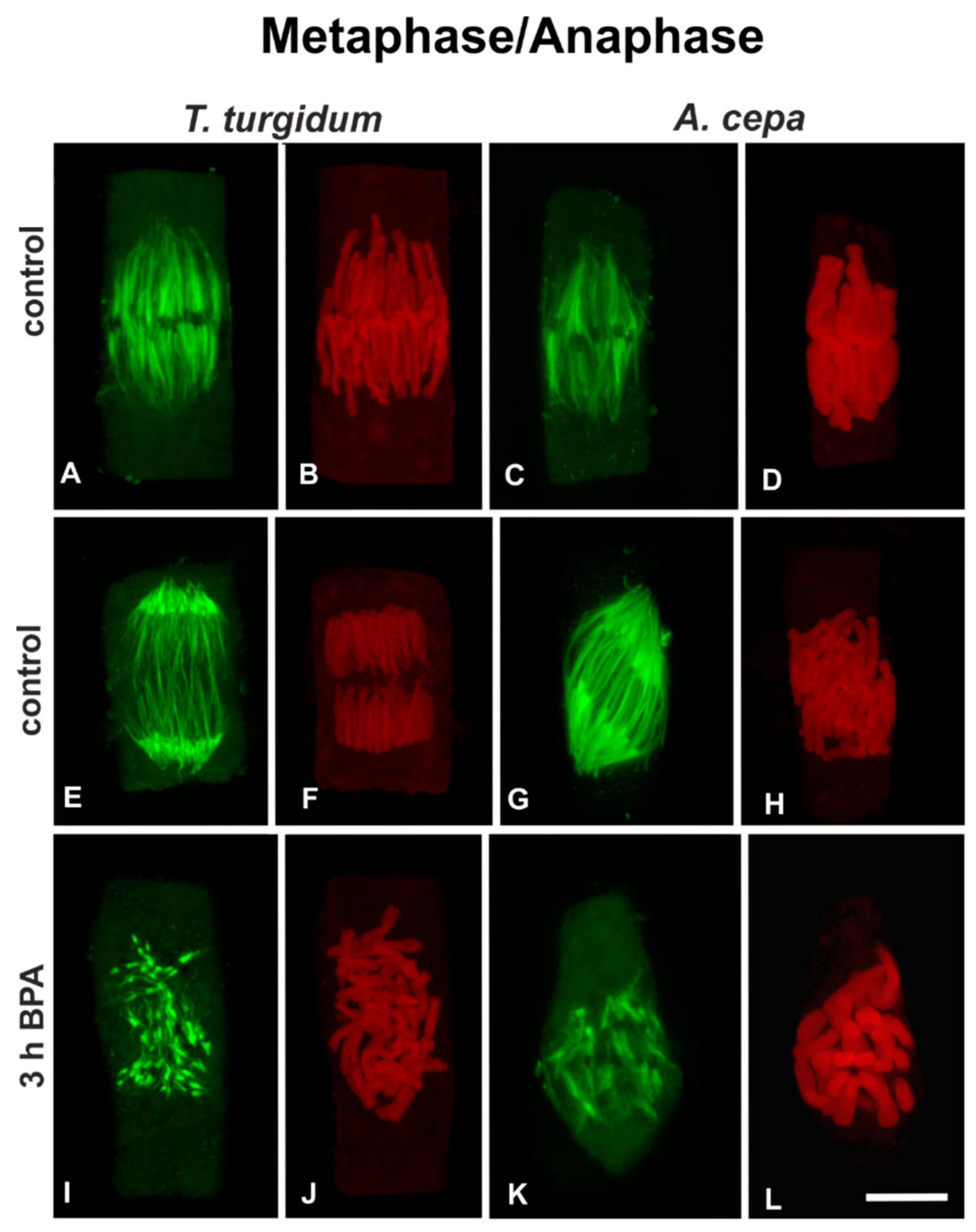
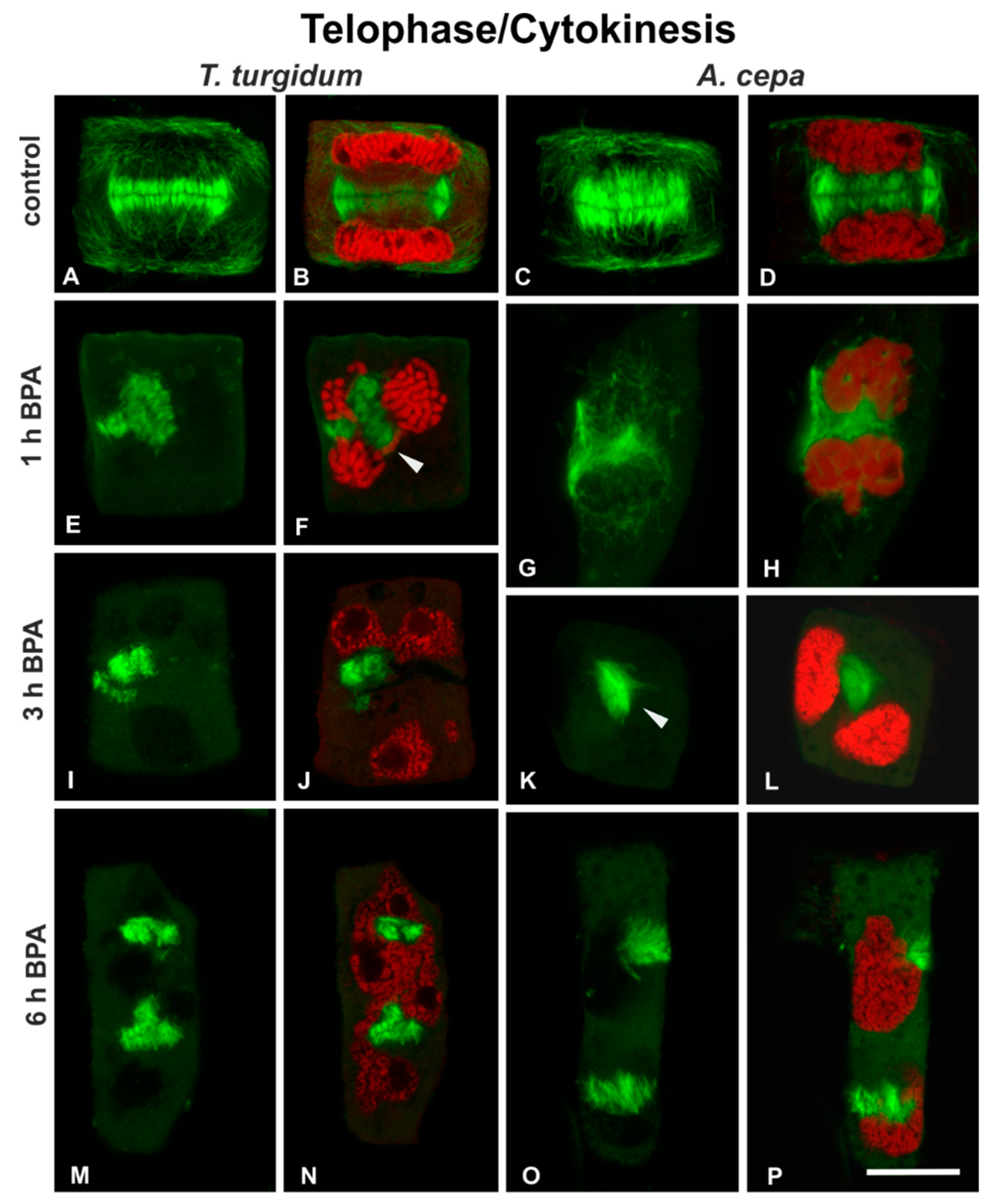
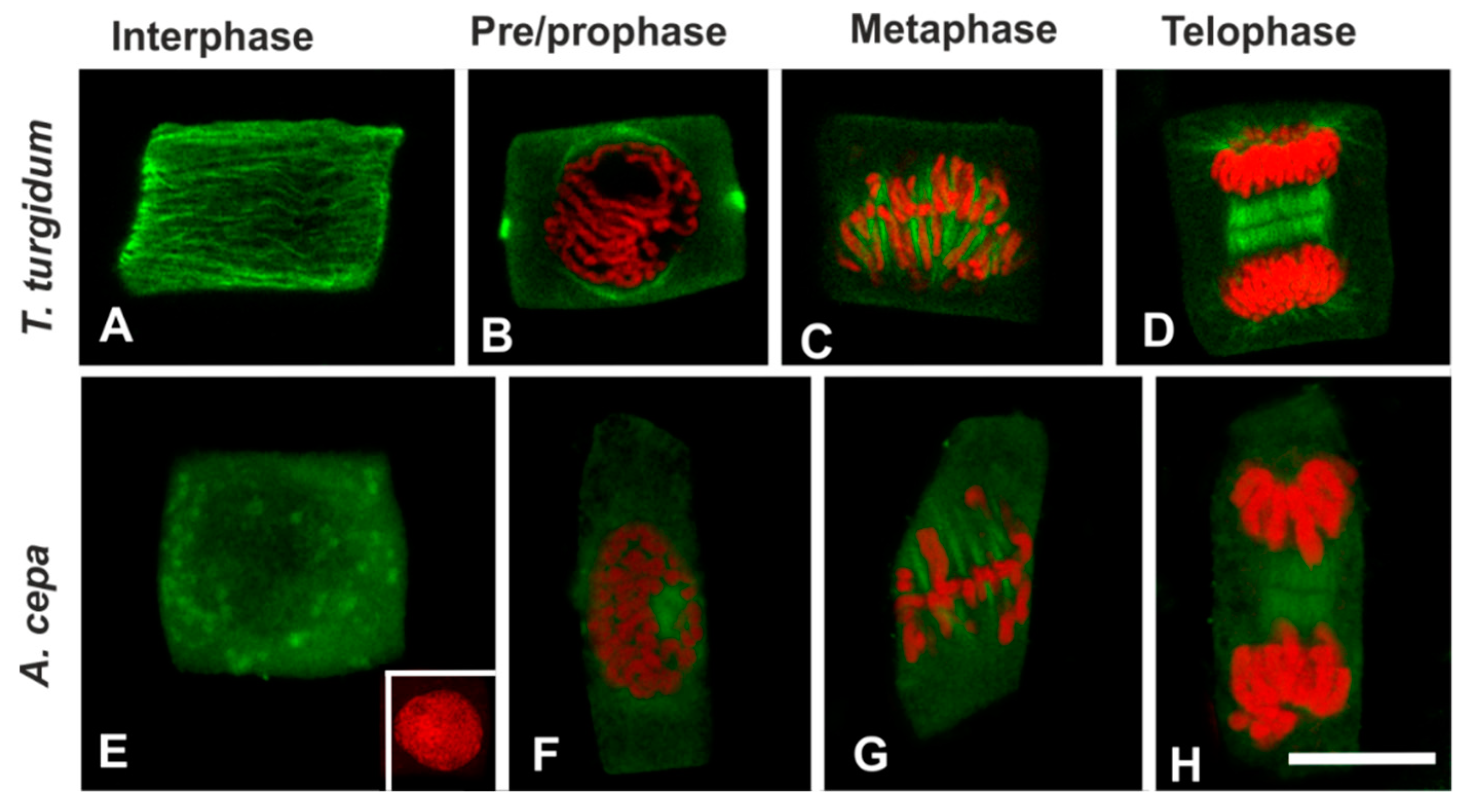
3.1. BPA Effects on Microtubules in Interphase and Mitotic Root Cells
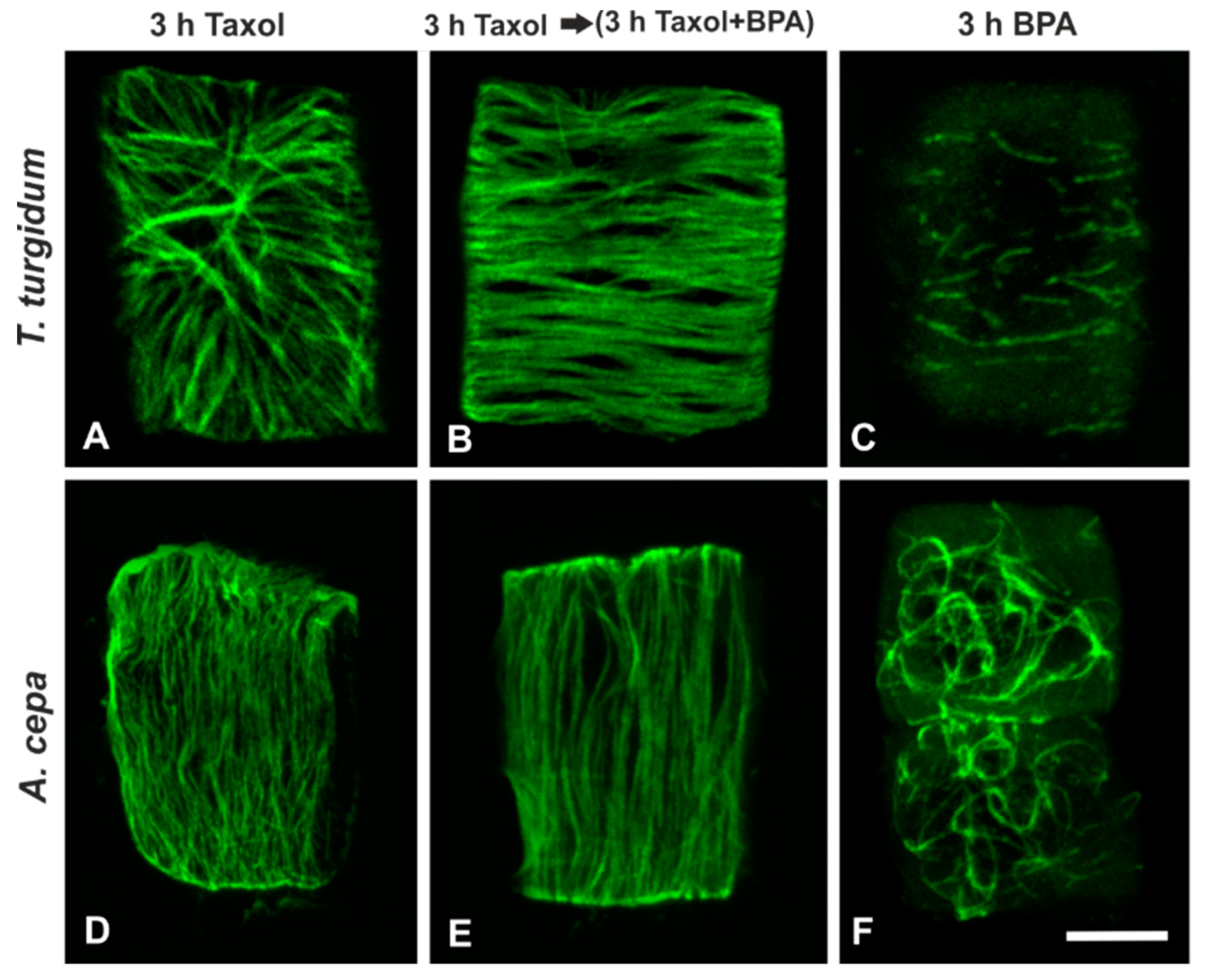
3.2. Combined Treatments with Anti-Microtubule Drugs and BPA
3.3. Presence of Acetylated α-Tubulin in the Microtubules of Interphase and Dividing Cells
3.4. Combined Treatments with TSA and BPA
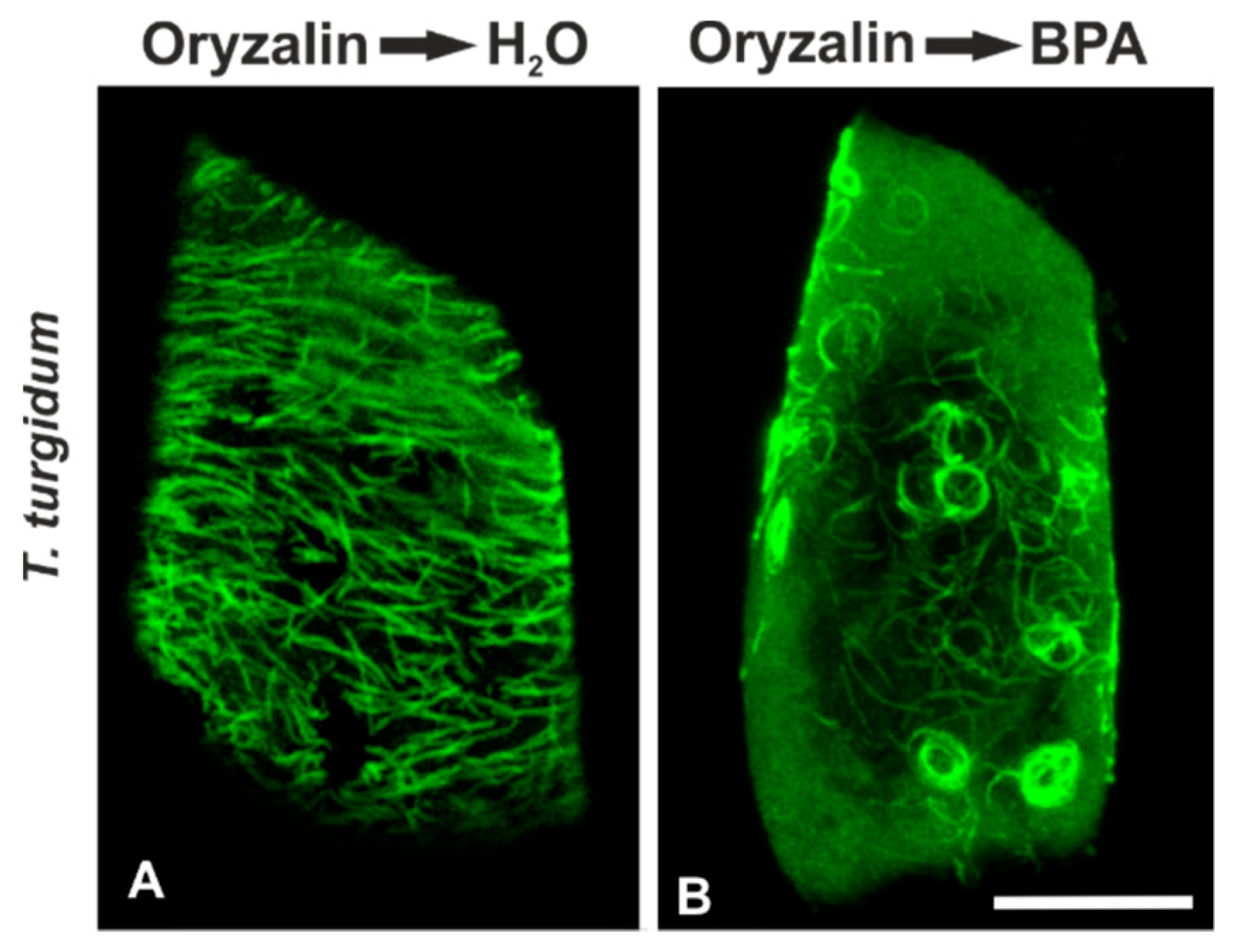
3.5. Recovery Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilcox, C.; Van Sebille, E.; Hardesty, B.D. Threat of plastic pollution to seabirds is global, pervasive, and increasing. PNAS 2015, 112, 11899–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigler, M. The effects of plastic pollution on aquatic wildlife: Current situations and future solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro (nano) plastics: A threat to human health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaich, E.M.; Friederich, U.; Caspers, N.; Hall, A.T.; Klecka, G.M.; Dimond, S.S.; Staples, C.A.; Ortego, L.S.; Hentges, S.G. Acute and chronic toxicity testing of bisphenol A with aquatic invertebrates and plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 5, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, S.; Markle, T.; Thompson, S.; Wallace, E. Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: A wildlife perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Kondo, F.; Katayama, Y. Human exposure to bisphenol A. Toxicology 2006, 226, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatidou, G.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Stasinakis, A.S.; Lekkas, T.D. Simultaneous determination of the endocrine disrupting compounds nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylates, triclosan and bisphenol A in wastewater and sewage sludge by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromat. A 2007, 1138, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothitou, P.; Voutsa, D. Endocrine disrupting compounds in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants in Northern Greece. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Gatidou, G.; Mamais, D.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Lekkas, T.D. Occurrence and fate of endocrine disrupters in Greek sewage treatment plants. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.H.; Carlson, E.M.; Chua, J.P.; Belcher, S.M. Bisphenol A is released from polycarbonate drinking bottles and mimics the neurotoxic actions of estrogen in developing cerebellar neurons. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Liao, C.; Song, G.J.; Ra, K.; Kannan, K.; Moon, H.B. Emission of bisphenol analogues including bisphenol A and bisphenol F from wastewater treatment plants in Korea. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Jonathan, N.; Steinmetz, R. Xenoestrogens: The emerging story of bisphenol A. Trends Endocrinol. Metabol. 1998, 9, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Ehrlich, S.; Belcher, S.M.; Ben-Jonathan, N.; Dolinoy, D.C.; Hugo, E.R.; Hunt, P.A.; Newbold, R.R.; Rubin, B.S.; Saili, K.S.; et al. Low dose effects of bisphenol A: An integrated review of in vitro, laboratory animal, and epidemiology studies. Endocr. Disruptors 2013, 1, e26490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: From emerging pollutants to emerged threat. Marine Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Machado, A.A.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C.; Hempel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics as an emerging threat to terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, T.; Tamura, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Hirose, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Nishimura, H.; Metzler, M.; Barrett, J.C. Mammalian cell transformation and aneuploidy induced by five bisphenols. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, P.A.; Koehler, K.E.; Susiarjo, M.; Hodges, C.A.; Ilagan, A.; Voigt, R.C.; Thomas, S.; Thomas, B.F.; Hassold, T.J. Bisphenol A exposure causes meiotic aneuploidy in the female mouse. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, O.; Bryant, B.K.; Chinnasamy, R.; Corona, C.; Arterburn, J.B.; Shuster, C.B. Bisphenol A directly targets tubulin to disrupt spindle organization in embryonic and somatic cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Gwon, D.; Kim, J.A.; Choi, H.; Jang, C.Y. Bisphenol A disrupts mitotic progression via disturbing spindle attachment to kinetochore and centriole duplication in cancer cell lines. Toxicol. in Vitro 2019, 59, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Cherianidou, A.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Effects of bisphenol A on the microtubule arrays in root meristematic cells of Pisum sativum L. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen 2013, 750, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Bisphenol A disrupts microtubules and induces multipolar spindles in dividing root tip cells of the gymnosperm Abies cephalonica. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulou, K.; Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Arseni, E.M.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Disruption of actin filaments in Zea mays by bisphenol A depends on their crosstalk with microtubules. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzler, M.; Pfeiffer, E. Effects of estrogens on microtubule polymerization in vitro: Correlation with estrogenicity. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdiz, D.; Mackeh, R.; Poüs, C.; Baillet, A. The ins and outs of tubulin acetylation: More than just a post-translational modification? Cell Signal 2011, 23, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, T.I.; Wilson, J.E.; Cork, A.; Williamson, R.E. Morphology and microtubule organization in Arabidopsis roots exposed to oryzalin or taxol. Plant Cell Physiol. 1994, 35, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adcock, I.M. HDAC inhibitors as anti-inflammatory agents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Mechanisms and clinical significance in cancer: HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis. In Programmed Cell Death in Cancer Progression and Therapy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 261–298. [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, G.; Fuller, M.T. Monoclonal antibodies specific for an acetylated form of alpha-tubulin recognize the antigen in cilia and flagella from a variety of organisms. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eshun-Wilson, L.; Zhang, R.; Portran, D.; Nachury, M.; Toso, D.; Lohr, T.; Vendruscolo, M.; Bonomi, M.; James, F.; Nogales, E. Effects of α-tubulin acetylation on microtubule structure and stability. bioRxiv 2019, 516591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smertenko, A.; Dràber, P.; Viklický, V.; Opatrný, Z. Heat stress affects the organization of microtubules and cell division in Nicotiana tabacum cells. Plant Cell Environ. 1997, 20, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzerová, K.; Zelenková, S.; Nick, P.; Opatrný, Z. Aluminum-induced rapid changes in the microtubular cytoskeleton of tobacco cell lines. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xue, P.; Meng, Q.; Zou, J.; Gu, J.; Jiang, W. Pb/Cu effects on the organization of microtubule cytoskeleton in interphase and mitotic cells of Allium sativum L. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Eleftheriou, E.P. The cortical microtubules are a universal target of tungsten toxicity among land plant taxa. J. Biol. Res. Thess. 2010, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Eleftheriou, E.P.; Michalopoulou, V.A.; Adamakis, I.D.S. Aberration of mitosis by hexavalent chromium in some Fabaceae members is mediated by species-specific microtubule disruption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7590–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Malea, P.; Panteris, E. The effects of Bisphenol A on the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa: Leaf elongation impairment and cytoskeleton disturbance. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmer, S.; Clay, P.; MacRae, T.H.; Fowke, L.C. Acetylated tubulin is found in all microtubule arrays of two species of pine. Protoplasma 1999, 207, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, O.; Khokhlova, L.; Belyaeva, N.; Chulkova, Y.; Garaeva, L. Cytoskeleton-induced alterations of the lectin activity in winter wheat under cold hardening and abscisic acid (ABA). Cell Biol. Intern. 2000, 24, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberman, Y.; Ballestrem, C.; Carramusa, L.; Mazitschek, R.; Khochbin, S.; Bershadsky, A. Regulation of microtubule dynamics by inhibition of the tubulin deacetylase HDAC6. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3531–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyake, Y.; Keusch, J.J.; Wang, L.; Saito, M.; Hess, D.; Wang, X.; Melancon, B.J.; Helquist, P.; Gut, H.; Matthias, P. Structural insights into HDAC6 tubulin deacetylation and its selective inhibition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrotta, L.; Cresti, M.; Cai, G. Accumulation and post-translational modifications of plant tubulins. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayevsky, A.V.; Sharifi, M.; Samofalova, D.A.; Karpov, P.A.; Blume, Y.B. Structural and functional features of lysine acetylation of plant and animal tubulins. Cell Biol. Intern. 2017, 16, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, D.R.; Borisy, G.G. Microtubules are acetylated in domains that turn over slowly. J. Cell Sci. 1989, 92, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Howes, S.C.; Alushin, G.M.; Shida, T.; Nachury, M.V.; Nogales, E. Effects of tubulin acetylation and tubulin acetyltransferase binding on microtubule structure. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Schaedel, L.; Portran, D.; Aguilar, A.; Gaillard, J.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Manuel, T.; Nachury, M.V. Microtubules acquire resistance from mechanical breakage through intralumenal acetylation. Science 2017, 356, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G. Assembly and disassembly of plant microtubules: Tubulin modifications and binding to MAPs. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Shaw, S.L. Update: Plant cortical microtubule arrays. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavrdová, T.; Samaj, J.; Komis, G. Phosphorylation of plant Microtubule-Associated Proteins during cell division. Front Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morejohn, L.C.; Fosket, D.E. The biochemistry of compounds with anti-microtubule activity in plant cells. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 51, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, L.; Metzler, M. Bisphenol A and its methylated congeners inhibit growth and interfere with microtubules in human fibroblasts in vitro. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2004, 147, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| BPA | Triticum turgidum | Allium cepa |
|---|---|---|
| 50 mg/L | 1, 2, 3, 6 | 1, 2, 3, 6 |
| Plant | Treatment | Post-Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Allium cepa | 50 mg/L BPA + 20 μM taxol, 3 h | ---- |
| Triticum turgidum | 50 mg/L BPA, 3 h 20 μM taxol, 3 h 50 mg/L BPA + 20 μM taxol, 3 h 5 μM oryzalin, 12 h 5 μM oryzalin, 12 h | 50 mg/L BPA + 20 μM taxol, 3 h 50 mg/L BPA + 20 μM taxol, 3 h ---- 50 mg/L BPA, 12 h H2O, 12 h |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adamakis, I.-D.S.; Panteris, E.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Tubulin Acetylation Mediates Bisphenol A Effects on the Microtubule Arrays of Allium cepa and Triticum turgidum. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050185
Adamakis I-DS, Panteris E, Eleftheriou EP. Tubulin Acetylation Mediates Bisphenol A Effects on the Microtubule Arrays of Allium cepa and Triticum turgidum. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(5):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050185
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdamakis, Ioannis-Dimosthenis S., Emmanuel Panteris, and Eleftherios P. Eleftheriou. 2019. "Tubulin Acetylation Mediates Bisphenol A Effects on the Microtubule Arrays of Allium cepa and Triticum turgidum" Biomolecules 9, no. 5: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050185
APA StyleAdamakis, I.-D. S., Panteris, E., & Eleftheriou, E. P. (2019). Tubulin Acetylation Mediates Bisphenol A Effects on the Microtubule Arrays of Allium cepa and Triticum turgidum. Biomolecules, 9(5), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9050185






