β-Caryophyllene Mitigates Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) in Mice Through a Cross-Talk between CB2 and PPAR-γ Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
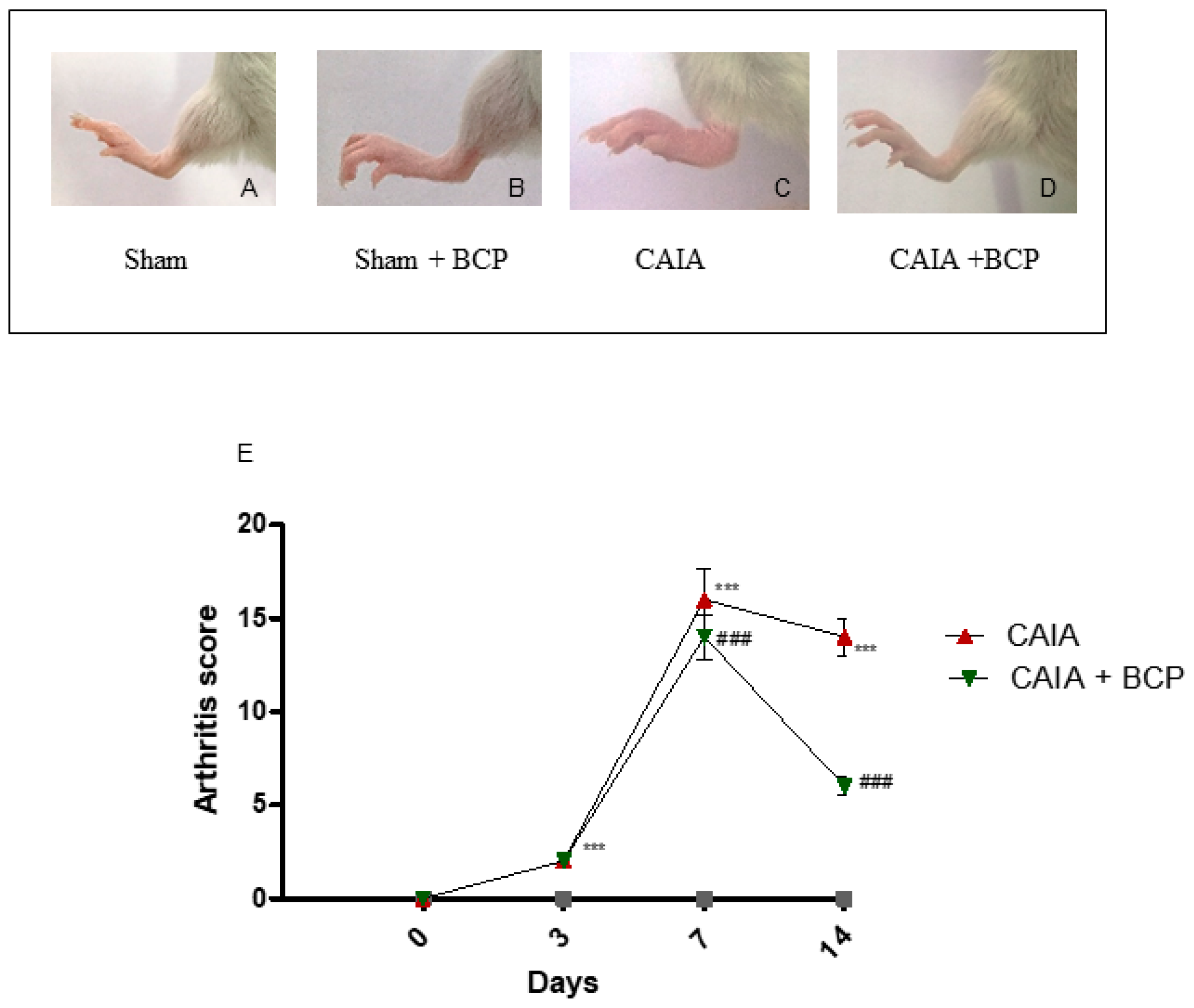
2.1. BCP Treatment Reduces the Severity of Arthritis
2.2. BCP Preserves Articular Cartilage
2.3. BCP Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Activity by Reducing Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Levels and Expression
2.4. BCP Protects Articular Cartilage by Modulating Metalloproteinases 3 and 9 Expression
2.5. BCP Acts Through NF-ĸB and PPARγ Modulation
2.6. BCP Anti-Arthritic Effect Occurs Through PPAR-γ and PGC-1α Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. CAIA Induction and Treatment
4.2. Evaluation of Arthritis
4.3. Cell Cultures and Treatments
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. Quantification of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Real Time (RT) PCR Assay
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanpoor, M. The genetic pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic insight of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Genet. 2018, 95, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.C.; Lu, M.C. The roles of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019, 31, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Bozec, A.; Ramming, A.; Schett, G. Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y. Metalloproteinases in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Potential Therapeutic Targets to Improve Current Therapies. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 148, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hazlewood, G.S.; Barnabe, C.; Tomlinson, G.; Marshall, D.; Devoe, D.J.; Bombardier, C. Methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate combination therapy with traditional and biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, CD010227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlewood, G.S.; Bombardier, C.; Tomlinson, G.; Thorne, C.; Bykerk, V.P.; Thompson, A.; Tin, D.; Marshall, D.A. Treatment preferences of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: A discrete-choice experiment. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Barnabe, C.; Barber, C.E.; Bykerk, V.; Pope, J.E.; Hazlewood, G.S. Randomized controlled trials of biologic treatment with methotrexate in RA may not reflect real world practice: A systematic review and assessment of pragmaticism. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2018, 71, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donges, E.; Staatz, C.E.; Benham, H.; Kubler, P.; Hollingworth, S.A. Patterns in use and costs of conventional and biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in Australia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, K.D.C.; Islam, M.T.; Ali, E.S.; Rouf, R.; Uddin, S.J.; Dev, S.; Shilpi, J.A.; Shill, M.C.; Reza, H.M.; Das, A.K.; et al. A systematic review on the neuroprotective perspectives of beta-caryophyllene. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2376–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.B. Beyond Cannabis: Plants and the Endocannabinoid System. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Liu, Q.R.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Brusco, A.; Uhl, G.R. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: Immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Porta, C.; Bura, S.A.; Llorente-Onaindia, J.; Pastor, A.; Navarrete, F.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; De la Torre, R.; Manzanares, J.; Monfort, J.; Maldonado, R. Role of the endocannabinoid system in the emotional manifestations of osteoarthritis pain. Pain 2015, 156, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidyt, K.; Fiedorowicz, A.; Strządała, L.; Szumny, A. β-caryophyllene and β-caryophyllene oxide-natural compounds of anticancer and analgesic properties. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames-Sibin, A.P.; Barizão, C.L.; Castro-Ghizoni, C.V.; Silva, F.M.S.; Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; Bracht, L.; Bersani-Amado, C.A.; Marçal-Natali, M.R.; Bracht, A.; Comar, J.F. β-Caryophyllene, the major constituent of copaiba oil, reduces systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in arthritic rats. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 163, 1334–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.A.; El-Fayoumi, H.M.; Mahmoud, M.F. Beta-caryophyllene alleviates diet-induced neurobehavioral changes in rats: The role of CB2 and PPAR-γ receptors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.A.; El-Fayoumi, H.M.; Mahmoud, M.F. Beta-caryophyllene protects against diet-induced dyslipidemia and vascular inflammation in rats: Involvement of CB2 and PPAR-γ receptors. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 297, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Al Kaabi, J.M.; Nurulain, S.M.; Goyal, S.N.; Kamal, M.A.; Ojha, S. Polypharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Potential of β-Caryophyllene: A Dietary Phytocannabinoid of Pharmaceutical Promise. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 3237–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.J.; Park, E.J.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.R.; Cho, M.; Kim, J. PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone inhibits migration and invasion by downregulating Cyr61 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasheghani, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Blati, M.; Fahmi, H.; Lussier, B.; Roughley, P.; Lagares, D.; Endisha, H.; Saffar, B.; et al. PPARγ deficiency results in severe, accelerated osteoarthritis associated with aberrant mTOR signalling in the articular cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.C.; Jiang, D.M. PPAR-γ agonist pioglitazone affects rat gouty arthritis by regulating cytokines. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 6577–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favalli, E.G.; Raimondo, M.G.; Becciolini, A.; Crotti, C.; Biggioggero, M.; Caporali, R. The management of first-line biologic therapy failures in rheumatoid arthritis: Current practice and future perspectives. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudics, S.; Langan, D.; Meka, R.R.; Venkatesha, S.H.; Berman, B.M.; Che, C.T.; Moudgil, K.D. Natural Products for the Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis: Their Mechanisms of Action, Targeted Delivery, and Interplay with the Host Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albini, A.; Bassani, B.; Baci, D.; Dallaglio, K.; Gallazzi, M.; Corradino, P.; Bruno, A.; Noonan, D.M. Nutraceuticals and “repurposed” drugs of phytochemical origin in prevention and interception of chronic degenerative disease and cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Otieno, F.; Akpan, A.; Moots, R.J. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Considerations for the Pharmacological Management of Elderly Patients. Drugs Aging 2017, 34, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSalvo, J.C.; Skiba, M.B.; Howe, C.L.; Haiber, K.E.; Funk, J.L. Natural Product Dietary Supplement Use by Individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Scoping Review. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2018, 71, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.J.; Dissanayake, T.D.; Lau, D.; Katz, S.J. Self-reported use of natural health products among rheumatology patients: A cross-sectional survey. Musculoskelet. Care 2017, 15, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.J.; Galettis, P.; Schneider, J. The pharmacokinetics and the pharmacodynamics of cannabinoids. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillooly, K.M.; Pulicicchio, C.; Pattoli, M.A.; Cheng, L.; Skala, S.; Heimrich, E.M.; McIntyre, K.W.; Taylor, T.L.; Kukral, D.W.; Dudhgaonkar, S.; et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor BMS-986142 in experimental models of rheumatoid arthritis enhances efficacy of agents representing clinical standard-of-care. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.P.; Gan, Y.H.; Zhang, C.G.; Zhou, C.Y.; Ma, K.T.; Meng, J.H.; Ma, X.C. Requirement of the NF-κB pathway for induction of Wnt-5A by interleukin-1β in condylar chondrocytes of the temporomandibular joint: Functional crosstalk between the Wnt-5A and NF-κB signaling pathways. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, S.E. Cannabinoids go nuclear: Evidence for activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistis, M.; O’Sullivan, S.E. The Role of Nuclear Hormone Receptors in Cannabinoid Function. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 291–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving Bioscience Research Reporting: The ARRIVE Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutamekalin, P.; Saito, T.; Yamaki, K.; Mizutani, N.; Brand, D.D.; Waritani, T.; Terato, K.; Yoshino, S. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice: Development of a new arthritogenic 5-clone cocktail of monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 343, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, H.; Polito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Irrera, N.; Minutoli, L.; Calò, M.; Adamo, E.B.; Vaccaro, M.; Squadrito, F.; Bitto, A. Genistein aglycone improves skin repair in an incisional model of wound healing: A comparison with raloxifene and oestradiol in ovariectomized rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irrera, N.; D’Ascola, A.; Pallio, G.; Bitto, A.; Mazzon, E.; Mannino, F.; Squadrito, V.; Arcoraci, V.; Minutoli, L.; Campo, G.M.; et al. β-Caryophyllene Mitigates Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) in Mice Through a Cross-Talk between CB2 and PPAR-γ Receptors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080326
Irrera N, D’Ascola A, Pallio G, Bitto A, Mazzon E, Mannino F, Squadrito V, Arcoraci V, Minutoli L, Campo GM, et al. β-Caryophyllene Mitigates Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) in Mice Through a Cross-Talk between CB2 and PPAR-γ Receptors. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(8):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080326
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrrera, Natasha, Angela D’Ascola, Giovanni Pallio, Alessandra Bitto, Emanuela Mazzon, Federica Mannino, Violetta Squadrito, Vincenzo Arcoraci, Letteria Minutoli, Giuseppe Maurizio Campo, and et al. 2019. "β-Caryophyllene Mitigates Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) in Mice Through a Cross-Talk between CB2 and PPAR-γ Receptors" Biomolecules 9, no. 8: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080326
APA StyleIrrera, N., D’Ascola, A., Pallio, G., Bitto, A., Mazzon, E., Mannino, F., Squadrito, V., Arcoraci, V., Minutoli, L., Campo, G. M., Avenoso, A., Bongiorno, E. B., Vaccaro, M., Squadrito, F., & Altavilla, D. (2019). β-Caryophyllene Mitigates Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) in Mice Through a Cross-Talk between CB2 and PPAR-γ Receptors. Biomolecules, 9(8), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080326







