Abstract
This paper presents a collaborative manufacturing cell implemented in a laboratory setting, focusing on developing learning-based interaction abilities to enhance versatility and ease of use. The key components of the system include 3D real-time volumetric monitoring for safety, visual recognition of hand gestures for human-to-robot communication, classification of physical-contact-based interaction primitives during handover operations, and detection of hand–object interactions to anticipate human intentions. Due to the nature and complexity of perception, deep-learning-based techniques were used to enhance robustness and adaptability. The main components are integrated in a system containing multiple functionalities, coordinated through a dedicated state machine. This ensures appropriate actions and reactions based on events, enabling the execution of specific modules to complete a given multi-step task. An ROS-based architecture supports the software infrastructure among sensor interfacing, data processing, and robot and gripper controllers nodes. The result is demonstrated by a functional use case that involves multiple tasks and behaviors, paving the way for the deployment of more advanced collaborative cells in manufacturing contexts.
1. Introduction
Moving beyond efficiency and productivity, Industry 5.0 focuses on building human-centric industrial systems by developing technologies that enable the collaboration between humans and robots [1,2]. Collaborative robotics is becoming a very relevant field with the increasing number of situations where humans and robots can coexist and perform joint tasks together. In line with this, automation concepts like human–robot collaboration (HRC) are expected to impact and transform the way we live and work across diverse domains. The industrial domain is no exception, and manufacturing cells are evolving in a direction where humans and robots coexist seamlessly and, moreover, interact mutually in numerous collaborative tasks. The combination of human skills and robotic capabilities holds the potential to significantly improve the execution of complex tasks in targeted application areas like assembly, manufacturing, and material handling.
As the field of HRC continues to advance, three key research areas are emerging as critical [3,4,5,6]: the design of safe and ergonomic workcells, the development of multimodal interaction abilities, and the implementation of data-driven learning techniques. Safety and ergonomics remain primary considerations when integrating robots into industrial environments [7,8,9]. Collaborative robots must seamlessly interact with human workers while minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries. Achieving this balance requires robust safety mechanisms, including advanced sensing technologies, real-time risk monitoring, and adaptive control strategies [10,11,12]. Researchers are also continually exploring innovative approaches to enhance ergonomic aspects, with the ultimate goal of improving the well-being and comfort of human workers [13,14,15].
A key challenge in human–robot collaboration is to develop robots with multimodal interaction abilities, leading to more natural and productive work environments. These abilities should allow them to understand and respond to humans through various communication channels, as discussed in [16,17]. In contrast to traditional robotic systems that rely primarily on visual data and programming interfaces, the current trend involves the integration of multiple modalities, such as vision, speech, touch, and haptic feedback. These advancements stem partly from efforts to endow robots with multimodal perception capabilities, enabling them to gather information from various sensory sources, including depth cameras and force/torque sensors. Researchers are exploring new techniques to allow workers to effectively communicate their intentions, as well as to simplify robot programming and control [18].
Despite advances, the effective coordination of actions and natural communication between human and robotic partners remain critical bottlenecks that need to be further addressed. In particular, research on interaction through physical contact [19,20,21] and the anticipation of human intentions [22,23,24,25] holds significant promise for enhancing operational efficiency and user experience. On the one hand, current robots frequently encounter difficulties in understanding the subtle nuances of tactile interactions and the safe execution of coordinated movements during tasks requiring physical contact (e.g., during handover tasks [26,27]). Conversely, the ability to accurately predict human intentions can significantly enhance the quality of collaborative partnerships, enabling robots to respond intuitively and proactively to human actions. However, the precise nature of anticipation and the underlying mechanisms supporting it remain open questions in robotics research. Ongoing investigations aim to address fundamental questions, such as how anticipatory processes can be modeled and implemented within robotic systems and what impacts may result.
Bearing this in mind, the integration of learning-based techniques is becoming increasingly essential in dealing with HRC systems that can learn from experience and adapt to changing conditions [28]. Robots can acquire new skills and adapt their behavior based on large amounts of data collected from sensors, enabling them to perform complex tasks with increased efficiency and autonomy. In this context, the main challenges to be addressed include the real-time operation, the adaptability to real-world scenarios with variations, and the effective generalization to new and unseen situations [29,30]. Learning algorithms trained on biased datasets may exhibit poor performance in real-world applications. This is particularly concerning in HRC, where robots must interact with humans from different backgrounds and abilities. At the same time, traditional learning techniques often exhibit difficulties in generalizing their knowledge to new situations or environments. This can be problematic in HRC, where robots must adapt to the dynamic and often unpredictable nature of human interactions. It is also important to highlight that current learning techniques focus on predicting immediate outcomes rather than anticipating future events. This limits the robot’s ability to understand human intentions and human–robot interactions, leading to inefficient and potentially unsafe interactions.
The Augmanity project has faced some of these challenges and carried out research and developments in this domain. In this context, a prototype of a manufacturing cell (Figure 1) was built, where several innovative features were successfully implemented and tested. This paper presents the work on developing learning-based technologies to facilitate natural human–robot collaboration. We focus on core interaction abilities such as workspace awareness, hand gesture recognition, interaction through physical contact, and human intention anticipation. Each interaction ability is described and experimental results are provided to validate the approach in real-time scenarios. We detail the architectural components and implementation options to elucidate their advantages and limitations, while also highlighting key design choices and their impact on prediction accuracy using real data. The challenge was not focused only on the individual abilities, but also in their integration in a fully functional use case. In line with this, the second part of the paper presents an integrated multimodal system through a tailored use case demonstration.
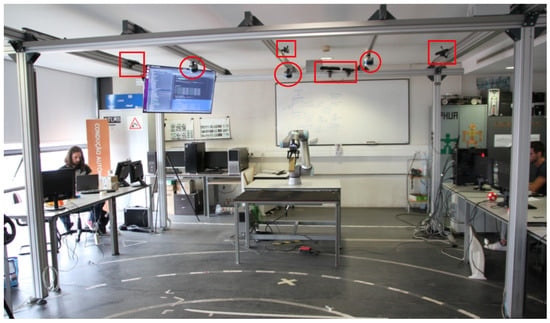
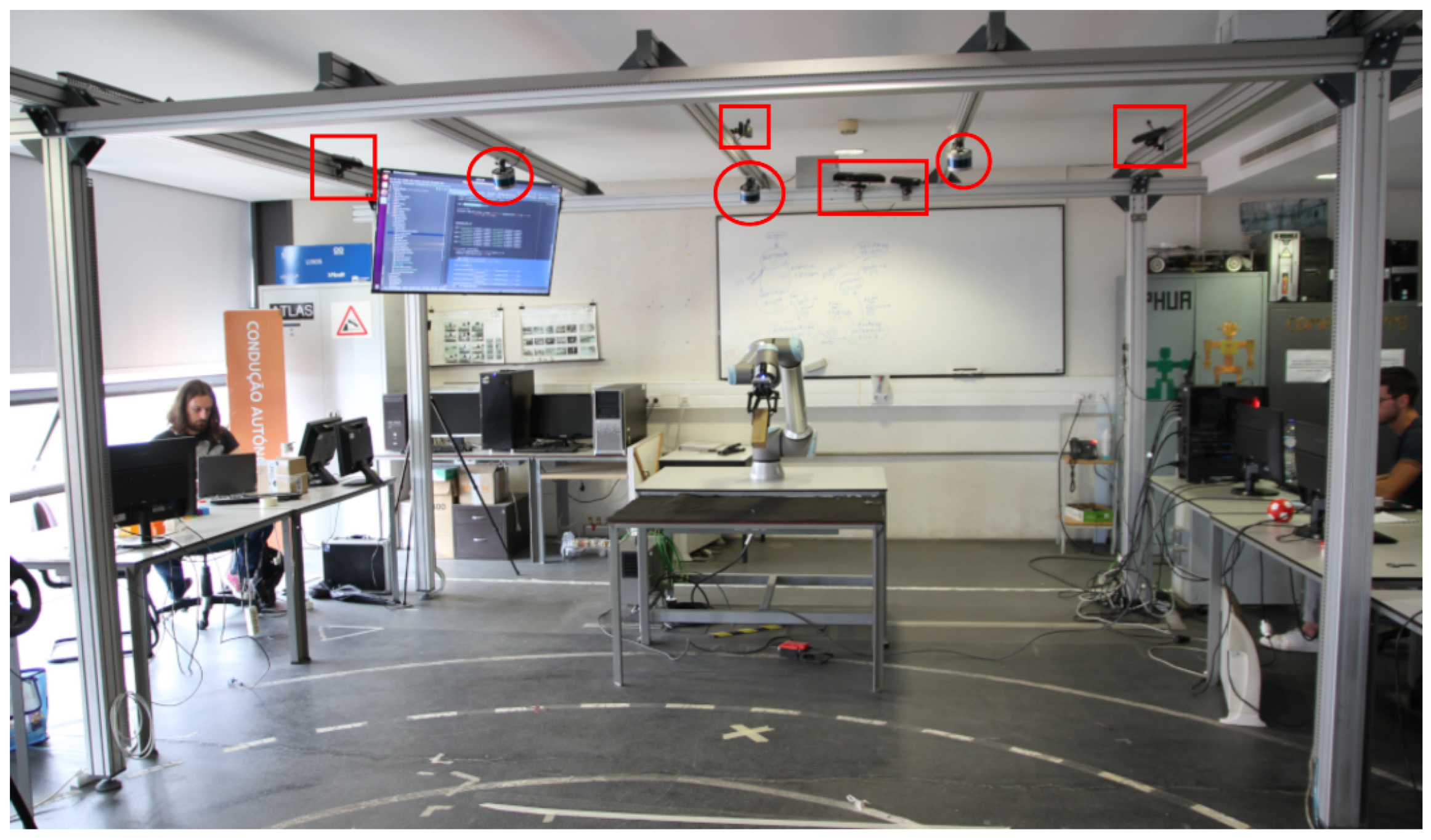
Figure 1.
The prototype collaborative manufacturing cell: LARCC. Several sensors cover the robot and operator spaces for volumetric monitoring and gesture interaction, including LiDARs (red circles) and RGB-D cameras (red rectangles). The cell includes a UR10e COBOT with a Robotiq 2F gripper.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides an overview of the collaborative cell and explores the design considerations regarding the core interaction abilities. Section 3 and Section 4 describes the methodologies and implementation of these interaction abilities, distinguishing between supervised and proactive collaboration, respectively. Section 5 outlines the integration of these abilities into an application case study. The most important results and considerations arising from the work are discussed in Section 6. Finally, Section 7 concludes the paper.
2. Overview of the Collaborative Cell
2.1. The Prototype Manufacturing Cell
LARCC, the Laboratory for Automation and Robotics’ Collaborative Cell, is a prototype collaborative cell housed in the Laboratory for Automation and Robotics at the University of Aveiro. The collaborative robotic system integrates specific technological components that play a crucial role in its operation. On the sensory side, the LARCC is equipped with multimodal devices, including three LiDAR Velodyne VLP-16 sensors and four Orbec Astra Pro 3D-cameras strategically positioned throughout the volume of the cell. This arrangement ensures adequate coverage and data acquisition from various perspectives.
The robotic system consists of a UR10e collaborative robot equipped with a Robotiq 2F gripper. The main computing unit is based on a dedicated computer platform equipped with a 11th Generation Intel Core i7-11700 CPU running at 2.50 GHz. The 128 GB RAM memory and the inclusion of two NVIDIA RTX 3080 GPUs provide ample computational capacity for the tasks to be carried out, namely in the offline training of deep learning models. The computer runs on Ubuntu 20.04, ensuring stability and compatibility with the software components.
In terms of software development and integration, the project adopts a design approach based on the Robot Operating System (ROS) middleware [31]. The ROS framework is based on the concepts of modularity and reusability that suit both exploratory research and industrial applications. In this context, this study represents an effort towards actively exploring the integration of ROSs into collaborative industrial settings to leverage their flexibility, extensive libraries, and large community support.
2.2. Core Interaction Abilities
The coordination between a human operator and a robot can be achieved through different collaboration strategies. The first strategy that is assumed to be essential is one in which a human operator act as a supervisor through the full or partial control of the robot’s actions. Controlling robots based on direct interactions requires interfaces that effectively allow humans to communicate their goals. For that purpose, the collaborative system is endowed with nonverbal communication interfaces in the form of hand gestures and physical interaction by contact. On the one hand, hand gestures help to communicate an action or a correction to the robot, being a powerful strategy even in noisy industrial environments. On the other hand, the communication using physical contact is a promising strategy found in human–human teams to improve fluency and comfort in challenging tasks (e.g., during the contact phase in object handover). These interfaces rely on the assumption of some level of mutual attention or participation.
Conversely, the operation of humans and robots as independent collaborators also offers numerous advantages. A major concern of the project is the safety of human operators, the robotic system, and objects present in the environment. In this context, a volumetric detection system was developed in order to provide an additional level of security that contributes to safe collaborative work. An additional example of indirect interaction with potential benefits arises in scenarios where robots are assigned tasks to provide assistance, offering help as required. To address these requirements, two additional interaction abilities, namely workspace awareness and human intention anticipation, were devised to support and complement supervised collaboration. Thereby, the robot can anticipate needs, react proactively, and ultimately improve the efficiency and safety of the collaborative process without requiring explicit instruction. These abilities reduce the human’s cognitive load as they are relieved from the need to request assistance or coordinate every aspect of task execution.
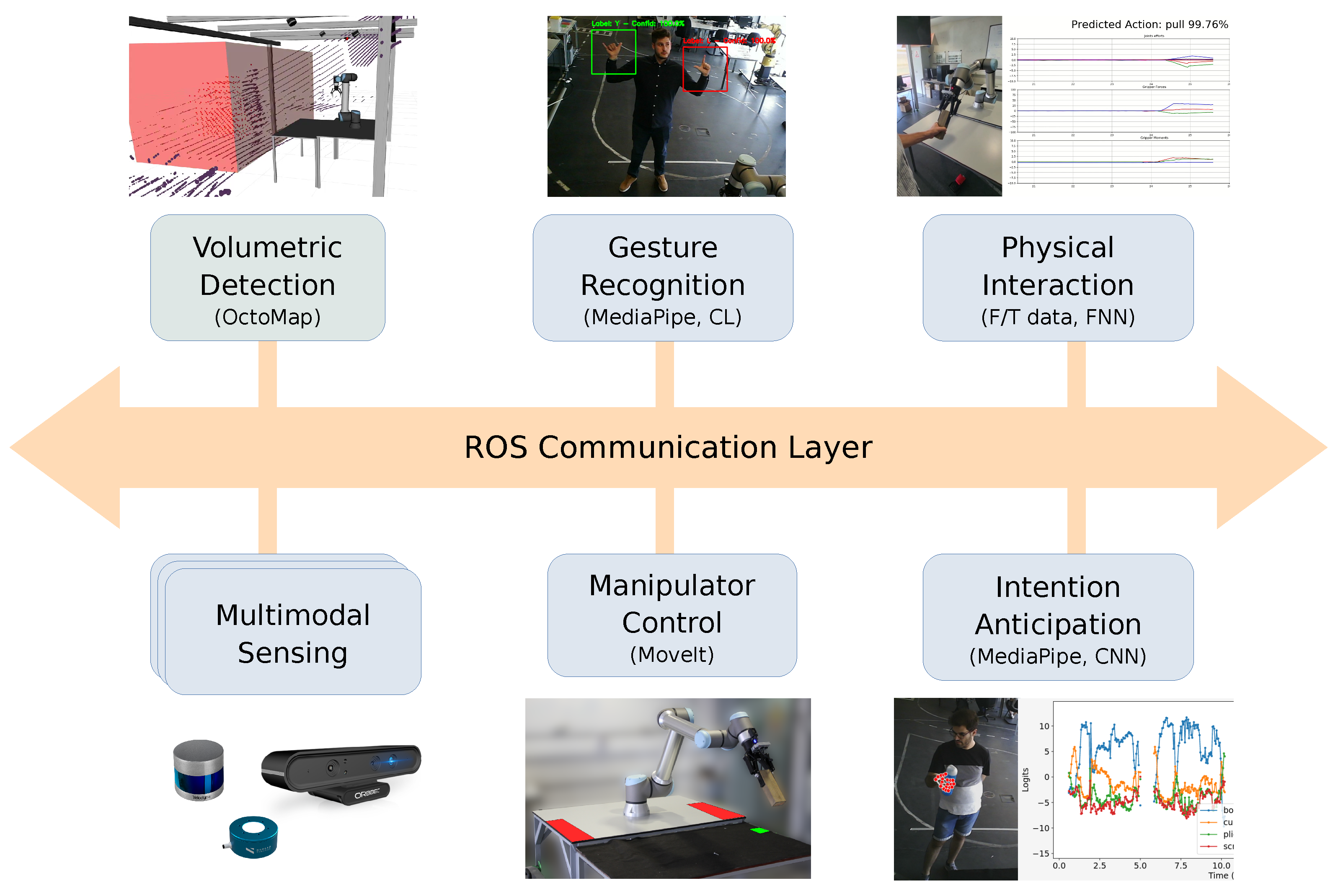
The manufacturing cell operates through the integration of these robotic technologies oriented toward collaborative processes. The design approach adopted by the Augmanity project emphasizes a set of interaction abilities that can be applied across various domains, regardless of the specific application (e.g., assembling, quality control and inspection). An overview of the ROS-based system architecture is depicted in Figure 2. The system functionalities cover the basic building blocks related to sensory feedback and manipulator control. The 3D perception and monitoring of the collaborative cell ensures, in real time, a complete awareness of the human and COBOT activities within the shared space, with automatic sensor configuration and calibration [32,33].
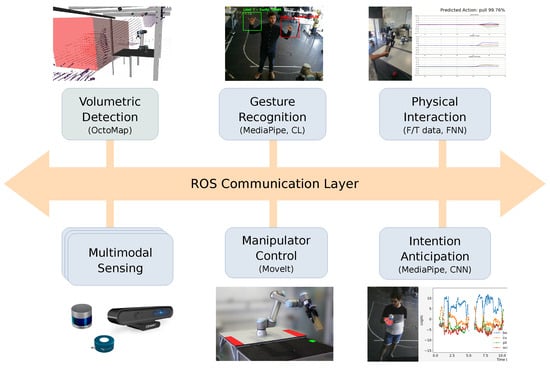
Figure 2.
Overview of the system architecture.
This paper extends existing decision models developed for hand gesture recognition ([34]), physical interaction classification [35], volumetric detection [36], and human intention anticipation [37]. Here, we enhance these decision models by incorporating additional features and considerations essential for their effective real-time integration into the ROS framework. In line with this, an illustrative fully functional use case of human–robot collaboration is provided, wherein the autonomous system is governed by a finite-state machine that triggers the sequence of sub-tasks to be executed.
2.3. Contributions and Novelty
This section highlights the key contributions and novel aspects of our proposed collaborative cell design; while individual components like gesture recognition, physical interaction classification, workspace awareness, and human intention anticipation have been explored in previous research, our work presents a novel integration of these functionalities within a complete, real-time operational framework utilizing ROS for seamless communication and control. This integrated approach goes beyond existing research by offering a more comprehensive and user-friendly solution for human–robot collaboration in industrial settings. It promotes efficient communication, proactive assistance, and real-time adaptation, leading to an enhanced user experience in human–robot collaboration (HRC) scenarios. It offers a flexible, adaptable, and safe framework for human–robot interaction, paving the way for improved efficiency, productivity, and user experience in industrial settings.
The integration of the core interaction abilities emphasizes two important design considerations. First, these abilities are designed to be non-domain-specific and can be applied across various collaborative tasks in diverse industrial settings. This flexibility allows for broader application and adaptation compared to solutions focused on specific tasks. Second, we adopt a complementary strategy by combining supervised (human control) and proactive (robot assistance) collaboration strategies. Supervised interaction is facilitated by hand gestures and physical contact, enabling intuitive communication. Proactive assistance is achieved through workspace awareness and human intention anticipation, reducing the human cognitive load and improving overall efficiency.
From the perspective of enhanced adaptability, our system utilizes deep learning techniques for hand gesture recognition, physical contact classification, and human intention anticipation. These approaches offer adaptability to variations in human actions and environmental conditions. They can learn and improve their performance over time by continuously processing new data. Additionally, our design emphasizes real-time operation and addresses challenges like variations in human behavior and limited training data. This approach offers practical significance in real-world industrial applications, where robots must interact with diverse human collaborators and adapt to dynamic situations.
In summary, the contributions of this paper cover the following:
- The introduction of a collaborative cell endowed with learning-based core interaction abilities that can be applied across various domains (non-domain-specific abilities).
- The evaluation of communication interfaces allowing direct interaction with the cell, employing contrastive learning (CL) for the recognition of user-specific visual gestures and a feedforward neural network (FNN) for the classification of contact-based interaction primitives.
- The development of coordination strategies featuring proactive monitoring of shared spaces and anticipation of human intentions based on hand–object interactions.
- The presentation of a full functional use case demonstrating the real-time operation of the collaborative cell.
3. Supervised Collaboration
3.1. Hand Gesture Recognition
The hand gesture recognition (HGR) module is a communication system based on computer vision and deep neural networks that enables human operators to demonstrate their intentions to robots. The real-time HGR system consists of two sequential components: hand detection and gesture classification (illustrated in Figure 3). The hand-detection process utilizes the human pose detection and tracking module of MediaPipe [38] to estimate 33 key points of the human pose. From these key points, we extracted a small window centered on the hand to be used for classification. To overcome the false classification problem, the detection module incorporates the verification of three constraints, as follows:
- Hand level constraint: The module calculates the midpoint of the operator’s chest. The constraint is satisfied if the center of the hand is above this limit.
- Hands overlapping constraint: The module checks if the bounding boxes of the left and right hands overlap. The constraint fails if there is an overlap between the bounding boxes.
- Overlapping face constraint: The module examines whether any of the MediaPipe key points associated with the face (anatomical landmarks on the face) are inside the bounding box of the hand. The constraint fails if any face key point is found within that bounding box.
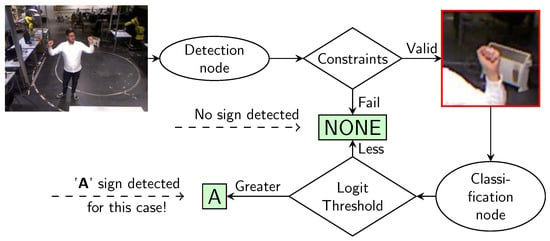
Figure 3.
Overview of the hand gesture recognition system.
Figure 3.
Overview of the hand gesture recognition system.
If any of these constraints fail, then the system does not proceed to the classification step. This verification ensures that gesture classification is performed under conditions similar to the training.
The gesture classification module employs an Inception-v3 architecture [39] trained with a simultaneous multi-loss contrastive learning method [34]. This training approach achieves excellent performance on datasets with images featuring complex backgrounds, and generalizes well to datasets encompassing different users and illumination conditions. These properties make it ideal for an industrial-use system. The convolutional neural network was trained using a dataset consisting of four gestures derived from American Sign Language (ASL), namely A, L, F, and Y. This implementation allows the programming of the COBOT with four different behaviors triggered by the performed gesture. The gesture is determined by analyzing the output of the CNN and selecting the class with the highest value. However, this approach could lead to false classifications if the operator is not performing any of the expected gestures.
To address this issue, an analysis of the logits (inputs of the SOFTMAX layer in the CNN) is performed. For the chosen class, a threshold is applied to the logit value. If the value is below the threshold, the image is classified as a fifth class, NONE, representing the absence of any valid gesture. Optimal thresholds for each class were determined by acquiring a new dataset, where none of the four ASL gestures were performed. The logit distributions for hand images performing the respective gesture and those not performing the gesture were compared, and thresholds were set to maximize the precision score of each class.
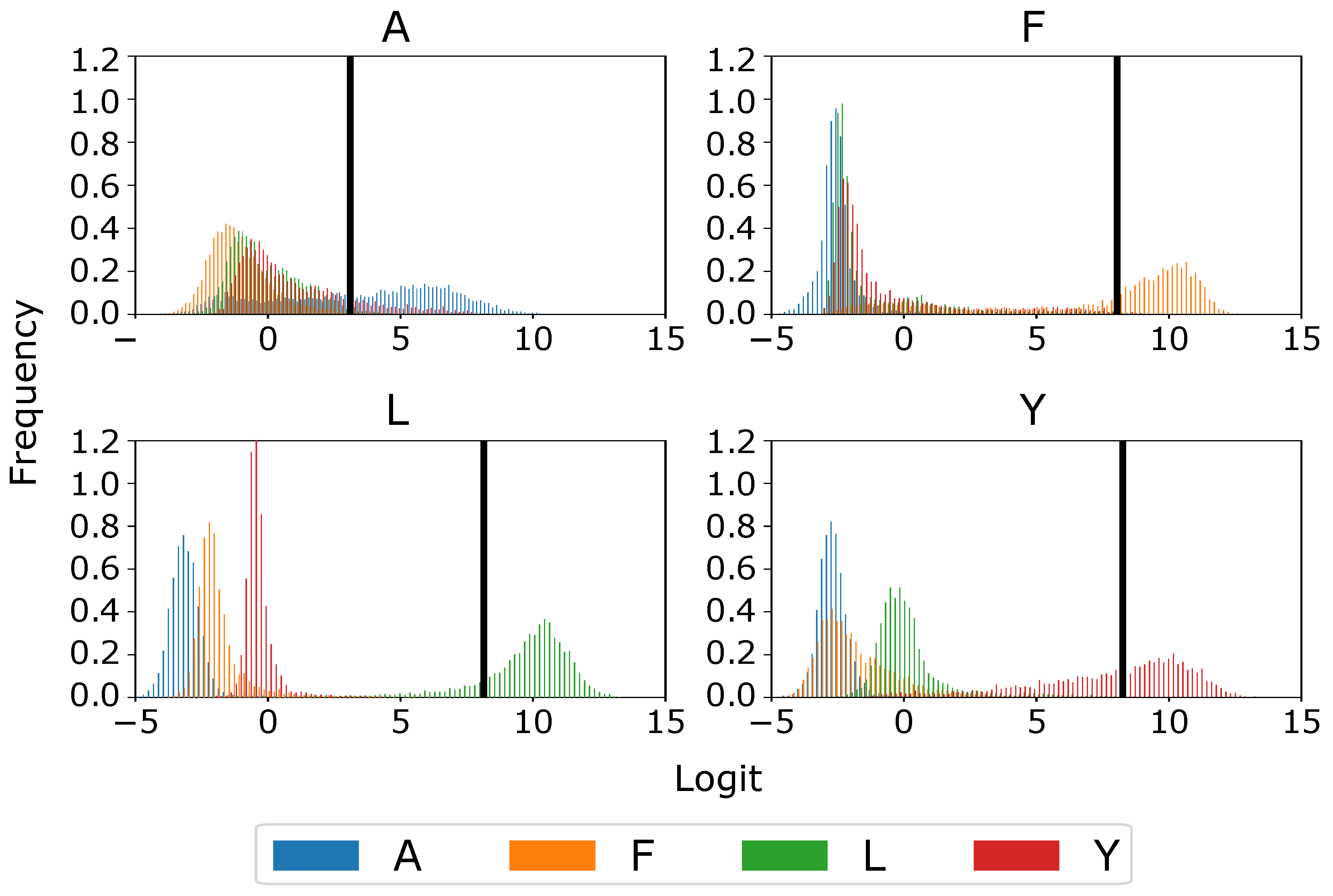
Figure 4 shows the logit distributions for images showing a hand gesture, where it can be seen that, for example, the L and F classes have very strong logit values, making them more easily separable. On the other hand, A class has a sparse logit distribution; but even so, it is reasonably separable with the right threshold, which is nonetheless much smaller than the ones for the other three classes. Despite these considerations, the classifier remains prone to potential misclassification among the four original classes, compromising the intended communication between humans and machines; while these misclassifications can be considered outliers, they are likely to occur in a system that runs continuously. In order to address this concern, we propose an approach to enhance gesture estimation by applying data filtering techniques.
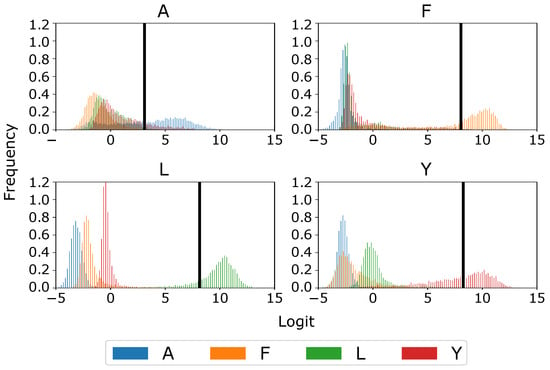
Figure 4.
The four histograms represent the logit distribution of the four classes when passing images from one class through the hand classification model. In each histogram, the black line represents the threshold value that optimizes the precision score.
To achieve this, we analyze a sequence of classifications and implement a method to reduce the influence of outliers that may occur in practical implementations. The analysis uses the values obtained in a confusion matrix in a test dataset normalized by columns, which indicates the precision for each class. This evaluation is described in Algorithm 1, which uses classifications generated by the system described in Figure 3. This procedure is performed continuously for each classification. The input is an ordered list of indexes of the last N frame classifications. The stores the values of the confusion matrix normalized by columns, where the lines correspond to the ground truths and the columns to the predictions.
Lastly, the algorithm weights the sequential classifications linearly, placing more emphasis on the most recent classifications. The maximum weight is 1 and the minimum is the configurable parameter .
| Algorithm 1 Gesture filtering. |
Input: ; ;
|
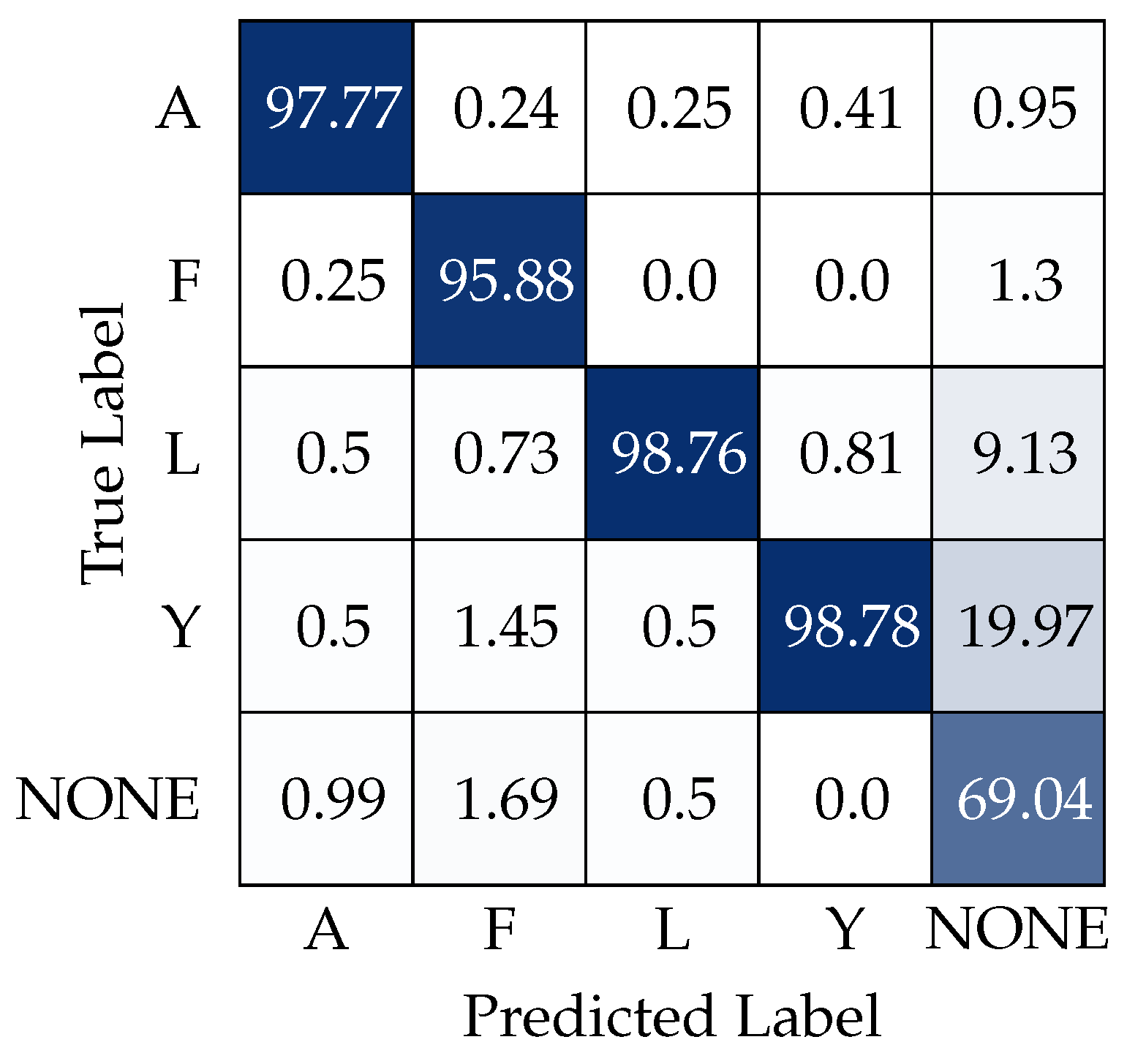
By utilizing both logit thresholds and gesture filtering, we can significantly reduce the misclassification rate of our model, resulting in a more robust system suitable for deployment in unstructured environments. This improvement is evidenced by the confusion matrix presented in Figure 5. To accurately interpret this matrix, it is essential to understand that classes A–Y are considered positive, transmitting some form of information to the robot or triggering specific events. Conversely, the NONE class is regarded as negative, indicating an absence of transmitted information.
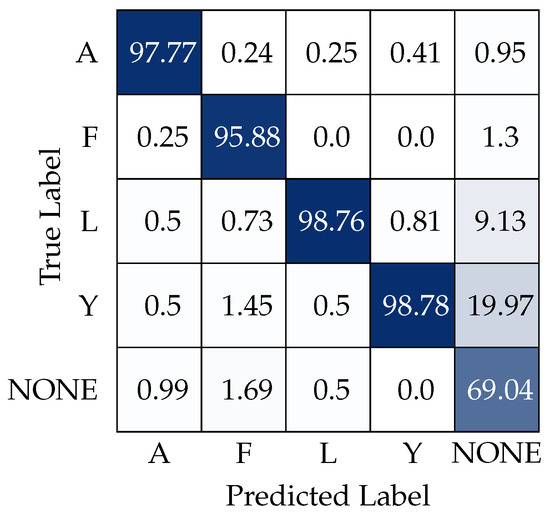
Figure 5.
Confusion matrix, in percentage (%), obtained using logit thresholds and gesture filtering. The confusion matrix is normalized by the column.
This distinction is crucial because our methods are specifically designed to enhance the precision of the positive classes, thereby reducing potential confusion. The effectiveness of this approach is evident, as the positive classes achieve an accuracy of nearly 98%, which represents a significant improvement over previous iterations of the system. However, it is important to note that the model misclassifies the NONE class 30% of the time, leading to a loss of the intended message from the user.
Despite this challenge, the system demonstrates strong performance with a tested inference rate of 20 frames per second (FPS), maintaining a maximum inference time of approximately 300 milliseconds. This trade-off between speed and accuracy is necessary; by sacrificing some of the model’s responsiveness, we have achieved much greater precision and safety. This balance is crucial for applications in unstructured environments, where the reliability of the system’s responses is paramount.
3.2. Physical Interaction Classification
One of the most inevitable requirements to perform coordinated and conjoint jobs is object transfer between coworkers. Object handover in HRC emerged as a major field of investigation and development, where human–robot physical contact stands as the ultimate challenge to the efficiency and success of collaborative tasks. By the moment when both agents are simultaneously in physical contact with the held object, the intervening parties should have the same level of understanding of the other intentions. This type of perception demands a communication channel between the human and the robot based on physical interactions. Given that typically available sensorial measurements in COBOTs are joints torque and six-axis force–torque sensors ([35]), we defined a set of contact primitives to allow a basic ”vocabulary” that utilizes these exact same values. To effectively capture the operator’s intentions, these contact primitives are designed to be intuitive for humans:
- pull—a force applied in the direction towards the operator;
- push—a force applied in the direction away from the operator;
- shake—a fast, short, amplitude-alternating action imposed by the human hand on the object;
- twist—a torsion imposed on an axis along the human arm–hand.
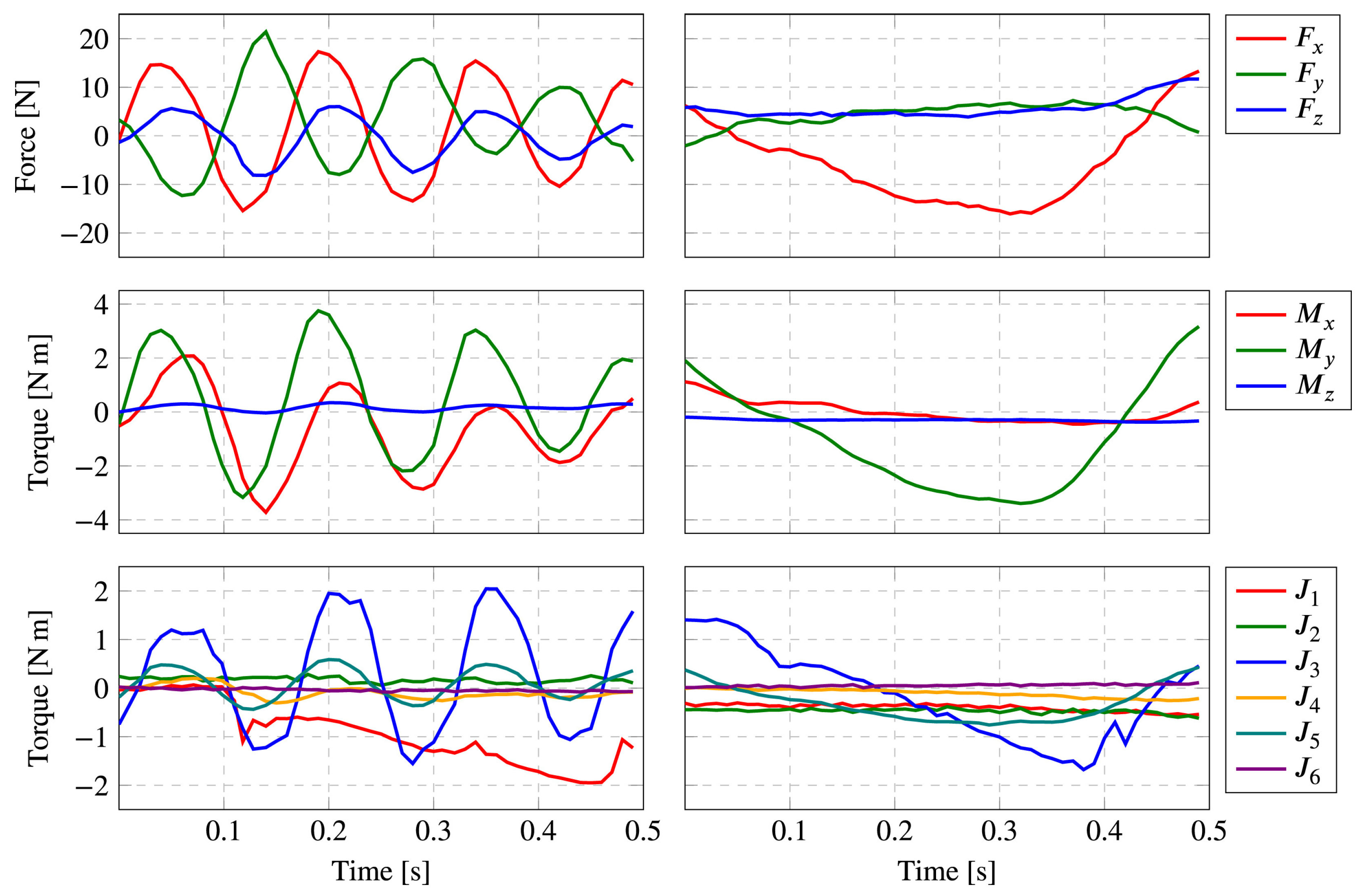
The system should perceive this vocabulary, despite the human operator variability when performing physical interactions: users with different heights will produce distinct force/torque patterns, for example. Moreover, tiredness and the used arm also have high impact on the sensorial data behavior. Although these are simple to perform for humans, the four primitives generate complex combinations of torques and forces along the robot manipulator that are difficult for the correct sensor to output and analyze. For example, Figure 6 shows the forces and torques produced by two distinct applied shakes.
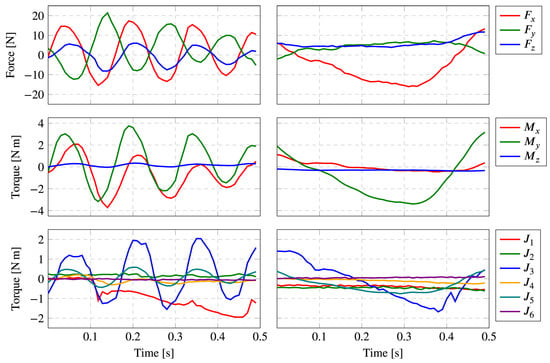
Figure 6.
Timeline behavior of FT values, for two different shake primitives [35]. The top two rows depict the end-effector forces and torques along the three axes. Last row depicts the six robot joint-captured torques.
Concerning this significant inconsistency, the primitive classification process demands cognitive knowledge to correctly identify the human intention by their physical interaction: it was developed a learning-based approach to classify the user’s primitive actions, such that a supervised model should associate the COBOT real-time sensorial data with the class of the intended human action.
The aimed physical communication channel is ensured through the development of a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network (which is the simplest and most traditional form of deep neural network). This feedforward neural network (FFNN) is fed with the torques of each one of the siz joints, the three-axis-component forces, and the three-axis-component torques on the gripper, along a 0.2 s time window. The input for the model is given by Equation (1):
where indices vary from 0 to , indicating the time instant of the data acquisition. Thus, the set of inputs for the neural network is constituted by 260 values corresponding to sequential measurements of the 13 synchronous parameters. To improve the classification results, the network structure was optimized to achieve the most suitable NN for this time-series classification. The search space of this optimization, for each parameter, is defined as follows:
- Number of hidden layers: 2, 3, 4.
- Neurons in each hidden layer: 16, 32, 64, 128.
- Dropout for the last hidden layer: 0%, 20%, 50%.
- Activation function: ReLU, SELU, sigmoid.
- Optimizer: Adam, SGD, RMSprop.
- Batch size: between 32 and 128.
- Starting learning rate: between 0.0001 and 0.1.
The optimized neural network model consists of an input layer with 260 neurons and 3 fully-connected hidden layers. The first hidden layer is composed of 64 neurons with ReLU as the activation function. The second and third layers are composed of 32 neurons with SELU as activation function. The third hidden layer uses 20% dropout to improve the generalization capability. Finally, the output layer, with four neurons, indicates the confidence of each one of the predefined classifications (pull, push, shake, and twist). This output layer uses softmax as the activation function, which makes the sum of all four output values equal to 1.
To achieve real-time classification, while supporting the deep learning model, an algorithm was developed, considering two main assumptions. Firstly, the study specified a fixed location for the object exchange, establishing a predefined ergonomic posture for the COBOT during the handover process. This posture involves the robot’s arm being extended towards the operator, holding an object in its gripper, and the end-effector being positioned at a mid-range tilted angle of about 45° relative to the operator. Further investigations confirmed the system’s robustness to slight variations around this handover configuration. Secondly, the model considered the force and torque exerted by the gripper and the held object on the robot’s sensors as an initial offset during the interaction phase. This approach allowed the methodology to be independent of the weight and shape of new objects, making it adaptable to various scenarios.
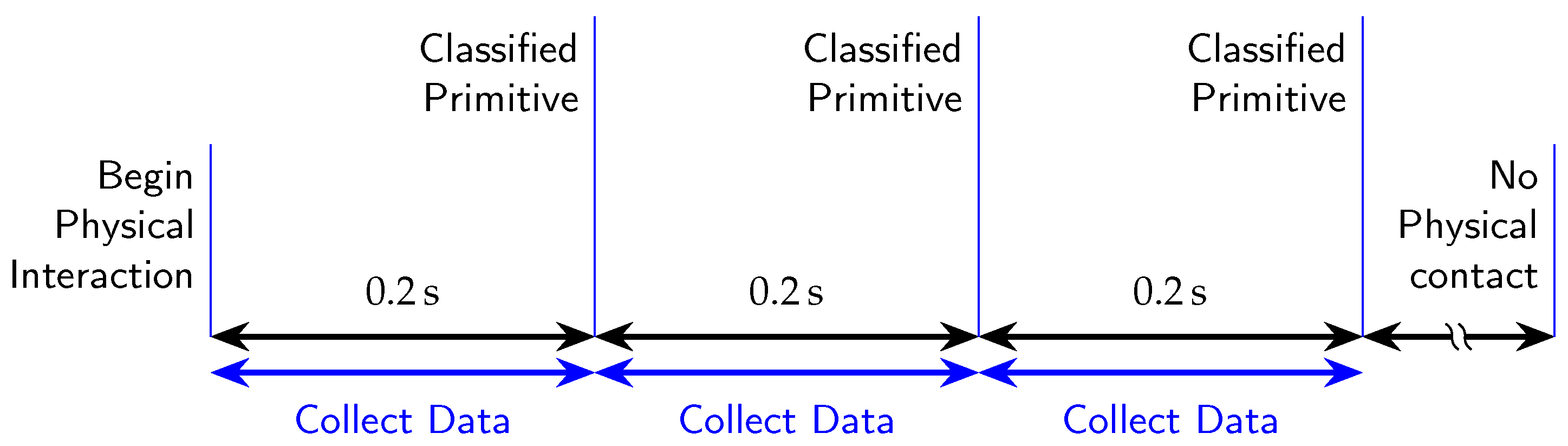
Figure 7 depicts an example of a timeline where the robot classified three contact primitives generated by the human operator. The algorithm for this real-time classification operates in a loop and consists of three steps: recognizing that a physical interaction has begun, collecting all the force and torque values for 0.2 s, and feeding the feedforward neural network with the collected data to obtain the classification results. The first step acquires external forces without any interaction, which are then used to define the trigger and subtract environmental forces during subsequent interactions. After that, the trigger step waits for a force that is strong and sustained enough to be considered an interaction, at which point the trigger is activated. The data collection step acquires sensor data and presents it to the decision model to return a classification of the interaction primitive.
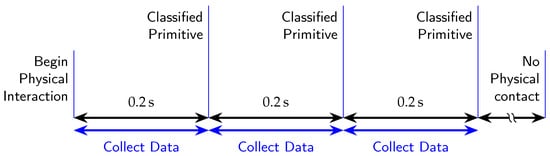
Figure 7.
Online primitive classification timeline example with three physical interactions.
To endow the robot with the capability of perceiving these physical interactions, a dataset of human-produced primitives was collected. Part of this dataset was used for the training of the neural network and the remaining part, used for testing, is composed of 1239 action samples (310 pulls, 287 pushes, 319 shakes, and 323 twists), performed by eight different users. Testing the trained feedforward neural network with this dataset resulted in the total classifications presented in Table 1, where it is possible to also visualize the mean output confidence and the standard deviation for each group of results (true positive, false positive, and false negative) for each one of the defined primitives.

Table 1.
Total classifications for each group of predictions (TP, FP, and FN) for each interaction primitive. The mean, and the related standard deviation, of the neural network output confidences are presented.
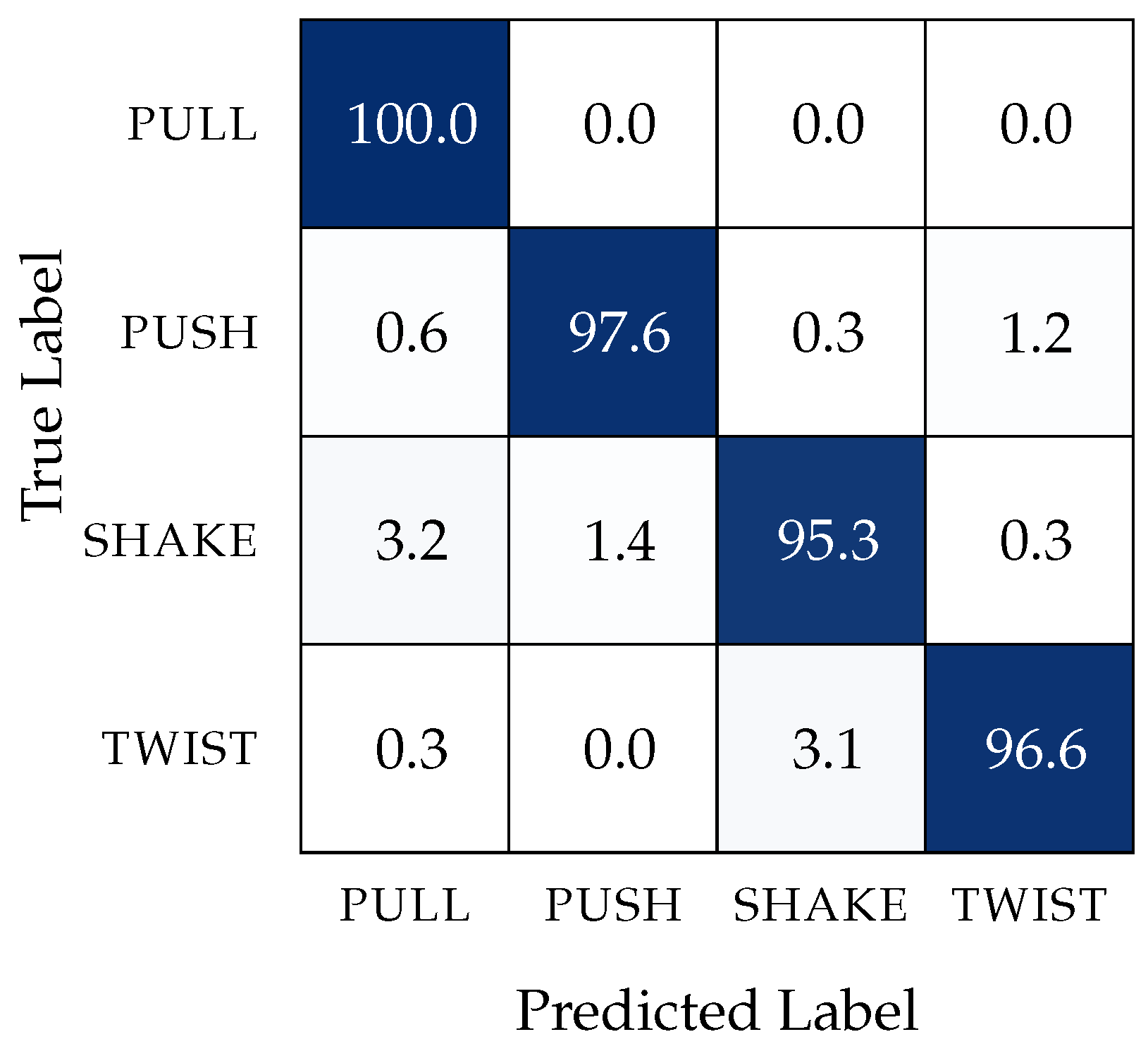
The conflict between the total predictions and the real actions for each primitive is represented, in percentage, on the confusion matrix in Figure 8. This confusion matrix evinces the distinction between the percentage of true positives for all the defined contact primitives.
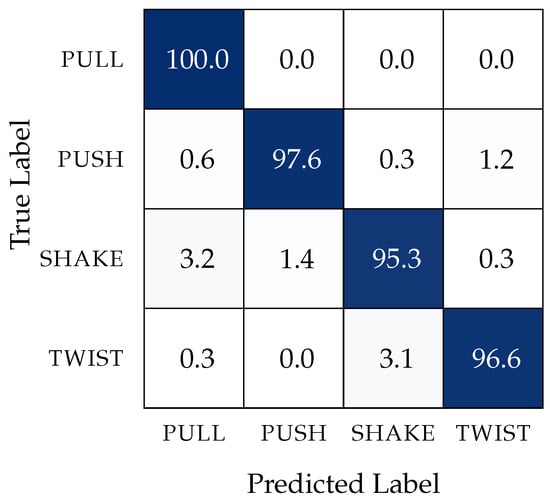
Figure 8.
Confusion matrix in percentage (%) obtained after testing the feedforward trained network.
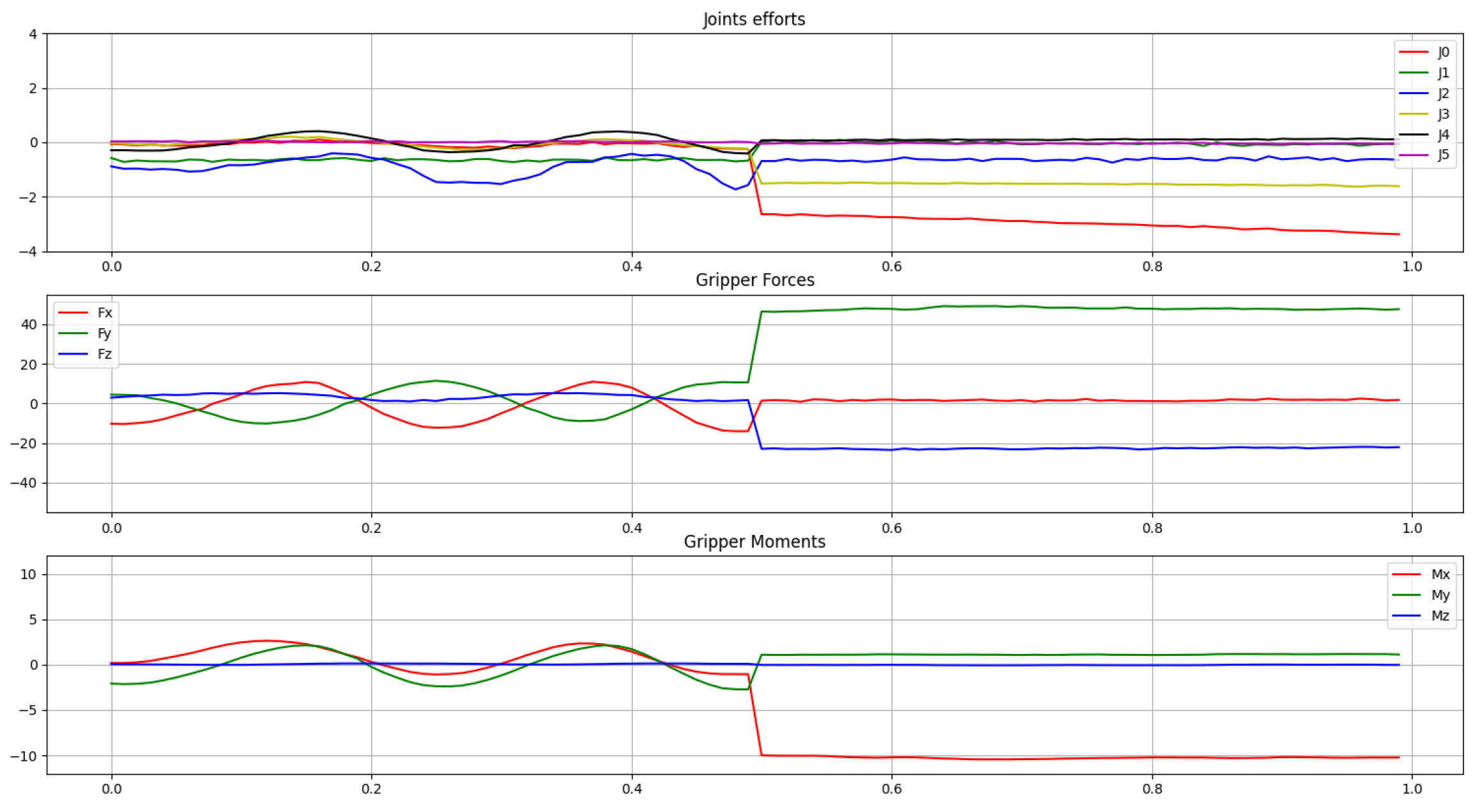
Moreover, this learning-based approach should also be able to correctly identify several continuously performed physical interactions, i.e., the human operator could establish not only one single haptic primitive but a full contact vocabulary. To test the adaptability of the proposed approach to this more complex purpose, the agent produced two sequential physical contacts. One example of the force and torque values collected in this experiment is presented in Figure 9.
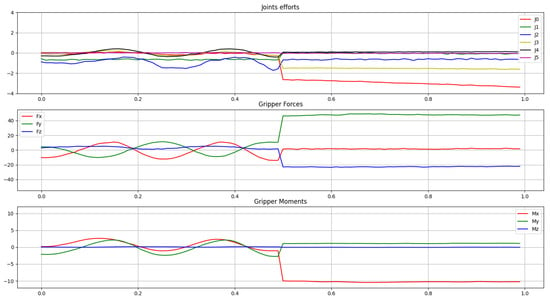
Figure 9.
Example of joint efforts (Nm) and wrist torques (Nm) and forces (N) felt by two sequential performed contact primitives, for period of 1 s.
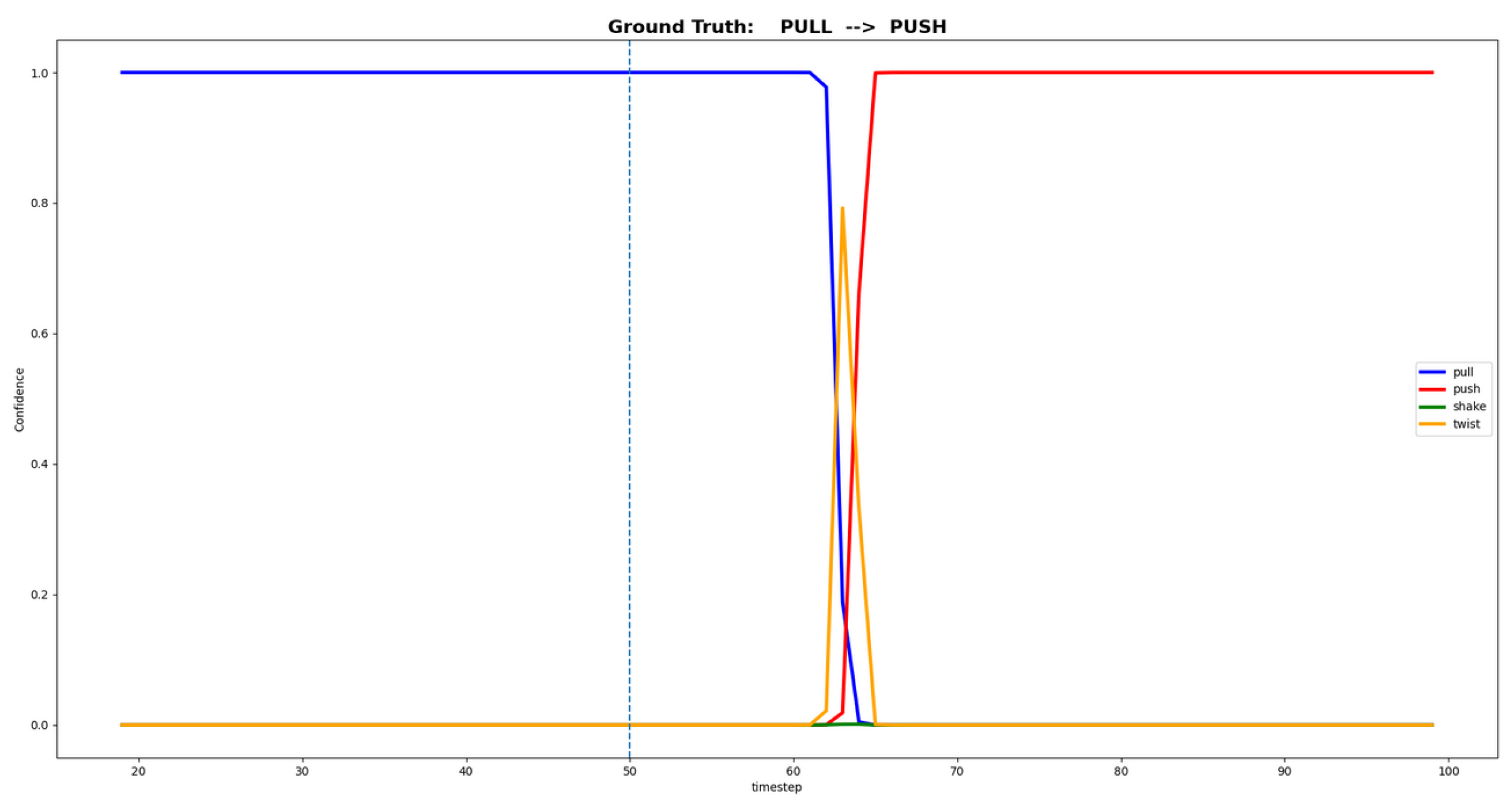
By having the deep learning model classifying in real time, the confidence neural network outputs for each one of the four predefined primitives (pull, push, shake, twist), when an agent in consecutive interacting with two distinct physical contacts, is shown in Figure 10. The presented results prove that the proposed deep learning solution is applicable to classify human–robot physical contacts, being able to tackle most of the problematic interactions, and even efficiently classifying several continuously performed haptic primitives.
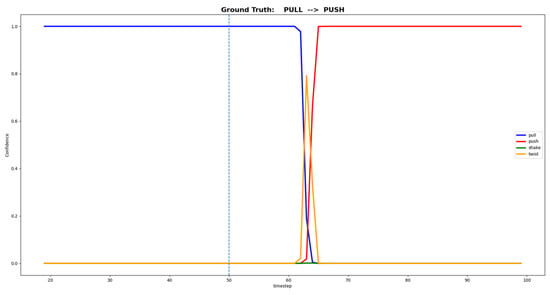
Figure 10.
Example of neural network output confidences for two sequentially performed contact primitives. In this case, the ground truth is composed of 0.5 s of pull, followed by 0.5 s of push. At each time step, the sum of all four output confidences is equal to 1, since the output layer uses softmax as the activation function.
4. Human-Centric Proactive Interaction
4.1. Volumetric Detection
Volumetric detection plays a crucial role as a foundational element in enabling effective human–robot collaboration. This capability is essential for robots to develop a comprehensive understanding of their surrounding environment in terms of spatial perception. Without reliable volumetric detection, robots lack the necessary awareness of the objects and obstacles present around them, potentially leading to hazardous situations. To solve this, other approaches have been adapted the robot movement in relation to external payloads, either at the beginning or at the end of contact [40]; such approaches have used the knowledge of the human pose to adapt the manipulator planning [41]. Our approach uses a occupancy mapping framework to accurately evaluate the presence of individuals within a defined work volume, leveraging spatial analysis techniques to enhance precision and reliability in monitoring human activity.
In our implementation of volumetric detection, we utilized OctoMap, a mapping framework that employs octrees to represent space and offers a flexible and high-resolution mapping solution [42]. OctoMap utilizes a probabilistic model, enabling efficient storage, real-time updates, and accurate mapping in 3D environments. The output of OctoMap consists of a list of occupied and free voxels.
The selection of OctoMap as the preferred volumetric mapping approach is attributed to the in-depth comparative study conducted in [36]. The study evaluated different volumetric mapping techniques and explored various parameters within each approach. It was observed that configuring OctoMap with a minimum voxel size of 0.1 m, a hit probability of 1, and a miss probability of 0.4 resulted in optimal results. These settings contributed to the superior qualitative and quantitative outcomes achieved using OctoMap compared to other mapping approaches analyzed [36].
To enable volumetric detection within the context of this collaborative cell, a specific work volume was defined. This work volume took the form of a rectangular prism and was positioned in front of the robotic manipulator. In order to classify a cell as fully occupied, OctoMap must detect the presence of occupied voxels within the work volume. To achieve this, we implemented a point-in-polyhedron algorithm. This algorithm computes the normal vectors for each face of the rectangular prism, which has dimensions of length l, width w, and height h. Equation (2) is utilized to determine whether a voxel center lies inside the prism:
By utilizing the provided equation, the coordinate vector of the voxel center is determined with respect to the coordinate vector of the prism’s center (represented as ). Following this calculation, the dot product between this vector and each normal vector is computed. This computation facilitates an evaluation of the position of the voxel relative to the center of the prism along a particular direction. If the resulting value exceeds half of the corresponding dimension of the prism, the voxel is outside its boundaries.
Once the number of occupied voxels inside the work volume has been determined, a decision-making process takes place. Instead of setting a fixed threshold for the number of voxels required to classify a cell as fully occupied, which would render the system less robust due to potential changes in the dimensions of the work volume, we employ a percentage-based decision strategy. This decision is based on the ratio of the occupied voxel volume to the total volume of the work volume, denoted as , as calculated in Equation (3):
By multiplying the number of voxels in the work volume by the cube of their resolution R, we obtain the occupied volume detected by OctoMap. Dividing this by the total volume of the cell yields the desired ratio. With this ratio established, we can empirically define a threshold for cell occupancy. In our case, the threshold was set at 15%. Further details can be observed in Figure 11.
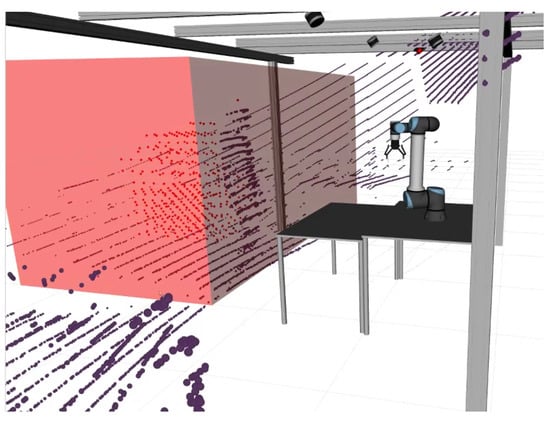
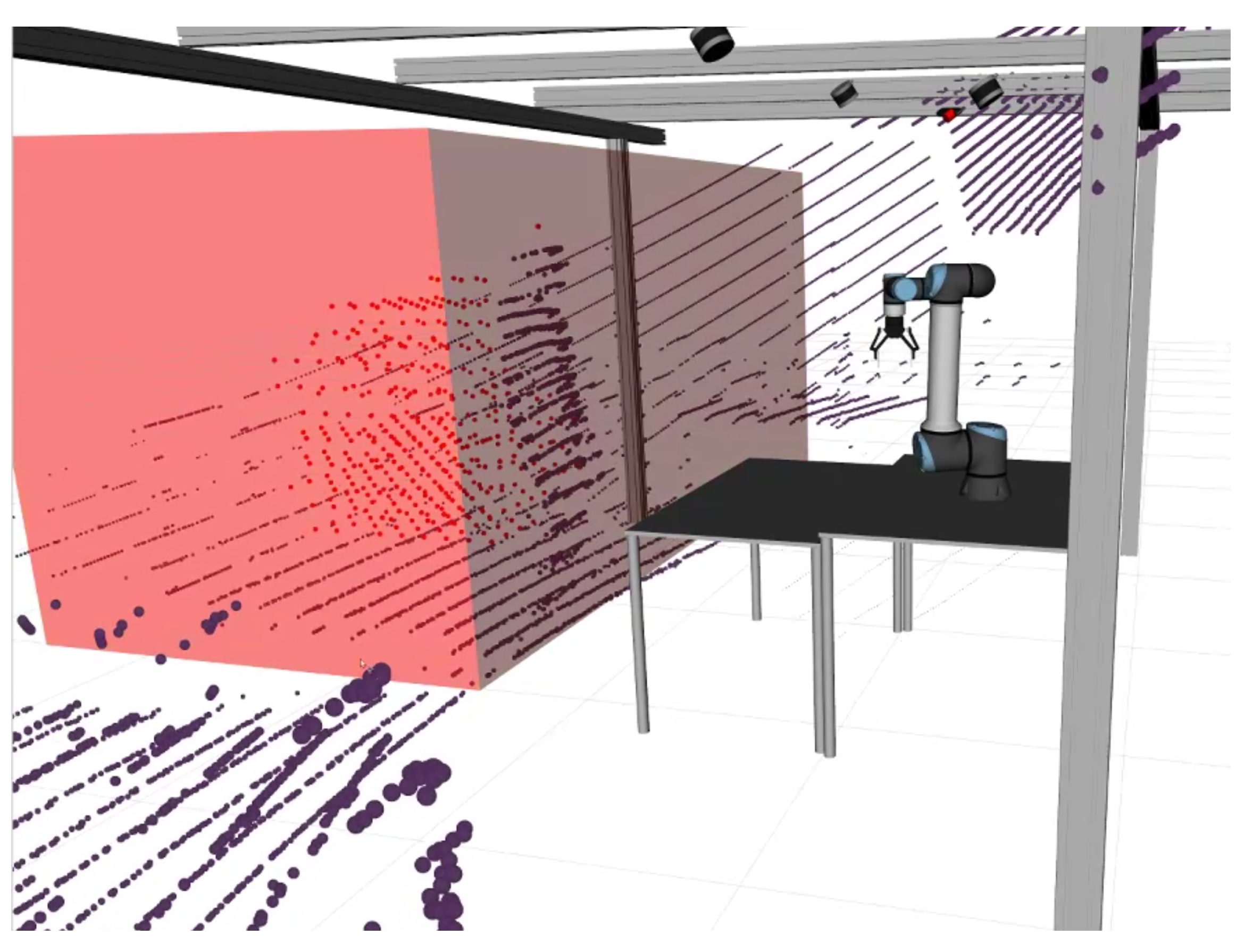
Figure 11.
Volumetric detection within the collaborative cell. The work volume is depicted by the prominent red prism, while the purple dots represent the point cloud captured by one of the LiDARs. The red dots correspond to the centers of the occupied voxels detected by OctoMap.
4.2. Human Intention Anticipation
The concept of anticipation has been studied across diverse research domains. For example, in biology, experimental findings have demonstrated anticipatory processes at various organizational levels [43]. In general terms, anticipation refers to the influence of predictions on the current behavior of a system, whether natural or artificial. Prediction models provide insights into potential future states of the environment or system. This perspective of looking to the future aims to integrate such information into decision-making or planning processes. Consequently, a system becomes anticipatory as it incorporates such a model and adjusts its current behavior accordingly. The ability to adjust behavior in anticipation of future events influences the execution of behavior and learning in living organisms. Similarly, anticipation is considered a crucial ability for cognitive robots operating in dynamically changing environments, helping the design of robots capable of proactive behavior; while most current robots can react based on what they sense and remember, they lack the ability to consider future outcomes (i.e., to connect the robot’s actions in the present to its final goal).
Robot assistants in manufacturing or assembly tasks provide a prime example where anticipating human intentions and/or needs is critical for an effective workflow, potentially impacting safety and cycle time. This can be accomplished through various methods, which can be broadly categorized into two approaches: those that focus on human motion prediction and those that focus on human intent recognition based on environmental cues. On the one hand, methods that focus on detailed human motion prediction, like probabilistic movement primitives (ProMPs) [44], can be computationally expensive for real-time applications in industrial settings; while they are powerful for complex motion sequences, ProMPs require the modeling and prediction of entire human motion trajectories. On the other hand, recognizing subtle cues and monitoring task progress fall into the latter category. Among them, eye gaze has deserved particular attention as a powerful tool for discerning the operator’s potential intentions [45].
In contrast to previous approaches, our work emphasizes the robot’s ability to perceive and recognize the object being manipulated by the human operator as a key component for making predictions about its needs. Knowing the object in the user’s hand can provide valuable contextual information, revealing both current activity and future intentions. The solution adopted in our work focuses on detecting and tracking the hand and finger key points from visual data. The proposed framework combines the strengths of Mediapipe in detecting hand landmarks in an RGB image with a deep multi-class classifier that predicts the grasped object from a set of 21 key points.This focus on hand–object interaction (HOI) allows for a computationally efficient and real-time applicable strategy for intention anticipation, particularly suited for industrial collaborative tasks. The advantages and limitations of using this novel approach for the recognition of human-grasped objects can be found elsewhere [37].
In this work, we developed an object-recognition module by leveraging a pretrained convolutional neural network (CNN) that was optimized in our previous work [37]. This CNN, while originally trained for a different set of objects, was fine-tuned for the task of recognizing screwdrivers, pliers, Rubik’s cubes, and water bottles. The training dataset was obtained using images of hand postures holding these objects, captured and annotated according to the previously established protocol. The exact number of samples of the entire dataset per class and per user is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Number of samples in the dataset per class and user.
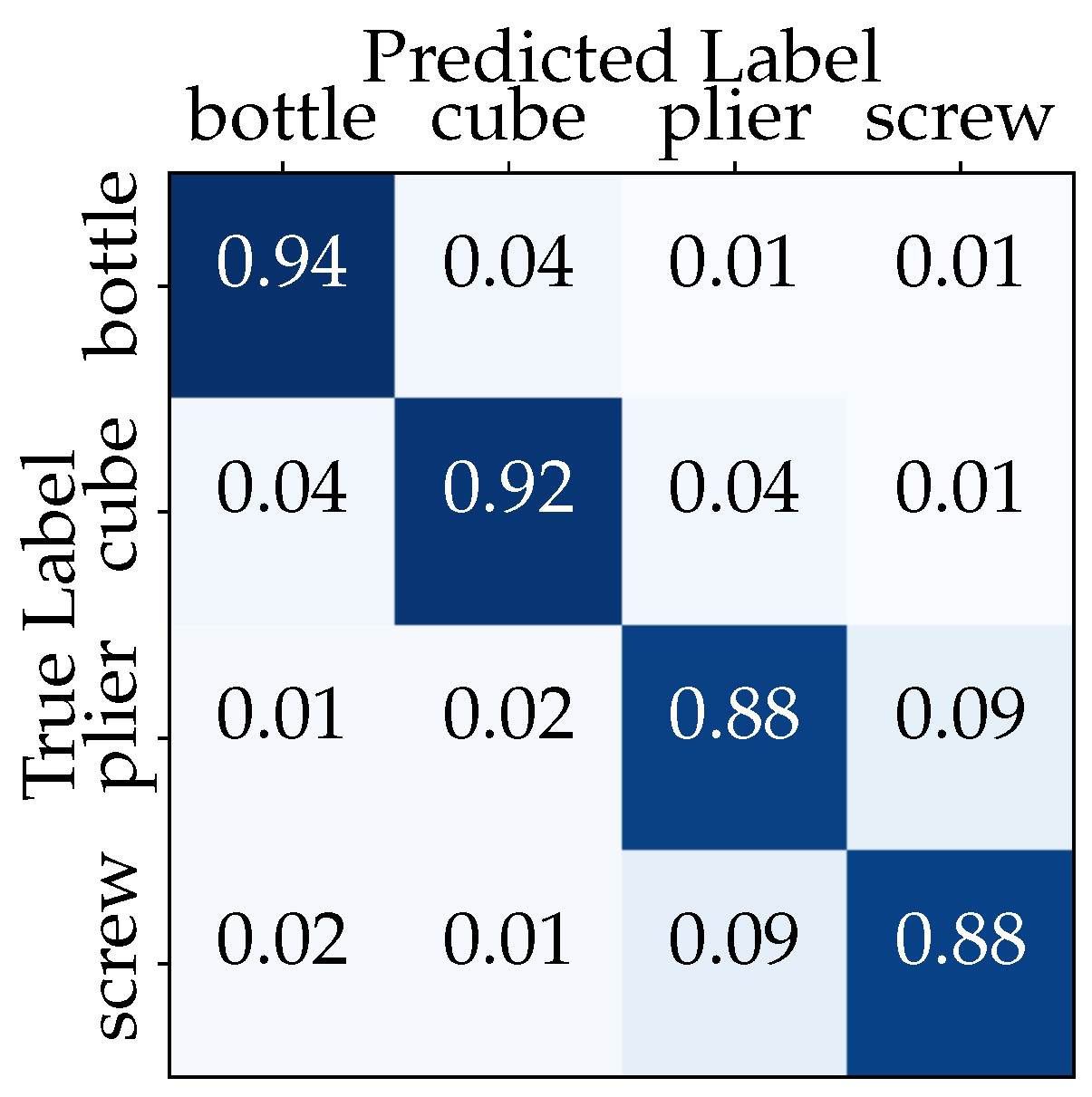
The classification model achieved a high overall accuracy of 90.5% on the held-out test set, comprising 20% of the original dataset. A confusion matrix was generated to visualize the classification performance for each object class (Figure 12). The diagonal elements represent correctly classified instances, while off-diagonal elements indicate misclassifications between object categories. The confusion matrix highlights the high precision and recall rates for most objects, with some confusion observed between the pliers and the screwdriver.
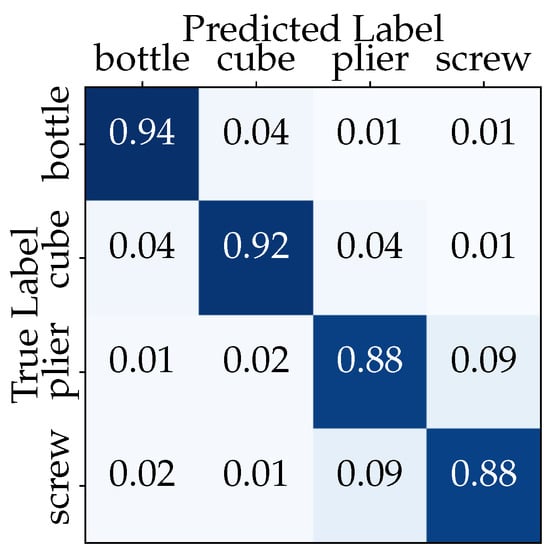
Figure 12.
Confusion matrix for object classification using a CNN model.
Subsequently, the object-recognition module was tested in a real-time setting within a collaborative human–robot interaction scenario. The experiments conducted to validate the proposed anticipation system involve a task where the robot assists a human in a tabletop scenario by recognizing objects held in the hand based on their grasping pattern. The experimental setup comprises a UR10e robot, two Orbbec Astra Pro RGB-D cameras, and a set of four objects positioned on a table (Figure 13).

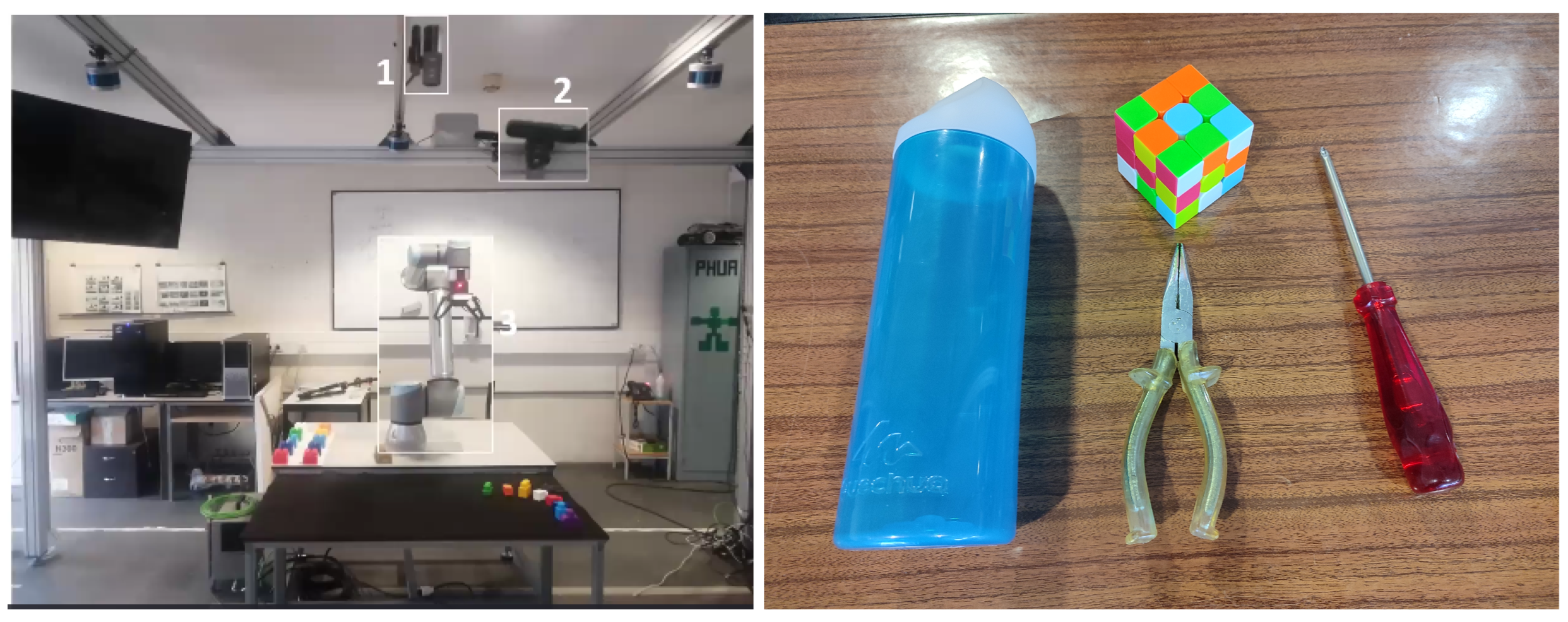
Figure 13.
Experimental setup depicting the collaborative cell where the study was conducted. On the left, it features two RGB-D cameras (marked as white rectangles 1 and 2) and the UR10e COBOT (marked as white rectangle 3). On the right are the objects used to discriminate based on their grasping patterns.
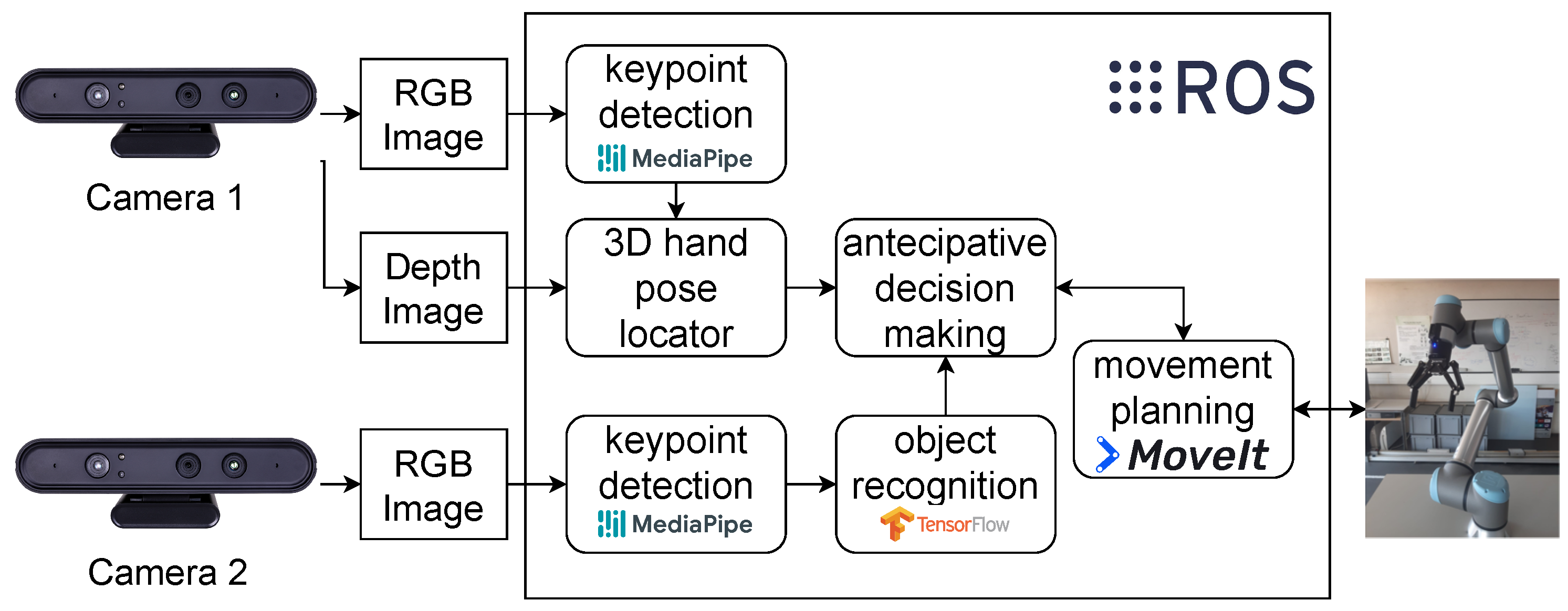
The robot observes the worker’s hand, while a real-time CNN deep model identifies the specific object being grasped. Upon object recognition, the robot delivers the corresponding tool or part to assist the worker. The functional blocks of the anticipatory system were developed separately. The prediction model offers the possibility of incorporating action selection in their planning through a decision-making block. Figure 14 illustrates the developed anticipatory system, including the decision-making block and movement planning using the MoveIt library.
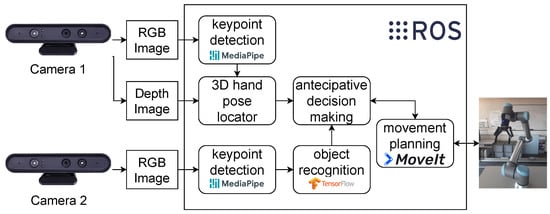
Figure 14.
Functional blocks of the anticipatory robotic system.
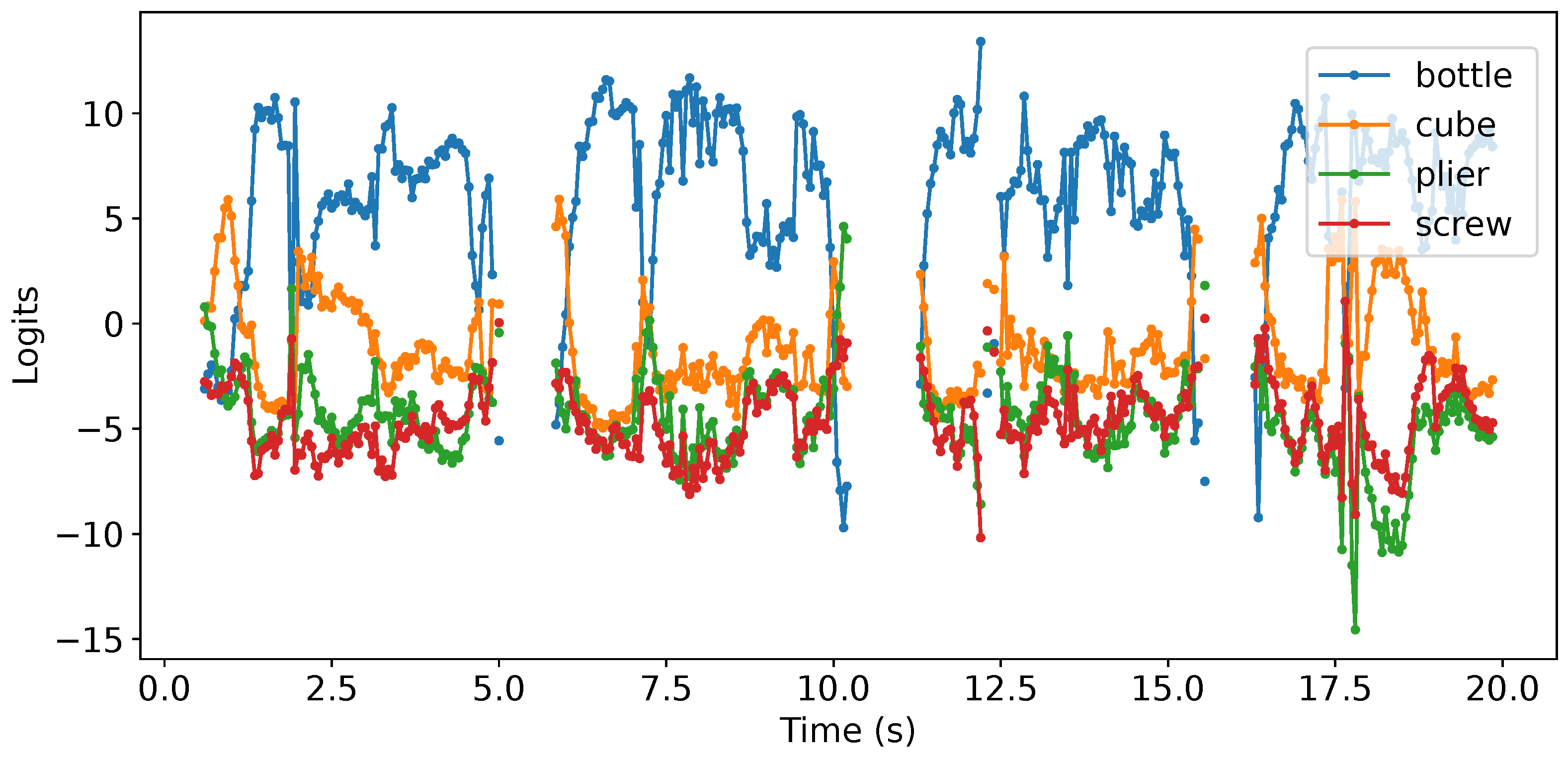
The classifier employs logits, which are the raw, non-normalized output values produced by the neural network model. To illustrate this, Figure 15 depicts the temporal evolution of the logits for each object class when the grasped object is a bottle. This figure showcases how these raw scores change over time during the network’s prediction process. The real-time classification process also relies on thresholds determined from an analysis of the output values obtained during repeated pick-and-place movements performed with each object. By comparing these logits to pre-established thresholds that are specific to each object, the classifier determines the identity of the object being grasped. This approach allows for efficient and accurate object recognition, enabling the robot to reliably respond to the user’s actions in real-time scenarios; while the initial results show promise, further efforts are ongoing to facilitate the integration of anticipation and planning within uncertain contexts, especially considering the inherent variability of human behavior.
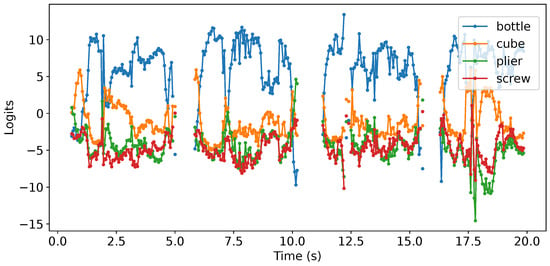
Figure 15.
Temporal evolution of CNN object classifier logits by picking up and dropping the bottle four times.
5. Application Case Study
The methods described in the preceding section have been developed specifically for setups that involve human–robot collaboration. The overall system incorporates human awareness, human–robot communication, and object handover capabilities, enabling the resolution of a large set of industrial use cases that require collaboration between humans and robots. The application case study presented in this paper is based on a typical human–robot interaction scenario, where a human operator interacts with a palletizing robotic arm to inspect the object it is holding. The robot’s behavior is represented by a finite-state machine, which uses the output of the decision models to transition between states.
5.1. Demonstration’s Software
The application case study presented in this paper utilizes specific software components that play a crucial role in its operation of the collaborative cell. The movement control of the UR10e was achieved using MoveIt [46], a widely adopted motion planning framework in ROS. This framework offers various joint planners, simplifying the implementation of different robot motions. Furthermore, the MoveIt drivers enabled real-time sensor data acquisition from the robot at a maximum frequency of 500 Hz, enhancing the responsiveness of the system.
Additionally, the framework offers the capability to utilize ROS actions, a communication mechanism that is inherent to ROS that facilitates the execution of long-running tasks and enables asynchronous behavior between different components of a robotic system. Actions enable non-blocking execution, allowing the robot to engage in other operations while waiting for the completion of a particular action. This simultaneous operation enhances the robot’s responsiveness to external interactions, such as hand gestures or physical engagements, while concurrently executing other commands.
To facilitate the implementation of a robust and scalable control, sensing, and decision-making system, the logic of the finite-state machine was implemented using the SMACH library [47]. SMACH provides a comprehensive set of classes and functions that enable the modular implementation of states and triggers. This modular approach not only enhances the system’s robustness but also facilitates scalability, allowing for the seamless addition of new functionalities as needed. In terms of decision models, the hand gesture recognition is implemented in Pytorch, and also uses MediaPipe. The physical interaction module is programmed in Keras API, from TensorFlow2. The third decision module uses OctoMap, as mentioned in Section 4.1. All these systems are integrated in the ROS framework.
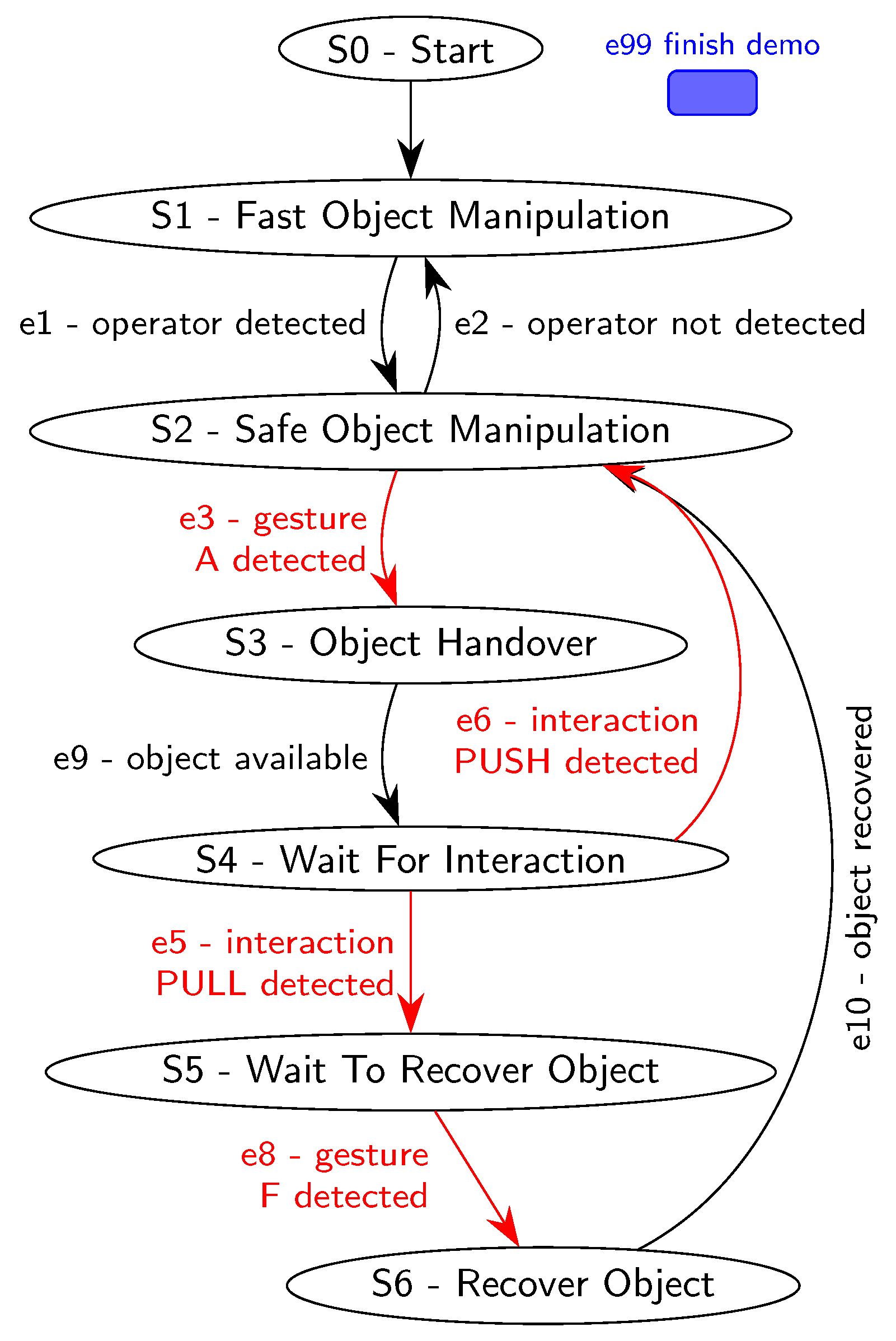
5.2. State Machine
The robotic arm is controlled by a finite-state machine with six states. Each state encompasses specific configurations of arm and gripper movements, velocities, and accelerations. Transitions between states are triggered by events generated by the decision models previously described. Figure 16 provides a diagram of the finite-state machine.
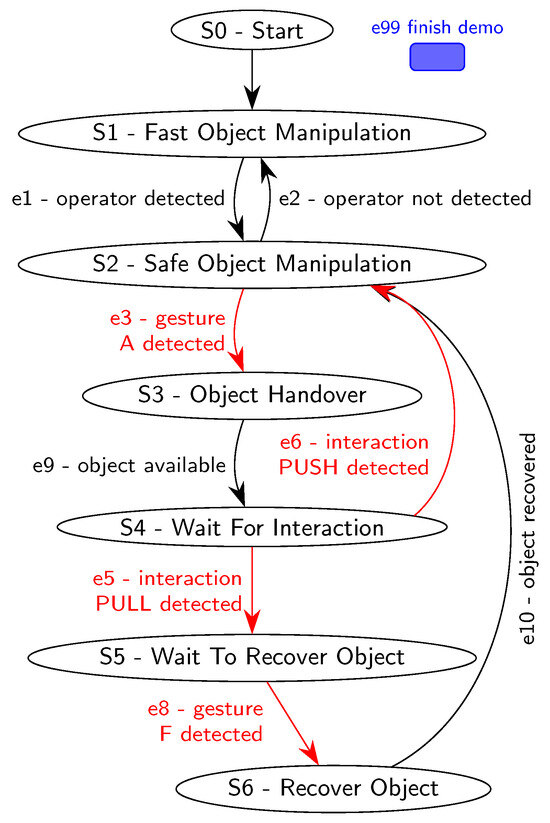
Figure 16.
Demonstration’s state machine diagram; Sn labels are prefixes for states, and en labels are prefixes for events (triggers). Events triggered by user interaction are marked in red.
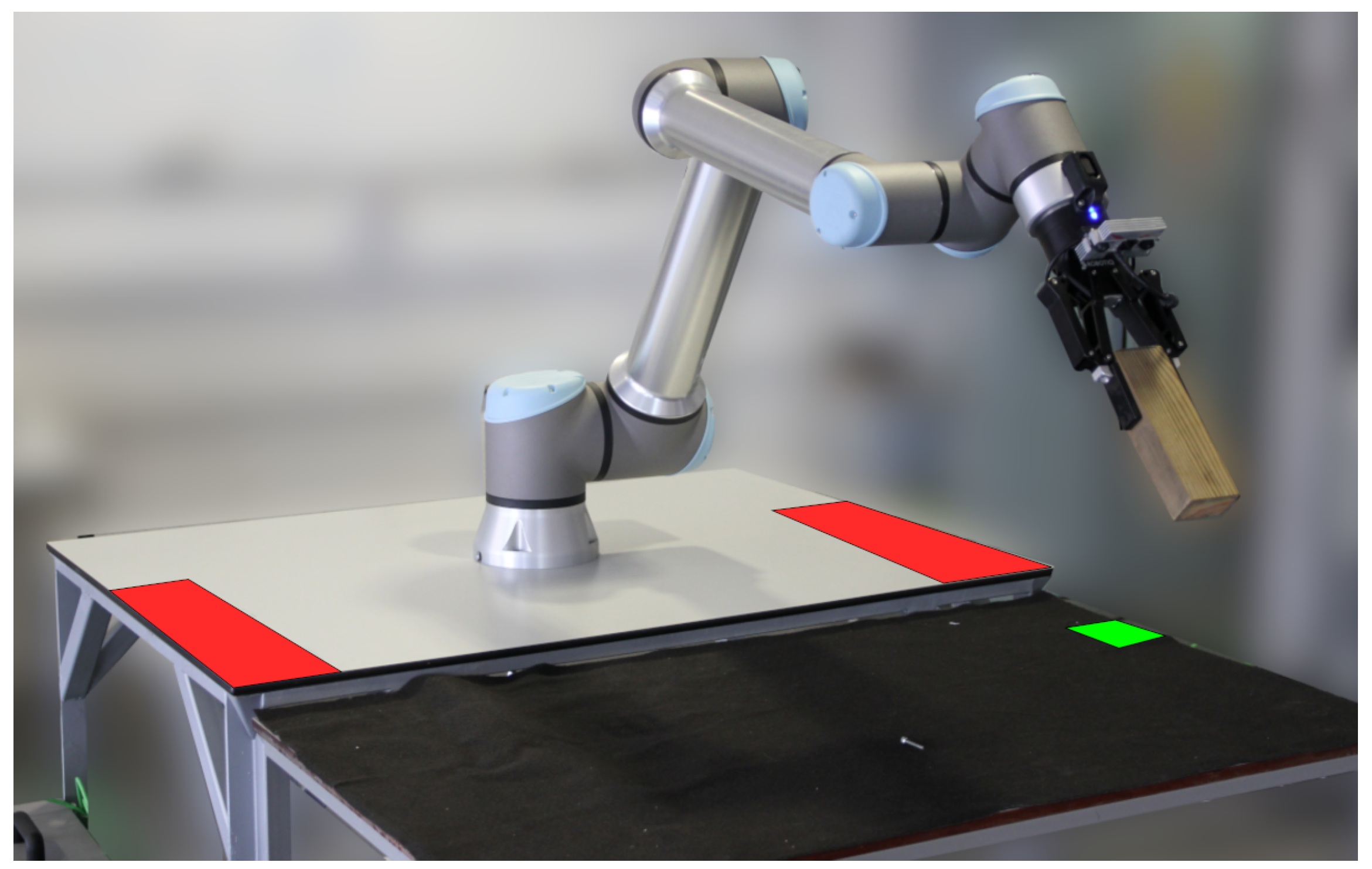
- State 1—Fast Object Manipulation. The demonstration begins in State 0, which is an initiation state that immediately switches to State 1. In this State 1, the robotic arm carries out a palletizing task, manipulating two objects 1 and 2 between two distinct positions, as depicted by the red zones in Figure 17. The arm operates at maximum speed, performing wide movements to minimize task cycle time. The state machine monitors the output of the volumetric detection node, which detects the presence of a human operator. If an operator is detected within the monitored volume, the state machine switches to State 2.
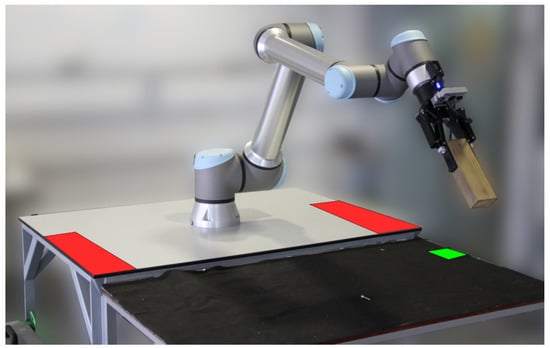 Figure 17. View of the human–robot interaction space. The red zones are the regions that the robot uses to continuously place and swap objects 1 and 2. The green zone is the designated area for object recovery. The robot is in a position ready for operator physical interaction.
Figure 17. View of the human–robot interaction space. The red zones are the regions that the robot uses to continuously place and swap objects 1 and 2. The green zone is the designated area for object recovery. The robot is in a position ready for operator physical interaction. - State 2—Safe Object Manipulation. While the operator is present and there is no engagement with the robot, the state machine remains in State 2. In this state, the robot performs in a slower motion and more retracted movements, displaying awareness of the operator’s presence. However, it continues the initial palletizing task for objects 1 and 2. There are two triggers to exit State 2. If the volumetric detection module detects the operator leaving the monitored volume, the state machine goes back to State 1. Alternatively, if the hand gesture recognition module detects the operator correctly performing the A hand gesture, and the robot possesses an object in the gripper, the state machine goes to State 3. If the robot does not have an object, the program waits for the robot to grasp one before switching states.
- State 3—Object Handover. State 3 acts as a transient state between States 2 and 4. The transition from State 2 to State 3 occurs when the operator requests an object. In State 3, the robotic arm moves to a handover position. The trigger to switch to State 4 is an internal robot event that verifies if it has reached the handover position.
- State 4—Wait for Interaction. In this state, the robot remains stationary in the handover position, placing the object at about a 45° angle, in a configuration similar to the one represented in Figure 17. The state machine monitors the output of the physical interaction classification module, which recognizes two available interactions: PUSH and PULL. The PUSH interaction results in the rejection of the object held by the robot, prompting a return to State 2 to resume palletizing. On the other hand, the PULL interaction triggers the gripper to release the object, allowing the operator to retrieve it. Subsequently, the robot retracts to a safe position and goes to State 5.
- State 5—Wait to Recover Object. During this phase, the human operator is handling the object. Once the inspection is complete, the operator places the object in an area designated for object recovery, as indicated by the green zone in Figure 17. To signal the intent of object recovery to the robot, the operator performs the F gesture. This triggers the state machine to transition to State 6.
- State 6—Recover Object. State 6 initiates a slow movement to retrieve the object from the designated object-recovery area. Upon completing the movement, the state machine automatically switches back to State 2.
6. Discussion and Results
The solutions proposed in this paper introduce several aspects to enhance human–robot collaboration, with a focus on safety, interaction abilities, and industrial applications. We have integrated multimodal sensing capabilities to improve the robot’s awareness of the human operator. This increased awareness enables the robot to adjust its behavior and movements for safe interaction, switching to slower and more cautious movements in the presence of the operator to prioritize safety and minimize the risk of accidents or collisions. This also promotes task efficiency, as the system employs rapid object manipulation when there is no risk of collision. The incorporated hand gestures and physical interaction recognition enable intuitive and natural communication for the human. Moreover, using ASL for hand gesture recognition and simple interaction primitives for physical interaction further allowed for a straightforward and easily comprehensible communication system.
Although the collaborative system is user-friendly, it accommodate a wide range of possible events, resulting in complex human–robot interaction when necessary. The integration of these features into a comprehensive solution confirms their suitability not only as standalone components but also in complex applications. Furthermore, we considered ergonomics when designing the finite-state machine that governs the robot’s behavior. We defined specific robot configurations, velocities, and accelerations in each state to ensure comfortable and ergonomic task performance during human interaction. Our approach is specifically tailored to industrial use cases, such as palletizing tasks. By integrating decision models, sensing modules, and the finite-state machine within a collaborative cell, we demonstrate the practicality and adaptability of our approach to real-time operation.
Each described feature has its own performance assessed by metrics published in specific papers, as reported in the previous section. However, the integration of those features in a global solution is a result that confirms their suitability not only in standalone mode, but also in complex applications. Table 3 includes a set of links for video clips and other sources of information available on online platforms that illustrate the performance and functionality of the integrated cell, as well as demonstrations in standalone actions.

Table 3.
Qualitative indicators of performance.
However, the development of collaborative cells for real-world scenarios presents a number of significant challenges requiring further research. The use of learning-based methods in industrial settings requires the system to be able to deal with the variability in human behavior and a number of different users. Learning models may need to adapt to different user preferences, work styles, or even physical capabilities; while challenges exist, integrating data acquisition for personalized modeling holds promise for the future of human–robot collaboration in industrial settings. As technology advances and costs decrease, it could become a more widely adopted approach to deal with specific users distributions.
In addition to overcoming technical challenges, moving knowledge from research labs to real-world industries poses a significant engineering barrier. Often, there is a lack of established processes, evident in the absence of comprehensive architectural models and methods. In the context of robotics, widely-used standardized components, software frameworks, and systems play a crucial role in application development. These resources are valued for their adoption and compatibility across different hardware and software platforms. However, due to lack of standards, building robotic systems often requires expertise instead of following established engineering protocols. For example, integration frameworks and middleware serve different development objectives. On the one hand, academic platforms like ROS and YARP prioritize flexibility, making them ideal for exploratory research. On the other hand, business-oriented platforms like OpenRTM and SmartSoft emphasize structured role separation and robust support for the development environment.
7. Conclusions
This work investigated the integration of safety, multimodal communication interfaces, and deep learning techniques in order to advance the potential of collaborative robotics in industry. The focus was on the methodological and software aspects adopted during the system development and integration process. At this point, it is pertinent to make the following comments. First, the developed framework ensures awareness of human and robot activities, showing promising features to be applied in advanced adaptive control strategies. Second, the learning techniques adopted in the communication interfaces proved to be suitable for real-time operation. Furthermore, the proposed methodology to classify contact-based interactions paves the way for more effective forms of communicating human intentions through a haptic channel. Third, this study presented the practical implementation of a case study and the usefulness of ROS for a seamless integration and interoperability among different modules.
The core abilities addressed in our study provide a technology and application independent way of characterizing the entire system performance; while the current study establishes the feasibility of the system, future work will focus on a comprehensive evaluation of the system’s performance and user experience. This includes conducting user studies with human collaborators to assess the system’s usability and acceptability in real-world scenarios. Additionally, quantitative evaluation will be conducted to measure the accuracy and response times of the individual modules, providing concrete evidence for the system’s overall effectiveness. These evaluations will further strengthen the presented work and pave the way for future research on optimizing human–robot collaboration in industrial settings. It is expected that the development of reusable building blocks with clearly defined properties could help the technology transfer from research to industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B., A.C., M.G., P.A., V.S., F.S. and M.O.; investigation, J.B., A.C., M.G. and P.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.B., A.C., M.G., P.A., V.S., F.S. and M.O.; writing—review and editing, J.B., A.C., M.G., P.A., V.S., F.S. and M.O.; supervision, V.S., F.S. and M.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present study was developed in the scope of the Project Augmented Humanity [POCI-01-0247-FEDER-046103], financed by Portugal 2020, under the Competitiveness and Internationalization Operational Program, the Lisbon Regional Operational Program, and by the European Regional Development Fund. Afonso Castro was supported by the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT), Portugal under the grant 2021.06664.BD.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These data can be found here: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/joelbaptista/hand-gestures-for-human--robot-interaction; https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/pedromiglou/human-grasping-patterns-for-object-recognition (accessed on 8 July 2024).
Acknowledgments
This study has also the support of FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology, in the context of project UIDB/00127/2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Demir, K.A.; Döven, G.; Sezen, B. Industry 5.0 and human–robot co-working. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Kiyokawa, T.; Ricardez, G.A.G.; Ramirez-Alpizar, I.G.; Venture, G.; Yamanobe, N. Evaluating quality in human–robot interaction: A systematic search and classification of performance and human-centered factors, measures and metrics towards an industry 5.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 63, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, V.; Pini, F.; Leali, F.; Secchi, C. Survey on human–robot collaboration in industrial settings: Safety, intuitive interfaces and applications. Mechatronics 2018, 55, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Savur, C.; Sahin, F. Survey of human–robot collaboration in industrial settings: Awareness, intelligence, and compliance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 51, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Silva, F.; Santos, V. Trends of human–robot collaboration in industry contexts: Handover, learning, and metrics. Sensors 2021, 21, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, S.; Chrysostomou, D. Human–robot collaboration in industrial environments: A literature review on non-destructive disassembly. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, L.; Rauch, E.; Vidoni, R. Emerging research fields in safety and ergonomics in industrial collaborative robotics: A systematic literature review. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, A.; Pinto, A.; Santos, J.; Pinheiro, S.; Romero, D. Designing human–robot collaboration (HRC) workspaces in industrial settings: A systematic literature review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, M.; Lagomarsino, M.; Fortini, L.; Gholami, S.; Ajoudani, A. Ergonomic human–robot collaboration in industry: A review. Front. Robot. AI 2023, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalos, G.; Makris, S.; Tsarouchi, P.; Guasch, T.; Kontovrakis, D.; Chryssolouris, G. Design considerations for safe human–robot collaborative workplaces. Procedia CIrP 2015, 37, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadekar, P.; Gopinath, V.; Johansen, K. Safe layout design and evaluation of a human–robot collaborative application cell through risk assessment–a computer aided approach. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 25, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlini, M.; Neri, F.; Scoccia, C.; Carbonari, L.; Palmieri, G. Collision Avoidance in Collaborative Robotics Based on Real-Time Skeleton Tracking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics in Alpe-Adria Danube Region, Bled, Slovenia, 14–16 June 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Lorenzini, M.; Balatti, P.; Nguyen, P.D.; Pattacini, U.; Tikhanoff, V.; Peternel, L.; Fantacci, C.; Natale, L.; Metta, G.; et al. Adaptable workstations for human–robot collaboration: A reconfigurable framework for improving worker ergonomics and productivity. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2019, 26, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, L.; Palomba, I.; Merati, F.A.; Rauch, E.; Vidoni, R. Design of human-centered collaborative assembly workstations for the improvement of operators’ physical ergonomics and production efficiency: A case study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, M.; Lorenzini, M.; Balatti, P.; De Momi, E.; Ajoudani, A. Pick the right co-worker: Online assessment of cognitive ergonomics in human–robot collaborative assembly. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 15, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurtua, I.; Fernandez, I.; Tellaeche, A.; Kildal, J.; Susperregi, L.; Ibarguren, A.; Sierra, B. Natural multimodal communication for human–robot collaboration. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417716043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Sandoval, J.; Laribi, M.A. Recent advancements in multimodal human–robot interaction. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 17, 1084000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zaatari, S.; Marei, M.; Li, W.; Usman, Z. Cobot programming for collaborative industrial tasks: An overview. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 116, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, A.; Passama, R.; Crosnier, A.; Lasnier, A.; Fraisse, P. Collaborative manufacturing with physical human–robot interaction. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2016, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogenyi, U.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Ju, Z.; Liu, H. Physical human–robot collaboration: Robotic systems, learning methods, collaborative strategies, sensors, and actuators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Pan, Z.; Han, M. Progress and prospects of multimodal fusion methods in physical human–robot interaction: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 10355–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.M.; Mutlu, B. Anticipatory robot control for efficient human–robot collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Christchurch, New Zealand, 7–10 March 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Lee, J.; Peternel, L.; Tsagarakis, N.; Ajoudani, A. Anticipatory robot assistance for the prevention of human static joint overloading in human–robot collaboration. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, N.F.; Raković, M.; Tasevski, J.; Coco, M.I.; Billard, A.; Santos-Victor, J. Action anticipation: Reading the intentions of humans and robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 4132–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bütepage, J.; Kjellström, H.; Kragic, D. Anticipating many futures: Online human motion prediction and generation for human–robot interaction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–26 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 4563–4570. [Google Scholar]
- Ortenzi, V.; Cosgun, A.; Pardi, T.; Chan, W.P.; Croft, E.; Kulić, D. Object handovers: A review for robotics. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1855–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, M.; Lorenzini, M.; Constable, M.D.; De Momi, E.; Becchio, C.; Ajoudani, A. Maximising Coefficiency of Human-Robot Handovers through Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwakatare, L.; Raj, A.; Crnkovic, I.; Bosch, J.; Olsson, H.H. Large-scale machine learning systems in real-world industrial settings: A review of challenges and solutions. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2020, 127, 106368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Gupta, K.; Chang, L.H.; Najjaran, H. A survey of robot learning strategies for human–robot collaboration in industrial settings. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajwan, M.; Singh, S. A Review on the Effectiveness of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms for Collaborative Robot. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3489–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Conley, K.; Gerkey, B.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs, J.; Wheeler, R.; Ng, A.Y. ROS: An open-source Robot Operating System. In ICRA Workshop on Open Source Software, Kobe, Japan, 2009; Volume 3, p. 5. Available online: http://robotics.stanford.edu/~ang/papers/icraoss09-ROS.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Oliveira, M.; Pedrosa, E.; Aguiar, A.; Rato, D.; Santos, F.; Dias, P.; Santos, V. ATOM: A general calibration framework for multi-modal, multi-sensor systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rato, D.; Oliveira, M.; Santos, V.; Gomes, M.; Sappa, A. A Sensor-to-Pattern Calibration Framework for Multi-Modal Industrial Collaborative Cells. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 64, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, J.; Santos, V.; Silva, F.; Pinho, D. Domain Adaptation with Contrastive Simultaneous Multi-Loss Training for Hand Gesture Recognition. Sensors 2023, 23, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Baptista, J.; Silva, F.; Santos, V. Classification of handover interaction primitives in a COBOT–human context with a deep neural network. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 68, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.; Oliveira, M.; Santos, V. Volumetric Occupancy Detection: A Comparative Analysis of Mapping Algorithms. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.03089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, P.; Silva, F.; Santos, V. Recognition of Grasping Patterns Using Deep Learning for Human–Robot Collaboration. Sensors 2023, 23, 8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugaresi, C.; Tang, J.; Nash, H.; McClanahan, C.; Uboweja, E.; Hays, M.; Zhang, F.; Chang, C.; Yong, M.G.; Lee, J.; et al. MediaPipe: A Framework for Building Perception Pipelines. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.00567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibilia, A.; Laghi, M.; De Momi, E.; Peternel, L.; Ajoudani, A. A Self-Adaptive Robot Control Framework for Improved Tracking and Interaction Performances in Low-Stiffness Teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE-RAS 18th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Beijing, China, 6–9 November 2018; pp. 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroni, M.; Beschi, M.; Pedrocchi, N. Safety-Aware Time-Optimal Motion Planning With Uncertain Human State Estimation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 12219–12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, A.; Wurm, K.; Bennewitz, M.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. OctoMap: An Efficient Probabilistic 3D Mapping Framework Based on Octrees. Auton. Robot. 2013, 34, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, C. Biological Prescience: The Role of Anticipation in Organismal Processes. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 672457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschos, A.; Daniel, C.; Peters, J.; Neumann, G. Using probabilistic movement primitives in robotics. Auton. Robot. 2018, 42, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.M.; Andrist, S.; Sauppé, A.; Mutlu, B. Using gaze patterns to predict task intent in collaboration. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 144956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.; Șucan, I.A.; Chitta, S.; Correll, N. Reducing the Barrier to Entry of Complex Robotic Software: A MoveIt! Case Study. J. Softw. Eng. Robot. 2014, 5, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, J.; Cousins, S. The SMACH High-Level Executive [ROS News]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2010, 17, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).