Revealing the Influence of the Fine-Scale Built Environment on Urban Rail Ridership with a Semiparametric GWPR Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Study Area and Data Sources
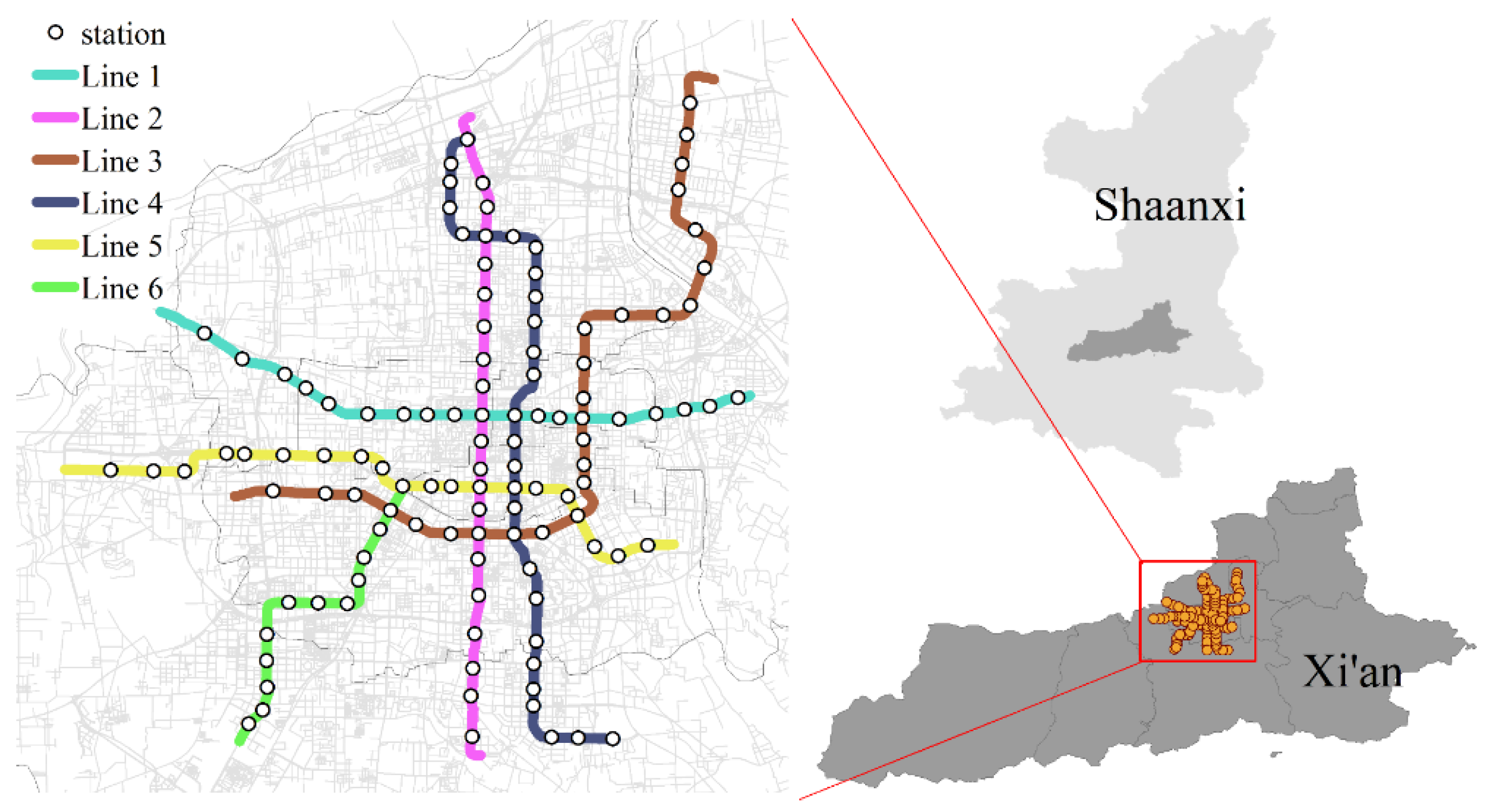
3.1. Study Area
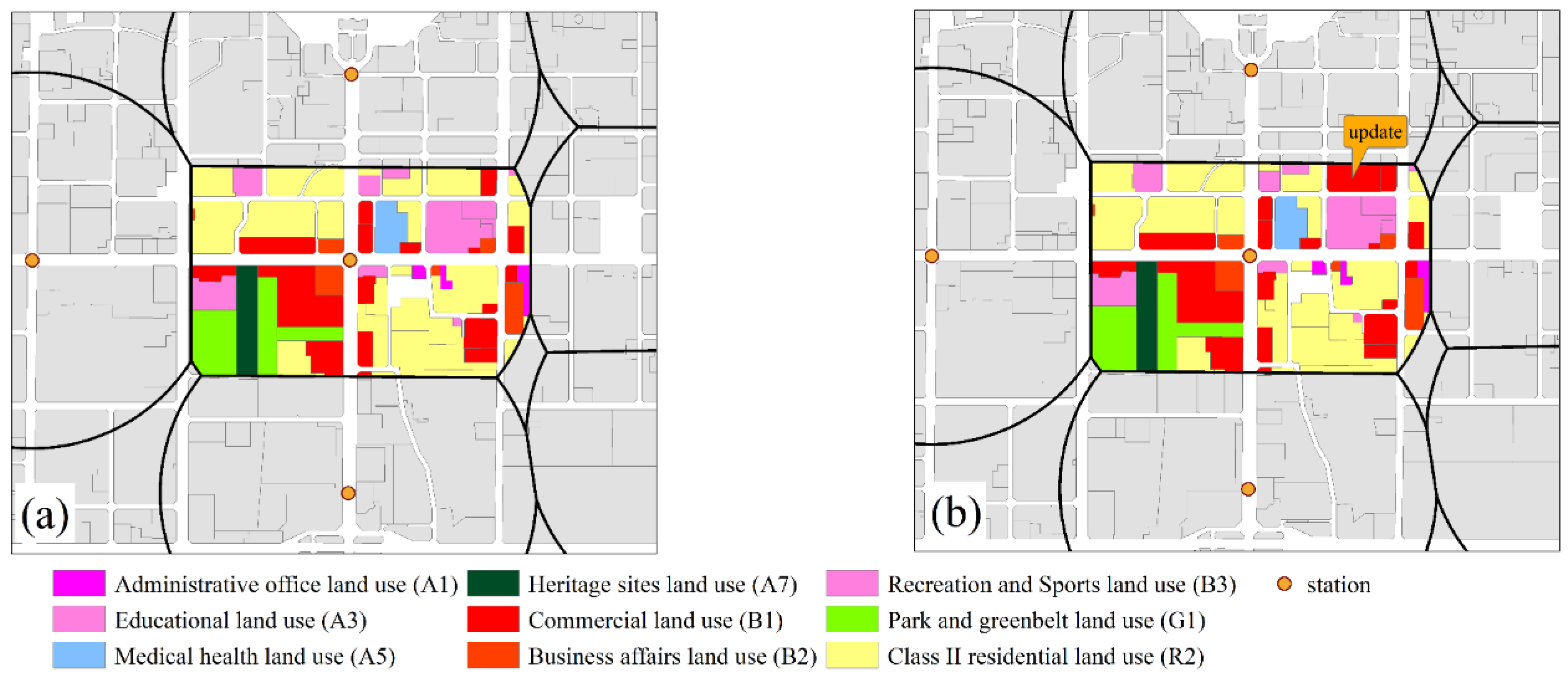
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Summary of Variables
4. Methodology
4.1. Multicollinearity and Spatial Autocorrelation
4.2. Semi-Parametric Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Model Performance
5.2. Spatial Analysis of Coefficients from the sGWPR Model
6. Scenario Application
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GB 50137-2011; Code for Classification of Urban Land Use and Planning Standards of Development Land. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Wang, D.; Zhou, M. The built environment and travel behavior in urban China: A literature review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Deng, J. Spatio-temporal analysis of rail station ridership determinants in the built environment. Transportation 2019, 46, 2269–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, K.; Shim, H. Factors generating boardings at metro stations in the Seoul metropolitan area. Cities 2010, 27, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Wang, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model to explore the spatiotemporal influence of built environment on transit ridership. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 70, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lyu, D.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Gao, F.; Huang, G.; Wu, Z. The varying patterns of rail transit ridership and their relationships with fine-scale built environment factors: Big data analytics from Guangzhou. Cities 2020, 99, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lyu, D.; Huang, G.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X. Spatially varying impacts of built environment factors on rail transit ridership at station level: A case study in Guangzhou, China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 82, 102631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuby, M.; Barranda, A.; Upchurch, C. Factors influencing light-rail station boardings in the United States. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2004, 38, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, B.P.; Chen, C.; Chan, E.T. Rail-based transit-oriented development: Lessons from New York City and Hong Kong. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obelheiro, M.R.; da Silva, A.R.; Nodari, C.T.; Cybis, H.B.B.; Lindau, L.A. A new zone system to analyze the spatial relationships between the built environment and traffic safety. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 84, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Choi, K.; Lee, S.; Cheon, S. Exploring the impacts of land use by service coverage and station-level accessibility on rail transit ridership. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 36, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Zhu, T.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q. Exploring metro vibrancy and its relationship with built environment: A cross-city comparison using multi-source urban data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 25, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovski, M.; Grillo, N.; Varga, C.; Saeed, T.U.; El-Hakim, M. Subway Ridership: Accounting for Regional Variation across Land-Use and Socioeconomic Settings. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2021, 27, 04021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Sinniah, G.K.; Li, R. Identify impacting factor for urban rail ridership from built environment spatial heterogeneity. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2022, 10, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, O.D.; García-Palomares, J.C.; Gutiérrez, J. Application of geographically weighted regression to the direct forecasting of transit ridership at station-level. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wen, Y.; Muneeb Abid, M. Spatially Varying Relation between Built Environment and Station-Level Subway Passenger-Distance. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 7542560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Xu, Q.; Chen, P.; Hu, J.; Zhu, Y. Spatial characteristics of urban rail transit passenger flows and fine-scale built environment. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2021, 6, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, T.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically weighted Poisson regression for disease association mapping. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 2695–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Geographically weighted poisson regression under linear model of coregionalization assistance: Application to a bicycle crash study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 159, 106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Feng, T.; Ding, C.; Yu, B.; Yao, B. Examining the spatial-temporal relationship between urban built environment and taxi ridership: Results of a semi-parametric GWPR model. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 96, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Cao, X.; Liu, C. How does the station-area built environment influence Metrorail ridership? Using gradient boosting decision trees to identify non-linear thresholds. J. Transp. 2019, 77, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munira, S.; Sener, I.N. A geographically weighted regression model to examine the spatial variation of the socioeconomic and land-use factors associated with Strava bike activity in Austin, Texas. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 88, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, W.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y. What influences Metro station ridership in China? Insights from Nanjing. Cities 2013, 35, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.J.; Choi, K.; Jeong, J.E.; Kwon, K.H.; Kim, H.J. Land use characteristics of subway catchment areas and their influence on subway ridership in Seoul. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 48, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Tong, X.; Liu, K.; Chan, E.H. Understanding the impact of built environment on metro ridership using open source in Shanghai. Cities 2019, 93, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Jin, C. Spatial interaction modeling of OD flow data: Comparing geographically weighted negative binomial regression (GWNBR) and OLS (GWOLSR). ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, N.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D. Understanding job-housing relationship and commuting pattern in Chinese cities: Past, present and future. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable Category | Variable Name | Definition | Min | Max | Mean | SD | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variables | Entry ridership | Station entry ridership in 60-min period | 0 | 6452 | 811.7 | 878.9 | - |
| Exit ridership | Station exit ridership in 60-min period | 2 | 9970 | 816.1 | 938.7 | - | |
| Socioeconomic and demographics | Population density (PD) * | Number of resident population | 292 | 134,134 | 35,030.5 | 27,388.6 | 5.384 |
| Employment density (ED) | Number of employment population | 154 | 142,150 | 27,665.7 | 23,882.2 | 4.587 | |
| House price (HP) * | Average house price (CNY/m2) | 6799.6 | 36,027.1 | 16,766.5 | 5142.1 | 2.234 | |
| Land use characteristics | Class II residential (R2) * | The area of the second-level residential LU (m2) | 0 | 1,240,517.1 | 572,415.6 | 288,016.3 | 7.187 |
| Administrative office (A1) * | The area of administrative office LU (m2) | 0 | 152,827.7 | 21,652.2 | 34,452.6 | 1.834 | |
| Cultural facility (A2) * | The area of cultural facility LU (m2) | 0 | 294,717.3 | 19,396.4 | 46,196.6 | 1.939 | |
| Educational (A3) * | The area of educational research LU (m2) | 0 | 624,846.7 | 116,422.3 | 13,2747.1 | 2.916 | |
| Sports (A4) | The area of sports LU (m2) | 0 | 613,139.4 | 13,447.4 | 64,595.9 | 1.547 | |
| Medical health (A5) | The area of medical and health LU (m2) | 0 | 475,058.6 | 21,514.3 | 53,987.9 | 2.099 | |
| Social welfare (A6) | The area of social welfare facility LU (m2) | 0 | 17,306.9 | 337.0 | 1844.9 | 1.291 | |
| Heritage sites (A7) * | The area of heritage sites LU (m2) | 0 | 735,163.3 | 20,098.4 | 85,308.5 | 1.803 | |
| Other administration and public service (A89) * | The area of other administration and public service LU (m2) | 0 | 87,973.4 | 1445.9 | 9178.4 | 1.417 | |
| Commercial and recreation (B13) * | The area of commercial, recreation and sports LU (m2) | 0 | 63,4781.3 | 155,585.9 | 121,377.2 | 2.836 | |
| Business affairs (B2) * | The area of business affairs LU (m2) | 0 | 634,968.6 | 59,505.8 | 115,307.1 | 2.547 | |
| Municipal utility outlet (B4) | The area of municipal utility outlet LU (m2) | 0 | 20,395.3 | 1386.1 | 3065.2 | 1.498 | |
| Park and greenbelt (G1) | The area of park and greenbelt LU (m2) | 0 | 724,110.2 | 146,059.9 | 120,917.6 | 2.491 | |
| Other park and square (G23) * | The area of other park and square LU (m2) | 0 | 405,827.3 | 41,507.6 | 68,006.5 | 3.452 | |
| Industrial (M) * | The area of industrial LU (m2) | 0 | 1,103,616.1 | 75,547.8 | 203,630.4 | 4.184 | |
| street and transportation (S) * | The area of street and transportation LU (m2) | 0 | 654,855.6 | 25,939.5 | 78,612.1 | 3.735 | |
| Municipal utility (U) * | The area of municipal utility LU (m2) | 0 | 671,838.3 | 20,258.5 | 65,000.1 | 1.779 | |
| Logistics and warehouse (W) | The area of logistics and warehouse LU (m2) | 0 | 39,990.3 | 760.6 | 4782.4 | 1.404 | |
| Other land (Other) * | The area of other LU (m2) | 186,640.2 | 1,713,577.9 | 417,614.0 | 229,157.1 | 4.761 | |
| FAROR(FR) * | Average floor area ratio of residential land | 0 | 7.42 | 2.44 | 1.23 | 3.770 | |
| FAROA(FA) * | Average floor area ratio of administration and public services land | 0 | 2.38 | 1.13 | 0.68 | 4.190 | |
| FAROB(FB) * | Average floor area ratio of commercial and business facilities land | 0 | 4.80 | 1.94 | 1.41 | 2.584 | |
| Entropy(E) | Land use entropy | 0.16 | 0.69 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 4.146 | |
| External connection facility | Arterial density (AD) * | Sum of arterial road lengths (m) | 0 | 24,158 | 7937 | 3969 | 1.706 |
| Secondary trunk density (STD) * | Sum of secondary trunk road lengths (m) | 0 | 35,270 | 8496 | 6901 | 2.171 | |
| Branch way density (BWD) * | Sum of branch way lengths (m) | 0 | 22,929 | 7062 | 4430 | 2.330 | |
| Intersections (IS) * | Number of motor road intersections | 2 | 59 | 18.72 | 10.37 | 2.778 | |
| Shuttle bus (SB) * | Number of shuttle bus | 0 | 32 | 10.49 | 6.26 | 2.437 | |
| Overlap bus (OB) * | Number of overlap bus | 0 | 36 | 7.34 | 6.44 | 3.625 | |
| Station characteristics | Entrances/exits (EE) * | Number of station entrances or exits | 2 | 20 | 4.59 | 2.36 | 7.295 |
| Betweenness centrality (BC) * | Betweenness centrality calculated based on rail network | 0 | 6076 | 1226.1 | 1124.3 | 3.144 | |
| Closeness centrality (CC) | Closeness centrality calculated based on rail network | 0.000034 | 0.000103 | 0.000070 | 0.000018 | 1.858 | |
| Hub station (HS) * | Hub station or not (1 = yes, 0 = no) | 0 | 1 | 0.026 | 0.16 | 2.761 | |
| Operation time (OT) * | The number of months of station operation until November 2021 | 11 | 122 | 59.98 | 40.01 | 2.188 | |
| Terminal station (TS) * | Terminal station or not (1 = yes, 0 = no) | 0 | 1 | 0.078 | 0.27 | 2.020 |
| Constant | PD | R2 | A1 | A7 | S | FB | FR | IS | SB | OB | BC | EE | OT | ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | −183.5 ** | 2.4 ** | 383.8 ** | 475.7 * | 7.1 * | 2.7 ** | 164.6 * | ||||||||
| 7 | −649.9 ** | 9.6 ** | 1945.5 ** | 1796.3 * | 123.8 * | −20.9 ** | 34.4 ** | 8.7 ** | 573.9 * | ||||||
| 8 | −836.6 ** | 12.9 ** | 2120.1 ** | 2243.7 * | 36.7 ** | 9.6 ** | 600.9 * | ||||||||
| 9 | −342.0 ** | 3.4 ** | 471.9 ** | 795.2 ** | 72.4 ** | 12.9 ** | 5.6 ** | 351.8 ** | |||||||
| 10 | −214.8 ** | 219.2 ** | 1537.9 ** | 912.5 ** | 44.6 ** | 11.3 ** | 6.3 ** | 4.4 ** | 189.1 * | ||||||
| 11 | −167.4 ** | 1762.7 ** | 1128.8 ** | 59.8 ** | 12.3 ** | 7.2 ** | 4.4 ** | 181.7 * | |||||||
| 12 | −208.3 ** | 89.5 ** | 15.8 ** | 20.3 * | 5.2 ** | 285.2 ** | |||||||||
| 13 | −224.7 ** | 90.5 ** | 18.8 ** | 20.5 * | 5.7 ** | 274.2 ** | |||||||||
| 14 | −287.7 ** | 82.7 ** | 16.3 ** | 5.8 * | 27.5 * | 5.7 ** | 307.1 ** | ||||||||
| 15 | −380.8 ** | 1564.2 ** | 86.8 ** | 14.8 ** | 9.1 ** | 44.4 ** | 5.2 ** | ||||||||
| 16 | −446.8 ** | 108.1 ** | 16.5 ** | 10.7 ** | 56.3 ** | 6.2 ** | 398.7 ** | ||||||||
| 17 | −361.4 * | 327.3 ** | 29.2 ** | 99.2 ** | 7.1 ** | ||||||||||
| 18 | −472.6 ** | 358.9 ** | 57.4 ** | 53.3 ** | 132.8 ** | ||||||||||
| 19 | −492.6 ** | 181.7 ** | 26.7 ** | 108.2 ** | 4.7 ** | ||||||||||
| 20 | −426.0 ** | 136.5 ** | 15.6 ** | 94.1 ** | 3.2 ** | ||||||||||
| 21 | −403.9 ** | 133.6 ** | 15.5 * | 109.2 ** | |||||||||||
| 22 | −317.7 ** | 106.5 ** | 96.4 ** | ||||||||||||
| 23 | −92.8 ** | 16.3 ** | 17.8 ** | 0.7 ** |
| Constant | PD | R2 | A3 | A7 | B2 | S | FB | FR | SB | OB | BC | EE | OT | HS | ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0 | 3.6 ** | 1.0** | |||||||||||||
| 7 | 0 | 1028.1 * | 30.5 ** | 7.1 ** | 661.4 ** | |||||||||||
| 8 | 0 | 3096.9 ** | 576.9 ** | 70.5 ** | 138.1 ** | |||||||||||
| 9 | −504.7 ** | 961.9 * | 217.3 ** | 26.5 ** | 27.4 ** | 82.4 ** | 3.1 * | |||||||||
| 10 | −324.4 ** | 1390.2 ** | 96.7 ** | 11.5 ** | 8.4 ** | 42.7 ** | 4.3 ** | |||||||||
| 11 | −302.8 ** | 89.4 ** | 10.3 * | 59.2 ** | 4.6 ** | |||||||||||
| 12 | −327.7 ** | 97.3 ** | 11.2 ** | 59.1 ** | 4.8 ** | |||||||||||
| 13 | −365.3 ** | 108.0 ** | 12.4 ** | 66.8 ** | 5.1 ** | |||||||||||
| 14 | −450.8 ** | 111.6 ** | 12.8 * | 86.7 ** | 5.4 ** | |||||||||||
| 15 | −359.1 ** | 81.2 ** | 17.0 ** | 66.4 ** | 5.3 ** | |||||||||||
| 16 | −403.8 ** | 212.8 * | 76.1 ** | 18.9 ** | 49.2 ** | 5.9 ** | 237.5 ** | |||||||||
| 17 | −580.2 ** | 4.4 ** | 542.4 ** | 866.2 * | 84.9 ** | 22.8 ** | 54.3 ** | 6.9 ** | 382.2 ** | |||||||
| 18 | −1220.2 ** | 9.9 ** | 1564.5 ** | 2137.3 ** | 136.8 * | 44.6 ** | 71.9 * | 11.5 ** | 531.9 ** | |||||||
| 19 | −673.6 ** | 6.1 ** | 1059.1 ** | 1172.6 * | 39.2 ** | 48.7 * | 8.2 ** | |||||||||
| 20 | −471.6 ** | 3.9 ** | 509.9 ** | 710.2 * | 45.2 * | 20.6 ** | 24.1 * | 4.7 ** | −486.4 ** | 288.3 ** | ||||||
| 21 | −251.0 ** | 3.9 ** | 404.6 ** | 492.1 * | 18.8 ** | 3.9 ** | −442.1 ** | 224.9 ** | ||||||||
| 22 | −236.1 ** | 3.2 ** | 337.1 ** | 420.5 * | 13.8 ** | 3.4 ** | −244.1 * | 191.7 ** | ||||||||
| 23 | −85.4 ** | 1.1 ** | 105.1 ** | 4.7 ** | 1.5 ** | −91.3 * | 83.3 ** |
| Period | Entry Ridership | Exit Ridership | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAR | CPR | Error | UPR | CAR | CPR | Error | UPR | |
| 6:00–7:00 | 308 | 443 | 135 (43%) | 431 | 166 | 301 | 135 (81%) | 301 |
| 7:00–8:00 | 1555 | 1881 | 326 (20%) | 1827 | 1871 | 2411 | 540 (28%) | 2411 |
| 8:00–9:00 | 2179 | 2067 | 112 (5%) | 2018 | 5754 | 5304 | 450 (7%) | 5317 |
| 9:00–10:00 | 1204 | 1233 | 29 (2%) | 1218 | 2742 | 2619 | 123 (4%) | 2622 |
| 10:00–11:00 | 998 | 1073 | 75 (7%) | 1062 | 1450 | 1637 | 187 (12%) | 1640 |
| 11:00–12:00 | 1050 | 1168 | 118 (11%) | 1170 | 1212 | 1405 | 193 (16%) | 1407 |
| 12:00–13:00 | 1169 | 1241 | 72 (6%) | 1242 | 1200 | 1477 | 277 (23%) | 1479 |
| 13:00–14:00 | 1214 | 1291 | 77 (6%) | 1293 | 1351 | 1614 | 263 (19%) | 1617 |
| 14:00–15:00 | 1319 | 1533 | 214 (16%) | 1535 | 1408 | 1766 | 358 (25%) | 1769 |
| 15:00–16:00 | 1428 | 1724 | 296 (20%) | 1728 | 1266 | 1492 | 226 (17%) | 1494 |
| 16:00–17:00 | 1677 | 2089 | 412 (24%) | 2093 | 1242 | 1434 | 192 (15%) | 1424 |
| 17:00–18:00 | 3327 | 3382 | 55 (1%) | 3388 | 1676 | 1892 | 216 (12%) | 1882 |
| 18:00–19:00 | 4081 | 3724 | 357 (8%) | 3730 | 3010 | 3067 | 57 (2%) | 3025 |
| 19:00–20:00 | 2117 | 2310 | 193 (9%) | 2311 | 1994 | 1829 | 165 (8%) | 1812 |
| 20:00–21:00 | 1684 | 1747 | 63 (3%) | 1748 | 1083 | 1149 | 66 (6%) | 1129 |
| 21:00–22:00 | 1457 | 1347 | 110 (7%) | 1351 | 836 | 760 | 76 (9%) | 755 |
| 22:00–23:00 | 1024 | 1089 | 65 (6%) | 1095 | 628 | 582 | 46 (7%) | 577 |
| 23:00–24:00 | 317 | 276 | 41 (13%) | 277 | 264 | 228 | 36 (13%) | 228 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Ai, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. Revealing the Influence of the Fine-Scale Built Environment on Urban Rail Ridership with a Semiparametric GWPR Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060218
Wang J, Zhao M, Ai T, Wang Q, Liu Y. Revealing the Influence of the Fine-Scale Built Environment on Urban Rail Ridership with a Semiparametric GWPR Model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2023; 12(6):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060218
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianpo, Meng Zhao, Teng Ai, Qushun Wang, and Yufan Liu. 2023. "Revealing the Influence of the Fine-Scale Built Environment on Urban Rail Ridership with a Semiparametric GWPR Model" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 12, no. 6: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060218
APA StyleWang, J., Zhao, M., Ai, T., Wang, Q., & Liu, Y. (2023). Revealing the Influence of the Fine-Scale Built Environment on Urban Rail Ridership with a Semiparametric GWPR Model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 12(6), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060218




